Mapping Linear Networks Based on Cellular Phone Tracking
|
|
|
- Jeffery Lane
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ronen RYBOWSKI, Aaron BELLER and Yerach DOYTSHER, Israel Key words: Cellular Phones, Cellular Network, Linear Networks, Mapping. ABSTRACT The paper investigates the ability of accurately mapping linear road networks from cellular phone tracks. Cellular phone tracking records the location of a cell phone for a string of time stamps. Such tracking does require an active call because of roaming. There are various methodologies of determining the location of a cell phone based on the signal strength to nearby antennae (base stations). Cellular networks which support the location functionality have a Location Manager (MLC) that translates the signal strengths to various base stations to the coordinates of the cell phone. Standards like the US E911, which has been the engine behind the rapid technological development in the field, required the US cellular providers to measure the location in accuracy of meters in 67% of the time and up to 150 meters in 95% of the time since the year of We plan to use multiple tracks of cell phones location data provided by cellular providers to map linear road networks. Though cell phone locations are not accurate, we plan to use statistical methods to extract an accurate mapping of linear road networks. This possible since we are assuming that the multiple tracks will behave as random variables. This would allow rapid mapping where there is cellular coverage without any other mapping data. The technology would also enable updating linear road networks almost on the fly. Furthermore, since more and more cellular phones will have an embedded GPS, the same technology could be used along with such GPS data. The paper reviews the current findings of this research, the development of a new geometricstatistical approach for filtering inaccurate locations and extracting approximately the original path from simulate data of cell phones locations. Moreover we will discuss future research which will include using true data to create a linear road network. TS 6B SIM Algorithms and Techniques 1/8
2 Ronen RYBOWSKI, Aaron BELLER and Yerach DOYTSHER, Israel INTRODUCTION Historically mapping has been important for governmental, economic and military purposes and mostly dealt with roads, borders and properties. Today mapping is used as a basis planning, construction, government and military needs. The common mapping methods today include global positioning systems (GPS), Airborne and Satellite Photogrammetry and surveying. Managing, displaying and analyzing the data are carried out by Geographic Information Systems GIS). GPS is one of the most common and available systems that provide accurate location for navigating all over the world (Zogg J. M., 2002). Signals which carry the satellite location and the time of transmission are sent by the satellite and received by ground receivers. Calculation of location requires data from at least four satellites. A less accurate but more prevalent technology for measuring location is based on cell phones. The cell phones are constantly tracked by the cellular providers at an accuracy of about 50 to 100 meters. Since cell phones are ubiquitous there is a potential for developing statistical methods that can quickly collect, create and update spatial data over a wide area based on cellular technologies. Such technology is being used to calculate real time traffic information (Drane et al., 1998) and other location based applications, but has not yet been used to actually acquire the coordinates and nodes of linear road networks. The purpose of our research is to develop a mechanism for mapping linear road networks accurately with the use of multiple tracks of cell phones location data provided by cellular providers. In chapter 2 we shall describe the cellular technology with emphasis on the ability to measure cell phones location. On chapter 3 we shall present the simulator developed for building data base of cellular tracks for the research needs. Chapter 4 will follow the practical experiments that were done so far. Chapter 5 will present the future plans on the research issues. 1. CELLULAR TECHNOLOGY Development in cellular technology has let to the mass use of cell phones, making this technology to an integral part of everyday life. Cellular companies have expanded their services to include location based services (LBS), which enables numerous possibilities such as rescue, real time road traffic analysis (Drane et al., 1998), billing based on location, LBS advertising, accumulated tracking data is allows cellular companies to plan more effective deployment of cellular networks, studying the social characteristics based on time-space and a true and valid planning for public systems (Ahas & Ular, 2005). 2/8
3 LBS is enabled by the ability to accurately measure the location of a cellular device. The location can be determined by the cellular device itself or by the cellular network. When the cell phone has an independent measuring device (e.g. GPS) the location determination is called Device Based. When the location of the phone is calculated by various measurements between the cell phone and the bases stations, the location determination is called Network Based. There are two types of network based location determination: A. Cell ID based - calls are monitored by nearby base stations that provide the initial spatial boundary of the phone. This is further refined by technologies for measuring the transmission strength and the spatial distribution of the base station (using triangulation) (Kiran et al., 2007). B. Network based - the measurements of the transmission strength (also defined as the distance from the basis station) and the signal direction are combined from the nearby base stations. The location of the cell phone is intersected by the distance and angles (Drane et al., 1998). Accurate determination of cell phone location infringes on user's privacy (Fosca et al., 2005). Thus any use of cellular location to map linear road networks will have to overcome this problem. There are numerous possibilities: anonymity, user agreement and user ability to turn on and off location tracking and other means. This is why some of the research is based on simulation data. Currently there are many programs using cell location data such as: Emergency services Knowledge discovery Giannotti et al. (2005). Changxuan et al. (2005) offered a method of improving the public transportation planning using movement patterns taken from cellular tracking data. Forecasting heavy traffic requires the attribution of measured location to a mapped linear road network (Nanne, 2001). In any case, we will not discuss privacy issue in this paper and only assume that it is possible to overcome this issue. 2. SIMULATOR FOR CELL PHONES TRACKING Our initial research is based on simulating cell phone tracking to test feasibility and develop technologies. The simulator was built to create a collection of cell phones locations on a mapped linear road network. The mapped linear road network and other parameters defined by the simulator user are the input. The output is two sets of locations: real locations along the road, and measured locations that represent the location if it was calculated by the cellular providers existing technology. Using the simulator creates a controlled working environment for the mapping process that we try to develop on this research. The following figure is a screenshot of the simulator: 3/8
4 Figure 1 - The parameters: Right row (from top to bottom): a. Number of sampled cell phones; b. Average sampling rate for each phone (minutes); c. Average speed along the road (km/h); d. Threshold error 1 and 2 (meters); e. Maximal error (meters) for the range above threshold 2; f. Deviation to the north/south and deviation to the east/west (meters); Left row (from top to bottom) a. Deviation from the average speed (percentage); b. Threshold value 1 and 2 (percentage); c. Occurrence of deviation (percentage); After loading the chosen road, the number of sampled cell phones are defined. Each cell phone will be sampled in equal time intervals according to the average sampling rate (minutes). The average speed along the road (km/h) is set to all the devices, but there is a permissible deviation according to the deviation percentage from the average speed. The "measured" location must match the maximal deviation range from the "real" location. This is set according to threshold errors 1 and 2, and the maximal error (meters). The occurrence percentage in each of the deviation ranges is set by the threshold values 1 and 2. For some cases a deviation error is activated in the north/south and east/west directions according to the occurrence percentage of the defined deviation. 3. PRACTICAL EXPERIMENTS Note that simulations create random tracks and the situation in the real world may require further refinement of the algorithms used. The measured locations of cell phones are not accurate enough for mapping needs. The locations have 3 kinds of errors: random, deviation and severe. Filtering the severe errors and smoothing the other errors is essential for the first step of mapping. A geometric-statistic method was developed to deal with the errors and an approximate release of the original linear road is also done, with no reference to connections between locations (e.g. a single cell phone holding a number of locations). The method's steps are: first, an organized geometric network of cells is spread above the location data space. Then, each of the locations is attributed in space to one of the network's cells. A representation point is determined for each cell by calculating the center of gravity for all the locations attributed to the specific cell. The network cells are classified into four categories according to the number of locations attributed to each cell: in the upper category 4/8
