SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Harper
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service Takuya Shinozaki, Etsuko Matsubara, Masahiro Kadono and Mayumi Takahashi DoCoMo s SMS Roaming Service and SMS Interworking Service have been launched. It now became possible to make use of SMS in roaming environments and message transmission between DoCoMo and overseas operators. 1. Introduction DoCoMo s Short Message Service (SMS) Roaming Service (outbound roaming and packet outbound roaming) and SMS Interworking Service were launched in December 2004 and February 2005, respectively, as new services of the international roaming services, WORLD WING [1][2] and WORLD WALK- ER PLUS/G-CARD [2]. With the launch of the SMS Roaming Service, it has become possible for outbound roaming users in overseas locations to receive and transmit SMS in addition to conventional voice call-based roaming. SMS is widely used in Europe, Asian countries and other parts of the world, and is a basic service provided by the majority of overseas operators; the environment required for SMS roaming has thus been mostly ready. Moreover, the demand for text-based communication is high in Japan as well, which lead us to launch SMS Roaming Service. Since only the receiver s telephone number needs to be specified for the address in the same way as within Japan, the user convenience to send SMS from abroad is maintained. Also, the roaming services that allow users of overseas operators to use DoCoMo networks were already launched in May Roaming users can thus use both voice and SMS services within DoCoMo networks. The SMS Interworking Service made the SMS service available to users of overseas operators as well, which used to be provided among s only. Currently, voice and video phone calls to overseas locations are provided via the WORLD CALL service. With this new additional service, we promote further globalization and aim to improve the user convenience. An SMS is sent from a FOMA terminal supporting the service 60
2 NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal Vol. 7 No.2 SMSC MPS IWMSC/GMSC STP SS7 signaling transport network NSTP VLR MSC STP: Signaling Transfer Point NSTP: New Signaling Transfer Point Figure 1 Network configuration in SMS roaming service by entering + first, which is the international call identifier, followed by country code and then telephone number. A very simple transmission procedure is adopted in order to provide services that are easy to use for users. No special subscription is required to use the SMS Interworking Service, and s can use it freely. Moreover, SMS Roaming Service is automatically made available for users who have subscribed to the international roaming service. This article provides an overview of the controls adopted within the DoCoMo networks and explains how the operation is coordinated with overseas networks in SMS Roaming Service and the SMS Interworking Service. Note that the same control is used for WORLD WALKER PLUS/G-CARD users as well in terms of SMS outbound roaming. 2. SMS Roaming Service Figure 1 shows the network configuration for providing SMS Roaming Service. A DoCoMo network and an overseas network are connected via SS7 signaling transport network. The specific controls are explained below. 2.1 Controlling SMS Transmission/Reception of Outbound Roaming Users 1) Location Registration Control Figure 2 shows an overview of the processing performed when a registers his/her location in an overseas network. A location registration is sent from the mobile terminal to a Serving General packet radio service Support Node () of the overseas network (1). Subscriber (e.g. SMS subscription ) (1) Location registration (6) The status of SMS service provision by the overseas network is stored (2) Authentication acquisition (3) Location registration (5) Subscriber acquisition (4) Subscriber deletion Figure 2 Overview of processing at location registration ( in range of overseas network) After authenticating the, the /the Visitor Location Register (VLR) of the overseas network sends a location registration to a New Mobile Service Control Point () (2), (3). The, upon receiving the location registration, recognizes that the subscriber has roamed out to the overseas network based on their /VLR numbers of the registered network, and deletes the subscriber in the previously registered network (4). Next, it judges whether or not the network that the roaming user is connected to is part of the Circuit Switching (CS) service/packet Switching (PS) service roaming agreement, whether or not the user is a roaming service subscriber, and whether or not any roaming restrictions apply to the user. If all these requirements are satisfied, the downloads the subscriber, including the SMS subscription, to the /VLR of the overseas network and completes the location registration (5). If DoCoMo has only made a roaming agreement for CS services 61
3 with the overseas operator, only the CS service location registration is completed. This allows the user to use SMS at the roaming destination. Not all overseas networks provide SMS services. If an overseas network does not support SMS services, it is notified to the in response to the authentication acquisition. Based on the, the stores the status of SMS service provision for the overseas network, making it possible to avoid unnecessary call reception control (6). The details of this call reception avoidance processing are explained in 2). 2) SMS Transmission/Reception Control Figure 3 shows an overview of the processing involved in SMS transmission/reception between outbound roaming users. If an outbound roaming user sends an SMS to a FOMA user, an SMS transmission is sent from the mobile terminal to a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) of the overseas network (or an in the overseas network) (1). The MSC in the overseas network judges whether or not the caller is an SMS subscriber and, if he/she is a subscriber, sends an SMS transmission to the representative Message Processing System (MPS) number stored in the User Identity Module (UIM). This signal is tentatively received by a representative Gateway/Transit Mobile Multimedia switching System () via the SS7 signaling transport network (2). This is necessary because the representative MPS number is in fact a non-existing switching system number, and it is hence necessary to terminate the signal at the and relay it after determining the actual MPS number of the SMS registration destination and the number of the that handles the MPS in question (3). The representative sends the SMS transmission to the handling the MPS (4) and the SMS is stored in the MPS (5). Upon receiving an SMS transfer from the MPS (6), the sends a reception read to the in order to acquire the of the network to which the receiving user is registered (the and MSC numbers of the registered network) (7). If the receiving user is also outbound roaming, the checks the status of SMS service provision of the overseas network (8). If the overseas network does not provide SMS services, the does not return the registered network to the and the SMS is not sent to the receiving user. If, on the other hand, the overseas network does provide SMS services, the returns a reception read response containing the registered network to the (9). The then sends an SMS transfer based on the registered network and the mobile terminal receives the SMS (10), (11). 