2014 Fall COURSE 3 Doc, I m Seeing Double. COPE Course NO
|
|
|
- Cody Jayson Crawford
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2014 Fall COURSE 3 Doc, I m Seeing Double COPE Course NO SCO HOMECOMING / FALL CE WEEKEND OCTOBER 9-12, 2014
2
3 Levels of disease Dennis Mathews, O.D. Partner, Eye Specialty Group Associate Professor, Southern College of Optometry Diplomate, American Board of Optometry Peripheral- neurogenic, myogenic, neuromuscular juncture, restrictive Nuclear-brainstem Supranuclear palsies- brainstem, cerebellum, Conjugate palsies- cerebrum Binocular diplopia patient Evaluate 3 cranial nerves responsible for eye movements Forced duction test with evaluation of orbital signs Evaluate other cranial nerves to determine brainstem signs Always consider myasthenia gravis with appropriate workup if positive signs Oculomotor nerve palsy Oculomotor nerve innervates medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique, with ptosis from levator muscle involvement Can be painful on onset, greater pain associated with aneurysm Presents with eye down and out with ptosis Pupil dilated indicates aneurysm of posterior communicating artery until proven otherwise Oculomotor nerve palsy etiology Microvascular disease MS Posterior communicator artery aneurysm MG Polyneuritis Tumor Trauma Transtentorial compression 75 year old black female History high blood pressure No diabetes Binocular diplopia for 3 months History of cancer with intracranial metastasis MRI and MRA negative for vascular disease 1
4 Treatment of oculomotor nerve palsy 3 rd nerve palsy associated with metastatic brain cancer and surgery Microvascular workup Orbital imaging Brain imaging Arteriogram if blown pupil Patch for diplopia May consider prism or surgery after spread of commitentcy several months Isolated trochlear nerve palsy 3-Step Test Vertical Deviations Remember nerves decusate above facial nerve nucleus Park s three step test isolates muscles involved in cases of vertical palsies Must remember skew deviation during evaluation Superior Opposite Lower Same Toward Oblique Away Rectus Trochlear nerve palsy etiology Microvascular Trauma MS MG Aneurysm Tumor Abducens nerve palsy- isolated Lateral rectus involved Abductional deficit Microvascular MS MG Brain stem tumor Trauma Polyneuritis Increased ICP 2
5 Gradenigo s Syndrome Congenital bilateral abducens nerve palsies No brainstem lesions No Mobius Syndrome with facial nerve palsies 6 th nerve palsy Middle-ear infection Mastoiditis Pain on ipsilateral side of face Neurogenic hearing loss Mobius Syndrome 6 th nerve palsy 7 th nerve palsy Congenital, bilateral Differential Diagnosis Duane s retraction syndrome Duane s syndrome Type 1- no abduction, retraction and narrowing of palpebral opening upon adduction and nystagmus of contralateral abducted eye Type 2- exotropia, reduced adduction and abduction, retraction of globe on adduction Type 3- poor ad and abduction, esotropic or exotropic, retraction on adduction 35 year old female History optomotor abnormality since childhood No diplopia 3
6 Bilateral Duane s Syndrome 60 year old male History optomotor abnormality since childhood No diplopia 6 th Cranial Nerve Palsy If pediatric case, with acquired ET (6 th cranial nerve palsy), pontine glioma until proven otherwise! 72 year old male Recent onset horizontal diplopia No other symptoms History high blood pressure 4
7 6 th nerve palsy, unknown etiology 72 year old male, no hx of diabetes, hx of HBP All lab and MRI of brain neg 4 weeks later with no treatment 55 year old male History HBP 6 th nerve palsy right eye 47 year old male History progressive 6 th nerve palsy Medical history negative otherwise No other neurologic symptoms Brainstem syndromes Medulla- rostral (posterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome) Pons- caudal ventral, (Millard-Gubler syndrome), caudal tegmental (syndrome of Foville) Mid-brain- ventral (Weber), medial (Benedikt), dorsal (Parinaud s) Cranial nerve location in brainstem Rule of 4 Nerves 12, 11,10,9 in medulla Nerves 8, 7, 6, 5 in pons Nerves 4,3 in midbrain Nerve 2 in thalamus Nerve 1 in limbic lobe 5
8 Medulla lesions Because of location of pyramids and fact that fibers are pre-decussated within the corticospinal tracts, lesions may cause ipsilateral cranial nerve palsy at level of lesion with contralateral palsy of lower cranial nerves and hemiparesis Middle lesions may involve spinal thalamic tract and nucleus ambiguus with contralateral paresthesias and ipsilateral motor involvement of nerves 9,10 and 11 Medulla Upper lesions may result from occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (pica) with solitary nucleus, inferior cerebral peduncle, and vestibular nuclei involved with taste defect, and nonpyramidal motor insuficiency with nystagmus Medial lemniscus involvement yields fine motor and proprioception defects post decusation after nucleus gracilis and cuneatus Trigeminal sensory