40 Gigabit Ethernet on Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches: How It Works
|
|
|
- Augustus Hancock
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 White Paper 40 Gigabit Ethernet on Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches: How It Works Sridhar Subramanian, Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco Shawn Wargo, Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco White Paper April Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 20
2 Executive Summary This white paper explains the high-level architecture and packet flow details of the 6904 line card in the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch. The paper assumes knowledge of the basic concepts of Policy Feature Card 4 (PFC4) and associated terminology detailed in the white paper Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor 2T Architecture. This document focuses on hardware that is shipping as of the date of this publication, and is not meant to be a configuration guide. Configuration examples are used throughout this paper to help explain the operational modes and features of the line card as applicable in the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series platform. For syntax reference of the command structures, please refer to the configuration and command guides for the 6500 Series at: Overview The Cisco Catalyst Port 40 Gigabit Ethernet Line Card, known by its product ID WS-X G-2T, is the first line card in the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series platform to offer 40 Gigabit Ethernet per port solution, along with a host of new software features. According to IEEE, from a compute and a networking point of view, server I/O capacity doubles every two years, and the networking technology doubles in speed every 18 months. Apart from having many market drivers such as consumer and broadband access, content providers, video on demand, highperformance computing and data center interconnect, 40 Gigabit Ethernet is now part of the IEEE 802.3ba standard. The WS-X G-2T module is designed with 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet fiber interfaces in order to meet the increasing demand for the 40 Gigabit Ethernet, as well as to offer the flexibility for aggregation of 10 Gigabit Ethernet in the campus and data center. This white paper will provide an architectural overview of the line card and the packet flow along with use cases. For the purposes of this document, we will interchangeably use 6904 module and WS-X G-2T module to refer to this line card. High-Level Description of WS-X G-2T The 6904 module, shown in Figure 1, is based on the fourth generation Policy Feature Card (PFC4). Along with the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Supervisor Engine 2T (Sup2T), the module enables the system to deliver three times the performance and four times the scalability of that possible with the previous generation Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series line cards. Belonging to the family of 6900 Series line cards that provide 80 Gigabit Ethernet per slot bandwidth, the 6904 provides both 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports. When running in 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode, the 6904 can provide a maximum of 4 ports, but in 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode, it can provide a maximum of 16 ports. This flexibility is possible as each port can accept a 40 Gigabit Ethernet C Form-Factor Pluggable (CFP) optics module or be divided further into to four ports each of 10 Gigabit Ethernet with a FourX adapter. To extend this flexibility even further, you can use the module in mixed mode, where one side of the card can use two CFP modules for 2 x 40 Gigabit Ethernet ports and the other side can use to FourX adapters for 8 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 20
3 Figure 1. Cisco 6904 (WS-X G-2T) Module The 6904 module contains a number of new hardware and software capabilities over the previous generation of line cards, including the following: Built-in Distributed Forwarding Card (DFC4) standard and XL modes Support for IEEE 802.1Qbh based VN-Tag protocol and Virtual Interface (VIF) processing Two-level, Strict Priority queuing in ingress and egress Two-level, quality-of-service (QoS) shaping on egress ports - per-queue and per-port Ingress buffer (5-MB/40 Gigabit Ethernet port, and 1.25-MB/10 Gigabit Ethernet port) Egress buffer (88-MB/40 Gigabit Ethernet port, and 21-MB/10 Gigabit Ethernet port) Support for Deficit Weighted Round Robin (DWRR) and Shaped Round Robin (SRR) congestion avoidance techniques IEEE 802.1ae (MACsec) encryption and authentication on all ports in 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet modes Support for up to eight Security Associations (SA) per port for Layer 2 and Layer 3 Cisco TrustSec Egress multicast replication at up to 80Gbps Virtual switch link (VSL) support on all ports in both 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet modes Blue Beacon LED on the front panel complimenting the line card status LED, for easy module identification in densely populated network environments Port Beacon LEDs on the front panel complimenting the port status LED, for easy port identification in densely populated chassis Quack chip support for counterfeit protection of field replaceable units (FRUs) 2 x 40 Gigabit Ethernet connections into the Switch fabric Up to 60-Mpps local forwarding System-Level Requirements The WS G-2T comes in standard or XL versions and is designed to operate in any Cisco Catalyst 6500-E Series chassis. The module will not be supported in any of the earlier non E-Series chassis. Table 1 provides details of the supported and unsupported chassis and Supervisor Engines for the 6904 module Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 20
4 Table 1. System Options for WS G-2T Supported Chassis Unsupported Chassis 6503-E, 6504-E, 6506-E, 6509-E, 6509-V-E, 6513-E 6503, 6506, 6509, 6509-NEB, 6509-NEB-A, 6513, 7603, 7603-S, 7604, 7606, 7606-S, 7609, OSR-7609, 7609-S, 7613 Supported Supervisors VS-S2T-10G, VS-S2T-10G-XL Unsupported Supervisors Sup1A, Sup2, WS-S720-1G, VS-S720-10G Except for the supervisor designated slots, all other slots in the 6500-E Series chassis can be used to populate the 6904 module. As for the port transceivers, both short-range and long-range fiber optics are supported. Table 2 provides details of the supported optics and transceiver types. Table 2. Supported Optics for WS-X G-2T Product ID Transceiver Type Media Type Distance CFP-40G-SR4 40GBASE-SR4 (MMF) Multimode Fiber 850nm 100m over OM3 Multimode Fiber CFP-40G-LR4 40GBASE-LR4 (SMF) Single Mode Fiber 1310nm CWDM 10 km CVR-CFP-410GSFP FourX Adapter: Converts each 40 GE CFP port to 4 10 GE SFP+ ports or 4 1GE SFP ports N/A N/A SFP-10G-SR SFP-10G-LR SFP-10G-LRM SFP-10G-ER SFP-H10GB-CU1M SFP-H10GB-CU3M SFP-H10GB-CU5M Supported SFP+ transceivers with FourX adapter MMF (OM3) SMF (G.652) MMF (FDDI grade) SMF(G.652) Copper TwinAx cable Copper TwinAx cable Copper TwinAx cable Up to 300m 10km 220m 40km 1m 3m 5m GLC-SX-MMD GLC-LH-SMD GLC-T Supported SFP transceivers with FourX adapter MMF (50 μm/ 62.5 μm FDDI) SMF/MMF Category 5 unshielded twisted pair copper cabling 550m/220m 10km (SMF)/550m (MMF) 100m Port Numbering Port numbering for the 6904 module has been assigned with the operational mode flexibility in perspective. Port numbers 1 to 4 pertain to the 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode of operation, and port numbers 5 to 20 pertain to the 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode. The naming on the front panel ports is shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The front panel ports can be logically divided in to two halves and for the purposes of illustration in this document, we will refer to ports 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 as the left half of the front panel ports, and we will refer to ports 3, 4, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, and 20 as the right half of the front panel ports. Figure 2. Port Numbering for 40 Gigabit Ethernet Ports 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 20
5 Figure 3. Port Numbering for 10 Gigabit Ethernet Ports Port Speed Operational Modes The front panel ports are logically grouped in to two portgroups: the left-half ports are grouped in to portgroup 1, and right-half ports are grouped in to portgroup 2. From a port speed configuration point of view, there are three modes of operation on the 6904 module: namely, 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode, 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode, and mixed mode. The default status of the port operation mode can be identified using the show hw-module slot # operation mode command, as follows: 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2#sh hw-module slot 3 operation mode Module 3 port group 1 is running in FortyGigabitEthernet mode Module 3 port group 2 is running in FortyGigabitEthernet mode 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2# 40 Gigabit Ethernet Port Operational Mode The default mode of operation will be 40 G mode and the four front panel ports will be prefixed by the keyword FortyGigabitEthernet in startup and running configuration files. For example, port 2 of a 6904 module in slot 3 of a 6500 E Series chassis will be named FortyGigabitEthernet3/2. A CFP adapter of the types listed in Table 2 will need to be plugged into the 6904 module front panel to use the port in 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode. Figure 4 shows a multi mode CFP-40G-SR transceiver. In the 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode, a maximum of four CFP adapters to provide 4 x 40 Gigabit Ethernet ports. Figure 4. Multimode CFP Transceiver for 40 Gigabit Ethernet Mode of Operation 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 20
