In This Lecture. SQL Data Definition SQL SQL. Notes. Non-Procedural Programming. Database Systems Lecture 5 Natasha Alechina
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Bailey
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This Lecture Database Systems Lecture 5 Natasha Alechina The language, the relational model, and E/R diagrams CREATE TABLE Columns Primary Keys Foreign Keys For more information Connolly and Begg chapter 6 Ullman and Widom 3.2, 6.6. Originally Sequel - Structured English query Language, part of an IBM project in the 70 s Sequel was already taken, so it became - Structured Query Language ANSI Standards (2) -99 (3) Most modern DBMS use a variety of Most based on 2, increasingly 3 Few (if any) are true to the standard provides A data definition language (DDL) A data manipulation language (DML) A data control language (DCL) addition Can be used from other languages Is often extended to provide common programming constructs (such as ifthen tests, loops, variables, etc.) Notes Non-Procedural Programming is (usually) not case-sensitive, but we ll write keywords in upper case for emphasis statements will be written in BOLD COURIER FONT Strings in are surrounded by single quotes: 'I AM A STRING' Single quotes within a string are doubled: 'I''M A STRING' The empty string:'' is a declarative (non-procedural) language Procedural - say exactly what the computer has to do Non-procedural describe the required result (not the way to compute it) ple: Given a database with tables with attributes,, with attributes, with attributes, Get a list of students who take the module Database Systems 1
2 Procedural Programming Non-Procedural () Set M to be the first Record /* Find module code for */ = /* Database Systems */ While (M is not null) and ( = ) If (M. = Database Systems ) Then = M. Set M to be the next Record Set NAMES to be empty /* A list of student names */ Set S to be the first Record While S is not null /* For each student... */ Set E to be the first Record While E is not null /* For each enrolment... */ If (E. = S.) And /* If this student is */ (E. = ) Then /* enrolled in DB Systems */ NAMES = NAMES + S.NAME /* add them to the list */ Set E to be the next Record Set S to be the next Record Return NAMES SELECT FROM, WHERE (. =.) AND (. = (SELECT FROM WHERE = Database Systems )), the Relational Model, and E/R Design Relations, Entities, Tables is based on the relational model It has many of the same ideas Databases that support are often described as relational databases It is not always true to the model E/R designs can be implemented in Entities, attributes, and relationships can all be expressed in terms of Many-to-many relationships are a problem, so should be removed Relational model E/R Diagram Relation Tuple Attribute Foreign Key Primary Key Entity Table stance Row Attribute Column or Field M:1 Relationship Foreign Key Primary Key Implementing E/R Designs Entities and Attributes Given an E/R design The entities become tables Attributes of an entity become columns in the corresponding table Relationships may be represented by foreign keys Each entity becomes a table in the database The name of the table is often the name of the entity The attributes become columns of the table with the same name A table called With columns for,,, and 2
3 CREATE TABLE Column Definitions CREATE TABLE <name> ( <col-def-1>, <col-def-2>, : <col-def-n>, <constraint-1>, : <constraint-k>) You supply A name for the table A list of column definitions A list of constraints (such as keys) <col-name> <type> [NULL NOT NULL] [DEFAULT <val>] [constraint-1 [, constraint-2[,...]]] Each column has a name and a type Common types INT REAL CHAR(n) VARCHAR(n) DATE Column Definitions ple Columns can be specified as NULL or NOT NULL NOT NULL columns cannot have missing values If neither is given then columns are assumed NULL Columns can be given a default value You just use the keyword DEFAULT followed by the value, eg: num INT DEFAULT 0 CREATE TABLE ( stu INT NOT NULL, stu VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, stu VARCHAR(50), stu INT DEFAULT 1) Constraints Primary Keys CONSTRAINT <name> <type> <details> Common <type>s PRIMARY KEY UNIQUE FOREIGN KEY INDEX Each constraint is given a name - Access requires a name, but some others don t Constraints which refer to single columns can be included in their definition Primary Keys are defined through constraints A PRIMARY KEY constraint also includes a UNIQUE constraint and makes the columns involved NOT NULL The <details> for a primary key is a list of columns which make up the key PRIMARY KEY (col1, col2, ) 3
4 Unique Constraints ple As well as a single primary key, any set of columns can be specified as UNIQUE This has the effect of making candidate keys in the table The <details> for a unique constraint are a list of columns which make up the candidate key UNIQUE (col1, col2, ) CREATE TABLE ( stu INT NOT NULL, stu VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, stu VARCHAR(50), stu INT DEFAULT 1, CONSTRAINT pk PRIMARY KEY (stu)) Relationships Representing Relationships Depends on the type 1:1 are usually not used, or can be treated as a special case of M:1 M:1 are represented as a foreign key from the M-side to the 1 M:M are split into two M:1 relationships The table Will have columns for the and attributes Will have a foreign key to for the has relationship Will have a foreign key to for the in relationship Foreign Keys ple Foreign Keys are also defined as constraints You need to give The columns which make up the FK The referenced table The columns which are referenced by the FK FOREIGN KEY (col1,col2, ) REFERENCES <table> [(ref1,ref2, )] If the FK references the PK of <table> you don t need to list the columns CREATE TABLE ( stu INT NOT NULL, mod CHAR(6) NOT NULL, enr INT, enr INT, CONSTRAINT enrpk PRIMARY KEY (stu, mod), CONSTRAINT enrstu FOREIGN KEY (stu) REFERENCES (stu), CONSTRAINT enrmod FOREIGN KEY (mod) REFERENCES (mod)) 4
5 Next Lecture More DROP TABLE ALTER TABLE INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE Data dictionary Sequences For more information Connolly and Begg chapters 5 and 6 Ullman and Widom 6.5 Coursework Cw1: Entity-relationship diagram and table definitions deadline 29 February at 3, submit to the School Office. Cw2: creating tables in Oracle marked in the labs on 20/02, latest submission by to me 22/02. Labs start on the 13 th of February (next week). This week there are still no labs, but you can start on your own: Set up an Oracle account (instructions on Start creating tables required in the first exercise (cw2) 5
SQL Data Definition. Database Systems Lecture 5 Natasha Alechina
 Database Systems Lecture 5 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture SQL The SQL language SQL, the relational model, and E/R diagrams CREATE TABLE Columns Primary Keys Foreign Keys For more information Connolly
Database Systems Lecture 5 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture SQL The SQL language SQL, the relational model, and E/R diagrams CREATE TABLE Columns Primary Keys Foreign Keys For more information Connolly
Entity/Relationship Modelling. Database Systems Lecture 4 Natasha Alechina
 Entity/Relationship Modelling Database Systems Lecture 4 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture Entity/Relationship models Entities and Attributes Relationships Attributes E/R Diagrams For more information Connolly
Entity/Relationship Modelling Database Systems Lecture 4 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture Entity/Relationship models Entities and Attributes Relationships Attributes E/R Diagrams For more information Connolly
In This Lecture. Security and Integrity. Database Security. DBMS Security Support. Privileges in SQL. Permissions and Privilege.
