ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY. Solutions with you in mind
|
|
|
- Brook Small
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ALL ABOUT SPASTICITY Solutions with you in mind
2 WHAT IS SPASTICITY? The muscles of the body maintain what is called normal muscle tone, a level of muscle tension that allows us to hold ourselves up. When the tension in these muscles increases they become rigid and are said to be spastic. When muscles become spastic, their range of motion decreases and movement of these muscles can be painful. Spasticity is one of the most common symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS) and is defined as muscle stiffness that is frequently generalized and that causes more or less continuous rigidity. It is normally associated with temporary periods of worsening, in the form of involuntary muscle spasms, all the while muscle function is progressively lost. It is one of the primary reasons for disability in MS since it tends to be associated with pain (continuous or due to spasms), changes in bladder function and in sleep, the inability to walk and perform other movements, including those required for personal hygiene. Spasms are involuntary muscular movements in the limbs and torso. There are three kinds of spasms: Flexors: make the limbs bend at the joints. Extensors: make the limbs extend themselves. Adductors: make the limbs close tightly to the body s midline (arms pulled toward trunk, the legs close together, etc.).
3 WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS? People suffering from spasticity associated with MS, may present with a variety of symptoms, including: Hypertonicity (increased muscle tone), which can, in some cases, lead to muscle stiffness, rigid joints and bladder dysfunction Spontaneous muscle activity in the form of uncontrollable muscle spasms that are either isolated in nature or present as a series of rapid muscle contractions (called clonus) Exaggerated tendon reflexes Which is associated with: Pain that can range from slight (tense muscles) to severe (painful spasms in the limbs). Nocturnal awakening: due to pain and/or bladder dysfunction. Deterioration of muscle function that may affect walking, all other types of movements and speech. These symptoms of spasticity can result in functional disabilities including changes in posture caused by an increase in muscle tone (muscle tension or activity state). Muscles must normally sustain an adequate level of muscle tone in order to keep the body upright and allow for movement, while at the same time permitting flexibility and speed during movement. Spasticity is the result of increased muscle tone, which results in a loss of muscle response. These effects can notably increase fatigue and make performing daily activities challenging.
4 Spasticity can also lead to the following: Problems using the legs and arms: people suffering from spasticity associated with MS tend to see their mobility reduced, which often implies a reduced quality of life and a change in daily activities. Fatigue/lack of energy: presents in more than 90% of patients with MS. MS-associated fatigue can have dramatic effects on the professional and social interactions of patients. Bladder dysfunction: is a very common problem in MS patients. A high percentage of patients have to go to the bathroom frequently as a result. Sleep disorders: is the factor that most contributes to fatigue in patients with MS. Spasms: sudden, painful muscle contractions that can disturb sleep and contribute to daytime fatigue. Spasticity can make walking, sitting down or getting up from a chair, bathing, stretching, getting dressed or other daily activities difficult. In addition, some patients report that uncontrollable spasms often cause uncomfortable situations. Spasticity can lower your self-esteem. As a result, the patient should talk frankly and freely with those around him or her (i.e., family members, friend, medical personnel). Not all patients who suffer from spasticity have pain. When there is pain, it is usually due to muscle rigidity, which causes the tendons to shorten, making it difficult to bend or extend the limbs. The tissues become knotted (contracted) and the result is pain. Some people with spasticity suffer from deep, continuous pain in the joints. On occasion, a certain degree of spasticity can help to compensate for motor weakness in the legs, allowing patients to walk, stand up or move from one seat to another. WHY DOES IT OCCUR? The basic cells of the nervous system are called neurons and are protected with a kind of sheath made out of a protein called myelin (in the same way an electrical cable is protected by plastic). Neurons transmit the signals needed for the normal functioning of our motor skills and senses. The central nervous system (which includes
5 the brain, the cerebellum and the spinal cord) is responsible for processing these functions, which allows, for example, some muscles to contract while other relax when carrying out a particular movement. This takes place because the brain sends messages to the spinal cord and from there to the muscles. In MS, these messages are not transmitted properly because the paths between the brain, the spinal cord and the muscles are damaged. The messages are scrambled and several muscle groups contract at the same time when they should not. Precise motor control is lost progressively and simultaneous contraction of the extensor and flexor muscles leads to a lack of coordination, often with painful and debilitating results. As with all symptoms associated with MS, spasticity is the result of progressive degradation of myelin and of the nerve fibers. This results in a corresponding degradation of the signal that is transmitted by the neurons responsible for carrying impulses from the brain and the spinal cord to the muscles, thereby causing excessive activation. The alpha motor neurons (responsible for initiating muscle contractions) are particularly affected.
