Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
|
|
|
- Daisy Foster
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Reproduction Growth and development Tissue removal Example An amoeba, a single-celled eukaryote, divides into two cells. Each new cell will be an individual organism. A sand dollar embryo forms two cells shortly after the fertilized egg is divided. Dividing bone marrow cells will give rise to new blood cells. 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? The cell cycle is the life of a cell from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two daughter cells. Concept 12.1 Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells 3. What is the meaning of genome? A genome is a cell s endowment of DNA, its genetic information. 4. How many chromosomes are in a human somatic cell? Name two types of somatic cells in your body. Possible examples include any cells in the body, except for reproductive cells. 6. What is a gamete? A reproductive cell 7. Name the two types of gametes. Sperm and eggs 8. How many chromosomes in a human gamete? Define chromatin. The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes. When the cell is not dividing, chromatin exists in its dispersed form, as a mass of very long, thin fibers that are not visible with a light microscope. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
2 10. Think carefully, now. How many DNA molecules are in each of your somatic cells? You are going to have to learn the difference between several similar-sounding terms. The sketch below that looks like an X represents a replicated chromosome that has two sister chromatids. The narrow waist represents the location of the centromere. Students often get all these terms confused, so take time now to label the indicated areas of the figure and then define each of the terms below. See page 229 of your text for the labeled figure. chromosome: A cellular structure carrying genetic material, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins. (A bacterial chromosome usually consists of a single circular DNA molecule and associated proteins. It is found in the nucleoid region, which is not membrane bounded.) See also chromatin. chromatid: One of two identical joined copies of the original chromosome centromere: In a duplicated chromosome, the region on each sister chromatid where they are most closely attached to each other by proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences; this close attachment causes a constriction in the condensed chromosome. chromatin: The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes. When the cell is not dividing, chromatin exists in its dispersed form, as a mass of very long, thin fibers that are not visible with a light microscope. 12. Study Figure 12.5 in your text. Label the figure below, and summarize what occurs at the DNA level in each stage. See page 230 of your text for the labeled figure. One of the multiple chromosomes in a eukaryotic cell is represented here, not yet duplicated. Normally it would be a long, thin chromatin fiber containing one DNA molecule and associated proteins; here its condensed form is shown for illustration purposes only. Once duplicated, a chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected along their entire lengths by sister chromatid cohesion. Each chromatid contains a copy of the DNA molecule. Molecular and mechanical processes separate the sister chromatids into two chromosomes and distribute them to two daughter cells. 13. What is mitosis? How is it different from cytokinesis? Mitosis, the division of the genetic material in the nucleus, is usually followed immediately by cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
3 14. What occurs in meiosis? How is the chromosome number of daughter cells different? The human body produces gametes eggs or sperm by a variation of cell division called meiosis, which yields nonidentical daughter cells that have only one set of chromosomes (23), half as many chromosomes as the parent cell. 15. Select either mitosis or meiosis to answer the following questions. Mitosis By what process are the damaged cells in a wound replaced? Meiosis By what process are eggs formed? Mitosis By what process does a zygote develop into a multicellular organism? Mitosis In which process are identical daughter cells produced? Meiosis Which process reduces chromosome number of daughter cells? 16. Don t skip the Concept Check Questions! They are a good way to verify your understanding. Here is a variation of question 3. Answer it here: A hedgehog has 90 chromosomes in its somatic cells. a. How many chromosomes did the hedgehog inherit from each parent 45 b. How many chromosomes are in each of the hedgehog s gametes? 45 c. How many chromosomes will be in each somatic cell of the hedgehog s offspring 90 Concept 12.2 The mitotic phase alternates with interphase in the cell cycle 17. Label each of the parts of the cell cycle listed below, and give a brief explanation of what happens in each phase. See page 231 of your text for the labeled figure. G 1 : First Gap The first part of interphase S: Synthesis When the chromosomes duplicate G 2 : Second Gap The last part of interphase M: In the M phase, mitosis distributes the daughter chromosomes to daughter nuclei, and cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm, producing two daughter cells. 18. What are the components of the mitotic spindle? What is the source of these components? This structure consists of fibers made of microtubules and associated proteins. While the mitotic spindle assembles, the other microtubules of the cytoskeleton partially disassemble, providing the Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
