Overactive Bladder (OAB) Patient Informational Handout
|
|
|
- Samson George Simmons
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Patient Informational Handout 5/1/2014 BJF I. GENERAL INFORMATION Definition of Urge Incontinence/Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder (OAB) is a syndrome of urinary urge, frequency, nocturia (getting up at night to void) and urge incontinence. You only need one of the symptoms to have OAB. Many patients start out with urge and then progress to frequency and eventually incontinence. When the bladder is healthy, we are in control and can decide when and where to urinate. When the urge to urinate is actually strong enough, we need to stop what we are doing and walk to the bathroom and empty our bladders voluntarily. OAB can occur in as many as 10% of people and increase with age. OAB is not a life-threatening condition but can significantly decrease quality of life. Definition of Refractory Overactive Bladder Refractory Overactive Bladder, also known as ROAB, is a condition that is seen commonly in Urology, Female Pelvic Medicine and Urogynecology practices. If the overactive bladder is related to a neurologic condition it is often referred to as NOAB. If it is of an unknown cause (idiopathic) it is commonly referred to as IOAB. ROAB may be due to either neurogenic cause or Idiopathic causes. Patients are considered refractory when they have failed at least two medications for overactive bladder and/or simpler measures, such as self-care, or pelvic floor therapy. Management of Refractory Overactive Bladder can be challenging but fortunately in 2014 and beyond, we have multiple medications to treat OAB. We have Botox therapy, Percutaneous Tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) and sacral nerve Stimulation (SNS). In the past, as recent as 1998 the only treatment that was considered after failure of one single overactive bladder drug (Ditropan also know as generic Oxybutynin) was Bladder Augmentation. Bladder Augmentation is a large surgical procedure that is only indicated in the most refractory of cases as this procedure is effective in enlarging the bladder but has significant complications and can sometimes lead to chronic urinary tract infections or the need for intermittent catheterization. What are the symptoms of overactive bladder? These symptoms include urinary urgency frequency, urgency incontinence, and nocturia. Patients with ROAB have tried simple measures such as self-care, reducing fluids, avoiding caffeine, alcohol and other bladder irritants. In addition the patient has tried at least two medications for Overactive Bladder know as antimuscarinics, anti-cholinergics or OAB meds. Patients have failed the therapy in that their symptoms did not resolve or they were unable to tolerate the side effects of the overactive bladder medications. These symptoms are now significant and patients are considered refractory hence urology/ urogynecologic involvement is often necessary at this point. Causes and Diagnosis: The cause of OAB is unclear in most cases (85%). In some cases it is related to a neurologic condition such as Multiple sclerosis (MS), SCI (spinal cord injury), Parkinson s disease and spina bifida. OAB is a diagnosis of exclusion that is conditions such as UTI, bladder cancer and BPH (men only, enlarged prostate) should be ruled out first. Work-up may include history, physical, bladder log, questionnaires, pad test, urine analysis, cystoscopy, ultrasound and urodynamics. In most instances OAB can be treated empirically following non-invasive tests. For ROAB cases more advanced testing is usually necessary. II. TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR OAB Self-care
2 Behavioral therapy, physical therapy, biofeedback Pharmacologic therapy, medications 2 Self Care: Diet/Fluid Intake/Weight Loss/Smoking Cessation/Hygiene: Avoid food and drink that are known bladder irritants and/or diuretics such as coffee, tea, soda pop, alcohol (beer, wine, liquor), Drink oz ( ml) of fluid/day that is 6 or 8, 8 oz glasses. This based on a 175lb man. This may require slight increase or decrease in hot or cold weather or on your body weight. Another option is drink only if you are thirsty or if your urine looks or swells concentrated. Any more fluid than 2000 ml has no proven health benefit. If your are thirsty due to dry Colorado Climate or medication than chew gum, suck on hardy candy ort use artificial saliva. What comes in must come out. If you drink 4000ml of fluid/day you will urinate ml/day. If your bladder holds 250 ml then you will have to void 16/24 hours. Belly fat sits on your bladder and causes urgency. Also make your cloths tight so your belt squeezes the bladder. Weight loss will allow better mobility and reaction time for prompt toileting. Tobacco and cannabis can irritate the bladder lining and can cause OAB and eventually lead to bladder cancer Avoid tight fitting pants or shirts as they can squeeze the bladder and cause urge If you have incontinence change your pad and bath frequently to prevent skin breakdown, rashes and infections (vaginal and bladder) Behavioral Therapy/Physical Therapy/Biofeedback Bladder Retraining: Timed voiding or bladder retraining drills are very helpful and usually the first line of therapy for Overactive Bladder. This excellent treatment is free, completely safe and effective in curing or improving symptoms in two thirds of women suffering from this very common disorder. In timed voiding you may fill out a chart of voiding and leaking such as the voiding diary mentioned in the last paragraph. From the patterns that appear in the