Pain after stroke. Spasticity and contractures. How is spasticity treated? Stroke Helpline: Website: stroke.org.uk
|
|
|
- Barrie Cooper
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
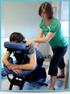
1 Stroke Helpline: Website: stroke.org.uk Pain after stroke After a stroke you might experience various physical effects, such as weakness, paralysis or changes in sensation. Unfortunately you may also experience pain. This factsheet will help you to understand some of the causes of pain after stroke and the treatments that may be available. It also gives details of useful organisations that can provide you with further information and support. There are many different types of pain you may experience after having a stroke. Weakness on one side of your body is one of the most common effects of stroke. This can lead to painful conditions such as muscle stiffness (spasticity) and shoulder problems. Some people also experience central poststroke pain, headaches and sore swollen hands after stroke. As with many effects of stroke, pain may persist for some time, but treatments such as medication and physiotherapy are often successful in relieving pain. Many people also benefit from attending pain management clinics and learn coping techniques to help them to manage any long-term pain (see page 7 for details). Spasticity and contractures After a stroke you may find that you have muscle tightness or stiffness this is called spasticity. It is a common problem and affects over a third of stroke survivors. Usually it occurs on the weaker side of your body. Spasticity happens when there is damage to the area of your brain that controls your muscles. If you have spasticity you will have increased muscle tone. Muscle tone is the amount of resistance or tension in your muscles, and it is what enables us to hold our bodies in a particular position. This increased muscle tone can make it difficult to move your limbs. Spasticity may also cause your muscles to tense and contract abnormally, causing spasms, which can be very painful. Spasticity can also damage your tissues and joints and can sometimes cause painful night cramps. It is important to treat spasticity as soon as possible because your joints and muscles may become so stiff that it is impossible to move them (this is called a contracture). How is spasticity treated? If you have weakness after your stroke you should be assessed for spasticity. A team of specialists will decide on the best treatment for you. This may include a combination of physiotherapy, medication and Botox. 1
2 Physiotherapy If you have spasticity you should have physiotherapy every day to move your joints. This will help to stretch your muscles, keeping them flexible and reducing the possibility of contractures. Your physiotherapist will gently place your affected limb into as many different positions as possible. This is called passive stretching and should be taught to your family and carers so that they can help you to practise your exercises. See our factsheet F16, Physiotherapy after stroke for more information. Botox If spasticity affects only one or two specific parts of your body, you may be given botulinum toxin A (Botox) as an injection directly into your muscle. Botox works by blocking the action of the nerves on the muscle, reducing your muscle s ability to contract. It reduces muscle tone, which can help you to straighten out your limbs. Botox is only useful for small muscles, such as those in the hands. The muscle-relaxing effects of Botox usually last for about three months and you should not notice any changes in sensation in your muscles. Botox treatment should be given with further rehabilitation such as physiotherapy, or other treatments like splinting or casting. You should also have an assessment three to four months after the treatment, and be offered further Botox treatments if helpful. Medication If you find that you are still experiencing muscle stiffness, you may be prescribed 2 medication to help reduce this stiffness and the pain that often accompanies muscle spasms. There are different types of drugs that you could be given. They all work in slightly different ways, but they all help to relax your muscles. When your muscles are relaxed they can move more easily and you can stretch them further. You may also find that it becomes easier to straighten or bend your affected limbs, and you may notice fewer muscle spasms. You will usually be prescribed baclofen or tizanidine first. If these drugs do not work, there are other drugs that may help, but they should only be prescribed by someone who specialises in managing spasticity. How are contractures treated? Splinting and casting If your spasticity is not fully controlled and you develop contractures, your physiotherapist may use a splint or a cast that moulds to or lies along your affected limb and holds it in place. This treatment helps to stretch out the muscles in your tight limbs and is usually combined with physiotherapy. Sometimes this treatment is used to try to prevent contractures from forming by making sure that your body is not in an abnormal position. Unfortunately sometimes splints and casts can be uncomfortable. Talk to your physiotherapist about what would be best for you. Surgery If you have severe contractures, you may need surgery to lengthen your tendons. Tendons are the bands that connect your muscle to the bone, and lengthening your tendons allows the joint to be stretched
