William Shaw, Ph.D. The Great Plains Laboratory, Inc., Lenexa, Kansas, USA
|
|
|
- Joy Burke
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inhibition of dopamine conversion to norepinephrine by Clostridia metabolites appears to be a (the) major cause of autism, schizophrenia, and other neuropsychiatric disorders. All these factors can now be monitored in The Great Plains Laboratory Organic Acids Test. William Shaw, Ph.D. The Great Plains Laboratory, Inc., Lenexa, Kansas, USA
2 Concentrations of the dopamine metabolite homovanillic acid, or HVA, have been reported to be much higher in the urine of children with autism compared to controls. In the same study, severity of autism symptoms was directly related to the concentration of HVA. There was a relation between the urinary HVA concentration and increased agitation, stereotypical behaviors, and reduced spontaneous behavior. Furthermore, vitamin B6, which has been shown to decrease autistic symptoms, decreases urinary HVA concentrations. Excess dopamine has been implicated in the etiology of psychotic behavior and schizophrenia for over 40 years. Drugs that inhibit dopamine binding to dopaminergic receptors have been some of the most widely used pharmaceuticals used as antipsychotic drugs and have been widely used in the treatment of autism. Recent evidence reviewed below indicates that dopamine in high concentrations may be toxic to the brain. Figure 1. Toxicity of excess dopamine.
3 Dopamine is a very reactive molecule compared with other neurotransmitters, and dopamine degradation naturally produces oxidative species (Figure 1). More than 90 percent of dopamine in dopaminergic neurons is stored in abundant terminal vesicles and is protected from degradation. However, a small fraction of dopamine is cytosolic, and it is the major source of dopamine metabolism and presumed toxicity. Cytosolic dopamine (Figure 1) undergoes degradation to form 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) and homovanillic acid (HVA) via the monoamine oxidase pathway. Alternatively, dopamine undergoes oxidation in the presence of excess iron or copper (common in autism and schizophrenia) to form dopamine cyclized o-quinone, which is then converted to dopamine cyclized o-semiquinone, depleting NADPH in the process. Dopamine cyclized o-semiquinone then reacts with molecular oxygen to form oxygen superoxide free radical, an extremely toxic oxidizing agent. In the process, dopamine cyclized o-quinone is reformed, resulting in a vicious cycle extremely toxic to tissues producing dopamine, including the brain, peripheral nerves, and the adrenal gland. It is estimated that each molecule of dopamine cyclized o-quinone produces thousands of molecules of oxygen superoxide free radical in addition to depleting NADPH. The o-quinone also reacts with cysteine residues on glutathione or proteins to form cysteinyl-dopamine conjugates (Figure 1). One of these dopamine conjugates is converted to N-acetylcysteinyl dopamine thioether, which causes apoptosis (programmed cell death) of dopaminergic cells. These biochemical abnormalities cause severe neurodegeneration in pathways that utilize dopamine as a neurotransmitter. Neurodegeneration is due to depletion of brain glutathione and NADPH as well as the overproduction of oxygen superoxide free radicals and neurotoxic N-acetylcysteinyl dopamine thioether. In addition, the depletion of NADPH also results in a diminished ability to convert oxidized glutathione back to its reduced form. What is the likely cause of elevated dopamine in autism? A significant number of studies have documented increased incidence of stool cultures positive for certain species of Clostridia bacteria in the intestine in children with autism using culture and PCR techniques. All these studies have indicated a disproportionate increase in various Clostridia species in stool samples compared to normal controls. In addition, metabolic testing has identified the metabolites 3-(3-hydroxyphenl)-3- hydroxypropionic acid (HPHPA) and 4-cresol from Clostridia bacteria at significantly higher concentrations in the urine samples of children with autism and in schizophrenia. Treatment with antibiotics against Clostridia species, such as metronidazole and vancomycin, eliminates these urinary metabolites with reported concomitant improvement in autistic symptoms. In addition, I had noticed a correlation between elevated HPHPA and elevated urine homovanillic acid (HVA). The probable mechanism for this correlation is that certain Clostridia metabolites have the ability to inactivate dopamine beta-hydroxylase, which is needed for the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine (Figure 2).