4 material used to construct the spindle. The spindle microtubules elongate (polymerize) by incorporating more subunits of the protein tubulin and shorten (depolymerize) by losing subunits. The source of these components is the cytoplasm during prophase. 19. In animal cells, the assembly of spindle microtubules starts at the centrosome. What is another name for the centrosome? Microtubule-organizing center 20. Sketch and label a centrosome with two centrioles. See page 232 in your text to view the G 2 of Interphase portion of the figure. 21. What are the components of the mitotic spindle? This structure consists of fibers made of microtubules and associated proteins. While the mitotic spindle assembles, the other microtubules of the cytoskeleton partially disassemble, providing the material used to construct the spindle. 22. Describe what happens to the centrosome during interphase and then prophase. During interphase, a cell that is about to divide grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division. During prophase, the centrosomes move away from each other, propelled partly by the lengthening microtubules around them. 23. What is a kinetochore? Read your text carefully, and then make a labeled sketch that shows a replicated chromosome with two kinetochores and some attached spindle fibers. Figure 12.8 in your text may help. See page 236 of your text for the labeled figure. A structure of proteins attached to the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle 24. You will need to spend some serious time with Figure 12.7 in your text. Use it to help you label this figure. Label each phase by name; then label the smaller structures. Finally, make two or three summary statements that indicate important features to note about the phase. Phase G 2 of interphase Prophase Important Features of Phase Prometaphase Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
5 Metaphase Anaphase Telophase and cytokinesis 25. Explain the difference between kinetochore and nonkinetechore microtubules. What is the function of each? During prometaphase, some of the spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores; these are called kinetochore microtubules. Meanwhile, microtubules that do not attach to kinetochores have been elongating, and by metaphase they overlap and interact with other nonkinetochore microtubules from the opposite pole of the spindle. 26. At which end do kinetochore microtubules shorten during anaphase? Explain the Inquiry Figure that supports where this shortening occurs. As the chromosomes moved poleward, the microtubule segments on the kinetochore side of the mark shortened, while those on the spindle pole side stayed the same length. During anaphase in this cell type, chromosome movement is correlated with kinetochore microtubules shortening at their kinetochore ends and not at their spindle pole ends. This experiment supports the hypothesis that during anaphase, a chromosome is walked along a microtubule as the microtubule depolymerizes at its kinetochore end, releasing tubulin subunits. 27. Describe cytokinesis in an animal cell. Use a labeled sketch that shows the cleavage furrow. See page 235 of your text for the labeled figure (12.10a). In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs by a process known as cleavage. The first sign of cleavage is the appearance of a cleavage furrow, a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate. On the cytoplasmic side of the furrow is a contractile ring of actin microfilaments associated with molecules of the protein myosin. The actin microfilaments interact with the myosin molecules, causing the ring to contract. The contraction of the dividing cell s ring of microfilaments is like the pulling of a drawstring. The cleavage furrow deepens until the parent cell is pinched in two, producing two completely separated cells, each with its own nucleus and share of cytosol, organelles, and other subcellular structures. 28. Describe cytokinesis in a plant cell. Use a labeled sketch that shows the cell plate. See page 235 of your text for the labeled figure (12.10b). Cytokinesis in plant cells, which have cell walls, is markedly different. There is no cleavage furrow. Instead, during telophase, vesicles derived from the Golgi apparatus move along microtubules to the middle of the cell, where they coalesce, producing a cell plate. Cell wall materials carried in the vesicles collect in the cell plate as it grows. The cell plate enlarges until its Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
6 surrounding membrane fuses with the plasma membrane along the perimeter of the cell. Two daughter cells result, each with its own plasma membrane. Meanwhile, a new cell wall arising from the contents of the cell plate has formed between the daughter cells. 29. How is the cell plate formed? What is the source of the material for the cell plate? Vesicles derived from the Golgi apparatus move along microtubules to the middle of the cell, where they coalesce, producing a cell plate. 30. Prokaryote reproduction does not involve mitosis, but instead occurs by binary fission. This process involves an origin of replication. Describe binary fission. A method of asexual reproduction by division in half. In prokaryotes, binary fission does not involve mitosis, but in single-celled eukaryotes that undergo binary fission, mitosis is part of the process. 31. Notice that now you are learning a number of differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Besides the fact that prokaryotes lack a membrane-bounded nucleus, describe the following differences: Mode of reproduction? Prokaryotes divide by fission, and eukaryotes by mitosis. Number of chromosomes? Prokaryotic cells have a single circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotic cells have distinct linear chromosomes. The number varies by species in eukaryotes. Shape of the bacterial chromosome? Circular (prokaryotes) versus linear (eukaryotes) Concept 12.3 The eukaryotic cell cycle is regulated by a molecular control system 32. What controls the cell cycle? Study the Inquiry Figure in your text to help you answer this question. Molecules present in the cytoplasm during the S or M phase control the progression to those phases. 