p21 Cell cycle arrest / genetic repair
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Davidson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Application Note Silencing of expression with Thermo Scientific Dharmacon Accell sirna causes inhibition of the DNA damage response in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells and protects primary cortical neurons from β-amyloid toxicity Zaklina Strezoska 1 and Tamara Seredenina 2. 1 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lafayette, CO, USA. 2 Siena Biotech, Siena, Italy. Introduction Neuroblastoma cell lines and primary neuronal cultures are commonly used as cellular model systems for studying cancer and neuronal development as well as being highly relevant cells for the study of neurodegenerative diseases. However, most neuroblastoma cell lines and primary neuronal cells suffer from low transfection efficiency due to the refractory nature of the cells to lipid-based transfection reagents. As such, application of small, interfering RNA (sirna) for inducing RNA interference (RNAi), has limited utility in these cell types; thus hindering the development of functional assays for screening and discovery of novel diseaserelevant genes. Thermo Scientific Dharmacon Accell sirna enables efficient delivery in a wide range of cell lines and primary cells. Accell sirna reagents carry a novel chemical modification pattern that facilitates the delivery of sirna without a need for transfection reagents. To demonstrate the utility of Accell sirna reagents in neuronal cells, the effects of silencing the expression of was examined. is a tumor suppressor that regulates the cellular response to different DNA damaging or cellular stress agents by controlling the expression of a wide variety of genes involved in cell growth, repair and survival or causing the cell to enter apoptosis if damage can not be repaired (Figure 1). Here we describe how application of Accell sirna enabled the development of a high content assay for multiplex analysis of and p21 expression in p21 Stress Cell survival Death of damaged cells Figure 1. is a a tumor suppressor protein that mediates cellular response to different stress agents. Cell exposure to damaging agents induces rapid increase of protein levels in the nucleus, leading to the induction of its transcription targets controlling cellular responses such as cell cycle arrest, repair and cell survival (p21waf1/cip1, GAD45α, α) and/or apoptosis (e.g. Bax, Apaf1, Casp-9). IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells as well as a whole-culture cell viability assay in IMR-32 and primary rat cortical neurons. The ability to modulate gene expression in neuronal cell lines and primary neurons using Accell sirna demonstrates potential new opportunities for functional genomic sirna screens in the field of neuroscience. Results Efficient target mrna knockdown in IMR-32 by Accell sirna In order to examine whether the Accell sirna delivery protocol can be applied to IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells, several Accell sirna controls were tested for silencing efficiency and maintenance of cell viability. This neuroblastoma cell line was chosen since it contains wild type and could be further DNA damaging agents (e.g. camptothecin) neurotoxins (e.g. amyloid-β) UV, hypoxia, etc GAD45α σ Bax Apaf-1 Casp -9 Cell cycle arrest / genetic repair P Mdm2 Apoptosis used for examination of the cellular effects of knockdown on the DNA damage response. Accell and Non-targeting () control pools as well as an Thermo Scientific Dharmacon Accell sirna SMARTpool and two individual sirnas targeting mrna were delivered at 1 µm concentration in Accell delivery media. Target mrna knockdown and cell viability were assessed at 72 hours post-transfection (Figure 2). Efficient target mrna knockdown (> 75%) with no detrimental effect on cell viability was observed for all targeting sirna. Silencing of by Accell sirnas increases the survival of IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells after camptothecin treatment The function of is to keep the cell from progressing through the cell cycle if there is DNA
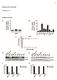
2 Normalized relative target expression and cell viability (%) Figure 3. Knockdown of increases the survival of IMR-32 after camptothecin treatment. 1 µm Accell sirna control pools ( or ) and SMARTpool sirna reagent or individual sirnas targeting were delivered to IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells in Accell delivery media. At 48 hours posttransfection cells were treated with the indicated doses of camptothecin for 24 hours. Cell viability was assessed at 72 hrs post-transfection by phase contrast cell images (A) or resazurin assay (B). A Control () B Normalized cell viability (%) Target mrna levels Cell viability Figure 2. Efficient target mrna knockdown in IMR-32 by Accell sirna. 1 µm Accell sirnas control pools ( or ) and SMARTpool sirna reagent or individual sirna duplexes against (,, and ) were delivered in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells in Accell delivery media. Knockdown of and and cell viability were assessed at 72 hrs post-transfection. Experiments were performed in biological triplicate for all samples No drug No drug 4 µm Camptothecin dose 4 µm camptothecin 1 µm Accell Media.25 µm damage by either holding the cell at a checkpoint until repairs can be made and/or by causing the cell to enter apoptosis if the damage cannot be repaired (reviewed in (Vousden and Lu, 22; Helton and Chen, 27). DNA damaging drugs, such as camptothecin, trigger rapid and extensive apoptosis in chemosensitive human neuroblastoma cell lines. Inactivation of, either by the human papillomavirus type 16 E6 protein or by a dominant-negative mutant (R175H), protects cell lines with wild type from drug-triggered apoptosis (Cui et al., 22). In order to demonstrate that knockdown of by Accell sirna would lead to similar protective effects, IMR-32 cells were incubated with Accell sirnas against or control sirna pools (, ) for 72 hours and assayed for cell viability upon treatment with different camptothecin doses for the last 24 hours (Figure 3). The Accell SMARTpool and two individual Accell sirnas targeting caused a striking rescue from camptothecin-induced cell death, as seen in the phase contrast cell images (Figure 3A), and an observed 3-fold increase in cell survival (Figure 3B). High content analysis for the induction of and its downstream target p21 upon camptothecin treatment in IMR-32 cells is normally maintained at low levels by continuous ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by the 26S proteasome. However, when the cell is stressed, ubiquitination is suppressed and accumulates in the nucleus, where it is activated and stabilized (reviewed in Lavin and Gueven, 26). Once activated, functions as a transcription factor to turn on or off various genes that affect cell cycle progression and repair (e.g. p21waf1/cip1, GAD45α, σ) and/or apoptosis (e.g. Bax, Apaf1, Casp-9; Figure 1) (reviewed in Riley et al., 28). The Thermo Scientific Cellomics HCS Reagent Kits for multiplex
