Cluster analysis with SPSS: K-Means Cluster Analysis
|
|
|
- Cordelia Webster
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
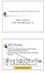
1 analysis with SPSS: K-Means Analysis analysis is a type of data classification carried out by separating the data into groups. The aim of cluster analysis is to categorize n objects in k (k>1) groups, called clusters, by using p (p>0) variables. As with many other types of statistical, cluster analysis has several variants, each with its own clustering procedure. There are two main sub-divisions of clustering procedures. In the first procedure the number of clusters is pre-defined. This is known as the K-Means ing method. When the number of the clusters is not predefined we use Hierarchical analysis. The great variety of clustering procedures results from the metrics which are used between different objects. The most commonly used metrics are the Euclidean metric, Manhattan metric, Chebyshev metric and others. There are also different rules used for creating the clusters. Some allow members to share different clusters, whilst others only allow exclusive membership. K-Means Analysis From the main menu of SPSS consecutively click Analyze Classify K- Means. Figure 1.
2 Mark the variables on the basis of which clustering will be done and send them to Variables - the box for entering the variables. The Label Cases by box is used for entering a string variable which marks the units. After that we determine the number of desired clusters in the Number of s box. In our case in the Method box we mark Iterate and Classify. Unlike the alternative method Classify only, which, defines fixed cluster centers, this one defines the successive iterations and determines how the final clustering is to be carried out. Figure 2. In the Centers box we specify the file (if there is one), which contains the initial cluster centers and the file (if required), which contains the final cluster centers. In Read initial from we specify the file which contains the initial cluster centers, and in Write final as we specify the file which contains the final cluster centers. With the Iterate button we can determine the criteria for updating the cluster centers, in Maximum Iterations we can determine the maximum number of the iterations (no more than 999), and in Convergence Criterion we decide which rule halts the iteration process. By default 10 iterations and convergence criterion 0 are given. Furthermore, it is possible to mark the option Use running means. If this is selected, the cluster centers change after the addition of each object. If this option is not selected, cluster centers are calculated after all objects have been allocated to a given cluster. In
3 both cases we receive different results and therefore the way in which the clustering is achieved must be specified. We proceed by clicking on Continue. Figure 3. Using the Save button we can save new variables in a data file which indicates the cluster membership of each object ( Membership) and distance from cluster center for each object (Distance from Center). Fgure 4. The Options button gives the option of displaying additional statistics initial cluster centers (Initial cluster centers), dispersion analysis table (ANOVA table) and information for cluster membership of each object ( information in each case?). It is desirable that all three options are selected. We obtain the final result by clicking OK. Figure 5.
4 Let us briefly go through the different stages of K-Means Analysis using the data from the example with UniCredit Bulbank (Table 1 from the chapter First Steps in SPSS). We determine the number of clusters to be 4, and the initial cluster centers are evaluated based on the data. We use squared Euclidean Distance for the divergence measure between units. Also we choose the cluster centers to be calculated after all objects have been assigned to a given cluster, i.e. we don t put a tick in Use running means box. The initial cluster centers are given in Table 1 (Initial Centers). They are vectors with their values based on the five variables, which refer to 2000 (first cluster), 2005 (second cluster), 2006 (third cluster) and 2003 (fourth cluster). These 4 years are at maximum index distance from each other. Table 1. Initial Centers Net profit 160,065 96, ,654 89,752 Own funds 602, , , ,026 Assets 2559, , , ,439 Client deposits 1692, , , ,781 Loans 316, , , ,634 In Table 2 we can see the number of the iterations and the changes in the cluster centers. In the first iteration year 2001 joins year 2000 and the cluster center is updated. The year 2004 joins the second cluster the year 2005, and year 2002 joins the fourth cluster the year The third cluster does not change. In the second iteration the process of redistribution of the units stops because there are no changes in the cluster centers. Table 2. Iteration History (a) Change in Centers Iteration , ,959, ,515 2,000,000,000,000 (a) Convergence achieved due to no or small change in cluster centers. The maximum absolute coordinate change for any center is,000. The current iteration is 2. The minimum distance between initial centers is 821,273.
5 The results are summarized in Table 3, i.e. which cluster each unit belongs to and the new cluster centers. The first cluster is formed by the years 2000 and 2001, the second by 2004 and 2005, the third only by 2006 and the fourth by the years 2002 and In Table 4 we can see the final cluster centers, and in Table 5 - the distance between the final cluster centers. Table 3. Membership Case Number Distance 1: ,730 2: ,730 3: ,515 4: ,515 5: ,959 6: ,959 7: ,000 Table 4. Final Centers Net profit 114,489 91, ,654 84,441 Own funds 546, , , ,638 Assets 2645, , , ,710 Client deposits 1856, , , ,869 Loans 339, , , ,285 Table 5. Distances between Final Centers , , , , , , , , , , , ,395 If we compare the results from Table 1 and Table 4 we will see that the cluster center of the third cluster does not change. Since in our case the groups are formed deliberately in accordance with the distance between them in the multidimensional space, i.e. the condition for randomness
6 of the observations in the different groups is not met, the results from the dispersion analysis are purely descriptive. In other words, we cannot use the significance level (Sign. column in ANOVA Table dispersion analysis of clustering results) to check the hypothesis about the mean variables. Nevertheless, the differences between the F-ratios (F column in the ANOVA Table) makes it possible to draw general conclusions about the role of the different mean variables in the forming of the clusters. In Table 6 are given the results from the dispersion analysis. They show that assets have the greatest influence in the forming of the clusters and net profit has the least influence. Table 6. ANOVA Error Mean Square df Mean Square df F Sig. Net profit 495, ,744 3,349,795 Own funds 2878, , ,134,460 Assets , , ,387,002 Client deposits , , ,788,021 Loans , , ,598,012 The F tests should be used only for descriptive purposes because the clusters have been chosen to maximize the differences among cases in different clusters. The observed significance levels are not corrected for this and thus cannot be interpreted as tests of the hypothesis that the cluster means are equal. Table 7. Number of Cases in each 1 2, , , ,000 Valid 7,000 Missing,000 Table 7 presents data for the number of units in each cluster as well as their total number and missing units (if there are any). Now we will present the results from the same clustering procedure with the difference that we choose the cluster centers to be changed after the joining of each object to a given cluster and we select the option Use running means.