2.2 Controlling SMS Transmission/Reception of Inbound Roaming Users 1) Location Registration Control Figure 4 shows an overview of the processing performed when a user of an overseas network registers his/her location to a DoCoMo network. A location registration is sent from the mobile termi- (1) SMS transmission (3) Determination of MPS number of registration destination and number handling MPS (2) SMS transmission Representative (10) SMS transfer (11) SMS reception (5) SMS storage (4) SMS transmission (9) Reception read response MPS (6) SMS transfer (7) Reception read (8) In case of outbound roaming, the status of SMS service provision of the overseas network is checked and the registered network is returned Figure 3 Overview of processing at SMS transmission/reception (between outbound roaming users) 62
4 NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal Vol. 7 No.2 (5) Subscriber acquisition (3) Location registration (2) Authentication acquisition (4) Subscriber deletion Subscriber (e.g. SMS subscription ) (1) Location registration Overseas network user Figure 4 Overview of processing at location registration (overseas network user in range of DoCoMo network) nal to the Local Mobile Multimedia switching System ()/serving/gateway GPRS Support Node () of the DoCoMo network (1). The / authenticates the and judges whether or not the caller is a subscriber of a network that is part of the roaming agreement (2). If the network is part of the roaming agreement, the / sends the location registration to a Home Location Register () of the overseas network (3). Subscriber including the SMS subscription is then downloaded from the of the overseas network to the /. The location registration is completed when the / retains this (4), (5). 2) SMS Transmission/Reception Control Figure 5 shows an overview of the processing involved in SMS transmission/reception between overseas network users. If an overseas network user sends an SMS, an SMS transmission is sent from the mobile terminal to an / (1). The / judges whether or not the overseas network user is an SMS subscriber and whether or not the SMS registration destination is part of the roaming agreement (2). The / maintains the overseas network s SMSC number and is thus able to judge whether or not the SMS registration destination is part of the roaming agreement. If the requirements are satisfied, the / sends an SMS transmission to a Short Message Service Center (SMSC) of the overseas network via an InterWorking Mobile Switching Center (IWMSC) of the overseas network (3), and the SMS is stored in the SMSC of the overseas network (4). Upon receiving an SMS transfer from the SMSC of the overseas network (5), a Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC) of the overseas network reads of the network to which the receiving user is registered (the and MSC numbers of the registered network) from the of the overseas network (6) and sends an SMS transfer based on this (7), whereupon the mobile terminal receives the SMS (8). 2.3 Billing Control User billing and settlement among operators related to outbound roaming users are handled according to billing created for individual roaming destinations, which is obtained via a clearing house *. / nodes are equipped with detailed bill creation functions for handling billing of inbound roaming users in overseas networks and settlement among operators. In case of SMS transmission from an inbound roaming user, a detailed bill is created when an SMS is stored in an overseas network SMSC. In case of SMS transfer to an inbound roaming user, a detailed * Clearing house: A third party organization that settles costs involved in international roaming, including network usage fees generated among mobile communication carriers. (4) SMS storage SMSC (5) SMS transfer (6) Reception reading (2) It is judged whether or not the caller is an SMS subscriber and whether or not the SMS registration destination is a network that is part of the roaming agreement IWMSC GMSC (7) SMS transfer (3) SMS transmission (1) SMS transmission (8) SMS reception Overseas network user Overseas network user Figure 5 Overview of processing at SMS transmission/reception (between overseas network users) 63
5 bill is created when an SMS is stored in the mobile terminal. 3. SMS Interworking Service The configuration of the connected networks for providing the SMS Interworking Service is the same as for SMS Roaming Service (Fig. 1). The specific controls are explained below. 3.1 SMS Transmission/Reception Control (From a FOMA User to an Overseas Network User) Figure 6 shows an overview of the processing involved in SMS transmission/reception from a in range of a DoCoMo network to an overseas network user in the range of his/her own network. If a in range of a DoCoMo network sends an SMS to an overseas network user, an SMS transmission is sent from the mobile terminal to an / (1). The / determines the MPS number of the SMS registration destination and the number of the handling the MPS in question, and sends an SMS transmission to the handling the MPS (2). Upon receiving the SMS transmission, the judges whether or not the telephone number of the SMS transmission destination belongs to the overseas network and whether or not the number is a telephone number of a network that is part of the international SMS agreement (3). If it is a telephone number belonging to a network that is part of the international SMS agreement, the sends an SMS transmission to the MPS (5) and the SMS is stored in the MPS (6). If the operator belongs to a network that is part of the international SMS agreement and is situated in a country that conforms to Mobile Number Portability (MNP), it is not possible to identify whether or not the number is a telephone number of a network that is part of the international SMS agreement based on the telephone number alone, and one of the following cases may occur. An