3 out. This procedure is performed under anaesthetic. Surgery is always a last resort. Shoulder pain Shoulder pain is common after a stroke, and usually affects the side of your body that is affected by the stroke. There are different types of shoulder pain that you might experience and experts do not yet fully understand the exact causes. Frozen shoulder After a stroke you may find that your shoulder is very stiff and that it hurts when you move it. This is called frozen shoulder or capsulitis. Muscles and ligaments around our shoulder joints hold the bone in our upper arms in place. There is a layer of tissue that surrounds this joint which is called a capsule. If your arm muscles are very weak, stiff or paralysed, the effect of gravity puts a strain on your ligaments and your capsule. This can cause these parts of your shoulder joint to become inflamed, stretched and damaged. Having weakness in your arm muscles may contribute to this pain in your shoulder. Subluxation Another cause of shoulder pain is shoulder subluxation. This means partial dislocation where the bone of the upper arm and the shoulder blade have moved apart. This might be because the muscles that normally hold this joint in place are too weak to do this properly. How is shoulder pain treated? Prevention If you have weakness in your arm following your stroke, your medical team will try to prevent shoulder pain developing. They will make sure that anyone who handles your arm knows how to do so with care and without causing strain on your shoulder joint. They should also ensure that your arm and shoulder are positioned correctly. Correct positioning is vital because it can help to reduce the strain on your ligaments and capsule, helping to prevent frozen shoulder from developing. It may also help to prevent your shoulder blade and upper arm bone from moving apart (subluxation). Your medical team may use foam supports to make sure that your shoulder is supported in the correct position. Your arm can also be supported using a pillow. Overhead arm slings should not be used because there is not enough evidence that they work and they may increase your risk of developing shoulder pain or contractures. Your physiotherapist may use cuffs or straps to keep your arm and shoulder in the correct position, but for some people this may lead to spasticity. Your physiotherapist may also use electrical stimulation on the muscles around your shoulder to help prevent or treat subluxation. (See page 6 for further information about electrical stimulation.) Reducing pain You may be given painkillers such as paracetamol or codeine to help relieve the pain in your shoulder. For more severe pain you may be given a non-steroidal 3
4 anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as diclofenac or ibuprofen. These types of drug help to relieve pain and can also help to reduce swelling in your shoulder capsule. If you have an inflamed shoulder a steroid, such as triamcinolone, may be injected into your joint to help reduce the pain. Botox can sometimes be injected into specific muscles around your shoulder to help reduce pain and increase flexibility, particularly where the pain is associated with spasticity. Moving your shoulder It is important to keep the muscles in your shoulder and arm active so that any stiffness does not get worse. Your physiotherapist may use stretching exercises to move your shoulder joint in all directions. They can also provide you with advice about how to protect your shoulder during everyday movements such as reaching for something or getting dressed. Central post-stroke pain (CPSP) Up to 12 per cent of people who have a stroke will develop a particular type of pain called central post-stroke pain (CPSP). This is also known as Dejerine Roussy Syndrome, or central pain syndrome. There are different types of pain you might experience if you have CPSP. Many people describe it as an icy burning sensation, or a throbbing or shooting pain. Some people also experience pins and needles or numbness in the areas affected by the pain. For most stroke survivors with CPSP, the pain occurs in the side of their body that has been affected by the stroke. The pain may begin immediately after your stroke but more often it begins several months later. 4 Some people find this pain becomes worse because of other factors such as movement or a change in temperature. The exact cause of CPSP is unknown, but it is thought to be due to damage to certain parts of the brain and body. CPSP is a form of neuropathic pain, which means that the painful sensation does not occur because your body is injured or because something is making it hurt. The pain may be caused by damage to the brain, brainstem or spinal cord (together, these are called the central nervous system) or be due to damage to the sensory pathways. These are pathways between the brain and the body which carry messages about pain. In some cases, CPSP is due to damage to the thalamus, which is the brain s pain centre. When this part of the brain is damaged it can sometimes cause feelings of pain when you are feeling a sensation that is not normally painful. How is CPSP treated? Unfortunately there is no cure for CPSP, but around 70 per cent of stroke survivors with CPSP find that medication helps to relieve their pain. Ordinary painkillers are not usually helpful in relieving CPSP, but some drugs which were originally created for treating other conditions are helpful for some people. They include amitriptyline, which is a drug used to treat depression, and gabapentin and pregabalin, which are used to treat epilepsy. You will usually be started on a low dose, which is then gradually increased. If the first medication you try does not work, you should be offered another drug to try either with, or instead of, the first one.
