Introduction to Game Theory IIIii. Payoffs: Probability and Expected Utility
|
|
|
- Veronica Watkins
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Game Theory IIIii Payoffs: Probability and Expected Utility Lecture Summary 1. Introduction 2. Probability Theory 3. Expected Values and Expected Utility.
2 1. Introduction We continue further discussion of characterizing payoffs in games. In many situations, players are confronted with uncertainty. We need to be able to describe their preferences over uncertain outcomes The standard economic tool is Expected Utility. We also need tools to describe how they learn over the play of a game The tool we use for this is Probability Theory. 2. Probability and Uncertainty
3 Probabilities We use the notion of probabilities to formalize the notion that many aspects of life are uncertain. to define probabilities, we need first to describe everything that might possibly occur (the Sample Space ) the Sample Space is a set of elements called events or outcomes. For example, the sample space for flipping a coin is {H,T} The sample space for a simplified weather prediction might be {sunny, cloudy, rainy, snowy}. It is important to note that a sample space must include all possible outcomes. Therefore in the weather example, I have either ruled out sleet or included it in rainy. Probabilities: Addition Rule This leads directly into a computation rule that partly helps us figure out the likelihood that sets of events occur. (That is, A OR B take place.) the probability that two or more non-overlapping (disjoint) sets of events occurs can be computed by adding up the individual probabilities. Example: Two (fair) coin tosses SS={HH,HT,TH,TT}. What is the probability of seeing at least one H?
4 Probabilities: Addition Rule There are three distinct events in which an H occurs, {HH,HT,TH,TT}. The probability that an H occurs is =.75. (Prob HH OR HT OR TH). The probability that a repeated H OR a repeated T occurs is =.5 Note: This rule ONLY works if the set of events are disjoint. (The event HH is distinct from any of the events, HT and TH.) The set of events, at least one H, and the set of events, first and last flips repeat are {HH,HT,TH,TT} and {HH,TT}. What is the probability that either of these sets occur? Modified Addition Rule Modified addition rule: If the two or more events are overlapping, we need to subtract the probability of the overlapping event to avoid double-counting. Example: The probability of drawing an ace is 1/13=4/52. The probability of drawing a spade is 1/4 =13/52. What is the probability of drawing an ace OR a spade?
5 Modified Addition Rule Answer: It is possible that when we draw a spade we draw the ace of spades. So adding 4/52+13/52=17/52 would cause us to double count. The probability of drawing the ace of spades is 1/52. Therefore, the correct probability is Prob[Ace]+Prob[Spade]-Prob[Ace and Space]= 4/52+13/52-1/52. Answer to past slide Prob[At least one H AND Repeat]=1/4. Therefore, Prob[At least one H OR Repeat]=3/4+1/2-1/4=1. Why? The Multiplication Rule A set of events, A is independent of another set of events, B if the probability A occurs is the same whether or not B is known to have occurred. The probability of multiple independent events is the product of the individual probabilities. Example: The probability that a head and then a tail occurs in two independent tosses of a fair coin is.5*.5=.25. The probability of drawing two hearts in a row (after replacing the first card) is 1/52*1/52.
6 Modified Multiplication Rule: Many sets of events are NOT independent, however. Suppose that the probability of rain given it is cloudy is 1/3. (The conditional probability of rain given clouds.) We can write this as 1/3=Prob[Rain Cloud]. Suppose that the unconditional probability of clouds is 1/2. That is, 1/2 = Prob[Cloud]. Suppose that the unconditional probability of rain is 1/4. That is, 1/4 = Prob[Rain]. Since 1/4 is not equal to 1/3, the two events, Rain and Cloudy are not independent. Modified Multiplication Rule: What is the probability that it both rains AND is cloudy? Prob[Clouds AND Rain]=Prob[Clouds]*Prob[Rain Cloudy] =1/2*1/3=1/6. General: If X=Y AND Z, Prob[X]=ProbY*Prob[Z Y].
7 Modified Multiplication Rule: Bayes Rule Note that we can use this rule to derive another important rule -- Bayes Rule. This rule tells us the reverse conditional probability. Prob[Cloudy Rain] Answer: We need to know the unconditional probability of rain, say it is 1/4. We apply our earlier result two different ways to tell us : Prob[Clouds AND Rain]=Prob[Clouds]*Prob[Rain Clouds] and Prob[Clouds AND Rain]=Prob[Rain]*Prob[Clouds Rain] Modified Multiplication Rule: Bayes Rule We can combine these to get Prob[Clouds]*Prob[Rain Clouds]=Prob[Rain]*Prob[Clouds Rain] Substituting in gives 1/2*1/3=1/4* Prob[Clouds Rain] or 2/3= Prob[Clouds Rain]. That is, 2/3 of the time that it rains, it is cloudy. more generally ProbY*Prob[Z Y] = ProbZ*Prob[Y Z]. This is the general form of Bayes Rule.
8 An Example of Using Bayes Rule Suppose you are a manager who hires a worker. The worker is drawn from a labor pool 25% of which are lazy and never work hard, 75% always work hard. You do not see how hard the worker works but, if he works hard, you get high profits with 8%. If he does not work hard, you get high profits with 2%. Suppose you experience high profits. What is the probability the worker is lazy? An Example of Using Bayes Rule Answer: We are looking for Prob[Lazy High]. Bayes rule says Prob[H]*Prob[L H]=Prob[L]*Prob[H L]. Using the data from the problem,.65prob[l H]=.25*.2=.5. (Where does the 65% come from?) Therefore, the likelihood the worker is lazy has fallen to 7.7%. Is this reasonable? Should you fire the worker? Redo the problem with Prob[H NL]=.6.
9 3. Expected Value and Expected Utility Expected Value Suppose that a set of random events can be expressed as real numbers: Example -- SS={1,3,5}, and the associated probabilities are 1/4,1/3,5/12. The expected value (or mean or average) of these random events is the sum of the values each multiplied by its probability -- EV=1/4*1+1/3*3+5/12*5 =4/12. Example: Suppose that a lottery offers a one in 5 million chance at $1 Million. The expected value of the lottery is (1/5M)*$1M=$2.