nucleus into medulla, ipsilateral facial paresthesia Medulla Summary Causes contralateral paresis, paresthesias, taste defects, nystagmus, proprioception defects, with ipsilateral cranial nerve involvement at the level of lesion Pons lesions Inferior lesions yield abducens palsy with contralateral hemiparesis with bulbar involvement If facial nerve is involved with mid pons lesions, is Millard-Gubler syndrome If trigeminal nucleus involved, mastication and facial sensory involved on ipsilateral side If MLF involved, contralateral INO called Foville syndrome Pons lesions Pontocerebellar angle- trigimenal ganglion involvement, peripheral facial nerve palsy with intact brow and lower face involved, and acoustic-vestibular nerve involvement with hearing loss, vertigo, nystagmus- caused from acoustic- neuroma, also called Schwann cell neuroma Pons lesion summary 6 th and 7 th nerve palsy Contralateral paresis INO possible 6
9 Midbrain lesions-summary Weber s syndrome- oculomotor palsy with contralateral hemiparesis Benedikt s syndrome- oculomotor palsy with contralateral hemiparesis and hemiparesthesia Parinaud s syndrome- near light dissociation with superior gaze palsy, upbeat nystagmus, ptosis 63 year old male History intracranial aneurysm with surgery of midbrain 10 months before this exam Diplopia since surgery Left side paresis of leg and arm Right 3 rd nerve palsy, left INO with vertical down beating nystagmus\ Benedict s syndrome Parinaud s Midbrain Syndrome Dorsal midbrain compression Superior gaze palsy with up-beating nystagmus and near-light dissociation of pupils Most common cause is pineal gland tumor Brown s syndrome Inability to raise adducted eye above mid horizontal plane with adduction May have downshoot of adducting eye Exodeviation increased with upward movement in midline Positive forced duction test Attachment of tendon of superior oblique to Tenon s capsule WE COULD CERTAINLY SLOW THE AGING PROCESS DOWN IF IT HAD TO WORK ITS WAY THROUGH CONGRESS. Will Rogers MAYBE IT IS TRUE THAT LIFE BEGINS AT FIFTY.. BUT EVEREYTHING ELSE STARTS TO WEAR OUT, FALL OUT, OR SPREAD OUT. Phyllis Diller 7
10 MY LUCK IS SO BAD THAT IF I BOUGHT A CEMETERY, PEOPLE WOULD STOP DYING Rodney Dangerfield ONLY IRISH COFFEE PROVIDES IN A SIGLE GLASS ALL FOUR ESSENTIAL FOOD GROUPS; ALCOHOL, CAFFEINE, SUGAR, AND FAT Alex Levine Progressive supranuclear palsy BY THE TIME A MAN IS WISE ENOUGH TO WATCH HIS STEP, HE IS TOO OLD TO GO ANYWHERE Billy Crystal Down gaze firstly restricted, then horizontal and up gaze affected Early saccadic defects, slowed and cogwheel pursuits Degeneration of basal ganglia, midbrain tegmentum, and periaquaductal gray Parkinsonism 73 year old male Slow development of poor eye movements No complaints of diplopia Progressive supranuclear ophthalmoplegia Cog-wheel movement of skeletal muscles and pursuits, glabellar reflex hyperreflexia, mask face, tremor at rest, running type walk Oculogyric crisis- irritative lesions causing conjugate ocular deviations which can last for several hours Abnormal substantia nigra in midbrain 8
11 Cerebellar disease Un-moniotored VOR Un-monitored voluntary or involuntary movements No pursuits Intention tremor Nystagmus Skew deviation Lesion in brainstem, cerebellum Seen with INO No cycloversional defect with hyper deviation which helps to differentiate from 4 nerve palsy Usually commitant deviation Internuclear ophthalmoplegia MLF lesion Adduction defect contralateral to lesion unless lesion at 6 th nerve nucleus PPRF lesion causes conjugate gaze palsy toward side of lesion with no adduction on ipsilateral side- 1 ½ syndrome Anterior INO- convergence involved Bilateral-MS, unilateral-basilar artery branch infarct- skew deviation due to nucleus of Cajal 75 year old female Sudden onset of binocular diplopia History of HBP No jaw claudication, temporal head tenderness, weight loss, or fever Brain stem MRI, intracranial MRA negative Sed rate, c-reactive protein, CBC, lyme titer, FTA-ABS, Hem A1-c, FANA all negative ETIOPATHIC INO, possibly associated with HBP 32 year old female Diabetes INO 9
12 Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia Bilateral ptosis Motility defects, starting with superior gaze No diplopia Kearns-Sayre disease is included Ragged red fibers in EOM s Associated with cardiac muscle disease Associated with mitocondrial disease 48 year old white male Poor ocular motilities for 10 years No other health problems, including no heart disease CPEO Bell s Palsy Differentiate from Ramsey-Hunt disease Differentiate from CNS 7 th nerve palsy Associated with inflammation of nerve in canal in mastoid bone Treat with steroids Controversy on use of Acyclovir routinely Watch for exposure keratopathy and lacrimal gland insufficienty 80 year old black female Medical history of HBP and diabetes Longstanding history of facial twitching Previous MRI of the brain negative Hemi-facial spasm Botox injections for treatment Blelpharospasm 10