3 analysis of and p21 expression was used to monitor the effects of down-regulating by Accell sirna. The reduction of the signal and the induction on one of its downstream targets, p21 upon camptothecin treatment was quantified. IMR-32 cells were found to be a challenging cell line for HCA due to their loose attachment to the tissue culture plates, so gentle fixing was necessary. This low adherence was further exacerbated by the response of IMR-32 cells to the Accell sirna delivery conditions. Accell delivery media contains no serum, as high levels of serum are known to interfere with Accell sirna efficacy. However, the addition of up to 3% serum to Accell delivery media is suggested for Accell sirna application in cases where either the cell line or the assay is sensitive to prolonged serum-free conditions. Upon examination of IMR-32 cells under these modified Accell sirna application conditions, it was found that the addition of 2% serum did not affect the target mrna knockdown (Figure 4), but greatly improved cell adherence and fixation steps. The effects of knockdown by Accell sirna on the camptothecin-induced Figure 4. Efficient target mrna knockdown in IMR-32 by Accell sirna delivered in Accell delivery media supplemented with low quantity of serum. 1 µm Accell sirnas control pools ( or ) and SMARTpool sirna reagent or individual sirna duplexes against were delivered in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells in Accell delivery media or in Accell delivery media with 2% FBS. Knockdown of and was assessed at 72 hrs posttransfection. Relative target expression (%) and p21 protein levels were examined next. Treatment with 4 µm camptothecin for hours was found to be the optimal concentration and time for induction of the and p21 protein for the HCA assay in IMR-32 cells (data not shown). IMR-32 cells were incubated with Accell control sirna pools (, ), Accell SMARTpool, or two individual sirnas against. At 52 hours post-delivery the cells were either treated with 4 µm camptothecin for 2 hours or left untreated. At 72 hours cells were fixed and stained with the Cellomics multiplexed and p21 detection kit. Cells were analyzed with the Target Detection BioApplication software module. Mean fluorescent intensities of or p21 staining in the nucleus were measured and quantified (Figure 5A). The results show that knockdown of in IMR-32 cells inhibited the and p21 induction following camptothecin treatment. In order to better visualize the effect of knockdown on camptothecin-dependent induction of and p21, 5 cells treated with either Accell pool or Accell SMARTpool sirna reagent were selected and their nuclear intensity (Hoechst stain) was Accell delivery media Accell delivery media-2% FBS plotted versus the intensity for p21 stain or stain (Figure 5B). As expected, knockdown of by Accell sirna resulted in a significant decrease of and p21 staining intensities in the cell population, indicating that the cells do not enter cell cycle arrest upon the camptothecin treatment as they do when is not silenced. Thus, we demonstrated that knockdown of by Accell sirna in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cell line results in inhibition of the dependent DNA damage response upon camptothecin treatment. Delivery optimization in primary cortical neurons Primary neuronal cultures are widely employed as a highly relevant cellular model system for the study of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurons are post-mitotic, differentiated cells that are cultured under specific conditions. Standard methods applied for modification of target expression by overexpression or by RNAi are often not efficient enough to obtain robust data employing common biochemical assays. The successful application of Accell sirna for delivery into primary neurons would provide great opportunities for RNAi use in target discovery and validation in the field of neuroscience. For this reason, Accell sirna delivery was tested and optimized in primary rat cortical neurons. Primary cortical neurons require specific culturing conditions and are extremely sensitive to media changes. Therefore a series of experiments was performed in order to assess the effect of Accell delivery conditions on neuronal viability. Primary cortical rat neurons (Goslin and Banker, 1989) harvested from 18-day embryos (E18) cultured 4 days in vitro (DIV) were incubated either in complete Neurobasal media, Accell delivery media, Accell delivery media with B27 supplements or a 5:5 mix of Accell delivery media and complete Neurobasal
4 A 2 p21 induction 7 induction P21 induction (nuclear intensities) P53 induction (nuclear intensities) B p21 intensity No treatment 4 µm camptothecin No treatment 4 µm camptothecin P53pool intensity P53pool Figure 5. HCA shows reduction in and p21 following camptothecin treatment when is silenced. At 48 hrs after sirna delivery, cells were treated with 4 µm camptothecin for 2 hrs or were left untreated. At 72 hrs after sirna delivery, cells were fixed and stained with the Cellomics Multiplexed and p21 Detection Kit. (A) Mean intensities of the nuclear p21 and staining for different sirna treatments. (B) Shows the nuclear Hoechst versus p21 or staining for each individual cell in the population (5 cells) for and sirnas during camptothecin treatment. Normalized cell viability (%) NB NB+AM Figure 6. Testing media compatibility for Accell sirna delivery in primary neurons. Primary E18 rat cortical neurons at 4 DIV were treated for 48 hours with different media conditions: complete Neurobasal media (NB), Accell delivery media (AM), Accell delivery media with B27 supplements (AM + B27) or a 5:5 mix of Accell delivery media and Neurobasal media (NB +AM). MTT