Dizziness and balance problems
|
|
|
- Brittany Barber
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dizziness and balance problems Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
2 Dizziness and balance problems This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have balance or dizziness problems. If you are concerned about your balance or have balance problems, or you are feeling dizzy, you should visit your GP. Read this factsheet to find out: Why do I feel dizzy? How is balance controlled? What causes balance problems? How do I know if I have a problem with my balance? What treatment is there for balance problems? How long does it take to recover? Where can I get further information? If you would like this factsheet on audio tape, in Braille or in large print, please contact our helpline see the front page for contact details. Medical disclaimer The information given in this factsheet is not medical advice, and by providing it we do not undertake any responsibility for your medical care, nor accept you as a patient. Before acting on the information contained in this factsheet, or deciding on a course of treatment, you should discuss the matter with your GP or other medical professional. Why do I feel dizzy? Everyone feels dizzy sometimes. Dizziness is a normal feeling that you get when your brain receives conflicting messages from your inner ears or from your eyes. You can feel dizzy for many different reasons and in many ordinary situations. For example: If you move your head suddenly, you may feel dizzy. You might feel dizzy if you ve drunk too much alcohol. Fairground rides often make people feel dizzy, as do many kinds of travel. If you are very dizzy, you may feel sick or actually be sick because your balance organs are stimulated for example, if you are on a boat when the sea is rough. Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
3 These are day-to-day reasons for feeling dizzy, and people are not usually worried about them, even if they find them unpleasant. This is because the effects are usually temporary and the symptoms disappear when your balance system is given a chance to settle down. How is balance controlled? You use your balance every time you move from one position to another and when you walk, stand, sit or lie down, but it is something you are usually hardly aware of. You only realise how much you rely on your balance if it stops working properly. You get your sense of balance from three sources: vision your eyes give you a picture of the world and where you are in relation to everything in it sensors in your joints, muscles and feet balance organs within your inner ears. Your inner ear holds both your organ of hearing, the cochlea, and your organ of balance, the labyrinth. The labyrinth is made up of five sections. Each section detects head movement in a different direction. The sections contain tiny hair-like cells, which send messages to your brain when you move your head about. The information from your balance organs, vision and sensors in your joints passes to your brain, where the information is put together. This allows you to control your eye movements so that your vision is steady and you move naturally without having to think about it. Normally, the information coming from your ears perfectly matches the information coming from your eyes and the sensors in your joints. The result is that you feel steady and don t have any balance problems. What causes balance problems? At first, many people with balance symptoms are worried that they may be suffering from a serious illness, such as a stroke or a brain tumour. Fortunately, this is very unlikely although you should see a doctor if you are worried about your balance. There are immediately recognisable symptoms of stroke: see the Stroke Association s website for more information on the FAST test. Most balance problems are rarely serious, even though the symptoms can be very unpleasant. Many different medical conditions can give you symptoms of dizziness and unsteadiness, although the most common causes are problems with the inner ear. Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
4 Migraine Migraine is a very common cause of dizziness, particularly in children, but it is also quite common in adults. Often the dizziness is severe and is accompanied by vomiting, but it is important to understand that a migraine may make you feel dizzy whether or not you have a headache. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo This is a specific inner ear disorder that can give you severe, short spells of dizziness, especially if you tip your head backwards for example, if you look up at the sky, or when you first lie down in bed. It is thought that this condition is caused by small crystals floating in the fluid in the inner ear falling onto one of your balance sections. Your specialist can alleviate some, if not all, of the symptoms by using a particle repositioning procedure known as the Epley or Semont manoeuvre. The movements move the crystals into another part of the inner ear where they do not cause balance problems. Ménière s disease Ménière s disease is caused by changes in the pressure of the fluid in the inner ear, which lead to sudden attacks of severe dizziness. An attack lasts between 30 minutes and several hours and is usually accompanied by nausea and vomiting, as well as hearing loss and tinnitus. Ménière s disease develops differently over time from person to person. There are many different treatments for Ménière s disease and most people can find one that works for them. For more information, see our factsheet Ménière s disease. Infections The most common cause of a sudden episode of dizziness is a simple viral infection in your inner ear or in the nerve taking information from your ear to your brain. Although your immune system removes the virus quite quickly, your balance organs may have been damaged while you had the infection. You may feel dizzy until your brain can compensate for the damage. This sort of balance problem is usually helped by vestibular rehabilitation physiotherapy, which includes head and balance exercises. Serious infections such as meningitis can lead to balance problems, as can the antibiotics used to treat life-threatening infections (see Prescription drugs on page 5). Bifocal glasses Some older people find that wearing bifocal glasses often makes them feel unsteady and unstable. If this happens to you, see your optician, who may be able to suggest different glasses. Any person with a balance disorder will find changing glasses disorientating. Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