10 Expected Utility If people do not value money one for one, then the expected utility or value they place on a lottery will be different than the expected value of the lottery itself. Example: Suppose the utility from $1M is approximately 5M utility points and the utility from $1.5 is 1.25 utility points. Should I pay $1.5 for the lottery ticket? Answer: Expected utility from the ticket=1/5m*5m +=1 utility point Expected utility from $1.5 (which I have for sure if I do not buy the ticket) =1.25 utility points. Don t buy the ticket. A consumer like this exhibits risk aversion: the expected utility from the gamble (1) is less than the expected value of the gamble (2). In Game Theory, we interpret payoffs in games in expected utility terms. Expected Utility Ranking gambles (or lotteries) Gamble A Gamble B Which is better? 1.5 $45 $1 vs..5 $ Definition of expected utility Desirable properties of expected utility rationality (consistency) monotonicity (more is better) measurability (any two gambles can be ranked)
11 Three Attitudes towards risk The main attitudes risk neutral risk averse risk seeking An individual is said to be risk neutral if she is indifferent between accepting a gamble and a certain payment which equals the expected value of the gamble. An individual is said to be risk averse if she is strictly prefers a certain payment which equals the expected value of a gamble to the gamble itself. An individual is risk averse if the marginal gain from an extra dollar declines as she gets more dollars. (The utility function is concave.) Risk seeking? We typically expect individuals (firms?) to be risk neutral or risk averse. Small Business, imperfect information 5, g a p(good) 1 Not 1, p(bad) b Not 1,
12 Small Business, risk-neutral player u(x) = x g 5K a.2 1 Not 1K.8 b Not 1K Small Business, risk-averse player u(x) = x ½ g a.2 1 Not 1.8 b Not 1
13 Small Business, risk-seeking player u(x) = ½ x 2 g a.2 1 Not b Not 1
Choice Under Uncertainty
 Decision Making Under Uncertainty Choice Under Uncertainty Econ 422: Investment, Capital & Finance University of ashington Summer 2006 August 15, 2006 Course Chronology: 1. Intertemporal Choice: Exchange
Decision Making Under Uncertainty Choice Under Uncertainty Econ 422: Investment, Capital & Finance University of ashington Summer 2006 August 15, 2006 Course Chronology: 1. Intertemporal Choice: Exchange
.4 120 +.1 80 +.5 100 = 48 + 8 + 50 = 106.
 Chapter 16. Risk and Uncertainty Part A 2009, Kwan Choi Expected Value X i = outcome i, p i = probability of X i EV = pix For instance, suppose a person has an idle fund, $100, for one month, and is considering
Chapter 16. Risk and Uncertainty Part A 2009, Kwan Choi Expected Value X i = outcome i, p i = probability of X i EV = pix For instance, suppose a person has an idle fund, $100, for one month, and is considering
Choice Under Uncertainty Insurance Diversification & Risk Sharing AIG. Uncertainty
 Uncertainty Table of Contents 1 Choice Under Uncertainty Budget Constraint Preferences 2 Insurance Choice Framework Expected Utility Theory 3 Diversification & Risk Sharing 4 AIG States of Nature and Contingent
Uncertainty Table of Contents 1 Choice Under Uncertainty Budget Constraint Preferences 2 Insurance Choice Framework Expected Utility Theory 3 Diversification & Risk Sharing 4 AIG States of Nature and Contingent
Lecture 11 Uncertainty
 Lecture 11 Uncertainty 1. Contingent Claims and the State-Preference Model 1) Contingent Commodities and Contingent Claims Using the simple two-good model we have developed throughout this course, think
Lecture 11 Uncertainty 1. Contingent Claims and the State-Preference Model 1) Contingent Commodities and Contingent Claims Using the simple two-good model we have developed throughout this course, think
Demand and supply of health insurance. Folland et al Chapter 8
 Demand and supply of health Folland et al Chapter 8 Chris Auld Economics 317 February 9, 2011 What is insurance? From an individual s perspective, insurance transfers wealth from good states of the world
Demand and supply of health Folland et al Chapter 8 Chris Auld Economics 317 February 9, 2011 What is insurance? From an individual s perspective, insurance transfers wealth from good states of the world
Decision Making Under Uncertainty. Professor Peter Cramton Economics 300
 Decision Making Under Uncertainty Professor Peter Cramton Economics 300 Uncertainty Consumers and firms are usually uncertain about the payoffs from their choices Example 1: A farmer chooses to cultivate
Decision Making Under Uncertainty Professor Peter Cramton Economics 300 Uncertainty Consumers and firms are usually uncertain about the payoffs from their choices Example 1: A farmer chooses to cultivate
Choice under Uncertainty
 Choice under Uncertainty Part 1: Expected Utility Function, Attitudes towards Risk, Demand for Insurance Slide 1 Choice under Uncertainty We ll analyze the underlying assumptions of expected utility theory
Choice under Uncertainty Part 1: Expected Utility Function, Attitudes towards Risk, Demand for Insurance Slide 1 Choice under Uncertainty We ll analyze the underlying assumptions of expected utility theory
1 Uncertainty and Preferences
 In this chapter, we present the theory of consumer preferences on risky outcomes. The theory is then applied to study the demand for insurance. Consider the following story. John wants to mail a package
In this chapter, we present the theory of consumer preferences on risky outcomes. The theory is then applied to study the demand for insurance. Consider the following story. John wants to mail a package
Econ 132 C. Health Insurance: U.S., Risk Pooling, Risk Aversion, Moral Hazard, Rand Study 7
 Econ 132 C. Health Insurance: U.S., Risk Pooling, Risk Aversion, Moral Hazard, Rand Study 7 C2. Health Insurance: Risk Pooling Health insurance works by pooling individuals together to reduce the variability
Econ 132 C. Health Insurance: U.S., Risk Pooling, Risk Aversion, Moral Hazard, Rand Study 7 C2. Health Insurance: Risk Pooling Health insurance works by pooling individuals together to reduce the variability
Chapter 7 Probability. Example of a random circumstance. Random Circumstance. What does probability mean?? Goals in this chapter
 Homework (due Wed, Oct 27) Chapter 7: #17, 27, 28 Announcements: Midterm exams keys on web. (For a few hours the answer to MC#1 was incorrect on Version A.) No grade disputes now. Will have a chance to
Homework (due Wed, Oct 27) Chapter 7: #17, 27, 28 Announcements: Midterm exams keys on web. (For a few hours the answer to MC#1 was incorrect on Version A.) No grade disputes now. Will have a chance to
Basic Probability. Probability: The part of Mathematics devoted to quantify uncertainty
 AMS 5 PROBABILITY Basic Probability Probability: The part of Mathematics devoted to quantify uncertainty Frequency Theory Bayesian Theory Game: Playing Backgammon. The chance of getting (6,6) is 1/36.
AMS 5 PROBABILITY Basic Probability Probability: The part of Mathematics devoted to quantify uncertainty Frequency Theory Bayesian Theory Game: Playing Backgammon. The chance of getting (6,6) is 1/36.
