How did the Solar System form?
|
|
|
- Nelson Fletcher
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How did the Solar System form? Is our solar system unique? Are there other Earth-like planets, or are we a fluke? Under what conditions can Earth-like planets form? Is life common or rare?
2 Ways to Find Out Look at our own solar system, and think about how it might have formed Look at other solar systems while they form Look for and study other solar systems Create computer models and see if you can produce a solar system
3 Ways to Find Out Look at our own solar system, and think about how it might have formed Look at other solar systems while they form Look for and study other solar systems Create computer models and see if you can produce a solar system
4 Solar System Geometry Terrestrial planets closer than gas/water giants Planets get smaller beyond Jupiter Most planets orbit in the same plane Some small bodies are tilted
5 Summary of Planetary Interiors
6
7 Summary (Things a formation theory must explain) The sun, with most of the system mass Giant planets with solid cores (far from sun) Terrestrial planets (close to sun) Most planets orbit in a flat plane Many planets have moons
8 Our theory Solar system formation begins because of gravity - most stuff ends up in the sun A disk is formed because of rotation Planet cores form in the disk because rocks hit and/or gravitationally attract each other If there s ice around (> 5 AU from the star, where it s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks
9 Why might material in clouds collapse to form stars? What force keeps clouds from collapsing?
10 Why might material in clouds collapse to form stars? gas pressure pushes out (like in a balloon) What force keeps clouds from collapsing?
11 Why might material in clouds collapse to form stars? What force helps clouds collapse?
12 Why might material in clouds collapse to form stars? gravity pulls inwards What force helps clouds collapse?
13 If the cloud is big and cold, gravity will win out and the cloud will collapse. gravity pulls inwards
14 The cloud is spinning. What happens as it collapses? (Think of the water in your bathtub drain) gravity pulls inwards
15 The cloud spins faster and faster, until it can t support itself, and flattens out (think pizza dough)
16 Lucky for us, this is the perfect way to form a solar system. disk = future solar system blob = future sun
17 Formation basics
18
19 Ways to Find Out Look at our own solar system, and think about how it might have formed Look at other solar systems while they form Look for and study other solar systems Create computer models and see if you can produce a solar system
20 Stars form in Dense Clouds of Dust and Gas What do we mean by dust? What do we mean by gas?
21 The Orion Nebula
22 Disks really exist!
23 Disks really exist!
24 Young stars have asteroid belts and Kuiper belts but notice how much bigger this is than the solar system!
25 In reality, disks are very hard to image. Why do you think this is?
26 In reality, disks are very hard to image. Why do you think this is? So we usually use spectroscopy to study disks. Here s what stars look like with a spectrograph. What would it look like with a disk around it?
27 In reality, disks are very hard to image. Why do you think this is? So we usually use spectroscopy to study disks. Here s what stars look like with a spectrograph. What would it look like with a disk around it? Disks produce infrared light (just like planets)
28 Our theory: What do we think now? Solar system formation begins because of gravity - most stuff ends up in the sun A disk is formed because of rotation Planet cores form in the disk because rocks hit and/or gravitationally attract each other If there s ice around (> 5 AU from the star, where it s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks
29 Ways to Find Out Look at our own solar system, and think about how it might have formed Look at other solar systems while they form Look for and study other solar systems Create computer models and see if you can produce a solar system
30 Ways to Find Out Look at our own solar system, and think about how it might have formed Look at other solar systems while they form Look for and study other solar systems Create computer models and see if you can produce a solar system
31
32
33 Ways to Find Out Look at our own solar system, and think about how it might have formed Look at other solar systems while they form Look for and study other solar systems Create computer models and see if you can produce a solar system
34 Our theory: What do we think now? Solar system formation begins because of gravity - most stuff ends up in the sun A disk is formed because of rotation Planet cores form in the disk because rocks hit and/or gravitationally attract each other If there s ice around (> 5 AU from the star, where it s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks
35 How do you design a computer simulation? Why can t we make a huge computer simulation to explain everything?
36 What models would you create?
37
38 A model of planets growing in a disk.
39
40
41 Some things we ve learned from models: Our basic theory holds up pretty well, but... It s hard to get little particles to stick to each other when they collide. It takes a really, really long time to make planets (maybe too long??) It s hard to form planetary systems as flat as ours.
42 Solar System Formation: Take-away messages Theory: Solar system formation begins because of gravity - most stuff ends up in the sun A disk is formed because of rotation Planet cores form in the disk because rocks hit and/or gravitationally attract each other If there s ice around (> 5 AU from the star, where it s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks Observations generally agree with theory, but it s hard to see details. They also show us that stars and disks are all very different from each other. And, they gave us the surprising observation of outflows. Simulations also agree with theory, but they can t model everything at once, and there are some problems (things take too long, for one)
43 Is our solar system unique? Are there other Earth-like planets, or are we a fluke? Under what conditions can Earth-like planets form? Is life common or rare?