6 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port Operational Mode The 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode of operation can be enabled using a configuration command that affects portgroups rather than individual ports. For example, portgroup 1 can be configured in 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode using the command hw-module slot # operation-mode port-group 1 TenGigabitEthernet. This will result in all ports on the left-half side of the front panel getting configured for 10 Gigabit Ethernet port operational mode. 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2(config)#hw-module slot 3 operation-mode port-group 1? TenGigabitEthernet Set the TenGigabitEthernet operation mode 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2(config)#hw-module slot 3 operation-mode port-group 1 TengigabitEthernet Operation mode change will reset the whole module and all the ports config will be lost. Do you want to continue with reset? Powercycling module 3 due to operational mode change 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2(config)# The same command will need to be repeated for portgroup 2 in order to get all ports on the right-half side of the front panel configured for 10 Gigabit Ethernet port operational mode. Since port ASICs and associated framer chips need to be reset for a different speed of operation, the entire 6904 module will undergo a power reset for this operational mode to take effect. A FourX adapter along with SFP+ transceivers of the types listed in Table 2 will need to be plugged into the 6904 module front panel to use the port in 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode. Figure 5 shows a FourX adapter. A maximum of four can be used in 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode for providing 16 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports. Figure 5. FourX Adapter for 10 Gigabit Ethernet Mode of Operation Mixed Mode In the mixed mode of operation, the 6904 module maintains the left half of the front panel ports in either the 10 Gigabit Ethernet or 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode and the right half of the front panel ports in a different mode. That will mean one half-side to support 2 x CFP for providing 2 x 40 Gigabit Ethernet ports, and the other half-side with 2 x FourX for supporting 8 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports. There is no additional CLI for running the 6904 in mixed mode. The configuration command for converting the 6904 in to 10 Gigabit Ethernet or 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode of operation will need to be used for changing the module from one mode to another. In accordance with the port numbering detailed in Figures 2 and 3, the interface naming in the software configurations for a mixed operational mode with 40 Gigabit Ethernet on left half and 10 Gigabit Ethernet on right half of the front panel ports is as follows: interface FortyGigabitEthernet <slot/1-2> interface TenGigabitEthernet <slot/13-20> 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 20
7 Port Performance Modes The 6904 module has two performance modes: oversubscription mode and performance mode. Note that these modes affect portgroups rather than an individual port. By default, the module operates in oversubscription mode since a backplane capacity of 80 GB per slot feeds 4 x 40 Gigabit Ethernet or 16 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports, resulting in a 2:1 oversubscription ratio. The default port performance mode can be identified using a show command: 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2#sh hw-module slot 3 oversubscription port-group 1 enabled 2 enabled oversubscription-mode Performance mode can be enabled by issuing a configuration command that will result in shutting down certain ports in the selected portgroup so as to make the port-to-fabric bandwidth come down from 2:1 to 1:1. In 40 Gigabit Ethernet performance mode, ports 1 and 3 will be active and the remaining ports will be shut down. In 10 Gigabit Ethernet performance mode, ports 5, 6, 7, 8 and 13, 14, 15, 16 will be active, and the remaining ports will be shut down. 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2(config)#no hw-module slot 3 oversubscription port-group 1 WARNING: Switch to TRANSPARENT mode on module 3 port-group E.S2T.SA.DUT2(config)# : *Dec 19 04:20:11.606: %C6K_PLATFORM-6- ESTELLE_NON_OVERSUBSCRIPTION_TEN_GIG: Ports 9, 10, 11, 12, of slot 3 disabled to prevent module bandwidth oversubscription. 6513E.S2T.SA.DUT2(config)# Line Card Architecture The WS-X G connects to the Supervisor Engine 2T switch fabric via 2 x 40-Gbps full-duplex channels (for a total of 80-Gbps full-duplex backplane). There is a next-generation Fabric Interface ASIC that connects these 2 x 40-Gbps channels to the switch fabric, and logically separates the module into two halves. Note: This is why 10 or 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode is configured on one-half of the module. The Fabric Interface ASIC then connects to 4 x 20-Gbps full-duplex Fabric Interface ASICs, which each connect to 4 x Replication Engine ASICs. The Replication Engine ASICs are responsible for making bridging frames between the Fabric Interface ASIC and Port ASIC, making any necessary frame copies (for example, IP multicast and Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN), and communicating with the Forwarding Engine ASICs (that is, the DFC4) for all Layer 2, 3, and 4 forwarding and policy lookup processing Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 20
8 Figure 6 is a block diagram of the WS-X G-2T architecture. Figure 6. WS-X G-2T Architecture Block Diagram These architecture components are the same in behavior and performance as for other 6900 Series modules (for example, the WS-X G). The WS-X G architecture requires a new Port ASIC design, to support both 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode on a single ASIC complex. This uniquely flexible Port ASIC design also introduces special behavior and performance characteristics. To support both 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode, the Port ASIC complex is separated into two major components. The first component is the Cisco TrustSec and physical (PHY) interface, which must serialize and de-serialize the individual bits as they are either received or transmitted onto the Ethernet medium. This component also provides line-rate 802.1ae encryption and de-encryption, if enabled. The second component is the separate (full-duplex) transmit and receive MUX multiplex and demultiplex (MUX) Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), which must distribute the incoming and outgoing frames between the appropriate Replicate Engine ASIC and Cisco TrustSec/PHY ASIC. The RX MUX FPGA connects 4 x 16-Gbps ingress channels to the Replication Engine ASIC, and the Replication Engine ASIC connects 2 x 20-Gbps egress channels to the TX MUX FPGA. Packet Path Theory of Operation Ingress Mode To support both 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode, the new Port ASIC design makes it necessary to evenly load-balance frames across the multiple data paths, and behavior depends on the operation mode and direction (ingress or egress) of the flow. See the architecture block diagram (Figure 6) for ASIC and data path details Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 8 of 20
9 40 Gigabit Ethernet Mode at Ingress In this mode, the incoming 40 Gigabit Ethernet traffic flows must be load-balanced across 4 x 16-Gbps channels: Figure 7 shows the packet forwarding flow, which is also summarized here: 1. Individual bits enter the 40 Gigabit Ethernet CFP transceiver and are assembled into frames. 2. Individual frames are sent (interleaved) from the CFP to 4 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Cisco TrustSec/PHY paths. Decryption is performed if 802.1ae (MACsec) is enabled, and the flow is reassembled. 3. The flow procedes to the RX MUX FPGA. 4. The RX MUX FPGA then directs the flow onto one of 4 x 16-Gbps ingress channels to Replication Engine ASICs, based on the hash result. 5. The Replication Engine ASIC then requests a Layer 2, 3, or 4 forwarding and policy lookup on the DFC4, and receives the lookup result. 6. The flow is then sent on to the fabric interface and Fabric ASIC (remote destination) or returned to the TX MUX FPGA (local destination). Figure Gigabit Ethernet Ingress Packet Forwarding 10 Gigabit Ethernet Mode at Ingress In this mode, the incoming 10 Gigabit Ethernet traffic flows are 1:1 mapped to one of the 4 x 16-Gbps channels, and no hashing considerations are required. Figure 8 shows the ingress packet forwarding, and the steps in the process are summarized here: 1. Individual bits enter the 10 Gigabit Ethernet SFP+ transceiver and are assembled into frames. Each SFP+ slot is 1:1 mapped to one of the 4 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet paths. 2. Individual frames are sent from the SFP+ to the Cisco TrustSec/PHY ASIC. Decryption is performed if 802.1ae (MACsec) is enabled. 3. The flow procedes to the RX MUX FPGA. 4. The RX MUX FPGA then directs the flow onto one of 4 x 16-Gbps paths to one of the two Replication Engine ASICs, based on 1:1 mapping. 5. The Replication Engine ASIC then requests a Layer 2, 3, or 4 fowarding and policy lookup on the DFC4, and receives the lookup result Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 20
10 6. The flow is then sent on to the fabric interface and Fabric ASIC (remote destination) or returned to the TX MUX FPGA (local destination). Figure Gigabit Ethernet Ingress Packet Forwarding Ingress Flow Hash Incoming traffic flows on 40 Gigabit Ethernet ports must be load-balanced across 4 x 16-Gbps channels. This is required since both the 10 Gigabit Ethernet and 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode are supported by a single Port ASIC. As a result, the load-balancing need be done for ingress packet forwarding only when the line card operates in 40 Gigabit Ethernet operation mode. Independent flows are load-balanced across the four ingress channels, using a configurable hash algorithm similar to EtherChannel. The default hash input is src-dst-ip. Note: The 40 Gigabit Ethernet input hash computation is independent of (and/or in addition to) the EtherChannel hash computation of the Forwarding Engine ASIC (PFC4/DFC4). Thus it is very important to understand how traffic will arrive on a given 40 Gigabit Ethernet interface, in order to achieve 40 Gigabit Ethernet throughout each interface. With this architecture design, it is not possible to achieve line-rate with a single traffic flow. A minimum of four unique hash input values are necessary to achieve optimal load-balancing. A given data flow is defined by its unique combination of Layer 2, 3, and 4 packet headers. A single data transmission (flow) between host A and host B is different from the return transmission from host B to host A. Likewise, host A may transmit an HTTP flow to host B, and also transmit a separate FTP flow to host B. Hence, the variable purpose and network-layer placement of the 40 Gigabit Ethernet interface will determine the optimal ingress hash algorithm to configure. Several common scenarios are described below, and the default hash input of src-dst-ip will cover most cases. The load-balance algorithm is configured at the interface level for each, 40 Gigabit Ethernet interface. [no] load-blance<hash option> 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 10 of 20