Economics 1011a: Intermediate Microeconomics
 Lecture 12: More Uncertainty Economics 1011a: Intermediate Microeconomics Lecture 12: More on Uncertainty Thursday, October 23, 2008 Last class we introduced choice under uncertainty. Today we will explore
Lecture 12: More Uncertainty Economics 1011a: Intermediate Microeconomics Lecture 12: More on Uncertainty Thursday, October 23, 2008 Last class we introduced choice under uncertainty. Today we will explore
Economics 1011a: Intermediate Microeconomics
 Lecture 11: Choice Under Uncertainty Economics 1011a: Intermediate Microeconomics Lecture 11: Choice Under Uncertainty Tuesday, October 21, 2008 Last class we wrapped up consumption over time. Today we
Lecture 11: Choice Under Uncertainty Economics 1011a: Intermediate Microeconomics Lecture 11: Choice Under Uncertainty Tuesday, October 21, 2008 Last class we wrapped up consumption over time. Today we
Homework Assignment #2: Answer Key
 Homework Assignment #2: Answer Key Chapter 4: #3 Assuming that the current interest rate is 3 percent, compute the value of a five-year, 5 percent coupon bond with a face value of $,000. What happens if
Homework Assignment #2: Answer Key Chapter 4: #3 Assuming that the current interest rate is 3 percent, compute the value of a five-year, 5 percent coupon bond with a face value of $,000. What happens if
Decision Making under Uncertainty
 6.825 Techniques in Artificial Intelligence Decision Making under Uncertainty How to make one decision in the face of uncertainty Lecture 19 1 In the next two lectures, we ll look at the question of how
6.825 Techniques in Artificial Intelligence Decision Making under Uncertainty How to make one decision in the face of uncertainty Lecture 19 1 In the next two lectures, we ll look at the question of how
Fundamentals of Decision Theory
 Fundamentals of Decision Theory Chapter 16 Mausam (Based on slides of someone from NPS, Maria Fasli) Decision Theory an analytic and systematic approach to the study of decision making Good decisions:
Fundamentals of Decision Theory Chapter 16 Mausam (Based on slides of someone from NPS, Maria Fasli) Decision Theory an analytic and systematic approach to the study of decision making Good decisions:
Risk and Uncertainty. Vani K Borooah University of Ulster
 Risk and Uncertainty Vani K Borooah University of Ulster Basic Concepts Gamble: An action with more than one possible outcome, such that with each outcome there is an associated probability of that outcome
Risk and Uncertainty Vani K Borooah University of Ulster Basic Concepts Gamble: An action with more than one possible outcome, such that with each outcome there is an associated probability of that outcome
Applied Economics For Managers Recitation 5 Tuesday July 6th 2004
 Applied Economics For Managers Recitation 5 Tuesday July 6th 2004 Outline 1 Uncertainty and asset prices 2 Informational efficiency - rational expectations, random walks 3 Asymmetric information - lemons,
Applied Economics For Managers Recitation 5 Tuesday July 6th 2004 Outline 1 Uncertainty and asset prices 2 Informational efficiency - rational expectations, random walks 3 Asymmetric information - lemons,
Decision & Risk Analysis Lecture 6. Risk and Utility
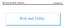 Risk and Utility Risk - Introduction Payoff Game 1 $14.50 0.5 0.5 $30 - $1 EMV 30*0.5+(-1)*0.5= 14.5 Game 2 Which game will you play? Which game is risky? $50.00 Figure 13.1 0.5 0.5 $2,000 - $1,900 EMV
Risk and Utility Risk - Introduction Payoff Game 1 $14.50 0.5 0.5 $30 - $1 EMV 30*0.5+(-1)*0.5= 14.5 Game 2 Which game will you play? Which game is risky? $50.00 Figure 13.1 0.5 0.5 $2,000 - $1,900 EMV
Intermediate Micro. Expected Utility
 Intermediate Micro Expected Utility Workhorse model of intermediate micro Utility maximization problem Consumers Max U(x,y) subject to the budget constraint, I=P x x + P y y Health Economics Spring 2015
Intermediate Micro Expected Utility Workhorse model of intermediate micro Utility maximization problem Consumers Max U(x,y) subject to the budget constraint, I=P x x + P y y Health Economics Spring 2015
MA 1125 Lecture 14 - Expected Values. Friday, February 28, 2014. Objectives: Introduce expected values.
 MA 5 Lecture 4 - Expected Values Friday, February 2, 24. Objectives: Introduce expected values.. Means, Variances, and Standard Deviations of Probability Distributions Two classes ago, we computed the
MA 5 Lecture 4 - Expected Values Friday, February 2, 24. Objectives: Introduce expected values.. Means, Variances, and Standard Deviations of Probability Distributions Two classes ago, we computed the
AMS 5 CHANCE VARIABILITY
 AMS 5 CHANCE VARIABILITY The Law of Averages When tossing a fair coin the chances of tails and heads are the same: 50% and 50%. So if the coin is tossed a large number of times, the number of heads and
AMS 5 CHANCE VARIABILITY The Law of Averages When tossing a fair coin the chances of tails and heads are the same: 50% and 50%. So if the coin is tossed a large number of times, the number of heads and
Lecture 13. Understanding Probability and Long-Term Expectations
 Lecture 13 Understanding Probability and Long-Term Expectations Thinking Challenge What s the probability of getting a head on the toss of a single fair coin? Use a scale from 0 (no way) to 1 (sure thing).
Lecture 13 Understanding Probability and Long-Term Expectations Thinking Challenge What s the probability of getting a head on the toss of a single fair coin? Use a scale from 0 (no way) to 1 (sure thing).