The Layout of the Solar System
 The Layout of the Solar System Planets fall into two main categories Terrestrial (i.e. Earth-like) Jovian (i.e. Jupiter-like or gaseous) [~5000 kg/m 3 ] [~1300 kg/m 3 ] What is density? Average density
The Layout of the Solar System Planets fall into two main categories Terrestrial (i.e. Earth-like) Jovian (i.e. Jupiter-like or gaseous) [~5000 kg/m 3 ] [~1300 kg/m 3 ] What is density? Average density
Lecture 7 Formation of the Solar System. Nebular Theory. Origin of the Solar System. Origin of the Solar System. The Solar Nebula
 Origin of the Solar System Lecture 7 Formation of the Solar System Reading: Chapter 9 Quiz#2 Today: Lecture 60 minutes, then quiz 20 minutes. Homework#1 will be returned on Thursday. Our theory must explain
Origin of the Solar System Lecture 7 Formation of the Solar System Reading: Chapter 9 Quiz#2 Today: Lecture 60 minutes, then quiz 20 minutes. Homework#1 will be returned on Thursday. Our theory must explain
Lecture 10 Formation of the Solar System January 6c, 2014
 1 Lecture 10 Formation of the Solar System January 6c, 2014 2 Orbits of the Planets 3 Clues for the Formation of the SS All planets orbit in roughly the same plane about the Sun. All planets orbit in the
1 Lecture 10 Formation of the Solar System January 6c, 2014 2 Orbits of the Planets 3 Clues for the Formation of the SS All planets orbit in roughly the same plane about the Sun. All planets orbit in the
Summary: Four Major Features of our Solar System
 Summary: Four Major Features of our Solar System How did the solar system form? According to the nebular theory, our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant cloud of interstellar
Summary: Four Major Features of our Solar System How did the solar system form? According to the nebular theory, our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant cloud of interstellar
Chapter 8 Formation of the Solar System. What theory best explains the features of our solar system? Close Encounter Hypothesis
 Chapter 8 Formation of the Solar System What properties of our solar system must a formation theory explain? 1. Patterns of motion of the large bodies Orbit in same direction and plane 2. Existence of
Chapter 8 Formation of the Solar System What properties of our solar system must a formation theory explain? 1. Patterns of motion of the large bodies Orbit in same direction and plane 2. Existence of
Chapter 8 Welcome to the Solar System
 Chapter 8 Welcome to the Solar System 8.1 The Search for Origins What properties of our solar system must a formation theory explain? What theory best explains the features of our solar system? What properties
Chapter 8 Welcome to the Solar System 8.1 The Search for Origins What properties of our solar system must a formation theory explain? What theory best explains the features of our solar system? What properties
Chapter 8 Formation of the Solar System Agenda
 Chapter 8 Formation of the Solar System Agenda Announce: Mercury Transit Part 2 of Projects due next Thursday Ch. 8 Formation of the Solar System Philip on The Physics of Star Trek Radiometric Dating Lab
Chapter 8 Formation of the Solar System Agenda Announce: Mercury Transit Part 2 of Projects due next Thursday Ch. 8 Formation of the Solar System Philip on The Physics of Star Trek Radiometric Dating Lab
Solar System Formation
 Solar System Formation Solar System Formation Question: How did our solar system and other planetary systems form? Comparative planetology has helped us understand Compare the differences and similarities
Solar System Formation Solar System Formation Question: How did our solar system and other planetary systems form? Comparative planetology has helped us understand Compare the differences and similarities
Unit 8 Lesson 2 Gravity and the Solar System
 Unit 8 Lesson 2 Gravity and the Solar System Gravity What is gravity? Gravity is a force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses and the distances between them. Every object in the universe
Unit 8 Lesson 2 Gravity and the Solar System Gravity What is gravity? Gravity is a force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses and the distances between them. Every object in the universe
L3: The formation of the Solar System
 credit: NASA L3: The formation of the Solar System UCL Certificate of astronomy Dr. Ingo Waldmann A stable home The presence of life forms elsewhere in the Universe requires a stable environment where
credit: NASA L3: The formation of the Solar System UCL Certificate of astronomy Dr. Ingo Waldmann A stable home The presence of life forms elsewhere in the Universe requires a stable environment where
The Solar System. Unit 4 covers the following framework standards: ES 10 and PS 11. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 4 The Solar System Chapter 7 ~ The History of the Solar System o Section 1 ~ The Formation of the Solar System o Section 2 ~ Observing the Solar System Chapter 8 ~ The Parts the Solar System o Section
Unit 4 The Solar System Chapter 7 ~ The History of the Solar System o Section 1 ~ The Formation of the Solar System o Section 2 ~ Observing the Solar System Chapter 8 ~ The Parts the Solar System o Section
The Main Point. Lecture #34: Solar System Origin II. Chemical Condensation ( Lewis ) Model. How did the solar system form? Reading: Chapter 8.