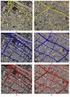
5 are the cells holding the maximal number of locations and in the lower category are the cells holding the minimal number of locations. The approximate road extrication process is calculated by adding some of the representation points from the two top categories according to a defined algorithm. In such way the severe errors are filtered, and the other errors are smoothed. Operating the method on a number of cellular tracking sets (produced by the simulator) has reached the following conclusions: A. The method can extricate an approximate linear road networks. B. The maximal improvement for the approximate road in accordance with the crude data is about 70%. C. There is a minimal value for the number of cell phones needed to reach an optimal result. A number of questions were raised: A. What is the optimal size for network cells? B. Does the road angle in relation to the network have an effect? To answer these questions a vast number of tests were taken in front of different sets of locations. The following conclusions were reached: A. The optimal size of a cell network is a function of threshold error 2 (as defined in the simulator) set by the user. Figure 2: X axis Size of network cell (meters); Y axis Distance (meters); Graph 1 The distance of the original road turning points to the approximate road; Graph 2 The distance of the approximate road turning points to the original road. The graph's intersection point has a value of 150 meters, and that is the value of threshold error 2 defined to this set of data. 5/8
6 B. The road angle in relation to the network is insignificant. Figure 3: X axis Network angle in relation to the road (angles); Y axis Distance (meters); The four graphs present the average distance of the points after filtered from the original road in the different angles. The blue graph presents the preliminary situation. The red, green and purple graphs present distance from networks in 25, 50 and 100 meters size respectively. The network angle in relation to the original road is insignificant. After using the geometric-statistical method, filtered locations of the cell phones and an approximate traffic line in ±10 meters accuracy are acquired. A possible method to improve the level of accuracy is based on matching polynomials by segments. The original road is cut into segments (e.g. linear segments) and the polynomials are matched to each segment by its type. A set of measured locations was built along a linear line to find if this method works. The geometric-statistical method was operated on the data and a matching polynomials algorithm was operated on the representation points from the two upper categories. The result shows that using this method increase the mapping accuracy to ±3 meters. 4. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK Currently, most research tries to match locations to an existing digital road map, for determining factors such as traffic, but not to map the roads themselves from scratch. The research operated a geometric-statistical method on different kinds of sets built by simulator and operated matching polynomials methods on segments. This work suggests a significant potential for extraction an original linear road networks out of measured data from cell phones. The extraction of the original traffic line will permit accurate mapping. The methods and tools developed in this research will allow an accurate and rapid mapping of road networks by using only the cell phones location data. More and more cellular phones are being equipped with GPS devices. If the above research program works, including cellular devices with GPS technology will speed up the convergence of the linear road networks. 6/8
7 Future work will focus on the following issues: 1. Building an algorithm to match polynomials by segments which are identified on the basis of the approximate road. After finishing the mapping process from the first step of crude data to the last step of mapping the original road, the process will be tested on real cellular location data. 2. Collecting cellular location data from accurately mapped road networks. 3. Operating the algorithm on the real location data and testing the product's compatibility to existing accurate maps. 4. Since the positioning of base stations may cause biased results, we will need a method to eliminate this bias. It would help to use cellular tracks from multiple cellular companies to reduce bias. 5. Develop a methodology for detecting and defining the nodes of linear road networks. 6. Develop a methodology for detecting one way, two way roads (and their center lines) and turn restrictions. 7. Develop a methodology for detecting the number of lanes in each direction and their centerlines. 8. Develop a methodology for detecting bridges and clover leaf structure. 9. Testing the effect of the different parameters on the quality of the solution. REFERENCES 1. Ahas R., Ular M., Location Based Services - New Challenges for Planning and Public Administration. Futures, 37, pp C. Drane, M. Macnaughtan, C. Scott, Positioning GSM Telephones. IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 36, no. 4, pp Changxuan Pan, Jiangang Lu, Shan Di, Bin Ran, A Cellular - Based Data Extracting Method for Trip Distribution. 4. F. Giannotti, A. Mazzoni, S. Puntoni, C. Renso, Synthetic Generation of Cellular Network Positioning Data. In Proc. of ACM GIS 05, Bremen. 5. Fosca Giannotti, Mirco Nanni, Dino Pedreschi1, Chiara Renso, GeoPKDD Geographic Privacy-aware Knowledge Discovery. 6. Kiran G.S., Bhoolakshmi M., G. Varaprasad, Algorithm for Finding the Mobile Phone in a Cellular Network. IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL. 7 No Nanne J. van der Zijpp, A MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD MAP MATCHING ALGORITHM. The 13th Mini - EURO Conference Mon Nov Wise S., GIS Basics. 9. Wolf P.R., B.A. Dewitt, Elements of Photogrammetry: with applications in GIS. 10. Zogg J. M., GPS Basic. 7/8
8 BIOGRAPHICAL NOTES Ronen Rybowski received an Engineering degree in Geo-information from the Technion Israel Institute of Technology in He is currently a candidate on the M.Sc track in Mapping and Geo-Information Engineering at the Technion. Dr. Aaron Beller received a Ph.D. in Mathematics from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Lectured in the Department of Decision Sciences, The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania and the School of Business Administration, Hebrew University of Jerusalem from Worked in numerous software compnaies in Israel and the US. Currently a GIS developer and consultant. Prof. Yerach Doytsher graduated from the Technion Israel Institute of Technology in Civil Engineering in He received a M.Sc. (1972) and D.Sc. (1979) in Geodetic Engineering also from Technion. Until 1995 he was involved in geodetic and mapping projects and consultations within the private and public sectors in Israel. Since 1996 he is a faculty staff member in Civil Engineering and Environmental at the Technion, and currently the Dean of the Faculty of Architecture and Town Planning. He also heads the Geodesy and Mapping Research Center at the Technion. CONTACTS Mr. Ronen Rybowski Technion Israel Institute of Technology Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Geva Binyamin 63, Geva Binyamin Israel Tel [email protected] Dr. Aaron Beller Technion Israel Institute of Technology Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering [email protected] Prof. Yerach Doytsher Technion Israel Institute of Technology Faculty of Architecture and Town Planning Technion City Haifa Israel Tel Fax [email protected] 8/8
Quality of Map-Matching Procedures Based on DGPS and Stand-Alone GPS Positioning in an Urban Area
 Quality of Map-Matching Procedures Based on DGPS and Stand-Alone GPS Positioning in an Urban Area Konstantinos LAKAKIS, Paraskevas SAVVAIDIS, Ioannis M. IFADIS and Ioannis D. DOUKAS, Greece Key words:
Quality of Map-Matching Procedures Based on DGPS and Stand-Alone GPS Positioning in an Urban Area Konstantinos LAKAKIS, Paraskevas SAVVAIDIS, Ioannis M. IFADIS and Ioannis D. DOUKAS, Greece Key words:
Forced Low latency Handoff in Mobile Cellular Data Networks
 Forced Low latency Handoff in Mobile Cellular Data Networks N. Moayedian, Faramarz Hendessi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan, IRAN [email protected]
Forced Low latency Handoff in Mobile Cellular Data Networks N. Moayedian, Faramarz Hendessi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan, IRAN [email protected]
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches
 Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
Total Program's Units
 Associate Degree Program Department of Civil and Architectural Technology Major : Survey Technology First Semester NO 5 6 Code SRV 0 SRV 0 SRV 0 ENG 0 MTH 7 CMT 0 Course Title Land survey Survey drawing
Associate Degree Program Department of Civil and Architectural Technology Major : Survey Technology First Semester NO 5 6 Code SRV 0 SRV 0 SRV 0 ENG 0 MTH 7 CMT 0 Course Title Land survey Survey drawing
KEY WORDS: Geoinformatics, Geoinformation technique, Remote Sensing, Information technique, Curriculum, Surveyor.
