An Overview of Organizational Behavior
|
|
|
- Edwina Shields
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Organizational Behavior MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Ans: D Page: 3 Group Ans: A Page: 3 Group Page: 4 AACSB: Communication Analytic skills Group Page: 4-5 Group 1. No matter how effective a manager might be, all organizational successes, and failures, are the results of a. effective strategic planning. b. comprehensive human resource selection. c. the organizations themselves. d. the behaviors of many people. e. the dynamics of the reward system of the organization. 2. Organizational behavior (OB) includes the study of all of the following, except a. international trade laws. b. the interface between people and organizations. c. human behavior in organizations. d. organizations themselves. e. All of these are included in OB. 3. The goal of a consultant hired to solve a problem in an organization should be to a. recognize that the organization has always been this way and little can be done to change it. b. learn as much as possible about the organization and the people within it. c. generate an action plan, with specific targets and completion dates. d. focus exclusively on changing the reward system, since everything else depends on it. e. make sure employees know the consultant has come to solve the company s problems. 4. Which is not an important reason for understanding organizational behavior? a. Most people are born and educated in organizations. b. Government organizations regulate many of our activities. c. Most employees will eventually become business managers. d. Organizational behavior offers specific perspectives on the human side of management. e. Most adults spend the better part of their lives working in organizations. Type K = Knowledge Question Type U = Understanding Question
2 2 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior Page: 6 Ans: E Page: 6 principles Ans: E Page: 7 AACSB: Diversity Analytic Page: 5 AACSB: Diversity HRM 5. Organizational behavior focuses on a. the economic side of management. b. the control side of management. c. the human side of management. d. the financial side of management. e. the production side of management. 6. Which of the following managers would you be least likely to find in an organization? a. Chief financial officer b. Marketing manager c. Director of public relations d. Vice president for human resources e. Organizational behavior manager 7. In dealing with the work related activities of people, managers must have an understanding of all of the following except a. leadership b. decision-making c. organizational structure and design d. organizational culture e. how to be an effective negotiator 8. The four groups of resources that organizations use in the pursuit of their goals and objectives include a. organizing, directing, decision making, and planning. b. investors, employees, unions, and government regulators. c. human, financial, physical, and/or information. d. spokesperson, figurehead, liaison, and monitor. e. time management skills, technical skills, transactional, and job design. 9. Leading is the process of a. designing jobs, grouping jobs into units, and establishing patterns of authority between jobs and units. b. determining the organization s desired future position and deciding how best to get there. c. motivating the organization s members to work together toward the organization s goals. d. monitoring and correcting the actions of the organization and its members to keep them directed toward their goals. e. utilizing organizational resources with the ultimate goal of attaining organizational goals efficiently and effectively. 10. A manager who creates and staffs a new sales division within the organization is performing which managerial function? a. Planning b. Organizing c. Controlling d. Supervising e. Leading
3 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 3 Page: 16 Reflective Thinking Ans: E Page: 12 Page: 9 Ans: E Ans: E AACSB: Reflective thinking skills AACSB: Communication abilities 11. suggests that in most organizations situations and outcomes are influenced by other variables. a. The systems approach to management b. The conceptual approach to management c. The situational perspective d. The interactionalism approach to management e. None of these 12. Evaluating performance, implementing reward systems, and verifying inventory levels are all examples of a. leading. b. decision making. c. organizing. d. planning. e. controlling. 13. Interpersonal roles of a manager include all of the following except a. figurehead b. leader c. monitor d. liaison e. All of these are interpersonal roles. 14. In the role of liaison, a manager would be most likely to a. attend the funeral of a former employee. b. hold a press conference announcing the introduction of a new product. c. hire, train, and motivate workers. d. inform employees about new government safety standards. e. negotiate the price of raw materials with an external supplier. 15. Which of the following managerial roles might include reading trade magazines to learn more about competitors? a. Spokesperson b. Disseminator c. Leader d. Resource allocator e. Monitor 16. A manager performing the role of disseminator is most likely to do which of the following? a. Speak at a Chamber of Commerce meeting b. Hire a new Human Resource Manager for the company c. Inform subordinates of newly founded competitors d. Develop a new strategic five-year plan for the company e. Design a new customer response system for the company
4 4 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior Ans: D Group Page: 11 Creation of Value Ans: D Page: 11 AACSB: Communication abilities Group Ans: D Page: 11 Reflective Thinking 17. The role of entrepreneur primarily involves a. dealing with others outside the organization. b. resolving disputes between various parties. c. being the voluntary initiator of change. d. serving as a representative of the organization. e. seeking information for strategic decisions. 18. A manager acting in the role of a resource allocator will a. choose the best resources to most effectively and efficiently produce the organization s product or service. b. verify the quality of resources that pass through the organization. c. determine how organizational resources will be released in the environment. d. decide how resources will be distributed among various individuals and groups within the organization. e. identify the various suppliers the organization will utilize to acquire resources. 19. A manager who develops a new chemical formula for a Dow Corning product is demonstrating effective a. interpersonal skills. b. technical skills. c. diagnostic skills. d. conceptual skills. e. leadership skills. 20. The manager s ability to communicate with, understand, and motivate individuals and groups is determined by her or his a. conceptual skills. b. time management skills. c. diagnostic skills. d. interpersonal skills. e. technical skills. 21. A manager who can see how the various tasks within the organization fit together and how each task contributes toward the big picture has strong a. problem-solving skills. b. diagnostic skills. c. technical skills. d. conceptual skills. e. interpersonal skills.
5 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 5 Ans: D Page: 11 Ans: D Page: 12 AACSB: Motivation Concepts Page: 12 Reflective Thinking Ans: E Page: 12 Motivation Concepts Page: 14 Group Page: 13 AACSB: Analytic Group 22. A manager who understands cause and effect relationships and recognizes optimal solutions to problems has strong a. interpersonal skills. b. problem-solving skills. c. conceptual skills. d. diagnostic skills. e. technical skills. 23. First-line managers need to depend more on their for success in the organization. a. diagnostic and interpersonal skills b. conceptual and diagnostic skills c. problem-solving and time management skills d. technical skills and interpersonal skills e. conceptual and technical skills 24. Upper-level managers must depend upon their for success in the organization. a. diagnostic and interpersonal skills b. conceptual and diagnostic skills c. problem-solving and time management skills d. technical skills and interpersonal skills e. conceptual and technical skills 25. Compared to lower-level and top-level managers, middle managers require more of which skill? a. Diagnostic b. Interpersonal c. Conceptual d. Technical e. Middle managers require an even distribution across all four above skills. 26. Information from which of the following disciplines would be least helpful in your study of organizational behavior? a. Political science b. Agriculture c. Medicine d. Anthropology e. Economics 27. Which of the following disciplines has helped to understand the behavior of people in organizational settings? a. Psychology b. Organizational Psychology c. Anthropology d. Engineering e. Medicine
6 6 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior Page: 12 Reflective Thinking Page: 14 Creation of Value Page: 14 AACSB: Reflective Thinking Group Page: 14 Group Ans: A Page: 16 Creation of Value Ans: D Page: 16 Environmental Influence 28. Contemporary organizational behavior is both in focus and in nature. a. dynamic; prescriptive b. stable; consistent c. interdisciplinary; descriptive d. cross-cultural; proscriptive e. interactional; behavioral 29. The field of engineering has helped managers better understand a. the causes and consequences of stress. b. productivity measurement. c. how and why people acquire power. d. conflict. e. coalition formation. 30. The descriptive nature of organizational behavior allows researchers to a. predict with certainty that changing a specific set of workplace variables will improve an individual s performance. b. suggest that certain general concepts or variables tend to relate to one another in a particular setting. c. prescribe the correct way to manage people. d. stabilize the complexities inherent in studying human behavior. e. increase the job satisfaction of nearly all workers. 31. The central processes of interest in organizational behavior can be grouped into which of the following basic categories? a. Contextual, situational, and industrial b., interpersonal, and organizational c. Referential, supplemental, and complementary d. Transactional, transformational, and interactional e. Dynamic, static, and semi-static 32. Under the systems perspective, a system is defined as a. an interrelated set of elements that functions as a whole. b. a procedure for fair and impartial performance appraisals. c. a collection of independent organizations. d. the central technology of the organization. e. the ideal process for completing a particular job. 33. All of the following are inputs an organization receives from its environment, except a. money. b. materials. c. people. d. services. e. information.