4 Figure 2. Effect of Clostridia metabolites on human catecholamine metabolism. DHPPA, 4-cresol, HPHPA, HVA, and VMA are all measured in The Great Plains Laboratory Organic Acids Test. Such metabolites are not found at only trace levels. The concentration of the Clostridia metabolite HPHPA in children with autism may sometimes exceed the urinary concentration of the norepinephrine metabolite vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) by a thousand fold on a molar basis and may be the major organic acid in urine in those with severe gastrointestinal Clostridia overgrowth, and even exceed the concentration of all the other organic acids combined. Dopamine beta hydroxylase that converts dopamine to norepinephrine in serum of severely retarded children with autism was much lower than in those who were higher functioning. Decreased urine output of the major norepinephrine metabolite meta-hydroxyphenolglycol (MHPG) was decreased in urine samples of children with autism, consistent with inhibition of dopamine beta hydroxylase. Many physicians treating children with autism have noted that the severity of autistic symptoms is related to the concentration of the Clostridia marker 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic acid (HPHPA) in urine. These are probably the children with autism with severe and even psychotic behavior treated with Risperdal and other anti-psychotic drugs, which block the activation of dopamine receptors by excess dopamine. I have identified a number of species of Clostridia species that produce HPHPA including C. sporogenes, C.botulinum, C. caloritolerans, C. mangenoti, C. ghoni, C.bifermentans, C. difficile, and C. sordellii. All species of Clostridia are spore formers and thus may persist for long periods of time in the gastrointestinal tracts even after antibiotic treatment with oral vancomycin and metronidazole.
5 How do the changes in brain neurotransmitters caused by Clostridia metabolites alter behavior? The increase in phenolic Clostridia metabolites common in autism significantly decreases brain dopamine beta hydroxylase activity. This leads to overproduction of brain dopamine and reduced concentrations of brain norepinephrine, and can cause obsessive, compulsive, stereotypical behaviors associated with brain dopamine excess and reduced exploratory behavior and learning in novel environments that are associated with brain norepinephrine deficiency. Such increases in dopamine in autism have been verified by finding marked increases in the major dopamine metabolite homovanillic acid (HVA) in urine. The increased concentrations of HVA in urine samples of children with autism are directly related to the degree of abnormal behavior. The concentrations of HVA in the urine of some children with autism are markedly abnormal. In addition to alteration of brain neurotransmitters, the inhibition of the production of norepinephrine and epinephrine by Clostridia metabolites may have a prominent effect on the production of neurotransmitters by the sympathetic nervous system and the adrenal gland. The major neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system that regulates the eyes, sweat glands, blood vessels, heart, lungs, stomach, and intestine is norepinephrine. An inadequate supply of norepinephrine or a substitution of dopamine for norepinephrine might result in profound systemic effects on physiology. The adrenal gland which produces both norepinephrine and epinephrine might also begin to release dopamine instead, causing profound alteration in all physiological functions. In addition to abnormal physiology caused by dopamine substitution for norepinephrine and epinephrine, dopamine excess causes free radical damage to the tissues producing it, perhaps leading to permanent damage of the brain, adrenal glands, and sympathetic nervous system if the Clostridia metabolites persist for prolonged periods of time, if glutathione is severely depleted, and if there is apoptotic damage caused by the dopamine metabolite N- acetylcysteinyl dopamine thioether. Depletion of glutathione can be monitored in The Great Plains Laboratory Organic Acids Test by tracking the metabolite pyroglutamic acid, which is increased in both blood and urine when glutathione is depleted. In addition, The Great Plains Laboratory also tests the other molecules involved in this toxic pathway, the dopamine metabolite homovanillic acid (HVA), the epinephrine and norepinephrine metabolite VMA and the Clostridia metabolites HPHPA and 4-cresol. In summary, gastrointestinal Clostridia bacteria have the ability to markedly alter behavior in autism and other neuropsychiatric diseases by production of phenolic compounds that dramatically alter the balance of both dopamine and norepinephrine. Excess dopamine not only causes abnormal behavior but also depletes the brain of glutathione and NADPH and causes a vicious cycle producing large quantities of oxygen superoxide that causes severe brain damage. Such alterations appear to be a (the) major factor in the causation of autism and schizophrenia. The Organic Acids Test (see sample Organic Acids Test report below) now has the ability to unravel a major mystery in the causation of autism, schizophrenia, and other neuropsychiatric diseases, namely the reason for dopamine excess in these disorders. In the past, some physicians would order the Organic Acids Test once a year or less. With the new knowledge of the mechanism of Clostridia toxicity via inhibition of dopamine beta-hydroxylase, it seems that the control of such toxic organisms needs to monitored much more frequently to prevent serious brain, adrenal gland, and sympathetic nervous system damage caused by excess dopamine and oxygen superoxide. Below is a test report of a child with autism tested with The Great Plains Laboratory Organic Acids Test.