13 Myasthenia Gravis Always a consideration with any optomotor defect Acetycholine receptor antibody titer and tensilon test would help to rule out Ice test Scan thymus gland 65 year old male History binocular, transient ptosis Transient diplopia also noted Acetylcholine receptor antibodies, blocking and binding 10 times normal Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Paraneoplastic syndrome Looks and smells like MG Differential by EMG Screen for lung cancer 70 year old male Vision loss and diplopia for 6 years Pigmentary retinopathy, vision of counting fingers both eyes All test neg. except high FTA-ABS Signs of orbital disease Docholiectasis internal carotid artery, transient diplopia Pain Progression Proptosis Palpation Pulsation Periorbital changes 11
14 Orbital pseudotumor Idiopathic orbital inflammation Mass effect with exophthalmos Histopathology- cellular infiltration into orbit to include muscles, fat, lacrimal gland-eosinophilia noted, particularly in children Optic nerve, cranial nerve involvement, muscle inflammation Unilateral involvement in adults, can be bilateral in children 56 year old black female Sudden onset of binocular diplopia Red right eye with pain No other symptoms Medical history negative No vision loss Visual fields normal both eyes Orbital myositis Extraocular muscle inflammation Note orbital aching with diplopia Sectoral episcleral injection Possible positive forced duction Differential includes collagen vascular disease, sarcoidosis, muscle tumor, Grave s orbitopathy, polymyositis Orbital cellulitis Infectious disease of orbit Bacterial, viral, fungal possible With diabetes, consider mucor infection Painful rapid exopthalmos with fever, ophthalmopledgia, vision loss Can lead to cavernous sinus thrombosis or cranial abscess Treat aggressively, may need orbital culture Superior orbital fissure syndrome 62 year old male History pain and swelling around OS for 4 days History of liver transplant with antiimmune treatment White cell cound 500/cubic mm Sent to ER, admitted, started on IV vancomycin and rhocephin Spheno-cavernous syndrome Inflammation of superior orbital fissure area Cranial nerves II, III, IV, VI and ophthalmic V involved Oculo-sympathetic denervation Conjunctival congestion Pathology includes cavernous sinus thrombosis, Tolosa-Hunt syndrome 12
15 66 year old white male Diplopia for 4 days with lid shut History of lymphoma, in remission Off chemotherapy Orbital mass extending from sphenoid wing and cavernous sinus, meningioma Grave s orbitopathy-thyroid related orbitopathy (TRO) Most common cause of exophthalmos in adults, lid retraction, lid lag, inflammation Usually bilateral Age 30-50, women 4 times more common than men Systemic signs of Grave s diseasediffuse hyperplastic goiter, tachycardia, sweating, weight loss, pre-tibial myxedema Grave s orbitopathy 20% have normal chemical endocrine tests (called euthyroid) Immune etiology- an anti-thyroid immunoglobulin is produced called TSI(thyroid-stimulating Ig), previously called LATS for long-acting thyroid stimulator This antibody binds to the TSH site on the thyroid follicular cell causing the gland to function autonomous Possible decrease in T- cell suppressor activity allowing B- cells to produce more antibody 37 yo black female, hx slowly developing ptosis OD that is transient VA 20/20 OD, OS, fields WNL OD, OS Ductional restrictions superior and right gaze OD Bilateral exophthalmos of 30 mm OD and 26 mm OS 30 year old female Gradual onset of binocular diplopia Had no history of dysthyroid 13
16 Orbital tumors Medicine work-up revealed abnormal thyroid function Was also screened for M/G, negative Metastatic- from carcinoma of breast, lung, colon, prostate May expand quickly with mass effect and inflammation Nasopharyngeal carcinoma may easily spread due to close proximity Paranasal sinuses also important location of metastatic location Primary orbital tumors Hamartomas- glioma and meningioma of the optic nerve- gradual vision loss with optic neuropathy, opticociliary shunt vessels Choristomas- dermoid cysts or tumors Lacrimal gland tumors 61 YEAR OLD FEMALE HX DIPLOPIA FOR 3 MONTHS PRESENTED FIRSTLY AS 6 TH NERVE PALSY MEDICAL HISTORY NEG. FIRST MRI AND MRA OF HEAD NEGATIVE 75 year old female, exophthalmos for 2 years Sent for imaging, refused Sent to oculoplastics, refused Probable mucocele Reviewed cranial nerve palsies Reviewed brainstem lesions Reviewed orbital disease Hope you are still awake! THANK YOU 14
Doctor, I See Double : Managing Cranial Nerve Palsies
 1 Doctor, I See Double : Managing Cranial Nerve Palsies Joseph W. Sowka, OD, FAAO, Diplomate Professor of Optometry Nova Southeastern University, College of Optometry 3200 South University Drive Fort Lauderdale,
1 Doctor, I See Double : Managing Cranial Nerve Palsies Joseph W. Sowka, OD, FAAO, Diplomate Professor of Optometry Nova Southeastern University, College of Optometry 3200 South University Drive Fort Lauderdale,