7 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 7 Page: 17 AASCB: Analytic skills Creation of Value Ans: A Page: 17 Technology Ans: A Page: 18 Strategy Ans: A Page: 18 Group Ans: A Page: Under the systems view, the information Wal-Mart managers receive concerning expected customer demand for certain products is one type of a. technology. b. output. c. input. d. transformation. e. contingency. 35. The systems view is important to managers because it a. underscores the importance of the organization s environment. b. gives them a set procedure for making decisions. c. allows them to eliminate the interaction among various elements of the organization. d. reduces their risk of human error. e. shifts the focus from outside the company to inside the company. 36. Which of the following perspectives argues that universal rules, solutions, guidelines, predictions, and principles are not feasible when applied to organizations? a. The situational perspective b. Behavioral organization theory c. The systems perspective d. The interactional perspective e. Classical organization theory 37. Which perspective of management would most likely refute the notion that one style of leadership would enhance employee satisfaction and job performance under any condition? a. Situational perspective b. Classical perspective c. Behavioral perspective d. Interactional perspective e. Universal perspective 38. attempts to explain how people select, interpret, and change various situations. a. Interactionalism b. Contextualism c. Universalism d. ism e. Systems theory
8 8 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior Ans: E Page: Which of the following is not studied as an individual-level outcome in organizational behavior? a. Productivity b. Absenteeism c. Turnover d. Performance e. Cohesiveness Ans: D Page: 21 Strategy 40. Some outcomes can be studied at the individual, group and organization levels. Which of the following is generally assessed only at the organizational level? a. Satisfaction b. Performance c. Organizing d. Profitability e. Planning TRUE-FALSE QUESTIONS Page: 3 Group Page: 3 Ans: False Page: 4 Group Ans: False Strategy 41. T F Organizational behavior is the study of human behavior in organizational settings, the interface between human behavior and the organization, and the organizational itself. 42. T F The best managers try to understand workers behavior and the organization. 43. T F Organizational behavior is a designated business function just like marketing and accounting. 44. T F Deciding to gain a larger market share by charging a lower price for the organization s product is part of the planning function.
9 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 9 Ans: False Ans: False HRM Ans: False Page: 11 AACSB: Reflective Thinking Page: 11 Page: T F Organizing is the process of determining what the organization s position and situation should be at some point in the future and deciding how best to get there. 46. T F Leading is the process of motivating members of the organization to work together toward the organization s goal. 47. T F The controlling function includes designing jobs, grouping jobs into manageable units, and establishing patterns of authority among jobs and groups of jobs. 48. T F Managers in the roles of liaison and spokesperson both deal with people outside of the organization. 49. T F Figurehead, leader, and liaison are all interpersonal roles that a manager can perform in an organization. 50. T F The ability to think in the abstract comes from a manager s diagnostic skills. 51. T F Managers use their interpersonal skills to motivate individuals and groups. 52. T F Top managers need stronger conceptual and diagnostic skills more than technical and interpersonal skills.
10 10 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior Page: 13 Motivation Concepts Page: 14 Page: 14 AACSB: Diversity Page: 16 Strategy Page: 17 AACSB: Strategy Creation of Value Ans: False Page: 17 Technology Page: 17 AACSB: Reflective Thinking Strategy Page: 17 Group 53. T F Organizational behavior draws on research from the fields of psychology, sociology, and engineering. 54. T F Decision-making roles include disturbance handler, resource allocator, and negotiator. 55. T F Anthropology is concerned with the interactions between people and their environments, especially their cultural environment. 56. T F A system is an interrelated set of elements that function as a whole. 57. T F An organizational system receives inputs from the environment, combines and transforms them, and then returns them to the environment. 58. T F A systems perspective keeps managers focused on internal processes and prevents them from being distracted by the environment. 59. T F In organizations, most situations and outcomes are contingent; the precise relationship between any two variables is likely to be situational, dependent on other variables. 60. T F Over time, organizational behavior has gradually shifted from a universal perspective to a situational perspective.
11 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 11 Page: 16 Strategy Page: 17 Page: 20 Page: 19 AACSB: Creation of Value Page: T F The organizational system has four basic categories of input from its environment: information, financial, material, and human. 62. T F The notion that the relation between workers skill levels and their performance levels depends on their degree of loyalty illustrates a situational perspective. 63. T F Interactionalism attempts to explain how people select, interpret, and change various situations. 64. T F Productivity can be measured at the individual and organizational levels. 65. T F A manager who pays workers high wages may increase workers satisfaction, but may also lower important organizational-level outcomes. COMPLETION Ans: Organizational behavior Page: 3 ACSB: Analytic skills Group Ans: people Page: 3 Group 66. can be defined as the study of human behavior in organizational settings, the interface between human behavior and the organization, and the organization itself. 67. Regardless of size, scope, or location, all organizations have at least one thing in common; they are made up of.
12 12 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior Ans: organizational behavior Page: 5 Group Ans: social context Page: 7 Group Ans: organizing Strategy 68. The study of can greatly clarify the factors that affect how managers manage. 69. Whether a business is large or small, domestic or international, growing or stagnating, its managers perform their work within a. 70. By designing jobs and establishing patterns of authority, the manager is performing the function. Ans: Leading 71. is the process of motivating employees of an organization to work together toward the organization s goals. Ans: controlling Group Ans: leader HRM Ans: liaison 72. Performance evaluation, reward systems, and motivation all apply to. 73. Managers that hire, train, and motivate employees are filling the role of. 74. The role includes setting up ongoing purchasing arrangements for the organization with an external supplier.