6 Discussion of patient results In the graph above, the vertical bar is the upper limit of normal and the patient s value is plotted inside a diamond (red for abnormal, black for normal). The above results were from a boy with severe autism. The HPHPA Clostridia marker was very high (979 mmol/mol creatinine), about 4.5 times the upper limit of normal. However, the metabolite due to Clostridium difficile was in the normal range, indicating that Clostridium difficile was unlikely to be the Clostridium bacteria producing the high HPHPA. In other words, a different Clostridia species was implicated. The major dopamine metabolite homovanillic acid (HVA) was extremely high (87 mmol/mol creatinine), almost 7 times the upper limit of normal. The major metabolite of epinephrine and norepinephrine, VMA was in the normal range. The HVA/VMA ratio was 15, more than five times higher than the upper limit of normal, indicating a severe imbalance in the production of epinephrine/norepinephrine and that of dopamine. The very high dopamine metabolite, HVA, indicates that the brain, adrenal glands, and sympathetic nervous system may be subject to severe oxidative stress due to superoxide free radicals and that brain damage due to severe oxidative stress might result if the Clostridia bacteria are left untreated. Below the same patient s results are displayed in a form that is related to the metabolic pathways. This graphical result now appears on all organic acid results from The Great Plains Laboratory.
7 Reference: Shaw W. Increased urinary excretion of a 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic acid (HPHPA), an abnormal phenylalanine metabolite of Clostridia spp. in the gastrointestinal tract, in urine samples from patients with autism and schizophrenia. Nutr Neurosci Jun;13(3):
PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture. Adrenergic Agents
 PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture Adrenergic Agents Introduction Introduction Adrenergic agents are a broad class of agents employed in the treatment of many disorders. They are those chemical agents that exert
PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture Adrenergic Agents Introduction Introduction Adrenergic agents are a broad class of agents employed in the treatment of many disorders. They are those chemical agents that exert
Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function
 Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function Alvin Stein, MD Neurotransmitters are chemicals manufactured by our bodies that allow our nervous system to function properly. When the body requires
Amino Acid Therapy to Restore Neurotransmitter Function Alvin Stein, MD Neurotransmitters are chemicals manufactured by our bodies that allow our nervous system to function properly. When the body requires
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION.
 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Absorption of Drugs. Transport of a drug from the GI tract
 Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Slide 1: Introduction Introduce the purpose of your presentation. Indicate that you will explain how the brain basically works and how and where
 Slide 1: Introduction Introduce the purpose of your presentation. Indicate that you will explain how the brain basically works and how and where drugs such as heroin and cocaine work in the brain. Tell
Slide 1: Introduction Introduce the purpose of your presentation. Indicate that you will explain how the brain basically works and how and where drugs such as heroin and cocaine work in the brain. Tell
Chapter 4. The Adrenal Medulla
 Chapter 4 The Adrenal Medulla Introduction Induction of cortisol production requires several minutes, and full elaboration of cortisol action requires several hours. In contrast, the adrenal medullary
Chapter 4 The Adrenal Medulla Introduction Induction of cortisol production requires several minutes, and full elaboration of cortisol action requires several hours. In contrast, the adrenal medullary
Stress & Catecholamines - Overview
 Stress & Catecholamines - Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR II SEMINAR VJ Temple Stress can due to: What is
Stress & Catecholamines - Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR II SEMINAR VJ Temple Stress can due to: What is
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
Endocrine Responses to Resistance Exercise
 chapter 3 Endocrine Responses to Resistance Exercise Chapter Objectives Understand basic concepts of endocrinology. Explain the physiological roles of anabolic hormones. Describe hormonal responses to
chapter 3 Endocrine Responses to Resistance Exercise Chapter Objectives Understand basic concepts of endocrinology. Explain the physiological roles of anabolic hormones. Describe hormonal responses to
regulation of ECF composition and volume regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon
 Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Norepinephrine Effects On the System
 Norepinephrine Effects On the System NE Conversion to Epinephrine in the Circulation Under stress, the increased norepinephrine produced is transmitted throughout the system. This increased level represents