 In This Lecture Database Systems Lecture 14 Natasha Alechina Database Security Aspects of security Access to databases Privileges and views Database Integrity View updating, Integrity constraints For more
In This Lecture Database Systems Lecture 14 Natasha Alechina Database Security Aspects of security Access to databases Privileges and views Database Integrity View updating, Integrity constraints For more
Databases What the Specification Says
 Databases What the Specification Says Describe flat files and relational databases, explaining the differences between them; Design a simple relational database to the third normal form (3NF), using entityrelationship
Databases What the Specification Says Describe flat files and relational databases, explaining the differences between them; Design a simple relational database to the third normal form (3NF), using entityrelationship
In This Lecture. Physical Design. RAID Arrays. RAID Level 0. RAID Level 1. Physical DB Issues, Indexes, Query Optimisation. Physical DB Issues
 In This Lecture Physical DB Issues, Indexes, Query Optimisation Database Systems Lecture 13 Natasha Alechina Physical DB Issues RAID arrays for recovery and speed Indexes and query efficiency Query optimisation
In This Lecture Physical DB Issues, Indexes, Query Optimisation Database Systems Lecture 13 Natasha Alechina Physical DB Issues RAID arrays for recovery and speed Indexes and query efficiency Query optimisation
Relational Databases. Christopher Simpkins [email protected]
 Relational Databases Christopher Simpkins [email protected] Relational Databases A relational database is a collection of data stored in one or more tables A relational database management system
Relational Databases Christopher Simpkins [email protected] Relational Databases A relational database is a collection of data stored in one or more tables A relational database management system
www.gr8ambitionz.com
 Data Base Management Systems (DBMS) Study Material (Objective Type questions with Answers) Shared by Akhil Arora Powered by www. your A to Z competitive exam guide Database Objective type questions Q.1
Data Base Management Systems (DBMS) Study Material (Objective Type questions with Answers) Shared by Akhil Arora Powered by www. your A to Z competitive exam guide Database Objective type questions Q.1
Fundamentals of Database Design
 Fundamentals of Database Design Zornitsa Zaharieva CERN Data Management Section - Controls Group Accelerators and Beams Department /AB-CO-DM/ 23-FEB-2005 Contents : Introduction to Databases : Main Database
Fundamentals of Database Design Zornitsa Zaharieva CERN Data Management Section - Controls Group Accelerators and Beams Department /AB-CO-DM/ 23-FEB-2005 Contents : Introduction to Databases : Main Database
IT2305 Database Systems I (Compulsory)
 Database Systems I (Compulsory) INTRODUCTION This is one of the 4 modules designed for Semester 2 of Bachelor of Information Technology Degree program. CREDITS: 04 LEARNING OUTCOMES On completion of this
Database Systems I (Compulsory) INTRODUCTION This is one of the 4 modules designed for Semester 2 of Bachelor of Information Technology Degree program. CREDITS: 04 LEARNING OUTCOMES On completion of this
1. INTRODUCTION TO RDBMS
 Oracle For Beginners Page: 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO RDBMS What is DBMS? Data Models Relational database management system (RDBMS) Relational Algebra Structured query language (SQL) What Is DBMS? Data is one
Oracle For Beginners Page: 1 1. INTRODUCTION TO RDBMS What is DBMS? Data Models Relational database management system (RDBMS) Relational Algebra Structured query language (SQL) What Is DBMS? Data is one
In this Lecture SQL SELECT. Example Tables. SQL SELECT Overview. WHERE Clauses. DISTINCT and ALL SQL SELECT. For more information
 In this Lecture SQL SELECT Database Systems Lecture 7 Natasha Alechina SQL SELECT WHERE clauses SELECT from multiple tables JOINs For more information Connolly and Begg Chapter 5 Ullman and Widom Chapter
In this Lecture SQL SELECT Database Systems Lecture 7 Natasha Alechina SQL SELECT WHERE clauses SELECT from multiple tables JOINs For more information Connolly and Begg Chapter 5 Ullman and Widom Chapter
IT2304: Database Systems 1 (DBS 1)
 : Database Systems 1 (DBS 1) (Compulsory) 1. OUTLINE OF SYLLABUS Topic Minimum number of hours Introduction to DBMS 07 Relational Data Model 03 Data manipulation using Relational Algebra 06 Data manipulation
: Database Systems 1 (DBS 1) (Compulsory) 1. OUTLINE OF SYLLABUS Topic Minimum number of hours Introduction to DBMS 07 Relational Data Model 03 Data manipulation using Relational Algebra 06 Data manipulation
Database Query 1: SQL Basics
 Database Query 1: SQL Basics CIS 3730 Designing and Managing Data J.G. Zheng Fall 2010 1 Overview Using Structured Query Language (SQL) to get the data you want from relational databases Learning basic
Database Query 1: SQL Basics CIS 3730 Designing and Managing Data J.G. Zheng Fall 2010 1 Overview Using Structured Query Language (SQL) to get the data you want from relational databases Learning basic
Lecture 6. SQL, Logical DB Design
 Lecture 6 SQL, Logical DB Design Relational Query Languages A major strength of the relational model: supports simple, powerful querying of data. Queries can be written intuitively, and the DBMS is responsible
Lecture 6 SQL, Logical DB Design Relational Query Languages A major strength of the relational model: supports simple, powerful querying of data. Queries can be written intuitively, and the DBMS is responsible
Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals NEW
 Oracle University Contact Us: + 38516306373 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals NEW Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals training delivers the