Management Approach to Isolated Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies
 Management Approach to Isolated Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies Alfredo A. Sadun, MD, PhD Thornton Professor of Vision Doheny Eye Institute Departments of Ophthalmology and Neurosurgery Keck/USC School of Medicine
Management Approach to Isolated Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies Alfredo A. Sadun, MD, PhD Thornton Professor of Vision Doheny Eye Institute Departments of Ophthalmology and Neurosurgery Keck/USC School of Medicine
Eye movement problems in adults
 Eye movement problems in adults 07/12/2015 A. Dahlmann-Noor Dr med PhD FRCOphth FRCS(Ed) DipMedEd Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Trials Lead Paediatric Ophthalmology Horizontal misalignment (Cyclo)vertical
Eye movement problems in adults 07/12/2015 A. Dahlmann-Noor Dr med PhD FRCOphth FRCS(Ed) DipMedEd Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Trials Lead Paediatric Ophthalmology Horizontal misalignment (Cyclo)vertical
Primary Motor Pathway
 Understanding Eye Movements Abdullah Moh. El-Menaisy, MD, FRCS Chief, Neuro-ophthalmology ophthalmology & Investigation Units, Dhahran Eye Specialist Hospital, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Primary Motor Pathway
Understanding Eye Movements Abdullah Moh. El-Menaisy, MD, FRCS Chief, Neuro-ophthalmology ophthalmology & Investigation Units, Dhahran Eye Specialist Hospital, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Primary Motor Pathway
Institute of Ophthalmology. Thyroid Eye Disease. aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy
 Institute of Ophthalmology Thyroid Eye Disease aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy Causes TED/TAO is an eye disease associated with disease of the thyroid gland Most commonly, it occurs with an overactive
Institute of Ophthalmology Thyroid Eye Disease aka Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy Causes TED/TAO is an eye disease associated with disease of the thyroid gland Most commonly, it occurs with an overactive
Pseudoabducens palsy: When a VI nerve palsy is not a VI nerve palsy
 Pseudoabducens palsy: When a VI nerve palsy is not a VI nerve palsy Emily S. Birkholz, MD, and Michael Wall, MD December 30, 2009 CC: 44 year old male with diplopia HPI: This 44 year old man with a history
Pseudoabducens palsy: When a VI nerve palsy is not a VI nerve palsy Emily S. Birkholz, MD, and Michael Wall, MD December 30, 2009 CC: 44 year old male with diplopia HPI: This 44 year old man with a history
Common visual symptoms and findings in MS: Clues and Identification
 Common visual symptoms and findings in MS: Clues and Identification Teresa C Frohman, PA-C, MSCS Neuro-ophthalmology Research Manager, UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas Professor Biomedical Engineering,
Common visual symptoms and findings in MS: Clues and Identification Teresa C Frohman, PA-C, MSCS Neuro-ophthalmology Research Manager, UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas Professor Biomedical Engineering,
Cranial Nerves. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve. Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve
 Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Cranial Nerves Examination of Cranial Nerves and Palsies Drs Nathan Kerr and Shenton Chew 1 Olfactory On 2 Optic Old 3 Oculomotor Olympus 4 Trochlear Towering 5 Trigeminal Top 6 Abducens A 7 Facial Finn
Fourth Nerve Palsy (a.k.a. Superior Oblique Palsy)
 Hypertropia Hypertropia is a type of strabismus characterized by vertical misalignment of the eyes. Among the many causes of vertical strabismus, one of the most common is a fourth nerve palsy (also known
Hypertropia Hypertropia is a type of strabismus characterized by vertical misalignment of the eyes. Among the many causes of vertical strabismus, one of the most common is a fourth nerve palsy (also known
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Paraneoplastic Antibodies in Clinical Practice. Mohammed El lahawi New Cross Hospital Wolverhampton
 Paraneoplastic Antibodies in Clinical Practice Mohammed El lahawi New Cross Hospital Wolverhampton 1 Effects of Neoplasm Direct mass ( pressure ) effect Metastasis effect Remote effect 2 The Nervous System
Paraneoplastic Antibodies in Clinical Practice Mohammed El lahawi New Cross Hospital Wolverhampton 1 Effects of Neoplasm Direct mass ( pressure ) effect Metastasis effect Remote effect 2 The Nervous System
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain
 Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Angela Wilkin May 2013
 Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
Angela Wilkin May 2013 Upper Motor Neuron v Lower Motor Neuron Lesions UMN Lesion LMN Lesion Forehead usually unaffected (bilateral innervation) Forehead affected Contralateral side Ipsilateral side Often
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd.