Norepinephrine Effects On the System NE Conversion to Epinephrine in the Circulation Under stress, the increased norepinephrine produced is transmitted throughout the system. This increased level represents
Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I
 Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I By: James L. Holly, MD Oxidative Stress refers to effects from endogenous (produced in the body) toxins (free radicals) produced in the body by normal metabolism
Glutathione and Oxidative Stress - Part I By: James L. Holly, MD Oxidative Stress refers to effects from endogenous (produced in the body) toxins (free radicals) produced in the body by normal metabolism
Journal Club. Parkinsonismo iatrogeno
 PROGETTO UNIVA 2013 Journal Club Parkinsonismo iatrogeno Pietro Gareri, MD, PhD Geriatra ASP Catanzaro Lamezia Terme 3 Luglio 2013 Drug-induced parkinsonism (DIP) was recognized in the early 1950s as a
PROGETTO UNIVA 2013 Journal Club Parkinsonismo iatrogeno Pietro Gareri, MD, PhD Geriatra ASP Catanzaro Lamezia Terme 3 Luglio 2013 Drug-induced parkinsonism (DIP) was recognized in the early 1950s as a
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS
 WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS BY: SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGI UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS Include vitamin
WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS BY: SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGI UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS Include vitamin
Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction When there is an overwhelming threat to the
Response to Stress Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction When there is an overwhelming threat to the
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
BIOMARKERS AND TOXICITY MECHANISMS 06 Mechanisms Metabolism & Detoxification. Luděk Bláha, PřF MU, RECETOX www.recetox.cz
 BIOMARKERS AND TOXICITY MECHANISMS 06 Mechanisms Metabolism & Detoxification Luděk Bláha, PřF MU, RECETOX www.recetox.cz Metabolism and detoxification Chemicals enter body... mostly via food Pass directly
BIOMARKERS AND TOXICITY MECHANISMS 06 Mechanisms Metabolism & Detoxification Luděk Bláha, PřF MU, RECETOX www.recetox.cz Metabolism and detoxification Chemicals enter body... mostly via food Pass directly
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior
 Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major categories
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major categories
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Graduate and Postdoctoral Affairs School of Biomedical Sciences College of Medicine. Graduate Certificate. Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine
 Graduate and Postdoctoral Affairs School of Biomedical Sciences College of Medicine Graduate Certificate in Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Graduate Certificate Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Purpose
Graduate and Postdoctoral Affairs School of Biomedical Sciences College of Medicine Graduate Certificate in Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Graduate Certificate Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Purpose
BSc in Medical Sciences with PHARMACOLOGY
 BSc in Medical Sciences with PHARMACOLOGY Course Director Dr Christopher John Module Leaders Dr Robert Dickinson (Module 1) Dr Anabel Varela Carver (Module 2) Dr Sohag Saleh (Module 3) Course Administrator
BSc in Medical Sciences with PHARMACOLOGY Course Director Dr Christopher John Module Leaders Dr Robert Dickinson (Module 1) Dr Anabel Varela Carver (Module 2) Dr Sohag Saleh (Module 3) Course Administrator
Definition: What is the Microbiome- A Big Picture
 The Microbiome What is the Microbiome- A Big Picture Definition: The collection of genomes of the microbes (bacteria, bacteriophages, fungi, protozoa, and viruses) that live inside a human body Are we
The Microbiome What is the Microbiome- A Big Picture Definition: The collection of genomes of the microbes (bacteria, bacteriophages, fungi, protozoa, and viruses) that live inside a human body Are we
The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9
 Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain.
 Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security
 Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
Disability Evaluation Under Social Security Revised Medical Criteria for Evaluating Endocrine Disorders Effective June 7, 2011 Why a Revision? Social Security revisions reflect: SSA s adjudicative experience.
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
The Testosterone Report
 The Testosterone Report Contents 1. What is Testosterone? 2. Why is Testosterone necessary? 3. Why do my Testosterone Levels decrease? 4. What does low Testosterone cause? 5. How Do I raise my Testosterone?
The Testosterone Report Contents 1. What is Testosterone? 2. Why is Testosterone necessary? 3. Why do my Testosterone Levels decrease? 4. What does low Testosterone cause? 5. How Do I raise my Testosterone?
