17 : 2. Arup Kumar Kundu, Kolkata ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Sherilyn Hawkins
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 17 : 2 Targets of Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder of unknown aetiology characterized by joint erosion and destruction. It is the most common inflammatory arthritis and is a major cause of disability. Recent advances in understanding the cytokine networks that are responsible for the ongoing inflammatory response, targeted therapy in RA has been attempted. The treatment of RA has been revolutionized by advances in the understanding of disease at cellular as well as molecular level accompanied by the technology to target specific mediators of disease. Targeting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) or interleukin-1 (IL-1) is well established in clinical care of RA patients. However, lack or loss of clinical response occurs in up to 25% of the patients in the long run. New strategies beyond these targets, namely blocking T-cells by abatacept or B-cells by rituximab, have been introduced recently. Current knowledge of different pathogenetic mechanisms of RA has been translated into clinical practice by the scientists. Newer targets are oriented against other interleukins, agents for T-cell or B-cell inhibitions, and small molecule inhibitors with possible peroral administration. This monogram will review the outline of targets of treatment in RA i.e., different cytokine inhibitors and modulators of immune response currently on use or under ongoing clinical trials. Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic, autoimmune, inflammatory disease which primarily targets the synovial tissue. The disease follows a chronic course with substantial disability and morbidity, which results in a shortened life span. RA affects nearly 0.8% of adult population worldwide, and is more common in women (M:F=3:1). As on today, although the precise pathogenesis of RA remains unclear, it has been postulated that multiple exogenous or endogenous antigenic triggers, or both, act in the presence of a background genetic predisposition to initiate a self-perpetuating series of autoimmune responses in the synovial compartment. Many cell populations, including monocytes, macrophages, B-cells, T-cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, participate in the ongoing inflammatory process. 1-3 Cytokines are the key mediators of immune functions. Though RA is a T helper 1 (Th1) predominant state, B-cells have been shown to participate in chronic rheumatoid synovitis; they undergo antigendependent clonal expansion, affinity maturation, and differentiation Arup Kumar Kundu, Kolkata into plasma cells, and produce rheumatoid factor (RF), a wellrecognized prognostic factor for aggressive RA. 2 Hence, the key biologic targets of the currently recommended treatment for RA includes aggressive combination therapy, and use of agents that targets cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1), and B-cells. A fraction of RA patients still remain non-responders to such treatments, however, due to still-undefined mechanisms of resistance. Because of the high prevalence of RA, the clinical impact of this subgroup is important. Early Diagnosis The diagnosis of RA can not be established by a single laboratory test or procedure but is aided by American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria, meticulous physical examination and physician s insight. Joint damage occurs early in the disease process as proved by 30% radiographic bone erosions at the time of diagnosis which increases to 60% by two years, and unfortunately bony erosions and deformities are largely irreversible. Initiation of treatment with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) within three months after the diagnosis of RA is crucial, and thus early diagnosis, although challenging, is critical. ATTRACT (Anti-TNF Therapy in RA with Concomitant Therapy) study encourages use of biologics in early RA. Outline of Current Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Medications that are used to treat RA are divided into three main classes: 1. NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), 2. Corticosteroids 3. DMARDs i. Synthetic (the classical DMARDs) ii. Biologic (biologic response modifiers) NSAIDs and corticosteroids are not within the purview of discussion in this monogram under targeted treatment of RA. Synthetic DMARDs have the potential to reduce or prevent joint damage.