SMS is sent to a user who moved out from a network that is part of the international SMS agreement in a country supporting MNP to a network not part of the international SMS agreement. An SMS cannot be sent to a user who moved into a network that is part of the international SMS agreement from a network not part of the international SMS agreement in a country supporting MNP. In order to deal with these problems, if a receiving an SMS transmission (2) recognizes a telephone number of an overseas network from the number, it judges whether it is a telephone number of a country conforming to MNP or not (3). If it is a telephone number of a country conforming to MNP, it acquires the reception from an of the overseas network and obtains the user s International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) in order to identify the operator (4). If, on the other hand, the caller is a subscriber of a network that is part of the international SMS agreement, the sends an SMS transmission to the MPS (5) and the SMS is stored in the MPS (6). In order to implement this procedure, the manages about MNP conformity for each telephone number and interna- MPS (6) SMS storage (7) SMS transfer (4) Reception reading (8) Reception reading (10) SMS reception (9) SMS transfer (2) SMS transmission (1) SMS transmission (5) SMS transmission (3) It is judged whether or not the country conforms to MNP from the telephone number of the SMS transmission destination In case of a country conforming to MNP It is judged whether or not the caller is a subscriber of a network that is part of the international SMS agreement based on the IMSI after performing step (4) In case of a country not conforming to MNP It is judged whether or not the caller is a subscriber of a network that is part of the international SMS agreement based on the telephone number without performing step (4) Overseas network user Figure 6 Overview of processing at SMS transmission/reception (from to overseas network user) 64
6 NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal Vol. 7 No.2 tional SMS agreement status for each operator. By implementing these procedures, we managed to solve the problems above and achieved correct SMS transmission to users in countries conforming to MNP. Based on the telephone number of the SMS transmission destination, the receiving an SMS transfer from the MPS (7) recognizes that the receiving user is a subscriber of an overseas network and reads the reception from an of the overseas network in order to obtain of the network to which the receiving user is registered (the and MSC numbers of the registered network) (8) by acquiring the reception. The then sends an SMS transmission based on the registered network obtained from the of the overseas network (9) and the mobile terminal receives the SMS (10). judges whether or not the network is part of the international SMS agreement based on the SMSC number stored in the reception read (6). In the case where the network is part of the international SMS agreement, the returns a reception read response containing the registered network to the GMSC of the overseas network (7). The GMSC of the overseas network then sends an SMS transfer based on the registered network acquired from the (8) and the mobile terminal receives the SMS (9). The same reception control is performed regardless of whether the sender of the SMS is in a country conforming to MNP or a country not conforming to MNP, because the judgment of networks taking part in the international SMS is performed based on SMSC numbers. 3.2 SMS Transmission/Reception Control (From an Overseas Network User to a FOMA User) Figure 7 shows an overview of the processing involved in SMS transmission from an overseas network user in range of his/her network to a. If an overseas network user sends an SMS to a (1), the SMS is stored in an SMSC of the overseas network via an IWMSC of the overseas network (2), (3). The SMSC of the overseas network then sends an SMS transfer to a GMSC of the overseas network (4), which in turn sends a reception read to an on the FOMA side in order to acquire the of the network to which the receiving user is registered (the and MSC numbers of the registered network) (5). The 3.3 Countermeasures against Spam Mails After the launch of the SMS Interworking Service, there is a risk that spam mails may be sent from overseas networks via the Internet. As a countermeasure against this, s regulate SMS transmission from overseas network users to s in excess of a certain amount. Since an is the first device to receive transmissions from an overseas network user to a, it serves as a guard function for the entire DoCoMo network by implementing this function. 4. Conclusion This article explained the control processing carried out within the DoCoMo networks and the interworking with overseas networks in SMS Roaming Service and the SMS (3) SMS storage SMSC (4) SMS transfer (6) It is judged whether or not the network is part of the overseas SMS agreement based on the SMSC number (5) Reception read IWMSC GMSC (7) Reception read response (2) SMS transmission (8) SMS transfer (1) SMS transmission (9) SMS reception Overseas network user Figure 7 Overview of processing at SMS transmission/reception (from overseas network user to ) 65
7 Interworking Service. Both services play important roles in supporting DoCoMo s international services. For this reason, we will aggressively promote expansion of the countries and regions where these services are available and make efforts to improve the convenience for DoCoMo users to upgrade DoCoMo s international services. References [1] M. Kikkawa et al.: FOMA International Roaming Service, NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal, Vol. 5, No. 2, pp , Sep [2] DoCoMo World Service Website: How to use the roaming service ; ml Abbreviations CS: Circuit Switching GMMS: Gateway Mobile Multimedia switching System GMSC: Gateway Mobile Switching Center : Home Location Register IMSI: International Mobile Subscriber Identity IWMSC: InterWorking Mobile Switching Center : Local Mobile Multimedia switching System MNP: Mobile Number Portability MPS: Message Processing System MSC: Mobile Switching Center : New Mobile Service Control Point NSTP: New Signaling Tranfer Point PS: Packet Switching : Serving General packet radio service Support Node SMS: Short Message Service SMSC: Short Message Service Center STP: Signaling Tranfer Point TMMS: Transit Mobile Multimedia switching System UIM: User Identity Module VLR: Visitor Location Register : serving/gateway GPRS Support Node 66
How To Send An Msc To A Cell Phone From A Corporate Server In Ntokdomo (Ntimo) (Ntok) (Ntokdomo) (For A Ppl) ( For A Pn)