We rst consider the game from the player's point of view: Suppose you have picked a number and placed your bet. The probability of winning is
 Roulette: On an American roulette wheel here are 38 compartments where the ball can land. They are numbered 1-36, and there are two compartments labeled 0 and 00. Half of the compartments numbered 1-36
Roulette: On an American roulette wheel here are 38 compartments where the ball can land. They are numbered 1-36, and there are two compartments labeled 0 and 00. Half of the compartments numbered 1-36
V. RANDOM VARIABLES, PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS, EXPECTED VALUE
 V. RANDOM VARIABLES, PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS, EXPETED VALUE A game of chance featured at an amusement park is played as follows: You pay $ to play. A penny and a nickel are flipped. You win $ if either
V. RANDOM VARIABLES, PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS, EXPETED VALUE A game of chance featured at an amusement park is played as follows: You pay $ to play. A penny and a nickel are flipped. You win $ if either
Informatics 2D Reasoning and Agents Semester 2, 2015-16
 Informatics 2D Reasoning and Agents Semester 2, 2015-16 Alex Lascarides alex@inf.ed.ac.uk Lecture 29 Decision Making Under Uncertainty 24th March 2016 Informatics UoE Informatics 2D 1 Where are we? Last
Informatics 2D Reasoning and Agents Semester 2, 2015-16 Alex Lascarides alex@inf.ed.ac.uk Lecture 29 Decision Making Under Uncertainty 24th March 2016 Informatics UoE Informatics 2D 1 Where are we? Last
We never talked directly about the next two questions, but THINK about them they are related to everything we ve talked about during the past week:
 ECO 220 Intermediate Microeconomics Professor Mike Rizzo Third COLLECTED Problem Set SOLUTIONS This is an assignment that WILL be collected and graded. Please feel free to talk about the assignment with
ECO 220 Intermediate Microeconomics Professor Mike Rizzo Third COLLECTED Problem Set SOLUTIONS This is an assignment that WILL be collected and graded. Please feel free to talk about the assignment with
Decision making in the presence of uncertainty II
 CS 274 Knowledge representation Lecture 23 Decision making in the presence of uncertainty II Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Information-gathering actions Many actions and their
CS 274 Knowledge representation Lecture 23 Decision making in the presence of uncertainty II Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Information-gathering actions Many actions and their
Lesson 1. Basics of Probability. Principles of Mathematics 12: Explained! www.math12.com 314
 Lesson 1 Basics of Probability www.math12.com 314 Sample Spaces: Probability Lesson 1 Part I: Basic Elements of Probability Consider the following situation: A six sided die is rolled The sample space
Lesson 1 Basics of Probability www.math12.com 314 Sample Spaces: Probability Lesson 1 Part I: Basic Elements of Probability Consider the following situation: A six sided die is rolled The sample space
Lecture Note 1 Set and Probability Theory. MIT 14.30 Spring 2006 Herman Bennett
 Lecture Note 1 Set and Probability Theory MIT 14.30 Spring 2006 Herman Bennett 1 Set Theory 1.1 Definitions and Theorems 1. Experiment: any action or process whose outcome is subject to uncertainty. 2.
Lecture Note 1 Set and Probability Theory MIT 14.30 Spring 2006 Herman Bennett 1 Set Theory 1.1 Definitions and Theorems 1. Experiment: any action or process whose outcome is subject to uncertainty. 2.
Betting systems: how not to lose your money gambling
 Betting systems: how not to lose your money gambling G. Berkolaiko Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University 28 April 2007 / Mini Fair, Math Awareness Month 2007 Gambling and Games of Chance Simple
Betting systems: how not to lose your money gambling G. Berkolaiko Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University 28 April 2007 / Mini Fair, Math Awareness Month 2007 Gambling and Games of Chance Simple
Lecture 10 - Risk and Insurance
 Lecture 10 - Risk and Insurance 14.03 Spring 2003 1 Risk Aversion and Insurance: Introduction To have a passably usable model of choice, we need to be able to say something about how risk affects choice
Lecture 10 - Risk and Insurance 14.03 Spring 2003 1 Risk Aversion and Insurance: Introduction To have a passably usable model of choice, we need to be able to say something about how risk affects choice
In the situations that we will encounter, we may generally calculate the probability of an event
 What does it mean for something to be random? An event is called random if the process which produces the outcome is sufficiently complicated that we are unable to predict the precise result and are instead
What does it mean for something to be random? An event is called random if the process which produces the outcome is sufficiently complicated that we are unable to predict the precise result and are instead
DECISION MAKING UNDER UNCERTAINTY:
 DECISION MAKING UNDER UNCERTAINTY: Models and Choices Charles A. Holloway Stanford University TECHNISCHE HOCHSCHULE DARMSTADT Fachbereich 1 Gesamtbibliothek Betrtebswirtscrtaftslehre tnventar-nr. :...2>2&,...S'.?S7.
DECISION MAKING UNDER UNCERTAINTY: Models and Choices Charles A. Holloway Stanford University TECHNISCHE HOCHSCHULE DARMSTADT Fachbereich 1 Gesamtbibliothek Betrtebswirtscrtaftslehre tnventar-nr. :...2>2&,...S'.?S7.
36 Odds, Expected Value, and Conditional Probability
 36 Odds, Expected Value, and Conditional Probability What s the difference between probabilities and odds? To answer this question, let s consider a game that involves rolling a die. If one gets the face
36 Odds, Expected Value, and Conditional Probability What s the difference between probabilities and odds? To answer this question, let s consider a game that involves rolling a die. If one gets the face
Find an expected value involving two events. Find an expected value involving multiple events. Use expected value to make investment decisions.
 374 Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Likelihood 8.3 Expected Value Find an expected value involving two events. Find an expected value involving multiple events. Use expected value to make investment decisions.
374 Chapter 8 The Mathematics of Likelihood 8.3 Expected Value Find an expected value involving two events. Find an expected value involving multiple events. Use expected value to make investment decisions.
Chapter 16. Law of averages. Chance. Example 1: rolling two dice Sum of draws. Setting up a. Example 2: American roulette. Summary.
 Overview Box Part V Variability The Averages Box We will look at various chance : Tossing coins, rolling, playing Sampling voters We will use something called s to analyze these. Box s help to translate
Overview Box Part V Variability The Averages Box We will look at various chance : Tossing coins, rolling, playing Sampling voters We will use something called s to analyze these. Box s help to translate
Standard 12: The student will explain and evaluate the financial impact and consequences of gambling.