voiding chart, you can plan to empty before you would otherwise leak. The intervals that you urinate at can gradually be lengthened by 15 minutes each week while you are awake. In this way, you may stretch or increase the intervals at which you void. Another similar approach to bladder drills is to begin voiding every hour on the hour, except while in bed, whether the urge is felt or not. This pattern is continued for two weeks. Then, you move up to voiding every hour and a half. Every two weeks, you increase the interval between voids by 30 minutes, until you have retrained yourself up to voiding at a comfortable interval of, for example every three to four hours. This biofeedback technique known as bladder training can alter or change the bladder schedule for storing or emptying urine. These techniques are effective for overactive bladder. Kegel Exercises: Pelvic muscle exercises (Kegel) are used to strengthen or retrain the muscles of the pelvic floor. Regular daily exercising of the pelvic muscles can improve and even prevent urinary incontinence. This is helpful for younger woman. The Kegel exercises should be performed times daily for eight weeks before you may notice any difference. Most Kegel exercises do not require equipment. Pelvic Floor Stimulation: Other biofeedback techniques such as pelvic floor electrical stimulation also improve urge incontinence. This technique will help women identify their pelvic muscles. It works with a little bit of effort on your part. The electrical stimulation exercises the pelvic muscle for you. A small instrument is inserted into the vagina to deliver a tiny electrical pulse that causes the pelvic muscles to contract for you. It feels like a hum and a pull in your pelvic muscle and is not uncomfortable. This technique may reduce urgency, frequency symptoms, overactive bladder and especially urgency incontinence. Pharmacologic Therapy/Medications: Some medications prevent contractions of an overactive bladder. Your physician to improve your urgency, frequency and urge incontinence symptoms may utilize several prescription medications. Estrogen or HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy) is believed to cause the muscles and nerves in urination to function normally. Estrogen must be used with progesterone, if you have not had a hysterectomy, because estrogen therapy alone has been associated with an increased risk of cancer of the uterus. Talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of long-term use of hormone replacement therapy.
3 HRT may improve the way your muscles and nerves of the pelvic floor and bladder function and may reduce incontinence. HRT is available in pill form, patch, vaginal form pill, cream, or ring and used under the direction of your doctor. If you fail the usual OAB medications, which are, all anti-muscarincs (ditropan, detrol, vesicare, sanctura, oxytrol, enablex, gelnique) a consideration would be a new class of drugs called Beta-3 agonist like Myrbetriq (Mirabegron). This drug works well especially in those that have had side effects from the 1 st or 2 nd tier OAB medications as is it a Beta-3 agonist which do not cause the usual ant-muscarincs side effects including dry mouth, dry eyes, constipation and cognitive impairment. The down side of the medication is that is extremely expensive. It is not always covered by insurance. The side effect could be that it could raise your blood pressure by as much as ten points but this is usually not clinically significant. Another option for pharmacologic therapy would be dose escalation beyond what is the recommended dose. It is not uncommon that we double or sometimes even triple the recommended dose. This is effective but does lead to more side effects and more cost as insurance companies and prescription plans commonly do not cover dose escalation. The next strategy for pharmacologic therapy would be using an antimuscarinic and a beta-3 agonist in combination such as using Vesicare with Myrbetriq. This is an effective therapy but does lead to poly-pharmacy and increased cost. 3 III. TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ROAB In these cases we recommend the patient continue standard treatments for OAB as outlined above (self-care, medications, etc..) in addition to one of the following therapies Botox therapy Neuromodulation (PTNS and SNS) Bladder enlargement (augmentation) Botox (onabotulinumtoxina) Therapy Botox (produced by Allergan) is an office-based treatment and considered 2nd tier therapy for those who do not respond to simpler measures as mentioned in the OAB discussion. Botox bladder injection is a novel treatment that we have offered at the University of Colorado for many years. University of Colorado has a rich history of Botox therapy and was developed in part by Dr. Rick Schmidt. We have been using Botox therapy in Urology since 2004 well before FDA approval. In fact we have been fortunate enough to be involved in late Phase III and post market trials on Botox therapy. Botox is placed through a needle that is directed by a cyctoscope. We can inject anywhere from 50 to as much as 300 units. The dose is adjusted based on the patients needs. If the patient is voiding normally and does not wish to perform intermittent catheterization typically we inject units. If the patient is catheterization dependent we more commonly inject units. The therapy is effective for urinary urgency incontinence especially. The down side is the drug does need to be re-injected every 6-12 months the cost is sometimes prohibitive and there is inconvenience of having to have an office procedure to have the drug injected.