6 HOW FREQUENTLY DOES IT OCCUR? Spasticity occurs in the great majority of patients with MS, in varying degrees. MS is a very variable disease with respect to how it presents and progresses. From the point of view of the symptoms (e.g., spasticity), flares are most frequently observed initially. An flare is considered to be any new and abrupt neurological change or symptom (lasting more than 24 hours) or a clear worsening of previous symptoms (in the absence of fever or any kind of medication that could worsen the patient s general health status, like sedatives). Spasticity flares can vary greatly in their intensity, duration and recovery period among different patients. Their intensity can range from mild, where they do not affect daily life at all, to severe, where they greatly affect a person s daily activities. The duration of the flares can range between a few days (always more than 24 hours) to several weeks, with the recovery period lasting between a few days to up to 3 months. Over time, for the majority of patients, MS symptoms stop appearing in flares and simply remain continuously. This is also the case with spasticity, where a continuous degree of rigidity is maintained, with more or fewer spasms. DIAGNOSIS AND MONITORING Various tests can be conducted to diagnose and monitor the progression of the spasticity. These tests evaluate muscular activity: Analyzing the characteristics of voluntary and involuntary movements of the arms and legs. Measuring the frequency and intensity of spontaneous muscular activity (spasms, clonus). Asking the patient, caretaker or healthcare worker for his or her overall impression. Evaluating the patient s ability to carry out certain activities, like walking or personal care tasks, or the patient s general quality of life.
7 Measurement scales are available to help evaluate the degree of spasticity from a clinical point of view such as the Ashworth Scale, the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) the overall clinical impression, etc No spasticity Significant degree of spasticity TREATMENTS People who suffer from MS are likely to be treated by a multidisciplinary team composed of medical and nursing specialists, psychologists, speech therapists and/or physical therapists. These people will determine what the best option is for your situation. The objectives when treating spasticity are: Mobility: to improve the use of affected limbs and a person s ability to carry out their daily activities.
8 Comfort: to reduce the pain and discomfort associated with stiffness or spasms. Personal care: to improve posture and facilitate independent personal hygiene. Quality of life: to improve or retain the ability to carry out daily activities (mobility, work, family, recreational activities...). For informational purposes, the available guidelines for treating spasticity associated with MS are described below: 1. Non-pharmacological treatments a) Physical therapy Physical therapy (rehabilitation) is a key part of the treatment of symptoms of MS and includes the following different options: Physical therapy: passive range of motion exercises that include instructions for performing the exercises regularly, as they help to strengthen, stretch and relax the muscles and, at the same time, improve joint mobility and increase blood flow. The physical therapist will likely also provide a series of exercises to do at home. Before deciding on a treatment to follow, the physical therapist will examine the patient to get an idea of how he/she is doing and how he/she moves. Physical therapy may help to improve symptoms and also ensure that bad posture or bad habits
9 during movement that could worsen the spasticity are not adopted. The patient may have to change the way he/she walks or, in some cases, use an aid device that will allow the him or her to move more easily and, in this way, prevent muscle spasms. With mild MS, patients are usually told to maintain a good level of physical fitness by performing stretching and strengthening exercises. In the case of moderate to severe spasticity, the physical therapist may include exercises and postures that reduce muscle tone (to avoid excessive muscle tone so that the muscles are less rigid), cooling therapy and muscle mobilization techniques. The physical therapist usually provides the patient with a stretching exercise program to attempt to maintain proper muscle length, thereby increasing the chances that the spasms become less frequent and there is less rigidity. The stretching exercises can be active (performed by the patient) or passive (completed with the help of another person), which is why the physical therapist will also include the caretaker in the instruction.