11 Egress 40 Gigabit Ethernet Mode at Egress In this mode, the outgoing 40 Gigabit Ethernet traffic flows must be load-balanced across 2 x 20-Gbps channels. The forwarding lookup processing has already occurred (at ingress). Figure 9 and the following steps summarize the egress packet forwarding. 1. Individual frames arrive at the Fabric ASIC over one of the 2 x 40 Gigabit Ethernet switch fabric channels, with a 32Bytes fabric header, which contains the lookup result from ingress stage. 2. Each frame is directed to one of the 2 x Fabric Interface ASICs, based on the lookup result contained in the fabric header. 3. The flow procedes to the Replication Engine ASIC. The Replication Engine requests an egress lookup (for example, MAC learning) and either bridges the frame directly to the Port ASIC, or performs packet replication (for example, IP multicast or SPAN). 4. The flow arrives on the TX MUX FPGA, which merges multiple flows from both upstream Replication Engines, and then sends individual frames to the Cisco TrustSec/PHY ASIC. 5. Individual frames are sent (interleaved) over the 4 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Cisco TrustSec/PHY paths to the CFP. Encryption is performed if 802.1ae (MACsec) is enabled. 6. The CFP serializes the frames into individual bits and transmits over the medium. Figure Gigabit Ethernet Egress Packet Forwarding 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 11 of 20
12 10 Gigabit Ethernet Mode at Egress In this mode, the incoming 10 Gigabit Ethernet traffic flows are 1:2 mapped to one of the 2 x 20-Gbps channels. The forwarding lookup processing has already occurred (at ingress). For a summary, see Figure 10 and the following steps. 1. Individual frames arrive at the Fabric ASIC over one of the 2 x 40 Gigabit Ethernet switch fabric channels, with a 32Bytes fabric header, which contains the lookup result from ingress stage. 2. Each frame is directed to one of the 2 x Fabric Interface ASICs, based on the lookup result contained in the fabric header. 3. The flow procedes to the Replication Engine ASIC. The Replication Engine requests an egress lookup (for example, MAC learning) and either bridges the frame directly to the Port ASIC, or performs packet replication (for example, IP multicast or SPAN). 4. The flow arrives on the TX MUX FPGA and then sends individual frames to the Cisco TrustSec/PHY ASIC, based on 1:1 port mapping. 5. Individual frames are sent (interleaved) over the 4 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Cisco TrustSec/PHY paths to the CFP. Encryption is performed if 802.1ae (MACsec) is enabled. 6. The SFP+ serializes the frames into individual bits and transmits over the medium. Figure Gigabit Ethernet Egress Packet Forwarding EtherChannel Considerations EtherChannel is supported on both 10 Gigabit Ethernet and 40 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. There are no restrictions for EtherChannel on the 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports, but there are some restrictions when operating in 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode. These restrictions and best practices are explained in detail below Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 12 of 20
13 40 Gigabit Ethernet Mode A maximum of four 40 Gigabit Ethernet links, whether on one module or spread across multiple modules, is allowed in a single EtherChannel. This does not affect other modules or EtherChannels in the system. This is due to the fact that we need to use some resources for the egress load-balancing between Replication ASICs. 10 Gigabit Ethernet Mode Up to eight 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports can be used in an EtherChannel, whether on one module or spread across multiple modules. Best Practices EtherChannel members should be 2 or 4 (or 8, for 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode) ports. Use the adaptive hash algorithm for better performance during EtherChannel changes. Do not use three links in an EtherChannel because this will result in failure to reach 40 Gigabit Ethernet throughput. Quality of Service (QoS) WS-X G-2T module offers a set of new QoS capabilities, including: Dual strict priority queuing Two level Shaping: port level and queue level Before we look at the new capabilities, it is important to understand the enhancements and limitations in some traditional Cisco Catalyst 6500 output queue congestion management mechanisms as applicable to the 6904 module. Output Queue Congestion Management and Scheduling The 6904 module has four different congestion management mechanisms, which are Weighted Random Early Discard (WRED), Weighted Round Robin (WRR), Deficit Weighted Round Robin (DWRR), and Shaped Round Robin (SRR). The SRR and DWRR methods will be detailed in this paper as those operate differently in the 6904 module compared to what was possible with previous generation Cisco Catalyst 6500 line cards. Shaped Round Robin (SRR) Enhancements In general traffic shaping is a behavior that tends to buffer excess packets in a way as to shape the outbound traffic to a stated rate. In the Cisco Catalyst 6500, SRR is a best effort scheduler-based algorithm that attempts to shape the outbound traffic with a contingency on the room available for buffering in a queue. As a result, line cards with limited room on output queues can shape only to the extent of absorbing a traffic spike, thereby creating only a burst smoothening of the outbound traffic. With the introduction of the 6904 module, the Cisco Catalyst 6500 supports a leaky bucket-based SRR mechanism, which removes SRR limitations arising from limited room on output queues. In addition to port or queue buffers, each queue in the 6904 port ASIC maintains a leaky bucket hardware resource that is usable for traffic shaping. There is no separate configuration command necessary to enable the SRR enhancements on the 6904 module Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 13 of 20
14 Deficit Weighted Round Robin (DWRR) DWRR is a round robin scheduling technique that uses the class of service (CoS) tag inside an Ethernet frame to provide enhanced buffer management and outbound scheduling. It offers an improvement over Weighted Round Robin (WRR) in that each queue will use bandwidth that is much closer to the configured amount for that queue. It is important to note that effective bandwidth distribution using the DWRR algorithm requires all traffic flows entering a front panel port to be hashed into the same virtual port (VP) of the port ASIC interfacing with the fabric interface replication engine. In the 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode of operation, the 6904 conforms to this behavior, and bandwidth distribution is guaranteed as each front panel port is mapped to a unique VP of the port ASIC. DWRR Limitations in 40 Gigabit Ethernet Mode In 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode of operation, the 6904 module has each front panel port mapping to four virtual ports (VPs) of the port ASIC. Whereas in the 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode, each port buffer composed of a set of queues is tied to a unique VP, in the 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode four sets of queues can be mapped to any of the four VPs in the port ASIC based on traffic flows. As a result, the port ASIC in the 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode performs two-stage scheduling, as illustrated in Figure 11, to distribute the traffic from each set of queues to the receive MUX FPGA. The first stage DWRR occurs across all queues of one virtual port, followed by a second stage DWRR across all virtual ports. Figure Gigabit Ethernet DWRR Ingress Behavior in 6904 Port ASIC Due to the nature of DWRR implementation in the port ASIC, DWRR bandwidth distribution can be guaranteed only across all traffic flows hashing into the same VP. In addition, traffic flow distribution must take into account two parameters, packet size and CoS value, in order to minimize the possible unfairness across the four VPs and a head-of-line (HoL) blocking possibility because of the same CoS value packets getting mapped into the same queue across different VPs. Dual Strict Priority Queuing The 6904 module is the first of the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series line cards to come with two strict-priority queues on a per-port basis in hardware. Table 3 lists the queue type configurations with and without dual- strict-priority queuing Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 14 of 20
15 Table 3. Queue Type Capabilities on Cisco Catalyst 6904 Module Queue Type Ingress (Rx) Egress (Tx) Single priority queue (default) 1p7q4t 1p7q4t Dual priority queue 2p6q4t 2p6q4t By default, the 6904 module will operate in single priority queue mode and software configuration options will be available for enabling two-level priority queuing, which means the hardware will get reconfigured to create two priority queues and six regular queues. This means that the module will be capable of two levels of priority configurable via software for class map assignments - the highest level of priority useable for critical control traffic such as BPDU and the second level priority can be used for other time sensitive traffic. The configuration of this feature is listed in the following example Router(config-pmap-c)#class-map type lan-queuing pri_level1 Router(config-cmap)#match cos 6 Router(config-cmap)#class-map type lan-queuing pri_level2 Router(config-cmap)#match cos 5 Router(config-cmap)#policy-map type lan-queuing pri Router(config-pmap)#class priority_level1 Router(config-pmap-c)#priority level 1 Router(config-pmap-c)#class pri_level2 Router(config-pmap-c)#priority level 2 Router(config)#int gi6/1 Router(config-if)#service-policy type lan-queuing in priority Port-Level and Queue-Level Shaping The Cisco Catalyst 6904 module is the first of the line cards for the 6500 Series to support traffic shaping QoS feature. Two levels of shaping are possible; the capability exists on egress ports on a per queue basis. Traffic gets shaped first in the queue and then at the port level. It is important to note that port-level shaping is different from policing, in that a shaper allows for traffic in excess of the stated rate to get buffered rather than dropped. This new feature brings shaping support natively on the 6904 module and complements the existing shaped round robin (SRR) mechanism. In previous solutions, SRR and priority queuing could not be configured on the same queuing policy. With the introduction of native port-level shaping capability, a policy can have a class with priority queue, and the priority queue can support shaping. The 6904 module also supports priority queue shaping in order to not use full bandwidth of the priority queue. The configuration for the queue-level shaping is shown in the following example: Router(config-pmap)#class-map type lan-queuing cos1 Router(config-cmap)#match cos 1 Router(config-cmap)#class-map type lan-queuing cos2 Router(config-cmap)#match cos Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 15 of 20