 Lecture #34: Solar System Origin II How did the solar system form? Chemical Condensation ("Lewis") Model. Formation of the Terrestrial Planets. Formation of the Giant Planets. Planetary Evolution. Reading:
Lecture #34: Solar System Origin II How did the solar system form? Chemical Condensation ("Lewis") Model. Formation of the Terrestrial Planets. Formation of the Giant Planets. Planetary Evolution. Reading:
Introduction to the Solar System
 Introduction to the Solar System Lesson Objectives Describe some early ideas about our solar system. Name the planets, and describe their motion around the Sun. Explain how the solar system formed. Introduction
Introduction to the Solar System Lesson Objectives Describe some early ideas about our solar system. Name the planets, and describe their motion around the Sun. Explain how the solar system formed. Introduction
1 A Solar System Is Born
 CHAPTER 3 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Formation of the Solar System BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a nebula? How did our solar system
CHAPTER 3 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Formation of the Solar System BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a nebula? How did our solar system
Chapter 6 Formation of Planetary Systems Our Solar System and Beyond
 Chapter 6 Formation of Planetary Systems Our Solar System and Beyond The solar system exhibits clear patterns of composition and motion. Sun Over 99.9% of solar system s mass Made mostly of H/He gas (plasma)
Chapter 6 Formation of Planetary Systems Our Solar System and Beyond The solar system exhibits clear patterns of composition and motion. Sun Over 99.9% of solar system s mass Made mostly of H/He gas (plasma)
Our Planetary System. Earth, as viewed by the Voyager spacecraft. 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Our Planetary System Earth, as viewed by the Voyager spacecraft 7.1 Studying the Solar System Our goals for learning: What does the solar system look like? What can we learn by comparing the planets to
Our Planetary System Earth, as viewed by the Voyager spacecraft 7.1 Studying the Solar System Our goals for learning: What does the solar system look like? What can we learn by comparing the planets to
NOTES: GEORGIA HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE TEST THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 NOTES: GEORGIA HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE TEST THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1.What is a Solar system? A solar system consists of: * one central star, the Sun and * nine planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn,
NOTES: GEORGIA HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE TEST THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1.What is a Solar system? A solar system consists of: * one central star, the Sun and * nine planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn,
A Solar System Coloring Book
 A Solar System Coloring Book Courtesy of the Windows to the Universe Project http://www.windows2universe.org The Sun Size: The Sun is wider than 100 Earths. Temperature: ~27,000,000 F in the center, ~10,000
A Solar System Coloring Book Courtesy of the Windows to the Universe Project http://www.windows2universe.org The Sun Size: The Sun is wider than 100 Earths. Temperature: ~27,000,000 F in the center, ~10,000
A SOLAR SYSTEM COLORING BOOK
 A SOLAR SYSTEM COLORING BOOK Brought to you by: THE SUN Size: The Sun is wider than 100 Earths. 1 Temperature: 27,000,000 F in the center, 10,000 F at the surface. So that s REALLY hot anywhere on the
A SOLAR SYSTEM COLORING BOOK Brought to you by: THE SUN Size: The Sun is wider than 100 Earths. 1 Temperature: 27,000,000 F in the center, 10,000 F at the surface. So that s REALLY hot anywhere on the
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L
 4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets come from the clouds of gas and dust that
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets come from the clouds of gas and dust that
Lecture 7: Formation of the Solar System
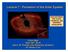 Lecture 7: Formation of the Solar System Dust and debris disk around Fomalhaut, with embedded young planet! Claire Max April 24 th, 2014 Astro 18: Planets and Planetary Systems UC Santa Cruz Solar System
Lecture 7: Formation of the Solar System Dust and debris disk around Fomalhaut, with embedded young planet! Claire Max April 24 th, 2014 Astro 18: Planets and Planetary Systems UC Santa Cruz Solar System
The Solar System. Source http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/starchild/solar_system_level1/solar_system.html
 The Solar System What is the solar system? It is our Sun and everything that travels around it. Our solar system is elliptical in shape. That means it is shaped like an egg. Earth s orbit is nearly circular.
The Solar System What is the solar system? It is our Sun and everything that travels around it. Our solar system is elliptical in shape. That means it is shaped like an egg. Earth s orbit is nearly circular.
Chapter 15.3 Galaxy Evolution
 Chapter 15.3 Galaxy Evolution Elliptical Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Irregular Galaxies Are there any connections between the three types of galaxies? How do galaxies form? How do galaxies evolve? P.S. You
Chapter 15.3 Galaxy Evolution Elliptical Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Irregular Galaxies Are there any connections between the three types of galaxies? How do galaxies form? How do galaxies evolve? P.S. You
The Expanding Universe
 Stars, Galaxies, Guided Reading and Study This section explains how astronomers think the universe and the solar system formed. Use Target Reading Skills As you read about the evidence that supports the
Stars, Galaxies, Guided Reading and Study This section explains how astronomers think the universe and the solar system formed. Use Target Reading Skills As you read about the evidence that supports the
Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations
 Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Our Solar System is a collection of gravitationally interacting bodies that include Earth and the Moon. Universal
Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Our Solar System is a collection of gravitationally interacting bodies that include Earth and the Moon. Universal
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 1020L
 4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 1020L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets are born from the clouds of gas and dust
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 1020L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets are born from the clouds of gas and dust
Welcome to Class 4: Our Solar System (and a bit of cosmology at the start) Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room
 Welcome to Class 4: Our Solar System (and a bit of cosmology at the start) Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What is the difference between dark ENERGY and dark MATTER? Is Earth unique,
Welcome to Class 4: Our Solar System (and a bit of cosmology at the start) Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What is the difference between dark ENERGY and dark MATTER? Is Earth unique,
Study Guide: Solar System
 Study Guide: Solar System 1. How many planets are there in the solar system? 2. What is the correct order of all the planets in the solar system? 3. Where can a comet be located in the solar system? 4.