5 Chronic middle ear disease If you have chronic middle ear disease, this may affect your balance. This is fairly rare, but if you become dizzy and notice a discharge (liquid) from your ear, you must see your GP or specialist immediately. Glue ear Children with glue ear (also known as otitis media with effusion ) may feel dizzy. For more information, see our factsheet Glue ear. Head injury or whiplash Injuries, including mild bangs to the head, can cause balance problems. The type of problem and how severe it is depends on the severity of the head injury. Neck-related dizziness Whiplash injuries or neck manipulations performed by health professionals, such as in physiotherapy, can make you dizzy, especially if you already have an inner ear upset. This kind of dizziness is not usually severe but may continue for a long time. Neurological causes Very rarely, a problem in the brain can cause balance problems. This usually affects people who have already been diagnosed as suffering from a neurological brain or nerve disease. It is extremely unusual for a balance problem to be the only symptom of a neurological disease. Operations If you have an operation on your ear, it may affect your balance, either temporarily or permanently. Prescription drugs Occasionally, certain antibiotics used for the treatment of life-threatening infections can damage your balance organs. This type of damage can be quite severe. A particular type of physiotherapy balance retraining rehabilitation physiotherapy can help if you have this sort of balance problem. If these life-saving antibiotics have caused your loss of balance, you should avoid situations where your balance is under stress. Never swim alone or underwater, and do not stand at the edge of train platforms or cliffs. Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
6 Other prescribed drugs may also cause balance problems, such as drugs that you take for high or low blood pressure, or drugs with an effect on the central nervous system, such as antidepressants, sedatives, tranquillisers and anticonvulsants. How do I know if I have a problem with my balance? You might feel dizzy, light-headed or unsteady. You may notice that your vision is slightly blurred or out of focus. When you walk, you may feel as though the world is bobbing up and down. You may also feel pulled to one side, or, in extreme cases, actually fall over. Some of these symptoms can be very severe if there is a sudden loss of balance function in the inner ear. You may feel you are spinning around as if on a roundabout. You might be sick, and find you can t walk across a room. You may also develop symptoms such as: anxiety, panic attacks, depression, difficulty concentrating fatigue (tiredness) headaches and neck pain. In this section, we look at the symptoms that are often associated with balance problems. Anxiety, panic attacks and depression You may find that your balance problems make you anxious, depressed, or give you panic attacks. This happens because of connections in the brain to the centres controlling emotion and thought processes. It may be that you are afraid that you will feel dizzy away from home and you may worry about not being able to cope. Or you may be concerned about what is causing the dizziness. These symptoms can be more difficult to cope with than the dizziness or unsteadiness itself and can slow down your recovery. Fatigue If you have balance problems, you have to concentrate a lot to keep your balance and carry on as normal. This can make you feel more tired. Headaches and neck pain When some people get dizzy, they hold their heads very still because they find that moving them around makes them dizzier. However, holding your head very still can cause tension in your neck muscles, which begin to ache, and the pain may then go on up into your Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
7 head. Headaches and neck pain can make people wrongly think their dizziness is caused by a neck problem. If you keep your head still, you will also slow down your recovery. What treatment is there for balance problems? Drugs Simple treatments can help with sudden, severe dizziness problems. You might be prescribed a short course of an anti-sickness drug to help your nausea and a drug to ease your dizziness, known as a vestibular sedative. If you re being sick and can t keep pills down, you may be prescribed drugs that can be absorbed in your mouth without swallowing, or you may be given suppositories (medicine you put up your bottom). You should only take the drugs prescribed for dizziness and sickness for a few days. If they are used for longer periods they may slow down your natural recovery. Getting better naturally Fortunately, the brain is very good at readjusting to balance problems and after a few days or several weeks most people feel better. This happens despite the fact that the balance information sent to your brain is still upset in some way. This recovery process is known as cerebral compensation. In the early stages of recovery, compensation is not always 100 per cent efficient. You may feel better on some days than on others. This does not mean that the original condition is coming back or that the problem is getting worse. If you are feeling extremely dizzy and sick, it can take from a few hours to two or three days to settle. Unsteady and slight dizzy feelings may take weeks to go away and eventually disappear. You will help your recovery if you carry out normal movements. This means that your brain will receive the important information it needs to adapt and make up for the balance upset. If your symptoms are still affecting you after a period of about six weeks, or you do not get better naturally, your doctor may refer you to a specialist. Specialist help and treatment for balance problems The specialist will examine your eye movements, inner ears and joint sensors. Special balance tests will find out how well you are using the information from your eyes, ears and joints to keep your balance. If you have joint problems, such as arthritis, your specialist will discuss treatment options. They will also recommend that you have any sight problems corrected. For example, you may need new glasses. Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