Oracle University Contact Us: + 38516306373 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals NEW Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals training delivers the
How To Create A Table In Sql 2.5.2.2 (Ahem)
 Database Systems Unit 5 Database Implementation: SQL Data Definition Language Learning Goals In this unit you will learn how to transfer a logical data model into a physical database, how to extend or
Database Systems Unit 5 Database Implementation: SQL Data Definition Language Learning Goals In this unit you will learn how to transfer a logical data model into a physical database, how to extend or
Oracle SQL. Course Summary. Duration. Objectives
 Oracle SQL Course Summary Identify the major structural components of the Oracle Database 11g Create reports of aggregated data Write SELECT statements that include queries Retrieve row and column data
Oracle SQL Course Summary Identify the major structural components of the Oracle Database 11g Create reports of aggregated data Write SELECT statements that include queries Retrieve row and column data
SQL DATA DEFINITION: KEY CONSTRAINTS. CS121: Introduction to Relational Database Systems Fall 2015 Lecture 7
 SQL DATA DEFINITION: KEY CONSTRAINTS CS121: Introduction to Relational Database Systems Fall 2015 Lecture 7 Data Definition 2 Covered most of SQL data manipulation operations Continue exploration of SQL
SQL DATA DEFINITION: KEY CONSTRAINTS CS121: Introduction to Relational Database Systems Fall 2015 Lecture 7 Data Definition 2 Covered most of SQL data manipulation operations Continue exploration of SQL
Database Design. Marta Jakubowska-Sobczak IT/ADC based on slides prepared by Paula Figueiredo, IT/DB
 Marta Jakubowska-Sobczak IT/ADC based on slides prepared by Paula Figueiredo, IT/DB Outline Database concepts Conceptual Design Logical Design Communicating with the RDBMS 2 Some concepts Database: an
Marta Jakubowska-Sobczak IT/ADC based on slides prepared by Paula Figueiredo, IT/DB Outline Database concepts Conceptual Design Logical Design Communicating with the RDBMS 2 Some concepts Database: an
Programming with SQL
 Unit 43: Programming with SQL Learning Outcomes A candidate following a programme of learning leading to this unit will be able to: Create queries to retrieve information from relational databases using
Unit 43: Programming with SQL Learning Outcomes A candidate following a programme of learning leading to this unit will be able to: Create queries to retrieve information from relational databases using
Chapter 9 Java and SQL. Wang Yang [email protected]
 Chapter 9 Java and SQL Wang Yang [email protected] Outline Concern Data - File & IO vs. Database &SQL Database & SQL How Connect Java to SQL - Java Model for Database Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
Chapter 9 Java and SQL Wang Yang [email protected] Outline Concern Data - File & IO vs. Database &SQL Database & SQL How Connect Java to SQL - Java Model for Database Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
The Relational Model. Ramakrishnan&Gehrke, Chapter 3 CS4320 1
 The Relational Model Ramakrishnan&Gehrke, Chapter 3 CS4320 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in older models
The Relational Model Ramakrishnan&Gehrke, Chapter 3 CS4320 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in older models
EECS 647: Introduction to Database Systems
 EECS 647: Introduction to Database Systems Instructor: Luke Huan Spring 2013 Administrative Take home background survey is due this coming Friday The grader of this course is Ms. Xiaoli Li and her email
EECS 647: Introduction to Database Systems Instructor: Luke Huan Spring 2013 Administrative Take home background survey is due this coming Friday The grader of this course is Ms. Xiaoli Li and her email
DBMS Questions. 3.) For which two constraints are indexes created when the constraint is added?
 DBMS Questions 1.) Which type of file is part of the Oracle database? A.) B.) C.) D.) Control file Password file Parameter files Archived log files 2.) Which statements are use to UNLOCK the user? A.)
DBMS Questions 1.) Which type of file is part of the Oracle database? A.) B.) C.) D.) Control file Password file Parameter files Archived log files 2.) Which statements are use to UNLOCK the user? A.)
COMP 5138 Relational Database Management Systems. Week 5 : Basic SQL. Today s Agenda. Overview. Basic SQL Queries. Joins Queries
 COMP 5138 Relational Database Management Systems Week 5 : Basic COMP5138 "Relational Database Managment Systems" J. Davis 2006 5-1 Today s Agenda Overview Basic Queries Joins Queries Aggregate Functions
COMP 5138 Relational Database Management Systems Week 5 : Basic COMP5138 "Relational Database Managment Systems" J. Davis 2006 5-1 Today s Agenda Overview Basic Queries Joins Queries Aggregate Functions
Oracle 10g PL/SQL Training
 Oracle 10g PL/SQL Training Course Number: ORCL PS01 Length: 3 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exams: 1Z0 042 1Z0 043 Course Overview PL/SQL is Oracle's Procedural
Oracle 10g PL/SQL Training Course Number: ORCL PS01 Length: 3 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exams: 1Z0 042 1Z0 043 Course Overview PL/SQL is Oracle's Procedural
The Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model?
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Instructor: Vladimir Zadorozhny [email protected] Information Science Program School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh 1 Why Study the Relational Model?
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Instructor: Vladimir Zadorozhny [email protected] Information Science Program School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh 1 Why Study the Relational Model?