5 In rare cases, if your pain is severe and other treatments have been unsuccessful, your medical team may offer you deep brain stimulation. This is a procedure where small electrical leads are placed deep within your brain and are connected to a batterypowered machine, which sits under your skin. This procedure can only be carried out in specialist centres and it is not suitable for everyone. Research shows that deep brain stimulation is effective in reducing pain for some people, though only a small number of people have taken part in the studies. Other painful conditions Swollen hand You might find that after your stroke your hand swells up and becomes painful. This usually happens if you are not moving your hand very much, for example, if it is paralysed. The swelling happens because the fluid in the tissue in your hand cannot circulate properly because the muscles are not moving. When your muscles are not moving regularly, this fluid can collect, causing swelling and discomfort. This can get worse if your hand is often hanging downwards. This painful swelling can make it even more difficult to move your hand and arm, which can make spasticity worse. To overcome this problem it is best to raise your hand and place it on a pillow or a cushion, and to get your hand moving again gently with the help of your physiotherapist. Wearing a tight-fitting glove can sometimes help to push the fluid out of your hand this is called an oedema glove. This will need to be fitted correctly to avoid causing too much pressure. Your physiotherapist should be able to make a referral for you to have this done. You might find that painkillers such as paracetamol help to relieve the pain caused by this swelling in your hand. Headache There are many reasons why you might experience headaches following your stroke. Some reasons might be the same as before your stroke, such as stress, depression or lack of sleep. If you are having headaches after your stroke, they could be a side effect of medication that you have started taking. Common examples include nifedipine (Adalat), which is given for high blood pressure, dipyridamole (Persantin), a blood-thinning medication, and glyceryl trinitrate, which is given for angina and to lower blood pressure. Talk to your doctor, because if you are experiencing headaches or any other side effects from medication, there may be an alternative drug you can try instead. Occasionally, headaches may be a direct after-effect of your stroke if there is swelling of the brain. This swelling, which can be caused by a stroke, can irritate the membrane that covers the brain, resulting in a headache. This is more common if you have had a stroke caused by a bleed in the brain. Headaches can also occur because of a change to the levels of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This is the fluid that fills the space between our brain and our skull. If there is an increased or reduced amount of CSF, this can cause headaches. The pain from the headaches you are experiencing should lessen over time and can usually be controlled by painkillers such as paracetamol. You should not take aspirin if your stroke was caused by a bleed. 5
6 Drinking plenty of water (two to three litres per day) and avoiding caffeine and alcohol (which cause dehydration) may help to reduce these headaches. Increasing the amount of fluid in your body will improve the blood circulation to your brain. Sometimes taking painkillers for headaches too often (for more than about 10 days a month) can cause headaches. Treatment usually involves stopping all pain relief medication for one month, but talk to your GP first if you think this is the cause of your headaches. Do not stop taking any medication without getting medical advice. If you ever experience a sudden, severe headache or a persistent headache, you should seek medical attention urgently to find out what is causing it. One of the symptoms of a stroke caused by bleeding on the surface of the brain (subarachnoid haemorrhage) is a very sudden and severe headache, as if you have been hit on the back of the head. For more information about strokes caused by bleeding, please see our factsheet F25, Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke. Alternative methods of treating pain If you find that medication and/or physiotherapy has not helped to relieve your pain, you may wish to try some alternative techniques. You may gain temporary relief from TeNS, massage or acupuncture. Learning a relaxation technique, such as meditation or yoga, or speaking to a counsellor may also help you to cope. A pain clinic can give you more advice about your options (see page 7). Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TeNS) If you have severe and persistent pain, your medical team may consider treating this with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TeNS). TeNS treatment uses electrical impulses to reduce pain. Sticky pads are attached to your skin close to the area that hurts. These pads are linked to leads called electrodes, which are attached to a battery-operated machine. Electrical impulses are then sent from the machine, through the electrodes and onto your skin. These impulses can help to block the pain signals from travelling along the nerve pathways to your brain. At a low frequency, TeNS can help your body to release natural painkillers called endorphins. There is not enough evidence to say definitively whether TeNS is an effective and reliable way of reducing pain. Clinical trials have shown that it works well for some people but not for others, and that the amount of pain relief and the length of time that this lasts for varies from person to person. The majority of people who have found TeNS to be effective noticed benefits whilst the machine was switched on, but found the pain relief did not last. This form of pain management is widely used by hospitals and pain clinics throughout most of the UK (see the section on Pain clinics and pain management programmes). TeNS could be a helpful way to manage your pain but it is important to check with your doctor first before trying this treatment. This is because there are lots of different causes of pain and types of pain, and TeNS has not yet been 6