 CURRICULUM OF GEOINFORMATICS INTEGRATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Kirsi VIRRANTAUS*, Henrik HAGGRÉN** Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Department of Surveying
CURRICULUM OF GEOINFORMATICS INTEGRATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Kirsi VIRRANTAUS*, Henrik HAGGRÉN** Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Department of Surveying
Mobile Phone Location Tracking by the Combination of GPS, Wi-Fi and Cell Location Technology
 IBIMA Publishing Communications of the IBIMA http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/cibima/cibima.html Vol. 2010 (2010), Article ID 566928, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2010.566928 Mobile Phone Location Tracking
IBIMA Publishing Communications of the IBIMA http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/cibima/cibima.html Vol. 2010 (2010), Article ID 566928, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2010.566928 Mobile Phone Location Tracking
RF Coverage Validation and Prediction with GPS Technology
 RF Coverage Validation and Prediction with GPS Technology By: Jin Yu Berkeley Varitronics Systems, Inc. 255 Liberty Street Metuchen, NJ 08840 It has taken many years for wireless engineers to tame wireless
RF Coverage Validation and Prediction with GPS Technology By: Jin Yu Berkeley Varitronics Systems, Inc. 255 Liberty Street Metuchen, NJ 08840 It has taken many years for wireless engineers to tame wireless
CELL PHONE TRACKING. Index. Purpose. Description. Relevance for Large Scale Events. Options. Technologies. Impacts. Integration potential
 CELL PHONE TRACKING Index Purpose Description Relevance for Large Scale Events Options Technologies Impacts Integration potential Implementation Best Cases and Examples 1 of 10 Purpose Cell phone tracking
CELL PHONE TRACKING Index Purpose Description Relevance for Large Scale Events Options Technologies Impacts Integration potential Implementation Best Cases and Examples 1 of 10 Purpose Cell phone tracking
Measuring the Optimal Transmission Power of GSM Cellular Network: A Case Study
 216 Measuring the Optimal Transmission Power of GSM Cellular Network: A Case Study Measuring the Optimal Transmission Power of GSM Cellular Network: A Case Study Dr Basil M Kasasbeh, Applied Science University,
216 Measuring the Optimal Transmission Power of GSM Cellular Network: A Case Study Measuring the Optimal Transmission Power of GSM Cellular Network: A Case Study Dr Basil M Kasasbeh, Applied Science University,
Use of mobile phone data to estimate mobility flows. Measuring urban population and inter-city mobility using big data in an integrated approach
 Use of mobile phone data to estimate mobility flows. Measuring urban population and inter-city mobility using big data in an integrated approach Barbara Furletti, Lorenzo Gabrielli, Giuseppe Garofalo,
Use of mobile phone data to estimate mobility flows. Measuring urban population and inter-city mobility using big data in an integrated approach Barbara Furletti, Lorenzo Gabrielli, Giuseppe Garofalo,
VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM USING GPS. 1 Student, ME (IT) Pursuing, SCOE, Vadgaon, Pune. 2 Asst. Professor, SCOE, Vadgaon, Pune
 VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM USING GPS Pooja P. Dehankar 1, 1 Student, ME (IT) Pursuing, SCOE, Vadgaon, Pune Prof. S. P. Potdar 2 2 Asst. Professor, SCOE, Vadgaon, Pune Abstract- Global Positioning System is
VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM USING GPS Pooja P. Dehankar 1, 1 Student, ME (IT) Pursuing, SCOE, Vadgaon, Pune Prof. S. P. Potdar 2 2 Asst. Professor, SCOE, Vadgaon, Pune Abstract- Global Positioning System is
2002 IEEE. Reprinted with permission.
 Laiho J., Kylväjä M. and Höglund A., 2002, Utilization of Advanced Analysis Methods in UMTS Networks, Proceedings of the 55th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference ( Spring), vol. 2, pp. 726-730. 2002 IEEE.
Laiho J., Kylväjä M. and Höglund A., 2002, Utilization of Advanced Analysis Methods in UMTS Networks, Proceedings of the 55th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference ( Spring), vol. 2, pp. 726-730. 2002 IEEE.