2 Medicine Update 2010 Vol. 20 Table 1 : Biological (targeted) therapies for rheumatoid arthritis currently in use 2 TNF-α inhibitors: Infliximab human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody Etanercept soluble TNF receptors Adalimumab fully humanized monoclonal antibody IL-1 inhibitor Anakinra IL-1 receptor antagonist IL-6 inhibitor Tocilizumab humanized monoclonal anti-il-6 receptor antibody B-lymphocyte depletion Rituximab monoclonal anti-cd20 antibody Co-stimulation blockers Abatacept fusion protein CTLA-4 Ig (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 with immunoglobulin 1) Therefore, early and universal use of DMARDs is fundamental to all current treatment strategies for RA. Commonly used DMARDs are methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, sulphasalazine and leflunomide while infrequently used agents are gold, cyclosporine-a, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, D-penicillamine and minocycline. Synthetic DMARDs are costeffective and widely used. The following 7 biologic response modifiers (Table 1) are now recommended to treat RA. Infliximab (anti-tnf therapy) a chimeric (25% mouse and 75% human) monoclonal antibody dose is 3 mg/kg, I.V infusion at 0, 2 and 6 weeks followed by maintenance dose every 8 weeks thereafter. It should always be used in conjunction with methotrexate (10-25 mg/once a wk) to block the deleterious effects of HACA (human antichimeric antibody; developed after use of infliximab) contraindications: hypersensitivity, active infections (screen for tuberculosis), uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, surgery (withhold for 2 weeks postoperatively) Etanercept (anti-tnf therapy) a fusion protein of p75 soluble TNF receptor with Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1); manufactured from mammalian cells. Etanercept mops out the circulating cytokine dose is 25 mg, S.C twice a week, or 50 mg, S.C once a week. May or may not be co-prescribed with methotrexate contraindications: same as infliximab Adalimumab (anti-tnf therapy) recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody that specifically blocks TNF activity; binds with circulating and cell surface TNF-α dose is 40 mg, S.C, 2 weekly. As it is fully humanized, HACA is not generated. In RA, used as monotherapy or with methotrexate contraindications: hypersensitivity, active infections Anakinra (anti-il-1 therapy) recombinant native human IL-1Ra (receptor antagonist); IL- 1Ra + IL-1 receptor blocks signaling; acts by competitive inhibition of cellular receptors. dose is 100 mg, S.C, daily; used as monotherapy or with methotrexate contraindications: hypersensitivity, active infections Tocilizumab (anti-il-6 therapy) first IL-6 receptor-inhibiting monoclonal antibody developed for the treatment of RA dose is 8 mg/kg, I.V, every 4 weeks given as an I.V infusion over 1 h. Used in combination with methotrexate; indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe RA contraindications: infusion reactions, active infections Rituximab [B-cells (anti-cd20 therapy)] 4 Genetically engineered human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody. A CD20 antagonist and B-cell action depletor dose is 1000 mg per infusion on days 1 and 15 (slow infusion for several hours) with 100 mg I.V methylprednisolone contraindications: hypersensitivity, active infections, severe heart failure Abatacept [T-cells (CTLA-4 Ig)] 5 only co-stimulatory blocking agent (CD80/86) approved by USA. It modulates the immune response by binding to CD80/CD86 on an antigen presenting cell (e.g. dendritic cell), and thereby preventing co-stimulatory binding of CD28 on naive T-cells and attenuating T-cell activation dose is 10 mg/kg, I.V every 2 weekly for 3 doses, followed by every 4 weekly contraindications: hypersensitivity, active infections, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases Adverse reactions of biologic response modifiers: 1. Injection site reactions and infusion reactions. 2. Infections (especially, risk of activation of latent tuberculosis or developing new tuberculosis). 3. Neutropenia, aplastic anaemia. 4. Mild reversible lupus-like syndrome. 5. Congestive cardiac failure. 812
3 Targets of Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis 6. Malignancy (as TNF provides immune surveillance for malignancy). 7. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) positivity. 8. Demyelinating neurological diseases. Targets of Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis 6 Over the past decade, biologicals have been a welcome addition to our armamentarium, biological therapy has become a cornerstone in the treatment of RA with inadequate response to standard DMARDs. As on today, seven approved biological agents are available to the rheumatologists (Table 1). Though biological therapy targeting molecules and cells specific for processes associated with the pathogenesis of RA is very efficient, yet unable to induce remission or even cure in most patients. Every time a novel biological agent emerges in the market, it comes with its own benefits and risks; clinical studies prove their realistic worth in patients with RA and this should be the area of focus. Expanding spectrum of potential therapies is currently being tested in various stages of clinical trials throughout the globe. Guidelines