7 Table 8. Table 9. Iteration History(a) Membership Change in Centers Iteration , ,973,000, ,786 50,658,000, ,446 16,886,000, ,362 5,629,000,000 5,840 1,876,000,000 6,210,625,000,000 7,053,208,000,000 8,013,069,000,000 9,003,023,000,000 10,001,008,000,000 Case Number Distance 1: ,856 2: ,021 3: ,434 4: ,000 5: ,963 6: ,955 7: ,000 (a) Iterations stopped because the maximum number of iterations was performed. Iterations failed to converge. The maximum absolute coordinate change for any center is,005. The current iteration is 10. The minimum distance between initial centers is 821,273. Table 10. Final Centers Net profit 102,702 91, ,654 89,752 Own funds 535, , , ,026 Assets 2671, , , ,439 Client deposits 1921, , , ,781 Loans 414, , , ,634 Table 11. Distances between Final Centers , , , , , , , , , , , ,372 Table 12. ANOVA Error Mean Square df Mean Square df F Sig. Net profit 236, ,767 3,141,929 Own funds 2856, , ,116,465 Assets , , ,764,002 Client deposits , , ,255,025 Loans , , ,687,008 The F tests should be used only for descriptive purposes because the clusters have been chosen to maximize the differences between cases in different clusters. The observed significance levels are not corrected for this and thus cannot be interpreted as tests of the hypothesis that the cluster means are equal.
8 Table 13. Number of Cases in each 1 3, , , ,000 Valid 7,000 Missing,000 From the presented data (Table 9) we see that now the first cluster is formed by years 2000, 2001 and 2002, the second by 2004 and 2005, the third by 2006 and the fourth only by the year According to the data presented in the ANOVA table, assets once again have maximum influence in forming the clusters and net profit the least. Author: Dessislava Vojnikova, Plovdiv University, 4 th year Bachelor program in Applied Mathematics Supervisor: Snezhana Gocheva-Ilieva
STATISTICA. Clustering Techniques. Case Study: Defining Clusters of Shopping Center Patrons. and
 Clustering Techniques and STATISTICA Case Study: Defining Clusters of Shopping Center Patrons STATISTICA Solutions for Business Intelligence, Data Mining, Quality Control, and Web-based Analytics Table
Clustering Techniques and STATISTICA Case Study: Defining Clusters of Shopping Center Patrons STATISTICA Solutions for Business Intelligence, Data Mining, Quality Control, and Web-based Analytics Table
Machine Learning using MapReduce
 Machine Learning using MapReduce What is Machine Learning Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence concerned with techniques that allow computers to improve their outputs based on previous
Machine Learning using MapReduce What is Machine Learning Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence concerned with techniques that allow computers to improve their outputs based on previous
Mixed 2 x 3 ANOVA. Notes
 Mixed 2 x 3 ANOVA This section explains how to perform an ANOVA when one of the variables takes the form of repeated measures and the other variable is between-subjects that is, independent groups of participants
Mixed 2 x 3 ANOVA This section explains how to perform an ANOVA when one of the variables takes the form of repeated measures and the other variable is between-subjects that is, independent groups of participants
There are a number of different methods that can be used to carry out a cluster analysis; these methods can be classified as follows:
 Statistics: Rosie Cornish. 2007. 3.1 Cluster Analysis 1 Introduction This handout is designed to provide only a brief introduction to cluster analysis and how it is done. Books giving further details are
Statistics: Rosie Cornish. 2007. 3.1 Cluster Analysis 1 Introduction This handout is designed to provide only a brief introduction to cluster analysis and how it is done. Books giving further details are
Cluster Analysis. Alison Merikangas Data Analysis Seminar 18 November 2009
 Cluster Analysis Alison Merikangas Data Analysis Seminar 18 November 2009 Overview What is cluster analysis? Types of cluster Distance functions Clustering methods Agglomerative K-means Density-based Interpretation
Cluster Analysis Alison Merikangas Data Analysis Seminar 18 November 2009 Overview What is cluster analysis? Types of cluster Distance functions Clustering methods Agglomerative K-means Density-based Interpretation
Setting Up Outlook on Workstation to Capture Emails
 Setting Up Outlook on Workstation to Capture Emails Setting up Outlook to allow email to pass directly to M-Files requires a number of steps to assure that all of the data required is sent to the correct
Setting Up Outlook on Workstation to Capture Emails Setting up Outlook to allow email to pass directly to M-Files requires a number of steps to assure that all of the data required is sent to the correct
K-Means Clustering Tutorial
 K-Means Clustering Tutorial By Kardi Teknomo,PhD Preferable reference for this tutorial is Teknomo, Kardi. K-Means Clustering Tutorials. http:\\people.revoledu.com\kardi\ tutorial\kmean\ Last Update: July
K-Means Clustering Tutorial By Kardi Teknomo,PhD Preferable reference for this tutorial is Teknomo, Kardi. K-Means Clustering Tutorials. http:\\people.revoledu.com\kardi\ tutorial\kmean\ Last Update: July
Social Media Mining. Data Mining Essentials
 Introduction Data production rate has been increased dramatically (Big Data) and we are able store much more data than before E.g., purchase data, social media data, mobile phone data Businesses and customers
Introduction Data production rate has been increased dramatically (Big Data) and we are able store much more data than before E.g., purchase data, social media data, mobile phone data Businesses and customers
STATISTICA Formula Guide: Logistic Regression. Table of Contents
 : Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
: Table of Contents... 1 Overview of Model... 1 Dispersion... 2 Parameterization... 3 Sigma-Restricted Model... 3 Overparameterized Model... 4 Reference Coding... 4 Model Summary (Summary Tab)... 5 Summary
SPSS Guide: Regression Analysis
 SPSS Guide: Regression Analysis I put this together to give you a step-by-step guide for replicating what we did in the computer lab. It should help you run the tests we covered. The best way to get familiar
SPSS Guide: Regression Analysis I put this together to give you a step-by-step guide for replicating what we did in the computer lab. It should help you run the tests we covered. The best way to get familiar
The Science and Art of Market Segmentation Using PROC FASTCLUS Mark E. Thompson, Forefront Economics Inc, Beaverton, Oregon