Adrenergic agonists. R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka
 Adrenergic agonists R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka Outline Recall Introduction to adrenergic agonists Classification of adrenergic
Adrenergic agonists R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka Outline Recall Introduction to adrenergic agonists Classification of adrenergic
Chapter 12. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation. Heat Balance. An Overview of Heat Balance. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Liver Function Tests. Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB
 Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
The Physiology of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species. I. Introduction Definition, Source, function and Purpose
 The Physiology of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species I. Introduction Definition, Source, function and Purpose A. Definition of free radicals and reactive oxygen species
The Physiology of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species I. Introduction Definition, Source, function and Purpose A. Definition of free radicals and reactive oxygen species
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
5.111 Principles of Chemical Science
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.111 Principles
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.111 Principles
Antioxidant Products. A comprehensive range of. Antioxidants
 Antioxidant Products A comprehensive range of ALB BIL FERR GR Ransel Ransod antioxidant TAS testing TIBC kits TF BIL FERR GR Ransel Ransod TAS TIBC TF UA A FERR GR Ransel Ransod TAS TIBC TF UA ALB GR Ransel
Antioxidant Products A comprehensive range of ALB BIL FERR GR Ransel Ransod antioxidant TAS testing TIBC kits TF BIL FERR GR Ransel Ransod TAS TIBC TF UA A FERR GR Ransel Ransod TAS TIBC TF UA ALB GR Ransel
Blood Testing Protocols. Disclaimer
 Blood Testing Protocols / Page 2 Blood Testing Protocols Here are the specific test protocols recommend by Dr. J.E. Williams. You may request these from your doctor or visit www.readyourbloodtest.com to
Blood Testing Protocols / Page 2 Blood Testing Protocols Here are the specific test protocols recommend by Dr. J.E. Williams. You may request these from your doctor or visit www.readyourbloodtest.com to
Hormones & Chemical Signaling
 Hormones & Chemical Signaling Part 2 modulation of signal pathways and hormone classification & function How are these pathways controlled? Receptors are proteins! Subject to Specificity of binding Competition
Hormones & Chemical Signaling Part 2 modulation of signal pathways and hormone classification & function How are these pathways controlled? Receptors are proteins! Subject to Specificity of binding Competition
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Guidance for Industry Safety Testing of Drug Metabolites
 Guidance for Industry Safety Testing of Drug Metabolites U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) February 2008 Pharmacology
Guidance for Industry Safety Testing of Drug Metabolites U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) February 2008 Pharmacology
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
ADHD A Focus on the Brain
 ADHD A Focus on the Brain Laurie Hayes Center for Advanced Research and Technology Clovis, California Carrie Newdigger Macksville High School Macksville, Kansas In collaboration with Susanna Visser 1 and
ADHD A Focus on the Brain Laurie Hayes Center for Advanced Research and Technology Clovis, California Carrie Newdigger Macksville High School Macksville, Kansas In collaboration with Susanna Visser 1 and
Treatments for Major Depression. Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are:
 Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Treatments for Major Depression Drug Treatments The two (2) classes of drugs that are typical antidepressants are: 1. 2. These 2 classes of drugs increase the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters through
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Long-Term Effects of Drug Addiction
 Long-Term Effects of Drug Addiction Part 1: Addiction is a chronic disease Drug addiction is considered a chronic brain disease because drugs cause long-lasting changes in brain structure and function.
Long-Term Effects of Drug Addiction Part 1: Addiction is a chronic disease Drug addiction is considered a chronic brain disease because drugs cause long-lasting changes in brain structure and function.