 Corporate Solutions SMS Communications Module SMS Center Push Service Infrastructure for Enterprise Solutions There has been increasing need recently for new functionality in enterprise solutions, such
Corporate Solutions SMS Communications Module SMS Center Push Service Infrastructure for Enterprise Solutions There has been increasing need recently for new functionality in enterprise solutions, such
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Implementing LTE International Data Roaming
 Implementing International Data Roaming Data Roaming Standardization Implementing International Data Roaming On completion of EPC standardization at 3GPP, specifications for international roaming between
Implementing International Data Roaming Data Roaming Standardization Implementing International Data Roaming On completion of EPC standardization at 3GPP, specifications for international roaming between
NTT DOCOMO Technical Journal. Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications
 M2M 3GPP Standardization Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications The number
M2M 3GPP Standardization Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends Core Network Infrastructure and Congestion Control Technology for M2M Communications The number
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Office Link System for FOMA Internal Line Connections
 Enterprise-oriented Internal Line Service FOMA Internal Line Service Internal Line Optional Functions Office Link System for FOMA Internal Line Connections Although we have previously offered OFFICEED,
Enterprise-oriented Internal Line Service FOMA Internal Line Service Internal Line Optional Functions Office Link System for FOMA Internal Line Connections Although we have previously offered OFFICEED,
CS Fallback Function for Combined LTE and 3G Circuit Switched Services
 EPC Voice over Circuit Switched Services Special Articles on SAE Standardization Technology CS Fallback Function for Combined and Circuit Switched Services The PP, an international standardization body
EPC Voice over Circuit Switched Services Special Articles on SAE Standardization Technology CS Fallback Function for Combined and Circuit Switched Services The PP, an international standardization body
of the existing VoLTE roaming and interconnection architecture. This article compares existing circuit-switched models with the earlier
 VoLTE 3GPP Roaming Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends VoLTE Roaming and ion Standard Technology In 3GPP Release 11, the VoLTE roaming and interconnection architecture
VoLTE 3GPP Roaming Further Development of LTE/LTE-Advanced LTE Release 10/11 Standardization Trends VoLTE Roaming and ion Standard Technology In 3GPP Release 11, the VoLTE roaming and interconnection architecture
Call Forwarding Service
 Regarding Use of This Guide This guide is intended for users of DOCOMO mobile phones with a DOCOMO UIM Card (or otherwise a FOMA Card or DOCOMO mini UIM Card. Hereinafter the same applies). If the SIM
Regarding Use of This Guide This guide is intended for users of DOCOMO mobile phones with a DOCOMO UIM Card (or otherwise a FOMA Card or DOCOMO mini UIM Card. Hereinafter the same applies). If the SIM
PushTalk Service System
 PushTalk Service System Naomasa Yoshida, Masaharu Nakagawa, Makoto Nakayama, Youhei Ikai, Miya Matsuda and Masanobu Yamagiwa We have developed a system for providing the PushTalk service, which allows
PushTalk Service System Naomasa Yoshida, Masaharu Nakagawa, Makoto Nakayama, Youhei Ikai, Miya Matsuda and Masanobu Yamagiwa We have developed a system for providing the PushTalk service, which allows
IMT-2000 Network Architecture
 IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
An Oracle White Paper November 2013. Typical Key Performance Indicator Reports for Performance Intelligence Centers
 An Oracle White Paper November 2013 Typical Key Performance Indicator Reports for Performance Intelligence Centers Disclaimer The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended
An Oracle White Paper November 2013 Typical Key Performance Indicator Reports for Performance Intelligence Centers Disclaimer The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended
Overview of GSMA VoLTE Profile. minimum required functions [3]. 2. Background
![Overview of GSMA VoLTE Profile. minimum required functions [3]. 2. Background Overview of GSMA VoLTE Profile. minimum required functions [3]. 2. Background](/thumbs/26/8506418.jpg) GSMA Overview of GSMA Profile It was agreed in the GSMA in February 2010 that voice services over LTE () shall use the platform standardized by the 3GPP with a view to maximizing international interoperability.
GSMA Overview of GSMA Profile It was agreed in the GSMA in February 2010 that voice services over LTE () shall use the platform standardized by the 3GPP with a view to maximizing international interoperability.
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
Voice mail Play messages Activate Deactivate. Voice mail. Activate? Voice mail. Play messages Activate Deactivate. Set ring time.
 Regarding Use of This Guide This guide is intended for users of DOCOMO mobile phones with a DOCOMO UIM Card (or otherwise a FOMA Card or DOCOMO mini UIM Card. Hereinafter the same applies). If the SIM
Regarding Use of This Guide This guide is intended for users of DOCOMO mobile phones with a DOCOMO UIM Card (or otherwise a FOMA Card or DOCOMO mini UIM Card. Hereinafter the same applies). If the SIM
LTE service area. 3G service area. EPS : Evolved Packet System. Currently Planning & Coordination Office 1 C *
 VoLTE esrvcc VSRVCC Inter-domain Handover Technologies in LTE for Voice (VoLTE) and TV Phone A data communication service called Xi (Crossy) has started in LTE. In the future, voice and TV phone services
VoLTE esrvcc VSRVCC Inter-domain Handover Technologies in LTE for Voice (VoLTE) and TV Phone A data communication service called Xi (Crossy) has started in LTE. In the future, voice and TV phone services
How To Use One Number Vip On A Cell Phone On A Sim Sim (Nto) On A Pnet (Ntok) On An Ipphone (Ntt) On Ntok (Ntk) On Pnet On A Mobile
 Core Network System for Implementation of One Number Service FMC Core Network System for Implementation of One Number Service As part of efforts to improve the usability of services from NTT DOCOMO, we
Core Network System for Implementation of One Number Service FMC Core Network System for Implementation of One Number Service As part of efforts to improve the usability of services from NTT DOCOMO, we
*1 sp-mode TM : sp-mode and sp-mode logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of. of NTT DOCOMO, INC.