16 Router(config-pmap-c)#policy-map type lan-queuing shape_queue Router(config-pmap)#class cos1 Router(config-pmap-c)#shape aver per 20 Router(config-pmap)#class cos2 Router(config-pmap-c)#shape aver per 30 The configuration for the port-level shaping is as follows: Router(config-if)#policy-map type lan-queuing shape_port Router(config-pmap)#class class-default Router(config-pmap-c)#shape aver per 40 Router(config-pmap-c)#service-policy type lan-queuing shape_queue Table 4 lists a summary of QoS features for the 6904 module. Table 4. Cisco Catalyst 6904 Module QoS Features QoS Features 40 Gigabit Ethernet Mode Ingress (Rx) 40 Gigabit Ethernet Mode Egress (Tx) 10 Gigabit Ethernet Mode Ingress (Rx) WRR/DWRR bandwidth Yes Yes Yes Yes Queue limit Yes Yes Yes Yes TailDrop threshold Yes Yes Yes Yes WRED threshold Yes Yes Yes Yes CoS-Q-T map Yes Yes Yes Yes DSCP Q map Yes Yes Yes Yes Shaped round robin (SRR) Yes Yes Yes Yes Port level Shaping No Yes No Yes Dual-strict-priority queuing Yes Yes No Yes 10 Gigabit Ethernet Mode Egress (Tx) Note that it is highly recommended that the QoS configuration guide for the software release in consideration be consulted for the availability of these features and the associated configuration commands. Buffers, Queues, and Threshold Size Values Due to the flexibility of operation in both 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet mode, the Cisco Catalyst 6904 module has different per-queue sizes based on the configured mode of operation. Table 5 shows the value of the queue and total buffer sizes in each mode. Please note that these buffer or queue sizes are the same irrespective of whether the module is operating in performance or oversubscription mode. This stands in contrast to the previous generation line card, the Cisco Catalyst 6716, which has buffer-size differences depending on the mode configured Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 16 of 20
17 Table 5. Buffers, Queues, and Thresholds in PFC4-Based Line Cards Module Description Total Buffer Size Rx Buffer Size Tx Buffer Size Rx Port Type Tx Port Type Rx Queue Size Tx Queue Size WS-X G 40 Gigabit Ethernet line card (40 Gigabit Ethernet mode) 93 MB 5 MB 88 MB 1p7q4t 1p7q4t WRR DWRR SRR* SP-640 KB Q7-640 KB Q6-640 KB Q5-640 KB Q4-640 KB Q3-640 KB Q2-640 KB Q1-640 KB SP-11 MB Q7-11 MB Q6-11 MB Q5-11 MB Q4-11 MB Q3-11 MB Q2-11 MB Q1-11 MB WS-X G (10 Gigabit Ethernet mode) 40 Gigabit Ethernet line card (10 Gigabit Ethernet mode) MB 1.25 MB 21 MB 8q4t 1p7q4t WRR DWRR SRR* Q8-160 KB Q7-160 KB Q6-160 KB Q5-160 KB Q4-160 KB Q3-160 KB Q2-160 KB Q1-160 KB Q MB Q MB Q MB Q MB Q MB Q MB Q MB Q MB To learn more about buffers and queues for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Ethernet line cards, visit Deployment Scenarios and Use Cases Traditional Campus In this network design, illustrated in Figure 12, the WS-X G module (operating in 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode) is placed at the distribution and/or core layer of the network, interconnecting other Layer 2 or Layer 3 multilayer switches. In a traditional campus deployment, the 6904 module can be deployed both in the core and distribution layer of the network. As access layers start to adopt 10 Gigabit Ethernet uplinks, the core and distribution layer interconnects will need to adopt higher bandwidth uplinks. In this network design, the 6904 module with 40 Gigabit Ethernet uplinks can be positioned at the distribution and core layers to provide more than 80 Gigabit worth of equal cost multipathing traffic, in addition to enabling 80 Gigabit Ethernet traffic flow at the etherchannel interconnecting the two cores. Figure 12. Traditional Campus Deployment Use Case 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 17 of 20
18 Virtualized Campus Virtualized campus deployments use the Virtual Switching System (VSSS) technology to double networking bandwidth and reduce operational manageability by eliminating the need to run Spanning Tree. With 10 Gigabit Ethernet uplinks in the access layer, these deployments enable 20 Gigabit Ethernet etherchannel uplinks to the distribution layer. The 6904 module operating in 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode can be positioned in the distribution and core layers of the network to interconnect the two VSS domains using 80 Gigabit Ethernet multichassis etherchannel (MEC) bundles and 80 Gigabit Ethernet Virtual Switching Link (VSL) interconnects, as shown in Figure 13. Figure 13. Virtualized Campus Deployment Use Case Data Center Interconnect (DCI) Data Center Interconnect technology can be used to extend data center VLANs over a layer 3 interconnect. In this deployment, the 6904 operating in 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode can be used at the Core layer of the network, to aggregate and interconnect remote data centers together, as illustrated in Figure 14. Figure 14. Data Center Interconnect Use Case 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 18 of 20
19 A Multiservice Provisioning Platform (MSPP) or Multiservice Transport Platform (MSTP) such as the Cisco ONS15454 can be used to multiplex and extend the 40 Gigabit Ethernet range of operation in the DCI use case. If the core or metropolitan Access Network (MAN) network is IP-based, the optimal hash algorithm options are srcip, dst-ip, or src-dst-ip. If the core or MAN network is MPLS-based, the optimal hash algorithm option is mpls. Examples CHANGE 40 GIGABIT INPUT HASH: C6506.SW2(config)#interface FortyGigabitEthernet 1/1 C6506.SW2(config-if)#load-balance? dst-ipdst IP Addr dst-mac Dst Mac Addr mpls Load Balancing for MPLS packets src-dst-ipsrc XOR Dst IP Addr src-dst-mac Src XOR Dst Mac Addr src-dst-port Src XOR Dst TCP/UDP Port src-ipsrc IP Addr src-mac Src MAC Addr vlanvlan C6506.SW2(config-if)#load-balance src-dst-port C6506.SW2(config-if)# 40 GIGABIT INPUT HASH: C6506.SW2#sho run int f1/1 Building configuration... Current configuration: 116 bytes! interface FortyGigabitEthernet1/1 noip address load-balance src-dst-port end C6506.SW2#sho int f1/1 load-balance FortyGigabitEthernet1/1 Ingress Load-Balancing Configuration: src-dst-port C6506.SW2# 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 19 of 20
20 Server Access In this network design, the WS-X G module (operating in 40 Gigabit Ethernet mode) is placed at the access layer of the network, directly connected to a server with a 40 Gigabit Ethernet NIC or to an intermediate Layer 2 switch with 40 Gigabit Ethernet ports. Note: The optimal server configuration for this design scenario is to use server virtualization (that is, multiples of 4 x virtual machines [VMs], per single physical server). In this design, the primary limitation is the use of only one to three flows. As each flow will be hashed to one of the 4 x 16-Gbps channels, each flow can only reach ~10 Gbps (so the perceivable throughput would be only 10 to 30 Gbps). If Layer 3 server virtualization is used (so that each VM has a separate IP address) in a north-to-south traffic design, the optimal hash algorithm options are src-ip, dst-ip, or src-dst-ip. If Layer 2 server virtualization is used (so that each VM has a separate MAC address) in an east-to-west design, the optimal hash algorithm options are src-mac, dst-mac, src-dst-mac, or vlan. Another option, if server virtualization is not possible (that is, you have a single physical server, with a single MAC and IP address), the optimal hash input options become src-port, dst-port, or src-dst-port using separate Layer 4 port numbers. Conclusion The Cisco Catalyst Port 40 Gigabit Ethernet Module is designed to meet the increasing demand for aggregation of 10 Gigabit Ethernet on campus and in the data center as well as for high-density 10 Gigabit Ethernet and 40 Gigabit Ethernet transport in the core. For more information about Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches, visit Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches. Printed in USA C / Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 20 of 20
6/8/2011. Document ID: 12023. Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used. Conventions. Introduction
 Page 1 of 9 Products & Services Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
Page 1 of 9 Products & Services Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions
How To Balance On A Cisco Catalyst Switch With The Etherchannel On A Fast Ipv2 (Powerline) On A Microsoft Ipv1 (Powergen) On An Ipv3 (Powergadget) On Ipv4
 Cisco - Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switch...Page 1 of 10 Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents
Cisco - Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switch...Page 1 of 10 Understanding EtherChannel Load Balancing and Redundancy on Catalyst Switches Document ID: 12023 Contents
Understanding Quality of Service on the Catalyst 6500 Switch
 . White Paper Understanding Quality of Service on the Catalyst 6500 Switch Carl Solder CCIE #2416 Technical Marketing Engineer Internetworking Systems Business Unit Patrick Warichet CCIE #14218 Technical
. White Paper Understanding Quality of Service on the Catalyst 6500 Switch Carl Solder CCIE #2416 Technical Marketing Engineer Internetworking Systems Business Unit Patrick Warichet CCIE #14218 Technical
- EtherChannel - Port Aggregation
 1 Port Aggregation - EtherChannel - A network will often span across multiple switches. Trunk ports are usually used to connect switches together. There are two issues with using only a single physical
1 Port Aggregation - EtherChannel - A network will often span across multiple switches. Trunk ports are usually used to connect switches together. There are two issues with using only a single physical
Catalyst 6500 Sup2T System QOS Architecture