Normalisation to 3NF. Database Systems Lecture 11 Natasha Alechina
 Normalisation to 3NF Database Systems Lecture 11 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture Normalisation to 3NF Data redundancy Functional dependencies Normal forms First, Second, and Third Normal Forms For more
Normalisation to 3NF Database Systems Lecture 11 Natasha Alechina In This Lecture Normalisation to 3NF Data redundancy Functional dependencies Normal forms First, Second, and Third Normal Forms For more
Basic Concepts of Database Systems
 CS2501 Topic 1: Basic Concepts 1.1 Basic Concepts of Database Systems Example Uses of Database Systems - account maintenance & access in banking - lending library systems - airline reservation systems
CS2501 Topic 1: Basic Concepts 1.1 Basic Concepts of Database Systems Example Uses of Database Systems - account maintenance & access in banking - lending library systems - airline reservation systems
Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals
 Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course is designed to deliver the fundamentals of SQL and PL/SQL along
Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This course is designed to deliver the fundamentals of SQL and PL/SQL along
2. Basic Relational Data Model
 2. Basic Relational Data Model 2.1 Introduction Basic concepts of information models, their realisation in databases comprising data objects and object relationships, and their management by DBMS s that
2. Basic Relational Data Model 2.1 Introduction Basic concepts of information models, their realisation in databases comprising data objects and object relationships, and their management by DBMS s that
Physical Design. Meeting the needs of the users is the gold standard against which we measure our success in creating a database.
 Physical Design Physical Database Design (Defined): Process of producing a description of the implementation of the database on secondary storage; it describes the base relations, file organizations, and
Physical Design Physical Database Design (Defined): Process of producing a description of the implementation of the database on secondary storage; it describes the base relations, file organizations, and
4 Logical Design : RDM Schema Definition with SQL / DDL
 4 Logical Design : RDM Schema Definition with SQL / DDL 4.1 SQL history and standards 4.2 SQL/DDL first steps 4.2.1 Basis Schema Definition using SQL / DDL 4.2.2 SQL Data types, domains, user defined types
4 Logical Design : RDM Schema Definition with SQL / DDL 4.1 SQL history and standards 4.2 SQL/DDL first steps 4.2.1 Basis Schema Definition using SQL / DDL 4.2.2 SQL Data types, domains, user defined types
Relational Database Concepts
 Relational Database Concepts IBM Information Management Cloud Computing Center of Competence IBM Canada Labs 1 2011 IBM Corporation Agenda Overview Information and Data Models The relational model Entity-Relationship
Relational Database Concepts IBM Information Management Cloud Computing Center of Competence IBM Canada Labs 1 2011 IBM Corporation Agenda Overview Information and Data Models The relational model Entity-Relationship
Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals
 Oracle University Contact Us: +966 12 739 894 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals training is designed to
Oracle University Contact Us: +966 12 739 894 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals training is designed to
Oracle Database 12c: Introduction to SQL Ed 1.1
 Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database 12c: Introduction to SQL Ed 1.1 Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: Introduction to SQL training helps you write subqueries,
Oracle University Contact Us: 1.800.529.0165 Oracle Database 12c: Introduction to SQL Ed 1.1 Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: Introduction to SQL training helps you write subqueries,
Introduction to Microsoft Jet SQL
 Introduction to Microsoft Jet SQL Microsoft Jet SQL is a relational database language based on the SQL 1989 standard of the American Standards Institute (ANSI). Microsoft Jet SQL contains two kinds of
Introduction to Microsoft Jet SQL Microsoft Jet SQL is a relational database language based on the SQL 1989 standard of the American Standards Institute (ANSI). Microsoft Jet SQL contains two kinds of
3. Relational Model and Relational Algebra
 ECS-165A WQ 11 36 3. Relational Model and Relational Algebra Contents Fundamental Concepts of the Relational Model Integrity Constraints Translation ER schema Relational Database Schema Relational Algebra
ECS-165A WQ 11 36 3. Relational Model and Relational Algebra Contents Fundamental Concepts of the Relational Model Integrity Constraints Translation ER schema Relational Database Schema Relational Algebra
Introduction to Database. Systems HANS- PETTER HALVORSEN, 2014.03.03
 Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Introduction to Database HANS- PETTER HALVORSEN, 2014.03.03 Systems Faculty of Technology, Postboks
Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Introduction to Database HANS- PETTER HALVORSEN, 2014.03.03 Systems Faculty of Technology, Postboks
A basic create statement for a simple student table would look like the following.
 Creating Tables A basic create statement for a simple student table would look like the following. create table Student (SID varchar(10), FirstName varchar(30), LastName varchar(30), EmailAddress varchar(30));
Creating Tables A basic create statement for a simple student table would look like the following. create table Student (SID varchar(10), FirstName varchar(30), LastName varchar(30), EmailAddress varchar(30));
Information Systems 2. 1. Modelling Information Systems I: Databases
 Information Systems 2 Information Systems 2 1. Modelling Information Systems I: Databases Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute for Business Economics and Information
Information Systems 2 Information Systems 2 1. Modelling Information Systems I: Databases Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute for Business Economics and Information
INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE SYSTEMS
 Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE SYSTEMS HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 9. DESEMBER 2009 Faculty of Technology,
Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE SYSTEMS HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 9. DESEMBER 2009 Faculty of Technology,
Programming Database lectures for mathema
 Programming Database lectures for mathematics students April 25, 2015 Functions Functions are defined in Postgres with CREATE FUNCTION name(parameter type,...) RETURNS result-type AS $$ function-body $$
Programming Database lectures for mathematics students April 25, 2015 Functions Functions are defined in Postgres with CREATE FUNCTION name(parameter type,...) RETURNS result-type AS $$ function-body $$
14 Triggers / Embedded SQL
 14 Triggers / Embedded SQL COMS20700 Databases Dr. Essam Ghadafi TRIGGERS A trigger is a procedure that is executed automatically whenever a specific event occurs. You can use triggers to enforce constraints
14 Triggers / Embedded SQL COMS20700 Databases Dr. Essam Ghadafi TRIGGERS A trigger is a procedure that is executed automatically whenever a specific event occurs. You can use triggers to enforce constraints
Chapter 1: Introduction. Database Management System (DBMS) University Database Example
 This image cannot currently be displayed. Chapter 1: Introduction Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Database Management System (DBMS) DBMS contains information
This image cannot currently be displayed. Chapter 1: Introduction Database System Concepts, 6 th Ed. See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Database Management System (DBMS) DBMS contains information
The Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model? Relational Database: Definitions. Chapter 3
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase,
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase,
Oracle Database 10g Express
 Oracle Database 10g Express This tutorial prepares the Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Developer to perform common development and administrative tasks of Oracle Database 10g Express Edition. Objectives
Oracle Database 10g Express This tutorial prepares the Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Developer to perform common development and administrative tasks of Oracle Database 10g Express Edition. Objectives
CSC 443 Data Base Management Systems. Basic SQL
 CSC 443 Data Base Management Systems Lecture 6 SQL As A Data Definition Language Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational databases SQL Structured
CSC 443 Data Base Management Systems Lecture 6 SQL As A Data Definition Language Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational databases SQL Structured
Relational Database Basics Review
 Relational Database Basics Review IT 4153 Advanced Database J.G. Zheng Spring 2012 Overview Database approach Database system Relational model Database development 2 File Processing Approaches Based on
Relational Database Basics Review IT 4153 Advanced Database J.G. Zheng Spring 2012 Overview Database approach Database system Relational model Database development 2 File Processing Approaches Based on
Information Systems SQL. Nikolaj Popov
 Information Systems SQL Nikolaj Popov Research Institute for Symbolic Computation Johannes Kepler University of Linz, Austria [email protected] Outline SQL Table Creation Populating and Modifying
Information Systems SQL Nikolaj Popov Research Institute for Symbolic Computation Johannes Kepler University of Linz, Austria [email protected] Outline SQL Table Creation Populating and Modifying
Introduction to Databases
 Page 1 of 5 Introduction to Databases An introductory example What is a database? Why do we need Database Management Systems? The three levels of data abstraction What is a Database Management System?