33. What is a cell cycle checkpoint? A control point in the cell cycle where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cycle 34. Summarize what happens at each checkpoint. You may add to this chart as you study this section. Checkpoint G 1 G 2 What Happens? How Is It Controlled? If a cell receives the go-ahead signal at this checkpoint, the cell cycle will continue. It is regulated by the cyclin-cdk complexes. When sufficient MPF accumulates, the G 2 checkpoint is passed, and mitosis is promoted. M The kinetochores must all be attached to spindle fibers during metaphase. This will activate an enzyme (separase), which allows the sister chromatids to separate and Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
7 anaphase will proceed. 35. What is the G 0 phase? Describe this phase. G 0 phase is a nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly, such as liver cells. 36. What is a protein kinase? An enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein, thus phosphorylating the protein. 37. Kinases drive the cell cycle, but they must be activated by attachment of a cyclin. 38. The activity of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDks) rises and falls. Why? The activity of CDks rises and falls with changes in the concentration of its cyclin partner, MPF. 39. What does MPF trigger? What are some specific activities that it triggers? MPF triggers the cell s passage past the G 2 checkpoint into M phase. 40. What happens if all the chromosome kinetochores are not attached to spindle fibers? When this occurs, which checkpoint is not passed? If all the chromosome kinetochores are not attached to spindle fibers, the sister chromatids remain together, delaying anaphase. When this occurs, the M phase checkpoint is not passed. 41. What are growth factors? How does platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulate fibroblast division? Growth factor is a protein released by certain cells that stimulates other cells to divide. Fibroblasts have PDGF receptors on their plasma membranes. The binding of PDGF molecules to these receptors triggers a signal transduction pathway that allows the cells to pass the G 1 checkpoint and divide. 42. Cancer cells exhibit different behaviors than normal cells. Here are two normal behaviors they no longer show. Explain each behavior. density-dependent inhibition: Cells normally divide until they form a single layer of cells on the inner surface of the culture container, at which point the cells stop dividing. If some cells are removed, those bordering the open space begin dividing again and continue until the vacancy is filled. Follow-up studies revealed that the binding of a cell-surface protein to its counterpart on an adjoining cell sends a growth-inhibiting signal to both cells, preventing them from moving forward in the cell cycle, even in the presence of growth factors. anchorage dependence: To divide, they must be attached to a substratum, such as the inside of culture jar or the extracellular matrix of a tissue. a Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
8 43. Cancer cells also show loss of cell cycle controls and may divide without being checked. The story of HeLa cells is worth noting. What is their source? How old are they? Note that, unlike normal cells, HeLa cells are immortal! HeLa cells original source was a tumor removed from a woman names Henrietta Lacks. This cell line has been reproducing in culture since What is transformation? What is metastasis? Transformation is the conversion of a normal animal cell to a cancerous cell. Metastasis is the spread of cancer cells to locations distant from their original site. 45. Distinguish between a benign tumor and a malignant tumor. A benign tumor is a mass of abnormal cells with specific genetic and cellular changes such that the cells are not capable of surviving at a new site and generally remain at the site of the tumor s origin. A malignant tumor is a cancerous tumor containing cells that have significant genetic and cellular changes and are capable of invading and surviving in new sites. Malignant tumors can impair the functions of one or more organs. 46. List two specific cancer treatments, and tell how each treatment works. Radiation, Chemotherapy A tumor that appears to be localized may be treated with high-energy radiation, which damages DNA in cancer cells much more than it does in normal cells, apparently because the majority of cancer cells have lost the ability to repair such damage. To treat known or suspected metastatic tumors, chemotherapy is used, in which drugs that are toxic to actively dividing cells are administered through the circulatory system. Chemotherapeutic drugs interfere with specific steps in the cell cycle. 47. In the light micrograph below of dividing cells near the tip of an onion root, identify a cell in each of the following stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. See page A-11 (Appendix) in your text for the labeled figure. Test Your Understanding Answers Now you should be ready to test your knowledge. Place your answers here: 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. c 5. a 6. b 7. (above) 8. a 9. e Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
If and when cancer cells stop dividing, they do so at random points, not at the normal checkpoints in the cell cycle.
 Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body s control mechanisms. Cancer cells do not stop dividing when
Cellular Reproduction
 9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
9 Cellular Reproduction section 1 Cellular Growth Before You Read Think about the life cycle of a human. On the lines below, write some of the stages that occur in the life cycle of a human. In this section,
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
Lecture 11 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis In this lecture Cell division Chromosomes The cell cycle Mitosis PPMAT Apoptosis What is cell division? Cells divide in order to reproduce themselves The cell cycle
1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells
 Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. When new cells are formed through the process of mitosis, the number of chromosomes in the new cells A. is half of that of the parent cell. B. remains the same as in the
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
Cell Division Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A Chromosome and Sister Chromatids Key Points About Chromosome Structure A chromosome consists of DNA that is wrapped around proteins (histones) and condensed Each
www.njctl.org PSI Biology Mitosis & Meiosis
 Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Classwork 1. Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis. 2. Provide an example of a type of cell in the human body that would undergo mitosis. 3. Does cell division
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257
 CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION P. 243-257 SECTION 9-1 CELLULAR GROWTH Page 244 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is it beneficial for cells to remain small? MAIN IDEA Cells grow until they reach their size limit,
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis
 The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
The cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis Learning objective This learning material is about the life cycle of a cell and the series of stages by which genetic materials are duplicated and partitioned to produce
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis
 Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
Lecture 7 Mitosis & Meiosis Cell Division Essential for body growth and tissue repair Interphase G 1 phase Primary cell growth phase S phase DNA replication G 2 phase Microtubule synthesis Mitosis Nuclear
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Los Angeles Mission College Biology 3 Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
Name Period Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know.
List, describe, diagram, and identify the stages of meiosis.
 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this topic we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells: meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell division, mitosis
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction
 Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 3A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 5 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a cell cannot move enough material
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
Name Period Concept 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Let s begin with a review of several terms that you may already know. Define: gene locus gamete male gamete female
1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes?
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 1. Why is mitosis alone insufficient for the life cycle of sexually reproducing eukaryotes? 2. Define: gamete zygote meiosis homologous chromosomes diploid haploid
The Somatic Cell Cycle
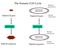 The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
The Somatic Cell Cycle Maternal chromosome Diploid Zygote Diploid Zygote Paternal chromosome MITOSIS MITOSIS Maternal chromosome Diploid organism Diploid organism Paternal chromosome Int terpha ase The
Guided Notes: Chapter 9 Cellular Reproduction
 Guided Notes: Cellular Reproduction When do cells divide? Cells grow and function normally until they become too. Cell size is because increases faster than This means that there is not enough area on
Guided Notes: Cellular Reproduction When do cells divide? Cells grow and function normally until they become too. Cell size is because increases faster than This means that there is not enough area on
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis
 K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
K.Muma Bio 6 Appendix C DNA Replication & Mitosis Study Objectives: Appendix C: DNA replication and Mitosis 1. Describe the structure of DNA and where it is found. 2. Explain complimentary base pairing:
Chapter 3. Cell Division. Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.
 Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
LAB 09 Cell Division
 LAB 09 Cell Division Introduction: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic information to the next generation. Cell division in individual bacteria and
LAB 09 Cell Division Introduction: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic information to the next generation. Cell division in individual bacteria and
From DNA to Protein
 Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
Nucleus Control center of the cell contains the genetic library encoded in the sequences of nucleotides in molecules of DNA code for the amino acid sequences of all proteins determines which specific proteins
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
 CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called chromosomes. These are rod-shaped structures made
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis
 Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction In this workshop you will examine how cells divide, including how they partition their genetic material (DNA) between the two resulting
Workshop: Cellular Reproduction via Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction In this workshop you will examine how cells divide, including how they partition their genetic material (DNA) between the two resulting
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION
 CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Cell division is an inherent property of living organisms. It is a process in which cells reproduce their own kind. The growth, differentiation, reproduction and
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB)
 Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA
 Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT TIP CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Adapted from Foundations of Biology I; Lab 6 Introduction to Microscopy Dr. John Robertson, Westminster College Biology Department,
Sample Questions for Exam 3
 Sample Questions for Exam 3 1. All of the following occur during prometaphase of mitosis in animal cells except a. the centrioles move toward opposite poles. b. the nucleolus can no longer be seen. c.
Sample Questions for Exam 3 1. All of the following occur during prometaphase of mitosis in animal cells except a. the centrioles move toward opposite poles. b. the nucleolus can no longer be seen. c.