 Smartphone e-mail Service New Services and Functions for Smartphones in 2010 e-mail Service for The market for smartphones has been expanding rapidly in recent years. It has been possible to freely download
Smartphone e-mail Service New Services and Functions for Smartphones in 2010 e-mail Service for The market for smartphones has been expanding rapidly in recent years. It has been possible to freely download
Mobile Networking. SS7 Network Architecture. Purpose. Mobile Network Signaling
 Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Collax Mail Server. Howto. This howto describes the setup of a Collax server as mail server.
 Collax Mail Server Howto This howto describes the setup of a Collax server as mail server. Requirements Collax Business Server Collax Groupware Suite Collax Platform Server including Collax Communication
Collax Mail Server Howto This howto describes the setup of a Collax server as mail server. Requirements Collax Business Server Collax Groupware Suite Collax Platform Server including Collax Communication
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN. Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification
 TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
TS-3GB-S.R0103-0v1.0 Network Firewall Configuration and Control (NFCC) - Stage 1 Requirements
 TS-3GB-S.R0103-0v1.0 Network Firewall Configuration and Control (NFCC) - Stage 1 Requirements Mar 3,2005 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE TS-3GB-S.R0103-0v1.0 Network Firewall Configuration and
TS-3GB-S.R0103-0v1.0 Network Firewall Configuration and Control (NFCC) - Stage 1 Requirements Mar 3,2005 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE TS-3GB-S.R0103-0v1.0 Network Firewall Configuration and
Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher Help for Mac OS X
 Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher Help for Mac OS X Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher allows you to manage and monitor the connection between your modem and the network. With Watcher, you can: Determine signal
Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher Help for Mac OS X Sierra Wireless AirCard Watcher allows you to manage and monitor the connection between your modem and the network. With Watcher, you can: Determine signal
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
SOLUTIONS FOR ROAMING AND INTEROPERABILITY PROBLEMS BETWEEN LTE AND 2G OR 3G NETWORKS
 Review of the Air Force Academy No 2 (24) 2013 SOLUTIONS FOR ROAMING AND INTEROPERABILITY PROBLEMS BETWEEN LTE AND 2G OR 3G NETWORKS Radu CURPEN, Florin SANDU, Cosmin COSTACHE, Gabriel Mihail DANCIU Transilvania
Review of the Air Force Academy No 2 (24) 2013 SOLUTIONS FOR ROAMING AND INTEROPERABILITY PROBLEMS BETWEEN LTE AND 2G OR 3G NETWORKS Radu CURPEN, Florin SANDU, Cosmin COSTACHE, Gabriel Mihail DANCIU Transilvania
All-IP Network Emergency Call Support
 GPP S.R0-0 Version.0 Version Date: October 00 All-IP Network Emergency Call Support Stage Requirements COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
GPP S.R0-0 Version.0 Version Date: October 00 All-IP Network Emergency Call Support Stage Requirements COPYRIGHT GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
Mobile SMS and Data Roaming Explained
 Mobile SMS and Data Roaming Explained Mobile SMS and data roaming explained Roaming is the ability of customers to use their mobile phones or other mobile devices outside the geographical coverage area
Mobile SMS and Data Roaming Explained Mobile SMS and data roaming explained Roaming is the ability of customers to use their mobile phones or other mobile devices outside the geographical coverage area
Updating Software. N900iG Quick Guide for Updating Software
 N900iG Quick Guide for Updating Software Check whether software in the FOMA terminal needs to be updated, and download a part of software to update the software by using the packet communication if necessary.
N900iG Quick Guide for Updating Software Check whether software in the FOMA terminal needs to be updated, and download a part of software to update the software by using the packet communication if necessary.
Systems for Personal Data Storage Services
 NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal Vol. 8 No.2 Systems for Personal Data Storage Services Makoto Hamatsu, Tetsuo Sato and Eiji Yano As part of DoCoMo s efforts toward secure and safe mobile terminals, we developed
NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal Vol. 8 No.2 Systems for Personal Data Storage Services Makoto Hamatsu, Tetsuo Sato and Eiji Yano As part of DoCoMo s efforts toward secure and safe mobile terminals, we developed
Mobility Management usually includes two parts: location management and handoff management.