13 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 13 Ans: monitor Ans: disseminator AACSB: Communication abilities Motivation Concepts Ans: spokesperson AACSB: Communication Abilities Ans: negotiator AACSB: Communication abilities Ans: disturbance handler AACSB: Communication abilities Group Ans: Diagnostic skills Page: 11 Reflective Thinking Ans: Anthropology Page: 13 AACSB: Diversity understanding Group 75. Attending a business convention to gather information about new industry developments would be part of the role. 76. A manager in the role of might tell employees about the company s retirement plan. 77. The role of involves speaking to external constituencies on behalf of the organization. 78. The serves as a representative of the organization in reaching agreements with other organizations, such as labor unions. 79. The helps settle disputes between various parties, such as other managers and their subordinates. 80. allow managers to better understand causeand-effect relationships and to recognize the optimal solution to problems. 81. is concerned with the interactions between people and their environments, especially their cultural environment.
14 14 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior Ans: psychology Page: 13 Group Ans: Sociology Page: 13 AACSB: Diversity understanding Group Ans: system Page: 16 Creation of Value Strategy Ans: outputs Page: 16 Creation of Value Ans: inputs Page: 16 Strategy Ans: Performance Page: 19 Group Ans: universal Page: According to your text, the field of study known as is the greatest contributor to the field of organizational behavior. 83. involves the study of social systems, such as families, occupational classes, and organizations. 84. A is an interrelated set of elements functioning as a whole. 85. Products and services, profits and losses, and employee behaviors are all types of that an organizational system releases to the environment. 86. Managers, office equipment, funds from stockholders, and sales forecasts are all examples of to an organizational system. 87. is made up of all work-related behaviors. 88. From a perspective, managers seek the one best way to solve problems under any conditions.
15 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 15 Ans: Interactionalism Page: 18 Group Ans: productivity Page: 19 Group 89. attempts to explain how people select, interpret, and change various situations. 90. A person s is an indicator of his or her efficiency and is measured in terms of the products or services created per unit of output. MATCHING QUESTIONS 91. study of human behavior a. relating to others 92. human side of management b. announces new products to press 93. basic management function c. sold to the consuming public 94. liaison role d. transformation of inputs to outputs 95. technical skills e. interrelated set of elements 96. conceptual skills f. organizing 97. organizational outputs g. level of outputs per input 98. technology h. aids study of organization culture 99. monitor i. leader 100. situation theory j. organizational behavior 101. entrepreneur k. universal conclusions impossible 102. diagnostic skills l. power and decision making 103. spokesperson m. think in the abstract 104. decision-making role n. cause-and-effect relationships 105. interpersonal role o. voluntary initiator of change 106. systems theory p. people as resources 107. productivity q. the field of medicine 108. anthropology r. resource allocator 109. stress s. seeks valuable information 110. political science t. accomplish specific tasks ANSWERS TO MATCHING QUESTIONS 91. j, Analytic skills Group 92. p, Analytic skills 93. f, Analytic skills 94. a, Group 95. t, Analytic skills 96. m, Reflective thinking skills Strategy 97. c, Analytic skills Strategy 98. d, Analytic skills Strategy 99. s, Analytic skills
16 16 Chapter 1: An Overview of Organizational Behavior 100. k, Analytic skills Strategy 101. o, Analytic skills 102. n, Reflective thinking skills Strategy 103. b, Communication abilities 104. r, Analytic skills Strategy 105. i, Analytic skills 106. e, Analytic skills Strategy 107. g, Analytic skills Strategy 108. h, Multicultural and diversity understanding Group 109. q, Analytic skills 110. l, Analytic skills ESSAY QUESTIONS 111. Define organizational behavior in terms of the individual, the individual-organizational interface, and the organization itself. AACSB: Analytic Group 112. Explain why it is important for managers to have a good understanding of organizational behavior. AACSB: Analytic skills Group 113. Discuss the four basic managerial functions and how they related to organizational behavior. AACSB: Analytic 114. Describe, discuss, and give examples of the central concepts of organizational behavior that are grouped into three basic categories. Group 115. Describe the relative importance of the four managerial skills for top managers versus lower-level managers Identify, discuss, and give examples of the contextual perspectives on Organizational Behavior. AACSB: Analytic skills Group 117. What is meant by the statement that organizational behavior has a descriptive, rather than prescriptive, nature? How does this relate to its importance as a managerial tool? Communication 118. Using the model presented in your text, briefly define systems theory. Give an example of each component of systems theory as it exists in an organization. Creation of Value 119. Compare and contrast the universal and situational perspectives in organizational behavior. AACSB: Analytic skills Group 120. Compare and contrast individual-level outcomes, group-level outcomes, and organizational-level outcomes. Group
Management levels. Middle-level managers
 MANAGEMENT LEVELS 2 Management levels Managers are organizational members who are responsible for the work performance of other organizational members. Managers have formal authority to use organizational
MANAGEMENT LEVELS 2 Management levels Managers are organizational members who are responsible for the work performance of other organizational members. Managers have formal authority to use organizational
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Department of Management
 Department of Management Course Student Learning Outcomes (ITM and MGMT) ITM 1270: Fundamentals of Information Systems and Applications Upon successful completion of the course, a student will be able
Department of Management Course Student Learning Outcomes (ITM and MGMT) ITM 1270: Fundamentals of Information Systems and Applications Upon successful completion of the course, a student will be able
Strategic Management and Leadership. Prepared by Mr Rabeel Sabar
 Strategic Management and Leadership Prepared by Mr Rabeel Sabar Strategy Defined as: A plan of action designed to achieve a longterm or overall aim (Oxford, 2011) Strategy in Business World Defined as:
Strategic Management and Leadership Prepared by Mr Rabeel Sabar Strategy Defined as: A plan of action designed to achieve a longterm or overall aim (Oxford, 2011) Strategy in Business World Defined as:
1.0 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT
 1.0 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT 1.1 INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT In most aspect of our lives we are member of one organization or another a college, a sport team, a musical, religions or theatre
1.0 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT 1.1 INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT In most aspect of our lives we are member of one organization or another a college, a sport team, a musical, religions or theatre
EMBA CURRICULUM - FIRST YEAR
 EMBA CURRICULUM - FIRST YEAR EMBA 0010 Professional Development Activities This required non-credit course is intended to provide opportunities to understand management skills and achieve a greater understanding