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
LABORATORY 2 THE CELL CYCLE AND THE STAGES OF MITOSIS LEARNING OBJECTIVES AFTER COMPLETING THIS LABORATORY, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the cell cycle. 2. Identify stages of mitosis from prepared
Meiosis is a special form of cell division.
 Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
Page 1 of 6 KEY CONCEPT Meiosis is a special form of cell division. BEFORE, you learned Mitosis produces two genetically identical cells In sexual reproduction, offspring inherit traits from both parents
5. The cells of a multicellular organism, other than gametes and the germ cells from which it develops, are known as
 1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
1. True or false? The chi square statistical test is used to determine how well the observed genetic data agree with the expectations derived from a hypothesis. True 2. True or false? Chromosomes in prokaryotic
Classify chromosomes in a karyotype according to size and centromere position. Identify metacentric, submetacentric and acrocentric chromosomes
 Mitosis, Meiosis and the Cell Cycle Prof. Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives By the end of the session the student shoud be able to: Define the meaning of chromosomes
Mitosis, Meiosis and the Cell Cycle Prof. Alfred Cuschieri University of Malta Department of Anatomy Objectives By the end of the session the student shoud be able to: Define the meaning of chromosomes
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Plasma Membrane hydrophilic polar heads
 The Parts of the Cell 3 main parts in ALL cells: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material this is about the parts of a generic eukaryotic cell Plasma Membrane -is a fluid mosaic model membrane is fluid
The Parts of the Cell 3 main parts in ALL cells: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material this is about the parts of a generic eukaryotic cell Plasma Membrane -is a fluid mosaic model membrane is fluid
Sexual Reproduction. The specialized cells that are required for sexual reproduction are known as. And come from the process of: GAMETES
 Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction We know all about asexual reproduction 1. Only one parent required. 2. Offspring are identical to parents. 3. The cells that produce the offspring are not usually
1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 3. Explain differences in mitosis between plant and animal cells.
 Mitosis Objectives Having completed the lab on mitosis, you should be able to: 1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 2. Describe the events during each phase
Mitosis Objectives Having completed the lab on mitosis, you should be able to: 1. Identify each phase of mitosis on the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula. 2. Describe the events during each phase
Lecture 4 Cell Membranes & Organelles
 Lecture 4 Cell Membranes & Organelles Structure of Animal Cells The Phospholipid Structure Phospholipid structure Encases all living cells Its basic structure is represented by the fluidmosaic model Phospholipid
Lecture 4 Cell Membranes & Organelles Structure of Animal Cells The Phospholipid Structure Phospholipid structure Encases all living cells Its basic structure is represented by the fluidmosaic model Phospholipid
The chromosomes are structures in living cells that contain
 Brooker Widmaier Graham Stiling: III. Nucleic Acid Structure and DNA Replication 15. Eukaryotic Chromosomes, Mitosis, 47 EUKARYOTIC CHROMOSOMES, MITOSIS, AND MEIOSIS C HAPTER O UTLINE 15.1 Molecular Structure
Brooker Widmaier Graham Stiling: III. Nucleic Acid Structure and DNA Replication 15. Eukaryotic Chromosomes, Mitosis, 47 EUKARYOTIC CHROMOSOMES, MITOSIS, AND MEIOSIS C HAPTER O UTLINE 15.1 Molecular Structure
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
Cell Structure and Function. Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron
 Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells: Blood Cells Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Cells: Bacteria Cell Structure and Function All living
Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cell: Neuron Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells: Blood Cells Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Cells: Bacteria Cell Structure and Function All living
Review of the Cell and Its Organelles
 Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
Biology Learning Centre Review of the Cell and Its Organelles Tips for most effective learning of this material: Memorize the names and structures over several days. This will help you retain what you
Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One
 Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One Introduction All living things are made of cells. Some living things, like plants and animals, are made of millions of cells. But some living things are
Cell Division Simulation: Bacteria Activity One Introduction All living things are made of cells. Some living things, like plants and animals, are made of millions of cells. But some living things are
The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities
 The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities Cancer Education Project University of Rochester Premise: Students learn best when exposed to a variety of activities Overview 1. Information Gathering:
The Cell Cycle: A series of modeling activities Cancer Education Project University of Rochester Premise: Students learn best when exposed to a variety of activities Overview 1. Information Gathering:
02-SciProbe9-Chap02 2/8/07 12:12 PM Page 32 32 NEL
 32 UNIT A REPRODUCTION Chapter 2 Cell Growth and Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 4 Human Reproduction Unit Preview Your body is made of many trillions of cells that came from a single
32 UNIT A REPRODUCTION Chapter 2 Cell Growth and Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 4 Human Reproduction Unit Preview Your body is made of many trillions of cells that came from a single
Biology Chapter 7 Practice Test
 Biology Chapter 7 Practice Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by
Biology Chapter 7 Practice Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by
Cell Structure & Function!