8 Balance retraining exercises If your balance problem is caused by damage to the inner ear, for example, from an infection or a head injury, balance retraining exercises may help you get better. These might be from a set list such as the Cawthorne-Cooksey exercises or you might be given exercises specifically for your problems. Exercises are usually taught by a physiotherapist or other professional with experience of helping people with balance problems. They will help you work out which movements you need to practise and you will be able to do them at your own pace. These exercises are designed to make you slightly dizzy, so that they help your brain to adapt and you will gradually find you don t feel so dizzy any more. You will need to do the exercises a couple of times each day for several weeks before they start to help. You should continue with your exercise programme until you can perform each exercise without feeling any balance symptoms. This may take six to nine months or even longer. Remember that everyone is different and there is no correct time that it will take to get better. These exercises are not suitable for some kinds of balance problems. If you have balance problems, you should always speak to your doctor before starting any kind of exercise. General exercise General exercise is important in helping people with balance problems get better. You should concentrate on whatever exercise you particularly enjoy. Cognitive behavioural therapy If you have had balance symptoms for a long time, you may well feel anxious, depressed or have panic attacks (see page 6). These symptoms need to be treated at the same time as the underlying cause of your balance problem. You may be offered cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as part of your therapy. CBT helps you take more control of your symptoms, especially in situations that make you anxious. Therapy is very effective in helping people develop a more normal lifestyle and tackle everyday tasks, which they may have come to avoid. This can help you recover more quickly. If you are depressed, you may need specific anti-depressant treatment and you should discuss this with your doctor. Surgery If you have severe dizziness that does not improve with drugs or other forms of treatment, you may be offered an operation. This is rarely necessary and is not a suitable option for most people. Your specialist will discuss surgery with you. Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
9 How long does it take to recover? Recovery takes time and there are many different factors that may slow down your recovery from balance problems. These include: being unable to move around a lot other illnesses, including a simple cold drugs that you might have been prescribed to deal with the severe symptoms, including anti-sickness and anti-dizziness drugs drugs that affect the central nervous system stressful situations sight problems joint problems. Your doctor will look at all these factors to make sure that you have the most effective recovery plan for your needs. Even when a balance problem is taking a very long time to improve there is almost always a rehabilitation programme that will help if you can stick with the exercises and the psychological support provided. If you stay positive, you will help your recovery. Balance symptoms can come back. This can happen even when you have totally recovered from previous balance problems. Be reassured, however, that you will be able to recover naturally again, usually much more rapidly than the first time. Again, keeping positive will help. Where can I get further information? Our helpline offers a wide range of information on many aspects of hearing loss. You can contact us for further copies of this factsheet and our full range of factsheets and leaflets see the cover page for contact details. Action on Hearing Loss Information, May 2011 The Royal National Institute for Deaf People. Registered Office: Featherstone Street, London EC1Y 8SL. A company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales No , Registered Charity Numbers (England and Wales) and SC (Scotland). Dizziness and balance problems, Action on Hearing Loss Information, May
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
 Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) UHN Information for Patients Patient Education Improving Health Through Education You have been told by your doctor that you have Benign Paroxysmal Positional
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) UHN Information for Patients Patient Education Improving Health Through Education You have been told by your doctor that you have Benign Paroxysmal Positional
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Inner ear balance problems. Department of Neuro-otology
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Inner ear balance problems Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Inner ear balance problems Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
Dizziness and Vertigo
 Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
The road to recovery. The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke
 The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Introduction Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury
 A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
This booklet is dedicated to the late Dorothy Gronwall O.B.E.