 About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
1 Always test and record vision wearing distance spectacles test each eye separately A 1mm pinhole will improve acuity in refractive errors
 Golden eye rules Examination techniques 1 Always test and record vision wearing distance spectacles test each eye separately A 1mm pinhole will improve acuity in refractive errors Snellen chart (6 metre)
Golden eye rules Examination techniques 1 Always test and record vision wearing distance spectacles test each eye separately A 1mm pinhole will improve acuity in refractive errors Snellen chart (6 metre)
F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s
 Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments NEUROOPTHALMOLOGY
 Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments NEUROOPTHALMOLOGY Neuroophthalmology focuses on conditions caused by brain or systemic abnormalities that result in visual disturbances, among other symptoms.
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments NEUROOPTHALMOLOGY Neuroophthalmology focuses on conditions caused by brain or systemic abnormalities that result in visual disturbances, among other symptoms.
Ptosis. Ptosis and Pupils. Ptosis. Palpebral fissure. Blepharospasm. Blepharospasm or ptosis? Bilateral, longstanding, familial: Palpebral fissure
 Ptosis and Pupils Ptosis Jack CF Chong, MS, MD 99/03/06 Ptosis Bilateral, longstanding, familial: CPEO (chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia) D/D: Acute, recent, unilateral Palpebral fissure Palpebral
Ptosis and Pupils Ptosis Jack CF Chong, MS, MD 99/03/06 Ptosis Bilateral, longstanding, familial: CPEO (chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia) D/D: Acute, recent, unilateral Palpebral fissure Palpebral
Anatomy: The sella is a depression in the sphenoid bone that makes up part of the skull base located behind the eye sockets.
 Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
Paralytic Strabismus: Third, Fourth, and Sixth Nerve Palsy
 Paralytic Strabismus: Third, Fourth, and Sixth Nerve Palsy Sashank Prasad, MD a, *, Nicholas J. Volpe, MD b KEYWORDS Paralytic strabismus Nerve palsy Ocular motor nerves Eye movement abnormalities ANATOMY
Paralytic Strabismus: Third, Fourth, and Sixth Nerve Palsy Sashank Prasad, MD a, *, Nicholas J. Volpe, MD b KEYWORDS Paralytic strabismus Nerve palsy Ocular motor nerves Eye movement abnormalities ANATOMY
Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014
 Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014 Richard Webster, Paediatric Neurologist Children s Hospital at Westmead Typical history Unilateral LMN facial weakness Acute onset over a day or
Paediatric Bell s Palsy Paediatric Update November 2014 Richard Webster, Paediatric Neurologist Children s Hospital at Westmead Typical history Unilateral LMN facial weakness Acute onset over a day or
List of diagnostic flowcharts
 List of diagnostic flowcharts Chapter 3 Visual loss Transient visual loss 43 Sudden or rapidly progressive visual loss 46 Gradual visual loss 61 Chapter 4 The red eye One red eye, decreased vision 83 One
List of diagnostic flowcharts Chapter 3 Visual loss Transient visual loss 43 Sudden or rapidly progressive visual loss 46 Gradual visual loss 61 Chapter 4 The red eye One red eye, decreased vision 83 One
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION. Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology
 PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
PUPILS AND NEAR VISION Akilesh Gokul PhD Research Fellow Department of Ophthalmology Iris Anatomy Two muscles: Radially oriented dilator (actually a myo-epithelium) - like the spokes of a wagon wheel Sphincter/constrictor
Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2
 Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2 1 Neurosurgery Department, Hospital de Braga, Braga, Portugal 2 Private Practice, Clínica Neurológica e da Coluna Vertebral, Braga, Portugal Disclosure Funding
Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2 1 Neurosurgery Department, Hospital de Braga, Braga, Portugal 2 Private Practice, Clínica Neurológica e da Coluna Vertebral, Braga, Portugal Disclosure Funding
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Original Article. A 3 Year Review of Cranial Nerve Palsies from the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital Eye Clinic, Nigeria