Big Data Collection and Utilization for Operational Support of Smarter Social Infrastructure
 Hitachi Review Vol. 63 (2014), No. 1 18 Big Data Collection and Utilization for Operational Support of Smarter Social Infrastructure Kazuaki Iwamura Hideki Tonooka Yoshihiro Mizuno Yuichi Mashita OVERVIEW:
Hitachi Review Vol. 63 (2014), No. 1 18 Big Data Collection and Utilization for Operational Support of Smarter Social Infrastructure Kazuaki Iwamura Hideki Tonooka Yoshihiro Mizuno Yuichi Mashita OVERVIEW:
Traffic Monitoring Systems. Technology and sensors
 Traffic Monitoring Systems Technology and sensors Technology Inductive loops Cameras Lidar/Ladar and laser Radar GPS etc Inductive loops Inductive loops signals Inductive loop sensor The inductance signal
Traffic Monitoring Systems Technology and sensors Technology Inductive loops Cameras Lidar/Ladar and laser Radar GPS etc Inductive loops Inductive loops signals Inductive loop sensor The inductance signal
USE OF STATE FLEET VEHICLE GPS DATA FOR TRAVEL TIME ANALYSIS
 USE OF STATE FLEET VEHICLE GPS DATA FOR TRAVEL TIME ANALYSIS David P. Racca Center for Applied Demography and Survey Research (CADSR) University of Delaware Graham Hall, Rm 284, Newark, Delaware 19716
USE OF STATE FLEET VEHICLE GPS DATA FOR TRAVEL TIME ANALYSIS David P. Racca Center for Applied Demography and Survey Research (CADSR) University of Delaware Graham Hall, Rm 284, Newark, Delaware 19716
Christian Bettstetter. Mobility Modeling, Connectivity, and Adaptive Clustering in Ad Hoc Networks
 Christian Bettstetter Mobility Modeling, Connectivity, and Adaptive Clustering in Ad Hoc Networks Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Ad Hoc Networking: Principles, Applications, and Research Issues 5 2.1 Fundamental
Christian Bettstetter Mobility Modeling, Connectivity, and Adaptive Clustering in Ad Hoc Networks Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Ad Hoc Networking: Principles, Applications, and Research Issues 5 2.1 Fundamental
Performance and Limitations of Cellular-Based Traffic Monitoring Systems. Cellint Traffic Solutions
 www.cellint.com Performance and Limitations of Cellular-Based Traffic Monitoring Systems Cellint Traffic Solutions 1 Leading provider of cellular-based traffic data collection solutions 2 Introduction
www.cellint.com Performance and Limitations of Cellular-Based Traffic Monitoring Systems Cellint Traffic Solutions 1 Leading provider of cellular-based traffic data collection solutions 2 Introduction
Technology Trends In Geoinformation
 Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: [email protected] www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
Technology Trends In Geoinformation Dato Prof. Sr Dr. Abdul Kadir Bin Taib Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia (JUPEM) Email: [email protected] www.jupem.gov.my NGIS 2008 3 rd. National GIS Conference
ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS FOR ADAPTIVE MANAGEMENT TRAFFIC LIGHT OBJECTS AT THE INTERSECTION
 The 10 th International Conference RELIABILITY and STATISTICS in TRANSPORTATION and COMMUNICATION - 2010 Proceedings of the 10th International Conference Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and
The 10 th International Conference RELIABILITY and STATISTICS in TRANSPORTATION and COMMUNICATION - 2010 Proceedings of the 10th International Conference Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and
The Department of Education. in Science and Technology
 The Department of Education in Science and Technology Graduate Studies M.Sc. and Ph.D. Programs January 2013 Table of Contents 1. Overview: M.Sc. and Ph.D. Graduate Studies programs in Science and Technology
The Department of Education in Science and Technology Graduate Studies M.Sc. and Ph.D. Programs January 2013 Table of Contents 1. Overview: M.Sc. and Ph.D. Graduate Studies programs in Science and Technology
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE: SDI & SIM 2013. Spatial Data Infrastructures & Spatial Information Management 2013
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE: Spatial Data Infrastructures & Spatial Information Management 2013 And Commission 3 Annual Meeting The 2013 Annual 'FIG Commission 3' Workshop and Meeting is joined by the 'FIG
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE: Spatial Data Infrastructures & Spatial Information Management 2013 And Commission 3 Annual Meeting The 2013 Annual 'FIG Commission 3' Workshop and Meeting is joined by the 'FIG
Effective Use of Android Sensors Based on Visualization of Sensor Information
 , pp.299-308 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2015.10.9.31 Effective Use of Android Sensors Based on Visualization of Sensor Information Young Jae Lee Faculty of Smartmedia, Jeonju University, 303 Cheonjam-ro,
, pp.299-308 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2015.10.9.31 Effective Use of Android Sensors Based on Visualization of Sensor Information Young Jae Lee Faculty of Smartmedia, Jeonju University, 303 Cheonjam-ro,
Real-Time Traffic Patrol Allocation for Abu Dhabi Emirate (UAE)
 Real-Time Traffic Patrol Allocation for Abu Dhabi Emirate (UAE) Hussain Al-Harthei Traffic and Patrols Directorate, Abu Dhabi Police, Email: [email protected] Oualid (Walid) Ben Ali University of Sharjah,
Real-Time Traffic Patrol Allocation for Abu Dhabi Emirate (UAE) Hussain Al-Harthei Traffic and Patrols Directorate, Abu Dhabi Police, Email: [email protected] Oualid (Walid) Ben Ali University of Sharjah,
Vehicle Tracking System using GPRS
 Urban Transport XIII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 409 Vehicle Tracking System using GPRS S. Ikram 1 & F. T. Shah 2 1 Seidco Communication L.L.C, Abu Dhabi, UAE 2 COMSATS Institute
Urban Transport XIII: Urban Transport and the Environment in the 21st Century 409 Vehicle Tracking System using GPRS S. Ikram 1 & F. T. Shah 2 1 Seidco Communication L.L.C, Abu Dhabi, UAE 2 COMSATS Institute
Traffic Prediction in Wireless Mesh Networks Using Process Mining Algorithms
 Traffic Prediction in Wireless Mesh Networks Using Process Mining Algorithms Kirill Krinkin Open Source and Linux lab Saint Petersburg, Russia [email protected] Eugene Kalishenko Saint Petersburg
Traffic Prediction in Wireless Mesh Networks Using Process Mining Algorithms Kirill Krinkin Open Source and Linux lab Saint Petersburg, Russia [email protected] Eugene Kalishenko Saint Petersburg
Frequency Assignment in Mobile Phone Systems
 Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin Takustraße 7 D-14195 Berlin-Dahlem Germany MARTIN GRÖTSCHEL Frequency Assignment in Mobile Phone Systems ZIB-Report 00-58 (Dezember 2000) Frequency Assignment
Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin Takustraße 7 D-14195 Berlin-Dahlem Germany MARTIN GRÖTSCHEL Frequency Assignment in Mobile Phone Systems ZIB-Report 00-58 (Dezember 2000) Frequency Assignment
GSM Frequency Planning with Band Segregation for the Broadcast Channel Carriers
 GSM Frequency Planning with Band Segregation for the Broadcast Channel Carriers F. Galliano (1), N.P. Magnani (1), G. Minerva (1), A. Rolando (2), P. Zanini (3) (1) CSELT - Via G. Reiss Romoli, 274 - Torino
GSM Frequency Planning with Band Segregation for the Broadcast Channel Carriers F. Galliano (1), N.P. Magnani (1), G. Minerva (1), A. Rolando (2), P. Zanini (3) (1) CSELT - Via G. Reiss Romoli, 274 - Torino
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Traffic mining in a road-network: How does the
 82 Int. J. Business Intelligence and Data Mining, Vol. 3, No. 1, 2008 Traffic mining in a road-network: How does the traffic flow? Irene Ntoutsi Department of Informatics, University of Piraeus, Greece
82 Int. J. Business Intelligence and Data Mining, Vol. 3, No. 1, 2008 Traffic mining in a road-network: How does the traffic flow? Irene Ntoutsi Department of Informatics, University of Piraeus, Greece
AUTOMATIC ACCIDENT DETECTION AND AMBULANCE RESCUE WITH INTELLIGENT TRAFFIC LIGHT SYSTEM
 AUTOMATIC ACCIDENT DETECTION AND AMBULANCE RESCUE WITH INTELLIGENT TRAFFIC LIGHT SYSTEM Mr.S.Iyyappan 1, Mr.V.Nandagopal 2 P.G Scholar, Dept. of EEE, Ganadipathy Tulis s Jain Engineering College, Vellore,
AUTOMATIC ACCIDENT DETECTION AND AMBULANCE RESCUE WITH INTELLIGENT TRAFFIC LIGHT SYSTEM Mr.S.Iyyappan 1, Mr.V.Nandagopal 2 P.G Scholar, Dept. of EEE, Ganadipathy Tulis s Jain Engineering College, Vellore,
Flexible mobility management strategy in cellular networks
 Flexible mobility management strategy in cellular networks JAN GAJDORUS Department of informatics and telecommunications (161114) Czech technical university in Prague, Faculty of transportation sciences
Flexible mobility management strategy in cellular networks JAN GAJDORUS Department of informatics and telecommunications (161114) Czech technical university in Prague, Faculty of transportation sciences
Procedure for Marine Traffic Simulation with AIS Data
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 1 March 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.01.07 Procedure for Marine Traffic Simulation with
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 1 March 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.01.07 Procedure for Marine Traffic Simulation with
Estimation of Human Mobility Patterns and Attributes Analyzing Anonymized Mobile Phone CDR:
 Estimation of Human Mobility Patterns and Attributes Analyzing Anonymized Mobile Phone CDR: Developing Real-time Census from Crowds of Greater Dhaka Ayumi Arai 1 and Ryosuke Shibasaki 1,2 1 Department
Estimation of Human Mobility Patterns and Attributes Analyzing Anonymized Mobile Phone CDR: Developing Real-time Census from Crowds of Greater Dhaka Ayumi Arai 1 and Ryosuke Shibasaki 1,2 1 Department
Mobile Tracking and Resource Reservation Scheme for Cellular Networks
 Mobile Tracking and Resource Reservation Scheme for Cellular Networks Subbiah Shenbagaraman, B. Prabhakaran, S. Venkatesan Department of Computer Science, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, USA,
Mobile Tracking and Resource Reservation Scheme for Cellular Networks Subbiah Shenbagaraman, B. Prabhakaran, S. Venkatesan Department of Computer Science, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, USA,
Android Tablet GIS Solution Transforms Well Inspection for Bucks County Health Department
 Android Tablet GIS Solution Transforms Well Inspection for Bucks County Health Department A Case Study Problem Statement The Bureau of Environmental Health (BEH) within the Bucks County Health Department
Android Tablet GIS Solution Transforms Well Inspection for Bucks County Health Department A Case Study Problem Statement The Bureau of Environmental Health (BEH) within the Bucks County Health Department
Location enhanced Call Center and IVR Services Technical Insights about Your Calling Customer s Location
 Location enhanced Call Center and IVR Services Technical Insights about Your Calling Customer s Location Executive Summary Enterprise operations can save money and increase profits by enhancing service
Location enhanced Call Center and IVR Services Technical Insights about Your Calling Customer s Location Executive Summary Enterprise operations can save money and increase profits by enhancing service
Basic Network Design
 Frequency Reuse and Planning Cellular Technology enables mobile communication because they use of a complex two-way radio system between the mobile unit and the wireless network. It uses radio frequencies
Frequency Reuse and Planning Cellular Technology enables mobile communication because they use of a complex two-way radio system between the mobile unit and the wireless network. It uses radio frequencies
Hydrogeological Data Visualization
 Conference of Junior Researchers in Civil Engineering 209 Hydrogeological Data Visualization Boglárka Sárközi BME Department of Photogrammetry and Geoinformatics, e-mail: [email protected] Abstract
Conference of Junior Researchers in Civil Engineering 209 Hydrogeological Data Visualization Boglárka Sárközi BME Department of Photogrammetry and Geoinformatics, e-mail: [email protected] Abstract
ELEMENTS OF SURVEYING FOR CADASTRAL MAPPING
 ELEMENTS OF SURVEYING FOR CADASTRAL MAPPING Chapter 4 2015 Cadastral Mapping Manual 4-0 Elements of Surveying and Mapping Utah's system of land surveying is the rectangular survey system as set forth on
ELEMENTS OF SURVEYING FOR CADASTRAL MAPPING Chapter 4 2015 Cadastral Mapping Manual 4-0 Elements of Surveying and Mapping Utah's system of land surveying is the rectangular survey system as set forth on
Semi-Supervised Learning in Inferring Mobile Device Locations
 Semi-Supervised Learning in Inferring Mobile Device Locations Rong Duan, Olivia Hong, Guangqin Ma rduan,ohong,gma @research.att.com AT&T Labs 200 S Laurel Ave Middletown, NJ 07748 Abstract With the development
Semi-Supervised Learning in Inferring Mobile Device Locations Rong Duan, Olivia Hong, Guangqin Ma rduan,ohong,gma @research.att.com AT&T Labs 200 S Laurel Ave Middletown, NJ 07748 Abstract With the development
Planning of UMTS Cellular Networks for Data Services Based on HSDPA
 Planning of UMTS Cellular Networks for Data Services Based on HSDPA Diana Ladeira, Pedro Costa, Luís M. Correia 1, Luís Santo 2 1 IST/IT Technical University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal 2 Optimus, Lisbon,
Planning of UMTS Cellular Networks for Data Services Based on HSDPA Diana Ladeira, Pedro Costa, Luís M. Correia 1, Luís Santo 2 1 IST/IT Technical University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal 2 Optimus, Lisbon,