 Cell Structure & Function! Chapter 3! The most exciting phrase to hear in science, the one that heralds new discoveries, is not 'Eureka!' but 'That's funny.! -- Isaac Asimov Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell
Cell Structure & Function! Chapter 3! The most exciting phrase to hear in science, the one that heralds new discoveries, is not 'Eureka!' but 'That's funny.! -- Isaac Asimov Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell
Given these characteristics of life, which of the following objects is considered a living organism? W. X. Y. Z.
 Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
the plant & animal cell
 6.1 Basic unit of life Biology Biology Structure & functions of 06 the plant & animal cell In 1665, Robert Hooke observed a section of a cork using a microscope prepared by him. He discovered a structure
6.1 Basic unit of life Biology Biology Structure & functions of 06 the plant & animal cell In 1665, Robert Hooke observed a section of a cork using a microscope prepared by him. He discovered a structure
The Cell Interior and Function
 The Cell Interior and Function 5 5.0 CHAPTER PREVIEW Investigate and understand the organization and function of the cell interior. Define the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell structure.
The Cell Interior and Function 5 5.0 CHAPTER PREVIEW Investigate and understand the organization and function of the cell interior. Define the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell structure.
CELL DIVISION. STAGES OF MITOTIC DIVISION (Diag. C1)
 1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
1 CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which cells replicate in order to replace cell loss, repair tissue damage and reproduce the organism. Two types of cell division are encountered in the Eukaryotic
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 12 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Concept Outline 12.1 Meiosis produces haploid cells from diploid cells. Discovery of Reduction Division. Sexual reproduction does not increase chromosome number because
12 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Concept Outline 12.1 Meiosis produces haploid cells from diploid cells. Discovery of Reduction Division. Sexual reproduction does not increase chromosome number because
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Cell Structure and Function
 CHAPTER 3 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Vocabulary Practice cell theory vacuole concentration gradient cytoplasm lysosome osmosis organelle centriole isotonic prokaryotic cell cell wall hypertonic eukaryotic
CHAPTER 3 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Vocabulary Practice cell theory vacuole concentration gradient cytoplasm lysosome osmosis organelle centriole isotonic prokaryotic cell cell wall hypertonic eukaryotic
Sexual Reproduction. and Meiosis. Sexual Reproduction
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Describe the stages of meiosis and how sex cells are produced. Explain why meiosis is needed for sexual reproduction. Name the cells that are involved in fertilization.
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis
 Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
Lab 3: Testing Hypotheses about Mitosis Why do cells divide? Lab today focuses on cellular division, also known as cellular reproduction. To become more familiar with why cells divide, the types of cell
Bacterial (Prokaryotic) Cell. Common features of all cells. Tour of the Cell. Eukaryotic Cell. Plasma Membrane defines inside from outside
 www.denniskunkel.com Tour of the Cell www.denniskunkel.com Today s Topics Properties of all cells Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Functions of Major Cellular Organelles Information, Synthesis&Transport,, Vesicles
www.denniskunkel.com Tour of the Cell www.denniskunkel.com Today s Topics Properties of all cells Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Functions of Major Cellular Organelles Information, Synthesis&Transport,, Vesicles
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen
 Concept 1 - Thinking Practice 1. If the following molecules were to undergo a dehydration synthesis reaction, what molecules would result? Circle the parts of each amino acid that will interact and draw
Concept 1 - Thinking Practice 1. If the following molecules were to undergo a dehydration synthesis reaction, what molecules would result? Circle the parts of each amino acid that will interact and draw
Compartmentalization of the Cell. Objectives. Recommended Reading. Professor Alfred Cuschieri. Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
Compartmentalization of the Cell Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Objectives By the end of this session the student should be able to: 1. Identify the different organelles
the!sun!to!sugars.!this!is!called!! photosynthesis.!the!byproduct!of!those! Nucleus! sugars!is!our!oxygen.!