 Original Article A 3 Year Review of Cranial Nerve Palsies from the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital Eye Clinic, Nigeria Chinyere Nnenne Pedro Egbe, Bassey Fiebai, Elizabeth Akon Awoyesuku
Original Article A 3 Year Review of Cranial Nerve Palsies from the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital Eye Clinic, Nigeria Chinyere Nnenne Pedro Egbe, Bassey Fiebai, Elizabeth Akon Awoyesuku
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy. Bells Palsy in Children
 Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy Definition Bells Palsy in Children Bell palsy is an acute, idiopathic unilateral lower motor neurone facial nerve palsy that is not associated
Guideline for the Management of Acute Peripheral Facial nerve palsy Definition Bells Palsy in Children Bell palsy is an acute, idiopathic unilateral lower motor neurone facial nerve palsy that is not associated
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink
 The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink Introduction We commonly perform nerve conduction studies on three cranial nerves. Two of these, the trigeminal nerve (CN V) and the facial nerve (CN
The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink Introduction We commonly perform nerve conduction studies on three cranial nerves. Two of these, the trigeminal nerve (CN V) and the facial nerve (CN
Complications of Strabismus Surgery
 Complications of Strabismus Surgery Tjeerd de Faber, Martha Tjon Rutger van Ruyven Alexis Damanakis Ondercorrectie Overcorrectie Wat vind je erger? 1 DELLEN Corneal dellen are small areas of thinning associated
Complications of Strabismus Surgery Tjeerd de Faber, Martha Tjon Rutger van Ruyven Alexis Damanakis Ondercorrectie Overcorrectie Wat vind je erger? 1 DELLEN Corneal dellen are small areas of thinning associated
Exotropias: A Brief Review. Leila M. Khazaeni, MD November 2, 2008
 Exotropias: A Brief Review Leila M. Khazaeni, MD November 2, 2008 Exotropia Myths Myth #1 He/she will grow out of it FALSE 75% of XTs show progression over a 3 year period Myth #2 The only treatment choice
Exotropias: A Brief Review Leila M. Khazaeni, MD November 2, 2008 Exotropia Myths Myth #1 He/she will grow out of it FALSE 75% of XTs show progression over a 3 year period Myth #2 The only treatment choice
Diplopia, or double vision, is a frequently encountered. Binocular Diplopia. A Practical Approach ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Practical Approach Janet C. Rucker, MD, and Robert L. Tomsak, MD, PhD Background: Diplopia is a common complaint in both inpatient and outpatient neurologic practice. Its causes are
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Practical Approach Janet C. Rucker, MD, and Robert L. Tomsak, MD, PhD Background: Diplopia is a common complaint in both inpatient and outpatient neurologic practice. Its causes are
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Concussion/MTBI Certification Series. Featuring: Frederick R Carrick, DC, PhD Distinguished Professor of Neurology, Life University
 Concussion/MTBI Certification Series Featuring: Frederick R Carrick, DC, PhD Distinguished Professor of Neurology, Life University Please note that spaces are limited for this specialty certification program.
Concussion/MTBI Certification Series Featuring: Frederick R Carrick, DC, PhD Distinguished Professor of Neurology, Life University Please note that spaces are limited for this specialty certification program.
Neuro-ophthalmology: Disorders of the Efferent Visual Pathway
 neurology Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Neurology Board Review Manual is a peer-reviewed study guide for residents and practicing physicians preparing for board
neurology Board Review Manual Statement of Editorial Purpose The Hospital Physician Neurology Board Review Manual is a peer-reviewed study guide for residents and practicing physicians preparing for board
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Esotropia (Crossed Eye(s))
 Esotropia (Crossed Eye(s)) Esotropia is a type of strabismus or eye misalignment in which the eyes are "crossed," that is, while one eye looks straight ahead, the other eye is turned in toward the nose.
Esotropia (Crossed Eye(s)) Esotropia is a type of strabismus or eye misalignment in which the eyes are "crossed," that is, while one eye looks straight ahead, the other eye is turned in toward the nose.
Neurology. Chapter 6. The Eyes Have It. by Tim Root. Hey, buddy how many fingers am I holding up?