 Part 9: Mobile Data / Mobility Management I. Mobile Data Services/ Management This broad area involves a lot of industrial applications. Mobile data services/ management is becoming another profitable
Part 9: Mobile Data / Mobility Management I. Mobile Data Services/ Management This broad area involves a lot of industrial applications. Mobile data services/ management is becoming another profitable
Mobility Management for All-IP Core Network
 Mobility Management for All-IP Core Network Mobility Management All-IP Core Network Standardization Special Articles on SAE Standardization Technology Mobility Management for All-IP Core Network PMIPv6
Mobility Management for All-IP Core Network Mobility Management All-IP Core Network Standardization Special Articles on SAE Standardization Technology Mobility Management for All-IP Core Network PMIPv6
Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks. Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802
 Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802 Contents Motivation Solution Overview Methodology Overview 3G Attack Graph
Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802 Contents Motivation Solution Overview Methodology Overview 3G Attack Graph
Reduce Mobile Phone Expense with Avaya Unified Communications
 Reduce Mobile Phone Expense with Avaya Unified Communications Table of Contents Section 1: Reduce Inbound Minutes... 2 Section 2: Reduce Outbound Minutes... 3 Section 3: Take Greater Advantage of Free
Reduce Mobile Phone Expense with Avaya Unified Communications Table of Contents Section 1: Reduce Inbound Minutes... 2 Section 2: Reduce Outbound Minutes... 3 Section 3: Take Greater Advantage of Free
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
3GPP TS 29.119 V7.0.0 (2007-06)
 TS 29.119 V7.0.0 (2007-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) specification for GLR (Release 7) The present
TS 29.119 V7.0.0 (2007-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) specification for GLR (Release 7) The present
SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005
 UN SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) This is an UN official document Security
UN SMS SS7 Fraud 3.1 16 February 2005 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) This is an UN official document Security
Nokia Siemens Networks his 700 Integrated signaling application solutions
 Nokia Siemens Networks his 700 Integrated signaling application solutions Today s and the next generation networks use the Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) to exchange information within and between the networks.
Nokia Siemens Networks his 700 Integrated signaling application solutions Today s and the next generation networks use the Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) to exchange information within and between the networks.
EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server
 Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET
 Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
1 Introduction. 2 Assumptions. Implementing roaming for OpenBTS
 Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Guidelines on International Gateway Access and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Issued by the Nigerian Communications Commission
 Guidelines on International Gateway Access and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Issued by the Nigerian Communications Commission 1. Background (1) The Nigerian Communications Commission ( the Commission
Guidelines on International Gateway Access and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Issued by the Nigerian Communications Commission 1. Background (1) The Nigerian Communications Commission ( the Commission
End-2-End QoS Provisioning in UMTS networks
 End-2-End QoS Provisioning in UMTS networks Haibo Wang Devendra Prasad October 28, 2004 Contents 1 QoS Support from end-to-end viewpoint 3 1.1 UMTS IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)................... 3 1.1.1
End-2-End QoS Provisioning in UMTS networks Haibo Wang Devendra Prasad October 28, 2004 Contents 1 QoS Support from end-to-end viewpoint 3 1.1 UMTS IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)................... 3 1.1.1
Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7. Tobias Engel <[email protected]> twitter: @2b_as
 Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7 Tobias Engel twitter: @2b_as What is Signalling System #7? protocol suite used by most telecommunications operators throughout the world
Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7 Tobias Engel twitter: @2b_as What is Signalling System #7? protocol suite used by most telecommunications operators throughout the world
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP Operations
 Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
Advanced S Series: S and 3GPP Operations, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been chosen by the 3GPP for establishing multimedia sessions in UMTS Release 5 (R5) networks.
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
Traffic Control by Influencing User Behavior
 Traffic Control by Influencing User Behavior We examined a means of influencing user behavior to reduce the number of repeated calls by providing information to users and controlling the traffic before
Traffic Control by Influencing User Behavior We examined a means of influencing user behavior to reduce the number of repeated calls by providing information to users and controlling the traffic before
3GPP TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12)
 TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
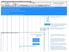 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Avaya one-x Mobile User Guide for iphone
 Avaya one-x Mobile User Guide for iphone Release 5.2 January 2010 0.3 2009 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved. Notice While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the information in this document was
Avaya one-x Mobile User Guide for iphone Release 5.2 January 2010 0.3 2009 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved. Notice While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the information in this document was
ESET Mobile Security Windows Mobile. Installation Manual and User Guide
 ESET Mobile Security Windows Mobile Installation Manual and User Guide Contents 1. Installation...3 of ESET Mobile Security 1.1 Minimum...3 system requirements 1.2 Installation...3 1.2.1 Installation...3
ESET Mobile Security Windows Mobile Installation Manual and User Guide Contents 1. Installation...3 of ESET Mobile Security 1.1 Minimum...3 system requirements 1.2 Installation...3 1.2.1 Installation...3
ESET Mobile Security Windows Mobile
 ESET Mobile Security Windows Mobile Installation Manual and User Guide Click here to download the most recent version of this document Contents 1. Installation...3 of ESET Mobile Security 1.1 Minimum...3