GENERAL INFORMATION ON GNSS AUGMENTATION SYSTEMS
 GENERAL INFORMATION ON GNSS AUGMENTATION SYSTEMS 1. INTRODUCTION Navigation technologies with precision approach and landing systems, for civilian and military purposes, enable aircrafts to perform their
GENERAL INFORMATION ON GNSS AUGMENTATION SYSTEMS 1. INTRODUCTION Navigation technologies with precision approach and landing systems, for civilian and military purposes, enable aircrafts to perform their
DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT
 270 COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT Degrees Offered: B.A., M.S. Chair: Liu, Shih-Sien ( 劉 士 仙 ) The Department Established in 1986, the Department of Transportation Management
270 COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT Degrees Offered: B.A., M.S. Chair: Liu, Shih-Sien ( 劉 士 仙 ) The Department Established in 1986, the Department of Transportation Management
Geospatial Data Integration
 Geospatial Data Integration 1. Research Team Project Leader: Other Faculty: Post Doc(s): Graduate Students: Industrial Partner(s): Prof. Craig Knoblock, Computer Science Prof. Cyrus Shahabi, Computer Science
Geospatial Data Integration 1. Research Team Project Leader: Other Faculty: Post Doc(s): Graduate Students: Industrial Partner(s): Prof. Craig Knoblock, Computer Science Prof. Cyrus Shahabi, Computer Science
MISSING NEIGHBOR ANALYSIS
 MISSING NEIGHBOR ANALYSIS For WiMAX networks? WIMAX HANDOVER TYPES MISSING NEIGHBORS HOW TO IDENTIFY MISSING NEIGHBORS 1. WiMAX Handovers All mobile wireless technologies require handovers to allow the
MISSING NEIGHBOR ANALYSIS For WiMAX networks? WIMAX HANDOVER TYPES MISSING NEIGHBORS HOW TO IDENTIFY MISSING NEIGHBORS 1. WiMAX Handovers All mobile wireless technologies require handovers to allow the
Automated Process for Generating Digitised Maps through GPS Data Compression
 Automated Process for Generating Digitised Maps through GPS Data Compression Stewart Worrall and Eduardo Nebot University of Sydney, Australia {s.worrall, e.nebot}@acfr.usyd.edu.au Abstract This paper
Automated Process for Generating Digitised Maps through GPS Data Compression Stewart Worrall and Eduardo Nebot University of Sydney, Australia {s.worrall, e.nebot}@acfr.usyd.edu.au Abstract This paper
Cell Phone Towers. Finding the Best Place For a New Cell Tower in Marblehead by Daniel Hudson
 Cell Phone Towers Finding the Best Place For a New Cell Tower in Marblehead by Daniel Hudson Types of Cell Towers The first tower is used to transmit data to other towers and to provide people with cellular
Cell Phone Towers Finding the Best Place For a New Cell Tower in Marblehead by Daniel Hudson Types of Cell Towers The first tower is used to transmit data to other towers and to provide people with cellular
Vehicle Scrutinizing using GPS & GSM Technologies Implemented with Ardunio controller
 Vehicle Scrutinizing using GPS & GSM Technologies Implemented with Ardunio controller A.Kalaiarasi 1, Raviram.P 2, Prabakaran. P M 3, ShanthoshKumar.K 4, Dheeraj B P 5 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE,
Vehicle Scrutinizing using GPS & GSM Technologies Implemented with Ardunio controller A.Kalaiarasi 1, Raviram.P 2, Prabakaran. P M 3, ShanthoshKumar.K 4, Dheeraj B P 5 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE,
Implementation of a Lightweight Service Advertisement and Discovery Protocol for Mobile Ad hoc Networks
 Implementation of a Lightweight Advertisement and Discovery Protocol for Mobile Ad hoc Networks Wenbin Ma * Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 19 Memorial Drive West, Lehigh University Bethlehem,
Implementation of a Lightweight Advertisement and Discovery Protocol for Mobile Ad hoc Networks Wenbin Ma * Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 19 Memorial Drive West, Lehigh University Bethlehem,
Integrating Data from Maps on the World-Wide Web
 Integrating Data from Maps on the World-Wide Web Eliyahu Safra 1, Yaron Kanza 2, Yehoshua Sagiv 3, and Yerach Doytsher 1 1 Department of Transportation and Geo-Information, Technion, Haifa, Israel {safra,
Integrating Data from Maps on the World-Wide Web Eliyahu Safra 1, Yaron Kanza 2, Yehoshua Sagiv 3, and Yerach Doytsher 1 1 Department of Transportation and Geo-Information, Technion, Haifa, Israel {safra,
Efficient Data Replication Scheme based on Hadoop Distributed File System
 , pp. 177-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.12.16 Efficient Data Replication Scheme based on Hadoop Distributed File System Jungha Lee 1, Jaehwa Chung 2 and Daewon Lee 3* 1 Division of Supercomputing,
, pp. 177-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.12.16 Efficient Data Replication Scheme based on Hadoop Distributed File System Jungha Lee 1, Jaehwa Chung 2 and Daewon Lee 3* 1 Division of Supercomputing,
Oracle8i Spatial: Experiences with Extensible Databases
 Oracle8i Spatial: Experiences with Extensible Databases Siva Ravada and Jayant Sharma Spatial Products Division Oracle Corporation One Oracle Drive Nashua NH-03062 {sravada,jsharma}@us.oracle.com 1 Introduction
Oracle8i Spatial: Experiences with Extensible Databases Siva Ravada and Jayant Sharma Spatial Products Division Oracle Corporation One Oracle Drive Nashua NH-03062 {sravada,jsharma}@us.oracle.com 1 Introduction
A Novel Decentralized Time Slot Allocation Algorithm in Dynamic TDD System
 A Novel Decentralized Time Slot Allocation Algorithm in Dynamic TDD System Young Sil Choi Email: [email protected] Illsoo Sohn Email: [email protected] Kwang Bok Lee Email: [email protected] Abstract
A Novel Decentralized Time Slot Allocation Algorithm in Dynamic TDD System Young Sil Choi Email: [email protected] Illsoo Sohn Email: [email protected] Kwang Bok Lee Email: [email protected] Abstract
D A T A M I N I N G C L A S S I F I C A T I O N
 D A T A M I N I N G C L A S S I F I C A T I O N FABRICIO VOZNIKA LEO NARDO VIA NA INTRODUCTION Nowadays there is huge amount of data being collected and stored in databases everywhere across the globe.
D A T A M I N I N G C L A S S I F I C A T I O N FABRICIO VOZNIKA LEO NARDO VIA NA INTRODUCTION Nowadays there is huge amount of data being collected and stored in databases everywhere across the globe.
1.1 OVERVIEW OF THE DOCUMENT 1.2 BACKGROUND TO THE PROJECT
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 OVERVIEW OF THE DOCUMENT This project thesis examines the task of learning to develop a cost-effective vehicle movement tracking system for companies to track their vehicles.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 OVERVIEW OF THE DOCUMENT This project thesis examines the task of learning to develop a cost-effective vehicle movement tracking system for companies to track their vehicles.
Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) Technology
 Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) Technology Dai Kimura Hiroyuki Seki Long Term Evolution (LTE) is a promising standard for next-generation cellular systems targeted to have a peak downlink bit
Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) Technology Dai Kimura Hiroyuki Seki Long Term Evolution (LTE) is a promising standard for next-generation cellular systems targeted to have a peak downlink bit
Study and Calculation of Travel Time Reliability Measures
 Center for Applied Demography & Survey Research University of Delaware Study and Calculation of Travel Time Reliability Measures by David P. Racca Daniel T. Brown Prepared for the Delaware Department of
Center for Applied Demography & Survey Research University of Delaware Study and Calculation of Travel Time Reliability Measures by David P. Racca Daniel T. Brown Prepared for the Delaware Department of
Real Time Bus Monitoring System by Sharing the Location Using Google Cloud Server Messaging
 Real Time Bus Monitoring System by Sharing the Location Using Google Cloud Server Messaging Aravind. P, Kalaiarasan.A 2, D. Rajini Girinath 3 PG Student, Dept. of CSE, Anand Institute of Higher Technology,
Real Time Bus Monitoring System by Sharing the Location Using Google Cloud Server Messaging Aravind. P, Kalaiarasan.A 2, D. Rajini Girinath 3 PG Student, Dept. of CSE, Anand Institute of Higher Technology,
Dr. Akram Aburas Advanced Communications & Electronics Systems Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Remote Monitoring Using Wireless Cellular Networks Dr. Akram Aburas Advanced Communications & Electronics Systems Prof. Khalid Al-Mashouq Electrical Engineering Department, King Saud University, Dr. Zeyad
Remote Monitoring Using Wireless Cellular Networks Dr. Akram Aburas Advanced Communications & Electronics Systems Prof. Khalid Al-Mashouq Electrical Engineering Department, King Saud University, Dr. Zeyad
An in-building multi-server cloud system based on shortest Path algorithm depending on the distance and measured Signal strength
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 1, Ver. I (Jan Feb. 2015), PP 38-42 www.iosrjournals.org An in-building multi-server cloud system based
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 1, Ver. I (Jan Feb. 2015), PP 38-42 www.iosrjournals.org An in-building multi-server cloud system based
A Virtual Machine Searching Method in Networks using a Vector Space Model and Routing Table Tree Architecture
 A Virtual Machine Searching Method in Networks using a Vector Space Model and Routing Table Tree Architecture Hyeon seok O, Namgi Kim1, Byoung-Dai Lee dept. of Computer Science. Kyonggi University, Suwon,
A Virtual Machine Searching Method in Networks using a Vector Space Model and Routing Table Tree Architecture Hyeon seok O, Namgi Kim1, Byoung-Dai Lee dept. of Computer Science. Kyonggi University, Suwon,
On the effect of forwarding table size on SDN network utilization
 IBM Haifa Research Lab On the effect of forwarding table size on SDN network utilization Rami Cohen IBM Haifa Research Lab Liane Lewin Eytan Yahoo Research, Haifa Seffi Naor CS Technion, Israel Danny Raz
IBM Haifa Research Lab On the effect of forwarding table size on SDN network utilization Rami Cohen IBM Haifa Research Lab Liane Lewin Eytan Yahoo Research, Haifa Seffi Naor CS Technion, Israel Danny Raz
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Engineering & Technology (IJARCET) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2014
 Real Time Wireless based Train Tracking, Track Identification and Collision avoidance System for Railway Sectors 1 R. Immanuel Rajkumar, 2 Dr.P. E. Sankaranarayanan, and 3 Dr.G.Sundari 1 Research Scholar,
Real Time Wireless based Train Tracking, Track Identification and Collision avoidance System for Railway Sectors 1 R. Immanuel Rajkumar, 2 Dr.P. E. Sankaranarayanan, and 3 Dr.G.Sundari 1 Research Scholar,
IMPACT OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS IN MANAGING CLOUD APPLICATION
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE IMPACT OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS IN MANAGING CLOUD APPLICATION N.Vijaya Sunder Sagar 1, M.Dileep Kumar 2, M.Nagesh 3, Lunavath Gandhi
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE IMPACT OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS IN MANAGING CLOUD APPLICATION N.Vijaya Sunder Sagar 1, M.Dileep Kumar 2, M.Nagesh 3, Lunavath Gandhi
The Vertical Handoff Algorithm using Fuzzy Decisions in Cellular Phone Networks
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering, 2(), 200, pp. 29-34 The Vertical Handoff Algorithm using Fuzzy Decisions in Cellular Phone Networks Chandrashekhar G.Patil & R.D.Kharadkar 2 Department
International Journal of Electronics Engineering, 2(), 200, pp. 29-34 The Vertical Handoff Algorithm using Fuzzy Decisions in Cellular Phone Networks Chandrashekhar G.Patil & R.D.Kharadkar 2 Department
COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS
 COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS B.K. Mohan and S. N. Ladha Centre for Studies in Resources Engineering IIT
COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS B.K. Mohan and S. N. Ladha Centre for Studies in Resources Engineering IIT
CHAPTER 3 AVI TRAVEL TIME DATA COLLECTION
 CHAPTER 3 AVI TRAVEL TIME DATA COLLECTION 3.1 - Introduction Travel time information is becoming more important for applications ranging from congestion measurement to real-time travel information. Several
CHAPTER 3 AVI TRAVEL TIME DATA COLLECTION 3.1 - Introduction Travel time information is becoming more important for applications ranging from congestion measurement to real-time travel information. Several
A WEB-BASED TRAFFIC INFORMATION SYSTEM USING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES
 Advanced OR and AI Methods in Transportation A WEB-BASED TRAFFIC INFORMATION SYSTEM USING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES Akmal ABDELFATAH 1, Abdul-Rahman AL-ALI 2 Abstract. This paper presents a procedure
Advanced OR and AI Methods in Transportation A WEB-BASED TRAFFIC INFORMATION SYSTEM USING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES Akmal ABDELFATAH 1, Abdul-Rahman AL-ALI 2 Abstract. This paper presents a procedure
System Design in Wireless Communication. Ali Khawaja
 System Design in Wireless Communication Ali Khawaja University of Texas at Dallas December 6, 1999 1 Abstract This paper deals with the micro and macro aspects of a wireless system design. With the growing
System Design in Wireless Communication Ali Khawaja University of Texas at Dallas December 6, 1999 1 Abstract This paper deals with the micro and macro aspects of a wireless system design. With the growing
VEHICLE TRACKING SYSTEM
 Real-Time Vehicle tracking solution Vehicle tracking solution enables to monitor the entire fleet in transit spread across India, which can be monitored from a central location. These locations are subject
Real-Time Vehicle tracking solution Vehicle tracking solution enables to monitor the entire fleet in transit spread across India, which can be monitored from a central location. These locations are subject
Flexible Deterministic Packet Marking: An IP Traceback Scheme Against DDOS Attacks
 Flexible Deterministic Packet Marking: An IP Traceback Scheme Against DDOS Attacks Prashil S. Waghmare PG student, Sinhgad College of Engineering, Vadgaon, Pune University, Maharashtra, India. [email protected]
Flexible Deterministic Packet Marking: An IP Traceback Scheme Against DDOS Attacks Prashil S. Waghmare PG student, Sinhgad College of Engineering, Vadgaon, Pune University, Maharashtra, India. [email protected]
Social Influence Analysis in Social Networking Big Data: Opportunities and Challenges. Presenter: Sancheng Peng Zhaoqing University