 Information about Mild Head Injury or Concussion This booklet is dedicated to the late Dorothy Gronwall O.B.E. This booklet has been produced following a research study into mild head injury, funded by
Information about Mild Head Injury or Concussion This booklet is dedicated to the late Dorothy Gronwall O.B.E. This booklet has been produced following a research study into mild head injury, funded by
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Migraine associated dizziness Department of Neuro-otology If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of
ABOUT CONCUSSION. Head Injury Fact sheet
 Head Injury Fact sheet 11 Somerset Street / PO Box 1168 Hamilton Telephone (07) 839 1191 Fax (07) 839 5648 Email: [email protected] ABOUT CONCUSSION CONTENTS Information compiled by D Gronwall, PhD
Head Injury Fact sheet 11 Somerset Street / PO Box 1168 Hamilton Telephone (07) 839 1191 Fax (07) 839 5648 Email: [email protected] ABOUT CONCUSSION CONTENTS Information compiled by D Gronwall, PhD
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Vestibular Injury. Vestibular Disorders Association www.vestibular.org Page 1 of 5
 PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 [email protected] WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Vestibular Injury Compensation, De-compensation, and Failure to Compensate By Thomas E. Boismier,
PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 [email protected] WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Vestibular Injury Compensation, De-compensation, and Failure to Compensate By Thomas E. Boismier,
Vestibular Injury: Compensation, Decompensation, and Failure to Compensate
 VESTIBULAR DISORDERS ASSOCIATION PO Box 13305 Portland, OR 97213 fax: (503) 229-8064 toll-free voice-mail: (800) 837-8428 [email protected] http://www.vestibular.org/ VEDA Publication No. F-26 Vestibular
VESTIBULAR DISORDERS ASSOCIATION PO Box 13305 Portland, OR 97213 fax: (503) 229-8064 toll-free voice-mail: (800) 837-8428 [email protected] http://www.vestibular.org/ VEDA Publication No. F-26 Vestibular
Why does my child have a hearing loss?
 Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Introduction This factsheet will tell you about the range of tests that can be carried out to try to find the cause of your child s hearing loss. The process to find out why a child is deaf is sometimes
Non-epileptic seizures
 Non-epileptic seizures a short guide for patients and families Information for patients Department of Neurology Royal Hallamshire Hospital What are non-epileptic seizures? In a seizure people lose control
Non-epileptic seizures a short guide for patients and families Information for patients Department of Neurology Royal Hallamshire Hospital What are non-epileptic seizures? In a seizure people lose control
Treating symptoms. An introduction to. Everyone diagnosed with MS can get treatment for their symptoms. The symptoms of MS. Who can get treatment?
 Everyone diagnosed with MS can get treatment for their symptoms This resource is an introduction to the treatments that are available. The symbol will point you to further resources. An introduction to
Everyone diagnosed with MS can get treatment for their symptoms This resource is an introduction to the treatments that are available. The symbol will point you to further resources. An introduction to
Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and
 Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site: www.cdc.gov/ncipc/tbi Contents About Brain
Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site: www.cdc.gov/ncipc/tbi Contents About Brain
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387
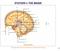 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Whiplash. Whiplash is part of our modern lives. One in 200 of us will suffer from it at some point but it is rarely serious.
 Whiplash www.physiofirst.org.uk Whiplash is part of our modern lives. One in 200 of us will suffer from it at some point but it is rarely serious. Most people make a full return to health. What you do
Whiplash www.physiofirst.org.uk Whiplash is part of our modern lives. One in 200 of us will suffer from it at some point but it is rarely serious. Most people make a full return to health. What you do
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults
 Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Medicines To Treat Alcohol Use Disorder A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor* said you have alcohol use disorder
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3.
 Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Cancer Pain. Relief from PALLIATIVE CARE
 PALLIATIVE CARE Relief from Cancer Pain National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care For more information on the National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care, go to www.hse.ie/palliativecareprogramme
PALLIATIVE CARE Relief from Cancer Pain National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care For more information on the National Clinical Programme for Palliative Care, go to www.hse.ie/palliativecareprogramme
Understanding. Depression. The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself. Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members
 TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
TM Understanding Depression The Road to Feeling Better Helping Yourself Your Treatment Options A Note for Family Members Understanding Depression Depression is a biological illness. It affects more than
Anxiety and breathing difficulties
 Patient information factsheet Anxiety and breathing difficulties Breathing is something that we all automatically do and we often take this for granted. Some chronic health conditions, for example asthma
Patient information factsheet Anxiety and breathing difficulties Breathing is something that we all automatically do and we often take this for granted. Some chronic health conditions, for example asthma
Emergency Department. Whiplash neck sprain. Advice for patients
 Emergency Department Whiplash neck sprain Advice for patients What is a whiplash neck sprain? A whiplash neck sprain occurs when your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement.
Emergency Department Whiplash neck sprain Advice for patients What is a whiplash neck sprain? A whiplash neck sprain occurs when your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement.