10 Hydrotherapy (exercises in a pool) can also help to relax the muscles. Sometimes the use of ice packs or similar items (cryotherapy) can also be useful. Massages also help to alleviate muscular rigidity. Occupational therapists, when it is possible, work together with the physical therapists. They try to determine how physical symptoms affect patients daily lives and help them maintain their independence by teaching them movements that take into account their spasticity symptoms. For example, they determine how spasticity affects the way in which patients get up from and sit down in a chair, or in other words, how moving to and from the chair affects their spasticity. An occupational therapist will also recommend devices that will help the patient perform daily movements and ensure that the bed, chair, or wheelchair being used by the patient are appropriate. b) Surgery Depending on the patient and the characteristics of his or her spasticity, surgery may be a viable alternative for severe cases of spasticity associated with MS. Different types of surgeries are used to treat spasticity. Orthopedic surgery can be an option if the surgeons decide to lengthen the tendons, fuse joints or treat malformations by any other means. Surgical correction, accompanied by the appropriate rehabilitation, can prolong rest periods, reduce pain and avoid bedsores (weakened skin tissue that becomes hard, dry and a pearly white, gray or black in color). c) Various orthopedic orthoses: Intended to force the correct posture of deformed limbs and allow them to be used.
11 d) Alternative treatments: Alternative treatments include acupuncture (for certain types of pain) and relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation. 2. Primary drug treatments There are various drugs that can be prescribed for the treatment of spasticity, ranging from muscle relaxants to low-dose antiepileptic drugs. The main drugs are described below. Oral muscle relaxants Benzodiazepines Permitted cannabinoids 3. Invasive (injectable) drug treatments Locally injectable drug treatments are a potential alternative for patients with spasticity that affects only a small area (focal spasticity) or that does not respond to oral medication. Various treatments exist: Neurotoxins: injected directly into the muscle, these reduce muscle tension and treat localized (focal) spasticity. The effects last for approximately 2-4 months. Tend to be part of a program that includes rehabilitation. Nerve blocks using neurolytic agents: injection of phenol or alcohol into the nerve ends in the affected area, destroying them and causing muscle relaxation. The results are relatively short-term and the procedure must be repeated every few months. Intrathecally administered muscle relaxants: a last resort for patients with spasticity in the lower limbs that does not respond adequately to other medications or if the patient cannot tolerate the other medications. Administered by inserting a catheter (small tube) into the thecal sac (the space that surrounds the spinal cord) and connecting it to a medication reservoir with an infusion pump. This is implanted surgically under the abdominal skin to directly administer the drug into the spinal cord. Requires special care.
12 Solutions with you in mind
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity
 Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Managing Spasticity. Spasticity Service
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Managing Spasticity Spasticity Service If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter please contact
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
What is the Spasticity Clinic?
 The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
The Spasticity Clinic This booklet can help you learn about: the Spasticity Clinic at McMaster Children s Hospital spasticity and how it may be treated Your therapist will give you more information and
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015
 Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
Spine Care Centre (SCC) protocols for Multiple Sclerosis Update 1 August 2015 Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nerves in the brain and spinal cord, causing a wide range of symptoms including
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis. ultimately lead to the crippling of the muscular system, there are many differences between these
 Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
Delirium. The signs of delirium are managed by treating the underlying cause of the medical condition causing the delirium.
 Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Mobility After Stroke
 Mobility After Stroke Issues facing stroke survivors and their families Regaining Mobility Moving around safely and easily is not something you may think about, until you have had a stroke. Each year more
Mobility After Stroke Issues facing stroke survivors and their families Regaining Mobility Moving around safely and easily is not something you may think about, until you have had a stroke. Each year more
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy. Jenny Wilson, MD [email protected] OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015
 Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD [email protected] OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
Tone Management in Cerebral Palsy Jenny Wilson, MD [email protected] OHSU and Shriners Hospital for Children October, 2015 Disclosures I am involved in a Dysport sponsored research study Goals Describe
What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information
 What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information Kim, diagnosed in 1986 What is MS? Multiple sclerosis (or MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease that attacks the central nervous system (brain and spinal
What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information Kim, diagnosed in 1986 What is MS? Multiple sclerosis (or MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease that attacks the central nervous system (brain and spinal
Surgery of the Upper Extremity in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy
 Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities
 Penn Comprehensive Neuroscience Center Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities Penn Neuro-Orthopaedics Service 1 Table of Contents Overview Overview 1 Treatment 2 Procedures 4 Achilles Tendon Lengthening
Penn Comprehensive Neuroscience Center Treatment of Spastic Foot Deformities Penn Neuro-Orthopaedics Service 1 Table of Contents Overview Overview 1 Treatment 2 Procedures 4 Achilles Tendon Lengthening
Staying Mobile & Active Post Stroke. Kevin Lockette PT Ohana Pacific Rehab Services, LLC Honoulu- Kailua www.ohanapacificrehab.