 Catalyst 6500 Sup2T System QOS Architecture White Paper April 13, 2011 Abstract This document explains the Quality of Service (QoS) capabilities available in the Catalyst 6500 Switch as it applies to Policy
Catalyst 6500 Sup2T System QOS Architecture White Paper April 13, 2011 Abstract This document explains the Quality of Service (QoS) capabilities available in the Catalyst 6500 Switch as it applies to Policy
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Improving Quality of Service
 Improving Quality of Service Using Dell PowerConnect 6024/6024F Switches Quality of service (QoS) mechanisms classify and prioritize network traffic to improve throughput. This article explains the basic
Improving Quality of Service Using Dell PowerConnect 6024/6024F Switches Quality of service (QoS) mechanisms classify and prioritize network traffic to improve throughput. This article explains the basic
Fiber Channel Over Ethernet (FCoE)
 Fiber Channel Over Ethernet (FCoE) Using Intel Ethernet Switch Family White Paper November, 2008 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
Fiber Channel Over Ethernet (FCoE) Using Intel Ethernet Switch Family White Paper November, 2008 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module
 CHAPTER 2 Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module This chapter describes how to configure the Catalyst 6500 series switch or the Cisco 7600 series router for use with the FWSM. Before completing
CHAPTER 2 Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module This chapter describes how to configure the Catalyst 6500 series switch or the Cisco 7600 series router for use with the FWSM. Before completing
Choosing Tap or SPAN for Data Center Monitoring
 Choosing Tap or SPAN for Data Center Monitoring Technical Brief Key Points Taps are passive, silent, and deliver a perfect record of link traffic, but require additional hardware and create a point of
Choosing Tap or SPAN for Data Center Monitoring Technical Brief Key Points Taps are passive, silent, and deliver a perfect record of link traffic, but require additional hardware and create a point of
48 GE PoE-Plus + 2 GE SFP L2 Managed Switch, 375W
 GEP-5070 Version: 1 48 GE PoE-Plus + 2 GE SFP L2 Managed Switch, 375W The LevelOne GEP-5070 is an intelligent L2 Managed Switch with 48 x 1000Base-T PoE-Plus ports and 2 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP (Small Form
GEP-5070 Version: 1 48 GE PoE-Plus + 2 GE SFP L2 Managed Switch, 375W The LevelOne GEP-5070 is an intelligent L2 Managed Switch with 48 x 1000Base-T PoE-Plus ports and 2 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP (Small Form
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing
 Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Alexander Paul [email protected] IBM Certified Advanced Technical Expert (C.A.T.E.) for Power Systems Certified Cisco Systems Instructor CCSI #32044
 Network Virtualization Deep dive and Network Troubleshooting in a virtualized Environment Alexander Paul [email protected] IBM Certified Advanced Technical Expert (C.A.T.E.) for Power Systems Certified
Network Virtualization Deep dive and Network Troubleshooting in a virtualized Environment Alexander Paul [email protected] IBM Certified Advanced Technical Expert (C.A.T.E.) for Power Systems Certified
Migrate from Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches to Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switches
 Migration Guide Migrate from Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches to Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switches Migration Guide November 2013 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is
Migration Guide Migrate from Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches to Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switches Migration Guide November 2013 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is
Configuring EtherChannels
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
High Performance 10Gigabit Ethernet Switch
 BDCOM S3900 Switch High Performance 10Gigabit Ethernet Switch BDCOM S3900 is a standard L3 congestion-less switch series, which are capable of multi-layer switching and wire-speed route forwarding. Its
BDCOM S3900 Switch High Performance 10Gigabit Ethernet Switch BDCOM S3900 is a standard L3 congestion-less switch series, which are capable of multi-layer switching and wire-speed route forwarding. Its
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks. Chapter 5: Ethernet
 CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
Cisco Integrators Cisco Partners installing and implementing the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches
 Implementing Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches (RSCAT6K) Fast Lane is proud to be once again on the cutting edge with this intensive 3-day Authorized course on the latest features and functionality of
Implementing Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches (RSCAT6K) Fast Lane is proud to be once again on the cutting edge with this intensive 3-day Authorized course on the latest features and functionality of
FWSM introduction Intro 5/1
 Intro 5/0 Content: FWSM introduction Requirements for FWSM 3.2 How the Firewall Services Module Works with the Switch Using the MSFC Firewall Mode Overview Stateful Inspection Overview Security Context
Intro 5/0 Content: FWSM introduction Requirements for FWSM 3.2 How the Firewall Services Module Works with the Switch Using the MSFC Firewall Mode Overview Stateful Inspection Overview Security Context
Cisco SLM2048 48-Port Gigabit Smart Switch Cisco Small Business Smart Switches
 Cisco SLM2048 48-Port Gigabit Smart Switch Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Secure Switching with Simplified Management for Your Growing Business Highlights Easy-to-use web browser interface
Cisco SLM2048 48-Port Gigabit Smart Switch Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Secure Switching with Simplified Management for Your Growing Business Highlights Easy-to-use web browser interface
Cisco Small Business Managed Switches
 Cisco SRW224P 24-Port 10/100 + 2-Port Gigabit Switch: WebView/PoE Cisco Small Business Managed Switches Secure, Reliable, Intelligent Switching with PoE for Growing Businesses Highlights Connects up to
Cisco SRW224P 24-Port 10/100 + 2-Port Gigabit Switch: WebView/PoE Cisco Small Business Managed Switches Secure, Reliable, Intelligent Switching with PoE for Growing Businesses Highlights Connects up to
Table of Contents. Network Critical NA LLC Tel: 716-558-7280 37 Franklin Street, Suite 100 Email: [email protected]
 Product Catalog Table of Contents Breakout TAPs...1-3 Fixed Aggregating Portable TAP...4-5 V-Line TM (Bypass) Portable TAPS...6 Breakout Portable TAP...7 V-Line (Bypass) TAPs...8-9 Smart Network Access
Product Catalog Table of Contents Breakout TAPs...1-3 Fixed Aggregating Portable TAP...4-5 V-Line TM (Bypass) Portable TAPS...6 Breakout Portable TAP...7 V-Line (Bypass) TAPs...8-9 Smart Network Access
ATC808. Low Cost 26 Port ATCA Switch KEY FEATURES THE POWER OF VISION
 ATC808 TM THE POWER OF VISION KEY FEATURES AdvancedTCA open standard form factor PICMG 3.1 compliant Managed Layer two switch GbE to Base Interface for 15 Node slots plus two Shelf One port to the update
ATC808 TM THE POWER OF VISION KEY FEATURES AdvancedTCA open standard form factor PICMG 3.1 compliant Managed Layer two switch GbE to Base Interface for 15 Node slots plus two Shelf One port to the update
hp ProLiant network adapter teaming
 hp networking june 2003 hp ProLiant network adapter teaming technical white paper table of contents introduction 2 executive summary 2 overview of network addressing 2 layer 2 vs. layer 3 addressing 2
hp networking june 2003 hp ProLiant network adapter teaming technical white paper table of contents introduction 2 executive summary 2 overview of network addressing 2 layer 2 vs. layer 3 addressing 2
40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet Technology Overview
 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet Technology Overview June 2010 Authors: John D Ambrosia, Force10 Networks David Law, 3COM Mark Nowell, Cisco Systems 1. This work represents the opinions of
40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet Technology Overview June 2010 Authors: John D Ambrosia, Force10 Networks David Law, 3COM Mark Nowell, Cisco Systems 1. This work represents the opinions of
TP-LINK. JetStream 28-Port Gigabit Stackable L3 Managed Switch. Overview. Datasheet T3700G-28TQ. www.tp-link.com
 TP-LINK JetStream 28-Port Gigabit Stackable L3 Managed Switch Overview TP-LINK s is an L3 managed switch designed to build a highly accessible, scalable, and robust network. The switch is equipped with
TP-LINK JetStream 28-Port Gigabit Stackable L3 Managed Switch Overview TP-LINK s is an L3 managed switch designed to build a highly accessible, scalable, and robust network. The switch is equipped with
Feature Support Cisco 2960 Cisco 2960S Brocade ICX 6450 Brocade ICX 6430 1 GE SFP, 2 10GE SFP+, 4 1GE SFP, 2 DUAL PURPOSE PORTS, 1GE OR SFP
 Feature Support Cisco 2960 Cisco 2960S Brocade ICX 6450 Brocade ICX 6430 Uplinks 1 GE SFP, 2 10GE SFP+, 4 1GE SFP, 2 DUAL PURPOSE PORTS, 1GE OR SFP 40G Stack bandwidth via std 10G ports 2x10G* Fiber aggregation
Feature Support Cisco 2960 Cisco 2960S Brocade ICX 6450 Brocade ICX 6430 Uplinks 1 GE SFP, 2 10GE SFP+, 4 1GE SFP, 2 DUAL PURPOSE PORTS, 1GE OR SFP 40G Stack bandwidth via std 10G ports 2x10G* Fiber aggregation
Cisco SLM2024 24-Port Gigabit Smart Switch Cisco Small Business Smart Switches
 Cisco SLM2024 24-Port Gigabit Smart Switch Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Secure Switching with Simplified Management for Your Small Business Highlights Easy-to-use web browser interface
Cisco SLM2024 24-Port Gigabit Smart Switch Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Secure Switching with Simplified Management for Your Small Business Highlights Easy-to-use web browser interface
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively on the Series 2600/2600-PWR and Series 2800 Switches
 6 Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively on the Series 2600/2600-PWR and Series 2800 Switches Contents Introduction................................................... 6-3 Terminology................................................
6 Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively on the Series 2600/2600-PWR and Series 2800 Switches Contents Introduction................................................... 6-3 Terminology................................................