Hopefully this information will be useful for people with dementia, their families, carers and medical professionals.
 et ision 2020 UK The right to sight ementia and Sight Loss Interest Group Cataracts and dementia Cataracts are a very common eye condition in older people. Most people with cataracts are over the age of
et ision 2020 UK The right to sight ementia and Sight Loss Interest Group Cataracts and dementia Cataracts are a very common eye condition in older people. Most people with cataracts are over the age of
Background on Brain Injury
 CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
Living with a lung condition:
 Living with a lung condition: how exercise and eating well can make a difference to your life This information is for people living with a lung condition in the UK and your family and carers. It will help
Living with a lung condition: how exercise and eating well can make a difference to your life This information is for people living with a lung condition in the UK and your family and carers. It will help
What is vascular dementia?
 alzheimers.org.uk What is vascular dementia? Vascular dementia is the second most common form of dementia after Alzheimer s disease. It is caused by problems in the supply of blood to the brain. This factsheet
alzheimers.org.uk What is vascular dementia? Vascular dementia is the second most common form of dementia after Alzheimer s disease. It is caused by problems in the supply of blood to the brain. This factsheet
Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease
 IS 20 October 2011 Information sheet Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Ebixa work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Ebixa have?... 2 How
IS 20 October 2011 Information sheet Memantine (Ebixa) Drug treatment for Alzheimer s disease Introduction... 1 How does Ebixa work?... 1 Who might benefit?... 2 What effect might Ebixa have?... 2 How
Depression in children and adolescents
 Patient information from the BMJ Group Depression in children and adolescents Depression is an illness that affects people of all ages, including children and teenagers. It can stop a child or teenager
Patient information from the BMJ Group Depression in children and adolescents Depression is an illness that affects people of all ages, including children and teenagers. It can stop a child or teenager
How To Understand The Effects Of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Knowing about your Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Knowing about mild TBI There is a distinction between visible injuries to the scalp ( Head Injuries ) and internal injuries to the brain itself ( Traumatic
Knowing about your Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Knowing about mild TBI There is a distinction between visible injuries to the scalp ( Head Injuries ) and internal injuries to the brain itself ( Traumatic
Balance and Vestibular Center Programs to treat dizziness and reduce your risk of falling
 Balance and Vestibular Center Programs to treat dizziness and reduce your risk of falling Helping you overcome dizziness and vertigo Most people will experience dizziness at some point in their lives.
Balance and Vestibular Center Programs to treat dizziness and reduce your risk of falling Helping you overcome dizziness and vertigo Most people will experience dizziness at some point in their lives.
Understanding posterior vitreous detachment
 Understanding posterior vitreous detachment About posterior vitreous detachment Causes of PVD Symptoms and diagnosis Treatment PVD and other eye conditions Coping Useful contacts About posterior vitreous
Understanding posterior vitreous detachment About posterior vitreous detachment Causes of PVD Symptoms and diagnosis Treatment PVD and other eye conditions Coping Useful contacts About posterior vitreous
PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR:
 PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: A Guide for Persons with Memory Problems and Their Care Partners Alzheimer s Association Table of Contents PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: When is Memory Loss a Problem? 2 What
PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: A Guide for Persons with Memory Problems and Their Care Partners Alzheimer s Association Table of Contents PARTNERING WITH YOUR DOCTOR: When is Memory Loss a Problem? 2 What
Depression: What You Need to Know
 Depression: What You Need to Know What is a Depressive Illness? A depressive illness is a whole-body illness, involving your body, mood, thoughts, and behavior. It affects the way you eat and sleep, the
Depression: What You Need to Know What is a Depressive Illness? A depressive illness is a whole-body illness, involving your body, mood, thoughts, and behavior. It affects the way you eat and sleep, the
Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy. Melissa Nelson
 Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy Melissa Nelson What is Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT)? VRT is an exercise-based program designed to promote CNS compensation for inner ear deficits. The goal
Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy Melissa Nelson What is Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT)? VRT is an exercise-based program designed to promote CNS compensation for inner ear deficits. The goal
HEALTH REPORT ISSUE #32
 ISSUE #32 DEPRESSION AND CHRONIC ILLNESS This edition of the Health Report looks at depression and chronic illness. Depression is a very real condition for many people living with a chronic illness, which
ISSUE #32 DEPRESSION AND CHRONIC ILLNESS This edition of the Health Report looks at depression and chronic illness. Depression is a very real condition for many people living with a chronic illness, which
Alcohol. Problems with drinking alcohol
 Alcohol Alcoholism is a word which many people use to mean alcohol dependence (alcohol addiction). Some people are problem drinkers without being dependent on alcohol. If you are alcohol- dependent then
Alcohol Alcoholism is a word which many people use to mean alcohol dependence (alcohol addiction). Some people are problem drinkers without being dependent on alcohol. If you are alcohol- dependent then
Occupational therapy after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke After a stroke, you are likely to need help to regain your abilities, learn new skills and cope with any remaining
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Occupational therapy after stroke After a stroke, you are likely to need help to regain your abilities, learn new skills and cope with any remaining
How to treat your injured neck
 How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
How to treat your injured neck Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your neck is made up of a number of bones bound together by strong discs and ligaments. It is also protected by strong muscles.