 Staying Mobile & Active Post Stroke Kevin Lockette PT Ohana Pacific Rehab Services, LLC Honoulu- Kailua www.ohanapacificrehab.com 808 262 1118 Aging Process Changes in body composition Loss of muscle tissue/increase
Staying Mobile & Active Post Stroke Kevin Lockette PT Ohana Pacific Rehab Services, LLC Honoulu- Kailua www.ohanapacificrehab.com 808 262 1118 Aging Process Changes in body composition Loss of muscle tissue/increase
Therapeutic Canine Massage
 Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
Meet our Certified Canine Massage Therapist, Stevi Quick After years of competitive grooming and handling several breeds in conformation, I became interested in training and competing with my dogs in the
It is much more than just feeling tired. It is described by people in many ways such as exhausting, overwhelming sleepiness and weakness.
 Choices Fatigue Fatigue is one of the most common invisible symptoms of MS and one which can have a major impact on all aspects of life. For some people it is the symptom that affects them the most. It
Choices Fatigue Fatigue is one of the most common invisible symptoms of MS and one which can have a major impact on all aspects of life. For some people it is the symptom that affects them the most. It
Massage Therapy & Multiple Sclerosis
 Massage Therapy & Multiple Sclerosis National Massage Therapy Awareness Week October 2008 Presented by the Massage Therapist Association of Saskatchewan, Inc. MTAS Inc., 2008 Researched & written by Cynthia
Massage Therapy & Multiple Sclerosis National Massage Therapy Awareness Week October 2008 Presented by the Massage Therapist Association of Saskatchewan, Inc. MTAS Inc., 2008 Researched & written by Cynthia
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Understanding. Multiple Sclerosis. Tim, diagnosed in 2004.
 Understanding Multiple Sclerosis Tim, diagnosed in 2004. What Is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurologic disorder that affects the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS includes the
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis Tim, diagnosed in 2004. What Is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurologic disorder that affects the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS includes the
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Multiple sclerosis and pain
 9 Multiple sclerosis and pain 2ND EDITION Multiple Sclerosis Society of New Zealand CONTENTS Introduction-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 How
9 Multiple sclerosis and pain 2ND EDITION Multiple Sclerosis Society of New Zealand CONTENTS Introduction-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 How
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
 Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion
 Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Lumbar or Thoracic Decompression and Fusion DO NOT TAKE ANY ASPIRIN PRODUCTS OR NON-STEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (ie NSAIDs, Advil, Celebrex, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Naprosyn, Aleve, etc) FOR 2 WEEKS
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
DENVER CHIROPRACTIC CENTER GLENN D. HYMAN, DC, CSCS
 DENVER CHIROPRACTIC CENTER GLENN D. HYMAN, DC, CSCS Are you in the right place? Please read this before proceeding with paperwork: At Denver Chiropractic Center, we specialize in treating muscles with
DENVER CHIROPRACTIC CENTER GLENN D. HYMAN, DC, CSCS Are you in the right place? Please read this before proceeding with paperwork: At Denver Chiropractic Center, we specialize in treating muscles with
INFORMATION FOR YOU. Lower Back Pain
 INFORMATION FOR YOU Lower Back Pain WHAT IS ACUTE LOWER BACK PAIN? Acute lower back pain is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced as aching, burning, stabbing, sharp
INFORMATION FOR YOU Lower Back Pain WHAT IS ACUTE LOWER BACK PAIN? Acute lower back pain is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced as aching, burning, stabbing, sharp
PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS
 PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS De Anna Looper, RN CHPN Corporate Clinical Consultant / Legal Nurse Consultant Carrefour Associates L.L.C. PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS
PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS De Anna Looper, RN CHPN Corporate Clinical Consultant / Legal Nurse Consultant Carrefour Associates L.L.C. PARKINSON S DISEASE IN LONG-TERM-CARE SETTINGS
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion
 Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
How To Cover Occupational Therapy
 Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination for Occupational Therapy These Guidelines for Medical Necessity Determination (Guidelines) identify the clinical information MassHealth needs to determine
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY?
 WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
WHAT IS CEREBRAL PALSY? Cerebral Palsy is a dysfunction in movement resulting from injury to or poor development of the brain prior to birth or in early childhood. Generally speaking, any injury or disease
SLEEP AND PARKINSON S DISEASE
 A Practical Guide on SLEEP AND PARKINSON S DISEASE MICHAELJFOX.ORG Introduction Many people with Parkinson s disease (PD) have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep at night. Some sleep problems are
A Practical Guide on SLEEP AND PARKINSON S DISEASE MICHAELJFOX.ORG Introduction Many people with Parkinson s disease (PD) have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep at night. Some sleep problems are
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
 Multiple sclerosis (MS) Summary Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an incurable disease of the central nervous system that can affect the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. The effects of MS are varied and unpredictable,
Multiple sclerosis (MS) Summary Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an incurable disease of the central nervous system that can affect the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. The effects of MS are varied and unpredictable,
Electrodiagnostic Testing
 Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Many people with MS use some form of conventional medical treatment, and many people also use complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
 Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) CAM therapies can generally be divided into the following categories: Biologically based therapies (eg, dietary supplements, diets, bee venom therapy, hyperbaric
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) CAM therapies can generally be divided into the following categories: Biologically based therapies (eg, dietary supplements, diets, bee venom therapy, hyperbaric
PAIN MANAGEMENT AT UM/SYLVESTER
 PAIN MANAGEMENT AT UM/SYLVESTER W HAT IS THE PURPOSE OF THIS BROCHURE? We created this brochure for patients receiving care from the University of Miami Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center and their
PAIN MANAGEMENT AT UM/SYLVESTER W HAT IS THE PURPOSE OF THIS BROCHURE? We created this brochure for patients receiving care from the University of Miami Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center and their
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Purpose/Goal: Care partners will have an understanding of Multiple Sclerosis and will demonstrate safety and promote independence while providing care to the client with MS. Introduction
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University
 Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
Michelle H. Cameron, M.D., P.T., M.C.R. Portland VA MS Center of Excellence- West, and Oregon Health & Science University Ileana Howard, M.D. VA Puget Sound, Seattle, WA and University of Washington PVA
X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary
 X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating
X-Plain Rheumatoid Arthritis Reference Summary Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating
Neuro-rehabilitation in Stroke. Amit Kumar Neuro-Occupational Therapist
 Neuro-rehabilitation in Stroke Amit Kumar Neuro-Occupational Therapist Neuro-rehabilitation A process whereby patients who suffer from impairment following neurologic diseases regain their former abilities
Neuro-rehabilitation in Stroke Amit Kumar Neuro-Occupational Therapist Neuro-rehabilitation A process whereby patients who suffer from impairment following neurologic diseases regain their former abilities
by Argyrios Stampas, MD, Carolin Dohle, MD, and Elizabeth Dominick, PT, DPT, NCS
 by Argyrios Stampas, MD, Carolin Dohle, MD, and Elizabeth Dominick, PT, DPT, NCS Therapist Jennifer Metz (right) helps a patient use a body-weight support treadmill system. Up and Moving Blending dedication
by Argyrios Stampas, MD, Carolin Dohle, MD, and Elizabeth Dominick, PT, DPT, NCS Therapist Jennifer Metz (right) helps a patient use a body-weight support treadmill system. Up and Moving Blending dedication
PARKINSON S DISEASE INTRODUCTION. Parkinson s disease is defined as a disease of the nervous system that affects voluntary movement.