7 recommended for all of them. There are no side effects to TeNS and you can use it alongside other medication. TeNS is unsuitable for some people, for example people fitted with a cardiac pacemaker, so if you are interested in trying TeNS to manage your pain, it is important to check with your doctor first. TeNS treatment may be available from your physiotherapist, or alternatively you can buy the machines from some pharmacies. Pain clinics and pain management programmes You should be referred to a specialist pain service if you are still in pain despite initial treatment, and it is causing you distress or significantly limiting what you are able to do. If this has not happened, ask your doctor to refer you to one. Pain clinics and pain management programmes can help you to find ways to manage your pain in the longer-term to improve your quality of life. At a pain clinic, you can have an assessment to determine the cause of your pain and they can provide treatment and advice to help you to manage this pain. The kinds of treatment that are available from pain clinics vary across the UK. More information about what pain services are available for you can be obtained from your local health service, for example your GP. Some pain clinics run pain management programmes. They use physical, psychological and practical methods to deal with managing your pain and the effects it has on your life. Carried out in groups, the programmes usually run for a set amount of time over a number of weeks. Doctors, nurses, psychologists, physiotherapists and occupational therapists will be there to carry out the programme. For example, a physiotherapist might help you to work on the physical difficulties that the pain causes by strengthening your muscles; a psychologist might help you to manage the emotional effects that pain can have, such as depression and frustration. Useful resources Pain relief audio tapes/cds A series of simple and effective audio resources for home use, describing techniques used on the pain management programme at the Walton Centre for Neurology and Neurosurgery. They are available from the Pain Relief Foundation (see Useful organisations). Titles: Coping with Pain, Coping with Back Pain, Coping with Headache and Migraine, Anxiety (all priced at 8.50 inc. P&P), The Relaxation Kit, and Feeling Good ( inc P&P). Books The Pain Relief Handbook: Self-help methods for managing pain. By Dr Chris Wells & Graham Nown Vermilion, London Available from book shops. Taking Control of your Pain. By Toni Battison. Age Concern Books (2005). Available from book shops. Pain Relief without Drugs. By Jan Sadler. (2007) Healing Arts Press (price 12.99). Available from The Pain Relief Foundation. 7
8 Useful organisations All organisations are UK wide unless otherwise stated. Stroke Association Stroke Helpline: Website: stroke.org.uk Contact us for information about stroke, emotional support and details of local services and support groups. Action on pain Tel: Website: Provides information and advice about pain. Campaigns and raises awareness of those living with chronic pain. The British Pain Society Tel: Website: Has various publications for patients and information about pain management. Central Pain Syndrome Alliance Website: International internet resource with online information and a discussion forum for support. Chronic Pain Policy Coalition Tel: Website: A forum uniting professionals, members of parliament and patients to campaign for improved strategies on chronic pain issues. Information about pain is available on their website. Pain Association Scotland Tel: Website: Provides information about pain and runs self-management programmes across Scotland for people living with chronic pain. Pain Concern Helpline: Website: Information and advice about pain is available through a range of publications and their helpline. Runs a radio programme called Airing Pain. They also have an online forum. The Pain Relief Foundation Tel: Website: Provides information about pain and pain management and supports research into treatments. PainSupport Website: Provides information about pain relief and advice about treatments. Offers an online forum and a contact club so that people suffering from pain can contact each other. SCOPE Helpline: Website: Provides information sheets about spasticity, splinting and Botox treatment. Talking Life Tel: Website: Runs training courses and produces materials for professionals. 8
9 TeNS Medical Services Ltd Tel: Website: Produces and sells TeNS machines. Disclaimer: The Stroke Association provides the details of other organisations for information only. Inclusion in this factsheet does not constitute a recommendation or endorsement. Glossary of terms Subarachnoid space = the space between the membranes that surround the brain and protect it from the skull. Subluxation = partial dislocation of the shoulder, where the bone of the upper arm and the shoulder blade have moved apart. TeNS = Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (a treatment that uses electrical impulses to block pain signals). Capsulitis = see Frozen shoulder. Central nervous system = the name for the system in the body containing the brain, brainstem and spinal cord. Contracture = abnormal shortening of a muscle that results in deformity. CPSP = central post-stroke pain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) = fluid that fills the space between the brain and skull. Frozen shoulder = a very stiff shoulder which can be painful. Lumbar puncture = a procedure to take a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, which can be used to diagnose conditions such as a subarachnoid haemorrhage. Oedema = an increase of fluid in the tissues which can cause swelling. Spasticity = a form of muscle tightening. Subarachnoid haemorrhage = a type of stroke caused by bleeding in the space between the brain and skull. 9