Chapter 4 Rate Limiting
 Chapter 4 Rate Limiting HP s rate limiting enables you to control the amount of bandwidth specific Ethernet traffic uses on specific interfaces, by limiting the amount of data the interface receives or
Chapter 4 Rate Limiting HP s rate limiting enables you to control the amount of bandwidth specific Ethernet traffic uses on specific interfaces, by limiting the amount of data the interface receives or
Technote: AIX EtherChannel Load Balancing Options
 AIX EtherChannel Load Balancing Options Document Author: Cindy K Young Additional Author(s): Jorge R Nogueras Doc. Organization: Document ID: TD101260 Advanced Technical Support Document Revised: 10/28/2003
AIX EtherChannel Load Balancing Options Document Author: Cindy K Young Additional Author(s): Jorge R Nogueras Doc. Organization: Document ID: TD101260 Advanced Technical Support Document Revised: 10/28/2003
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Mixed Media Gigabit Ethernet Modules
 Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Mixed Media Gigabit Ethernet Modules Product Overview The Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switch the premier modular multilayer switch delivers secure converged services from the
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Mixed Media Gigabit Ethernet Modules Product Overview The Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switch the premier modular multilayer switch delivers secure converged services from the
Leased Line + Remote Dial-in connectivity
 Leased Line + Remote Dial-in connectivity Client: One of the TELCO offices in a Southern state. The customer wanted to establish WAN Connectivity between central location and 10 remote locations. The customer
Leased Line + Remote Dial-in connectivity Client: One of the TELCO offices in a Southern state. The customer wanted to establish WAN Connectivity between central location and 10 remote locations. The customer
Whitepaper. 10 Things to Know Before Deploying 10 Gigabit Ethernet
 Whitepaper 10 Things to Know Before Deploying 10 Gigabit Ethernet Table of Contents Introduction... 3 10 Gigabit Ethernet and The Server Edge: Better Efficiency... 3 SAN versus Fibre Channel: Simpler and
Whitepaper 10 Things to Know Before Deploying 10 Gigabit Ethernet Table of Contents Introduction... 3 10 Gigabit Ethernet and The Server Edge: Better Efficiency... 3 SAN versus Fibre Channel: Simpler and
N5 NETWORKING BEST PRACTICES
 N5 NETWORKING BEST PRACTICES Table of Contents Nexgen N5 Networking... 2 Overview of Storage Networking Best Practices... 2 Recommended Switch features for an iscsi Network... 2 Setting up the iscsi Network
N5 NETWORKING BEST PRACTICES Table of Contents Nexgen N5 Networking... 2 Overview of Storage Networking Best Practices... 2 Recommended Switch features for an iscsi Network... 2 Setting up the iscsi Network
LINK AGGREGATION INTEROPERABILITY OF THE DELL POWERCONNECT 6200 SERIES
 LINK AGGREGATION INTEROPERABILITY OF THE DELL POWERCONNECT 6200 SERIES WITH CISCO IOS OR CISCO CATOS BASED SWITCHES By Bruce Holmes CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 LINK AGGREGATION WITH GIGABIT ETHERNET CISCO
LINK AGGREGATION INTEROPERABILITY OF THE DELL POWERCONNECT 6200 SERIES WITH CISCO IOS OR CISCO CATOS BASED SWITCHES By Bruce Holmes CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 LINK AGGREGATION WITH GIGABIT ETHERNET CISCO
White Paper Abstract Disclaimer
 White Paper Synopsis of the Data Streaming Logical Specification (Phase I) Based on: RapidIO Specification Part X: Data Streaming Logical Specification Rev. 1.2, 08/2004 Abstract The Data Streaming specification
White Paper Synopsis of the Data Streaming Logical Specification (Phase I) Based on: RapidIO Specification Part X: Data Streaming Logical Specification Rev. 1.2, 08/2004 Abstract The Data Streaming specification
Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide
 Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide Overview A virtual PortChannel (vpc) allows links that are physically connected to two different Cisco Nexus 5000 Series devices to appear as a single PortChannel
Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide Overview A virtual PortChannel (vpc) allows links that are physically connected to two different Cisco Nexus 5000 Series devices to appear as a single PortChannel
Intel Ethernet Switch Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) and Datacenter Bridging (DCB) Using Intel Ethernet Switch Family Switches
 Intel Ethernet Switch Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) and Datacenter Bridging (DCB) Using Intel Ethernet Switch Family Switches February, 2009 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION
Intel Ethernet Switch Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) and Datacenter Bridging (DCB) Using Intel Ethernet Switch Family Switches February, 2009 Legal INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION
What s New in VMware vsphere 5.5 Networking
 VMware vsphere 5.5 TECHNICAL MARKETING DOCUMENTATION Table of Contents Introduction.................................................................. 3 VMware vsphere Distributed Switch Enhancements..............................
VMware vsphere 5.5 TECHNICAL MARKETING DOCUMENTATION Table of Contents Introduction.................................................................. 3 VMware vsphere Distributed Switch Enhancements..............................
Deploying 10 Gigabit Ethernet on VMware vsphere 4.0 with Cisco Nexus 1000V and VMware vnetwork Standard and Distributed Switches - Version 1.
 Deploying 10 Gigabit Ethernet on VMware vsphere 4.0 with Cisco Nexus 1000V and VMware vnetwork Standard and Distributed Switches - Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Design Goals...3 VMware
Deploying 10 Gigabit Ethernet on VMware vsphere 4.0 with Cisco Nexus 1000V and VMware vnetwork Standard and Distributed Switches - Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Design Goals...3 VMware
Link Aggregation Interoperability of the Dell PowerConnect 5316M with Cisco IOS or Cisco CatOS based Switches. By Bruce Holmes
 Link Aggregation Interoperability of the Dell PowerConnect 5316M with Cisco IOS or Cisco CatOS based Switches By Bruce Holmes August 2005 Contents Introduction...3 Link Aggregation with Gigabit Ethernet
Link Aggregation Interoperability of the Dell PowerConnect 5316M with Cisco IOS or Cisco CatOS based Switches By Bruce Holmes August 2005 Contents Introduction...3 Link Aggregation with Gigabit Ethernet
Cisco Small Business Smart Switches
 Cisco SLM224G4S 24-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Smart Switch: RCT Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Highly Secure Switching with Simplified Management for Growing Businesses Highlights
Cisco SLM224G4S 24-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Smart Switch: RCT Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Highly Secure Switching with Simplified Management for Growing Businesses Highlights
Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes
 Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Table of Contents Description... 3 Benefits... 4 Theory of Operation... 4 Interaction with Other Features... 7
Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Application Note Gigabit Ethernet Port Modes Table of Contents Description... 3 Benefits... 4 Theory of Operation... 4 Interaction with Other Features... 7
Layer 3 Network + Dedicated Internet Connectivity
 Layer 3 Network + Dedicated Internet Connectivity Client: One of the IT Departments in a Northern State Customer's requirement: The customer wanted to establish CAN connectivity (Campus Area Network) for
Layer 3 Network + Dedicated Internet Connectivity Client: One of the IT Departments in a Northern State Customer's requirement: The customer wanted to establish CAN connectivity (Campus Area Network) for
Using a Fabric Extender with a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch
 CHAPTER Using a Fabric Extender with a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch This chapter describes the Cisco Nexus 000 Series Fabric Extenders (FEXs) and includes these sections: Information About, page - Cisco
CHAPTER Using a Fabric Extender with a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch This chapter describes the Cisco Nexus 000 Series Fabric Extenders (FEXs) and includes these sections: Information About, page - Cisco
Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable Modules for Gigabit Ethernet Applications
 Data Sheet Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable Modules for Gigabit Ethernet Applications The industry-standard Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Gigabit Interface Converter is a hot-swappable input/output
Data Sheet Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable Modules for Gigabit Ethernet Applications The industry-standard Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Gigabit Interface Converter is a hot-swappable input/output
Technology Overview. Class of Service Overview. Published: 2014-01-10. Copyright 2014, Juniper Networks, Inc.
 Technology Overview Class of Service Overview Published: 2014-01-10 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net Juniper Networks, Junos,
Technology Overview Class of Service Overview Published: 2014-01-10 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net Juniper Networks, Junos,
Link Aggregation Interoperability of the Dell PowerConnect M6220 with Cisco IOS or Cisco CatOS Based Switches
 Link Aggregation Interoperability of the Dell PowerConnect M6220 with Cisco IOS or Cisco CatOS Based Switches By Bruce Holmes Introduction This paper describes how to configure the Dell PowerConnect 6220M
Link Aggregation Interoperability of the Dell PowerConnect M6220 with Cisco IOS or Cisco CatOS Based Switches By Bruce Holmes Introduction This paper describes how to configure the Dell PowerConnect 6220M
The Load Balancing System Design of Service Based on IXP2400 Yi Shijun 1, a, Jing Xiaoping 1,b
 Advanced Engineering Forum Vol. 1 (2011) pp 42-46 Online: 2011-09-09 (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/aef.1.42 The Load Balancing System Design of Service Based
Advanced Engineering Forum Vol. 1 (2011) pp 42-46 Online: 2011-09-09 (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/aef.1.42 The Load Balancing System Design of Service Based
SummitStack in the Data Center
 SummitStack in the Data Center Abstract: This white paper describes the challenges in the virtualized server environment and the solution that Extreme Networks offers a highly virtualized, centrally manageable
SummitStack in the Data Center Abstract: This white paper describes the challenges in the virtualized server environment and the solution that Extreme Networks offers a highly virtualized, centrally manageable
Ethernet Fabric Requirements for FCoE in the Data Center
 Ethernet Fabric Requirements for FCoE in the Data Center Gary Lee Director of Product Marketing [email protected] February 2010 1 FCoE Market Overview FC networks are relatively high cost solutions
Ethernet Fabric Requirements for FCoE in the Data Center Gary Lee Director of Product Marketing [email protected] February 2010 1 FCoE Market Overview FC networks are relatively high cost solutions
ALL8894WMP. User s Manual. 8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4-port PoE. Web Management Switch
 ALL8894WMP 8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4-port PoE Web Management Switch User s Manual Content Content I Introduction..3 Product Overview.3 Web Management Feature.3 Specification..4 Mechanical...4 Performance...5
ALL8894WMP 8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4-port PoE Web Management Switch User s Manual Content Content I Introduction..3 Product Overview.3 Web Management Feature.3 Specification..4 Mechanical...4 Performance...5