 Chapter 6 Neurology The Eyes Have It I think my patient is faking blindness, but I can t tell. Let me see Hey, buddy how many fingers am I holding up? by Tim Root Definitely malingering. Neurology by Tim
Chapter 6 Neurology The Eyes Have It I think my patient is faking blindness, but I can t tell. Let me see Hey, buddy how many fingers am I holding up? by Tim Root Definitely malingering. Neurology by Tim
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections
 Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Headaches + Facial pain
 Headaches + Facial pain Introduction: Each of us experienced sporadically/ chronically headache 40% worldwide population suffers with severe, disabling headache at least annually Common ailment Presenting
Headaches + Facial pain Introduction: Each of us experienced sporadically/ chronically headache 40% worldwide population suffers with severe, disabling headache at least annually Common ailment Presenting
A Rare Image. Dean M. Cestari, MD Fred Jakobiec, MD Fred Hochberg, MD Joseph F. Rizzo III, MD Rebecca C. Stacy, MD PhD
 A Rare Image Dean M. Cestari, MD Fred Jakobiec, MD Fred Hochberg, MD Joseph F. Rizzo III, MD Rebecca C. Stacy, MD PhD Harvard Neuro-ophthalmology Service Boston, Massachusetts 51 year-old male financial
A Rare Image Dean M. Cestari, MD Fred Jakobiec, MD Fred Hochberg, MD Joseph F. Rizzo III, MD Rebecca C. Stacy, MD PhD Harvard Neuro-ophthalmology Service Boston, Massachusetts 51 year-old male financial
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE
 HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Surgical Outcome Of Incomitant Exotropia In Patients With Partial Third Nerve Palsy
 Surgical Outcome Of Incomitant Exotropia In Patients With Partial Third Nerve Palsy Amit Mohan, MS ; Sudhir Singh, MS ; Dr V.C. Bhatnagar, MS, DNB Dr Amit Mohan, MS Jr.Consultant Global Hospital Institute
Surgical Outcome Of Incomitant Exotropia In Patients With Partial Third Nerve Palsy Amit Mohan, MS ; Sudhir Singh, MS ; Dr V.C. Bhatnagar, MS, DNB Dr Amit Mohan, MS Jr.Consultant Global Hospital Institute
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function
 Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Evaluation of Diplopia: An Anatomic and Systematic Approach
 Clinical Review Article Evaluation of Diplopia: An Anatomic and Systematic Approach Victoria S. Pelak, MD Double vision, or diplopia, is a symptom with many potential causes that can involve many different
Clinical Review Article Evaluation of Diplopia: An Anatomic and Systematic Approach Victoria S. Pelak, MD Double vision, or diplopia, is a symptom with many potential causes that can involve many different
Management of sixth nerve palsy different approaches
 100 Prună et al Management of sixth nerve palsy Management of sixth nerve palsy different approaches Violeta-Ioana Prună 1,4, Ligia Gabriela Tătăranu 3, V.M. Prună 2, Daniela Cioplean 4, R.M. Gorgan 3
100 Prună et al Management of sixth nerve palsy Management of sixth nerve palsy different approaches Violeta-Ioana Prună 1,4, Ligia Gabriela Tătăranu 3, V.M. Prună 2, Daniela Cioplean 4, R.M. Gorgan 3
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 11 - Eye Movements www.tutis.ca/senses/
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 11 - Eye Movements www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 The 5 Types of Eye Movements... 2 The eyes are rotated by 6 extraocular muscles....
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 11 - Eye Movements www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 The 5 Types of Eye Movements... 2 The eyes are rotated by 6 extraocular muscles....
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGY/NEURO-OTOLOGY FELLOWSHIP CORE CURRICULUM
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGY/NEURO-OTOLOGY FELLOWSHIP CORE CURRICULUM A CURRICULUM FOR NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGY Definition and Scope Neuro-ophthalmology focuses on brain and systemic abnormalities
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGY/NEURO-OTOLOGY FELLOWSHIP CORE CURRICULUM A CURRICULUM FOR NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGY Definition and Scope Neuro-ophthalmology focuses on brain and systemic abnormalities
MRI Ordering Guide: MRA/MRV TO SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT: CALL (860) 714-XRAY (714-9729) or FAX REQUISITION TO (860) 714-8002
 SAINT SAINT FRANCIS Hospital and Hospital Medical and Medical Center Center MRI Ordering Guide: MRA/MRV MRA Abdomen AAA (abdominal aortic aneurysm Dissection Mesenteric Ischemia MRA Abdomen With & Without
SAINT SAINT FRANCIS Hospital and Hospital Medical and Medical Center Center MRI Ordering Guide: MRA/MRV MRA Abdomen AAA (abdominal aortic aneurysm Dissection Mesenteric Ischemia MRA Abdomen With & Without
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
MRI EXAM CPT CODE REFERENCE
 I EXAM REFERENCE Use this reference to quickly determine the correct exam for your patients based on the indications described herein and the for the order. Creatine levels should be obtained prior to
I EXAM REFERENCE Use this reference to quickly determine the correct exam for your patients based on the indications described herein and the for the order. Creatine levels should be obtained prior to