 The Science and Art of Market Segmentation Using PROC FASTCLUS Mark E. Thompson, Forefront Economics Inc, Beaverton, Oregon ABSTRACT Effective business development strategies often begin with market segmentation,
The Science and Art of Market Segmentation Using PROC FASTCLUS Mark E. Thompson, Forefront Economics Inc, Beaverton, Oregon ABSTRACT Effective business development strategies often begin with market segmentation,
Tutorial Segmentation and Classification
 MARKETING ENGINEERING FOR EXCEL TUTORIAL VERSION 1.0.8 Tutorial Segmentation and Classification Marketing Engineering for Excel is a Microsoft Excel add-in. The software runs from within Microsoft Excel
MARKETING ENGINEERING FOR EXCEL TUTORIAL VERSION 1.0.8 Tutorial Segmentation and Classification Marketing Engineering for Excel is a Microsoft Excel add-in. The software runs from within Microsoft Excel
Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms
 8 Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Cluster analysis divides data into groups (clusters) that are meaningful, useful, or both. If meaningful groups are the goal, then the clusters should
8 Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Cluster analysis divides data into groups (clusters) that are meaningful, useful, or both. If meaningful groups are the goal, then the clusters should
Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform
 Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry, LNBio, CNPEM Tutorial version 1.0, January 2014. Note: This tutorial was written based on the information
Tutorial for proteome data analysis using the Perseus software platform Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry, LNBio, CNPEM Tutorial version 1.0, January 2014. Note: This tutorial was written based on the information
Regression Clustering
 Chapter 449 Introduction This algorithm provides for clustering in the multiple regression setting in which you have a dependent variable Y and one or more independent variables, the X s. The algorithm
Chapter 449 Introduction This algorithm provides for clustering in the multiple regression setting in which you have a dependent variable Y and one or more independent variables, the X s. The algorithm
Clustering. Danilo Croce Web Mining & Retrieval a.a. 2015/201 16/03/2016
 Clustering Danilo Croce Web Mining & Retrieval a.a. 2015/201 16/03/2016 1 Supervised learning vs. unsupervised learning Supervised learning: discover patterns in the data that relate data attributes with
Clustering Danilo Croce Web Mining & Retrieval a.a. 2015/201 16/03/2016 1 Supervised learning vs. unsupervised learning Supervised learning: discover patterns in the data that relate data attributes with
A Basic Guide to Analyzing Individual Scores Data with SPSS
 A Basic Guide to Analyzing Individual Scores Data with SPSS Step 1. Clean the data file Open the Excel file with your data. You may get the following message: If you get this message, click yes. Delete
A Basic Guide to Analyzing Individual Scores Data with SPSS Step 1. Clean the data file Open the Excel file with your data. You may get the following message: If you get this message, click yes. Delete
Chapter 5 Analysis of variance SPSS Analysis of variance
 Chapter 5 Analysis of variance SPSS Analysis of variance Data file used: gss.sav How to get there: Analyze Compare Means One-way ANOVA To test the null hypothesis that several population means are equal,
Chapter 5 Analysis of variance SPSS Analysis of variance Data file used: gss.sav How to get there: Analyze Compare Means One-way ANOVA To test the null hypothesis that several population means are equal,
COSC 6397 Big Data Analytics. Mahout and 3 rd homework assignment. Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014. Mahout
 COSC 6397 Big Data Analytics Mahout and 3 rd homework assignment Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 Mahout Scalable machine learning library Built with MapReduce and Hadoop in mind Written in Java Focusing on three
COSC 6397 Big Data Analytics Mahout and 3 rd homework assignment Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 Mahout Scalable machine learning library Built with MapReduce and Hadoop in mind Written in Java Focusing on three
Binary Logistic Regression
 Binary Logistic Regression Main Effects Model Logistic regression will accept quantitative, binary or categorical predictors and will code the latter two in various ways. Here s a simple model including
Binary Logistic Regression Main Effects Model Logistic regression will accept quantitative, binary or categorical predictors and will code the latter two in various ways. Here s a simple model including
HES-SO Master of Science in Engineering. Clustering. Prof. Laura Elena Raileanu HES-SO Yverdon-les-Bains (HEIG-VD)
 HES-SO Master of Science in Engineering Clustering Prof. Laura Elena Raileanu HES-SO Yverdon-les-Bains (HEIG-VD) Plan Motivation Hierarchical Clustering K-Means Clustering 2 Problem Setup Arrange items
HES-SO Master of Science in Engineering Clustering Prof. Laura Elena Raileanu HES-SO Yverdon-les-Bains (HEIG-VD) Plan Motivation Hierarchical Clustering K-Means Clustering 2 Problem Setup Arrange items
Building Data Cubes and Mining Them. Jelena Jovanovic Email: [email protected]
 Building Data Cubes and Mining Them Jelena Jovanovic Email: [email protected] KDD Process KDD is an overall process of discovering useful knowledge from data. Data mining is a particular step in the
Building Data Cubes and Mining Them Jelena Jovanovic Email: [email protected] KDD Process KDD is an overall process of discovering useful knowledge from data. Data mining is a particular step in the
SAS Software to Fit the Generalized Linear Model
 SAS Software to Fit the Generalized Linear Model Gordon Johnston, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC Abstract In recent years, the class of generalized linear models has gained popularity as a statistical modeling
SAS Software to Fit the Generalized Linear Model Gordon Johnston, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC Abstract In recent years, the class of generalized linear models has gained popularity as a statistical modeling
Data Mining Project Report. Document Clustering. Meryem Uzun-Per
 Data Mining Project Report Document Clustering Meryem Uzun-Per 504112506 Table of Content Table of Content... 2 1. Project Definition... 3 2. Literature Survey... 3 3. Methods... 4 3.1. K-means algorithm...
Data Mining Project Report Document Clustering Meryem Uzun-Per 504112506 Table of Content Table of Content... 2 1. Project Definition... 3 2. Literature Survey... 3 3. Methods... 4 3.1. K-means algorithm...