10 Produced by the Stroke Association s Information Service. For sources used visit stroke.org.uk Stroke Association Factsheet 30, version 1 published September 2012 (next revision due September 2014). Item code: 01F30 5 could help us answer a helpline call from a desperately worried person looking for answers about stroke. Text stroke to to donate 5 today. Texts cost 5 plus your standard network rate of which a minimum 4.70 will go to the Stroke Association. Full terms and conditions at Stroke Association is a Company Limited by Guarantee, registered in England and Wales (No 61274). Registered office: Stroke Association House, 240 City Road, London EC1V 2PR. Registered as a Charity in England and Wales (No ) and in Scotland (SC037789). Also registered in Northern Ireland (XT33805) Isle of Man (No 945)and Jersey (NPO 369). 10
Occupational therapy after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke After a stroke, you are likely to need help to regain your abilities, learn new skills and cope with any remaining
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke After a stroke, you are likely to need help to regain your abilities, learn new skills and cope with any remaining
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Managing Spasticity. Spasticity Service
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
The road to recovery. The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke
 The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
Cervical Spondylosis. Understanding the neck
 Page 1 of 5 Cervical Spondylosis This leaflet is aimed at people who have been told they have cervical spondylosis as a cause of their neck symptoms. Cervical spondylosis is a 'wear and tear' of the vertebrae
Page 1 of 5 Cervical Spondylosis This leaflet is aimed at people who have been told they have cervical spondylosis as a cause of their neck symptoms. Cervical spondylosis is a 'wear and tear' of the vertebrae
What is the Spasticity Clinic?
 The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
Elbow arthroscopy. Key points
 Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
m y f o u n d a t i o n i n f o s h e e t
 Pain and Myeloma m y f o u n d a t i o n i n f o s h e e t Pain is the most common symptom of myeloma and can greatly affect all areas of your life, especially if it is untreated or poorly managed. This
Pain and Myeloma m y f o u n d a t i o n i n f o s h e e t Pain is the most common symptom of myeloma and can greatly affect all areas of your life, especially if it is untreated or poorly managed. This
Private treatment. Which treatments are available privately? Can I have private and NHS treatment together?
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Private treatment Because the NHS only offers limited access to some therapies after stroke, you might choose to explore the option of private treatment.
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Private treatment Because the NHS only offers limited access to some therapies after stroke, you might choose to explore the option of private treatment.
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Spinal cord stimulation
 Spinal cord stimulation This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having spinal cord stimulation. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to
Spinal cord stimulation This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having spinal cord stimulation. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to
Living with a lung condition:
 Living with a lung condition: how exercise and eating well can make a difference to your life This information is for people living with a lung condition in the UK and your family and carers. It will help
Living with a lung condition: how exercise and eating well can make a difference to your life This information is for people living with a lung condition in the UK and your family and carers. It will help
Cancer Pain. Relief from PALLIATIVE CARE
 PALLIATIVE CARE Relief from Cancer Pain National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care For more information on the National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care, go to www.hse.ie/palliativecareprogramme
PALLIATIVE CARE Relief from Cancer Pain National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care For more information on the National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care, go to www.hse.ie/palliativecareprogramme
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Speech and language therapy after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Speech and language therapy after stroke Speech and language therapy (SLT) can help if you have communication problems or swallowing problems after
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Speech and language therapy after stroke Speech and language therapy (SLT) can help if you have communication problems or swallowing problems after
Medications for chronic pain
 Medications for chronic pain When it comes to treating chronic pain with medications, there are many to choose from. Different types of pain medications are used for different pain conditions. You may
Medications for chronic pain When it comes to treating chronic pain with medications, there are many to choose from. Different types of pain medications are used for different pain conditions. You may
Whiplash Associated Disorder
 Whiplash Associated Disorder Bourassa & Associates Rehabilitation Centre What is Whiplash? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain following hyperflexion or hyperextension of the tissues
Whiplash Associated Disorder Bourassa & Associates Rehabilitation Centre What is Whiplash? Whiplash is a non-medical term used to describe neck pain following hyperflexion or hyperextension of the tissues
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY. www.almirall.com. Solutions with you in mind
 ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY www.almirall.com Solutions with you in mind WHAT IS SPASTICITY? The muscles of the body maintain what is called normal muscle tone, a level of muscle tension that allows us to hold
ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY www.almirall.com Solutions with you in mind WHAT IS SPASTICITY? The muscles of the body maintain what is called normal muscle tone, a level of muscle tension that allows us to hold
Emergency Department. Whiplash neck sprain. Advice for patients
 Emergency Department Whiplash neck sprain Advice for patients What is a whiplash neck sprain? A whiplash neck sprain occurs when your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement.