for the use of biologics: must have failed to response with at least 2 DMARDs including methotrexate (20-25 mg/wk) must have active disease have no major infections in preceding 6 months have no malignancies non-pregnant, non-breast feeding women Biological agents are divided into two classes: a. monoclonal antibodies b. small molecules Monoclonal Antibodies To start with, these treatments consisted of chimeric antibodies with human constant regions of light and heavy chain, and the variable murine binding site for the target molecule. In recent years, improved technology has led to a reduction of immunogenicity, and humanized and eventually fully human antibodies were manufactured. These monoclonal antibodies function by neutralizing a target cytokine or its receptor, blocking co-stimulation molecules, and inducing cytolysis, depletion of target cell molecules or apoptosis. a. TNF-α inhibitors infliximab, etanercept and adalimumab are being used for last few years with some success. Two additional TNF-α blocking agents are likely to be approved in 2009 for the treatment of RA are subcutaneously administered golimumab (CNTO148) 7 and certolizumab pegol. Both are humanized monoclonal anti-tnf-α antibody. b. IL-1 inhibitors Anakinra was in the basket, and to simplify the dosing and decrease the risks of local adverse events, a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting IL-1, canakinumab (ACZ885), has been recently developed with promising preliminary results on clinical trials. c. IL-6 inhibitors A humanized monoclonal antibody, tocilizumab, works against IL-6 receptor. 8 There is a favorable benefit-to-risk balance for tocilizumab in combination with methotrexate, and is now approved in the treatment of moderate to severe active RA in adult patients who have either responded inadequately or were intolerant to one or more DMARDs or TNF-α inhibitors. d. IL-15 inhibitor An open, placebo-controlled, double blind study proved the humanized monoclonal antibody against IL-15 (HuMaxIL-15) to be efficient in reduction of bone and cartilage destruction in patients with RA. 9 e. IL-17 inhibitor Production of several pro-inflammatory cytokines e.g., IL-1, IL-6, or TNF-α are increased by IL-17, which also regulates osteoclastogenesis. Th17 cells are the major source of IL-17. Clinical trial of a monoclonal antibody against IL-17 (AIN457) in RA is currently in progress. f. IL-12/IL-23 inhibitor Ongoing clinical trials in RA patients blocking pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-12 (a key inducer of Th1 polarization) and IL-23 (responsible for the proliferation of a Th17 subset of memory T-cells) by a specific monoclonal antibody ustekinumab has generated promising results. Ustekinumab works against the p40 subunit of cytokines IL-12 and IL g. Inhibitors of osteoclastogenesis Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody against receptor activator for nuclear factorkappa B ligand (RANKL), is in phase III clinical trial and is showing promising results in active RA patients by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis when administered subcutaneously at 6 months interval. 11 h. Inhibitors of the TNF superfamily members Clinical trial are on the way with baminercept (BG9924), an inhibitor of LT β (lymphotoxin-β), and belimumab, a fully human monoclonal anti-baff (B-cell activating factor) antibody. Encouraging results are coming out with atacicept (a recombinant fusion protein of BAFF), which shows a depletion of peripheral B-cells as well as decrease in RF and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA) in active RA patients. i. Inhibitors of chemokines and angiogenesis 12 It is wellknown that angiogenesis occurs in early part of RA and results in migration of inflammatory cells into the synovium. Bevacizumab, a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), is under trial. j. Apoptosis regulators 13 The Fas receptor (FasR) is the most intensely studied death receptor. Cells from synovial tissue of RA patients are resistant to apoptosis, and thus ac- 813
4 Medicine Update 2010 Vol. 20 tivated synovial fibroblasts may escape the effects of biologics. The first monoclonal anti-fas IgM antibody (ARG098) is under clinical trial (intra-articular injection) in patients with RA. Researchers opine that effects of methotrexate, sulphasalazine and infliximab in RA patients might be mediated by apoptosis. k. T-cell inhibitors A fusion protein CTLA-4 Ig (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 with immunoglobulin 1), abatacept, is the first in a new class of drugs known as costimulation blockers, is safe and efficacious and received approval for treating patients with RA. Currently clinical trials targeting T-cells are ongoing with alemtuzumab (anti-cd52), keliximab (chimeric monoclonal anti-cd4 antibody) or clenoliximab (the IgG4 version of the previous antibody), which showed severe lymphocytopenia and skin rash leading to discontinuation of the trials. l. B-cell inhibitors 14 Rituximab (monoclonal anti-cd20 antibody) is safe and received approval for treatment in patients with active RA. Clinical trials are on progress with encouraging results by ocrelizumab (a humanized monoclonal antibody), and ofatumumab (anti-cd20), in patients refractory to both methotrexate and TNF-α blockers. Small Molecules 15 The