University of Arkansas Libraries ArcGIS Desktop Tutorial. Section 2: Manipulating Display Parameters in ArcMap. Symbolizing Features and Rasters:
 : Manipulating Display Parameters in ArcMap Symbolizing Features and Rasters: Data sets that are added to ArcMap a default symbology. The user can change the default symbology for their features (point,
: Manipulating Display Parameters in ArcMap Symbolizing Features and Rasters: Data sets that are added to ArcMap a default symbology. The user can change the default symbology for their features (point,
The Chi-Square Test. STAT E-50 Introduction to Statistics
 STAT -50 Introduction to Statistics The Chi-Square Test The Chi-square test is a nonparametric test that is used to compare experimental results with theoretical models. That is, we will be comparing observed
STAT -50 Introduction to Statistics The Chi-Square Test The Chi-square test is a nonparametric test that is used to compare experimental results with theoretical models. That is, we will be comparing observed
DATA MINING CLUSTER ANALYSIS: BASIC CONCEPTS
 DATA MINING CLUSTER ANALYSIS: BASIC CONCEPTS 1 AND ALGORITHMS Chiara Renso KDD-LAB ISTI- CNR, Pisa, Italy WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group will be similar
DATA MINING CLUSTER ANALYSIS: BASIC CONCEPTS 1 AND ALGORITHMS Chiara Renso KDD-LAB ISTI- CNR, Pisa, Italy WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? Finding groups of objects such that the objects in a group will be similar
Introduction to Clustering
 Introduction to Clustering Yumi Kondo Student Seminar LSK301 Sep 25, 2010 Yumi Kondo (University of British Columbia) Introduction to Clustering Sep 25, 2010 1 / 36 Microarray Example N=65 P=1756 Yumi
Introduction to Clustering Yumi Kondo Student Seminar LSK301 Sep 25, 2010 Yumi Kondo (University of British Columbia) Introduction to Clustering Sep 25, 2010 1 / 36 Microarray Example N=65 P=1756 Yumi
Analysis of categorical data: Course quiz instructions for SPSS
 Analysis of categorical data: Course quiz instructions for SPSS The dataset Please download the Online sales dataset from the Download pod in the Course quiz resources screen. The filename is smr_bus_acd_clo_quiz_online_250.xls.
Analysis of categorical data: Course quiz instructions for SPSS The dataset Please download the Online sales dataset from the Download pod in the Course quiz resources screen. The filename is smr_bus_acd_clo_quiz_online_250.xls.
CLUSTERING LARGE DATA SETS WITH MIXED NUMERIC AND CATEGORICAL VALUES *
 CLUSTERING LARGE DATA SETS WITH MIED NUMERIC AND CATEGORICAL VALUES * ZHEUE HUANG CSIRO Mathematical and Information Sciences GPO Box Canberra ACT, AUSTRALIA [email protected] Efficient partitioning
CLUSTERING LARGE DATA SETS WITH MIED NUMERIC AND CATEGORICAL VALUES * ZHEUE HUANG CSIRO Mathematical and Information Sciences GPO Box Canberra ACT, AUSTRALIA [email protected] Efficient partitioning
NCSS Statistical Software Principal Components Regression. In ordinary least squares, the regression coefficients are estimated using the formula ( )
 Chapter 340 Principal Components Regression Introduction is a technique for analyzing multiple regression data that suffer from multicollinearity. When multicollinearity occurs, least squares estimates
Chapter 340 Principal Components Regression Introduction is a technique for analyzing multiple regression data that suffer from multicollinearity. When multicollinearity occurs, least squares estimates
Multiple Regression in SPSS This example shows you how to perform multiple regression. The basic command is regression : linear.
 Multiple Regression in SPSS This example shows you how to perform multiple regression. The basic command is regression : linear. In the main dialog box, input the dependent variable and several predictors.
Multiple Regression in SPSS This example shows you how to perform multiple regression. The basic command is regression : linear. In the main dialog box, input the dependent variable and several predictors.
Clustering. Data Mining. Abraham Otero. Data Mining. Agenda
 Clustering 1/46 Agenda Introduction Distance K-nearest neighbors Hierarchical clustering Quick reference 2/46 1 Introduction It seems logical that in a new situation we should act in a similar way as in
Clustering 1/46 Agenda Introduction Distance K-nearest neighbors Hierarchical clustering Quick reference 2/46 1 Introduction It seems logical that in a new situation we should act in a similar way as in
Decision Support System Methodology Using a Visual Approach for Cluster Analysis Problems
 Decision Support System Methodology Using a Visual Approach for Cluster Analysis Problems Ran M. Bittmann School of Business Administration Ph.D. Thesis Submitted to the Senate of Bar-Ilan University Ramat-Gan,
Decision Support System Methodology Using a Visual Approach for Cluster Analysis Problems Ran M. Bittmann School of Business Administration Ph.D. Thesis Submitted to the Senate of Bar-Ilan University Ramat-Gan,
IBM SPSS Statistics for Beginners for Windows
 ISS, NEWCASTLE UNIVERSITY IBM SPSS Statistics for Beginners for Windows A Training Manual for Beginners Dr. S. T. Kometa A Training Manual for Beginners Contents 1 Aims and Objectives... 3 1.1 Learning
ISS, NEWCASTLE UNIVERSITY IBM SPSS Statistics for Beginners for Windows A Training Manual for Beginners Dr. S. T. Kometa A Training Manual for Beginners Contents 1 Aims and Objectives... 3 1.1 Learning
Clustering UE 141 Spring 2013
 Clustering UE 141 Spring 013 Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Definition of Clustering Finding groups of obects such that the obects in a group will be similar (or related) to one another and different from (or
Clustering UE 141 Spring 013 Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Definition of Clustering Finding groups of obects such that the obects in a group will be similar (or related) to one another and different from (or
POST-HOC SEGMENTATION USING MARKETING RESEARCH
 Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 12(3), 2012, 39-48 39 POST-HOC SEGMENTATION USING MARKETING RESEARCH CRISTINEL CONSTANTIN * ABSTRACT: This paper is about an instrumental research conducted
Annals of the University of Petroşani, Economics, 12(3), 2012, 39-48 39 POST-HOC SEGMENTATION USING MARKETING RESEARCH CRISTINEL CONSTANTIN * ABSTRACT: This paper is about an instrumental research conducted
8. Comparing Means Using One Way ANOVA
 8. Comparing Means Using One Way ANOVA Objectives Calculate a one-way analysis of variance Run various multiple comparisons Calculate measures of effect size A One Way ANOVA is an analysis of variance
8. Comparing Means Using One Way ANOVA Objectives Calculate a one-way analysis of variance Run various multiple comparisons Calculate measures of effect size A One Way ANOVA is an analysis of variance
Multivariate Analysis
 Table Of Contents Multivariate Analysis... 1 Overview... 1 Principal Components... 2 Factor Analysis... 5 Cluster Observations... 12 Cluster Variables... 17 Cluster K-Means... 20 Discriminant Analysis...