ESET Mobile Security Windows Mobile Installation Manual and User Guide Click here to download the most recent version of this document Contents 1. Installation...3 of ESET Mobile Security 1.1 Minimum...3
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 1 Network Topology Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to: Specify what is meant by network topology
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 1 Network Topology Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to: Specify what is meant by network topology
ETSI TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06)
 TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
PARAMETERS TO BE MONITORED IN THE PROCESS OF OPERATION WHEN IMPLEMENTING NGN TECHNICAL MEANS IN PUBLIC TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS
 Draft Recommendation Q.3902 PARAMETERS TO BE MONITORED IN THE PROCESS OF OPERATION WHEN IMPLEMENTING NGN TECHNICAL MEANS IN PUBLIC TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS Summary This Recommendation describes the main
Draft Recommendation Q.3902 PARAMETERS TO BE MONITORED IN THE PROCESS OF OPERATION WHEN IMPLEMENTING NGN TECHNICAL MEANS IN PUBLIC TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS Summary This Recommendation describes the main
ETSI TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09)
 TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
GSM and IN Architecture
 GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP [email protected] Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP [email protected] Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
How To Understand Gsm (Gsm) And Gsm.Org (Gms)
 TSG-SA Working Group 1 (Services) meeting #2 Edinburgh, Scotland 9 th -12 th March 1999 TSGS1#2(99)116 Agenda Item: 9.4 Source: Coordinator Title: Document for: Information I Universal Mobile Telecommunications
TSG-SA Working Group 1 (Services) meeting #2 Edinburgh, Scotland 9 th -12 th March 1999 TSGS1#2(99)116 Agenda Item: 9.4 Source: Coordinator Title: Document for: Information I Universal Mobile Telecommunications
SIP Roaming Server Product Overview. Mobile Convergence Technology
 SIP Roaming Server Product Overview Mobile Convergence Technology CONNECTING NETW ORKS Roam, Talk and Text (without a Mobile Network) By interworking with existing communications infrastructures, Session
SIP Roaming Server Product Overview Mobile Convergence Technology CONNECTING NETW ORKS Roam, Talk and Text (without a Mobile Network) By interworking with existing communications infrastructures, Session
Control Traffic from Grey Routes and Boost Enterprise Messaging Revenue
 SAP Brief SAP Mobile Services SAP SMS Firewall 365 Objectives Control Traffic from Grey Routes and Boost Enterprise Messaging Revenue Cloud-based managed service helps control messaging abuse Cloud-based
SAP Brief SAP Mobile Services SAP SMS Firewall 365 Objectives Control Traffic from Grey Routes and Boost Enterprise Messaging Revenue Cloud-based managed service helps control messaging abuse Cloud-based
IN.08 SMS Hubbing Handbook
 IN.08 SMS Hubbing Handbook Version 2.0 7 May 2007 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) Unrestricted Version 2.0 Page
IN.08 SMS Hubbing Handbook Version 2.0 7 May 2007 This is a non-binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (see next page) Unrestricted Version 2.0 Page
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Cellular Data Communications Made Easy
 Cellular Data Communications Made Easy by Peter Rysavy Published July 1, 1997, Network Computing Copyright Peter Rysavy and Network Computing All rights reserved Huge numbers of people are hitting the
Cellular Data Communications Made Easy by Peter Rysavy Published July 1, 1997, Network Computing Copyright Peter Rysavy and Network Computing All rights reserved Huge numbers of people are hitting the
Network-Assisted Mobile Terminal Support Technology
 Network-Assisted Mobile Terminal Support Technology Daisuke Ochi, Kenichi Yamazaki and Satoshi Tanaka The processing power of mobile terminals is greatly limited due to wireless links that disconnect under
Network-Assisted Mobile Terminal Support Technology Daisuke Ochi, Kenichi Yamazaki and Satoshi Tanaka The processing power of mobile terminals is greatly limited due to wireless links that disconnect under
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP
 Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been selected as the main signaling protocol of the Third Generation Partnership Projects IP Multimedia
Advanced SIP Series: SIP and 3GPP, Award Solutions, Inc Abstract The Session Initiation Protocol has been selected as the main signaling protocol of the Third Generation Partnership Projects IP Multimedia
Multimedia Communications Voice over IP
 Multimedia Communications Voice over IP Anandi Giridharan Electrical Communication Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India Voice over IP (Real time protocols) Internet Telephony
Multimedia Communications Voice over IP Anandi Giridharan Electrical Communication Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India Voice over IP (Real time protocols) Internet Telephony
Vulnerability Analysis on Mobile VoIP Supplementary Services and MITM Attack
 Vulnerability Analysis on Mobile VoIP Supplementary Services and MITM Attack You Joung Ham Graduate School of Computer Engineering, Hanshin University, 411, Yangsan-dong, Osan, Gyeonggi, Rep. of Korea
Vulnerability Analysis on Mobile VoIP Supplementary Services and MITM Attack You Joung Ham Graduate School of Computer Engineering, Hanshin University, 411, Yangsan-dong, Osan, Gyeonggi, Rep. of Korea
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
How To Connect Gsm To Ip On A Gsm Network On A Pnet On A Microsoft Cell Phone On A Pc Or Ip On An Ip Onc (Gsm) On A Network On An Iph (Gms) On An
 THE STUDY OF THE INTERCONNECTION OF GSM MOBILE COMMUNCATION SYSTEM OVER IP BASED NETWORK+ Le-Pond Chin. Jyh-Hong Wen2, and Ting-Way Liu Department of Information Management Shih-Chien University, Taipei,
THE STUDY OF THE INTERCONNECTION OF GSM MOBILE COMMUNCATION SYSTEM OVER IP BASED NETWORK+ Le-Pond Chin. Jyh-Hong Wen2, and Ting-Way Liu Department of Information Management Shih-Chien University, Taipei,
FOMA (R) /Wireless LAN Dual Terminals, Wireless LAN Technology
 FOMA (R) /Wireless LAN Dual Terminals, Wireless LAN Technology SHINOHARA Masahito, ITOH Masashi, IWATA Shinichiro, NISHIMURA Yasunori, ZAITSU Makoto Abstract FOMA (R) /wireless LAN dual terminals are dual-phone
FOMA (R) /Wireless LAN Dual Terminals, Wireless LAN Technology SHINOHARA Masahito, ITOH Masashi, IWATA Shinichiro, NISHIMURA Yasunori, ZAITSU Makoto Abstract FOMA (R) /wireless LAN dual terminals are dual-phone
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke [email protected] Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke [email protected] Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Phone Calls 3 My Phone Number...3-2 Adjusting In-Call Volume... 3-2 Making Calls...3-2 Receiving Calls...3-5 In-Call Operations...