remarkable scientific advance and benefit of biologic therapies, particularly the TNF-α inhibitors is undisputed. It is observed that approximately 25-40% patients of RA fail to achieve ACR 70 response. Moreover, primary and secondary resistance to biologics is noted in a significant group of patients. Considering these facts, the future development of TNF antagonists is focusing on small molecule inhibitors. The molecular weights of small molecules do not exceed 1kDa. The goal of this approach is to develop orally effective agents with increased selectivity rather than generalized TNF blockade, where the agents should be efficacious as biological therapy, less expensive, and with a reduced risk of adverse effects. Currently, there are a significant number of these drugs in the pipeline for treatment of rheumatic diseases. a. Inhibitors of intracellular signaling molecules Binding of an extracellular factor (e.g. a cytokine) to a cell-surface receptor activates cytoplasmic kinases [mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38, JNK, ERK kinases) or tyrosin kinases (JAK, Syk)], which can regulate expression of target genes by modulating the activity of transcription factors. b. Inhibitors of MAP (mitogen activated protein) kinase p38 pathway Researchers are trying to develop inhibitors of MAP kinase p38 that predominantly impact its alpha subunit and are mostly in phase II clinical trials. c. Inhibitors of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway 16 Tyrosine Janus kinases (JAK) can be activated by interferon γ and other cytokines responsible for the pathogenesis of RA. The different pharmaceuticals are trying to develop a JAK3 inhibitor (CP-690,550); it is in phase II clinical trial and the results are encouraging. d. Inhibitor of Syk kinase 17 Intracellular Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) has significant immunomodulatory activity. Use of Fostamatinib disodium (a Syk kinase inhibitor) has produced promising results by reducing disease activity in RA patients with 12 weeks of peroral administration of 150 mg of the drug twice a day. e. Inhibitors of transcription factors Antagonists of transcription factor NF-κB (nuclear factor κb) activation are under study. f. Inhibitor of cytokines and chemokines Small molecule IL-12/IL-23 inhibitor (Apilimod mesylate) is under trial and decreases several pro-inflammatory cytokines and progression of RA. g. Inhibitors of cell surface markers RhuDex is a small molecule blocking the CD80 marker on antigen presenting cells and was used in clinical trials. The study was discontinued in 2008 due to death of a volunteer. CONCLUSION 18 An upcoming knowledge of the pathogenesis of autoimmune inflammatory disorders has expanded the spectrum of new molecules and therapeutic targets of RA. The promising therapeutic strategies of recent years are small molecules which are mostly inhibitors of intracellular signaling pathways with an advantage of peroral administration. Other targets in future for treatment of RA are regulatory T cells (Treg cells), innate immune system, Toll like receptors, 19 RNA interference or epigenetic alterations, 20 complement pathway mediated by C5a or adipokines (visfatin/ PBEF). Anti-IL-12 antibodies, protein-a immunoabsorption column and Alpha V Beta 3 Integrin are some other modalities under trial. Gene therapy in RA at present remains experimental. With the help of these newer drugs, the future may well see rheumatologists talking not about symptomatic relief but potential cure for RA. References 1. Vital EM, Emery P. The development of targeted therapies in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Autoimmunity 2008; 31: Okamoto H, Hoshi D, Kiire A, et al. Molecular targets of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation & Allergy - Drug Targets 2008; 7: Koller MD. Targeted therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Wien Med Wochenschr 2006; 156: Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: Buch M, Boyle D, Saleem B, et al. The selective co-stimulation modulator abatacept decreases synovial inflammation and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52 (Suppl): S Senolt L, Vencovsky J, Pavelka K, et al. Perspective new biological therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 2009 [Epub ahead of print]. 7. Kay J, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B, et al. Golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite treatment with methotrexate: a ran- 814
5 Targets of Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis domized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arthritis Rheum 2008, 58: Fonseca JE, Santos MJ, Canhao H, et al. Interleukin-6 as a key player in systemic inflammation and joint destruction. Autoimmun Rev 2009 [Epub ahead of print]. 9. Baslund B, Tvede N, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, et al. Targeting interleukin-15 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a proof-of-concept study. Arthritis Rheum 2005, 52: Leonardi CL, Kimball AB, Papp KA, et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 76-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 1). Lancet 2008, 17; 371: Cohen SB, Dore RK, Lane NE, et al. Denosumab treatment effects on structural damage, bone mineral density, and bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis: a twelve-month, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum 2008, 58: Grothey A, Ellis LM. Targeting angiogenesis driven by vascular endothelial growth factors using antibody-based therapies. Cancer J 2008, 14: Pope RM. Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology 2002; 2: Salvatore De Vita, Francesco Zaja, Stefania Sacco. Efficacy of Selective B Cell Blockade in the Treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46: Stanczyk J, Ospelt C, Gay S. Is there a future for small molecule drugs in the treatment of rheumatic diseases? Curr Opin Rheumatol 2008, 20: Walker JG, Smith MD. The Jak-STAT pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2005, 32: Weinblatt ME, Kavanaugh A, Burgos-Vargas R, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a syk kinase inhibitor: A twelve-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2008, 58: Tarner IH, Müller-Ladner U, Gay S. Emerging targets of biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2007, 3: Ospelt C, Kyburz D, Pierer M, et al. Toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis joint destruction mediated by two distinct pathways. Ann Rheum Dis 2004, 63 Suppl 2: ii90-ii Huber LC, Stanczyk J, Jüngel A, et al. Epigenetics in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum 2007, 56:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
Immune modulation in rheumatology. Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association
 Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists
 Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists 1. Which of the following matches of biologic targets that contribute to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and
Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists 1. Which of the following matches of biologic targets that contribute to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Outline. Treatment Goal 4/10/2013. Clinical evaluation New treatment options Future research Discussion
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Evidence-based Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (2009)
 CPLD reviews its distance learning programmes every twelve months to ensure currency. This update has been produced by an expert and should be read in conjunction with the Evidencebased Management of distance
CPLD reviews its distance learning programmes every twelve months to ensure currency. This update has been produced by an expert and should be read in conjunction with the Evidencebased Management of distance
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC)
 BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) September 2014 Review date: September 2017 Bulletin 203: Tocilizumab (subcutaneous) in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy for the treatment
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) September 2014 Review date: September 2017 Bulletin 203: Tocilizumab (subcutaneous) in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy for the treatment
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bonita S. Libman, M.D.
 The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
Biologic Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the New Millennium. Neal I. Shparago, D.O., FACP, FACR
 Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the New Millennium Neal I. Shparago, D.O., FACP, FACR What is RA? Symmetric inflammatory polyarthritis Rheumatoid factor positive in 80% Anti-CCP positive in approximately
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the New Millennium Neal I. Shparago, D.O., FACP, FACR What is RA? Symmetric inflammatory polyarthritis Rheumatoid factor positive in 80% Anti-CCP positive in approximately
påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã==
 påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã== adalimumab 40mg pre-filled syringe for subcutaneous injection (Humira ) No. (218/05) Abbott New indication: treatment of active and progressive psoriatic arthritis in adults
påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã== adalimumab 40mg pre-filled syringe for subcutaneous injection (Humira ) No. (218/05) Abbott New indication: treatment of active and progressive psoriatic arthritis in adults
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Update 2014 Mark Hulsey, MD FACR Rheumatoid Arthritis Key Features Symptoms >6 weeks duration Often lasts the remainder of the patient s life Inflammatory synovitis Palpable synovial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Update 2014 Mark Hulsey, MD FACR Rheumatoid Arthritis Key Features Symptoms >6 weeks duration Often lasts the remainder of the patient s life Inflammatory synovitis Palpable synovial
In the last decade, there have been major changes in the
 233 Promising New Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis The Kinase Inhibitors Yusuf Yazici, M.D., and Alexandra L. Regens, B.A. Abstract Three major advances over the last decade have impacted the way we
233 Promising New Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis The Kinase Inhibitors Yusuf Yazici, M.D., and Alexandra L. Regens, B.A. Abstract Three major advances over the last decade have impacted the way we
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist
 Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped?
 Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped? Robert L. DiGiovanni, DO, FACOI Program Director Largo Medical Center Rheumatology Fellowship [email protected] Do not pour strange medicines
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped? Robert L. DiGiovanni, DO, FACOI Program Director Largo Medical Center Rheumatology Fellowship [email protected] Do not pour strange medicines
Speaking Plainly. Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis
 in association with Plain English Campaign Speaking Plainly Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis A guide to help healthcare professionals talking to patients with rheumatoid arthritis Foreword
in association with Plain English Campaign Speaking Plainly Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis A guide to help healthcare professionals talking to patients with rheumatoid arthritis Foreword
ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd
 ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd 07 February 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd 07 February 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Swedish Society of Rheumatology, April 14, 2011
 Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Swedish Society of Rheumatology, April 14, 2011 Working party: Eva Baecklund, Helena Forsblad d Elia, Carl Turesson Background Our purpose
Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Swedish Society of Rheumatology, April 14, 2011 Working party: Eva Baecklund, Helena Forsblad d Elia, Carl Turesson Background Our purpose
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis While rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been feared as one of the most disabling types of arthritis, the outlook has dramatically improved for many newly diagnosed patients. Certainly
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Constantly Evolving Treatment Approaches
 Rheumatoid Arthritis: Constantly Evolving Treatment Approaches Jody Garry, Pharm.D. Primary Care Pharmacy Resident VA Medical Center - Iowa City Presentation Overview Pathophysiology & epidemiology Diagnostic
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Constantly Evolving Treatment Approaches Jody Garry, Pharm.D. Primary Care Pharmacy Resident VA Medical Center - Iowa City Presentation Overview Pathophysiology & epidemiology Diagnostic
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Immunosuppressive drugs
 Immunosuppressive drugs RJM ten Berge Afd. Inw. Geneeskunde AMC contents overview targets mechanism of action Effects on immune capacity measured by responses to vaccination Immune response 1 calcineurin
Immunosuppressive drugs RJM ten Berge Afd. Inw. Geneeskunde AMC contents overview targets mechanism of action Effects on immune capacity measured by responses to vaccination Immune response 1 calcineurin
subcutaneous initially every 4 weeks then every 12 weeks Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 02/24/2010
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Humira (adalimumab subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Humira (adalimumab subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
Media Release. Basel, 11 June 2009. RA patients with enhanced response identified
 Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease RA Final.indd 2 15. 6. 10. 11:23 Understanding what to expect can help you prepare for your transition into treatment. Rheumatoid Arthritis What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid
DISEASE-MODIFYING ANTIRHEUMATIC DRUG THERAPY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 DISEASE-MODIFYING ANTIRHEUMATIC DRUG THERAPY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS APPLICATIONS OBJECTIVE Purpose of Measure: ELIGIBLE POPULATION Which members are included? STANDARD OF CARE NCQA APPROVED CODES HEDIS
DISEASE-MODIFYING ANTIRHEUMATIC DRUG THERAPY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS APPLICATIONS OBJECTIVE Purpose of Measure: ELIGIBLE POPULATION Which members are included? STANDARD OF CARE NCQA APPROVED CODES HEDIS
Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy
 Media Release Basel, 6 June 2012 Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy Roche (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY) today announced
Media Release Basel, 6 June 2012 Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy Roche (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY) today announced
SYNOPSIS. 2-Year (0.5 DB + 1.5 OL) Addendum to Clinical Study Report
 Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Name of Finished Product: Abatacept () Name of Active Ingredient: Abatacept () Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier (For National Authority Use
Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Name of Finished Product: Abatacept () Name of Active Ingredient: Abatacept () Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier (For National Authority Use
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
DU maladies systémiques Biothérapies des maladies systémiques Le 25 mai 2012
 DU maladies systémiques Biothérapies des maladies systémiques Le 25 mai 2012 10h-10h10 10h10-10h40 10h40-11h10 11h10-11h40 11h40-12h10 12h10-12h40 -Introduction : Luc Mouthon -Immunoglobulines intraveineuses
DU maladies systémiques Biothérapies des maladies systémiques Le 25 mai 2012 10h-10h10 10h10-10h40 10h40-11h10 11h10-11h40 11h40-12h10 12h10-12h40 -Introduction : Luc Mouthon -Immunoglobulines intraveineuses
How To Choose A Biologic Drug
 North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
Patient Input Information Clinical Trials Outcomes Common Drug Review
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION USTEKINUMAB (Stelara Janssen Inc.) Indication: Psoriatic Arthritis Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that ustekinumab not be listed at the submitted
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION USTEKINUMAB (Stelara Janssen Inc.) Indication: Psoriatic Arthritis Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that ustekinumab not be listed at the submitted
ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 Review Article ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS M JOSHI* Our understanding of the pathology and management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has evolved significantly over last two decades.