Table Of Contents Multivariate Analysis... 1 Overview... 1 Principal Components... 2 Factor Analysis... 5 Cluster Observations... 12 Cluster Variables... 17 Cluster K-Means... 20 Discriminant Analysis...
Chapter 7. Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 7. Cluster Analysis. What is Cluster Analysis?. A Categorization of Major Clustering Methods. Partitioning Methods. Hierarchical Methods 5. Density-Based Methods 6. Grid-Based Methods 7. Model-Based
Chapter 7. Cluster Analysis. What is Cluster Analysis?. A Categorization of Major Clustering Methods. Partitioning Methods. Hierarchical Methods 5. Density-Based Methods 6. Grid-Based Methods 7. Model-Based
PUBLIC Model Manager User Guide
 SAP Predictive Analytics 2.4 2015-11-23 PUBLIC Content 1 Introduction....4 2 Concepts....5 2.1 Roles....5 2.2 Rights....6 2.3 Schedules....7 2.4 Tasks.... 7 3....8 3.1 My Model Manager....8 Overview....
SAP Predictive Analytics 2.4 2015-11-23 PUBLIC Content 1 Introduction....4 2 Concepts....5 2.1 Roles....5 2.2 Rights....6 2.3 Schedules....7 2.4 Tasks.... 7 3....8 3.1 My Model Manager....8 Overview....
Evolutionary Detection of Rules for Text Categorization. Application to Spam Filtering
 Advances in Intelligent Systems and Technologies Proceedings ECIT2004 - Third European Conference on Intelligent Systems and Technologies Iasi, Romania, July 21-23, 2004 Evolutionary Detection of Rules
Advances in Intelligent Systems and Technologies Proceedings ECIT2004 - Third European Conference on Intelligent Systems and Technologies Iasi, Romania, July 21-23, 2004 Evolutionary Detection of Rules
Instructions for SPSS 21
 1 Instructions for SPSS 21 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Opening the SPSS program... 2 1.2 General... 2 2 Data inputting and processing... 2 2.1 Manual input and data processing... 2 2.2 Saving data... 3 2.3
1 Instructions for SPSS 21 1 Introduction... 2 1.1 Opening the SPSS program... 2 1.2 General... 2 2 Data inputting and processing... 2 2.1 Manual input and data processing... 2 2.2 Saving data... 3 2.3
UNSUPERVISED MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES IN GENOMICS
 UNSUPERVISED MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES IN GENOMICS Dwijesh C. Mishra I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi-110 012 [email protected] What is Learning? "Learning denotes changes in a system that enable
UNSUPERVISED MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES IN GENOMICS Dwijesh C. Mishra I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi-110 012 [email protected] What is Learning? "Learning denotes changes in a system that enable
Comparables Sales Price
 Chapter 486 Comparables Sales Price Introduction Appraisers often estimate the market value (current sales price) of a subject property from a group of comparable properties that have recently sold. Since
Chapter 486 Comparables Sales Price Introduction Appraisers often estimate the market value (current sales price) of a subject property from a group of comparable properties that have recently sold. Since
Chapter ML:XI (continued)
 Chapter ML:XI (continued) XI. Cluster Analysis Data Mining Overview Cluster Analysis Basics Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Iterative Cluster Analysis Density-Based Cluster Analysis Cluster Evaluation Constrained
Chapter ML:XI (continued) XI. Cluster Analysis Data Mining Overview Cluster Analysis Basics Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Iterative Cluster Analysis Density-Based Cluster Analysis Cluster Evaluation Constrained
Using Data Mining for Mobile Communication Clustering and Characterization
 Using Data Mining for Mobile Communication Clustering and Characterization A. Bascacov *, C. Cernazanu ** and M. Marcu ** * Lasting Software, Timisoara, Romania ** Politehnica University of Timisoara/Computer
Using Data Mining for Mobile Communication Clustering and Characterization A. Bascacov *, C. Cernazanu ** and M. Marcu ** * Lasting Software, Timisoara, Romania ** Politehnica University of Timisoara/Computer
One-Way ANOVA using SPSS 11.0. SPSS ANOVA procedures found in the Compare Means analyses. Specifically, we demonstrate
 1 One-Way ANOVA using SPSS 11.0 This section covers steps for testing the difference between three or more group means using the SPSS ANOVA procedures found in the Compare Means analyses. Specifically,
1 One-Way ANOVA using SPSS 11.0 This section covers steps for testing the difference between three or more group means using the SPSS ANOVA procedures found in the Compare Means analyses. Specifically,
Clustering Connectionist and Statistical Language Processing
 Clustering Connectionist and Statistical Language Processing Frank Keller [email protected] Computerlinguistik Universität des Saarlandes Clustering p.1/21 Overview clustering vs. classification supervised
Clustering Connectionist and Statistical Language Processing Frank Keller [email protected] Computerlinguistik Universität des Saarlandes Clustering p.1/21 Overview clustering vs. classification supervised
IBM SPSS Statistics 20 Part 1: Descriptive Statistics
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES IBM SPSS Statistics 20 Part 1: Descriptive Statistics Summer 2013, Version 2.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES IBM SPSS Statistics 20 Part 1: Descriptive Statistics Summer 2013, Version 2.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
Medical Information Management & Mining. You Chen Jan,15, 2013 [email protected]
 Medical Information Management & Mining You Chen Jan,15, 2013 [email protected] 1 Trees Building Materials Trees cannot be used to build a house directly. How can we transform trees to building materials?
Medical Information Management & Mining You Chen Jan,15, 2013 [email protected] 1 Trees Building Materials Trees cannot be used to build a house directly. How can we transform trees to building materials?