Study Guide: Solar System 1. How many planets are there in the solar system? 2. What is the correct order of all the planets in the solar system? 3. Where can a comet be located in the solar system? 4.
Chapter 12 Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets. Asteroid Facts. What are asteroids like? Asteroids with Moons. 12.1 Asteroids and Meteorites
 Chapter 12 Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts What are asteroids like? 12.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our goals for learning:! What are asteroids like?! Why is there
Chapter 12 Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts What are asteroids like? 12.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our goals for learning:! What are asteroids like?! Why is there
Lecture 12: The Solar System Briefly
 Lecture 12: The Solar System Briefly Formation of the Moonhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WpOKztEiMqo&feature =related Formation of our Solar System Conservation of Angular Momentum Why are the larger,
Lecture 12: The Solar System Briefly Formation of the Moonhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WpOKztEiMqo&feature =related Formation of our Solar System Conservation of Angular Momentum Why are the larger,
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 890L
 4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 890L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets are born from the clouds of gas and dust
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 890L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets are born from the clouds of gas and dust
Solar System Overview
 Solar System Overview Planets: Four inner planets, Terrestrial planets Four outer planets, Jovian planets Asteroids: Minor planets (planetesimals) Meteroids: Chucks of rocks (smaller than asteroids) (Mercury,
Solar System Overview Planets: Four inner planets, Terrestrial planets Four outer planets, Jovian planets Asteroids: Minor planets (planetesimals) Meteroids: Chucks of rocks (smaller than asteroids) (Mercury,
Class 2 Solar System Characteristics Formation Exosolar Planets
 Class 1 Introduction, Background History of Modern Astronomy The Night Sky, Eclipses and the Seasons Kepler's Laws Newtonian Gravity General Relativity Matter and Light Telescopes Class 2 Solar System
Class 1 Introduction, Background History of Modern Astronomy The Night Sky, Eclipses and the Seasons Kepler's Laws Newtonian Gravity General Relativity Matter and Light Telescopes Class 2 Solar System
Lecture 19: Planet Formation I. Clues from the Solar System
 Lecture 19: Planet Formation I. Clues from the Solar System 1 Outline The Solar System:! Terrestrial planets! Jovian planets! Asteroid belt, Kuiper belt, Oort cloud Condensation and growth of solid bodies
Lecture 19: Planet Formation I. Clues from the Solar System 1 Outline The Solar System:! Terrestrial planets! Jovian planets! Asteroid belt, Kuiper belt, Oort cloud Condensation and growth of solid bodies
Chapter 7 Our Planetary System. What does the solar system look like? Thought Question How does the Earth-Sun distance compare with the Sun s radius
 Chapter 7 Our Planetary System 7.1 Studying the Solar System Our goals for learning:! What does the solar system look like?! What can we learn by comparing the planets to one another?! What are the major
Chapter 7 Our Planetary System 7.1 Studying the Solar System Our goals for learning:! What does the solar system look like?! What can we learn by comparing the planets to one another?! What are the major
7. Our Solar System. Planetary Orbits to Scale. The Eight Planetary Orbits
 7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
7. Our Solar System Terrestrial & Jovian planets Seven large satellites [moons] Chemical composition of the planets Asteroids & comets The Terrestrial & Jovian Planets Four small terrestrial planets Like
Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System
 Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System Objectives: Compare & Contrast geocentric and heliocentric models of the solar sytem. Describe the orbits of planets explain how gravity and inertia keep the planets
Chapter 25.1: Models of our Solar System Objectives: Compare & Contrast geocentric and heliocentric models of the solar sytem. Describe the orbits of planets explain how gravity and inertia keep the planets
Solar Nebula Theory. Basic properties of the Solar System that need to be explained:
 Solar Nebula Theory Basic properties of the Solar System that need to be explained: 1. All planets orbit the Sun in the same direction as the Sun s rotation 2. All planetary orbits are confined to the
Solar Nebula Theory Basic properties of the Solar System that need to be explained: 1. All planets orbit the Sun in the same direction as the Sun s rotation 2. All planetary orbits are confined to the
Chapter 7 Our Planetary System. Agenda. Intro Astronomy. Intro Astronomy. What does the solar system look like? A. General Basics
 Chapter 7 Our Planetary System Agenda Pass back & discuss Test 2 Where we are (at) Ch. 7 Our Planetary System Finish Einstein s Big Idea Earth, as viewed by the Voyager spacecraft A. General Basics Intro
Chapter 7 Our Planetary System Agenda Pass back & discuss Test 2 Where we are (at) Ch. 7 Our Planetary System Finish Einstein s Big Idea Earth, as viewed by the Voyager spacecraft A. General Basics Intro
STUDY GUIDE: Earth Sun Moon
 The Universe is thought to consist of trillions of galaxies. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, has billions of stars. One of those stars is our Sun. Our solar system consists of the Sun at the center, and all
The Universe is thought to consist of trillions of galaxies. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, has billions of stars. One of those stars is our Sun. Our solar system consists of the Sun at the center, and all
THE SOLAR SYSTEM - EXERCISES 1
 THE SOLAR SYSTEM - EXERCISES 1 THE SUN AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM Name the planets in their order from the sun. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The asteroid belt is between and Which planet has the most moons? About how many?