Reintegration. Recovery. Medication-Assisted Treatment for Alcohol Dependence. Reintegration. Resilience
 Reintegration Recovery Medication-Assisted Treatment for Alcohol Dependence Reintegration Resilience 02 How do you free yourself from the stress and risks of alcohol dependence? Most people cannot do it
Reintegration Recovery Medication-Assisted Treatment for Alcohol Dependence Reintegration Resilience 02 How do you free yourself from the stress and risks of alcohol dependence? Most people cannot do it
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression
 Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
Care Manager Resources: Common Questions & Answers about Treatments for Depression Questions about Medications 1. How do antidepressants work? Antidepressants help restore the correct balance of certain
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Whiplash Injury Advice Sheet
 Whiplash Injury Advice Sheet What is whiplash? You can get whiplash if your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement. This type of neck injury often happens in car crashes.
Whiplash Injury Advice Sheet What is whiplash? You can get whiplash if your head is suddenly jolted backwards and forwards in a whip-like movement. This type of neck injury often happens in car crashes.
Chemotherapy for head and neck cancers
 Chemotherapy for head and neck cancers This information is from the booklet Understanding head and neck cancers. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Chemotherapy for head and neck cancers This information is from the booklet Understanding head and neck cancers. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. Contents
Vestibular Rehabilitation
 PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 [email protected] WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Vestibular Rehabilitation An Effective, Evidence-Based Treatment By Anne Shumway-Cook, PT, PhD;
PO BOX 13305 PORTLAND, OR 97213 FAX: (503) 229-8064 (800) 837-8428 [email protected] WWW.VESTIBULAR.ORG Vestibular Rehabilitation An Effective, Evidence-Based Treatment By Anne Shumway-Cook, PT, PhD;
Headaches in Children
 Headaches in Children A headache is one of the most common complaints of children and teenagers. Fussiness, crankiness and not being able to sleep may be the only signs of head pain in children who are
Headaches in Children A headache is one of the most common complaints of children and teenagers. Fussiness, crankiness and not being able to sleep may be the only signs of head pain in children who are
Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery for Otosclerosis
 Patient information Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery for Otosclerosis Ear, Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 230 V6 Your Consultant / Doctor has advised you to have a Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery
Patient information Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery for Otosclerosis Ear, Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 230 V6 Your Consultant / Doctor has advised you to have a Stapedectomy / Stapedotomy / Surgery
Delirium. The signs of delirium are managed by treating the underlying cause of the medical condition causing the delirium.
 Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders
 Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Whiplash and Whiplash- Associated Disorders North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Whiplash? The term whiplash might be confusing because it describes both a mechanism of injury and
Understanding Relapse in Multiple Sclerosis. A guide for people with MS and their families
 Understanding Relapse in Multiple Sclerosis A guide for people with MS and their families Introduction You have been given this booklet because you have been diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and
Understanding Relapse in Multiple Sclerosis A guide for people with MS and their families Introduction You have been given this booklet because you have been diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and
Asthma, anxiety & depression
 Anxiety and are common in people with asthma. The good news is that there are effective treatments both for asthma and for anxiety and. With careful management, the symptoms of anxiety and can be treated
Anxiety and are common in people with asthma. The good news is that there are effective treatments both for asthma and for anxiety and. With careful management, the symptoms of anxiety and can be treated
Guide to Claims against General Practitioners (GPs)
 Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
Radiotherapy for a mesothelioma
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy for a mesothelioma Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been recommended treatment with
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy for a mesothelioma Information for patients Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been recommended treatment with
SUBSTANCE ABUSE. Key Concepts. Types of Drugs
 SUBSTANCE ABUSE You have to choose who you want to be in life. This happens by making lots of decisions every day. Using substances is a choice. This is a big choice, because substances have a very real
SUBSTANCE ABUSE You have to choose who you want to be in life. This happens by making lots of decisions every day. Using substances is a choice. This is a big choice, because substances have a very real
RECOVERING FROM A MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
 RECOVERING FROM A MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY An Information Guide BRAIN INJURY REHABILITATION SERVICE CONCUSSION CLINIC BURWOOD HOSPITAL TABLE OF CONTENTS AN INFORMATION GUIDE... 3 WHAT HAPPENS IN A TRAUMATIC
RECOVERING FROM A MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY An Information Guide BRAIN INJURY REHABILITATION SERVICE CONCUSSION CLINIC BURWOOD HOSPITAL TABLE OF CONTENTS AN INFORMATION GUIDE... 3 WHAT HAPPENS IN A TRAUMATIC
Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT)
 Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy What is cognitive behaviour therapy? 4 How does negative thinking start? 6 What type of problems can CBT help
Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) Making sense of cognitive behaviour therapy What is cognitive behaviour therapy? 4 How does negative thinking start? 6 What type of problems can CBT help
Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy department Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers Stem cell transplant exercise handout Thank you
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy department Stem cell transplant, you and your rehabilitation Information for patients and their carers Stem cell transplant exercise handout Thank you
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Managing Spasticity. Spasticity Service
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
STRESS. Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING AND YOUR BODY. www.neorthopt.
 Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause
Health & Wellness The Newsletter About Achieving and Maintaining Optimal Well-being UNDERSTANDING STRESS AND YOUR BODY Life s demands create stress and although some stress may be good, too much can cause
Understanding anxiety and depression
 Understanding anxiety and depression www.beyondblue.org.au 1300 22 4636 Anxiety Over two million people in Australia experience anxiety each year. On average, one in three women and one in fve men will
Understanding anxiety and depression www.beyondblue.org.au 1300 22 4636 Anxiety Over two million people in Australia experience anxiety each year. On average, one in three women and one in fve men will
Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT
 Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT Introduction Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a safe and effective treatment that may reduce symptoms related to depression or mental illness. During ECT, certain parts
Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT Introduction Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a safe and effective treatment that may reduce symptoms related to depression or mental illness. During ECT, certain parts
Young Person s Guide to CFS/ME
 Young Person s Guide to CFS/ME The Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health This leaflet has been developed as part of the Evidence based guideline for management of CFS/ME (Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Young Person s Guide to CFS/ME The Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health This leaflet has been developed as part of the Evidence based guideline for management of CFS/ME (Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
What Is. Norovirus? Learning how to control the spread of norovirus. Web Sites
 Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Web Sites Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) http://www.cdc.gov/norovirus/index.html Your Local Health Department http://www.azdhs.gov/diro/lhliaison/countymap.htm What Is Ocument dn Norovirus?
Registered Charity No. 5365
 THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: [email protected] www.ms-society.ie
THE MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SOCIETY OF IRELAND Dartmouth House, Grand Parade, Dublin 6. Telephone: (01) 269 4599. Fax: (01) 269 3746 MS Helpline: 1850 233 233 E-mail: [email protected] www.ms-society.ie
Methamphetamine. Like heroin, meth is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Meth is a highly addictive drug.
 Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Methamphetamine Introduction Methamphetamine is a very addictive stimulant drug. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she
Spinal cord stimulation
 Spinal cord stimulation This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having spinal cord stimulation. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to
Spinal cord stimulation This leaflet aims to answer your questions about having spinal cord stimulation. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives, as well as what you can expect when you come to
Surgery for cervical disc prolapse or cervical osteophyte
 Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Polymyalgia Rheumatica www.arthritis.org.nz
 Polymyalgia Rheumatica www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years. Polymyalgia rheumatica is a common rheumatic condition. It affects more women
Polymyalgia Rheumatica www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years. Polymyalgia rheumatica is a common rheumatic condition. It affects more women
Be Vocal about Viral Meningitis Guide for Employers
 Be Vocal about Viral Meningitis Guide for Employers Employers can face difficult business issues when an employee is affected by viral meningitis either if they have the disease themselves or if they need
Be Vocal about Viral Meningitis Guide for Employers Employers can face difficult business issues when an employee is affected by viral meningitis either if they have the disease themselves or if they need
BOTOX Treatment. for Chronic Migraine. Information for patients and their families. Botulinum Toxin Type A
 BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
BOTOX Treatment Botulinum Toxin Type A for Chronic Migraine Information for patients and their families. Is Chronic Migraine the same as Migraine? Chronic Migraine is similar to migraine as sufferers experience
Alcohol and drug abuse
 Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
Alcohol and drug abuse This chapter explores how alcohol abuse affects our families, relationships, and communities, as well as the health risks associated with drug and alcohol abuse. 1. Alcohol abuse
Your spinal Anaesthetic
 Your spinal Anaesthetic Information for patients Your spinal anaesthetic This information leaflet explains what to expect when you have an operation with a spinal anaesthetic. It has been written by patients,
Your spinal Anaesthetic Information for patients Your spinal anaesthetic This information leaflet explains what to expect when you have an operation with a spinal anaesthetic. It has been written by patients,
Premier patient information. Whiplash. Whiplash Exercises
 Premier patient information Whiplash Whiplash Exercises Keep moving! It may be painful but you ll get back to normal much quicker. Moving forward (in fact - moving in any direction!) Movement is the key
Premier patient information Whiplash Whiplash Exercises Keep moving! It may be painful but you ll get back to normal much quicker. Moving forward (in fact - moving in any direction!) Movement is the key
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Patient Information. Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression. Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Lumbar Spine Segmental Decompression Reference Number: TO 05 004 004 (version date: June 2015) Introduction