 Social Influence Analysis in Social Networking Big Data: Opportunities and Challenges Presenter: Sancheng Peng Zhaoqing University 1 2 3 4 35 46 7 Contents Introduction Relationship between SIA and BD
Social Influence Analysis in Social Networking Big Data: Opportunities and Challenges Presenter: Sancheng Peng Zhaoqing University 1 2 3 4 35 46 7 Contents Introduction Relationship between SIA and BD
How To Use Vehicle Gps Data To Understand Travel Time And Speed In Delaware
 USE OF STATE FLEET VEHICLE GPS DATA FOR TRAVEL TIME ANALYSIS David P. Racca Center for Applied Demography and Survey Research (CADSR) University of Delaware Graham Hall, Rm 284, Newark, Delaware 19716
USE OF STATE FLEET VEHICLE GPS DATA FOR TRAVEL TIME ANALYSIS David P. Racca Center for Applied Demography and Survey Research (CADSR) University of Delaware Graham Hall, Rm 284, Newark, Delaware 19716
Mobile Node Localization Using Cooperation and Static Beacons
 Mobile Node Localization Using Cooperation and Static Beacons Troy Johnson Department of Computer Science Central Michigan University Mount Pleasant, MI 8859 [email protected] Patrick Seeling Department
Mobile Node Localization Using Cooperation and Static Beacons Troy Johnson Department of Computer Science Central Michigan University Mount Pleasant, MI 8859 [email protected] Patrick Seeling Department
Bi-Directional DGPS for Range Safety Applications
 Bi-Directional DGPS for Range Safety Applications Ranjeet Shetty 234-A, Avionics Engineering Center, Russ College of Engineering and Technology, Ohio University Advisor: Dr. Chris Bartone Outline Background
Bi-Directional DGPS for Range Safety Applications Ranjeet Shetty 234-A, Avionics Engineering Center, Russ College of Engineering and Technology, Ohio University Advisor: Dr. Chris Bartone Outline Background
MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY ON MANSOURA UNIVERSITY, EGYPT
 MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY ON MANSOURA UNIVERSITY, EGYPT Asmaa Ahmed Hussein 1, Elkhedr Hassan Eibrahim 2, Aziza Asem 1 1 Faculty of Computer Sciences and information systems,
MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS: A CASE STUDY ON MANSOURA UNIVERSITY, EGYPT Asmaa Ahmed Hussein 1, Elkhedr Hassan Eibrahim 2, Aziza Asem 1 1 Faculty of Computer Sciences and information systems,
BR Workshop on the efficient use of the spectrum/orbit resource (Geneva, 6 May 2009)
 BR Workshop on the efficient use of the spectrum/orbit resource (Geneva, 6 May 2009) Spectrum inefficiencies resulting from the claimed use of steerable beams, multiple beams or large coverage area beams
BR Workshop on the efficient use of the spectrum/orbit resource (Geneva, 6 May 2009) Spectrum inefficiencies resulting from the claimed use of steerable beams, multiple beams or large coverage area beams
INSTITUTE OF HUMAN RESOURSE ADVANCEMENT (IHRA) UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO. M. Sc. in Geoinformatics 2014/2015
 INSTITUTE OF HUMAN RESOURSE ADVANCEMENT (IHRA) UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO Introduction M. Sc. in Geoinformatics 2014/2015 Course Conducted by the -IHRA, University of Colombo The Master of Science in Geoinformatics
INSTITUTE OF HUMAN RESOURSE ADVANCEMENT (IHRA) UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO Introduction M. Sc. in Geoinformatics 2014/2015 Course Conducted by the -IHRA, University of Colombo The Master of Science in Geoinformatics
GPS Based Low Cost Intelligent Vehicle Tracking System (IVTS)
 2012 International Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering (ICTTE 2012) IPCSIT vol. 26 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore GPS Based Low Cost Intelligent Vehicle Tracking System (IVTS) Dr.
2012 International Conference on Traffic and Transportation Engineering (ICTTE 2012) IPCSIT vol. 26 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore GPS Based Low Cost Intelligent Vehicle Tracking System (IVTS) Dr.
How To Understand And Understand The Power Of A Cdma/Ds System
 CDMA Technology : Pr. Dr. W. Skupin www.htwg-konstanz.de Pr. S. Flament www.greyc.fr/user/99 On line Course on CDMA Technology CDMA Technology : Introduction to Spread Spectrum Technology CDMA / DS : Principle
CDMA Technology : Pr. Dr. W. Skupin www.htwg-konstanz.de Pr. S. Flament www.greyc.fr/user/99 On line Course on CDMA Technology CDMA Technology : Introduction to Spread Spectrum Technology CDMA / DS : Principle
Use of a Web-Based GIS for Real-Time Traffic Information Fusion and Presentation over the Internet
 Use of a Web-Based GIS for Real-Time Traffic Information Fusion and Presentation over the Internet SUMMARY Dimitris Kotzinos 1, Poulicos Prastacos 2 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Crete
Use of a Web-Based GIS for Real-Time Traffic Information Fusion and Presentation over the Internet SUMMARY Dimitris Kotzinos 1, Poulicos Prastacos 2 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Crete
Verizon Wireless Family Locator 4.9 User Guide Contents
 Verizon Wireless Family Locator.9 User Guide Contents Let s get started... Sign up, then activate phones!... Use the Activation Wizard... Set Up an Android... Set Up a BlackBerry... 6 Set Up a Feature...
Verizon Wireless Family Locator.9 User Guide Contents Let s get started... Sign up, then activate phones!... Use the Activation Wizard... Set Up an Android... Set Up a BlackBerry... 6 Set Up a Feature...
BTS Backhaul by Satellite
 BTS Backhaul by Satellite Improving QoS & Optimizing Bandwidth The Mobile Market is experiencing solid growth in emerging countries. As an illustration, GSMA predicts the number of connections in Africa
BTS Backhaul by Satellite Improving QoS & Optimizing Bandwidth The Mobile Market is experiencing solid growth in emerging countries. As an illustration, GSMA predicts the number of connections in Africa
Random Map Generator v1.0 User s Guide
 Random Map Generator v1.0 User s Guide Jonathan Teutenberg 2003 1 Map Generation Overview...4 1.1 Command Line...4 1.2 Operation Flow...4 2 Map Initialisation...5 2.1 Initialisation Parameters...5 -w xxxxxxx...5
Random Map Generator v1.0 User s Guide Jonathan Teutenberg 2003 1 Map Generation Overview...4 1.1 Command Line...4 1.2 Operation Flow...4 2 Map Initialisation...5 2.1 Initialisation Parameters...5 -w xxxxxxx...5
Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field
 Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field Umut G. SEFERCIK, Murat ORUC and Mehmet ALKAN, Turkey Key words: Image Processing, Information Content, Image Understanding,
Adaptation of High Resolution Ikonos Images to Googleearth for Zonguldak Test Field Umut G. SEFERCIK, Murat ORUC and Mehmet ALKAN, Turkey Key words: Image Processing, Information Content, Image Understanding,
GEO-SPATIAL-TECHNOLOGIES", a trans-university new integrative master degree
 GEO-SPATIAL-TECHNOLOGIES", a trans-university new integrative master degree Wolfgang Sulzer Institute for Geography and Regional Science University of Graz, Austria Heinrichstrasse 36 A-8010 Graz, Austria
GEO-SPATIAL-TECHNOLOGIES", a trans-university new integrative master degree Wolfgang Sulzer Institute for Geography and Regional Science University of Graz, Austria Heinrichstrasse 36 A-8010 Graz, Austria
Mobile Adaptive Opportunistic Junction for Health Care Networking in Different Geographical Region
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 113-118 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Mobile
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 113-118 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Mobile
Keywords: Mobility Prediction, Location Prediction, Data Mining etc
 Volume 4, Issue 4, April 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Data Mining Approach
Volume 4, Issue 4, April 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Data Mining Approach