 PARKINSON S DISEASE INTRODUCTION Parkinson s disease is a disorder of the brain and the nervous system. It is one of the more common neurological diseases in people over the age of 60, and it is more common
PARKINSON S DISEASE INTRODUCTION Parkinson s disease is a disorder of the brain and the nervous system. It is one of the more common neurological diseases in people over the age of 60, and it is more common
HOPE EXERCISE RECOVERY RESOURCES RELATIONSHIPS INFORMATION REHABILITATION PREVENTION SELF ADVOCACY RELATIONSHIPS MOVEMENT. A Stroke Recovery Guide
 INFORMATION REHABILITATION PREVENTION SELF ADVOCACY RECOVERY HOPE A Stroke Recovery Guide RELATIONSHIPS MOVEMENT RESOURCES RELATIONSHIPS EXERCISE www.stroke.org CHAPTER FOUR Movement and Exercise Moving
INFORMATION REHABILITATION PREVENTION SELF ADVOCACY RECOVERY HOPE A Stroke Recovery Guide RELATIONSHIPS MOVEMENT RESOURCES RELATIONSHIPS EXERCISE www.stroke.org CHAPTER FOUR Movement and Exercise Moving
CP Factsheet An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy
 An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy The concept of ageing and cerebral palsy is now becoming more recognised and more research is being undertaken. However many people, including some professionals,
An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy The concept of ageing and cerebral palsy is now becoming more recognised and more research is being undertaken. However many people, including some professionals,
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
ALL ABOUT SEXUAL PROBLEMS. www.almirall.com. Solutions with you in mind
 ALL ABOUT SEXUAL PROBLEMS www.almirall.com Solutions with you in mind WHAT ARE THEY? Sexual problems in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) are defined as those emotional/ psychological and physiological
ALL ABOUT SEXUAL PROBLEMS www.almirall.com Solutions with you in mind WHAT ARE THEY? Sexual problems in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) are defined as those emotional/ psychological and physiological
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function
 Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Recovery After Stroke: Bladder & Bowel Function Problems with bladder and bowel function are common but distressing for stroke survivors. Going to the bathroom after suffering a stroke may be complicated
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard.
 world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS?
 SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
SPINAL STENOSIS Information for Patients WHAT IS SPINAL STENOSIS? The spinal canal is best imagined as a bony tube through which nerve fibres pass. The tube is interrupted between each pair of adjacent
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
CNH7 Provide Massage Therapy to clients
 B CNH7 Provide Massage Therapy to clients OVERVIEW Massage Therapy means the systematic use of classical Massage and soft tissue techniques, to improve physical and emotional well being. The Massage Therapist,
B CNH7 Provide Massage Therapy to clients OVERVIEW Massage Therapy means the systematic use of classical Massage and soft tissue techniques, to improve physical and emotional well being. The Massage Therapist,
Recognizing and Understanding Pain
 Because multiple myeloma is a cancer involving the bone marrow, a common myeloma symptom is bone pain. But the good news is that most pain can be managed. This resource can help you better understand pain
Because multiple myeloma is a cancer involving the bone marrow, a common myeloma symptom is bone pain. But the good news is that most pain can be managed. This resource can help you better understand pain
Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain
 Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain An Introduction to Low Back Pain Low back pain is the number two reason that Americans see a health care practitioner second only to colds and flu. While most people
Preventing & Treating Low Back Pain An Introduction to Low Back Pain Low back pain is the number two reason that Americans see a health care practitioner second only to colds and flu. While most people
Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU
 FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
A Range of Treatment Options Individualizes Spasticity Management
 VOLUME 21, NUMBER 2 2012 A Range of Treatment Options Individualizes Spasticity Management by Angela Sinner, D.O., pediatric rehabilitation medicine specialist and Debbie Song, M.D., pediatric neurosurgeon
VOLUME 21, NUMBER 2 2012 A Range of Treatment Options Individualizes Spasticity Management by Angela Sinner, D.O., pediatric rehabilitation medicine specialist and Debbie Song, M.D., pediatric neurosurgeon
WalkAide. Long term cost effectiveness of FES. J of Rehab Med 2013; 45(2):154 60 Humphreys et al
 WalkAide Long term cost effectiveness of FES J of Rehab Med 2013; 45(2):154 60 Humphreys et al 126 people (62 stroke, 39 MS, 7 SCI, 3 CP, 15 other) Mean time of FES use 3.6 years 33 using FES after 11.1
WalkAide Long term cost effectiveness of FES J of Rehab Med 2013; 45(2):154 60 Humphreys et al 126 people (62 stroke, 39 MS, 7 SCI, 3 CP, 15 other) Mean time of FES use 3.6 years 33 using FES after 11.1
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Standard of Care: Cervical Radiculopathy
 Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Diagnosis: Cervical radiculopathy, injury to one or more nerve roots, has multiple presentations. Symptoms may include pain in the cervical spine
Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Diagnosis: Cervical radiculopathy, injury to one or more nerve roots, has multiple presentations. Symptoms may include pain in the cervical spine
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
URINARY INCONTINENCE Information for Patients and Families Author: Chantale Dumoulin, PhD PT What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence (UI) is the loss of the ability to hold in urine. This can
Sleep Difficulties. Insomnia. By Thomas Freedom, MD and Johan Samanta, MD
 Sleep Difficulties By Thomas Freedom, MD and Johan Samanta, MD For most people, night is a time of rest and renewal; however, for many people with Parkinson s disease nighttime is a struggle to get the
Sleep Difficulties By Thomas Freedom, MD and Johan Samanta, MD For most people, night is a time of rest and renewal; however, for many people with Parkinson s disease nighttime is a struggle to get the
Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy
 Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Are Cervical Stenosis and Myelopathy? The cervical spine (neck) is made up of a series of connected bones called
Cervical Stenosis & Myelopathy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Are Cervical Stenosis and Myelopathy? The cervical spine (neck) is made up of a series of connected bones called
Throughout this reference summary, you will find out what massage therapy is, its benefits, risks, and what to expect during and after a massage.