Emergency Department Whiplash neck sprain Advice for patients What is a whiplash neck sprain? A whiplash neck sprain occurs when your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement.
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity
 Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet
 Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Cast removal what to expect #3 Patient Information Leaflet SM466 Now your cast is off, self help is the key! Follow the advice given to you by your doctor and the staff in the clinic. Your skin will be
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know. Patient information Leaflet
 Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis)
 Patient information Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information:
Patient information Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information:
Private treatment. What private treatments are available for stroke? What is private treatment? Why would I consider private treatment?
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Private treatment You can choose private health treatment for all medical conditions, including stroke. If you are considering private treatment this
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Private treatment You can choose private health treatment for all medical conditions, including stroke. If you are considering private treatment this
Physiotherapy and arthritis. Therapy Physiotherapy and arthritis. This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this therapy.
 Therapy Physiotherapy and arthritis Physiotherapy and arthritis This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this therapy. In association with Arthritis Research UK produce and
Therapy Physiotherapy and arthritis Physiotherapy and arthritis This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this therapy. In association with Arthritis Research UK produce and
Drug treatments for neuropathic pain
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Drug treatments for neuropathic pain NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Drug treatments for neuropathic pain NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Complex regional pain syndrome and osteoporosis
 Complex regional pain syndrome and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin
Complex regional pain syndrome and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma
 Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Controlling symptoms of mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Fibromyalgia FACTSHEET
 What is fibromyalgia? Fibromyalgia, or fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), is a condition where the whole body is affected by pain and tenderness lasting more than three months. People with fibromyalgia usually
What is fibromyalgia? Fibromyalgia, or fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), is a condition where the whole body is affected by pain and tenderness lasting more than three months. People with fibromyalgia usually
Massage therapy and energy-based therapies
 Massage therapy and energy-based therapies This information is an extract from the booklet Complementary therapies and cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
Massage therapy and energy-based therapies This information is an extract from the booklet Complementary therapies and cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Chiari malformations
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
Alcohol and stroke. How can drinking alcohol increase my risk of stroke? Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Alcohol and stroke Regularly drinking large amounts of alcohol greatly increases your risk of stroke. This factsheet explains how alcohol can increase
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Alcohol and stroke Regularly drinking large amounts of alcohol greatly increases your risk of stroke. This factsheet explains how alcohol can increase
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
 Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Neck Pain. www.physiofirst.org.uk
 Neck Pain www.physiofirst.org.uk Neck pain is common. The cause can be obvious like an accident or more subtle when related to a repetitive task or prolonged position. There are many triggers for neck
Neck Pain www.physiofirst.org.uk Neck pain is common. The cause can be obvious like an accident or more subtle when related to a repetitive task or prolonged position. There are many triggers for neck
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy. Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
A Patient s Guide to Post-Operative Physiotherapy Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee Introduction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the main supporting ligaments
Subacromial Decompression Surgery
 Subacromial Decompression Surgery Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet aims to help you gain the maximum benefit from your operation. It is not a substitute for professional medical
Subacromial Decompression Surgery Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet aims to help you gain the maximum benefit from your operation. It is not a substitute for professional medical
A whiplash injury, most commonly due to a car crash, causes neck pain. See separate leaflet called 'Whiplash Injury' for details.