Page 1 of 5 Introduction to Databases An introductory example What is a database? Why do we need Database Management Systems? The three levels of data abstraction What is a Database Management System?
Outline. Data Modeling. Conceptual Design. ER Model Basics: Entities. ER Model Basics: Relationships. Ternary Relationships. Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst
 Outline Data Modeling Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst v Conceptual Design: ER Model v Relational Model v Logical Design: from ER to Relational Slides Courtesy of R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 2 Conceptual
Outline Data Modeling Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst v Conceptual Design: ER Model v Relational Model v Logical Design: from ER to Relational Slides Courtesy of R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 2 Conceptual
CSE 530A Database Management Systems. Introduction. Washington University Fall 2013
 CSE 530A Database Management Systems Introduction Washington University Fall 2013 Overview Time: Mon/Wed 7:00-8:30 PM Location: Crow 206 Instructor: Michael Plezbert TA: Gene Lee Websites: http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/cse530/
CSE 530A Database Management Systems Introduction Washington University Fall 2013 Overview Time: Mon/Wed 7:00-8:30 PM Location: Crow 206 Instructor: Michael Plezbert TA: Gene Lee Websites: http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/cse530/
Advance DBMS. Structured Query Language (SQL)
 Structured Query Language (SQL) Introduction Commercial database systems use more user friendly language to specify the queries. SQL is the most influential commercially marketed product language. Other
Structured Query Language (SQL) Introduction Commercial database systems use more user friendly language to specify the queries. SQL is the most influential commercially marketed product language. Other
BCA. Database Management System
 BCA IV Sem Database Management System Multiple choice questions 1. A Database Management System (DBMS) is A. Collection of interrelated data B. Collection of programs to access data C. Collection of data
BCA IV Sem Database Management System Multiple choice questions 1. A Database Management System (DBMS) is A. Collection of interrelated data B. Collection of programs to access data C. Collection of data
SQL. Short introduction
 SQL Short introduction 1 Overview SQL, which stands for Structured Query Language, is used to communicate with a database. Through SQL one can create, manipulate, query and delete tables and contents.
SQL Short introduction 1 Overview SQL, which stands for Structured Query Language, is used to communicate with a database. Through SQL one can create, manipulate, query and delete tables and contents.
Database Design and Programming
 Database Design and Programming Peter Schneider-Kamp DM 505, Spring 2012, 3 rd Quarter 1 Course Organisation Literature Database Systems: The Complete Book Evaluation Project and 1-day take-home exam,
Database Design and Programming Peter Schneider-Kamp DM 505, Spring 2012, 3 rd Quarter 1 Course Organisation Literature Database Systems: The Complete Book Evaluation Project and 1-day take-home exam,
Ch.5 Database Security. Ch.5 Database Security Review
 User Authentication Access Control Database Security Ch.5 Database Security Hw_Ch3, due today Hw_Ch4, due on 2/23 Review Questions: 4.1, 4.3, 4.6, 4.10 Problems: 4.5, 4.7, 4.8 How about the pace of the
User Authentication Access Control Database Security Ch.5 Database Security Hw_Ch3, due today Hw_Ch4, due on 2/23 Review Questions: 4.1, 4.3, 4.6, 4.10 Problems: 4.5, 4.7, 4.8 How about the pace of the
Instant SQL Programming
 Instant SQL Programming Joe Celko Wrox Press Ltd. INSTANT Table of Contents Introduction 1 What Can SQL Do for Me? 2 Who Should Use This Book? 2 How To Use This Book 3 What You Should Know 3 Conventions
Instant SQL Programming Joe Celko Wrox Press Ltd. INSTANT Table of Contents Introduction 1 What Can SQL Do for Me? 2 Who Should Use This Book? 2 How To Use This Book 3 What You Should Know 3 Conventions
- Eliminating redundant data - Ensuring data dependencies makes sense. ie:- data is stored logically
 Normalization of databases Database normalization is a technique of organizing the data in the database. Normalization is a systematic approach of decomposing tables to eliminate data redundancy and undesirable
Normalization of databases Database normalization is a technique of organizing the data in the database. Normalization is a systematic approach of decomposing tables to eliminate data redundancy and undesirable
Databases and BigData
 Eduardo Cunha de Almeida [email protected] Outline of the course Introduction Database Systems (E. Almeida) Distributed Hash Tables and P2P (C. Cassagnes) NewSQL (D. Kim and J. Meira) NoSQL (D. Kim)
Eduardo Cunha de Almeida [email protected] Outline of the course Introduction Database Systems (E. Almeida) Distributed Hash Tables and P2P (C. Cassagnes) NewSQL (D. Kim and J. Meira) NoSQL (D. Kim)
Extracting META information from Interbase/Firebird SQL (INFORMATION_SCHEMA)
 13 November 2007 22:30 Extracting META information from Interbase/Firebird SQL (INFORMATION_SCHEMA) By: http://www.alberton.info/firebird_sql_meta_info.html The SQL 2003 Standard introduced a new schema