 STUDENT MODULE 12.1 GAMBLING PAGE 1 Standard 12: The student will explain and evaluate the financial impact and consequences of gambling. Risky Business Simone, Paula, and Randy meet in the library every
STUDENT MODULE 12.1 GAMBLING PAGE 1 Standard 12: The student will explain and evaluate the financial impact and consequences of gambling. Risky Business Simone, Paula, and Randy meet in the library every
Lecture 15. Ranking Payoff Distributions: Stochastic Dominance. First-Order Stochastic Dominance: higher distribution
 Lecture 15 Ranking Payoff Distributions: Stochastic Dominance First-Order Stochastic Dominance: higher distribution Definition 6.D.1: The distribution F( ) first-order stochastically dominates G( ) if
Lecture 15 Ranking Payoff Distributions: Stochastic Dominance First-Order Stochastic Dominance: higher distribution Definition 6.D.1: The distribution F( ) first-order stochastically dominates G( ) if
Probability. Sample space: all the possible outcomes of a probability experiment, i.e., the population of outcomes
 Probability Basic Concepts: Probability experiment: process that leads to welldefined results, called outcomes Outcome: result of a single trial of a probability experiment (a datum) Sample space: all
Probability Basic Concepts: Probability experiment: process that leads to welldefined results, called outcomes Outcome: result of a single trial of a probability experiment (a datum) Sample space: all
Contemporary Mathematics Online Math 1030 Sample Exam I Chapters 12-14 No Time Limit No Scratch Paper Calculator Allowed: Scientific
 Contemporary Mathematics Online Math 1030 Sample Exam I Chapters 12-14 No Time Limit No Scratch Paper Calculator Allowed: Scientific Name: The point value of each problem is in the left-hand margin. You
Contemporary Mathematics Online Math 1030 Sample Exam I Chapters 12-14 No Time Limit No Scratch Paper Calculator Allowed: Scientific Name: The point value of each problem is in the left-hand margin. You
Math 141. Lecture 2: More Probability! Albyn Jones 1. jones@reed.edu www.people.reed.edu/ jones/courses/141. 1 Library 304. Albyn Jones Math 141
 Math 141 Lecture 2: More Probability! Albyn Jones 1 1 Library 304 jones@reed.edu www.people.reed.edu/ jones/courses/141 Outline Law of total probability Bayes Theorem the Multiplication Rule, again Recall
Math 141 Lecture 2: More Probability! Albyn Jones 1 1 Library 304 jones@reed.edu www.people.reed.edu/ jones/courses/141 Outline Law of total probability Bayes Theorem the Multiplication Rule, again Recall
Elementary Statistics and Inference. Elementary Statistics and Inference. 17 Expected Value and Standard Error. 22S:025 or 7P:025.
 Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Lecture Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Chapter 7 A. The Expected Value In a chance process (probability experiment) the outcomes of
Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Lecture Elementary Statistics and Inference S:05 or 7P:05 Chapter 7 A. The Expected Value In a chance process (probability experiment) the outcomes of
Introductory Probability. MATH 107: Finite Mathematics University of Louisville. March 5, 2014
 Introductory Probability MATH 07: Finite Mathematics University of Louisville March 5, 204 What is probability? Counting and probability 2 / 3 Probability in our daily lives We see chances, odds, and probabilities
Introductory Probability MATH 07: Finite Mathematics University of Louisville March 5, 204 What is probability? Counting and probability 2 / 3 Probability in our daily lives We see chances, odds, and probabilities
Section 6.2 Definition of Probability
 Section 6.2 Definition of Probability Probability is a measure of the likelihood that an event occurs. For example, if there is a 20% chance of rain tomorrow, that means that the probability that it will
Section 6.2 Definition of Probability Probability is a measure of the likelihood that an event occurs. For example, if there is a 20% chance of rain tomorrow, that means that the probability that it will
Section 7C: The Law of Large Numbers
 Section 7C: The Law of Large Numbers Example. You flip a coin 00 times. Suppose the coin is fair. How many times would you expect to get heads? tails? One would expect a fair coin to come up heads half
Section 7C: The Law of Large Numbers Example. You flip a coin 00 times. Suppose the coin is fair. How many times would you expect to get heads? tails? One would expect a fair coin to come up heads half
Simple Decision Making
 Decision Making Under Uncertainty Ch 16 Simple Decision Making Many environments have multiple possible outcomes Some of these outcomes may be good; others may be bad Some may be very likely; others unlikely
Decision Making Under Uncertainty Ch 16 Simple Decision Making Many environments have multiple possible outcomes Some of these outcomes may be good; others may be bad Some may be very likely; others unlikely
An Introduction to Information Theory
 An Introduction to Information Theory Carlton Downey November 12, 2013 INTRODUCTION Today s recitation will be an introduction to Information Theory Information theory studies the quantification of Information
An Introduction to Information Theory Carlton Downey November 12, 2013 INTRODUCTION Today s recitation will be an introduction to Information Theory Information theory studies the quantification of Information
Chapter 4 Problems and Solutions
 ECO 3223 - Spring 2007 Chapter 4 1) Compute the future value of $100 at an 8 percent interest rate five, ten and fifteen years into the future. Future value in 5 years = $100*(1.08) 5 = $146.93 Future
ECO 3223 - Spring 2007 Chapter 4 1) Compute the future value of $100 at an 8 percent interest rate five, ten and fifteen years into the future. Future value in 5 years = $100*(1.08) 5 = $146.93 Future
Probability and Expected Value
 Probability and Expected Value This handout provides an introduction to probability and expected value. Some of you may already be familiar with some of these topics. Probability and expected value are
Probability and Expected Value This handout provides an introduction to probability and expected value. Some of you may already be familiar with some of these topics. Probability and expected value are
Lecture 13: Risk Aversion and Expected Utility
 Lecture 13: Risk Aversion and Expected Utility Uncertainty over monetary outcomes Let x denote a monetary outcome. C is a subset of the real line, i.e. [a, b]. A lottery L is a cumulative distribution
Lecture 13: Risk Aversion and Expected Utility Uncertainty over monetary outcomes Let x denote a monetary outcome. C is a subset of the real line, i.e. [a, b]. A lottery L is a cumulative distribution
Unit 19: Probability Models
 Unit 19: Probability Models Summary of Video Probability is the language of uncertainty. Using statistics, we can better predict the outcomes of random phenomena over the long term from the very complex,
Unit 19: Probability Models Summary of Video Probability is the language of uncertainty. Using statistics, we can better predict the outcomes of random phenomena over the long term from the very complex,
Practice Problems for Homework #8. Markov Chains. Read Sections 7.1-7.3. Solve the practice problems below.
 Practice Problems for Homework #8. Markov Chains. Read Sections 7.1-7.3 Solve the practice problems below. Open Homework Assignment #8 and solve the problems. 1. (10 marks) A computer system can operate
Practice Problems for Homework #8. Markov Chains. Read Sections 7.1-7.3 Solve the practice problems below. Open Homework Assignment #8 and solve the problems. 1. (10 marks) A computer system can operate
Basic Probability Theory II
 RECAP Basic Probability heory II Dr. om Ilvento FREC 408 We said the approach to establishing probabilities for events is to Define the experiment List the sample points Assign probabilities to the sample
RECAP Basic Probability heory II Dr. om Ilvento FREC 408 We said the approach to establishing probabilities for events is to Define the experiment List the sample points Assign probabilities to the sample
Coin Flip Questions. Suppose you flip a coin five times and write down the sequence of results, like HHHHH or HTTHT.