assay was performed to assess neuronal viability. AM+B27 Nuclear Intensity AM media. After 48 hours, neuronal viability was assessed by MTT assay (Figure 6). A decrease of cell viability was observed in Accell delivery media both with and without B27 supplements relative to Neurobasal media alone. However, the survival of cells in the 5:5 mixture of Accell delivery media and complete Neurobasal media was not dramatically affected and was further explored for supporting Accell sirna delivery in primary cortical neurons. To determine the optimal media conditions for the assay, primary E18 rat cortical neurons at 4 DIV were incubated with 1 µm Accell sirna in either Accell (AM) media alone, complete Neurobasal (NB) media alone, or different ratios of Accell and Neurobasal media. Following 48 hours Nuclear Intensity incubation, neuronal viability was assessed by visual inspection (Figure 7A-D) and by MTT assay (Figure 7E). When the primary cortical neurons were incubated in the Accell delivery media a substantial decrease in cell viability was observed (Figure 7A, 7E). Cell morphology was not significantly affected by the different ratios of media compared to NB media alone (Figure 7B-D). A decrease in neuronal viability correlated with the quantity of Accell media present in the delivery mix. Improved survival was obtained when no more than 5% of Accell media was used in the delivery mix. In parallel, the effect of the different media conditions on Accell sirna ability to knockdown target mrna was examined (Figure 7F). The expression of mrna
5 E % 5% 25% 1% 2 % Normalized cell viability (%) 12 %Accell Delivery Media F % 5% 25% 1% % H expression (%) 12 % Accell Delivery Media Figure 7. Testing cell viability and target mrna knockdown in primary neurons upon Accell sirna delivery in different media conditions. Primary E18 rat cortical neurons at 4 DIV were treated for 48 hrs with 1 µm Non- targeting control () or Accell sirna in different proportions of Accell delivery media and complete Neurobasal media. Phase contrast images of cells treated with sirna in: Accell delivery media (A), a 5:5 mix of Accell and Neurobasal media (B), a 25:75 mix of Accell and Neurobasal media (C) or complete Neurobasal (NB) media alone (D). Cell viability was also assessed by MTT assay (E) and sirna silencing was examined by measuring mrna knockdown (F). Figure 8. Analysis of sirna cellular uptake. Primary E18 rat cortical neurons at 4 DIV were incubated for 48 hrs with DY-547 labeled Accell sirna (1 µm) in a 5:5 mix of Accell delivery media and Neurobasal media. Cells were fixed and images were acquired using a confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM 51). Detailed analysis shows that sirnas (red) are localized in the cytoplasm in neuronal cell bodies and in neurites (C, D). Blue staining (Hoechst) indicates nuclei. Scale bar 1 µm. was significantly decreased in all conditions, with the least efficient knockdown (8%) in Neurobasal media and the highest knockdown efficiency (> 9%) obtained in Accell delivery media. To strike a balance between optimal cell viability and target silencing, all subsequent Accell sirna delivery experiments used a 5:5 ratio of Accell delivery media to Neurobasal media. In order to more closely examine the Accell sirna delivery, neurons that were incubated for 48 hours with Accell Red sirna (1 µm) in the optimal conditions (5: 5 mix of AM:NB) were fixed and images were acquired using a confocal microscope. Almost all neurons were positive for Accell Red sirna uptake (red, Figure 8A and B). Detailed analysis showed that sirnas are localized in the cytoplasm of neuronal cell bodies and in neurites (Figure 8C and D). Knockdown of protects primary neurons from toxicity induces by β-amyloid peptide Neuronal apoptosis can be induced by β-amyloid peptides that play a major role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer s disease. is a known mediator of β-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity (Fogarty et al., 23). Therefore we examine if silencing of expression using Accell sirna would provide a neuroprotective effect in primary cortical neurons from the β-amyloid peptide. Application of Accell sirna resulted in greater than 6% knockdown of mrna expression (Figure 9A). Different concentrations of β-amyloid peptide were added to the cells after 48 hours of incubation. The MTT assay was performed at both 48 hours (Figure 9B) and 72 hours (Figure 9C) in order to assess neuronal viability. Silencing of the pro-apoptotic gene leads to a significant increase of neuronal survival as compared to sirna. The neuroprotective effect declined with increased concentration and exposure to β-amyloid. The strongest protective effect was observed at 5 µm β-amyloid at both time points. Reporter-based assays have been described for the validation of
6 A. B. C. Relative expression (%) Cell viability (untreated control=1%) Cell viability (untreated control=1%) µm ** ** 1 µm 15 µm Figure 9. Silencing of by Accell sirna causes significant increase of the survival of primary cortical neurons following β-amyloid peptide treatment. Primary E18 rat cortical neurons at 4 DIV were treated with 1 µm Accell sirna pool and Accell sirna pool against (in a delivery media that represent a 5:5 mix of Accell delivery media and Neurobasal media). mrna knockdown was assessed at 48 hours post transfection (A). At 48 hours posttransfection, cells were treated with different concentrations of β-amyloid peptide. MTT assay was performed after 48 hours (B) and 72 hours (C) in order to assess neuronal viability. ** p <.1; # p <.5, t-test. functional effects of modulated target expression in neurons (Pollio et al., 28). However, reporter assays represent an indirect measure of neuronal viability. Moreover, increased toxicity associated with transfection makes it difficult to carry out an adequate evaluation of this phenotype. Here we demonstrate that Accell sirna delivery technology enables the use of whole culture, homogeneous biochemical assays for functional # β-amyloid peptide concentration 5 µm 1 µm 15 µm β-amyloid peptide concentration target validation in primary cortical neurons. Conclusions The refractory nature of neuronal cells to lipid-based transfection reagents may be overcome with the use of Accell sirna, enabling RNAi in these cell types. An optimization strategy is suggested for identification of conditions to maximize cell viability and target