 Phone Calls 3 My Phone Number...3-2 Adjusting In-Call Volume... 3-2 Making Calls...3-2 Making a Voice Call... 3-2 Calling from Contacts... 3-3 Calling from Call History... 3-3 Using Speed Dial... 3-3 Making
Phone Calls 3 My Phone Number...3-2 Adjusting In-Call Volume... 3-2 Making Calls...3-2 Making a Voice Call... 3-2 Calling from Contacts... 3-3 Calling from Call History... 3-3 Using Speed Dial... 3-3 Making
GPRS Overview. GPRS = General Packet Radio Service. GPRS Network
 GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
FAQs ACTIVATION / RELATED. You may also contact our customer care center for assistance to have the application downloaded on your handset.
 FAQs ACTIVATION / RELATED How to install and download the GETs application? Its easy to install the application - GSM customers: send sms to 53333 ( toll free) to fetch the download link. Just click
FAQs ACTIVATION / RELATED How to install and download the GETs application? Its easy to install the application - GSM customers: send sms to 53333 ( toll free) to fetch the download link. Just click
Software Update Simplified Operating Procedure SH902i SH902iS SH902iSL SH901iC SH901iS SH702iD SH700i SH700iS SH851i SH506iC
 Software Update Simplified Operating Procedure SH902i SH902iS SH902iSL SH901iC SH901iS SH702iD SH700i SH700iS SH851i SH506iC Refer to Updating Software of the user s guide for details. Note that the actual
Software Update Simplified Operating Procedure SH902i SH902iS SH902iSL SH901iC SH901iS SH702iD SH700i SH700iS SH851i SH506iC Refer to Updating Software of the user s guide for details. Note that the actual
TSGS#20(03)0247. Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects Meeting #20, Hämeenlinna, Finland, 09-12 June 2003
 Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects Meeting #20, Hämeenlinna, Finland, 09-12 June 2003 TSGS#20(03)0247 Source: SA1 Title: CR to 21.905 on 3GPP Generic User Profile (Rel-6) Document
Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects Meeting #20, Hämeenlinna, Finland, 09-12 June 2003 TSGS#20(03)0247 Source: SA1 Title: CR to 21.905 on 3GPP Generic User Profile (Rel-6) Document
The Basics of SMS Messaging
 The Basics of SMS Messaging Contents Introduction to SMS... 3 Types of SMS... 4 Standard Rate SMS... 4 Free to End User SMS (FTEU)... 4 Short Codes, Long Codes and Keywords... 5 Mobile Messaging Value
The Basics of SMS Messaging Contents Introduction to SMS... 3 Types of SMS... 4 Standard Rate SMS... 4 Free to End User SMS (FTEU)... 4 Short Codes, Long Codes and Keywords... 5 Mobile Messaging Value
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network
 Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin ([email protected]) Alexandre De Oliveira ([email protected]) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin ([email protected]) Alexandre De Oliveira ([email protected]) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
EXPLOITING SIMILARITIES BETWEEN SIP AND RAS: THE ROLE OF THE RAS PROVIDER IN INTERNET TELEPHONY. Nick Marly, Dominique Chantrain, Jurgen Hofkens
 Nick Marly, Dominique Chantrain, Jurgen Hofkens Alcatel Francis Wellesplein 1 B-2018 Antwerp Belgium Key Theme T3 Tel : (+32) 3 240 7767 Fax : (+32) 3 240 8485 E-mail : [email protected] Tel : (+32)
Nick Marly, Dominique Chantrain, Jurgen Hofkens Alcatel Francis Wellesplein 1 B-2018 Antwerp Belgium Key Theme T3 Tel : (+32) 3 240 7767 Fax : (+32) 3 240 8485 E-mail : [email protected] Tel : (+32)
Security Settings. Security codes. Restricting mail and calls. Restricting phone operations and functions. Using data security service
 Security Settings Security codes FOMA terminal security code............................ 126 Changing the terminal security code.... 127 Setting the PIN code.......................
Security Settings Security codes FOMA terminal security code............................ 126 Changing the terminal security code.... 127 Setting the PIN code.......................
An Oracle White Paper December 2013. The Value of Diameter Signaling in Security and Interworking Between 3G and LTE Networks
 An Oracle White Paper December 2013 The Value of Diameter Signaling in Security and Interworking Between 3G and LTE Networks Introduction Today s mobile networks are no longer limited to voice calls. With
An Oracle White Paper December 2013 The Value of Diameter Signaling in Security and Interworking Between 3G and LTE Networks Introduction Today s mobile networks are no longer limited to voice calls. With