EMBA CURRICULUM - FIRST YEAR EMBA 0010 Professional Development Activities This required non-credit course is intended to provide opportunities to understand management skills and achieve a greater understanding
MANAGEMENT COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1
 MANAGEMENT COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1 MGT 202: Business Professions 1. Describe and use the elements of effective decision making research, assessment and consequence. 2. Apply elements of effective
MANAGEMENT COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1 MGT 202: Business Professions 1. Describe and use the elements of effective decision making research, assessment and consequence. 2. Apply elements of effective
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions
 Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
whether you intend to work in HRM or not, most of these elements will affect you at some point in your
 MGT - 501 T his subject/course is designed to teach the basic principles of Human Resource Management (HRM) to diverse audience/students, including those who are studying this as a supporting subject for
MGT - 501 T his subject/course is designed to teach the basic principles of Human Resource Management (HRM) to diverse audience/students, including those who are studying this as a supporting subject for
Business Management and Leadership (MS)
 Business Management and Leadership (MS) ACADEMIC DIRECTOR: B. Loerinc Helft CUNY School of Professional Studies 101 West 31 st Street, 7 th Floor New York, NY 10001 Email Contact: B. Loerinc Helft, [email protected]
Business Management and Leadership (MS) ACADEMIC DIRECTOR: B. Loerinc Helft CUNY School of Professional Studies 101 West 31 st Street, 7 th Floor New York, NY 10001 Email Contact: B. Loerinc Helft, [email protected]
3.0 BACHELOR OF COMMERCE. 100 Series. BBA 100: Business Studies
 3.0 BACHELOR OF COMMERCE 100 Series BBA 100: Business Studies Introduction and definition of business, Interaction between business firms and society. Aim, Forms of business ownership: such as sole-proprietorship,
3.0 BACHELOR OF COMMERCE 100 Series BBA 100: Business Studies Introduction and definition of business, Interaction between business firms and society. Aim, Forms of business ownership: such as sole-proprietorship,
Human Resource Management at Work
 Human Resource Management at Work 1. Which of the following statements most accurately defines human resource management? a) Human resource management seeks to achieve competitive advantage through the
Human Resource Management at Work 1. Which of the following statements most accurately defines human resource management? a) Human resource management seeks to achieve competitive advantage through the
SOUTH SEATTLE COMMUNITY COLLEGE (Technical Education) COURSE OUTLINE Allen Stowers - Date: January 09. Executive Development and Leadership
 1 SOUTH SEATTLE COMMUNITY COLLEGE (Technical Education) COURSE OUTLINE Allen Stowers - Date: January 09 DEPARTMENT: CURRICULUM: COURSE TITLE: Supervision & Management (SMG) Supervision and Management Executive
1 SOUTH SEATTLE COMMUNITY COLLEGE (Technical Education) COURSE OUTLINE Allen Stowers - Date: January 09 DEPARTMENT: CURRICULUM: COURSE TITLE: Supervision & Management (SMG) Supervision and Management Executive
Information systems for management ดร. สล ล บ ญพราหมณ 2558
 1 Information systems for management ดร. สล ล บ ญพราหมณ 2558 2...ความสว สด ของข าพเจ าจะเก ดข นได ก ด วยบ านเม องของเราม ความเจร ญม นคงเป นปกต ส ข ความเจร ญม นคงท งน นจะส าเร จ ผลเป นจร งไปได ก ด วยท กคนท
1 Information systems for management ดร. สล ล บ ญพราหมณ 2558 2...ความสว สด ของข าพเจ าจะเก ดข นได ก ด วยบ านเม องของเราม ความเจร ญม นคงเป นปกต ส ข ความเจร ญม นคงท งน นจะส าเร จ ผลเป นจร งไปได ก ด วยท กคนท
SAMPLE JOB DESCRIPTIONS
 SAMPLE JOB DESCRIPTIONS In this section we have provided a number of sample job descriptions. We hope that they will provide you with guidance as you develop job descriptions(s). Level Title Page Consultant
SAMPLE JOB DESCRIPTIONS In this section we have provided a number of sample job descriptions. We hope that they will provide you with guidance as you develop job descriptions(s). Level Title Page Consultant
MBAProgramme. The College of The Bahamas
 c o u r s e o u t l i n e MBAProgramme The College of The Bahamas Year 1 Fall Financial/Managerial Accounting (3 credits) Introduces students to the financial and managerial accounting disciplines; develops
c o u r s e o u t l i n e MBAProgramme The College of The Bahamas Year 1 Fall Financial/Managerial Accounting (3 credits) Introduces students to the financial and managerial accounting disciplines; develops
Enhancing Decision Making
 Enhancing Decision Making Content Describe the different types of decisions and how the decision-making process works. Explain how information systems support the activities of managers and management
Enhancing Decision Making Content Describe the different types of decisions and how the decision-making process works. Explain how information systems support the activities of managers and management
UNDERSTANDING AND MANAGING ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 UNDERSTANDING AND MANAGING ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Delta Publishing Company 1 Copyright 2006 by DELTA PUBLISHING COMPANY P.O. Box 5332, Los Alamitos, CA 90721-5332 All rights reserved. No part of this
UNDERSTANDING AND MANAGING ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Delta Publishing Company 1 Copyright 2006 by DELTA PUBLISHING COMPANY P.O. Box 5332, Los Alamitos, CA 90721-5332 All rights reserved. No part of this
Master of Arts in Employment and Labor Relations (MAELR) http://www.clas.wayne.edu/maelr/ Labor @ Wayne
 Master of Arts in Employment and Labor Relations (MAELR) http://www.clas.wayne.edu/maelr/ Labor @ Wayne Director, Dr. Marick Masters Academic Advisors: Frank Koscielski/ [email protected] Linda J. Johnson/
Master of Arts in Employment and Labor Relations (MAELR) http://www.clas.wayne.edu/maelr/ Labor @ Wayne Director, Dr. Marick Masters Academic Advisors: Frank Koscielski/ [email protected] Linda J. Johnson/
Management Courses-1
 Management Courses-1 MGT 201/Management Principles and Practices Provides an introduction to the core concepts and theories of management. Emphasis is on developing a theoretical foundation in the various
Management Courses-1 MGT 201/Management Principles and Practices Provides an introduction to the core concepts and theories of management. Emphasis is on developing a theoretical foundation in the various
CHAPTER 1: A FRAMEWORK FOR INTERPERSONAL SKILL DEVELOPMENT
 CHAPTER 1: A FRAMEWORK FOR INTERPERSONAL SKILL DEVELOPMENT The first chapter sets the stage for improving interpersonal relations in organizations by presenting a framework for interpersonal skill development
CHAPTER 1: A FRAMEWORK FOR INTERPERSONAL SKILL DEVELOPMENT The first chapter sets the stage for improving interpersonal relations in organizations by presenting a framework for interpersonal skill development
Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration and Master's Degree course description
 Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration and Master's Degree course description Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration Department s Compulsory Requirements Course Description (402102) Principles
Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration and Master's Degree course description Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration Department s Compulsory Requirements Course Description (402102) Principles
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.
 OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
MBA REQUIRED (CORE) COURSES
 MBA REQUIRED (CORE) COURSES ACCT 720 - Strategic Cost Management Study of the role of cost management methods in aiding managers in all of their planning, controlling and evaluating activities; focus on
MBA REQUIRED (CORE) COURSES ACCT 720 - Strategic Cost Management Study of the role of cost management methods in aiding managers in all of their planning, controlling and evaluating activities; focus on
Supervision. Samuel C. Certo. Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College. I McGraw-Hill I Irwin
 Supervision Concepts and Skill-Building Seventh Edition Samuel C. Certo Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College I McGraw-Hill I Irwin Contents Preface iv About
Supervision Concepts and Skill-Building Seventh Edition Samuel C. Certo Steinmetz Professor of Management Crummer Graduate School of Business Rollins College I McGraw-Hill I Irwin Contents Preface iv About
International Business Programme, Bachelor Course Descriptions 2015-2016
 International Business Programme, Bachelor Course Descriptions 2015-2016 The following course descriptions briefly describe the course contents, how many credits the course is worth, if the course is given
International Business Programme, Bachelor Course Descriptions 2015-2016 The following course descriptions briefly describe the course contents, how many credits the course is worth, if the course is given
HUMAN RESOURCES ANALYST 3 1322
 HUMAN RESOURCES ANALYST 3 1322 GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CLASS Human Resource Analysts do strategic and operational management activities related to the performance of Human Resource in State agencies. Human
HUMAN RESOURCES ANALYST 3 1322 GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CLASS Human Resource Analysts do strategic and operational management activities related to the performance of Human Resource in State agencies. Human
Program of Study: Bachelor of Science in Health Care Administration
 Program of Study: Bachelor of Science in Administration Program Description The Bachelor of Science in Administration (BSHA) is an undergraduate professional degree designed to prepare students for entry-level
Program of Study: Bachelor of Science in Administration Program Description The Bachelor of Science in Administration (BSHA) is an undergraduate professional degree designed to prepare students for entry-level
DIPLOMA PROGRAM IN BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (DPBA)
 DIPLOMA PROGRAM IN BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (DPBA) General Information: This is a high level academic program based on theory-practice advances from business management to transmit specialized knowledge
DIPLOMA PROGRAM IN BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (DPBA) General Information: This is a high level academic program based on theory-practice advances from business management to transmit specialized knowledge
Revised Body of Knowledge And Required Professional Capabilities (RPCs)
 Revised Body of Knowledge And Required Professional Capabilities (RPCs) PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE Strategic contribution to organizational success RPC:1 Contributes to the development of the organization s
Revised Body of Knowledge And Required Professional Capabilities (RPCs) PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE Strategic contribution to organizational success RPC:1 Contributes to the development of the organization s
CHITTAGONG INDEPENDENT UNIVERSITY (CIU) MBA Program COURSE CURRICULUM
 CHITTAGONG INDEPENDENT UNIVERSITY (CIU) MBA Program COURSE CURRICULUM Requirements for the MBA Major in Human Resources Management Program a) In the School of Business graduate courses are grouped into
CHITTAGONG INDEPENDENT UNIVERSITY (CIU) MBA Program COURSE CURRICULUM Requirements for the MBA Major in Human Resources Management Program a) In the School of Business graduate courses are grouped into
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.
 OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
1. Global E Business and Collaboration. Lecture 2 TIM 50 Autumn 2012
 1. Global E Business and Collaboration Lecture 2 TIM 50 Autumn 2012 Objective of the Learning The Major Feature of Business Systems Performance of Business Organization Levels of Business management The
1. Global E Business and Collaboration Lecture 2 TIM 50 Autumn 2012 Objective of the Learning The Major Feature of Business Systems Performance of Business Organization Levels of Business management The
WASHBURN UNIVERSITY DUAL DEGREE PROGRAM School of Law (J.D.) & School of Business (M.B.A.)
 WASHBURN UNIVERSITY DUAL DEGREE PROGRAM School of Law (J.D.) & School of Business (M.B.A.) Recognizing that legal and business studies complement each other and that real-world problems often require solutions
WASHBURN UNIVERSITY DUAL DEGREE PROGRAM School of Law (J.D.) & School of Business (M.B.A.) Recognizing that legal and business studies complement each other and that real-world problems often require solutions
DIRECTOR OF HUMAN RESOURCES & EMPLOYER-EMPLOYEE RELATIONS-EEO, DIVERSITY COMPLIANCE & TRAINING,
 Page 1 of 6 DIRECTOR OF HUMAN RESOURCES & EMPLOYER-EMPLOYEE RELATIONS-EEO, DIVERSITY COMPLIANCE & TRAINING, JC #676 - Classified Management - Integrated Academic Administrator and Classified Manager Salary
Page 1 of 6 DIRECTOR OF HUMAN RESOURCES & EMPLOYER-EMPLOYEE RELATIONS-EEO, DIVERSITY COMPLIANCE & TRAINING, JC #676 - Classified Management - Integrated Academic Administrator and Classified Manager Salary
HUMAN RESOURCES. Administration I I I I I. Dive~ily. Training. See R1sk Managemenl section for budget del311s
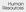 Human Resources HUMAN RESOURCES I Administration I I I I I I Dive~ily Training '" Lab-or and Employment Relations Organization E fleclive ness Program See R1sk Managemenl section for budget del311s Mission
Human Resources HUMAN RESOURCES I Administration I I I I I I Dive~ily Training '" Lab-or and Employment Relations Organization E fleclive ness Program See R1sk Managemenl section for budget del311s Mission
COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS
 COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS DEAN OF THE COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS OFFICE OF THE DEAN MISSION VALUES PROGRAMMATIC ACCREDITATION MAJOR DEGREE PROGRAMS MINORS DISCIPLINES (FIELDS OF STUDY) ACADEMIC
COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS DEAN OF THE COLLEGE OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS OFFICE OF THE DEAN MISSION VALUES PROGRAMMATIC ACCREDITATION MAJOR DEGREE PROGRAMS MINORS DISCIPLINES (FIELDS OF STUDY) ACADEMIC
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.
 OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
INFO1400. Define an organization and compare the technical definition of organizations with the behavioral definition.
 Chapter 3 INFO1400 Review Questions 1. Which features of organizations do managers need to know about to build and use information systems successfully? What is the impact of information systems on organizations?
Chapter 3 INFO1400 Review Questions 1. Which features of organizations do managers need to know about to build and use information systems successfully? What is the impact of information systems on organizations?