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
Overtraining with Resistance Exercise
 ACSM CURRENT COMMENT Overtraining with Resistance Exercise One of the fastest growing and most popular types of exercise in recent years is resistance exercise, whether used for the purpose of general
ACSM CURRENT COMMENT Overtraining with Resistance Exercise One of the fastest growing and most popular types of exercise in recent years is resistance exercise, whether used for the purpose of general
Alcohol and Brain Damage
 Alcohol and Brain Damage By: James L. Holly, MD O God, that men should put an enemy in their mouths to steal away their brains! That we should, with joy, pleasance, revel, and applause, transform ourselves
Alcohol and Brain Damage By: James L. Holly, MD O God, that men should put an enemy in their mouths to steal away their brains! That we should, with joy, pleasance, revel, and applause, transform ourselves
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Milwaukee School of Engineering [email protected]. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN
 FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN General Pantarhei Bioscience B.V. is an emerging specialty pharmaceutical company with a creative approach towards drug development. The Company
FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN General Pantarhei Bioscience B.V. is an emerging specialty pharmaceutical company with a creative approach towards drug development. The Company
Chapter 28. Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Chapter 28 Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease 1. Introduction Parkinsonism Tremors hands and head develop involuntary movements when at rest; pin rolling sign (finger and thumb) Muscle rigidity arthritis
Chapter 28 Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease 1. Introduction Parkinsonism Tremors hands and head develop involuntary movements when at rest; pin rolling sign (finger and thumb) Muscle rigidity arthritis
placebo-controlledcontrolled double-blind, blind,
 Clinical Potential of Minocycline for Depression with Psychotic Features Tsuyoshi Miyaoka Department of Psychiatry Shimane University School of Medicine Minocycline 1. Second-generation tetracycline which
Clinical Potential of Minocycline for Depression with Psychotic Features Tsuyoshi Miyaoka Department of Psychiatry Shimane University School of Medicine Minocycline 1. Second-generation tetracycline which
Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life
 Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life Vitality for Life supplements with patented Oligo Oligo U.S. Patent No. 8,273,393 Reinventing the Multivitamin Our modern diets have the majority of us gorging
Rediscover What It Means to Be Full of Life Vitality for Life supplements with patented Oligo Oligo U.S. Patent No. 8,273,393 Reinventing the Multivitamin Our modern diets have the majority of us gorging
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Activity 4 Long-Term Effects of Drug Addiction
 Activity 4 Long-Term Effects of Drug Addiction Core Concept: Addictive drugs may lead to long-term changes in brain function. Class time required: Approximately 60-80 minutes Teacher Provides: Copy of
Activity 4 Long-Term Effects of Drug Addiction Core Concept: Addictive drugs may lead to long-term changes in brain function. Class time required: Approximately 60-80 minutes Teacher Provides: Copy of
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model
 The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
Treating Mental Disorders. Types of Biological Treatment. Drug Treatments for Psychological Disorders
 Treating Mental Disorders Biological Treatments for Psychological Disorders Aims: Describe and Assess Biological Treatments Objectives By the end of this session you should be able to: Describe the use
Treating Mental Disorders Biological Treatments for Psychological Disorders Aims: Describe and Assess Biological Treatments Objectives By the end of this session you should be able to: Describe the use
DEPRESSION. William J. Walsh, Ph.D.
 DEPRESSION. William J. Walsh, Ph.D. Depression Database More than 3,000 patients diagnosed with clinical depression, > 250,000 assays of blood and urine, 50 to 150 symptoms or traits recorded for each
DEPRESSION. William J. Walsh, Ph.D. Depression Database More than 3,000 patients diagnosed with clinical depression, > 250,000 assays of blood and urine, 50 to 150 symptoms or traits recorded for each
PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement)
 1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action
 Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action Cai Li, Ph.D. Assistant professor Touchstone Center for Diabetes Research Departments of Physiology and Internal Medicine The University of
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action Cai Li, Ph.D. Assistant professor Touchstone Center for Diabetes Research Departments of Physiology and Internal Medicine The University of
Alzheimer Disease (AD)
 1 Alzheimer Disease (AD) 2 Alzheimer's disease is a progressive degenerative disease that attacks the brain and results in impaired memory, thinking and behavior. It was first described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer
1 Alzheimer Disease (AD) 2 Alzheimer's disease is a progressive degenerative disease that attacks the brain and results in impaired memory, thinking and behavior. It was first described by Dr. Alois Alzheimer
Wireless Radiation in the Etiology and Treatment of Autism: Clinical Observations and Mechanisms
 Wireless Radiation in the Etiology and Treatment of Autism: Clinical Observations and Mechanisms 1 Journal of the Australasian College of Nutritional & Environmental Medicine Tamara J Mariea and George
Wireless Radiation in the Etiology and Treatment of Autism: Clinical Observations and Mechanisms 1 Journal of the Australasian College of Nutritional & Environmental Medicine Tamara J Mariea and George
Regulation of Metabolism. By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
What Do We Learn about Hepatotoxicity Using Coumarin-Treated Rat Model?