 Coin Flip Questions Suppose you flip a coin five times and write down the sequence of results, like HHHHH or HTTHT. 1 How many ways can you get exactly 1 head? 2 How many ways can you get exactly 2 heads?
Coin Flip Questions Suppose you flip a coin five times and write down the sequence of results, like HHHHH or HTTHT. 1 How many ways can you get exactly 1 head? 2 How many ways can you get exactly 2 heads?
6.042/18.062J Mathematics for Computer Science. Expected Value I
 6.42/8.62J Mathematics for Computer Science Srini Devadas and Eric Lehman May 3, 25 Lecture otes Expected Value I The expectation or expected value of a random variable is a single number that tells you
6.42/8.62J Mathematics for Computer Science Srini Devadas and Eric Lehman May 3, 25 Lecture otes Expected Value I The expectation or expected value of a random variable is a single number that tells you
Why is Insurance Good? An Example Jon Bakija, Williams College (Revised October 2013)
 Why is Insurance Good? An Example Jon Bakija, Williams College (Revised October 2013) Introduction The United States government is, to a rough approximation, an insurance company with an army. 1 That is
Why is Insurance Good? An Example Jon Bakija, Williams College (Revised October 2013) Introduction The United States government is, to a rough approximation, an insurance company with an army. 1 That is
Chapter 14 Risk Analysis
 Chapter 14 Risk Analysis 1 Frequency definition of probability Given a situation in which a number of possible outcomes might occur, the probability of an outcome is the proportion of times that it occurs
Chapter 14 Risk Analysis 1 Frequency definition of probability Given a situation in which a number of possible outcomes might occur, the probability of an outcome is the proportion of times that it occurs
Elementary Statistics and Inference. Elementary Statistics and Inference. 16 The Law of Averages (cont.) 22S:025 or 7P:025.
 Elementary Statistics and Inference 22S:025 or 7P:025 Lecture 20 1 Elementary Statistics and Inference 22S:025 or 7P:025 Chapter 16 (cont.) 2 D. Making a Box Model Key Questions regarding box What numbers
Elementary Statistics and Inference 22S:025 or 7P:025 Lecture 20 1 Elementary Statistics and Inference 22S:025 or 7P:025 Chapter 16 (cont.) 2 D. Making a Box Model Key Questions regarding box What numbers
Chapter 5 Uncertainty and Consumer Behavior
 Chapter 5 Uncertainty and Consumer Behavior Questions for Review 1. What does it mean to say that a person is risk averse? Why are some people likely to be risk averse while others are risk lovers? A risk-averse
Chapter 5 Uncertainty and Consumer Behavior Questions for Review 1. What does it mean to say that a person is risk averse? Why are some people likely to be risk averse while others are risk lovers? A risk-averse
(Relevant to AAT Examination Paper 4: Business Economics and Financial Mathematics)
 Decision making made easy (Relevant to AAT Examination Paper 4: Business Economics and Financial Mathematics) YO Lam, SCOPE, City University of Hong Kong In the competitive world of business, we need to
Decision making made easy (Relevant to AAT Examination Paper 4: Business Economics and Financial Mathematics) YO Lam, SCOPE, City University of Hong Kong In the competitive world of business, we need to
Stat 20: Intro to Probability and Statistics
 Stat 20: Intro to Probability and Statistics Lecture 16: More Box Models Tessa L. Childers-Day UC Berkeley 22 July 2014 By the end of this lecture... You will be able to: Determine what we expect the sum
Stat 20: Intro to Probability and Statistics Lecture 16: More Box Models Tessa L. Childers-Day UC Berkeley 22 July 2014 By the end of this lecture... You will be able to: Determine what we expect the sum
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION, BACKGROUND, AND MOTIVATION. Over the last decades, risk analysis and corporate risk management activities have
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION, BACKGROUND, AND MOTIVATION 1.1 INTRODUCTION Over the last decades, risk analysis and corporate risk management activities have become very important elements for both financial
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION, BACKGROUND, AND MOTIVATION 1.1 INTRODUCTION Over the last decades, risk analysis and corporate risk management activities have become very important elements for both financial
Chapter 4 & 5 practice set. The actual exam is not multiple choice nor does it contain like questions.
 Chapter 4 & 5 practice set. The actual exam is not multiple choice nor does it contain like questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Chapter 4 & 5 practice set. The actual exam is not multiple choice nor does it contain like questions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Economics 2020a / HBS 4010 / HKS API-111 Fall 2011 Practice Problems for Lectures 1 to 11
 Economics 2020a / HBS 4010 / HKS API-111 Fall 2011 Practice Problems for Lectures 1 to 11 LECTURE 1: BUDGETS AND REVEALED PREFERENCE 1.1. Quantity Discounts and the Budget Constraint Suppose that a consumer
Economics 2020a / HBS 4010 / HKS API-111 Fall 2011 Practice Problems for Lectures 1 to 11 LECTURE 1: BUDGETS AND REVEALED PREFERENCE 1.1. Quantity Discounts and the Budget Constraint Suppose that a consumer
1 Combinations, Permutations, and Elementary Probability
 1 Combinations, Permutations, and Elementary Probability Roughly speaking, Permutations are ways of grouping things where the order is important. Combinations are ways of grouping things where the order
1 Combinations, Permutations, and Elementary Probability Roughly speaking, Permutations are ways of grouping things where the order is important. Combinations are ways of grouping things where the order
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Random Variables October 27, 2015 1 Section 4.1 Random Variables A random variable is typically a real-valued function defined on the sample space of some experiment. For instance,
Chapter 4 Lecture Notes Random Variables October 27, 2015 1 Section 4.1 Random Variables A random variable is typically a real-valued function defined on the sample space of some experiment. For instance,
Moral Hazard. Itay Goldstein. Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania
 Moral Hazard Itay Goldstein Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania 1 Principal-Agent Problem Basic problem in corporate finance: separation of ownership and control: o The owners of the firm are typically
Moral Hazard Itay Goldstein Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania 1 Principal-Agent Problem Basic problem in corporate finance: separation of ownership and control: o The owners of the firm are typically
OPRE504 Chapter Study Guide Chapter 7 Randomness and Probability. Terminology of Probability. Probability Rules:
 OPRE504 Chapter Study Guide Chapter 7 Randomness and Probability Terminology of Probability For a Random phenomenon, there are a number of possible Outcomes. For example, tossing a coin could result in
OPRE504 Chapter Study Guide Chapter 7 Randomness and Probability Terminology of Probability For a Random phenomenon, there are a number of possible Outcomes. For example, tossing a coin could result in
STAT 319 Probability and Statistics For Engineers PROBABILITY. Engineering College, Hail University, Saudi Arabia