How To Set Up A Virtual Network On Vsphere 5.0.5.2 (Vsphere) On A 2Nd Generation Vmkernel (Vklan) On An Ipv5 Vklan (Vmklan)
 Best Practices for Virtual Networking Karim Elatov Technical Support Engineer, GSS 2009 VMware Inc. All rights reserved Agenda Best Practices for Virtual Networking Virtual Network Overview vswitch Configurations
Best Practices for Virtual Networking Karim Elatov Technical Support Engineer, GSS 2009 VMware Inc. All rights reserved Agenda Best Practices for Virtual Networking Virtual Network Overview vswitch Configurations
Cisco NetFlow Generation Appliance (NGA) 3140
 Q&A Cisco NetFlow Generation Appliance (NGA) 3140 General Overview Q. What is Cisco NetFlow Generation Appliance (NGA) 3140? A. Cisco NetFlow Generation Appliance 3140 is purpose-built, high-performance
Q&A Cisco NetFlow Generation Appliance (NGA) 3140 General Overview Q. What is Cisco NetFlow Generation Appliance (NGA) 3140? A. Cisco NetFlow Generation Appliance 3140 is purpose-built, high-performance
100 GBE AND BEYOND. Greg Hankins <[email protected]> NANOG52. Diagram courtesy of the CFP MSA. NANOG52 2011/06/14
 100 GBE AND BEYOND Greg Hankins NANOG52 Diagram courtesy of the CFP MSA. NANOG52 2011/06/14 Agenda and What s Covered in This Presentation Ethernet interface technology Overview
100 GBE AND BEYOND Greg Hankins NANOG52 Diagram courtesy of the CFP MSA. NANOG52 2011/06/14 Agenda and What s Covered in This Presentation Ethernet interface technology Overview
Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY1 New Features and Hardware Support
 Product Bulletin Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY1 New Features and Hardware Support PB696622 Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY1 supports Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Supervisor Engine 2T only. Release
Product Bulletin Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY1 New Features and Hardware Support PB696622 Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0(1)SY1 supports Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Supervisor Engine 2T only. Release
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(37)SG for Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Supervisor Engines
 Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(37)SG for Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Engines PB403891 Overview This product bulletin describes the hardware and software features supported by Cisco IOS Software Release
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(37)SG for Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Engines PB403891 Overview This product bulletin describes the hardware and software features supported by Cisco IOS Software Release
LAN Switching and VLANs
 26 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the relationship of LAN switching to legacy internetworking devices such as bridges and routers. Understand the advantages of VLANs. Know the difference between access
26 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the relationship of LAN switching to legacy internetworking devices such as bridges and routers. Understand the advantages of VLANs. Know the difference between access
Chapter 3. Enterprise Campus Network Design
 Chapter 3 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1 Overview The network foundation hosting these technologies for an emerging enterprise should be efficient, highly available, scalable, and manageable. This
Chapter 3 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1 Overview The network foundation hosting these technologies for an emerging enterprise should be efficient, highly available, scalable, and manageable. This
Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. Networks: Fast Ethernet 1
 Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet Networks: Fast Ethernet 1 Fast Ethernet (100BASE-T) How to achieve 100 Mbps capacity? MII LLC MAC Convergence Sublayer Media Independent Interface Media Dependent Sublayer
Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet Networks: Fast Ethernet 1 Fast Ethernet (100BASE-T) How to achieve 100 Mbps capacity? MII LLC MAC Convergence Sublayer Media Independent Interface Media Dependent Sublayer
High Speed Ethernet. Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Professor School of Computing, UNF
 High Speed Ethernet Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Professor School of Computing, UNF Hubs and Switches Hubs and Switches Shared Medium Hub The total capacity in the shared medium hub configuration (figure
High Speed Ethernet Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Professor School of Computing, UNF Hubs and Switches Hubs and Switches Shared Medium Hub The total capacity in the shared medium hub configuration (figure
Cisco 7600 Series Routers Cisco 7600 Series: Ethernet Services 20G Line Cards for Carrier Ethernet
 . Data Sheet Cisco 7600 Series Routers Cisco 7600 Series: Ethernet Services 20G Line Cards for Carrier Ethernet The Cisco 7600 Series Ethernet Services 20 Gbps (ES20) Line Cards utilize an extensible design
. Data Sheet Cisco 7600 Series Routers Cisco 7600 Series: Ethernet Services 20G Line Cards for Carrier Ethernet The Cisco 7600 Series Ethernet Services 20 Gbps (ES20) Line Cards utilize an extensible design
Implementing Cisco Quality of Service QOS v2.5; 5 days, Instructor-led
 Implementing Cisco Quality of Service QOS v2.5; 5 days, Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements,
Implementing Cisco Quality of Service QOS v2.5; 5 days, Instructor-led Course Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements,
Networking Devices. Lesson 6
 Networking Devices Lesson 6 Objectives Exam Objective Matrix Technology Skill Covered Exam Objective Exam Objective Number Network Interface Cards Modems Media Converters Repeaters and Hubs Bridges and
Networking Devices Lesson 6 Objectives Exam Objective Matrix Technology Skill Covered Exam Objective Exam Objective Number Network Interface Cards Modems Media Converters Repeaters and Hubs Bridges and
IMPLEMENTING CISCO QUALITY OF SERVICE V2.5 (QOS)
 IMPLEMENTING CISCO QUALITY OF SERVICE V2.5 (QOS) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such
IMPLEMENTING CISCO QUALITY OF SERVICE V2.5 (QOS) COURSE OVERVIEW: Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such
Your Network. Our Connection. 10 Gigabit Ethernet
 Your Network. Our Connection. 10 Gigabit Ethernet t Agenda Why 10G? Applicable 10GbE Standards Distance Restrictions Copper Fiber Fiber Repeaters 3R s Fiber Module Types Form Factors of 10G modules Future
Your Network. Our Connection. 10 Gigabit Ethernet t Agenda Why 10G? Applicable 10GbE Standards Distance Restrictions Copper Fiber Fiber Repeaters 3R s Fiber Module Types Form Factors of 10G modules Future
Virtual PortChannels: Building Networks without Spanning Tree Protocol
 . White Paper Virtual PortChannels: Building Networks without Spanning Tree Protocol What You Will Learn This document provides an in-depth look at Cisco's virtual PortChannel (vpc) technology, as developed
. White Paper Virtual PortChannels: Building Networks without Spanning Tree Protocol What You Will Learn This document provides an in-depth look at Cisco's virtual PortChannel (vpc) technology, as developed
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
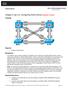 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Configuring QoS. Understanding QoS CHAPTER
 24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to certain types of traffic at the expense of others.
24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to certain types of traffic at the expense of others.
Cisco SLM248P 48-Port 10/100 + 2-Port Gigabit Smart Switch: SFPs/PoE
 Cisco SLM248P 48-Port 10/100 + 2-Port Gigabit Smart Switch: SFPs/PoE Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Secure Switching with Simplified Management and PoE for Your Growing Business Highlights
Cisco SLM248P 48-Port 10/100 + 2-Port Gigabit Smart Switch: SFPs/PoE Cisco Small Business Smart Switches Cost-Effective, Secure Switching with Simplified Management and PoE for Your Growing Business Highlights
The ABC of Direct Attach Cables
 The ABC of Direct Attach Cables Thomas Ko, RCDD Product Manager TE Connectivity Network Speed and Technology 10/40/100 Gbps the transition is occurring right now What are Customers Saying about their 10/40/100
The ABC of Direct Attach Cables Thomas Ko, RCDD Product Manager TE Connectivity Network Speed and Technology 10/40/100 Gbps the transition is occurring right now What are Customers Saying about their 10/40/100
20 GE + 4 GE Combo SFP + 2 10G Slots L3 Managed Stackable Switch
 GTL-2691 Version: 1 Modules are to be ordered separately. 20 GE + 4 GE Combo SFP + 2 10G Slots L3 Managed Stackable Switch The LevelOne GEL-2691 is a Layer 3 Managed switch with 24 x 1000Base-T ports associated
GTL-2691 Version: 1 Modules are to be ordered separately. 20 GE + 4 GE Combo SFP + 2 10G Slots L3 Managed Stackable Switch The LevelOne GEL-2691 is a Layer 3 Managed switch with 24 x 1000Base-T ports associated
"Charting the Course... ... to Your Success!" QOS - Implementing Cisco Quality of Service 2.5 Course Summary
 Course Summary Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such as best effort, IntServ, and DiffServ,
Course Summary Description Implementing Cisco Quality of Service (QOS) v2.5 provides learners with in-depth knowledge of QoS requirements, conceptual models such as best effort, IntServ, and DiffServ,
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example
 Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
TP-LINK. 48-Port Gigabit Smart Switch with 4 SFP Slots. Overview. Datasheet T1600G-52TS (TL-SG2452) www.tp-link.com
 TP-LINK 48-Port Gigabit Smart Switch with 4 SFP Slots Overview TP-LINK JetStream Gigabit Smart Switch T1600G-52TS is a cost-effective product solution for small and medium-sized business which provides
TP-LINK 48-Port Gigabit Smart Switch with 4 SFP Slots Overview TP-LINK JetStream Gigabit Smart Switch T1600G-52TS is a cost-effective product solution for small and medium-sized business which provides
10 Port L2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 2 Open SFP Slots - Rack Mountable
 10 Port L2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 2 Open SFP Slots - Rack Mountable StarTech ID: IES101002SFP The IES101002SFP 10-port Ethernet switch delivers flexibility and control of your network by
10 Port L2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 2 Open SFP Slots - Rack Mountable StarTech ID: IES101002SFP The IES101002SFP 10-port Ethernet switch delivers flexibility and control of your network by
MLPPP Deployment Using the PA-MC-T3-EC and PA-MC-2T3-EC
 MLPPP Deployment Using the PA-MC-T3-EC and PA-MC-2T3-EC Overview Summary The new enhanced-capability port adapters are targeted to replace the following Cisco port adapters: 1-port T3 Serial Port Adapter
MLPPP Deployment Using the PA-MC-T3-EC and PA-MC-2T3-EC Overview Summary The new enhanced-capability port adapters are targeted to replace the following Cisco port adapters: 1-port T3 Serial Port Adapter
Cisco Network Convergence System 6000 Series 10-Port 100-Gbps Multiservice Line Cards with Cisco AnyPort Technology
 Data Sheet Cisco Network Convergence System 6000 Series 10-Port 100-Gbps Multiservice Line Cards with Cisco AnyPort Technology The Cisco Network Convergence System (NCS) 6000 Series Routers offer exceptional
Data Sheet Cisco Network Convergence System 6000 Series 10-Port 100-Gbps Multiservice Line Cards with Cisco AnyPort Technology The Cisco Network Convergence System (NCS) 6000 Series Routers offer exceptional
A Dell Technical White Paper Dell PowerConnect Team
 Flow Control and Network Performance A Dell Technical White Paper Dell PowerConnect Team THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND MAY CONTAIN TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS AND TECHNICAL INACCURACIES.