 Neck Pain in Adults Who gets neck pain and what are the causes? Neck pain is common. More than half of people develop a bout of neck pain at some time in their life. One survey done in the UK found that,
Neck Pain in Adults Who gets neck pain and what are the causes? Neck pain is common. More than half of people develop a bout of neck pain at some time in their life. One survey done in the UK found that,
FROZEN SHOULDER OXFORD SHOULDER & ELBOW CLINIC INFORMATION FOR YOU. Frozen Shoulder FROZEN SHOULDER
 OXFORD SHOULDER & ELBOW CLINIC INFORMATION FOR YOU Frozen Shoulder The aim of this information sheet is to give you some understanding of the problem you may have with your shoulder. It has been divided
OXFORD SHOULDER & ELBOW CLINIC INFORMATION FOR YOU Frozen Shoulder The aim of this information sheet is to give you some understanding of the problem you may have with your shoulder. It has been divided
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders
 Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Recent Injuries. www.physiofirst.org.uk
 Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Recent Injuries www.physiofirst.org.uk A recent or acute injury can occur suddenly during any activity, from tripping over the kerb, to making the bed, to playing sport. In some cases, an acute injury
Nerve Root Pain. Your back pain diagnosis. Contact Details. Spinal Triage Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD
 Nerve Root Pain Contact Details Spinal Triage Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Nerve Pain Patient Information
Nerve Root Pain Contact Details Spinal Triage Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Nerve Pain Patient Information
Dizziness and balance problems
 Dizziness and balance problems Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May 2011 1 Dizziness and balance problems This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It
Dizziness and balance problems Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May 2011 1 Dizziness and balance problems This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It
INFORMATION FOR YOU. Lower Back Pain
 INFORMATION FOR YOU Lower Back Pain WHAT IS ACUTE LOWER BACK PAIN? Acute lower back pain is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced as aching, burning, stabbing, sharp
INFORMATION FOR YOU Lower Back Pain WHAT IS ACUTE LOWER BACK PAIN? Acute lower back pain is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced as aching, burning, stabbing, sharp
Neck Pain HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management
 HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 The neck (cervical spine) anatomy 2 What are the common types of neck pain? 3 What are the common symptoms associated with
HealthshareHull Information for Guided Patient Management Index Introduction 2 The neck (cervical spine) anatomy 2 What are the common types of neck pain? 3 What are the common symptoms associated with
Surgery for breast cancer in men
 Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Surgery for breast cancer in men This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer in men. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents
Physical therapies. Massage
 This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding complementary therapies. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. This information discusses eight physical
This information is an extract from the booklet, Understanding complementary therapies. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. This information discusses eight physical
Shared Decision Making
 Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
Deciding what to do about osteoarthritis of the knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your knee osteoarthritis. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you
Whiplash. Whiplash is part of our modern lives. One in 200 of us will suffer from it at some point but it is rarely serious.
 Whiplash www.physiofirst.org.uk Whiplash is part of our modern lives. One in 200 of us will suffer from it at some point but it is rarely serious. Most people make a full return to health. What you do
Whiplash www.physiofirst.org.uk Whiplash is part of our modern lives. One in 200 of us will suffer from it at some point but it is rarely serious. Most people make a full return to health. What you do
Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist
 Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist What do Physiotherapists do? We conduct assessments by asking detailed questions about your symptoms, medical
Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist What do Physiotherapists do? We conduct assessments by asking detailed questions about your symptoms, medical
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet
 Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
Knee arthroscopy advice sheet During an arthroscopy, a camera is inserted into the knee through two or three small puncture wounds. It allows the surgeon to look at the joint surfaces, cartilage and the
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
 ORTHOPAEDIC WARD: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
ORTHOPAEDIC WARD: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
Chronic Low Back Pain
 Chronic Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What is Chronic Pain? Low back pain is considered to be chronic if it has been present for longer than three months. Chronic low
Chronic Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What is Chronic Pain? Low back pain is considered to be chronic if it has been present for longer than three months. Chronic low
Whiplash Recovery Important Facts 1
 02866328200 Whiplash Recovery Important Facts 1 What is whiplash? You can get whiplash if your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement. The tissues around your neck are overstretched,
02866328200 Whiplash Recovery Important Facts 1 What is whiplash? You can get whiplash if your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement. The tissues around your neck are overstretched,
Multiple sclerosis and pain
 9 Multiple sclerosis and pain 2ND EDITION Multiple Sclerosis Society of New Zealand CONTENTS Introduction-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 How
9 Multiple sclerosis and pain 2ND EDITION Multiple Sclerosis Society of New Zealand CONTENTS Introduction-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 How
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
 Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Repetitive Strain Injury
 Page1 Repetitive Strain Injury Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury caused by repetitive use of muscles. For the purpose of this article I will refer to repetitive strain injury as RSI. It usually