4 4 Percutaneous Tibia Nerve Stimulation (PTNS), Ankle Stimulation PTNS (Urgent PC by Uroplasty) is an office-based treatment and considered 2nd tier therapy for those who do not respond to simpler measures as mentioned in the OAB discussion. This treatment requires a 30-minute/weekoffice treatment for 12 consecutive weeks. A needle is place percutaneously (through the skin to the tibial nerve that lies next to the ankle), therefore the therapy is commonly referred to as ankle stimulation. The electrode stimulates the tibial nerve and acts as a surrogate for the sacral nerve (the dominant nerve to the bladder) similar to acupuncture. Once the nerve is properly stimulated after about 3 to 4 treatments the patient will see noticeable improvement in their bladder over activity and an improvement in incontinence, frequency, urgency and urgency incontinence. After the 12-week treatment is complete the patient will then go on maintenance therapy that will require once a month treatment. In the future we hope that home therapy with a patient directed unit will be available but this is not available currently. Downside is PTNS is less effective then Botox or SNS. Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS) also known as Interstim Interstim (made by Medtronics) is an electronic device that has been FDA approved since This rd procedure is considered 3 tier therapy for OAB. It is more invasive than Botox of PTNS, but is a great option for people who do not want to have frequent office visits for Botox of PTNS. This therapy is indicated for people with urinary urgency, frequency, urgency incontinence, and bladder incomplete emptying and even idiopathic retention in younger women. The therapy works by placing a temporary electrode through the lower back to the sacral foramen (S3) to stimulate the S3 nerve. This is tested in the office under local anesthesia (PNE, percutaneous nerve stimulation). The patient is tested for approximately three to seven days and if they have a positive response (meaning more that 50% improvement in their bladder symptoms) then they would be candidate for permanent implantation. Permanent implantation would require a surgical procedure done in the operating room done under sedation. It consists of a battery-powered stimulator (the size of a stop watch) connected to a lead, which is placed near the root of the S3 nerves in the back. It is meant to 'down regulate' the bladder muscle s sensitivity and thereby decrease bladder contractions and the resulting urgency, frequency and urge incontinence. UCH Urology Clinic 1635 Aurora Court, Aurora, CO
5 This device is placed under the skin and therapy will last approximately 5-7 years depending on how much voltage is used from the battery. Currently the battery cannot be recharged and requires replacement (surgery) once the battery is discharged. Other issues with the device, is the lead can migrate or the patient can develop an open or short circuit, which also leads to surgical revision. The device is easily damaged if the patient falls or gets into a car accident. This often leads to short circuiting or open circuits. The device can be a fairly temperamental device and often requires need to be re-programming. Fortunately the device can be reprogrammed with a magnet and does not require open surgical revision. The patient will be set up with at least 4 programs and the patient will have a controller and may be able to turn the device on and off, increase or decrease the amplitude and change programs. Bladder Enlargement (Augmentation) Bladder augmentation, also known as augmentation cystoplasty, is a large surgical procedure used in men and women to physically enlarge the bladder in patients with small bladder capacity, impaired compliance high pressure or spasticity leading to incontinence that is refractory to simpler measure. There is 4 th tier therapy and reserved for the mist severe cases. Most patients have NOAB from a fixed neurologic lesion such as SCI or spina bifida but we may offer this in rare instance to those with IOAB. See handout on NGB, NOAB and Bladder augmentation for more detail. 5 IV: SUMMARY In summary refractory overactive bladder is a difficult problem to have. It does significantly affect quality of life. It does lead to significant economic impact due to the cost of sanitary pads and clothing. It does often lead to patient isolation and embarrassment. Fortunately, we have exciting treatments that are effective and rapidly evolving to become less invasive and more patient centered. We offer a step-wise approach that is individualized to the patient. We often guide the patient in which therapy to choose based on the predominance of a certain symptom or based on the etiology of their overactive bladder. Neurogenic patients are good candidates for Botox and PTNS they re not good candidates for SNS. Idiopathic overactive bladder patients are candidates for all three therapies. All patients are candidates for drug therapy. All of these therapies do require insurance authorization. Oftentimes insurance is not cooperative in providing these therapies, as they can be very expensive especially long term. We hope this handout is helpful and informative and we look forward to speaking to you in more detail about these therapies. IV: ADDITIONAL INFORMATION AND REFERENCES Glossary of terms: OAB: overactive bladder ROAB: refractory overactive bladder NOAB: neurogenic overactive bladder MS: Multiple sclerosis IOAB: idiopathic overactive bladder UUI: urinary urge incontinence Botox: onabotulinumtoxina PTNS: percutaneous nerve stimulation SNS: sacral nerve stimulation For more information regarding the treatment of urinary incontinence, please check the following links: Websites:
6 Women: American Urogynecology Society: Society of Gynecologic Surgeons: 6 Men and Women: National Multiple Sclerosis Society: National Association for Continence: American Urological Association: Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction: Wikpedia: Emedicine: Botox: PTNS (Urgent PC): SNS (Interstim): V. CONTACT INFORMATION UCH numbers: Main Hospital number Phone , Admissions , Medical records Julie Porcelli Surgery Coordinator: Call Julie to schedule surgery, preop and postop appointments, Insurance related Q s, etc..phone , Fax: , Julie.Porcelli@UCH.edu Urology Nurse Triage Line: Call the nurse line for Q s about postop complaints bathing, wound care, activity, diet, catheter care, uncontrolled pain, prescriptions, etc Phone option 2. M-F Leave a message and someone will get back with you as soon as possible. Urology Resident on Call: For urgent matters only. Routine Q s please wait until ordinary clinic hours. Phone , after hours, weekends, Holidays. Ask to speak to the Urology resident on 2 nd call. The operator will then page the resident and if available they will call back and speak with you at that time. Call 911: For emergencies such as chest pain, shortness of breath, passing out, etc.. Brian J. Flynn, M.D. Co- Director of Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Fellowship Director of Reconstructive Urology Associate Professor of Surgery/Urology University of Colorado Denver, Division of Urology
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or desire to pass
Saint Mary s Hospital. Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit. Overactive Bladder. Information for Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What is Overactive Bladder (OAB)? OAB is a condition that causes you to need to pass urine more often
Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence. A Review of the Research for Women
 Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence A Review of the Research for Women Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are a woman who is older than 18. You are having trouble holding your
Non-surgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence A Review of the Research for Women Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: You are a woman who is older than 18. You are having trouble holding your
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Managing Overactive Bladder
 Patient Educational Material Managing Overactive Bladder The bladder s job is pretty simple: hold urine until full, then empty when we get to a restroom. When you have an overactive bladder, the bladder
Patient Educational Material Managing Overactive Bladder The bladder s job is pretty simple: hold urine until full, then empty when we get to a restroom. When you have an overactive bladder, the bladder
9/24/2015. Incontinence and Prolapse 2015 Primary Care Update CME Symposium. Objectives. Mark Memo, DO, FACS NEO Urology September 25-27
 Incontinence and Prolapse 2015 Primary Care Update CME Symposium Mark Memo, DO, FACS NEO Urology September 25-27 Objectives Incontinence Pelvic Organ Prolapse Vaginal Mesh Litigation 1 Urinary Incontinence
Incontinence and Prolapse 2015 Primary Care Update CME Symposium Mark Memo, DO, FACS NEO Urology September 25-27 Objectives Incontinence Pelvic Organ Prolapse Vaginal Mesh Litigation 1 Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide
 Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Urinary Incontinence (Involuntary Loss of Urine) A Patient Guide Urinary Incontinence (Urine Loss) This booklet is intended to give you some facts on urinary incontinence - what it is, and is not, and
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Female Urinary Disorders and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Richard S. Bercik, M.D. Director, Division of Urogynecology & Reconstruction Pelvic Surgery Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences
Urinary Incontinence. Patient Information Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence Patient Information Sheet What is urinary incontinence (UI)? UI happens when you are not able to control when you urinate and you wet yourself. How common is urinary incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary Urinary (YOOR-in-air-ee) incontinence (in-kahn-tih-nens) is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have urinary incontinence, you re not alone.
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
Urinary Incontinence. Causes of Incontinence. What s Happening?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about her grandchildren and going to exercise classes with neighbors. But she s started to have
The Well Woman Centre. Adult Urinary Incontinence
 The Well Woman Centre Adult Urinary Incontinence 1 Adult Urinary Incontinence... 3 Stress Incontinence Symptoms... 3 Urge Incontinence Symptoms... 4 Mixed Incontinence Symptoms... 5 Where to Start?...
The Well Woman Centre Adult Urinary Incontinence 1 Adult Urinary Incontinence... 3 Stress Incontinence Symptoms... 3 Urge Incontinence Symptoms... 4 Mixed Incontinence Symptoms... 5 Where to Start?...
OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB)
 OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB) BLADDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION The bladder is hollow balloon-shaped muscle that acts as a storage organ, holding urine from your kidneys until a convenient time for you
OVERACTIVE BLADDER SYNDROME (OAB) BLADDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION The bladder is hollow balloon-shaped muscle that acts as a storage organ, holding urine from your kidneys until a convenient time for you
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS:
 2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
2014 OVERACTIVE BLADDER DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2012); Amended (2014) For Primary Care Providers OVERACTIVE BLADDER Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive
The overactive bladder and bladder retraining
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The overactive bladder and bladder retraining Information for patients Normal bladder function Your bladder normally stores urine produced by your kidneys. The kidneys
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The overactive bladder and bladder retraining Information for patients Normal bladder function Your bladder normally stores urine produced by your kidneys. The kidneys
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives Review the problem Feel confident
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
Management of Neurogenic Bladder Disorders Andrea Staack, MD, PhD Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Urinary Incontinence & Female Urology Department of Urology Loma Linda University, CA What will you learn
es of Urinary Incontinence:
 Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Reversible Cause Urinary incontinence is a loss of control over the passing of urine. Urine loss can occur in very small amounts (enough only to dampen underwear) to very large amounts (requiring a change
Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone
 Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Male urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) you are not alone Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Urinary Incontinence. Types
 Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
Urinary Incontinence Leakage of urine is called urinary incontinence. It is a common problem in women. Some women occasionally leak small amounts of urine. At other times, leakage of urine is frequent
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence
 Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Overactive bladder and urgency incontinence As a health care provider you can make a significant difference to the quality of life of patients like these by addressing urinary incontinence, introducing
Female Urinary Incontinence
 Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Female Urinary Incontinence Molly Heublein, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Medicine UCSF Women s Health Primary Care Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Objectives Which is most true? Review the problem
Urinary Incontinence Definitions
 (AADL) Program Urge Stress Overflow Functional Mixed DHIC (Detrussor hyperreflexia with impaired contractility) Reflex Incontinence Leakage of urine (usually larger volumes) because of inability to delay
(AADL) Program Urge Stress Overflow Functional Mixed DHIC (Detrussor hyperreflexia with impaired contractility) Reflex Incontinence Leakage of urine (usually larger volumes) because of inability to delay
Millions live with Overactive Bladder. Get help and break free!
 A PATIENT S GUIDE Millions live with Overactive Bladder. Get help and break free! IT S TIME TO TALK ABOUT OAB Table of Contents 1. Overactive Bladder Expert Advisory Panel Page 2 2. Overactive Bladder
A PATIENT S GUIDE Millions live with Overactive Bladder. Get help and break free! IT S TIME TO TALK ABOUT OAB Table of Contents 1. Overactive Bladder Expert Advisory Panel Page 2 2. Overactive Bladder
Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH
Managing Changes in Your Bladder Function After Cancer Treatment
 Managing Changes in Your Bladder Function After Cancer Treatment Information for cancer survivors UHN Read this resource to learn: What a urinary problem is What causes it What you can do to improve your
Managing Changes in Your Bladder Function After Cancer Treatment Information for cancer survivors UHN Read this resource to learn: What a urinary problem is What causes it What you can do to improve your
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS. Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center. Bladder Dysfunction
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in MS Tracy Walker, WOCN, MSCN, FNP C Nurse Practitioner MS Institute at Shepherd Center Bladder Dysfunction Approximately 75% of people with MS experience bladder problems
Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes Improving Urinary Urgency, Frequency and Urge Incontinence
 Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes Improving Urinary Urgency, Frequency and Urge Incontinence Manage your Fluid Intake: There is no scientific evidence that states we need eight 8 oz. glasses (64 oz.) of
Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes Improving Urinary Urgency, Frequency and Urge Incontinence Manage your Fluid Intake: There is no scientific evidence that states we need eight 8 oz. glasses (64 oz.) of
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center
 Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Women s Continence and Pelvic Health Center Committed to Caring 580-590 Court Street Keene, New Hampshire 03431 (603) 354-5454 Ext. 6643 URINARY INCONTINENCE QUESTIONNAIRE The purpose of this questionnaire
Registered Charity No. 5365
 THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: mscontact@ms-society.ie www.ms-society.ie
Las Vegas Urogynecology
 Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Urinary Incontinence in Women Urinary incontinence is an inability to hold your urine
Las Vegas Urogynecology 7500 Smoke Ranch Road - #200 Las Vegas, NV 89128 Telephone: (702) 233-0727 Fax: (702) 233-4799 Urinary Incontinence in Women Urinary incontinence is an inability to hold your urine
in 1996 by the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 13 million Americans are
 Seeking Treatment: What? When? Why? Who? How? & Where? In recent membership surveys, the National Association For Continence (NAFC) was distressed to learn that on average people were waiting years before
Seeking Treatment: What? When? Why? Who? How? & Where? In recent membership surveys, the National Association For Continence (NAFC) was distressed to learn that on average people were waiting years before
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
symptoms of Incontinence
 Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
Types, causes and symptoms of Urinary Incontinence Aims and Objectives Aim: To have an understanding of the types and causes of urinary incontinence. Objectives: To be aware of the incidence and prevalence
OAB (Overactive Bladder)
 OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
OAB (Overactive Bladder) PharmCon is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This webcast has been supported by an educational grant
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting
 Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Overview of Urinary Incontinence in the Long Term Care Setting Management Strategies for the Nursing Assistant Ann M. Spenard RN, C, MSN Courtney Lyder ND, GNP Learning Objectives Describe common types
Treatments for Overactive Bladder
 Treatments for Overactive Bladder Patient Information Author ID: SA Leaflet Number: Gyn 051 Name of Leaflet: Treatments for overactive bladder Date Produced: October 2014 Review Date: October 2016 Treatment
Treatments for Overactive Bladder Patient Information Author ID: SA Leaflet Number: Gyn 051 Name of Leaflet: Treatments for overactive bladder Date Produced: October 2014 Review Date: October 2016 Treatment
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Control Does Matter
 Bladder Control Does Matter Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Bladder Control Does Matter Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Urinary Incontinence in Women. Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine
 Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Urinary Incontinence in Women Susan Hingle, M.D. Department of Medicine Background Estimated 13 million Americans with urinary incontinence Women are affected twice as frequently as men Only 25% will seek
Daily Habits and Urinary Incontinence
 Effects of Daily Habits on the Bladder Many aspects of our daily life influence bladder and bowel function. Sometimes our daily habits may not be in the best interest of the bladder. A number of surprisingly
Effects of Daily Habits on the Bladder Many aspects of our daily life influence bladder and bowel function. Sometimes our daily habits may not be in the best interest of the bladder. A number of surprisingly
The Bathroom has been central in our lives through the ages. Bladder Control Problems. Bladder Control Problems. A Common Problem:
 When You Gotta Go. Understanding and Conquering Urinary Incontinence and the Overactive Bladder Syndrome Richard T. Kershen M.D. Assistant Professor UVM Department of Surgery, Division of Urology Director,
When You Gotta Go. Understanding and Conquering Urinary Incontinence and the Overactive Bladder Syndrome Richard T. Kershen M.D. Assistant Professor UVM Department of Surgery, Division of Urology Director,
Lifestyle changes. Pelvic floor muscle training
 Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
Incontinence, urinary - Treatment Treating urinary incontinence The treatment you receive for urinary incontinence will depend on the type of incontinence you have and the severity of your symptoms. If
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN
 URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is defined as involuntary loss of urine that is a social or hygienic problem (International Continence Society, 1973) Magnitude of the
1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
A PATIENT S GUIDE 1 in 3 women experience Stress Urinary Incontinence. It s time to talk about SUI Get the facts. This Patient s Guide is intended as a public resource on the issue of Stress Urinary Incontinence
WHAT IS INCONTINENCE?
 CNA Workbook WHAT IS INCONTINENCE? Incontinence is the inability to control the flow of urine or feces from your body. Approximately 26 million Americans are incontinent. Many people don t report it because
CNA Workbook WHAT IS INCONTINENCE? Incontinence is the inability to control the flow of urine or feces from your body. Approximately 26 million Americans are incontinent. Many people don t report it because
Management of refractory OAB conditions
 Management of refractory OAB conditions Neurotoxins and Neuromodulation Gary E. Lemack, M.D. Professor of Urology and Neurology Program Director in Urology UT-Southwestern Medical Center Overactive bladder
Management of refractory OAB conditions Neurotoxins and Neuromodulation Gary E. Lemack, M.D. Professor of Urology and Neurology Program Director in Urology UT-Southwestern Medical Center Overactive bladder
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
Managing Urinary Incontinence
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Managing Urinary Incontinence www.nshealth.ca Managing Urinary Incontinence What is the urinary system? Urine (pee) is made in the kidneys. It flows through tubes called ureters.
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Managing Urinary Incontinence www.nshealth.ca Managing Urinary Incontinence What is the urinary system? Urine (pee) is made in the kidneys. It flows through tubes called ureters.