13 November 2007 22:30 Extracting META information from Interbase/Firebird SQL (INFORMATION_SCHEMA) By: http://www.alberton.info/firebird_sql_meta_info.html The SQL 2003 Standard introduced a new schema
Information Technology NVEQ Level 2 Class X IT207-NQ2012-Database Development (Basic) Student s Handbook
 Students Handbook ... Accenture India s Corporate Citizenship Progra as well as access to their implementing partners (Dr. Reddy s Foundation supplement CBSE/ PSSCIVE s content. ren s life at Database
Students Handbook ... Accenture India s Corporate Citizenship Progra as well as access to their implementing partners (Dr. Reddy s Foundation supplement CBSE/ PSSCIVE s content. ren s life at Database
The Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model? Relational Database: Definitions
 The Relational Model Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in
The Relational Model Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in
Data Modeling. Database Systems: The Complete Book Ch. 4.1-4.5, 7.1-7.4
 Data Modeling Database Systems: The Complete Book Ch. 4.1-4.5, 7.1-7.4 Data Modeling Schema: The structure of the data Structured Data: Relational, XML-DTD, etc Unstructured Data: CSV, JSON But where does
Data Modeling Database Systems: The Complete Book Ch. 4.1-4.5, 7.1-7.4 Data Modeling Schema: The structure of the data Structured Data: Relational, XML-DTD, etc Unstructured Data: CSV, JSON But where does
Part A: Data Definition Language (DDL) Schema and Catalog CREAT TABLE. Referential Triggered Actions. CSC 742 Database Management Systems
 CSC 74 Database Management Systems Topic #0: SQL Part A: Data Definition Language (DDL) Spring 00 CSC 74: DBMS by Dr. Peng Ning Spring 00 CSC 74: DBMS by Dr. Peng Ning Schema and Catalog Schema A collection
CSC 74 Database Management Systems Topic #0: SQL Part A: Data Definition Language (DDL) Spring 00 CSC 74: DBMS by Dr. Peng Ning Spring 00 CSC 74: DBMS by Dr. Peng Ning Schema and Catalog Schema A collection
Database 10g Edition: All possible 10g features, either bundled or available at additional cost.
 Concepts Oracle Corporation offers a wide variety of products. The Oracle Database 10g, the product this exam focuses on, is the centerpiece of the Oracle product set. The "g" in "10g" stands for the Grid
Concepts Oracle Corporation offers a wide variety of products. The Oracle Database 10g, the product this exam focuses on, is the centerpiece of the Oracle product set. The "g" in "10g" stands for the Grid
6 CHAPTER. Relational Database Management Systems and SQL Chapter Objectives In this chapter you will learn the following:
 6 CHAPTER Relational Database Management Systems and SQL Chapter Objectives In this chapter you will learn the following: The history of relational database systems and SQL How the three-level architecture
6 CHAPTER Relational Database Management Systems and SQL Chapter Objectives In this chapter you will learn the following: The history of relational database systems and SQL How the three-level architecture
Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle End Users, Developers, Technical Consultants and Support Staff
 D80198GC10 Oracle Database 12c SQL and Fundamentals Summary Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle End Users, Developers, Technical Consultants and Support Staff Level Professional Delivery Method Instructor-led
D80198GC10 Oracle Database 12c SQL and Fundamentals Summary Duration Vendor Audience 5 Days Oracle End Users, Developers, Technical Consultants and Support Staff Level Professional Delivery Method Instructor-led
Lab 2: PostgreSQL Tutorial II: Command Line
 Lab 2: PostgreSQL Tutorial II: Command Line In the lab 1, we learned how to use PostgreSQL through the graphic interface, pgadmin. However, PostgreSQL may not be used through a graphical interface. This
Lab 2: PostgreSQL Tutorial II: Command Line In the lab 1, we learned how to use PostgreSQL through the graphic interface, pgadmin. However, PostgreSQL may not be used through a graphical interface. This
Information Management
 Information Management Dr Marilyn Rose McGee-Lennon [email protected] What is Information Management about Aim: to understand the ways in which databases contribute to the management of large amounts
Information Management Dr Marilyn Rose McGee-Lennon [email protected] What is Information Management about Aim: to understand the ways in which databases contribute to the management of large amounts
SQL, PL/SQL FALL Semester 2013
 SQL, PL/SQL FALL Semester 2013 Rana Umer Aziz MSc.IT (London, UK) Contact No. 0335-919 7775 [email protected] EDUCATION CONSULTANT Contact No. 0335-919 7775, 0321-515 3403 www.oeconsultant.co.uk
SQL, PL/SQL FALL Semester 2013 Rana Umer Aziz MSc.IT (London, UK) Contact No. 0335-919 7775 [email protected] EDUCATION CONSULTANT Contact No. 0335-919 7775, 0321-515 3403 www.oeconsultant.co.uk
SQL Simple Queries. Chapter 3.1 V3.0. Copyright @ Napier University Dr Gordon Russell
 SQL Simple Queries Chapter 3.1 V3.0 Copyright @ Napier University Dr Gordon Russell Introduction SQL is the Structured Query Language It is used to interact with the DBMS SQL can Create Schemas in the
SQL Simple Queries Chapter 3.1 V3.0 Copyright @ Napier University Dr Gordon Russell Introduction SQL is the Structured Query Language It is used to interact with the DBMS SQL can Create Schemas in the
Demystified CONTENTS Acknowledgments xvii Introduction xix CHAPTER 1 Database Fundamentals CHAPTER 2 Exploring Relational Database Components