Master of Arts (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) M.A. (Industrial and Organizational Psychology)
 Master of Arts (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) M.A. (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) Objectives The program aims to enable graduate students to analyze, to carry on the research projects,
Master of Arts (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) M.A. (Industrial and Organizational Psychology) Objectives The program aims to enable graduate students to analyze, to carry on the research projects,
C a r e e r C l u s t e r s F o c u s i n g education on the future. Preparing for Career Success in Business Management and Administration CC9004
 C a r e e r C l u s t e r s F o c u s i n g education on the future Preparing for Career Success in Business and Administration CC9004 Career Clusters Focusing Career Clusters Prepare All Students for
C a r e e r C l u s t e r s F o c u s i n g education on the future Preparing for Career Success in Business and Administration CC9004 Career Clusters Focusing Career Clusters Prepare All Students for
GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Federal Acquisition Service Mission Oriented Business Integrated Services (MOBIS) SCHEDULE PRICE LIST
 GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Federal Acquisition Service Mission Oriented Business Integrated Services (MOBIS) SCHEDULE PRICE LIST SIN 874-7 Interior Systems, Inc., dba ISI Professional Services 1201
GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Federal Acquisition Service Mission Oriented Business Integrated Services (MOBIS) SCHEDULE PRICE LIST SIN 874-7 Interior Systems, Inc., dba ISI Professional Services 1201
Finding the Right People for Your Program Evaluation Team: Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions
 : Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions I. Overview II. Sample Evaluator Job Description III. Evaluator Competencies IV. Recruiting members of your strategic evaluation planning team V. Recruiting
: Evaluator and Planning Team Job Descriptions I. Overview II. Sample Evaluator Job Description III. Evaluator Competencies IV. Recruiting members of your strategic evaluation planning team V. Recruiting
98 Business, Management, Marketing, and Technology
 98 Business, Management, Marketing, and Technology MI-SG-FLD098-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact
98 Business, Management, Marketing, and Technology MI-SG-FLD098-02 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1: General Information About the MTTC Program and Test Preparation OVERVIEW OF THE TESTING PROGRAM... 1-1 Contact
Master of Business Administration Program in the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics
 Master of Business Administration Program in the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics The Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at Haigazian University offers a degree program leading
Master of Business Administration Program in the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics The Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at Haigazian University offers a degree program leading
Master of Business Administration Program in the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics
 Master of Business Administration Program in the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics The Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at Haigazian University offers a degree program leading
Master of Business Administration Program in the Faculty of Business Administration and Economics The Faculty of Business Administration and Economics at Haigazian University offers a degree program leading
Certificate in Human Resources Management
 Certificate in Human Resources Management Looking for a Rewarding and Challenging Career in Human Resources? In today s turbulent marketplace the human resources professional faces many challenges. From
Certificate in Human Resources Management Looking for a Rewarding and Challenging Career in Human Resources? In today s turbulent marketplace the human resources professional faces many challenges. From
2013 HSC Business Studies Marking Guidelines
 2013 HSC Business Studies Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 D 2 B 3 C 4 A 5 A 6 B 7 D 8 D 9 C 10 D 11 B 12 C 13 C 14 D 15 A 16 A 17 B 18 A 19 D 20 C 1 Section II
2013 HSC Business Studies Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 D 2 B 3 C 4 A 5 A 6 B 7 D 8 D 9 C 10 D 11 B 12 C 13 C 14 D 15 A 16 A 17 B 18 A 19 D 20 C 1 Section II
The New Human Resource Department: A Cross-Functional Unit
 FORUM The New Human Resource Department: A Cross-Functional Unit Joan F. Marques As new trends in business operations take hold, the need for a redefined human resource department, including what it should
FORUM The New Human Resource Department: A Cross-Functional Unit Joan F. Marques As new trends in business operations take hold, the need for a redefined human resource department, including what it should
Video Game Design (3 Teams per state, 2 team members minimum)
 Content Area Standard Strand 21st-Century Life & Careers 9.4 Career and Technical Education: All students who complete a career and technical education program will acquire academic and technical skills
Content Area Standard Strand 21st-Century Life & Careers 9.4 Career and Technical Education: All students who complete a career and technical education program will acquire academic and technical skills
City of Portland Job Code: 30000537. CLASS SPECIFICATION Labor/Employee Relations Manager
 City of Portland Job Code: 30000537 CLASS SPECIFICATION Labor/Employee Relations Manager FLSA Status: Exempt Union Representation: Nonrepresented/Incumbents hired after May 25, 2011 are exempt from Civil
City of Portland Job Code: 30000537 CLASS SPECIFICATION Labor/Employee Relations Manager FLSA Status: Exempt Union Representation: Nonrepresented/Incumbents hired after May 25, 2011 are exempt from Civil
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.
 OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
THE MASTER OF ARTS PROGRAM IN INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCE NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
 THE MASTER OF ARTS PROGRAM IN INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCE NEW YORK UNIVERSITY Information Booklet for Applicants Director: Barry H. Cohen, Ph.D Telephone: 212-998-7815
THE MASTER OF ARTS PROGRAM IN INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCE NEW YORK UNIVERSITY Information Booklet for Applicants Director: Barry H. Cohen, Ph.D Telephone: 212-998-7815
Course Descriptions for the Business Essentials Program
 Course Descriptions for the Business Essentials Program Upon completion of one, two, three or four quarters, students will earn Certificates of Completion. All courses listed are required in order to earn
Course Descriptions for the Business Essentials Program Upon completion of one, two, three or four quarters, students will earn Certificates of Completion. All courses listed are required in order to earn
Digital Asset Manager, Digital Curator. Cultural Informatics, Cultural/ Art ICT Manager
 Role title Digital Cultural Asset Manager Also known as Relevant professions Summary statement Mission Digital Asset Manager, Digital Curator Cultural Informatics, Cultural/ Art ICT Manager Deals with
Role title Digital Cultural Asset Manager Also known as Relevant professions Summary statement Mission Digital Asset Manager, Digital Curator Cultural Informatics, Cultural/ Art ICT Manager Deals with
Pool Canvas. Add. Creation Settings. Chapter 1--Introduction to Cost Management. Description Instructions. Add Question Here
 1 of 13 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
1 of 13 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions.
MANAGEMENT. MGMT 0021 THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS 3 cr. MGMT 0022 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 3 cr. MGMT 0023 MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING 3 cr.
 MANAGEMENT MGMT 0021 THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS 3 cr. An introduction designed to emphasize the basic principles, practices, and terminology essential to the understanding of contemporary business and its
MANAGEMENT MGMT 0021 THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS 3 cr. An introduction designed to emphasize the basic principles, practices, and terminology essential to the understanding of contemporary business and its
BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (Non-EMBA) COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1
 BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (Non-EMBA) COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1 BA 100: Exploration of Business 1. Explain the culture of higher education. 2. Undertake critical examination and self-reflection
BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION (Non-EMBA) COURSES Student Learning Outcomes 1 BA 100: Exploration of Business 1. Explain the culture of higher education. 2. Undertake critical examination and self-reflection
EVALUATION OF THE CHIEF EXECUTIVE
 EVALUATION OF THE CHIEF EXECUTIVE A Briefing for Non-Profit Boards of Directors Prepared by: BERKELEY DEVELOPMENTAL RESOURCES WWW.BDRCONSULTANTS.COM Outline of Key Points: 1. What is Executive Evaluation?
EVALUATION OF THE CHIEF EXECUTIVE A Briefing for Non-Profit Boards of Directors Prepared by: BERKELEY DEVELOPMENTAL RESOURCES WWW.BDRCONSULTANTS.COM Outline of Key Points: 1. What is Executive Evaluation?
RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT
 RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT COURSE OBJECTIVE The objective of this course is to clarify the principles of Internal Audit along with the Audit process and arm internal auditors with a good knowledge of risk
RISK BASED INTERNAL AUDIT COURSE OBJECTIVE The objective of this course is to clarify the principles of Internal Audit along with the Audit process and arm internal auditors with a good knowledge of risk
How information systems are transforming business. Globalization opportunities. Introduction to Information Management IIM, NCKU
 Introduction to Information Management IIM, NCKU Define complementary assets and explain how they ensure that information systems provide genuine value to an organization. Describe the different academic
Introduction to Information Management IIM, NCKU Define complementary assets and explain how they ensure that information systems provide genuine value to an organization. Describe the different academic
B.S. in Tourism & Hospitality Management Curriculum
 B.S. in Tourism & Hospitality Management Curriculum School of Tourism & Hospitality Management Curriculum 64 Credits Foundation Requirements 25 Credits STHM 1113 STHM 2114 STHM 3185 STHM 4112 STHM 4185
B.S. in Tourism & Hospitality Management Curriculum School of Tourism & Hospitality Management Curriculum 64 Credits Foundation Requirements 25 Credits STHM 1113 STHM 2114 STHM 3185 STHM 4112 STHM 4185
JHU CCP Zambia Chief of Party
 JHU CCP Zambia Chief of Party General Job Description The Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Center for Communication Programs (JHU CCP) seeks a Chief of Party to provide strategic leadership
JHU CCP Zambia Chief of Party General Job Description The Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Center for Communication Programs (JHU CCP) seeks a Chief of Party to provide strategic leadership
BANGLADESH INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT 4 Sobhanbag, Mirpur Road, Dhaka-1207 POST-GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT SYLLABUS FOR PART-I
 BANGLADESH INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT POST-GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT SYLLABUS FOR PART-I Evaluation Criteria : Class Attendance : 10% Class Test : 20% Final Examination : 70% Name of Subjects
BANGLADESH INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT POST-GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT SYLLABUS FOR PART-I Evaluation Criteria : Class Attendance : 10% Class Test : 20% Final Examination : 70% Name of Subjects
AACSB Standards. from the Eligibility Procedures and Accreditation Standards for Business Accreditation Handbook, revised January 31, 2010
 AACSB Standards from the Eligibility Procedures and Accreditation Standards for Business Accreditation Handbook, revised January 31, 2010 Standard 1: The school publishes a mission statement or its equivalent
AACSB Standards from the Eligibility Procedures and Accreditation Standards for Business Accreditation Handbook, revised January 31, 2010 Standard 1: The school publishes a mission statement or its equivalent
Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA)
 Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Job details Reference Number: KRA/HR02/14 Job Title: Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Supervisor:
Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Job details Reference Number: KRA/HR02/14 Job Title: Chief Manager - HR Development and Performance Management Supervisor:
Human Resources Management Program Standard
 Human Resources Management Program Standard The approved program standard for Human Resources Management program of instruction leading to an Ontario College Graduate Certificate delivered by Ontario Colleges
Human Resources Management Program Standard The approved program standard for Human Resources Management program of instruction leading to an Ontario College Graduate Certificate delivered by Ontario Colleges
http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos086.htm Public Relations Specialists
 http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos086.htm Public Relations Specialists * Nature of the Work * Training, Other Qualifications, and Advancement * Employment * Job Outlook * Projections Data * Earnings * OES Data
http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos086.htm Public Relations Specialists * Nature of the Work * Training, Other Qualifications, and Advancement * Employment * Job Outlook * Projections Data * Earnings * OES Data
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.
 OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
Westfield State University Department of Economics and Management
 Westfield State University Department of Economics and Management The Department of Economics and Management at Westfield State University offers a Bachelor of Arts degree in Economics and Bachelor of
Westfield State University Department of Economics and Management The Department of Economics and Management at Westfield State University offers a Bachelor of Arts degree in Economics and Bachelor of
Course Author: Dr. Monica Belcourt, School of Human Resource Management, York University; Ron Alexandrowich and Mark Podolsky
 Strategic Human Resources Planning Course Author: Dr. Monica Belcourt, School of Human Resource Management, York University; Ron Alexandrowich and Mark Podolsky Description: The course provides students
Strategic Human Resources Planning Course Author: Dr. Monica Belcourt, School of Human Resource Management, York University; Ron Alexandrowich and Mark Podolsky Description: The course provides students
Master's Degree Program in Marketing (English Language)
 Master's Degree Program in Marketing (English Language) 1) Name of Curriculum: Master's Degree Program in Marketing (English Language) 2) Name of Degree: Master of Science in Marketing or M.S. (Marketing)
Master's Degree Program in Marketing (English Language) 1) Name of Curriculum: Master's Degree Program in Marketing (English Language) 2) Name of Degree: Master of Science in Marketing or M.S. (Marketing)
ROMANIAN - AMERICAN UNIVERSITY. School of Domestic and International Business, Banking and Finance
 Invest in People! Project co-financed by European Social Fund through the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resource Development 2007 2013 Priority Axis: 1. Education and training in support for growth
Invest in People! Project co-financed by European Social Fund through the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resource Development 2007 2013 Priority Axis: 1. Education and training in support for growth
Management. University of New Orleans/268
 Management MANG 2790 Business Communication Prerequisite: ENGL 1158 and BA 2780. This course will introduce students to the interaction of business communications and information technology in the 21st
Management MANG 2790 Business Communication Prerequisite: ENGL 1158 and BA 2780. This course will introduce students to the interaction of business communications and information technology in the 21st
Accounting. Management. Environment of Business. Business Law for Accountants. Stats Business & Econ I. Management
 Undergraduate Courses: Course # Course Title Course Description BUS201 Financial An introduction to basic accounting principles for measuring and Accounting communicating financial data about a business
Undergraduate Courses: Course # Course Title Course Description BUS201 Financial An introduction to basic accounting principles for measuring and Accounting communicating financial data about a business
Management Each of the three emphases in the major develops critical thinking, specialized conceptual knowledge and problem-solving techniques.
 Department of Management Donald W. Reynolds Center, Room 205 (501) 569-3484 fax (501) 683-7021 ualr.edu/management Chairperson: Cox, Susie S., Professor Professors: Bell, Joseph R. Leonard, Karen Stone,
Department of Management Donald W. Reynolds Center, Room 205 (501) 569-3484 fax (501) 683-7021 ualr.edu/management Chairperson: Cox, Susie S., Professor Professors: Bell, Joseph R. Leonard, Karen Stone,
PROPOSAL TO CONDUCT AN CLASSIFICATION AND COMPENSATION STUDY
 PROPOSAL TO CONDUCT AN CLASSIFICATION AND COMPENSATION STUDY FOR THE MARINA COAST WATER DISTRICT Prepared by: Bryce Consulting, Inc. 3436 American River Drive, Suite 7A Sacramento, CA 95864 (916) 974-0199
PROPOSAL TO CONDUCT AN CLASSIFICATION AND COMPENSATION STUDY FOR THE MARINA COAST WATER DISTRICT Prepared by: Bryce Consulting, Inc. 3436 American River Drive, Suite 7A Sacramento, CA 95864 (916) 974-0199
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.
 OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD (For use in the development of supply chain related job descriptions, performance evaluations, career development plans, etc.) Description of Position (As defined by the CSCSC Stakeholder
Master in Business Administration
 Master in Business Administration The M.B.A. program at Silliman is rooted in the principle of Christian stewardship and the husbanding of God s resources towards the fulfillment of a just and humane society.
Master in Business Administration The M.B.A. program at Silliman is rooted in the principle of Christian stewardship and the husbanding of God s resources towards the fulfillment of a just and humane society.