Surgery for Stress Incontinence
 Directorate of Women s Services Surgery for Stress Incontinence Tension Free Vaginal Tape Information for Patients Direct dial number Ward 40 0191 282 5640 Stress Incontinence Stress incontinence is a
Directorate of Women s Services Surgery for Stress Incontinence Tension Free Vaginal Tape Information for Patients Direct dial number Ward 40 0191 282 5640 Stress Incontinence Stress incontinence is a
How to Improve Bladder After Bowler Cancer
 Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
Bladder changes after bowel cancer treatment This information is from the booklet Managing the late effects of bowel cancer treatment. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN
 TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION: ONE OF SEVERAL NEW OPTIONS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN WOMEN Scott A Farrell MD Professor Dept of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Dalhousie University Declaration of
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust
 Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Gwen Griffith Clinical Nurse Specialist Bolton NHS foundation Trust Overview Setting the Scene Beginning of the journey & specialist nurse role Why people with MS experience bladder problems MS and the
Urgency and urge incontinence for patients with Multiple Sclerosis Patient Information Leaflet
 Urgency and urge incontinence for patients with Multiple Sclerosis Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future 2 Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about
Urgency and urge incontinence for patients with Multiple Sclerosis Patient Information Leaflet Shining a light on the future 2 Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence. Overview of Lecture
 Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
Primary Care Management Guidelines Female Urinary Incontinence Professor Don Wilson Department of Women s and Children s Health Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago GP Teaching for Roy Morris,
BLADDER CONTROL DURING PREGNANCY AND AFTER THE BIRTH OF YOUR BABY
 BLADDER CONTROL DURING PREGNANCY AND AFTER THE BIRTH OF YOUR BABY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 Contents Stress incontinence... 3 Pelvic floor exercises... 3 Urgency and frequency...
BLADDER CONTROL DURING PREGNANCY AND AFTER THE BIRTH OF YOUR BABY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 Contents Stress incontinence... 3 Pelvic floor exercises... 3 Urgency and frequency...
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function
 Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
1/07/2014 HOW COMMON? FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: OVERACTIVE BLADDER NORMAL BLADDER FUNCTION CAUSES OF URINARY INCONTINENCE HISTORY RISK FACTORS
 HOW COMMON? FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: OVERACTIVE BLADDER Judith Goh AO MBBS(Qld) FRANZCOG CU PhD Urogynaecologist Griffith University Greenslopes Private Hospital, Brisbane Pindara Private Hospital,
HOW COMMON? FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: OVERACTIVE BLADDER Judith Goh AO MBBS(Qld) FRANZCOG CU PhD Urogynaecologist Griffith University Greenslopes Private Hospital, Brisbane Pindara Private Hospital,
Your Comprehensive Guide to Overactive Bladder
 Your Comprehensive Guide to Overactive Bladder Learn more about OAB in the Powder Room www.powderroom.ca Table of Contents Learning about overactive bladder (OAB) 1 What is overactive bladder (OAB)? 2
Your Comprehensive Guide to Overactive Bladder Learn more about OAB in the Powder Room www.powderroom.ca Table of Contents Learning about overactive bladder (OAB) 1 What is overactive bladder (OAB)? 2
Information for patients. Sex and Incontinence. Royal Hallamshire Hospital
 Information for patients Sex and Incontinence Royal Hallamshire Hospital Why is sex important? We may choose to be sexual, regardless of our age, physical status or stage of life. Those with health problems
Information for patients Sex and Incontinence Royal Hallamshire Hospital Why is sex important? We may choose to be sexual, regardless of our age, physical status or stage of life. Those with health problems
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
It usually presents with a sudden urge to urinate that is very difficult to delay and may be associated with leakage. Other features include:
 visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
visited on Page 1 of 5 View this article online at http://patient.info/doctor/overactive-bladder Overactive Bladder This PatientPlus article is written for healthcare professionals so the language may
Dr Eva Fong. Urologist Auckland
 Dr Eva Fong Urologist Auckland Urinary incontinence: Treatment options GPCME 2013 Eva Fong Urologist Urinary incontinence Is not normal part of aging or childbearing We can make it better Urinary incontinence:
Dr Eva Fong Urologist Auckland Urinary incontinence: Treatment options GPCME 2013 Eva Fong Urologist Urinary incontinence Is not normal part of aging or childbearing We can make it better Urinary incontinence:
VAGINAL MESH FAQ. How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair?