 Acknowledgments xvii Introduction xix CHAPTER 1 Database Fundamentals 1 Properties of a Database 1 The Database Management System (DBMS) 2 Layers of Data Abstraction 3 Physical Data Independence 5 Logical
Acknowledgments xvii Introduction xix CHAPTER 1 Database Fundamentals 1 Properties of a Database 1 The Database Management System (DBMS) 2 Layers of Data Abstraction 3 Physical Data Independence 5 Logical
Introduction to Computing. Lectured by: Dr. Pham Tran Vu [email protected]
 Introduction to Computing Lectured by: Dr. Pham Tran Vu [email protected] Databases The Hierarchy of Data Keys and Attributes The Traditional Approach To Data Management Database A collection of
Introduction to Computing Lectured by: Dr. Pham Tran Vu [email protected] Databases The Hierarchy of Data Keys and Attributes The Traditional Approach To Data Management Database A collection of
2874CD1EssentialSQL.qxd 6/25/01 3:06 PM Page 1 Essential SQL Copyright 2001 SYBEX, Inc., Alameda, CA www.sybex.com
 Essential SQL 2 Essential SQL This bonus chapter is provided with Mastering Delphi 6. It is a basic introduction to SQL to accompany Chapter 14, Client/Server Programming. RDBMS packages are generally
Essential SQL 2 Essential SQL This bonus chapter is provided with Mastering Delphi 6. It is a basic introduction to SQL to accompany Chapter 14, Client/Server Programming. RDBMS packages are generally
Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals NEW
 Oracle University Contact Us: 001-855-844-3881 & 001-800-514-06-97 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals NEW Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals
Oracle University Contact Us: 001-855-844-3881 & 001-800-514-06-97 Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals NEW Duration: 5 Days What you will learn This Oracle Database: SQL and PL/SQL Fundamentals
More on SQL. Juliana Freire. Some slides adapted from J. Ullman, L. Delcambre, R. Ramakrishnan, G. Lindstrom and Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan
 More on SQL Some slides adapted from J. Ullman, L. Delcambre, R. Ramakrishnan, G. Lindstrom and Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan SELECT A1, A2,, Am FROM R1, R2,, Rn WHERE C1, C2,, Ck Interpreting a Query
More on SQL Some slides adapted from J. Ullman, L. Delcambre, R. Ramakrishnan, G. Lindstrom and Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan SELECT A1, A2,, Am FROM R1, R2,, Rn WHERE C1, C2,, Ck Interpreting a Query
ECS 165A: Introduction to Database Systems
 ECS 165A: Introduction to Database Systems Todd J. Green based on material and slides by Michael Gertz and Bertram Ludäscher Winter 2011 Dept. of Computer Science UC Davis ECS-165A WQ 11 1 1. Introduction
ECS 165A: Introduction to Database Systems Todd J. Green based on material and slides by Michael Gertz and Bertram Ludäscher Winter 2011 Dept. of Computer Science UC Davis ECS-165A WQ 11 1 1. Introduction
Databases in Engineering / Lab-1 (MS-Access/SQL)
 COVER PAGE Databases in Engineering / Lab-1 (MS-Access/SQL) ITU - Geomatics 2014 2015 Fall 1 Table of Contents COVER PAGE... 0 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 Fundamentals... 3 1.2 How To Create a Database File
COVER PAGE Databases in Engineering / Lab-1 (MS-Access/SQL) ITU - Geomatics 2014 2015 Fall 1 Table of Contents COVER PAGE... 0 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 Fundamentals... 3 1.2 How To Create a Database File
ATTACHMENT 6 SQL Server 2012 Programming Standards
 ATTACHMENT 6 SQL Server 2012 Programming Standards SQL Server Object Design and Programming Object Design and Programming Idaho Department of Lands Document Change/Revision Log Date Version Author Description
ATTACHMENT 6 SQL Server 2012 Programming Standards SQL Server Object Design and Programming Object Design and Programming Idaho Department of Lands Document Change/Revision Log Date Version Author Description
Database Systems. S. Adams. Dilbert. Available: http://dilbert.com. Hans-Petter Halvorsen, M.Sc.
 Database Systems S. Adams. Dilbert. Available: http://dilbert.com Hans-Petter Halvorsen, M.Sc. Old fashion Database (Data-storage) Systems Not too long ago, this was the only data-storage device most companies
Database Systems S. Adams. Dilbert. Available: http://dilbert.com Hans-Petter Halvorsen, M.Sc. Old fashion Database (Data-storage) Systems Not too long ago, this was the only data-storage device most companies
SQL Server Database Coding Standards and Guidelines
 SQL Server Database Coding Standards and Guidelines http://www.sqlauthority.com Naming Tables: Stored Procs: Triggers: Indexes: Primary Keys: Foreign Keys: Defaults: Columns: General Rules: Rules: Pascal
SQL Server Database Coding Standards and Guidelines http://www.sqlauthority.com Naming Tables: Stored Procs: Triggers: Indexes: Primary Keys: Foreign Keys: Defaults: Columns: General Rules: Rules: Pascal
2. Oracle SQL*PLUS. 60-539 Winter 2015. Some SQL Commands. To connect to a CS server, do:
 60-539 Winter 2015 Some SQL Commands 1 Using SSH Secure Shell 3.2.9 to login to CS Systems Note that if you do not have ssh secure shell on your PC, you can download it from www.uwindsor.ca/softwaredepot.
60-539 Winter 2015 Some SQL Commands 1 Using SSH Secure Shell 3.2.9 to login to CS Systems Note that if you do not have ssh secure shell on your PC, you can download it from www.uwindsor.ca/softwaredepot.