THE SOLAR SYSTEM - EXERCISES 1 THE SUN AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM Name the planets in their order from the sun. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The asteroid belt is between and Which planet has the most moons? About how many?
The orbit of Halley s Comet
 The orbit of Halley s Comet Given this information Orbital period = 76 yrs Aphelion distance = 35.3 AU Observed comet in 1682 and predicted return 1758 Questions: How close does HC approach the Sun? What
The orbit of Halley s Comet Given this information Orbital period = 76 yrs Aphelion distance = 35.3 AU Observed comet in 1682 and predicted return 1758 Questions: How close does HC approach the Sun? What
Why don t planets crash into each other?
 1 Just as we know that the sun will rise every morning, we expect the planets and the moon to stay in their orbits. And rightly so. For 400 years, people have understood that the movements of Earth, the
1 Just as we know that the sun will rise every morning, we expect the planets and the moon to stay in their orbits. And rightly so. For 400 years, people have understood that the movements of Earth, the
Group Leader: Group Members:
 THE SOLAR SYSTEM PROJECT: TOPIC: THE SUN Required Project Content for an Oral/Poster Presentation on THE SUN - What it s made of - Age and how it formed (provide pictures or diagrams) - What is an AU?
THE SOLAR SYSTEM PROJECT: TOPIC: THE SUN Required Project Content for an Oral/Poster Presentation on THE SUN - What it s made of - Age and how it formed (provide pictures or diagrams) - What is an AU?
Earth in the Solar System
 Copyright 2011 Study Island - All rights reserved. Directions: Challenge yourself! Print out the quiz or get a pen/pencil and paper and record your answers to the questions below. Check your answers with
Copyright 2011 Study Island - All rights reserved. Directions: Challenge yourself! Print out the quiz or get a pen/pencil and paper and record your answers to the questions below. Check your answers with
Solar System Formation
 Solar System Formation Background Information System: Many pieces that make up a whole Solar System: Anything that orbits the Sun Just like in the formation of of stars.. Gravity plays a major role. Gravitational
Solar System Formation Background Information System: Many pieces that make up a whole Solar System: Anything that orbits the Sun Just like in the formation of of stars.. Gravity plays a major role. Gravitational
Solar System Fundamentals. What is a Planet? Planetary orbits Planetary temperatures Planetary Atmospheres Origin of the Solar System
 Solar System Fundamentals What is a Planet? Planetary orbits Planetary temperatures Planetary Atmospheres Origin of the Solar System Properties of Planets What is a planet? Defined finally in August 2006!
Solar System Fundamentals What is a Planet? Planetary orbits Planetary temperatures Planetary Atmospheres Origin of the Solar System Properties of Planets What is a planet? Defined finally in August 2006!
DE2410: Learning Objectives. SOLAR SYSTEM Formation, Evolution and Death. Solar System: To Size Scale. Learning Objectives : This Lecture
 DE2410: Learning Objectives SOLAR SYSTEM Formation, Evolution and Death To become aware of our planet, solar system, and the Universe To know about how these objects and structures were formed, are evolving
DE2410: Learning Objectives SOLAR SYSTEM Formation, Evolution and Death To become aware of our planet, solar system, and the Universe To know about how these objects and structures were formed, are evolving
Chapter 9 Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets. Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts
 Chapter 9 Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroid Facts Asteroids are rocky leftovers of planet formation. The largest is Ceres, diameter ~1,000 km. There are 150,000
Chapter 9 Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets Their Nature, Orbits, and Impacts Asteroid Facts Asteroids are rocky leftovers of planet formation. The largest is Ceres, diameter ~1,000 km. There are 150,000
The Solar System. A Collaborative Science Activity for Key Stage 2. Teacher s Notes. Procedure
 The Solar System A Collaborative Science Activity for Key Stage 2 Teacher s Notes This material links reading and oral skills. The text is divided into three parts so that pupils have the task of collecting
The Solar System A Collaborative Science Activity for Key Stage 2 Teacher s Notes This material links reading and oral skills. The text is divided into three parts so that pupils have the task of collecting
1.1 A Modern View of the Universe" Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?"
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe What is our place in the universe? What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe What is our place in the universe? What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was
Related Standards and Background Information
 Related Standards and Background Information Earth Patterns, Cycles and Changes This strand focuses on student understanding of patterns in nature, natural cycles, and changes that occur both quickly and
Related Standards and Background Information Earth Patterns, Cycles and Changes This strand focuses on student understanding of patterns in nature, natural cycles, and changes that occur both quickly and
Educator Guide to S LAR SYSTEM. 1875 El Prado, San Diego CA 92101 (619) 238-1233 www.rhfleet.org
 Educator Guide to S LAR SYSTEM 1875 El Prado, San Diego CA 92101 (619) 238-1233 www.rhfleet.org Pre-Visit Activity: Orbital Paths Materials: Plastic Plate Marble Scissors To Do: 1. Put the plate on a flat
Educator Guide to S LAR SYSTEM 1875 El Prado, San Diego CA 92101 (619) 238-1233 www.rhfleet.org Pre-Visit Activity: Orbital Paths Materials: Plastic Plate Marble Scissors To Do: 1. Put the plate on a flat
Chapter 1: Our Place in the Universe. 2005 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 Chapter 1: Our Place in the Universe Topics Our modern view of the universe The scale of the universe Cinema graphic tour of the local universe Spaceship earth 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals
Chapter 1: Our Place in the Universe Topics Our modern view of the universe The scale of the universe Cinema graphic tour of the local universe Spaceship earth 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals
So What All Is Out There, Anyway?