 What Do We Learn about Hepatotoxicity Using Coumarin-Treated Rat Model? authors M. David Ho 1, Bob Xiong 1, S. Stellar 2, J. Proctor 2, J. Silva 2, H.K. Lim 2, Patrick Bennett 1, and Lily Li 1 Tandem Labs,
What Do We Learn about Hepatotoxicity Using Coumarin-Treated Rat Model? authors M. David Ho 1, Bob Xiong 1, S. Stellar 2, J. Proctor 2, J. Silva 2, H.K. Lim 2, Patrick Bennett 1, and Lily Li 1 Tandem Labs,
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP Summary of Product Characteristics
 Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP Summary of Product Characteristics 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP Summary of Product Characteristics 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Adrenaline (epinephrine) 1:1000 Injection BP 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to. women, and is a serious condition that can lead to. significant lifestyle changes.
 Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Overactive bladder is a common condition thought to FADE UP TO WIDE SHOT OF FEMALE MODEL WITH TRANSPARENT SKIN. URINARY BLADDER VISIBLE IN PELVIC REGION affect over 16 percent of adults. It affects men
Is Exercise the Best Antioxidant Supplement? Len Kravitz, Ph.D.
 Is Exercise the Best Antioxidant Supplement? Len Kravitz, Ph.D. As an unexpected consequence of the metabolic steps that convert food into energy, the body produces molecules commonly called free radicals.
Is Exercise the Best Antioxidant Supplement? Len Kravitz, Ph.D. As an unexpected consequence of the metabolic steps that convert food into energy, the body produces molecules commonly called free radicals.
Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death HST.035 Spring 2003 Overview of Cell Injury Cells
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death HST.035 Spring 2003 Overview of Cell Injury Cells
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
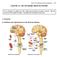 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
1-3.20 Defend medication administration by an EMT-Intermediate to effect positive therapeutic affect. (A-3)
 UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 1-3 At the completion of this unit, the EMT-Intermediate student will be able to understand the basic principles of pharmacology and be able to develop a drug profile for common
UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 1-3 At the completion of this unit, the EMT-Intermediate student will be able to understand the basic principles of pharmacology and be able to develop a drug profile for common
serum protein and A/ G ratio
 serum protein and A/ G ratio Blood plasma contains at least 125 individual proteins. Serum ( as contrasted with plasma) is deficient in those coagulation protein which are consumed during the process of
serum protein and A/ G ratio Blood plasma contains at least 125 individual proteins. Serum ( as contrasted with plasma) is deficient in those coagulation protein which are consumed during the process of
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON. created by Dr. Joanne Hsu
 NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
The diagram below summarizes the effects of the compounds that cells use to regulate their own metabolism.
 Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism Intracellular metabolic regulators Each of the control point steps in the carbohydrate metabolic pathways in effect regulates itself by responding to molecules that
Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism Intracellular metabolic regulators Each of the control point steps in the carbohydrate metabolic pathways in effect regulates itself by responding to molecules that
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2. 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany
 Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH
 Office of Communications www.broadinstitute.org T 617-714-7151 [email protected] 7 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142 GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH For decades,
Office of Communications www.broadinstitute.org T 617-714-7151 [email protected] 7 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142 GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH For decades,
Testosterone Therapy for Women
 Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels*
 Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY CONSENT FORM
 Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
Page 1 of 6 I, have been asked to read carefully all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described below on
Teriflunomide is the active metabolite of Leflunomide, a drug employed since 1994 for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (Baselt, 2011).
 Page 1 of 10 ANALYTE NAME AND STRUCTURE TERIFLUNOMIDE Teriflunomide TRADE NAME Aubagio CATEGORY Antimetabolite TEST CODE PURPOSE Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GENERAL RELEVANCY BACKGROUND sclerosis. The
Page 1 of 10 ANALYTE NAME AND STRUCTURE TERIFLUNOMIDE Teriflunomide TRADE NAME Aubagio CATEGORY Antimetabolite TEST CODE PURPOSE Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GENERAL RELEVANCY BACKGROUND sclerosis. The
Visual Acuity. Hearing. Height and Weight. Blood Pressure MEASURED VALUE
 TEST ITEM DESCRIPTION STANDARD LEVEL Standard level varies among different examination methods. Please check with your medical facility about normal level. MEASURED VALUE Visual Acuity You look at rings
TEST ITEM DESCRIPTION STANDARD LEVEL Standard level varies among different examination methods. Please check with your medical facility about normal level. MEASURED VALUE Visual Acuity You look at rings
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