SQL and Java. Database Systems Lecture 19 Natasha Alechina
 Database Systems Lecture 19 Natasha Alechina In this Lecture SQL in Java SQL from within other Languages SQL, Java, and JDBC For More Information Sun Java tutorial: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/jdbc
Database Systems Lecture 19 Natasha Alechina In this Lecture SQL in Java SQL from within other Languages SQL, Java, and JDBC For More Information Sun Java tutorial: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/jdbc
Bridge from Entity Relationship modeling to creating SQL databases, tables, & relations
 1 Topics for this week: 1. Good Design 2. Functional Dependencies 3. Normalization Readings for this week: 1. E&N, Ch. 10.1-10.6; 12.2 2. Quickstart, Ch. 3 3. Complete the tutorial at http://sqlcourse2.com/
1 Topics for this week: 1. Good Design 2. Functional Dependencies 3. Normalization Readings for this week: 1. E&N, Ch. 10.1-10.6; 12.2 2. Quickstart, Ch. 3 3. Complete the tutorial at http://sqlcourse2.com/
DATABASE INTRODUCTION
 Introduction The history of database system research is one of exceptional productivity and startling economic impact. We have learnt that from the days of file-based systems there are better ways to handle
Introduction The history of database system research is one of exceptional productivity and startling economic impact. We have learnt that from the days of file-based systems there are better ways to handle
Procedural Extension to SQL using Triggers. SS Chung
 Procedural Extension to SQL using Triggers SS Chung 1 Content 1 Limitations of Relational Data Model for performing Information Processing 2 Database Triggers in SQL 3 Using Database Triggers for Information
Procedural Extension to SQL using Triggers SS Chung 1 Content 1 Limitations of Relational Data Model for performing Information Processing 2 Database Triggers in SQL 3 Using Database Triggers for Information
Database 2 Lecture I. Alessandro Artale
 Free University of Bolzano Database 2. Lecture I, 2003/2004 A.Artale (1) Database 2 Lecture I Alessandro Artale Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bolzano Room: 221 [email protected] http://www.inf.unibz.it/
Free University of Bolzano Database 2. Lecture I, 2003/2004 A.Artale (1) Database 2 Lecture I Alessandro Artale Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bolzano Room: 221 [email protected] http://www.inf.unibz.it/
Database Design and Database Programming with SQL - 5 Day In Class Event Day 1 Activity Start Time Length
 Database Design and Database Programming with SQL - 5 Day In Class Event Day 1 Welcome & Introductions 9:00 AM 20 Lecture 9:20 AM 40 Practice 10:00 AM 20 Lecture 10:20 AM 40 Practice 11:15 AM 30 Lecture
Database Design and Database Programming with SQL - 5 Day In Class Event Day 1 Welcome & Introductions 9:00 AM 20 Lecture 9:20 AM 40 Practice 10:00 AM 20 Lecture 10:20 AM 40 Practice 11:15 AM 30 Lecture
Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server
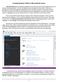 Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database server that stores and retrieves data for multi-user network-based applications. SQL Server databases are
Creating Database Tables in Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database server that stores and retrieves data for multi-user network-based applications. SQL Server databases are
5. CHANGING STRUCTURE AND DATA
 Oracle For Beginners Page : 1 5. CHANGING STRUCTURE AND DATA Altering the structure of a table Dropping a table Manipulating data Transaction Locking Read Consistency Summary Exercises Altering the structure
Oracle For Beginners Page : 1 5. CHANGING STRUCTURE AND DATA Altering the structure of a table Dropping a table Manipulating data Transaction Locking Read Consistency Summary Exercises Altering the structure
CSI 2132 Lab 3. Outline 09/02/2012. More on SQL. Destroying and Altering Relations. Exercise: DROP TABLE ALTER TABLE SELECT
 CSI 2132 Lab 3 More on SQL 1 Outline Destroying and Altering Relations DROP TABLE ALTER TABLE SELECT Exercise: Inserting more data into previous tables Single-table queries Multiple-table queries 2 1 Destroying
CSI 2132 Lab 3 More on SQL 1 Outline Destroying and Altering Relations DROP TABLE ALTER TABLE SELECT Exercise: Inserting more data into previous tables Single-table queries Multiple-table queries 2 1 Destroying
5.1 Database Schema. 5.1.1 Schema Generation in SQL
 5.1 Database Schema The database schema is the complete model of the structure of the application domain (here: relational schema): relations names of attributes domains of attributes keys additional constraints
5.1 Database Schema The database schema is the complete model of the structure of the application domain (here: relational schema): relations names of attributes domains of attributes keys additional constraints
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. Question Bank:
 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Question Bank: UNIT 1 1. Define Database? 2. What is a DBMS? 3. What is the need for database systems? 4. Define tupule? 5. What are the responsibilities of DBA? 6. Define schema?
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Question Bank: UNIT 1 1. Define Database? 2. What is a DBMS? 3. What is the need for database systems? 4. Define tupule? 5. What are the responsibilities of DBA? 6. Define schema?
php tek 2006 in Orlando Florida Lukas Kahwe Smith [email protected]
 Database Schema Deployment php tek 2006 in Orlando Florida Lukas Kahwe Smith [email protected] Agenda: The Challenge Diff Tools ER Tools Synchronisation Tools Logging Changes XML Formats SCM Tools Install
Database Schema Deployment php tek 2006 in Orlando Florida Lukas Kahwe Smith [email protected] Agenda: The Challenge Diff Tools ER Tools Synchronisation Tools Logging Changes XML Formats SCM Tools Install
There are five fields or columns, with names and types as shown above.
 3 THE RELATIONAL MODEL Exercise 3.1 Define the following terms: relation schema, relational database schema, domain, attribute, attribute domain, relation instance, relation cardinality, andrelation degree.
3 THE RELATIONAL MODEL Exercise 3.1 Define the following terms: relation schema, relational database schema, domain, attribute, attribute domain, relation instance, relation cardinality, andrelation degree.
Normal Form vs. Non-First Normal Form
 Normal Form vs. Non-First Normal Form Kristian Torp Department of Computer Science Aalborg Univeristy www.cs.aau.dk/ torp [email protected] September 1, 2009 daisy.aau.dk Kristian Torp (Aalborg University)
Normal Form vs. Non-First Normal Form Kristian Torp Department of Computer Science Aalborg Univeristy www.cs.aau.dk/ torp [email protected] September 1, 2009 daisy.aau.dk Kristian Torp (Aalborg University)