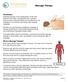 Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Massage Therapy Introduction Massage therapy is the manipulation of the soft tissues of the body, including the skin, tendons, muscles and connective tissue by a professional, for relaxation or to enhance
Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet
 Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet This fact sheets gives a summary of the main facts and issues relating to Multiple Sclerosis and gives an overview of the services offered by MS Ireland.
Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet This fact sheets gives a summary of the main facts and issues relating to Multiple Sclerosis and gives an overview of the services offered by MS Ireland.
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Lateral pterygoid muscle Medial pterygoid muscle
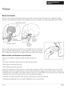 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. Mary Beth Rensberger, RN, BSN, MPH Author
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Mary Beth Rensberger, RN, BSN, MPH Author All rights reserved. Purchasers of this module are permitted to reproduce the forms contained herein for their individual internal use only.
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Mary Beth Rensberger, RN, BSN, MPH Author All rights reserved. Purchasers of this module are permitted to reproduce the forms contained herein for their individual internal use only.
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex
 Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
CBT IN THE CITY. adjusted to the news of being with MS? April 2013. Experts at your fingertips call now. Check out our new services in you local area
 April 2013 Experts at your fingertips call now CBT IN THE CITY Check out our new services in you local area contents. A message from Susie, Information Multiple Sclerosis CBT can make a difference on the
April 2013 Experts at your fingertips call now CBT IN THE CITY Check out our new services in you local area contents. A message from Susie, Information Multiple Sclerosis CBT can make a difference on the
Spina Bifida Occulta. Lo-Call 1890 20 22 60. Occulta Means Hidden
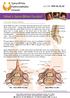 Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
Do you have Back Pain? Associated with:
 Do you have Back Pain? Associated with: Herniated Discs? Protruding Discs? Degenerative Disk Disease? Posterior Facet Syndrome? Sciatica? You may be a candidate for Decompression Therapy The Dynatronics
Do you have Back Pain? Associated with: Herniated Discs? Protruding Discs? Degenerative Disk Disease? Posterior Facet Syndrome? Sciatica? You may be a candidate for Decompression Therapy The Dynatronics
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis
 Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Marie Namey, RN, MSN, MSCN Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH Home of. Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Mellen Center Mission The Mellen Center remains committed
Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Marie Namey, RN, MSN, MSCN Mellen Center Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH Home of. Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Mellen Center Mission The Mellen Center remains committed
What are Core Muscles?... 2. A Healthy Lumbar Spine...3. What is Low Back Pain?...4. Rehabilitation...6. Stages of Rehabilitation...
 Table of Contents What are Core Muscles?... 2 A Healthy Lumbar Spine...3 What is Low Back Pain?...4 Rehabilitation...6 Stages of Rehabilitation...7 Pain Management....................... 8 Heat/Ice What
Table of Contents What are Core Muscles?... 2 A Healthy Lumbar Spine...3 What is Low Back Pain?...4 Rehabilitation...6 Stages of Rehabilitation...7 Pain Management....................... 8 Heat/Ice What
LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B LUMBAR. Hips R L B R L B
 1 Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your BACK/LEG (SCIATIC) PAIN has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
1 Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your BACK/LEG (SCIATIC) PAIN has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