Page1 Repetitive Strain Injury Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury caused by repetitive use of muscles. For the purpose of this article I will refer to repetitive strain injury as RSI. It usually
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain
 A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain Anatomy Where are the rib joints? Your rib cage is made up of twelve pairs of ribs. The ribs attach to the spine in the back, and to the breastbone in the front. The
A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain Anatomy Where are the rib joints? Your rib cage is made up of twelve pairs of ribs. The ribs attach to the spine in the back, and to the breastbone in the front. The
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Shoulder Tendonitis. Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696
 Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
Driving after stroke. Key points. Why can t I drive immediately after having a stroke? Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Driving after stroke After having a stroke, you may be eager to get back in the driving seat. This factsheet explains how stroke and transient ischaemic
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Driving after stroke After having a stroke, you may be eager to get back in the driving seat. This factsheet explains how stroke and transient ischaemic
Non-epileptic seizures
 Non-epileptic seizures a short guide for patients and families Information for patients Department of Neurology Royal Hallamshire Hospital What are non-epileptic seizures? In a seizure people lose control
Non-epileptic seizures a short guide for patients and families Information for patients Department of Neurology Royal Hallamshire Hospital What are non-epileptic seizures? In a seizure people lose control
Osteoarthritis of the ankle
 1 What is osteoarthritis of the ankle? The ankle joint is formed by the upper bone at the front of the foot (the talus) and the leg bones (the tibia and fibula). The ankle is made up of a hinge joint which
1 What is osteoarthritis of the ankle? The ankle joint is formed by the upper bone at the front of the foot (the talus) and the leg bones (the tibia and fibula). The ankle is made up of a hinge joint which
Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865
 Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Write questions or notes here: Level 1, 131-135 Summer Street ORANGE NSW 2800 Ph: 02 63631688 Fax: 02 63631865 Document Title: Total Knee Replacement Further Information and Feedback: Tell us how useful
Shoulder stabilisation surgery. Information for patients Orthopaedics
 Shoulder stabilisation surgery Information for patients Orthopaedics page 2 of 20 Introduction The upper limb unit team wants you and your family to understand as much as possible about the operation you
Shoulder stabilisation surgery Information for patients Orthopaedics page 2 of 20 Introduction The upper limb unit team wants you and your family to understand as much as possible about the operation you
Acute Oncology Service Patient Information Leaflet
 Spinal cord compression Acute Oncology Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction If you have been diagnosed with cancer, you need to know about spinal cord compression and the warning signs. What
Spinal cord compression Acute Oncology Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction If you have been diagnosed with cancer, you need to know about spinal cord compression and the warning signs. What
Ulnar nerve decompression
 Patient information Ulnar nerve decompression This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your condition and its treatment. It includes the following information:
Patient information Ulnar nerve decompression This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your condition and its treatment. It includes the following information:
A Guide to pain relief medicines For patients receiving Palliative Care
 A Guide to pain relief medicines For patients receiving Palliative Care 1 Which pain medicines are you taking? Contents Page No. Amitriptyline 8 Codeine 9 Co-codamol 10 Co-dydramol 11 Diclofenac (Voltarol
A Guide to pain relief medicines For patients receiving Palliative Care 1 Which pain medicines are you taking? Contents Page No. Amitriptyline 8 Codeine 9 Co-codamol 10 Co-dydramol 11 Diclofenac (Voltarol
Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD)
 Information for patients Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD) Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 05731-14(RP) Issue 3: December 2014 Review date: November 2017 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust,
Information for patients Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD) Physiotherapy Department Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 05731-14(RP) Issue 3: December 2014 Review date: November 2017 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust,
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
Cancer Pain. What is Pain?
 Cancer Pain What is Pain? The International Association for the Study of Pain says that pain is "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage." Pain
Cancer Pain What is Pain? The International Association for the Study of Pain says that pain is "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage." Pain
BOTOX Treatment. for Chronic Migraine. Information for patients and their families. Botulinum Toxin Type A
 BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Lumbar Spinal Stenosis? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
July 2012 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move
 Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Exercise Away Your Knee Pain It seems counterintuitive, but when it hurts to move your knee, the best thing you can do is move your knee. A 2009 study in the British Medical Journal found that supervised
Common medicines given to neurosurgery patients on discharge from hospital
 Common medicines given to neurosurgery patients on discharge from hospital This leaflet contains brief information about some of the medicines we commonly supply on discharge to patients who have been
Common medicines given to neurosurgery patients on discharge from hospital This leaflet contains brief information about some of the medicines we commonly supply on discharge to patients who have been
STRESS. Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING AND YOUR BODY. www.neorthopt.
 Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause
Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression and rotator cuff repair
 Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