gene silencing, while accounting for assay-specific requirements. Accell sirna delivery technology permits functional target validation in neuroblastoma cell lines as well as primary cortical neurons. Materials and methods Cell culture IMR-32 cells were obtained from ATCC and cultured under recommended media conditions. Cells were plated on collagen IV coated 96-well plates for the purpose of improving the fixation of the cells for HCA analysis. Rat cortical neurons were obtained from E18 pups following Banker, Goslin and Brewer s modified protocol (Goslin and Banker, 1989). The neurons were cultivated in Neurobasal media with B27 supplements and used for sirna delivery following 4 days in vitro (DIV). Accell sirna delivery in IMR-32 cells IMR-32 cells were plated at 2, cells per well in a 96-well plate and allowed to adhere overnight. Accell sirnas used in IMR-32 cells include: Accell Non Targeting pool (D-191-1), Accell Control Pool (D-193-1) and Accell sirna pool and individual sirnas against human (NM_546) (E-3329-, A and A ). Accell sirna was added to Accell delivery media (Cat # B-5-1, www. dharmacon.com) for a final concentration of 1 μm. 1 μl of the Accell sirna and media mixture was then added (per well) to the cells after the growth media had been aspirated. For the purpose of improving the fixation of the cells for the HCA analysis, the Accell delivery media was supplemented with 2% FBS. Cells were incubated for 72 hours at 37 ºC and 5% CO 2 at which point the plates were either analyzed for target mrna knockdown, assessed for cell viability, or fixed for HCA analysis. Accell sirna delivery in primary rat neurons Neurons at 4 DIV were incubated for 48 hours with 1 µm Accell sirna in media containing different proportions of Accell delivery media in complete Neurobasal media (1%, 5%, 25%, %) as indicated in the figure legends. Accell sirnas used in primary rat neurons include: Accell Control sirna (D-193-3), Accell Non-targeting sirna #1 (D-191-1), Accell SMARTpool against rat (NM_3989) (E-86--2) and Accell Non-targeting Pool (D-191-1). The cells were analyzed for target mrna knockdown at 48 hours although the protocol recommends a 72 hour time point. For the cellular uptake analysis DY547 labeled Accell Control sirna and Accell Non-targeting sirna were used. For the phenotypic assay the neurons at 4 DIV were treated with 1 μm Accell sirna in the 5:5 mix of Accell delivery media and complete Neurobasal media for 48 hours and then treated with different doses of β-amyloid peptide 1-42 (Californian peptides) for an additional hours. After treatment, the cell viability was assessed by MTT. The β-amyloid peptide 1-42 was prepared according to the protocol described in (Stine et al., 23). Assessment of target mrna knockdown Target mrna knockdown in IMR-32 cells was determined by RT-qPCR using Thermo Scientific Verso SYBR Green 2-Step Master Mix (Cat# AB-4112/B, and knockdown in primary neurons was determined using iq SYBR Green Supermix (Biorad). To calculate mrna expression levels the CT method was used for IMR-32 cells and the
7 standard curve method was used for primary neurons. The housekeeping gene, beta-actin was used to normalize gene expression. Expression levels were further normalized to Non-targeting control sirna wells. Experiments were performed in biological triplicate for all samples. Cell viability assays IMR-32 viability was assessed by resazurin assay. Resazurin was added to cells at a final concentration of 25 μg/ml 72 hours post-delivery. Cells were returned to the incubator for 1 to 3 hours. Plates were analyzed on a Wallac VICTOR 2 (Perkin Elmer Life Sciences) plate reader (Excitation 53 nm, Emission 59 nm and 1 second exposure). Viability of primary neurons was assessed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2- yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) colorimetric assay as described previously (Mosmann, 1983). High content screening assay and analysis IMR-32 cells at 72 hours posttransfection treated with or without 4 μm camptothecin for the last 2 hours were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained for and p21 proteins using the (product #8462, according to the protocol. The plates were imaged and quantitatively analyzed on the ArrayScan VTI HCS Reader using the Target Detection BioApplication software module. Three replicate wells for each sirna and treatment (-/+ campthotecin) were analyzed. Eight fields in each well were measured (>1 cells/field). Parameters used in this analysis included Mean Object Average Intensity in Channel 1 and Mean Average Intensity in Channel 2 and Channel 3. The averages and standard deviations were calculated for each treatment. Numeric data generated by the ArrayScan VTI HCS Reader were evaluated with the vhcs Discovery Toolbox. Confocal microscopy For confocal analysis cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde supplemented with Hoechst nuclear dye. Images were acquired using LSM51 confocal microscope (Zeiss). References Cui, H., Schroering, A., and Ding, H.-F. (22). Mediates DNA Damaging Drug-induced Apoptosis through a Caspase-9-dependent Pathway in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells. Mol Cancer Ther 1, Fogarty, M. P., Downer, E. J., and Campbell, V. (23). A role for c-jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1), but not JNK2, in the betaamyloid-mediated stabilization of protein and induction of the apoptotic cascade in cultured cortical neurons. Biochem J 371, Goslin, K., and Banker, G. (1989). Experimental observations on the development of polarity by hippocampal neurons in culture. J Cell Biol 18, Helton, E. S., and Chen, X. (27). modulation of the DNA damage response. J Cell Biochem 1, Lavin, M. F., and Gueven, N. (26). The complexity of stabilization and activation. Cell Death Differ 13, Mosmann, T. (1983). Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65, Pollio, G., Roncarati, R., Seredenina, T., Terstappen, G. C., and Caricasole, A. (28). A reporter assay for target validation in primary neuronal cultures. J Neurosci Methods 172, Riley, T., Sontag, E., Chen, P., and Levine, A. (28). Transcriptional control of human -regulated genes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9, Stine, W. B., Jr., Dahlgren, K. N., Krafft, G. A., and LaDu, M. J. (23). In Vitro Characterization of Conditions for Amyloid-beta Peptide Oligomerization and Fibrillogenesis. J Biol Chem 278, Vousden, K. H., and Lu, X. (22). Live or let die: the cell s response to. Nat Rev Cancer 2, Contact Information For technical questions regarding the use of sirna reagents, please contact Dharmacon Products Technical Support at: In America/Asia [email protected] In Europe/Israel [email protected] In Other Countries Please contact your appropriate distributor as listed on www. thermo.com/dharmacondistributors Copyright 29 Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The product(s) described herein ( Products ) are protected by patents, pending patents and other intellectual property owned or licensed by Dharmacon Inc. as set forth in Dharmacon s Terms and Conditions (found at or included with the Products when sold). By using the Product(s), users accept the Terms and Conditions, which expressly govern all use of the Product(s). The Product(s) are intended solely for research use and not for diagnostic, clinical or therapeutic uses. All other trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. and its subsidiaries. Literature Code: F-1-U
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna Libraries
 Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna Libraries Scientific innovation in sirna potency, specificity and delivery Superior sirna in comprehensive collections for reliable screens Market leading products for
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna Libraries Scientific innovation in sirna potency, specificity and delivery Superior sirna in comprehensive collections for reliable screens Market leading products for
岑 祥 股 份 有 限 公 司 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803
 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012. Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation. System
 Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
TOOLS sirna and mirna. User guide
 TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon ON-TARGETplus sirna The Standard for sirna Specificity
 Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna The Standard for sirna Specificity Reduce off-targets up to 90% with the market-leading sirna Combine higher target specificity with guaranteed silencing Increase confidence
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna The Standard for sirna Specificity Reduce off-targets up to 90% with the market-leading sirna Combine higher target specificity with guaranteed silencing Increase confidence
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
Cell Viability Assays: Microtitration (MTT) Viability Test Live/Dead Fluorescence Assay. Proliferation Assay: Anti-PCNA Staining
 Cell Viability Assays: Microtitration (MTT) Viability Test Live/Dead Fluorescence Assay Proliferation Assay: Anti-PCNA Staining Spring 2008 1 Objectives To determine the viability of cells under different
Cell Viability Assays: Microtitration (MTT) Viability Test Live/Dead Fluorescence Assay Proliferation Assay: Anti-PCNA Staining Spring 2008 1 Objectives To determine the viability of cells under different
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit
 Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr. 1 Introduction. Gene Expression Application Note No. 4
 Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
Steatosis Colorimetric Assay Kit
 Steatosis Colorimetric Assay Kit Item No. 10012643 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Steatosis Colorimetric Assay Kit Item No. 10012643 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer
 Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer Referees: PD Dr. Tobias Dick Prof. Dr. Wilfried Roth http://d-nb.info/1057851272 CONTENTS Summary 1 Zusammenfassung 2 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1
Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer Referees: PD Dr. Tobias Dick Prof. Dr. Wilfried Roth http://d-nb.info/1057851272 CONTENTS Summary 1 Zusammenfassung 2 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1
CytoSelect LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 Product Manual CytoSelect LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-241 960 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement and monitoring of cell cytotoxicity
Product Manual CytoSelect LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-241 960 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement and monitoring of cell cytotoxicity
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS
 EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
FITC Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with FITC annexin V and PI, for Flow Cytometry
 FITC Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with FITC annexin V and PI, for Flow Cytometry Catalog no. V13242 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage* Stability FITC annexin
FITC Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with FITC annexin V and PI, for Flow Cytometry Catalog no. V13242 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage* Stability FITC annexin
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay
 Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Quick Guide to AlphaScreen SureFire Assay Optimization
 PPLITION NOT lpha Technology Quick uide to lphascreen Sureire ssay Optimization Introduction Screening kinase activities in cell-based assays offers advantages over the more traditional biochemical approach
PPLITION NOT lpha Technology Quick uide to lphascreen Sureire ssay Optimization Introduction Screening kinase activities in cell-based assays offers advantages over the more traditional biochemical approach
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary GeneBLAzer RAR alpha DA Assay Kit GeneBLAzer RAR alpha-uas-bla GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1387, K1685 Target Description The retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha)
Validation & Assay Performance Summary GeneBLAzer RAR alpha DA Assay Kit GeneBLAzer RAR alpha-uas-bla GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1387, K1685 Target Description The retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha)
Measuring Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity: Cell Counting Kit-F
 Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
Introduction The Cell Counting Kit-F is a fluorometic assay for the determination of viable cell numbers. Calcein-AM in this kit passes through the cell membrane and is hydrolized by the esterase in the
PRODUCT INFORMATION...
 VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit
 ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab185915 Protein Sumoylation Assay Ultra Kit Instructions for Use For the measuring in vivo protein sumoylation in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Thermo Scientific DharmaFECT Transfection Reagents
 Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents Maintain cell viability with lipids specially formulated to deliver sirna Achieve robust sirna uptake for dependable gene silencing Expand your RNAi applications
Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents Maintain cell viability with lipids specially formulated to deliver sirna Achieve robust sirna uptake for dependable gene silencing Expand your RNAi applications
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent
 Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: [email protected]; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: [email protected]; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
PROTOCOL. Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry. Background. Materials and equipment required.
 PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
PROTOCOL Immunostaining for Flow Cytometry 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 Rev.0 Background The combination of single cell analysis using flow cytometry and the specificity of antibody-based
SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting
 Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Optimized Protocol sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells
 page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis
 ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
ab139418 Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry Kit for Cell Cycle Analysis Instructions for Use To determine cell cycle status in tissue culture cell lines by measuring DNA content using a flow cytometer. This
Supplemental Information. McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data
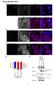
 1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Smart Fluorescence and Dual Live Cell Imaging
 Smart Fluorescence and Dual Live Cell Imaging Smart Fluorescence and Dual Live Cell Imaging Compact Real-Time Cell Analyzer Specialized For Fluorescence-Expressing Cell Joo, Jae Yeon and An, Seong Soo
Smart Fluorescence and Dual Live Cell Imaging Smart Fluorescence and Dual Live Cell Imaging Compact Real-Time Cell Analyzer Specialized For Fluorescence-Expressing Cell Joo, Jae Yeon and An, Seong Soo
use. 3,5 Apoptosis Viability Titration Assays
 Introduction Monitoring cell viability can provide critical insights into the effectiveness of biological protocols and the stability of biological systems including: the efficacy of cell harvesting procedures,
Introduction Monitoring cell viability can provide critical insights into the effectiveness of biological protocols and the stability of biological systems including: the efficacy of cell harvesting procedures,
CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format)
 Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA-071 CBA-071-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA-071 CBA-071-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes:
 icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Introduction Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis The skeletal muscle is one of the
icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Introduction Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis The skeletal muscle is one of the
protocol handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel
 handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
Dicer Substrate RNAi Design
 INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES, INC. Dicer Substrate RNAi Design How to design and order 27-mer Dicer-substrate Duplex RNAs for use as RNA interference reagents The following document provides a summary of
INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES, INC. Dicer Substrate RNAi Design How to design and order 27-mer Dicer-substrate Duplex RNAs for use as RNA interference reagents The following document provides a summary of
apoptosis detection Apoptosis assays for the Attune Acoustic Focusing Cytometer Apoptosis detection Attune Acoustic Focusing Cytometer
 apoptosis detection ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis detection poptosis assays for the ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis is a carefully regulated process of cell death that occurs as a
apoptosis detection ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis detection poptosis assays for the ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis is a carefully regulated process of cell death that occurs as a
Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab14153 Annexin V-EGFP Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR
 Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Gene Expression Assays
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL. 1 Standard sirna transfection of adherent cells... 2
 INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
MicroRNA formation. 4th International Symposium on Non-Surgical Contraceptive Methods of Pet Population Control
 MicroRNA formation mirna s are processed from several precursor stages Mammalian genomes seem to have 100 s of mirna s Nucleotides in positions 2-8 of an mirna are considered the mirna seed 5 Methyl-G
MicroRNA formation mirna s are processed from several precursor stages Mammalian genomes seem to have 100 s of mirna s Nucleotides in positions 2-8 of an mirna are considered the mirna seed 5 Methyl-G
HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook
 Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
MystiCq microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C
 microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Overexpression of untagged Ago2 inhibits the nuclear transport of the dotted foci of GFP-signal of myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut. (A C) HeLa cells expressing myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Overexpression of untagged Ago2 inhibits the nuclear transport of the dotted foci of GFP-signal of myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut. (A C) HeLa cells expressing myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections
 Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
Animal Cell Culture. Third Edition. A Practical Approach OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS
 Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
Animal Cell Culture Third Edition A Practical Approach Edited by John R. W. Masters 3rd Floor Research Laboratories, University College London OXJORD VNIVVRSITY 1'RVSS Contents List of protocols page xiii
OriGene Technologies, Inc. MicroRNA analysis: Detection, Perturbation, and Target Validation
 OriGene Technologies, Inc. MicroRNA analysis: Detection, Perturbation, and Target Validation -Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research project Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research
OriGene Technologies, Inc. MicroRNA analysis: Detection, Perturbation, and Target Validation -Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research project Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies. Biochemistry Journal. August 1, 2007 405, pp.
 Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products
 Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Cell Discovery 360: Explore more possibilities.
 Cell Discovery 360: Explore more possibilities. Flexible solutions for the BioPharma laboratory Blood Banking Capillary Electrophoresis Centrifugation Flow Cytometry Genomics Lab Automation Lab Tools Particle
Cell Discovery 360: Explore more possibilities. Flexible solutions for the BioPharma laboratory Blood Banking Capillary Electrophoresis Centrifugation Flow Cytometry Genomics Lab Automation Lab Tools Particle
Thermo Scientific ArrayScan XTI High Content Analysis Reader. revolutionizing cell biology with the power of high content
 Thermo Scientific ArrayScan XTI High Content Analysis Reader revolutionizing cell biology with the power of high content learn more about your cells using high content technology Thermo Scientific High
Thermo Scientific ArrayScan XTI High Content Analysis Reader revolutionizing cell biology with the power of high content learn more about your cells using high content technology Thermo Scientific High
a Beckman Coulter Life Sciences: White Paper
 a Beckman Coulter Life Sciences: White Paper Violet-Excited nim-da Allows Efficient and Reproducible Cell Cycle Analysis on the Gallios Flow Cytometer Authors: Valdez, Ben 1. Carr, Karen 2. Norman, John
a Beckman Coulter Life Sciences: White Paper Violet-Excited nim-da Allows Efficient and Reproducible Cell Cycle Analysis on the Gallios Flow Cytometer Authors: Valdez, Ben 1. Carr, Karen 2. Norman, John
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN
 REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
Product: Expression Arrest TM egfp control shrna vector
 Product: Expression Arrest TM egfp control vector Catalog #: RHS1702 Product Description The laboratory of Dr. Greg Hannon at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has created an RNAi Clone Library comprised
Product: Expression Arrest TM egfp control vector Catalog #: RHS1702 Product Description The laboratory of Dr. Greg Hannon at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has created an RNAi Clone Library comprised
sirna Duplexes & RNAi Explorer
 P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
Development and validation of neutralising anti-drug antibody (Nabs) assays
 Development and validation of neutralising anti-drug antibody (Nabs) assays Clare Kingsley Sector Manager, Bioanalytical Sciences, Quotient Bioresearch EBF 2012 Overview Anti-drug antibody and neutralising
Development and validation of neutralising anti-drug antibody (Nabs) assays Clare Kingsley Sector Manager, Bioanalytical Sciences, Quotient Bioresearch EBF 2012 Overview Anti-drug antibody and neutralising
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit
 ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
User Manual/Hand book. qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse)
 User Manual/Hand book qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse) Kit Components Cat. No. MA003...Human Whole Genome mirna qpcr Profiling Kit (-20 C) The following components are sufficient
User Manual/Hand book qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse) Kit Components Cat. No. MA003...Human Whole Genome mirna qpcr Profiling Kit (-20 C) The following components are sufficient
CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA. For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.
 METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
Z-Stacking and Z-Projection using a Scaffold-based 3D Cell Culture Model
 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Z-Stacking and Z-Projection using a Scaffold-based 3D Cell Culture Model Brad Larson and Peter Banks, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT Grant Cameron, TAP Biosystems
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Z-Stacking and Z-Projection using a Scaffold-based 3D Cell Culture Model Brad Larson and Peter Banks, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT Grant Cameron, TAP Biosystems
HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit. HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit. 96 Tests. Table of Contents.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit 96 Tests HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit Cat# 4690-096-K Cat# 4690-096-K Table of Contents
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit 96 Tests HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit Cat# 4690-096-K Cat# 4690-096-K Table of Contents
DUB Activity Assay Kit
 DUB Activity Assay Kit Item No. 15981 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Precautions 4 If You
DUB Activity Assay Kit Item No. 15981 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Precautions 4 If You
MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2
 page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit
 Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives
 Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives (with hypothetical learning materials that might populate the objective) The topics and central questions listed here are typical for an introductory undergraduate
Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives (with hypothetical learning materials that might populate the objective) The topics and central questions listed here are typical for an introductory undergraduate
Highly specific and sensitive quantitation
 PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
Knipholone anthrone from Kniphofia foliosa induces a rapid onset of necrotic cell death in cancer cells
 Knipholone anthrone from Kniphofia foliosa induces a rapid onset of necrotic cell death in cancer cells Fitoterapia, 11/18/2010 Habtemariam S The present study examines the comparative cytotoxicity of
Knipholone anthrone from Kniphofia foliosa induces a rapid onset of necrotic cell death in cancer cells Fitoterapia, 11/18/2010 Habtemariam S The present study examines the comparative cytotoxicity of
Cytell Cell Imaging System
 Cytell Cell Imaging System Simplify your cell analysis and start changing tomorrow today www.gelifesciences.com/cytell The Cytell Cell Imaging System is an intuitive cell analysis instrument that streamlines