Standardization and Its Effects on K-Means Clustering Algorithm
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(7): 399-3303, 03 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 03 Submitted: January 3, 03 Accepted: February 5, 03
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(7): 399-3303, 03 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 03 Submitted: January 3, 03 Accepted: February 5, 03
They can be obtained in HQJHQH format directly from the home page at: http://www.engene.cnb.uam.es/downloads/kobayashi.dat
 HQJHQH70 *XLGHG7RXU This document contains a Guided Tour through the HQJHQH platform and it was created for training purposes with respect to the system options and analysis possibilities. It is not intended
HQJHQH70 *XLGHG7RXU This document contains a Guided Tour through the HQJHQH platform and it was created for training purposes with respect to the system options and analysis possibilities. It is not intended
Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms
 Cluster Analsis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms What does it mean clustering? Applications Tpes of clustering K-means Intuition Algorithm Choosing initial centroids Bisecting K-means Post-processing Strengths
Cluster Analsis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms What does it mean clustering? Applications Tpes of clustering K-means Intuition Algorithm Choosing initial centroids Bisecting K-means Post-processing Strengths
Lesson 9. Reports. 1. Create a Visual Report. Create a visual report. Customize a visual report. Create a visual report template.
 Lesson 9. s Create a visual report. Customize a visual report. Create a visual report template. Introduction You have updated the cost information in your project plan. When presenting such varied information
Lesson 9. s Create a visual report. Customize a visual report. Create a visual report template. Introduction You have updated the cost information in your project plan. When presenting such varied information
To do a factor analysis, we need to select an extraction method and a rotation method. Hit the Extraction button to specify your extraction method.
 Factor Analysis in SPSS To conduct a Factor Analysis, start from the Analyze menu. This procedure is intended to reduce the complexity in a set of data, so we choose Data Reduction from the menu. And the
Factor Analysis in SPSS To conduct a Factor Analysis, start from the Analyze menu. This procedure is intended to reduce the complexity in a set of data, so we choose Data Reduction from the menu. And the
SPSS Resources. 1. See website (readings) for SPSS tutorial & Stats handout
 Analyzing Data SPSS Resources 1. See website (readings) for SPSS tutorial & Stats handout Don t have your own copy of SPSS? 1. Use the libraries to analyze your data 2. Download a trial version of SPSS
Analyzing Data SPSS Resources 1. See website (readings) for SPSS tutorial & Stats handout Don t have your own copy of SPSS? 1. Use the libraries to analyze your data 2. Download a trial version of SPSS
Setting Preferences in QuickBooks
 Setting Preferences in QuickBooks The following preferences should be set in Quickbooks: Setting QuickBooks to Display the Lowest Sub-Account Number The Default setting in QuickBooks for displaying Account
Setting Preferences in QuickBooks The following preferences should be set in Quickbooks: Setting QuickBooks to Display the Lowest Sub-Account Number The Default setting in QuickBooks for displaying Account
Introduction to Machine Learning Using Python. Vikram Kamath
 Introduction to Machine Learning Using Python Vikram Kamath Contents: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Introduction/Definition Where and Why ML is used Types of Learning Supervised Learning Linear Regression
Introduction to Machine Learning Using Python Vikram Kamath Contents: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Introduction/Definition Where and Why ML is used Types of Learning Supervised Learning Linear Regression
Payroll. 4. Print Checks. Table of Contents Print Checks...2 All...3 Department...4 Print Single Posting...5
 4. Print Checks Table of Contents Print Checks...2 All...3 Department...4 Print Single Posting...5 Click on 4. Print Checks from the Main Menu and the following window will appear: The best practice is
4. Print Checks Table of Contents Print Checks...2 All...3 Department...4 Print Single Posting...5 Click on 4. Print Checks from the Main Menu and the following window will appear: The best practice is
Neural Networks Lesson 5 - Cluster Analysis
 Neural Networks Lesson 5 - Cluster Analysis Prof. Michele Scarpiniti INFOCOM Dpt. - Sapienza University of Rome http://ispac.ing.uniroma1.it/scarpiniti/index.htm [email protected] Rome, 29
Neural Networks Lesson 5 - Cluster Analysis Prof. Michele Scarpiniti INFOCOM Dpt. - Sapienza University of Rome http://ispac.ing.uniroma1.it/scarpiniti/index.htm [email protected] Rome, 29
CLUSTER ANALYSIS FOR SEGMENTATION
 CLUSTER ANALYSIS FOR SEGMENTATION Introduction We all understand that consumers are not all alike. This provides a challenge for the development and marketing of profitable products and services. Not every
CLUSTER ANALYSIS FOR SEGMENTATION Introduction We all understand that consumers are not all alike. This provides a challenge for the development and marketing of profitable products and services. Not every
IBM SPSS Statistics 20 Part 4: Chi-Square and ANOVA
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES IBM SPSS Statistics 20 Part 4: Chi-Square and ANOVA Summer 2013, Version 2.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES IBM SPSS Statistics 20 Part 4: Chi-Square and ANOVA Summer 2013, Version 2.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading the
Package MixGHD. June 26, 2015
 Type Package Package MixGHD June 26, 2015 Title Model Based Clustering, Classification and Discriminant Analysis Using the Mixture of Generalized Hyperbolic Distributions Version 1.7 Date 2015-6-15 Author
Type Package Package MixGHD June 26, 2015 Title Model Based Clustering, Classification and Discriminant Analysis Using the Mixture of Generalized Hyperbolic Distributions Version 1.7 Date 2015-6-15 Author
Ira J. Haimowitz Henry Schwarz
 From: AAAI Technical Report WS-97-07. Compilation copyright 1997, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. Clustering and Prediction for Credit Line Optimization Ira J. Haimowitz Henry Schwarz General
From: AAAI Technical Report WS-97-07. Compilation copyright 1997, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. Clustering and Prediction for Credit Line Optimization Ira J. Haimowitz Henry Schwarz General
Email Message Classification user guide
 Email Message Classification user guide Introduction Email message classification tags each email used within the authority with one of three classifications chosen by a user dependant on the content of
Email Message Classification user guide Introduction Email message classification tags each email used within the authority with one of three classifications chosen by a user dependant on the content of
Didacticiel - Études de cas
 1 Topic Linear Discriminant Analysis Data Mining Tools Comparison (Tanagra, R, SAS and SPSS). Linear discriminant analysis is a popular method in domains of statistics, machine learning and pattern recognition.
1 Topic Linear Discriminant Analysis Data Mining Tools Comparison (Tanagra, R, SAS and SPSS). Linear discriminant analysis is a popular method in domains of statistics, machine learning and pattern recognition.
Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) Presentation
 Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) Presentation Spring 2011 Mike Kurtz Dr. Skalski Reality Television Pawn Stars Jon & Kate +8 A&E Biography Unsolved Mysteries Intervention Queer Eye for the Straight Guy Judge
Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) Presentation Spring 2011 Mike Kurtz Dr. Skalski Reality Television Pawn Stars Jon & Kate +8 A&E Biography Unsolved Mysteries Intervention Queer Eye for the Straight Guy Judge
Doing Multiple Regression with SPSS. In this case, we are interested in the Analyze options so we choose that menu. If gives us a number of choices:
 Doing Multiple Regression with SPSS Multiple Regression for Data Already in Data Editor Next we want to specify a multiple regression analysis for these data. The menu bar for SPSS offers several options:
Doing Multiple Regression with SPSS Multiple Regression for Data Already in Data Editor Next we want to specify a multiple regression analysis for these data. The menu bar for SPSS offers several options:
Testing Group Differences using T-tests, ANOVA, and Nonparametric Measures
 Testing Group Differences using T-tests, ANOVA, and Nonparametric Measures Jamie DeCoster Department of Psychology University of Alabama 348 Gordon Palmer Hall Box 870348 Tuscaloosa, AL 35487-0348 Phone:
Testing Group Differences using T-tests, ANOVA, and Nonparametric Measures Jamie DeCoster Department of Psychology University of Alabama 348 Gordon Palmer Hall Box 870348 Tuscaloosa, AL 35487-0348 Phone:
Comparison of K-means and Backpropagation Data Mining Algorithms
 Comparison of K-means and Backpropagation Data Mining Algorithms Nitu Mathuriya, Dr. Ashish Bansal Abstract Data mining has got more and more mature as a field of basic research in computer science and
Comparison of K-means and Backpropagation Data Mining Algorithms Nitu Mathuriya, Dr. Ashish Bansal Abstract Data mining has got more and more mature as a field of basic research in computer science and
MICROSOFT OUTLOOK 2010 WORK WITH CONTACTS
 MICROSOFT OUTLOOK 2010 WORK WITH CONTACTS Last Edited: 2012-07-09 1 Access to Outlook contacts area... 4 Manage Outlook contacts view... 5 Change the view of Contacts area... 5 Business Cards view... 6
MICROSOFT OUTLOOK 2010 WORK WITH CONTACTS Last Edited: 2012-07-09 1 Access to Outlook contacts area... 4 Manage Outlook contacts view... 5 Change the view of Contacts area... 5 Business Cards view... 6
SPSS: Getting Started. For Windows
 For Windows Updated: August 2012 Table of Contents Section 1: Overview... 3 1.1 Introduction to SPSS Tutorials... 3 1.2 Introduction to SPSS... 3 1.3 Overview of SPSS for Windows... 3 Section 2: Entering
For Windows Updated: August 2012 Table of Contents Section 1: Overview... 3 1.1 Introduction to SPSS Tutorials... 3 1.2 Introduction to SPSS... 3 1.3 Overview of SPSS for Windows... 3 Section 2: Entering
One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Example Problem
 One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Example Problem Introduction Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a hypothesis-testing technique used to test the equality of two or more population (or treatment) means
One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Example Problem Introduction Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a hypothesis-testing technique used to test the equality of two or more population (or treatment) means
Oracle Data Miner (Extension of SQL Developer 4.0)
 An Oracle White Paper September 2013 Oracle Data Miner (Extension of SQL Developer 4.0) Integrate Oracle R Enterprise Mining Algorithms into a workflow using the SQL Query node Denny Wong Oracle Data Mining
An Oracle White Paper September 2013 Oracle Data Miner (Extension of SQL Developer 4.0) Integrate Oracle R Enterprise Mining Algorithms into a workflow using the SQL Query node Denny Wong Oracle Data Mining
Rational Team Concert. Scrum Project Management Tutorial
 Rational Team Concert Scrum Project Management Tutorial 1 Contents Contents... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. Terminology... 4 3. Project Area Preparation... 4 3.1 Adding Users and specifying Roles... 5 3.2
Rational Team Concert Scrum Project Management Tutorial 1 Contents Contents... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. Terminology... 4 3. Project Area Preparation... 4 3.1 Adding Users and specifying Roles... 5 3.2
Visualizing non-hierarchical and hierarchical cluster analyses with clustergrams
 Visualizing non-hierarchical and hierarchical cluster analyses with clustergrams Matthias Schonlau RAND 7 Main Street Santa Monica, CA 947 USA Summary In hierarchical cluster analysis dendrogram graphs
Visualizing non-hierarchical and hierarchical cluster analyses with clustergrams Matthias Schonlau RAND 7 Main Street Santa Monica, CA 947 USA Summary In hierarchical cluster analysis dendrogram graphs
Analysis of kiva.com Microlending Service! Hoda Eydgahi Julia Ma Andy Bardagjy December 9, 2010 MAS.622j
 Analysis of kiva.com Microlending Service! Hoda Eydgahi Julia Ma Andy Bardagjy December 9, 2010 MAS.622j What is Kiva? An organization that allows people to lend small amounts of money via the Internet
Analysis of kiva.com Microlending Service! Hoda Eydgahi Julia Ma Andy Bardagjy December 9, 2010 MAS.622j What is Kiva? An organization that allows people to lend small amounts of money via the Internet
IBM SPSS Direct Marketing 23
 IBM SPSS Direct Marketing 23 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in Notices on page 25. Product Information This edition applies to version 23, release
IBM SPSS Direct Marketing 23 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in Notices on page 25. Product Information This edition applies to version 23, release
Chapter 6: The Information Function 129. CHAPTER 7 Test Calibration
 Chapter 6: The Information Function 129 CHAPTER 7 Test Calibration 130 Chapter 7: Test Calibration CHAPTER 7 Test Calibration For didactic purposes, all of the preceding chapters have assumed that the
Chapter 6: The Information Function 129 CHAPTER 7 Test Calibration 130 Chapter 7: Test Calibration CHAPTER 7 Test Calibration For didactic purposes, all of the preceding chapters have assumed that the
This chapter will demonstrate how to perform multiple linear regression with IBM SPSS
 CHAPTER 7B Multiple Regression: Statistical Methods Using IBM SPSS This chapter will demonstrate how to perform multiple linear regression with IBM SPSS first using the standard method and then using the
CHAPTER 7B Multiple Regression: Statistical Methods Using IBM SPSS This chapter will demonstrate how to perform multiple linear regression with IBM SPSS first using the standard method and then using the
SPSS INSTRUCTION CHAPTER 1
 SPSS INSTRUCTION CHAPTER 1 Performing the data manipulations described in Section 1.4 of the chapter require minimal computations, easily handled with a pencil, sheet of paper, and a calculator. However,
SPSS INSTRUCTION CHAPTER 1 Performing the data manipulations described in Section 1.4 of the chapter require minimal computations, easily handled with a pencil, sheet of paper, and a calculator. However,
How to Get More Value from Your Survey Data
 Technical report How to Get More Value from Your Survey Data Discover four advanced analysis techniques that make survey research more effective Table of contents Introduction..............................................................2
Technical report How to Get More Value from Your Survey Data Discover four advanced analysis techniques that make survey research more effective Table of contents Introduction..............................................................2
IBM SPSS Direct Marketing 22
 IBM SPSS Direct Marketing 22 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in Notices on page 25. Product Information This edition applies to version 22, release
IBM SPSS Direct Marketing 22 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in Notices on page 25. Product Information This edition applies to version 22, release
Support Vector Machines with Clustering for Training with Very Large Datasets
 Support Vector Machines with Clustering for Training with Very Large Datasets Theodoros Evgeniou Technology Management INSEAD Bd de Constance, Fontainebleau 77300, France [email protected] Massimiliano
Support Vector Machines with Clustering for Training with Very Large Datasets Theodoros Evgeniou Technology Management INSEAD Bd de Constance, Fontainebleau 77300, France [email protected] Massimiliano
Rational Quality Manager. Quick Start Tutorial
 Rational Quality Manager Quick Start Tutorial 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Terminology... 3 3. Project Area Preparation... 4 3.1 Adding Users and specifying Roles... 4 3.2 Managing Tool Associations...