 STAT 319 robability and Statistics For Engineers LECTURE 03 ROAILITY Engineering College, Hail University, Saudi Arabia Overview robability is the study of random events. The probability, or chance, that
STAT 319 robability and Statistics For Engineers LECTURE 03 ROAILITY Engineering College, Hail University, Saudi Arabia Overview robability is the study of random events. The probability, or chance, that
Fund Manager s Portfolio Choice
 Fund Manager s Portfolio Choice Zhiqing Zhang Advised by: Gu Wang September 5, 2014 Abstract Fund manager is allowed to invest the fund s assets and his personal wealth in two separate risky assets, modeled
Fund Manager s Portfolio Choice Zhiqing Zhang Advised by: Gu Wang September 5, 2014 Abstract Fund manager is allowed to invest the fund s assets and his personal wealth in two separate risky assets, modeled
Word Problems Involving Systems of Linear Equations
 Word Problems Involving Systems of Linear Equations Many word problems will give rise to systems of equations that is, a pair of equations like this: 2x+3y = 10 x 6y = 5 You can solve a system of equations
Word Problems Involving Systems of Linear Equations Many word problems will give rise to systems of equations that is, a pair of equations like this: 2x+3y = 10 x 6y = 5 You can solve a system of equations
Stat 20: Intro to Probability and Statistics
 Stat 20: Intro to Probability and Statistics Lecture 18: Simple Random Sampling Tessa L. Childers-Day UC Berkeley 24 July 2014 By the end of this lecture... You will be able to: Draw box models for real-world
Stat 20: Intro to Probability and Statistics Lecture 18: Simple Random Sampling Tessa L. Childers-Day UC Berkeley 24 July 2014 By the end of this lecture... You will be able to: Draw box models for real-world
2 What is Rational: Normative. 4 Lottery & Gambling
 1 Decision Making 2 What is Rational: Normative Key Question: Are you Rational? Deviations from rationality: Value is subjective (utility, and more..). Value is multidimensional (multiple budgets, not
1 Decision Making 2 What is Rational: Normative Key Question: Are you Rational? Deviations from rationality: Value is subjective (utility, and more..). Value is multidimensional (multiple budgets, not
The Cumulative Distribution and Stochastic Dominance
 The Cumulative Distribution and Stochastic Dominance L A T E X file: StochasticDominance Daniel A. Graham, September 1, 2011 A decision problem under uncertainty is frequently cast as the problem of choosing
The Cumulative Distribution and Stochastic Dominance L A T E X file: StochasticDominance Daniel A. Graham, September 1, 2011 A decision problem under uncertainty is frequently cast as the problem of choosing
Discrete Structures for Computer Science
 Discrete Structures for Computer Science Adam J. Lee adamlee@cs.pitt.edu 6111 Sennott Square Lecture #20: Bayes Theorem November 5, 2013 How can we incorporate prior knowledge? Sometimes we want to know
Discrete Structures for Computer Science Adam J. Lee adamlee@cs.pitt.edu 6111 Sennott Square Lecture #20: Bayes Theorem November 5, 2013 How can we incorporate prior knowledge? Sometimes we want to know
PROBABILITY SECOND EDITION
 PROBABILITY SECOND EDITION Table of Contents How to Use This Series........................................... v Foreword..................................................... vi Basics 1. Probability All
PROBABILITY SECOND EDITION Table of Contents How to Use This Series........................................... v Foreword..................................................... vi Basics 1. Probability All
Probability: Terminology and Examples Class 2, 18.05, Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom
 Probability: Terminology and Examples Class 2, 18.05, Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1 Learning Goals 1. Know the definitions of sample space, event and probability function. 2. Be able to
Probability: Terminology and Examples Class 2, 18.05, Spring 2014 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1 Learning Goals 1. Know the definitions of sample space, event and probability function. 2. Be able to
Combinatorics 3 poker hands and Some general probability
 Combinatorics 3 poker hands and Some general probability Play cards 13 ranks Heart 4 Suits Spade Diamond Club Total: 4X13=52 cards You pick one card from a shuffled deck. What is the probability that it
Combinatorics 3 poker hands and Some general probability Play cards 13 ranks Heart 4 Suits Spade Diamond Club Total: 4X13=52 cards You pick one card from a shuffled deck. What is the probability that it
Chapter 16: law of averages
 Chapter 16: law of averages Context................................................................... 2 Law of averages 3 Coin tossing experiment......................................................
Chapter 16: law of averages Context................................................................... 2 Law of averages 3 Coin tossing experiment......................................................
High School Statistics and Probability Common Core Sample Test Version 2
 High School Statistics and Probability Common Core Sample Test Version 2 Our High School Statistics and Probability sample test covers the twenty most common questions that we see targeted for this level.
High School Statistics and Probability Common Core Sample Test Version 2 Our High School Statistics and Probability sample test covers the twenty most common questions that we see targeted for this level.
Combining decision analysis and portfolio management to improve project selection in the exploration and production firm
 Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 44 (2004) 55 65 www.elsevier.com/locate/petrol Combining decision analysis and portfolio management to improve project selection in the exploration and production
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 44 (2004) 55 65 www.elsevier.com/locate/petrol Combining decision analysis and portfolio management to improve project selection in the exploration and production
Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley
 Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley Word Count: 2,486 Definition Prospect Theory is a psychological account that describes how people make decisions under conditions of uncertainty. These may
Prospect Theory Ayelet Gneezy & Nicholas Epley Word Count: 2,486 Definition Prospect Theory is a psychological account that describes how people make decisions under conditions of uncertainty. These may
14.4. Expected Value Objectives. Expected Value
 . Expected Value Objectives. Understand the meaning of expected value. 2. Calculate the expected value of lotteries and games of chance.. Use expected value to solve applied problems. Life and Health Insurers
. Expected Value Objectives. Understand the meaning of expected value. 2. Calculate the expected value of lotteries and games of chance.. Use expected value to solve applied problems. Life and Health Insurers
STATISTICS 230 COURSE NOTES. Chris Springer, revised by Jerry Lawless and Don McLeish
 STATISTICS 230 COURSE NOTES Chris Springer, revised by Jerry Lawless and Don McLeish JANUARY 2006 Contents 1. Introduction to Probability 1 2. Mathematical Probability Models 5 2.1 SampleSpacesandProbability...