Flow Control and Network Performance A Dell Technical White Paper Dell PowerConnect Team THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY, AND MAY CONTAIN TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS AND TECHNICAL INACCURACIES.
TP-LINK. 24-Port Gigabit Smart PoE Switch with 4 Combo SFP Slots. Overview. Datasheet TL-SG2424P. www.tp-link.com
 Power Budget TP-LINK 24-Port Gigabit Smart PoE Switch with 4 Combo SFP Slots Overview The provides 24 10/100/1000Mbps ports that supports 802.3at/af-compliant PoE, with a total PoE power supply up to 180W,
Power Budget TP-LINK 24-Port Gigabit Smart PoE Switch with 4 Combo SFP Slots Overview The provides 24 10/100/1000Mbps ports that supports 802.3at/af-compliant PoE, with a total PoE power supply up to 180W,
100 GIGABIT ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW & OUTLOOK. Joerg Ammon <[email protected]> Netnod spring meeting 2012
 100 GIGABIT ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW & OUTLOOK Joerg Ammon Netnod spring meeting 2012 Agenda Industry trends 100GE technology Outlook 2 Traffic growth NetNod:'Yearly' graph (1
100 GIGABIT ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW & OUTLOOK Joerg Ammon Netnod spring meeting 2012 Agenda Industry trends 100GE technology Outlook 2 Traffic growth NetNod:'Yearly' graph (1
How To Switch In Sonicos Enhanced 5.7.7 (Sonicwall) On A 2400Mmi 2400Mm2 (Solarwall Nametra) (Soulwall 2400Mm1) (Network) (
 You can read the recommendations in the user, the technical or the installation for SONICWALL SWITCHING NSA 2400MX IN SONICOS ENHANCED 5.7. You'll find the answers to all your questions on the SONICWALL
You can read the recommendations in the user, the technical or the installation for SONICWALL SWITCHING NSA 2400MX IN SONICOS ENHANCED 5.7. You'll find the answers to all your questions on the SONICWALL
Network Analysis Modules
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes the (NAMs) and contains the following sections: Network Analysis Module (WS-SVC-NAM-1), page 6-2 Network Analysis Module (WS-SVC-NAM-2), page 6-4 NAMs monitor and analyze
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes the (NAMs) and contains the following sections: Network Analysis Module (WS-SVC-NAM-1), page 6-2 Network Analysis Module (WS-SVC-NAM-2), page 6-4 NAMs monitor and analyze
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Line Cards
 Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Line Cards Secure, Flexible, Nonstop Communications Product Benefits The Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches with CenterFlex technology provide scalable nonblocking Layer 2 4
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Line Cards Secure, Flexible, Nonstop Communications Product Benefits The Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches with CenterFlex technology provide scalable nonblocking Layer 2 4
16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH
 16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH User s Manual (DN-95312) - 0 - Content Web Smart Switch Configure login ---------------------------------- 2 Administrator Authentication Configuration ---------------------------------------------
16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH User s Manual (DN-95312) - 0 - Content Web Smart Switch Configure login ---------------------------------- 2 Administrator Authentication Configuration ---------------------------------------------
White Paper. Intrusion Detection Deploying the Shomiti Century Tap
 White Paper Intrusion Detection Deploying the Shomiti Century Tap . Shomiti Tap Deployment Purpose of this Paper The scalability of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) is often an issue when deploying an
White Paper Intrusion Detection Deploying the Shomiti Century Tap . Shomiti Tap Deployment Purpose of this Paper The scalability of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) is often an issue when deploying an
Local Area Networks. Guest Instructor Elaine Wong. Elaine_06_I-1
 Local Area Networks Guest Instructor Elaine Wong Elaine_06_I-1 Outline Introduction to Local Area Networks (LANs) Network architecture Geographical area LAN applications LAN Technologies Ethernet Fiber
Local Area Networks Guest Instructor Elaine Wong Elaine_06_I-1 Outline Introduction to Local Area Networks (LANs) Network architecture Geographical area LAN applications LAN Technologies Ethernet Fiber
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R
 VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
VMware ESX Server 3 802.1Q VLAN Solutions W H I T E P A P E R Executive Summary The virtual switches in ESX Server 3 support VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) trunking. Using VLANs, you can enhance security and leverage
Chapter 5 Configuring QoS
 Chapter 5 Configuring QoS Configuring the Basic and Advanced QoS Settings The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a QoS tab that enables you to manage your FS700TS Smart Switch
Chapter 5 Configuring QoS Configuring the Basic and Advanced QoS Settings The navigation pane at the top of the web browser interface contains a QoS tab that enables you to manage your FS700TS Smart Switch
Isilon IQ Network Configuration Guide
 Isilon IQ Network Configuration Guide An Isilon Systems Best Practice Paper August 2008 ISILON SYSTEMS Table of Contents Cluster Networking Introduction...3 Assumptions...3 Cluster Networking Features...3
Isilon IQ Network Configuration Guide An Isilon Systems Best Practice Paper August 2008 ISILON SYSTEMS Table of Contents Cluster Networking Introduction...3 Assumptions...3 Cluster Networking Features...3
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000
 Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
Configuring LACP (802.3ad) Between a Catalyst 6500/6000 and a Catalyst 4500/4000 Document ID: 19642 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Difference
Dell EqualLogic Best Practices Series. Dell EqualLogic PS Series Reference Architecture for Cisco Catalyst 3750X Two-Switch SAN Reference
 Dell EqualLogic Best Practices Series Dell EqualLogic PS Series Reference Architecture for Cisco Catalyst 3750X Two-Switch SAN Reference Storage Infrastructure and Solutions Engineering Dell Product Group
Dell EqualLogic Best Practices Series Dell EqualLogic PS Series Reference Architecture for Cisco Catalyst 3750X Two-Switch SAN Reference Storage Infrastructure and Solutions Engineering Dell Product Group
WSG24POE Switch. User Manual
 WSG24POE Switch User Manual Version: 01/01/2011 Introduction! 4 Product Overview! 4 Specifications! 5 Package Contents! 5 Hardware Description! 6 Physical Dimensions/ Weight! 6 Front Panel! 6 LED Indicators!
WSG24POE Switch User Manual Version: 01/01/2011 Introduction! 4 Product Overview! 4 Specifications! 5 Package Contents! 5 Hardware Description! 6 Physical Dimensions/ Weight! 6 Front Panel! 6 LED Indicators!
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring Local SPAN and ERSPAN
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the Local and ER Ethernet switched port analyzer (SPAN) feature to monitor traffic and includes the following topics: Information About SPAN and ERSPAN,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the Local and ER Ethernet switched port analyzer (SPAN) feature to monitor traffic and includes the following topics: Information About SPAN and ERSPAN,
Computer Networks. Definition of LAN. Connection of Network. Key Points of LAN. Lecture 06 Connecting Networks
 Computer Networks Lecture 06 Connecting Networks Kuang-hua Chen Department of Library and Information Science National Taiwan University Local Area Networks (LAN) 5 kilometer IEEE 802.3 Ethernet IEEE 802.4
Computer Networks Lecture 06 Connecting Networks Kuang-hua Chen Department of Library and Information Science National Taiwan University Local Area Networks (LAN) 5 kilometer IEEE 802.3 Ethernet IEEE 802.4
Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. Computer Networks: Fast and Gigabit Ethernet
 Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet 1 Fast Ethernet (100BASE-T) How to achieve 100 Mbps capacity? MII LLC MAC Convergence Sublayer Media Independent Interface Media Dependent Sublayer Data Link Layer Physical
Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet 1 Fast Ethernet (100BASE-T) How to achieve 100 Mbps capacity? MII LLC MAC Convergence Sublayer Media Independent Interface Media Dependent Sublayer Data Link Layer Physical
QuickSpecs. Cisco Fabric Extender for HP BladeSystem. Overview
 Overview The (Model B22HP) provides an extension of the Cisco Nexus switch fabric to the HP server edge. Logically, it behaves like a remote line card to a parent Cisco Nexus 5000/6000/7000 series switch
Overview The (Model B22HP) provides an extension of the Cisco Nexus switch fabric to the HP server edge. Logically, it behaves like a remote line card to a parent Cisco Nexus 5000/6000/7000 series switch
Ethernet Link SGI-2424
 Ethernet Link SGI-2424 24 Combo Ports (10/100/1000Mbps Copper and Dual-Speed SFP) + 2G TP/SFP Combo Layer 2+ Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Overview LinkPro SGI-2424 is a layer-2+ gigabit access switch
Ethernet Link SGI-2424 24 Combo Ports (10/100/1000Mbps Copper and Dual-Speed SFP) + 2G TP/SFP Combo Layer 2+ Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Overview LinkPro SGI-2424 is a layer-2+ gigabit access switch