Rational Quality Manager Quick Start Tutorial 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Terminology... 3 3. Project Area Preparation... 4 3.1 Adding Users and specifying Roles... 4 3.2 Managing Tool Associations...
Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms. Lecture Notes for Chapter 8. Introduction to Data Mining
 Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Lecture Notes for Chapter 8 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining 4/8/2004 Hierarchical
Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Lecture Notes for Chapter 8 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining 4/8/2004 Hierarchical
Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods
 10 Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Imagine that you are the Director of Customer Relationships at AllElectronics, and you have five managers working for you. You would like to organize all
10 Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Imagine that you are the Director of Customer Relationships at AllElectronics, and you have five managers working for you. You would like to organize all
Using Microsoft Excel to Analyze Data
 Entering and Formatting Data Using Microsoft Excel to Analyze Data Open Excel. Set up the spreadsheet page (Sheet 1) so that anyone who reads it will understand the page. For the comparison of pipets:
Entering and Formatting Data Using Microsoft Excel to Analyze Data Open Excel. Set up the spreadsheet page (Sheet 1) so that anyone who reads it will understand the page. For the comparison of pipets:
Simple Predictive Analytics Curtis Seare
 Using Excel to Solve Business Problems: Simple Predictive Analytics Curtis Seare Copyright: Vault Analytics July 2010 Contents Section I: Background Information Why use Predictive Analytics? How to use
Using Excel to Solve Business Problems: Simple Predictive Analytics Curtis Seare Copyright: Vault Analytics July 2010 Contents Section I: Background Information Why use Predictive Analytics? How to use
Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA)
 Chapter 415 Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA) Introduction Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is an extension of common analysis of variance (ANOVA). In ANOVA, differences among various
Chapter 415 Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA) Introduction Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is an extension of common analysis of variance (ANOVA). In ANOVA, differences among various
A DATA ANALYSIS TOOL THAT ORGANIZES ANALYSIS BY VARIABLE TYPES. Rodney Carr Deakin University Australia
 A DATA ANALYSIS TOOL THAT ORGANIZES ANALYSIS BY VARIABLE TYPES Rodney Carr Deakin University Australia XLStatistics is a set of Excel workbooks for analysis of data that has the various analysis tools
A DATA ANALYSIS TOOL THAT ORGANIZES ANALYSIS BY VARIABLE TYPES Rodney Carr Deakin University Australia XLStatistics is a set of Excel workbooks for analysis of data that has the various analysis tools
Two Related Samples t Test
 Two Related Samples t Test In this example 1 students saw five pictures of attractive people and five pictures of unattractive people. For each picture, the students rated the friendliness of the person
Two Related Samples t Test In this example 1 students saw five pictures of attractive people and five pictures of unattractive people. For each picture, the students rated the friendliness of the person
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS IN DATA MINING IN WEKA
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS IN DATA MINING IN WEKA Prakash Singh 1, Aarohi Surya 2 1 Department of Finance, IIM Lucknow, Lucknow, India 2 Department of Computer Science, LNMIIT, Jaipur,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS IN DATA MINING IN WEKA Prakash Singh 1, Aarohi Surya 2 1 Department of Finance, IIM Lucknow, Lucknow, India 2 Department of Computer Science, LNMIIT, Jaipur,
Can SAS Enterprise Guide do all of that, with no programming required? Yes, it can.
 SAS Enterprise Guide for Educational Researchers: Data Import to Publication without Programming AnnMaria De Mars, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA ABSTRACT In this workshop, participants
SAS Enterprise Guide for Educational Researchers: Data Import to Publication without Programming AnnMaria De Mars, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA ABSTRACT In this workshop, participants
Data Mining Part 5. Prediction
 Data Mining Part 5. Prediction 5.1 Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Classification vs. Numeric Prediction Prediction Process Data Preparation Comparing Prediction Methods References Classification
Data Mining Part 5. Prediction 5.1 Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Classification vs. Numeric Prediction Prediction Process Data Preparation Comparing Prediction Methods References Classification
Bill Burton Albert Einstein College of Medicine [email protected] April 28, 2014 EERS: Managing the Tension Between Rigor and Resources 1
 Bill Burton Albert Einstein College of Medicine [email protected] April 28, 2014 EERS: Managing the Tension Between Rigor and Resources 1 Calculate counts, means, and standard deviations Produce
Bill Burton Albert Einstein College of Medicine [email protected] April 28, 2014 EERS: Managing the Tension Between Rigor and Resources 1 Calculate counts, means, and standard deviations Produce