STATISTICS 230 COURSE NOTES Chris Springer, revised by Jerry Lawless and Don McLeish JANUARY 2006 Contents 1. Introduction to Probability 1 2. Mathematical Probability Models 5 2.1 SampleSpacesandProbability...
How To Find The Sample Space Of A Random Experiment In R (Programming)
 Probability 4.1 Sample Spaces For a random experiment E, the set of all possible outcomes of E is called the sample space and is denoted by the letter S. For the coin-toss experiment, S would be the results
Probability 4.1 Sample Spaces For a random experiment E, the set of all possible outcomes of E is called the sample space and is denoted by the letter S. For the coin-toss experiment, S would be the results
Week 2: Conditional Probability and Bayes formula
 Week 2: Conditional Probability and Bayes formula We ask the following question: suppose we know that a certain event B has occurred. How does this impact the probability of some other A. This question
Week 2: Conditional Probability and Bayes formula We ask the following question: suppose we know that a certain event B has occurred. How does this impact the probability of some other A. This question
People have thought about, and defined, probability in different ways. important to note the consequences of the definition:
 PROBABILITY AND LIKELIHOOD, A BRIEF INTRODUCTION IN SUPPORT OF A COURSE ON MOLECULAR EVOLUTION (BIOL 3046) Probability The subject of PROBABILITY is a branch of mathematics dedicated to building models
PROBABILITY AND LIKELIHOOD, A BRIEF INTRODUCTION IN SUPPORT OF A COURSE ON MOLECULAR EVOLUTION (BIOL 3046) Probability The subject of PROBABILITY is a branch of mathematics dedicated to building models
POKER LOTTO LOTTERY GAME CONDITIONS These Game Conditions apply, until amended or revised, to the POKER LOTTO lottery game.
 POKER LOTTO LOTTERY GAME CONDITIONS These Game Conditions apply, until amended or revised, to the POKER LOTTO lottery game. 1.0 Rules 1.1 POKER LOTTO is governed by the Rules Respecting Lottery Games of
POKER LOTTO LOTTERY GAME CONDITIONS These Game Conditions apply, until amended or revised, to the POKER LOTTO lottery game. 1.0 Rules 1.1 POKER LOTTO is governed by the Rules Respecting Lottery Games of
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao, David Tse Note 10
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao, David Tse Note 10 Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability theory has its origins in gambling analyzing card games, dice,
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao, David Tse Note 10 Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability theory has its origins in gambling analyzing card games, dice,
Expected Value and the Game of Craps
 Expected Value and the Game of Craps Blake Thornton Craps is a gambling game found in most casinos based on rolling two six sided dice. Most players who walk into a casino and try to play craps for the
Expected Value and the Game of Craps Blake Thornton Craps is a gambling game found in most casinos based on rolling two six sided dice. Most players who walk into a casino and try to play craps for the
Question: What is the probability that a five-card poker hand contains a flush, that is, five cards of the same suit?
 ECS20 Discrete Mathematics Quarter: Spring 2007 Instructor: John Steinberger Assistant: Sophie Engle (prepared by Sophie Engle) Homework 8 Hints Due Wednesday June 6 th 2007 Section 6.1 #16 What is the
ECS20 Discrete Mathematics Quarter: Spring 2007 Instructor: John Steinberger Assistant: Sophie Engle (prepared by Sophie Engle) Homework 8 Hints Due Wednesday June 6 th 2007 Section 6.1 #16 What is the
Session 8 Probability
 Key Terms for This Session Session 8 Probability Previously Introduced frequency New in This Session binomial experiment binomial probability model experimental probability mathematical probability outcome
Key Terms for This Session Session 8 Probability Previously Introduced frequency New in This Session binomial experiment binomial probability model experimental probability mathematical probability outcome
Global Health Forecasting Working Group Background Paper
 Global Health Forecasting Working Group Background Paper An Introduction to Risk and Uncertainty By Owen Barder and Ruth Levine Abstract This paper lays out an economic framework to conceptualize the primary
Global Health Forecasting Working Group Background Paper An Introduction to Risk and Uncertainty By Owen Barder and Ruth Levine Abstract This paper lays out an economic framework to conceptualize the primary
ECE 316 Probability Theory and Random Processes
 ECE 316 Probability Theory and Random Processes Chapter 4 Solutions (Part 2) Xinxin Fan Problems 20. A gambling book recommends the following winning strategy for the game of roulette. It recommends that
ECE 316 Probability Theory and Random Processes Chapter 4 Solutions (Part 2) Xinxin Fan Problems 20. A gambling book recommends the following winning strategy for the game of roulette. It recommends that
An Introduction to Utility Theory
 An Introduction to Utility Theory John Norstad j-norstad@northwestern.edu http://www.norstad.org March 29, 1999 Updated: November 3, 2011 Abstract A gentle but reasonably rigorous introduction to utility
An Introduction to Utility Theory John Norstad j-norstad@northwestern.edu http://www.norstad.org March 29, 1999 Updated: November 3, 2011 Abstract A gentle but reasonably rigorous introduction to utility
Financial Services [Applications]
![Financial Services [Applications] Financial Services [Applications]](/thumbs/29/13811156.jpg) Financial Services [Applications] Tomáš Sedliačik Institute o Finance University o Vienna tomas.sedliacik@univie.ac.at 1 Organization Overall there will be 14 units (12 regular units + 2 exams) Course
Financial Services [Applications] Tomáš Sedliačik Institute o Finance University o Vienna tomas.sedliacik@univie.ac.at 1 Organization Overall there will be 14 units (12 regular units + 2 exams) Course
Mathematical Expectation
 Mathematical Expectation Properties of Mathematical Expectation I The concept of mathematical expectation arose in connection with games of chance. In its simplest form, mathematical expectation is the
Mathematical Expectation Properties of Mathematical Expectation I The concept of mathematical expectation arose in connection with games of chance. In its simplest form, mathematical expectation is the
Week 5: Expected value and Betting systems
 Week 5: Expected value and Betting systems Random variable A random variable represents a measurement in a random experiment. We usually denote random variable with capital letter X, Y,. If S is the sample
Week 5: Expected value and Betting systems Random variable A random variable represents a measurement in a random experiment. We usually denote random variable with capital letter X, Y,. If S is the sample
Mathematical goals. Starting points. Materials required. Time needed
 Level S2 of challenge: B/C S2 Mathematical goals Starting points Materials required Time needed Evaluating probability statements To help learners to: discuss and clarify some common misconceptions about
Level S2 of challenge: B/C S2 Mathematical goals Starting points Materials required Time needed Evaluating probability statements To help learners to: discuss and clarify some common misconceptions about