 Cytoplasm ANIMAL CELL Vacuoles Mitochondria Chromosomes GolgiApparatus Chloroplast+ TheChloroplastiswhatmakesthefood inthecell.they reonlyfoundinplant cellsandsomeprotists.everygreen plantyouseeisconvertingenergyfrom
Cytoplasm ANIMAL CELL Vacuoles Mitochondria Chromosomes GolgiApparatus Chloroplast+ TheChloroplastiswhatmakesthefood inthecell.they reonlyfoundinplant cellsandsomeprotists.everygreen plantyouseeisconvertingenergyfrom
Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell. 1. Cell Basics. Limits to Cell Size. 1. Cell Basics. 2. Prokaryotic Cells. 3. Eukaryotic Cells
 Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell 1. Cell Basics 2. Prokaryotic Cells 3. Eukaryotic Cells 1. Cell Basics Limits to Cell Size There are 2 main reasons why cells are so small: If cells get too large: 1) there
Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell 1. Cell Basics 2. Prokaryotic Cells 3. Eukaryotic Cells 1. Cell Basics Limits to Cell Size There are 2 main reasons why cells are so small: If cells get too large: 1) there
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams
 The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
The Cell: Organelle Diagrams Fig 7-4. A prokaryotic cell. Lacking a true nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell, the prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure. Only
Use of the Microscope and Cytology
 Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Use of the Microscope and Cytology Introduction: A true study of anatomy not only considers the large, visible structures of an organism, but also the small structures that provide the organism its form
Look for these related items from Learning Resources :
 Look for these related items from Learning Resources : LER 1901 Cross Section Plant Cell LER 1902 Cross Section Heart Model LER 1903 Cross Section Brain Model LER 2437 Cross Section Earth Model For a dealer
Look for these related items from Learning Resources : LER 1901 Cross Section Plant Cell LER 1902 Cross Section Heart Model LER 1903 Cross Section Brain Model LER 2437 Cross Section Earth Model For a dealer
7.2 Cell Structure. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Summary. Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and many specialized structures.
 7.2 Cell Structure Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the role of vacuoles, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton. Identify the role of ribosomes, endoplasmic
7.2 Cell Structure Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the role of vacuoles, lysosomes, and the cytoskeleton. Identify the role of ribosomes, endoplasmic
The Cell Teaching Notes and Answer Keys
 The Cell Teaching Notes and Answer Keys Subject area: Science / Biology Topic focus: The Cell: components, types of cells, organelles, levels of organization Learning Aims: describe similarities and differences
The Cell Teaching Notes and Answer Keys Subject area: Science / Biology Topic focus: The Cell: components, types of cells, organelles, levels of organization Learning Aims: describe similarities and differences
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Science 10-Biology Activity 14 Worksheet on Sexual Reproduction 10 Name Due Date Show Me NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 367-372 in Science Probe. 1. Sexual reproduction requires parents,
Test Two Study Guide
 Test Two Study Guide 1. Describe what is happening inside a cell during the following phases (pictures may help but try to use words): Interphase: : Consists of G1 / S / G2. Growing stage, cell doubles
Test Two Study Guide 1. Describe what is happening inside a cell during the following phases (pictures may help but try to use words): Interphase: : Consists of G1 / S / G2. Growing stage, cell doubles
Teacher s Guide. Mitosis. Grades 5-9 MTTV
 Teacher s Guide Mitosis Grades 5-9 MTTV CREDITS Program Production Sunburst Visual Media Teacher s Guide Terry Gates Print Material Design Cecile Foshee 2004 Sunburst Visual Media, a division of Global
Teacher s Guide Mitosis Grades 5-9 MTTV CREDITS Program Production Sunburst Visual Media Teacher s Guide Terry Gates Print Material Design Cecile Foshee 2004 Sunburst Visual Media, a division of Global
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. 10 pts.