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
The Cawthorne-Cooksey Exercises
 The Cawthorne-Cooksey Exercises To help with balance. For patients with dizziness, Ménière s Disease, vertigo and after some operations. Information for Patients Carers Relatives Physiotherapy Department
The Cawthorne-Cooksey Exercises To help with balance. For patients with dizziness, Ménière s Disease, vertigo and after some operations. Information for Patients Carers Relatives Physiotherapy Department
Borderline personality disorder
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Borderline personality disorder NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Borderline personality disorder NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases
Oxford University Hospitals. NHS Trust. Department of Neurology Natalizumab (Tysabri) for Multiple Sclerosis. Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Department of Neurology Natalizumab (Tysabri) for Multiple Sclerosis Information for patients page 2 What is Natalizumab and what is it used for? Natalizumab is an
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Department of Neurology Natalizumab (Tysabri) for Multiple Sclerosis Information for patients page 2 What is Natalizumab and what is it used for? Natalizumab is an
This is my information booklet: Introduction
 Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively new procedure which allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat hip disorders by providing a clear view of the inside of the hip with very small incisions. This is a more complicated
Radiotherapy for breast cancer
 Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy for breast cancer This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding breast cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 6. Contents Radiotherapy
Alcohol and Dependence
 The facts about... Alcohol and Dependence Five key things you need to know A glass of wine with dinner, a beer after work, a cocktail in the sunshine on holiday. Alcohol makes an appearance in so many
The facts about... Alcohol and Dependence Five key things you need to know A glass of wine with dinner, a beer after work, a cocktail in the sunshine on holiday. Alcohol makes an appearance in so many
A Guide to Alcoholism and Problem Drinking
 A Guide to Alcoholism and Problem Drinking Alcoholism is a word which many people use to mean alcohol dependence (alcohol addiction). Some people are problem drinkers without being dependent on alcohol.
A Guide to Alcoholism and Problem Drinking Alcoholism is a word which many people use to mean alcohol dependence (alcohol addiction). Some people are problem drinkers without being dependent on alcohol.
Balance problems and dizziness after brain injury: causes and treatment
 Balance problems and dizziness after brain injury: causes and treatment Introduction The ability to maintain balance and orient ourselves to the outside world is vitally important. However, most people
Balance problems and dizziness after brain injury: causes and treatment Introduction The ability to maintain balance and orient ourselves to the outside world is vitally important. However, most people
Cardiac Rehabilitation Your quick guide
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and
Cardiac Rehabilitation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and
Cocaine. Like heroin, cocaine is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Cocaine is a commonly abused drug.
 Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Cocaine Introduction Cocaine is a powerful drug that stimulates the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants
Alcoholism and Problem Drinking
 Page 1 of 5 Alcoholism and Problem Drinking Alcoholism is a word which many people use to mean 'alcohol dependence' (alcohol addiction). Some people are 'problem drinkers' without being dependent on alcohol.
Page 1 of 5 Alcoholism and Problem Drinking Alcoholism is a word which many people use to mean 'alcohol dependence' (alcohol addiction). Some people are 'problem drinkers' without being dependent on alcohol.
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know. Patient information Leaflet
 Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Middle ear conditions
 Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Middle ear conditions Middle ear conditions This factsheet is part of our Ears and ear problems range. It is written for people who have been diagnosed with a condition that affects the middle ear. Read
Speech and language therapy after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Speech and language therapy after stroke Speech and language therapy (SLT) can help if you have communication problems or swallowing problems after
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Speech and language therapy after stroke Speech and language therapy (SLT) can help if you have communication problems or swallowing problems after
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Treatment for Stress Incontinence Patient Decision Aid
 Treatment for Stress Incontinence Patient Decision Aid Patient Information Author ID: JD/NS Leaflet Number: Gyn 056 Version: 1 Name of Leaflet: Treatment for stress incontinence - Patient decision aid
Treatment for Stress Incontinence Patient Decision Aid Patient Information Author ID: JD/NS Leaflet Number: Gyn 056 Version: 1 Name of Leaflet: Treatment for stress incontinence - Patient decision aid
Treatment for pleural mesothelioma
 Treatment for pleural mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents Treatment
Treatment for pleural mesothelioma This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding mesothelioma. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 9. Contents Treatment