Cytell Cell Imaging System Simplify your cell analysis and start changing tomorrow today www.gelifesciences.com/cytell The Cytell Cell Imaging System is an intuitive cell analysis instrument that streamlines
NyONE - Cell imaging in a bird s eye view 4. NyONE...resolution matters! 8. Features & benefits 10. Fluorescence excitation channels 12
 Envisions confirmed Content NyONE - Cell imaging in a bird s eye view 4 From cells to numbers 6 NyONE...resolution matters! 8 Features & benefits 10 Fluorescence excitation channels 12 Technical specifications
Envisions confirmed Content NyONE - Cell imaging in a bird s eye view 4 From cells to numbers 6 NyONE...resolution matters! 8 Features & benefits 10 Fluorescence excitation channels 12 Technical specifications
Diabetes and Drug Development
 Diabetes and Drug Development Metabolic Disfunction Leads to Multiple Diseases Hypertension ( blood pressure) Metabolic Syndrome (Syndrome X) LDL HDL Lipoproteins Triglycerides FFA Hyperinsulinemia Insulin
Diabetes and Drug Development Metabolic Disfunction Leads to Multiple Diseases Hypertension ( blood pressure) Metabolic Syndrome (Syndrome X) LDL HDL Lipoproteins Triglycerides FFA Hyperinsulinemia Insulin
Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit
 Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
Proto col. GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells. Tech support: 877-994-8240. Luciferase Assay System
 Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
DNA Integrity Number (DIN) For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments
 DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials
 LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). This product is for research
Clonetics Conditionally Immortalized Human Cells. Relevant Cells for High Throughput Screening
 Clonetics Conditionally Immortalized Human Cells Relevant Cells for High Throughput Screening Clonetics Conditionally Immortalized Cell Strains Conditionally immortalized cell strains are primary cells
Clonetics Conditionally Immortalized Human Cells Relevant Cells for High Throughput Screening Clonetics Conditionally Immortalized Cell Strains Conditionally immortalized cell strains are primary cells
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship. Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the project
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the project
RNAi Shooting the Messenger!
 RNAi Shooting the Messenger! Bronya Keats, Ph.D. Department of Genetics Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center New Orleans Email: [email protected] RNA interference (RNAi) A mechanism by which
RNAi Shooting the Messenger! Bronya Keats, Ph.D. Department of Genetics Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center New Orleans Email: [email protected] RNA interference (RNAi) A mechanism by which
MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic DNA Extraction Kit. Performance Characteristics
 MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic DNA Extraction Kit Performance Characteristics Monolythix, Inc. 4720 Calle Carga Camarillo, CA 93012 Tel: (805) 484-8478 monolythix.com Page 2 of 9 MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic
MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic DNA Extraction Kit Performance Characteristics Monolythix, Inc. 4720 Calle Carga Camarillo, CA 93012 Tel: (805) 484-8478 monolythix.com Page 2 of 9 MLX BCG Buccal Cell Genomic
Annexin V Conjugates for Apoptosis Detection
 Annexin V Conjugates for Apoptosis Detection Table 1. Spectral characteristics and storage information. Catalog no. Material Annexin V conjugate Amount Ex/Em (nm)* Storage Stability A23202 Alexa Fluor
Annexin V Conjugates for Apoptosis Detection Table 1. Spectral characteristics and storage information. Catalog no. Material Annexin V conjugate Amount Ex/Em (nm)* Storage Stability A23202 Alexa Fluor
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection
 Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
ncounter Leukemia Fusion Gene Expression Assay Molecules That Count Product Highlights ncounter Leukemia Fusion Gene Expression Assay Overview
 ncounter Leukemia Fusion Gene Expression Assay Product Highlights Simultaneous detection and quantification of 25 fusion gene isoforms and 23 additional mrnas related to leukemia Compatible with a variety
ncounter Leukemia Fusion Gene Expression Assay Product Highlights Simultaneous detection and quantification of 25 fusion gene isoforms and 23 additional mrnas related to leukemia Compatible with a variety
Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit
 Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600050 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Hydrogen Peroxide Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600050 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Automating Cell Biology Annual general meeting, September 7, 2015. Phase Holographic Imaging www.phiab.se
 Automating Cell Biology Annual general meeting, September 7, 2015 www.phiab.se 1 PHASE HOLOGRAPHIC IMAGING (PHI) Began as a research project at Lund University, Sweden, in 2000 Founded in 2004 Sales in
Automating Cell Biology Annual general meeting, September 7, 2015 www.phiab.se 1 PHASE HOLOGRAPHIC IMAGING (PHI) Began as a research project at Lund University, Sweden, in 2000 Founded in 2004 Sales in
Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit
 Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600450 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600450 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results
 How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results Introduction The Biotin Streptavidin system continues to be used in many protein based biological research applications including; ELISAs, immunoprecipitation,
How to Biotinylate with Reproducible Results Introduction The Biotin Streptavidin system continues to be used in many protein based biological research applications including; ELISAs, immunoprecipitation,