 THE CELL model: Activity 4.1 Science / Biology Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. - Your models should clearly demonstrate the following
THE CELL model: Activity 4.1 Science / Biology Objective: On a team of no more than (2). Build to illustrate a 3D model of a PLANT or ANIMAL cell. - Your models should clearly demonstrate the following
Bio 101 Section 001: Practice Questions for First Exam
 Do the Practice Exam under exam conditions. Time yourself! MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. The substrate fits in the of an enzyme: (A) allosteric site (B) active site (C) reaction groove (D) Golgi body (E) inhibitor
Do the Practice Exam under exam conditions. Time yourself! MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. The substrate fits in the of an enzyme: (A) allosteric site (B) active site (C) reaction groove (D) Golgi body (E) inhibitor
Plant and Animal Cells
 Plant and Animal Cells a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow, divide and to make needed materials. S7L2a b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and
Plant and Animal Cells a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow, divide and to make needed materials. S7L2a b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis
 BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
BioSci 2200 General Genetics Problem Set 1 Answer Key Introduction and Mitosis/ Meiosis Introduction - Fields of Genetics To answer the following question, review the three traditional subdivisions of
Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells
 Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems All organisms
Introduction to the Cell: Plant and Animal Cells Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems All organisms
How Cancer Begins???????? Chithra Manikandan Nov 2009
 Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives
 Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives (with hypothetical learning materials that might populate the objective) The topics and central questions listed here are typical for an introductory undergraduate
Cell Biology Questions and Learning Objectives (with hypothetical learning materials that might populate the objective) The topics and central questions listed here are typical for an introductory undergraduate
Biology I. Chapter 7
 Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Biology 101 Chapter 4 Cells as the Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory Major Contributors: Galileo = first observations made with a microscope
 Biology 101 Chapter 4 Cells as the Basic Unit of Life The Cell Theory Major Contributors: Galileo = first observations made with a microscope Robert Hooke = first to observe small compartments in dead
Biology 101 Chapter 4 Cells as the Basic Unit of Life The Cell Theory Major Contributors: Galileo = first observations made with a microscope Robert Hooke = first to observe small compartments in dead
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
 Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Cell Division and Mitosis DNA. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. 2. Meiosis occurs in the reproductive organs, producing four haploid sex cells.
 ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
ell Division and Mitosis 1. he life cycle of a cell has two parts growth and development, and cell division. 2. In mitosis, the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four continuous
Cytology. Living organisms are made up of cells. Either PROKARYOTIC or EUKARYOTIC cells.
 CYTOLOGY Cytology Living organisms are made up of cells. Either PROKARYOTIC or EUKARYOTIC cells. A. two major cell types B. distinguished by structural organization See table on handout for differences.
CYTOLOGY Cytology Living organisms are made up of cells. Either PROKARYOTIC or EUKARYOTIC cells. A. two major cell types B. distinguished by structural organization See table on handout for differences.
Name Date Period. 2. When a molecule of double-stranded DNA undergoes replication, it results in
 DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis Keystone 1. During the process shown above, the two strands of one DNA molecule are unwound. Then, DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides to each strand which results
DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis Keystone 1. During the process shown above, the two strands of one DNA molecule are unwound. Then, DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides to each strand which results
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis
 Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
Lecture 2: Mitosis and meiosis 1. Chromosomes 2. Diploid life cycle 3. Cell cycle 4. Mitosis 5. Meiosis 6. Parallel behavior of genes and chromosomes Basic morphology of chromosomes telomere short arm
Control of Gene Expression
 Home Gene Regulation Is Necessary? Control of Gene Expression By switching genes off when they are not needed, cells can prevent resources from being wasted. There should be natural selection favoring
Home Gene Regulation Is Necessary? Control of Gene Expression By switching genes off when they are not needed, cells can prevent resources from being wasted. There should be natural selection favoring
Comparing Plant And Animal Cells
 Comparing Plant And Animal Cells http://khanacademy.org/video?v=hmwvj9x4gny Plant Cells shape - most plant cells are squarish or rectangular in shape. amyloplast (starch storage organelle)- an organelle
Comparing Plant And Animal Cells http://khanacademy.org/video?v=hmwvj9x4gny Plant Cells shape - most plant cells are squarish or rectangular in shape. amyloplast (starch storage organelle)- an organelle
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome.
 Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
AP Biology 2011 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Biology 2011 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded
AP Biology 2011 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to college success and opportunity. Founded
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Cells CHAPTER. 1.2.1 Prokaryotic Cells. 1.2.2 Eukaryotic Cells
 C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
C HAPTER 1CELLS AND CELL DIVISION CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction In genetics, we view cells as vessels for the genetic material. Our main interest is in the chromosomes and their environment. This being said,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1
 Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization 1 I. Introduction When you fall and scrape the skin off your hands or knees, how does your body make new skin cells to replace the skin cells that were scraped off? How
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions. Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions!
 AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
AS Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and Definitions Make sure you use these terms when answering exam questions! Chapter 7 Variation 7.1 Random Sampling Sampling a population to eliminate bias e.g. grid square