Outcome of Surgery for Bilateral Third Nerve Palsy
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Outcome of Surgery for Bilateral Third Nerve Palsy Kazuhiro Aoki, Tatsushi Sakaue, Nobue Kubota and Toshio Maruo Department of Ophthalmology, Teikyo University School of Medicine,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Outcome of Surgery for Bilateral Third Nerve Palsy Kazuhiro Aoki, Tatsushi Sakaue, Nobue Kubota and Toshio Maruo Department of Ophthalmology, Teikyo University School of Medicine,
A Flow Chart For Classification Of Nystagmus
 A Flow Chart For Classification Of Nystagmus Is fixation impaired because of a slow drift, or an intrusive saccade, away from the target? If a slow drift is culprit Jerk Pendular Unidrectional (constant
A Flow Chart For Classification Of Nystagmus Is fixation impaired because of a slow drift, or an intrusive saccade, away from the target? If a slow drift is culprit Jerk Pendular Unidrectional (constant
THYROID DISEASE IN CHILDREN
 THYROID DISEASE IN CHILDREN Douglas G. Rogers, M.D. Center for Pediatric and Adolescent Endocrinology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Unfortunately neither I nor any immediate family members have any financial
THYROID DISEASE IN CHILDREN Douglas G. Rogers, M.D. Center for Pediatric and Adolescent Endocrinology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Unfortunately neither I nor any immediate family members have any financial
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary
 X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the Neurology Rotation
 UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the Neurology Rotation Goals of the Program To acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to assess and provide a management plan for
UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the Neurology Rotation Goals of the Program To acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to assess and provide a management plan for
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Chapter 7 Complex Ocular Motor Disorders in Children
 Chapter 7 Complex Ocular Motor Disorders in Children Introduction A number of complex ocular motility disorders are discussed in this chapter. The diversity of these conditions reflects the need for the
Chapter 7 Complex Ocular Motor Disorders in Children Introduction A number of complex ocular motility disorders are discussed in this chapter. The diversity of these conditions reflects the need for the
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
DOCTOR, MY EYE HURTS BY ADREA R. BENKOFF, M.D.
 DOCTOR, MY EYE HURTS BY ADREA R. BENKOFF, M.D. HISTORY OF THIS EYE PAIN CHARACTER OF PAIN What makes it feel worse? What makes it feel better? Is the pain altered by eye movement? Does the pain begin in
DOCTOR, MY EYE HURTS BY ADREA R. BENKOFF, M.D. HISTORY OF THIS EYE PAIN CHARACTER OF PAIN What makes it feel worse? What makes it feel better? Is the pain altered by eye movement? Does the pain begin in
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia: recovery and plasticity
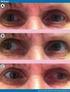 Internuclear ophthalmoplegia: recovery and plasticity M. J. Doslak, L. B. Kline, L. F. Dell'Osso, and R. B. Daroff We studied refixational eye movements of a patient during the gradual resolution of an
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia: recovery and plasticity M. J. Doslak, L. B. Kline, L. F. Dell'Osso, and R. B. Daroff We studied refixational eye movements of a patient during the gradual resolution of an
Disclosure Statement. I have no financial interest in any of material presented today
 The eyes have it PEARLS IN EVALUATION, TREATMENT, AND REFERRAL OF PEDIATRIC OCULAR CONDITIONS AND TRAUMA MICHAEL G. HUNT, MD PEDIATRIC EYE SPECIALISTS, LLP Disclosure Statement I have no financial interest
The eyes have it PEARLS IN EVALUATION, TREATMENT, AND REFERRAL OF PEDIATRIC OCULAR CONDITIONS AND TRAUMA MICHAEL G. HUNT, MD PEDIATRIC EYE SPECIALISTS, LLP Disclosure Statement I have no financial interest
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain
 1. Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain 2. Headache Page - 1 3. International Headache Society International Classification... 4. The Primary Headaches (1-4) Page - 2 5. The Secondary Headaches
1. Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain 2. Headache Page - 1 3. International Headache Society International Classification... 4. The Primary Headaches (1-4) Page - 2 5. The Secondary Headaches
The Normal Neurological Examination
 Normal Neurological Examination 1 of 10 The Normal Neurological Examination Introduction One of the most daunting aspects of the medical examination for the Emergency Physician and the primary care provider
Normal Neurological Examination 1 of 10 The Normal Neurological Examination Introduction One of the most daunting aspects of the medical examination for the Emergency Physician and the primary care provider
Normal CT scan of the chest
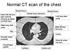 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy
 Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:

![Bell s Palsy ]]> <![CDATA[Bell's Palsy]]> Bell s Palsy ]]> <![CDATA[Bell's Palsy]]>](/thumbs/27/10105461.jpg)