 So What All Is Out There, Anyway? Imagine that, like Alice in Wonderland, you have taken a magic potion that makes you grow bigger and bigger. You get so big that soon you are a giant. You can barely make
So What All Is Out There, Anyway? Imagine that, like Alice in Wonderland, you have taken a magic potion that makes you grow bigger and bigger. You get so big that soon you are a giant. You can barely make
The Earth, Sun & Moon. The Universe. The Earth, Sun & Moon. The Universe
 Football Review- Earth, Moon, Sun 1. During a total solar eclipse, when almost all of the Sun's light traveling to the Earth is blocked by the Moon, what is the order of the Earth, Sun, and Moon? A. Moon,
Football Review- Earth, Moon, Sun 1. During a total solar eclipse, when almost all of the Sun's light traveling to the Earth is blocked by the Moon, what is the order of the Earth, Sun, and Moon? A. Moon,
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Science Grade 6. Unit Organizer: UNIVERSE AND SOLAR SYSTEM (Approximate Time 3 Weeks)
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe Syllabus 4 tests: June 18, June 30, July 10, July 21 Comprehensive Final - check schedule Website link on blackboard 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Our goals for
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe Syllabus 4 tests: June 18, June 30, July 10, July 21 Comprehensive Final - check schedule Website link on blackboard 1.1 Our Modern View of the Universe Our goals for
Name Class Date. true
 Exercises 131 The Falling Apple (page 233) 1 Describe the legend of Newton s discovery that gravity extends throughout the universe According to legend, Newton saw an apple fall from a tree and realized
Exercises 131 The Falling Apple (page 233) 1 Describe the legend of Newton s discovery that gravity extends throughout the universe According to legend, Newton saw an apple fall from a tree and realized
UNIT V. Earth and Space. Earth and the Solar System
 UNIT V Earth and Space Chapter 9 Earth and the Solar System EARTH AND OTHER PLANETS A solar system contains planets, moons, and other objects that orbit around a star or the star system. The solar system
UNIT V Earth and Space Chapter 9 Earth and the Solar System EARTH AND OTHER PLANETS A solar system contains planets, moons, and other objects that orbit around a star or the star system. The solar system
Planets beyond the solar system
 Planets beyond the solar system Review of our solar system Why search How to search Eclipses Motion of parent star Doppler Effect Extrasolar planet discoveries A star is 5 parsecs away, what is its parallax?
Planets beyond the solar system Review of our solar system Why search How to search Eclipses Motion of parent star Doppler Effect Extrasolar planet discoveries A star is 5 parsecs away, what is its parallax?
From Aristotle to Newton
 From Aristotle to Newton The history of the Solar System (and the universe to some extent) from ancient Greek times through to the beginnings of modern physics. The Geocentric Model Ancient Greek astronomers
From Aristotle to Newton The history of the Solar System (and the universe to some extent) from ancient Greek times through to the beginnings of modern physics. The Geocentric Model Ancient Greek astronomers
Appropriate space vocabulary for Primary School
 Appropriate space vocabulary for Primary School Stuff Looks like Gas Dust Rock Liquid Fatter (moon) Thinner (moon) Faster Slower Hot Cold Material Shape Straight at (an object) Direct (light) Indirect
Appropriate space vocabulary for Primary School Stuff Looks like Gas Dust Rock Liquid Fatter (moon) Thinner (moon) Faster Slower Hot Cold Material Shape Straight at (an object) Direct (light) Indirect
DESCRIPTION ACADEMIC STANDARDS INSTRUCTIONAL GOALS VOCABULARY BEFORE SHOWING. Subject Area: Science
 DESCRIPTION Host Tom Selleck conducts a stellar tour of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto--the outer planets of Earth's solar system. Information from the Voyager space probes plus computer models
DESCRIPTION Host Tom Selleck conducts a stellar tour of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto--the outer planets of Earth's solar system. Information from the Voyager space probes plus computer models
Pocket Solar System. Make a Scale Model of the Distances in our Solar System
 Pocket Solar System Make a Scale Model of the Distances in our Solar System About the Activity Using a strip of paper, construct a quick scale model of the distances between the orbits of the planets,
Pocket Solar System Make a Scale Model of the Distances in our Solar System About the Activity Using a strip of paper, construct a quick scale model of the distances between the orbits of the planets,
THE SOLAR SYSTEM Syllabus
 THE SOLAR SYSTEM Syllabus Course Title The Solar System: Earth and Space Science Course Description This course provides an overview of what we know about the Solar System: how it began and evolved, its
THE SOLAR SYSTEM Syllabus Course Title The Solar System: Earth and Space Science Course Description This course provides an overview of what we know about the Solar System: how it began and evolved, its