 VAGINAL MESH FAQ How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair? Each patient with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is considered individually. In younger women, women with an uncomplicated prolapse
VAGINAL MESH FAQ How do you decide who should get mesh as part of their repair? Each patient with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is considered individually. In younger women, women with an uncomplicated prolapse
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Regain Control of Your Active Life Treatment Options for Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Nearly one quarter of all women in the United States have some sort of pelvic floor disorder such as urinary
Bladder and Pelvic Health
 A Woman s Guide to Bladder and Pelvic Health Symptoms Tests Conditions Treatments 937-277-8988 1-888-808-1016 Dayton Center Englewood Center Huber Heights Center Trotwood Satellite Table of Contents About
A Woman s Guide to Bladder and Pelvic Health Symptoms Tests Conditions Treatments 937-277-8988 1-888-808-1016 Dayton Center Englewood Center Huber Heights Center Trotwood Satellite Table of Contents About
Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Millions of
Urinary Incontinence in Women National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Millions of
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Botulinum toxin injections for the bladder Department of Uro-Neurology If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Botulinum toxin injections for the bladder Department of Uro-Neurology If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services. 18/07/2008 Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust
 Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
Bladder and Bowel Assessment Ann Yates Director of Continence Services Types of continence problems Bladder Stress incontinence Urgency and urge Incontinence Mixed incontinence Obstructive incontinence
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder
 Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS. Ask a member of
Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS. Ask a member of
Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly. Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012
 1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
1 Topic review: Clinical presentation and diagnosis of urinary incontinence in the elderly Prapa Pattrapornpisut 7 June 2012 2 Urinary incontinence Definition the complaint of any involuntary leakage of
VAGINAL TAPE PROCEDURES FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS INCONTINENCE
 VAGINAL TAPE PROCEDURES FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS INCONTINENCE AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k
VAGINAL TAPE PROCEDURES FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS INCONTINENCE AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k
A Physical Therapist s Perspective
 You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
You Can Do Something About INCONTINENCE A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association 1 You Can Do Something About Urinary Incontinence Incontinence, involuntary loss of bladder
Self Catheterization Guide
 Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Self Catheterization Guide An introduction to intermittent self-catheterization Medical professionals have recommended that you selfcatheterize in order to completely empty your bladder. This prevents
Incontinence. in con ti nent. adjective. 1. unable to restrain natural discharges or evacuations of urine or faeces.
 PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Incontinence Incontinence can be upsetting and humiliating for the person with dementia as well as stressful for the carer. However, there are many ways in which the situation
PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Incontinence Incontinence can be upsetting and humiliating for the person with dementia as well as stressful for the carer. However, there are many ways in which the situation
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Becoming knowledgeable about urinary incontinence Uterus Normal Pelvic Anatomy
An illustrated guide to the management of incontinence.
 An illustrated guide to the management of incontinence. 1 The problem of incontinence The ACA describes incontinence as an involuntary loss of urine and/or bowel motion. The amount can vary from slight
An illustrated guide to the management of incontinence. 1 The problem of incontinence The ACA describes incontinence as an involuntary loss of urine and/or bowel motion. The amount can vary from slight
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture
 Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Overactive bladder (OAB) : Introduction and Medical Management R.J. Opsomer Cliniques St Luc, labo d urodynamique, UCL - Bruxelles Overactive Bladder (OAB) Content of the lecture The syndrome of Overactive
Types of urinary incontinence. Stress Incontinence. Urge Incontinence
 If you or someone you know is affected by loss of bladder control, you are not alone. An estimated 15-20 million people in the United States have bladder control problems. This condition affects men and
If you or someone you know is affected by loss of bladder control, you are not alone. An estimated 15-20 million people in the United States have bladder control problems. This condition affects men and
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
GreenLight laser prostatectomy
 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks GreenLight laser prostatectomy Information for day surgery patients This information sheet answers some of the questions you may have about having a GreenLight laser prostatectomy.
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks GreenLight laser prostatectomy Information for day surgery patients This information sheet answers some of the questions you may have about having a GreenLight laser prostatectomy.
Medication for Overactive Bladder
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Medication for Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What medication is available for overactive bladder? There are two types of medication
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Service Warrell Unit Medication for Overactive Bladder Information for Patients What medication is available for overactive bladder? There are two types of medication
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
The following document includes information about:
 Patient information WHAT TO EXPECT WHILE RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER Oncology Vitalité Zone : 1B 4 5 6 Facility : Dr. Léon-Richard Oncology Centre The following document includes information
Patient information WHAT TO EXPECT WHILE RECEIVING RADIATION THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER Oncology Vitalité Zone : 1B 4 5 6 Facility : Dr. Léon-Richard Oncology Centre The following document includes information
Bladder Control for Women
 What I need to know about Bladder Control for Women NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need
What I need to know about Bladder Control for Women NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation
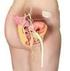 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Number 7.01.69 Effective
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation Number 7.01.69 Effective
Periurethral bulking agent for stress urinary incontinence (macroplastique)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet provides information about having an injection
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet provides information about having an injection
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant
 Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