DoDEA Personnel Center HR Competency Definitions
 DoDEA Personnel Center HR Competency Definitions ATTACHMENT 10 Business Management Competencies Business Process Reengineering Applies business process reengineering principles and techniques to reengineer
DoDEA Personnel Center HR Competency Definitions ATTACHMENT 10 Business Management Competencies Business Process Reengineering Applies business process reengineering principles and techniques to reengineer
1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION
 1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION (i) CHIEF MANAGER - COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS, AND HR ADMINISTRATION (Grade KRA 7 ) JOB DESCRIPTION FORM Date: Kenya Revenue Authority
1. CORPORATE SUPPORT SERVICES DEPARTMENT - HUMAN RESOURCES DIVISION (i) CHIEF MANAGER - COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS, AND HR ADMINISTRATION (Grade KRA 7 ) JOB DESCRIPTION FORM Date: Kenya Revenue Authority
Guidance for Labor Management Forum Metrics
 Guidance for Labor Management Forum Metrics 1 Scope of Guidance for Forums The guidance in this document was drafted on behalf of the National Council on Federal Labor Management Relations (Council). Each
Guidance for Labor Management Forum Metrics 1 Scope of Guidance for Forums The guidance in this document was drafted on behalf of the National Council on Federal Labor Management Relations (Council). Each
Introduction to Management Information Systems
 IntroductiontoManagementInformationSystems Summary 1. Explain why information systems are so essential in business today. Information systems are a foundation for conducting business today. In many industries,
IntroductiontoManagementInformationSystems Summary 1. Explain why information systems are so essential in business today. Information systems are a foundation for conducting business today. In many industries,
Industrial-Organizational Psychologists
 Industrial-Organizational Psychologists Description Apply principles of psychology to personnel, administration, management, sales, and marketing problems. Activities may include policy planning; employee
Industrial-Organizational Psychologists Description Apply principles of psychology to personnel, administration, management, sales, and marketing problems. Activities may include policy planning; employee
Level 1 Articulated Plan: The plan has established the mission, vision, goals, actions, and key
 S e s s i o n 2 S t r a t e g i c M a n a g e m e n t 1 Session 2 1.4 Levels of Strategic Planning After you ve decided that strategic management is the right tool for your organization, clarifying what
S e s s i o n 2 S t r a t e g i c M a n a g e m e n t 1 Session 2 1.4 Levels of Strategic Planning After you ve decided that strategic management is the right tool for your organization, clarifying what
MBA-ECO 510: Managerial Economics MBA-MAN 520: Organizational Behavior MBA-MKTG 530: Marketing Management MBA-FIN 540: Corporate Finance
 MBA Program of Study Semester One (October-February) Quarter One Quarter Two MBA-ACCT 501: Managerial Accounting MBA-STAT 505: Applied Statistics for Business Decisions MBA-COM 515: Leadership Communication
MBA Program of Study Semester One (October-February) Quarter One Quarter Two MBA-ACCT 501: Managerial Accounting MBA-STAT 505: Applied Statistics for Business Decisions MBA-COM 515: Leadership Communication
Strategic Aspects Of The Importance Of Employee Management Dean R. Manna, (Email: [email protected]), Robert Morris University
 Strategic Aspects Of The Importance Of Employee Management Dean R. Manna, (Email: [email protected]), Robert Morris University INTRODUCTION Emerging Importance Of Employee Management A ccording to the Herman
Strategic Aspects Of The Importance Of Employee Management Dean R. Manna, (Email: [email protected]), Robert Morris University INTRODUCTION Emerging Importance Of Employee Management A ccording to the Herman
GAO. Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government. Internal Control. United States General Accounting Office.
 GAO United States General Accounting Office Internal Control November 1999 Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government GAO/AIMD-00-21.3.1 Foreword Federal policymakers and program managers
GAO United States General Accounting Office Internal Control November 1999 Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government GAO/AIMD-00-21.3.1 Foreword Federal policymakers and program managers
ROCKHURST)UNIVERSITY) HELZBERG)SCHOOL)OF)MANAGEMENT) MASTER S)IN)BUSINESS)ADMINISTRATION)) PROGRAM)REVISION) 2011)
 ROCKHURST)UNIVERSITY) HELZBERG)SCHOOL)OF)MANAGEMENT) MASTER S)IN)BUSINESS)ADMINISTRATION)) PROGRAM)REVISION) 2011) ) The revised part-time evening Master s in Business Administration (MBA) program will
ROCKHURST)UNIVERSITY) HELZBERG)SCHOOL)OF)MANAGEMENT) MASTER S)IN)BUSINESS)ADMINISTRATION)) PROGRAM)REVISION) 2011) ) The revised part-time evening Master s in Business Administration (MBA) program will
Learning Objectives: Quick answer key: Question # Multiple Choice True/False
 0 Learning Objectives: 11.1 Describe the advantages and disadvantages of the most common forms of business ownership. 11.2 Identify the stakeholders of a business and describe why they are important. 11.3
0 Learning Objectives: 11.1 Describe the advantages and disadvantages of the most common forms of business ownership. 11.2 Identify the stakeholders of a business and describe why they are important. 11.3
Business Leadership. www.odessa.edu/dept/management. Faculty: Nancy Stewart, chair; Sue Jones, Connie Nichols
 Business Leadership www.odessa.edu/dept/management Faculty: Nancy Stewart, chair; Sue Jones, Connie Nichols The business leadership department philosophy states that everyone should manage all resources,
Business Leadership www.odessa.edu/dept/management Faculty: Nancy Stewart, chair; Sue Jones, Connie Nichols The business leadership department philosophy states that everyone should manage all resources,
INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZTIONAL PSYCHOLOGY
 SUBJECT INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZTIONAL PSYCHOLOGY SESSION 1 INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY Subject: Introduction Industrial Organizational Psychology Session 1 What Is Industrial
SUBJECT INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZTIONAL PSYCHOLOGY SESSION 1 INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY Subject: Introduction Industrial Organizational Psychology Session 1 What Is Industrial
Comprehensive Business Pathway Blueprint
 I. Finance A. Personal Finance 1. Describe the fundamental principles of money needed to make financial exchanges (a) Differentiate between different forms of financial exchange (cash, credit, debit, electronic
I. Finance A. Personal Finance 1. Describe the fundamental principles of money needed to make financial exchanges (a) Differentiate between different forms of financial exchange (cash, credit, debit, electronic
MBA COURSES MBA-ACC 501: Managerial Accounting Required, Finance certificate requirement MBA-STAT 505: Applied Statistics for Business Decisions
 MBA COURSES MBA-ACC 501: Managerial Accounting This course introduces the use and analysis of accounting data so that managers may better conduct planning, controlling, and decision-making. In the first
MBA COURSES MBA-ACC 501: Managerial Accounting This course introduces the use and analysis of accounting data so that managers may better conduct planning, controlling, and decision-making. In the first
U.S. Department of Agriculture EEOC FORM 715-01 PART E
 U.S. Department of Agriculture EEOC FORM 715-01 PART E U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission FEDERAL AGENCY ANNUAL EEO PROGRAM STATUS REPORT Department of Agriculture For Period Covering October
U.S. Department of Agriculture EEOC FORM 715-01 PART E U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission FEDERAL AGENCY ANNUAL EEO PROGRAM STATUS REPORT Department of Agriculture For Period Covering October
Farooq Ahmad MBA (Management) MS (Human Resource Management) Nursing Management & Administration
 Farooq Ahmad MBA (Management) MS (Human Resource Management) Nursing Management & Administration Inform student about management skills Application of management skills in nursing Management skill for
Farooq Ahmad MBA (Management) MS (Human Resource Management) Nursing Management & Administration Inform student about management skills Application of management skills in nursing Management skill for
When Jon Barron graduated with a bachelor s degree in. Career beginnings for business majors
 Career beginnings for business majors Dina Itkin Dina Itkin is an economist in the Office of Occupational Statistics and Employment Projections, BLS. She is available at (202) 691 5713 or itkin.dina@bls.
Career beginnings for business majors Dina Itkin Dina Itkin is an economist in the Office of Occupational Statistics and Employment Projections, BLS. She is available at (202) 691 5713 or itkin.dina@bls.