Orbital Dynamics. Orbital Dynamics 1/29/15
 Orbital Dynamics Orbital Dynamics 1/29/15 Announcements Reading for next class Chapter 5: Sections 5.1-5.4 Homework #2 due next class (Tuesday, Feb. 3) Project #1 topic ideas due next Tuesday (Feb. 3)
Orbital Dynamics Orbital Dynamics 1/29/15 Announcements Reading for next class Chapter 5: Sections 5.1-5.4 Homework #2 due next class (Tuesday, Feb. 3) Project #1 topic ideas due next Tuesday (Feb. 3)
The Solar System: Cosmic encounter with Pluto
 Earth and Space Sciences The Solar System: Cosmic encounter with Pluto The size and nature of our Solar System is truly awe inspiring, and things are going to get even more exciting once the New Horizons
Earth and Space Sciences The Solar System: Cosmic encounter with Pluto The size and nature of our Solar System is truly awe inspiring, and things are going to get even more exciting once the New Horizons
Voyage: A Journey through our Solar System. Grades 5-8. Lesson 1: Our Solar System
 Voyage: A Journey through our Solar System Grades 5-8 Lesson 1: Our Solar System On October 17, 2001, a one to ten billion scale model of the Solar System was permanently installed on the National Mall
Voyage: A Journey through our Solar System Grades 5-8 Lesson 1: Our Solar System On October 17, 2001, a one to ten billion scale model of the Solar System was permanently installed on the National Mall
Bangkok Christian College EIP Matayom Course Description Semester One 2011-2012
 Bangkok Christian College EIP Matayom Course Description Semester One 2011-2012 Subject: General Science Grade: Matayom 6 Course Description This semester the General Science course will continue covering
Bangkok Christian College EIP Matayom Course Description Semester One 2011-2012 Subject: General Science Grade: Matayom 6 Course Description This semester the General Science course will continue covering
Lab 7: Gravity and Jupiter's Moons
 Lab 7: Gravity and Jupiter's Moons Image of Galileo Spacecraft Gravity is the force that binds all astronomical structures. Clusters of galaxies are gravitationally bound into the largest structures in
Lab 7: Gravity and Jupiter's Moons Image of Galileo Spacecraft Gravity is the force that binds all astronomical structures. Clusters of galaxies are gravitationally bound into the largest structures in
Asteroids. Earth. Asteroids. Earth Distance from sun: 149,600,000 kilometers (92,960,000 miles) Diameter: 12,756 kilometers (7,926 miles) dotted line
 Image taken by NASA Asteroids About 6,000 asteroids have been discovered; several hundred more are found each year. There are likely hundreds of thousands more that are too small to be seen from Earth.
Image taken by NASA Asteroids About 6,000 asteroids have been discovered; several hundred more are found each year. There are likely hundreds of thousands more that are too small to be seen from Earth.
Astronomy 110 Homework #04 Assigned: 02/06/2007 Due: 02/13/2007. Name:
 Astronomy 110 Homework #04 Assigned: 02/06/2007 Due: 02/13/2007 Name: Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures this past week. Choose
Astronomy 110 Homework #04 Assigned: 02/06/2007 Due: 02/13/2007 Name: Directions: Listed below are twenty (20) multiple-choice questions based on the material covered by the lectures this past week. Choose
Name: João Fernando Alves da Silva Class: 7-4 Number: 10
 Name: João Fernando Alves da Silva Class: 7-4 Number: 10 What is the constitution of the Solar System? The Solar System is constituted not only by planets, which have satellites, but also by thousands
Name: João Fernando Alves da Silva Class: 7-4 Number: 10 What is the constitution of the Solar System? The Solar System is constituted not only by planets, which have satellites, but also by thousands
Background Information Students will learn about the Solar System while practicing communication skills.
 Teacher Information Background Information Students will learn about the Solar System while practicing communication skills. Materials clipboard for each student pencils copies of map and Available Destinations
Teacher Information Background Information Students will learn about the Solar System while practicing communication skills. Materials clipboard for each student pencils copies of map and Available Destinations
California Standards Grades 9 12 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping
 California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
Moon. Compiled by Donnette E Davis www.staidenshomeschool.com
 Moon Compiled by Donnette E Davis www.staidenshomeschool.com The Moon Moon Facts When we look at the Moon from Earth, we always see the same side. Until Luna 3 sent back photos in 1959, no-one knew what
Moon Compiled by Donnette E Davis www.staidenshomeschool.com The Moon Moon Facts When we look at the Moon from Earth, we always see the same side. Until Luna 3 sent back photos in 1959, no-one knew what
LER 2891. Ages. Grades. Solar System. A fun game of thinking & linking!
 Solar System Ages 7+ LER 2891 Grades 2+ Card Game A fun game of thinking & linking! Contents 45 Picture cards 45 Word cards 8 New Link cards 2 Super Link cards Setup Shuffle the two decks together to mix
Solar System Ages 7+ LER 2891 Grades 2+ Card Game A fun game of thinking & linking! Contents 45 Picture cards 45 Word cards 8 New Link cards 2 Super Link cards Setup Shuffle the two decks together to mix
Science 9 Worksheet 13-1 The Solar System
 Name Date Due Date Science 9 Read pages 264-287 of SP to help you answer the following questions: Also, go to a school computer connected to the internet. Go to Mr. Colgur s Webpage at http://sd67.bc.ca/teachers/dcolgur
Name Date Due Date Science 9 Read pages 264-287 of SP to help you answer the following questions: Also, go to a school computer connected to the internet. Go to Mr. Colgur s Webpage at http://sd67.bc.ca/teachers/dcolgur
1. Soaring Through Our Solar System By Laura G. Smith
 1. Soaring Through Our Solar System By Laura G. Smith 1 Five, four, three, two, one... BLAST OFF! Come along as we explore our solar system! If we were flying high above the Earth, what would you see?
1. Soaring Through Our Solar System By Laura G. Smith 1 Five, four, three, two, one... BLAST OFF! Come along as we explore our solar system! If we were flying high above the Earth, what would you see?
2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. The Jovian Planets
 The Jovian Planets The Jovian planets are gas giants - much larger than Earth Sizes of Jovian Planets Planets get larger as they get more massive up to a point... Planets more massive than Jupiter are
The Jovian Planets The Jovian planets are gas giants - much larger than Earth Sizes of Jovian Planets Planets get larger as they get more massive up to a point... Planets more massive than Jupiter are
Name: Date: Goals: to discuss the composition, components, and types of comets; to build a comet and test its strength and reaction to light
 Name: Date: 17 Building a Comet 17.1 Introduction Comets represent some of the earliest material left over from the formation of the solar system, and are therefore of great interest to planetary astronomers.
Name: Date: 17 Building a Comet 17.1 Introduction Comets represent some of the earliest material left over from the formation of the solar system, and are therefore of great interest to planetary astronomers.
Vocabulary - Understanding Revolution in. our Solar System
 Vocabulary - Understanding Revolution in Universe Galaxy Solar system Planet Moon Comet Asteroid Meteor(ite) Heliocentric Geocentric Satellite Terrestrial planets Jovian (gas) planets Gravity our Solar
Vocabulary - Understanding Revolution in Universe Galaxy Solar system Planet Moon Comet Asteroid Meteor(ite) Heliocentric Geocentric Satellite Terrestrial planets Jovian (gas) planets Gravity our Solar
What's Gravity Got To Do With It?
 Monday, December 16 What's Gravity Got To Do With It? By Erin Horner When you woke up this morning did you fly up to the ceiling? Of course not! When you woke up this morning you put both feet on the floor
Monday, December 16 What's Gravity Got To Do With It? By Erin Horner When you woke up this morning did you fly up to the ceiling? Of course not! When you woke up this morning you put both feet on the floor
165 points. Name Date Period. Column B a. Cepheid variables b. luminosity c. RR Lyrae variables d. Sagittarius e. variable stars
 Name Date Period 30 GALAXIES AND THE UNIVERSE SECTION 30.1 The Milky Way Galaxy In your textbook, read about discovering the Milky Way. (20 points) For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching
Name Date Period 30 GALAXIES AND THE UNIVERSE SECTION 30.1 The Milky Way Galaxy In your textbook, read about discovering the Milky Way. (20 points) For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision
 The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision Roeland van der Marel (STScI) [based on work with a team of collaborators reported in the Astrophysical Journal July 2012] Hubble Science Briefing
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision Roeland van der Marel (STScI) [based on work with a team of collaborators reported in the Astrophysical Journal July 2012] Hubble Science Briefing
Content Area: Earth Science Grade(s) 4. Essential Question(s) and Enduring Understandings
 Content Area: Earth Science Grade(s) 4 Unit Plan Title: Objects in the Universe Overview of Unit Students will make observations and record data to understand patterns of movement and relationships among
Content Area: Earth Science Grade(s) 4 Unit Plan Title: Objects in the Universe Overview of Unit Students will make observations and record data to understand patterns of movement and relationships among
Grade 6 Standard 3 Unit Test A Astronomy. 1. The four inner planets are rocky and small. Which description best fits the next four outer planets?
 Grade 6 Standard 3 Unit Test A Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. The four inner planets are rocky and small. Which description best fits the next four outer planets? A. They are also rocky and small. B. They
Grade 6 Standard 3 Unit Test A Astronomy Multiple Choice 1. The four inner planets are rocky and small. Which description best fits the next four outer planets? A. They are also rocky and small. B. They
Copyright 2006, Astronomical Society of the Pacific
 2 1 3 4 Diameter: 590 miles (950 km) Distance to Sun: 257 million miles (414 million km) Orbits: # 18 Composition: Outer layer probably ice and frozen ammonia, no Diameter: 750 miles (1200 km) Distance
2 1 3 4 Diameter: 590 miles (950 km) Distance to Sun: 257 million miles (414 million km) Orbits: # 18 Composition: Outer layer probably ice and frozen ammonia, no Diameter: 750 miles (1200 km) Distance