Review Article ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS M JOSHI* Our understanding of the pathology and management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has evolved significantly over last two decades.
Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab)
 Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab) Effective Date: 5/1/08 Committee Review Date: 1/6/01, 9/18/01, 1/15/02, 1/7/03, 1/20/04, 1/18/05, 12/7/05, 10/15/06, 7/2/07, 11/5/07, 3/25/08 Policy Statements:
Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab) Effective Date: 5/1/08 Committee Review Date: 1/6/01, 9/18/01, 1/15/02, 1/7/03, 1/20/04, 1/18/05, 12/7/05, 10/15/06, 7/2/07, 11/5/07, 3/25/08 Policy Statements:
Commercial Insight: Disease Modification in Rheumatoid Arthritis - Market awaits game changing therapies and strategies
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1504775/ Commercial Insight: Disease Modification in Rheumatoid Arthritis - Market awaits game changing therapies and strategies
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1504775/ Commercial Insight: Disease Modification in Rheumatoid Arthritis - Market awaits game changing therapies and strategies
9/16/2014. Anti-Immunoglobulin E (IgE) Omalizumab (Xolair ) Dosing Guidance
 Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest New Therapies for Asthma Including Omalizumab and Anti-Cytokine Therapies Marsha Dangler, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist James H. Quillen VA Medical
Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest New Therapies for Asthma Including Omalizumab and Anti-Cytokine Therapies Marsha Dangler, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist James H. Quillen VA Medical
Let s talk about Arthritis
 Let s talk about Arthritis Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis Kam Shojania, MD, FRCPC Clinical Professor and Head, St. Paul s, UBC and VGH Divisions of Rheumatology Slides with thanks to: Cheryl Koehn
Let s talk about Arthritis Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis Kam Shojania, MD, FRCPC Clinical Professor and Head, St. Paul s, UBC and VGH Divisions of Rheumatology Slides with thanks to: Cheryl Koehn
Specialty DRUGS. For Decision Makers in Managed Care Supplement 1 2011. Focus on. Rheumatoid Arthritis
 For Decision Makers in Managed Care Supplement 1 2011 Specialty DRUGS Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis contents Departments Features 3 Editorial by Kjel A. Johnson, PharmD, Publisher Five points to consider
For Decision Makers in Managed Care Supplement 1 2011 Specialty DRUGS Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis contents Departments Features 3 Editorial by Kjel A. Johnson, PharmD, Publisher Five points to consider
Inflammation, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cytokines
 Inflammation, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cytokines Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the commonest inflammatory joint disease with considerable morbidity and mortality. Conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic
Inflammation, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cytokines Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the commonest inflammatory joint disease with considerable morbidity and mortality. Conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic
CLINICAL POLICY Department: Medical Management Document Name: Rheumatoid & Juvenile Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatments
 Page: 1 of 18 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
Page: 1 of 18 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
Disclosures. Consultant and Speaker for Biogen Idec, TEVA Neuroscience, EMD Serrono, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Genzyme, Accorda Therapeutics
 Mitzi Joi Williams, MD Neurologist MS Center of Atlanta, Atlanta, GA Disclosures Consultant and Speaker for Biogen Idec, TEVA Neuroscience, EMD Serrono, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Genzyme, Accorda Therapeutics
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD Neurologist MS Center of Atlanta, Atlanta, GA Disclosures Consultant and Speaker for Biogen Idec, TEVA Neuroscience, EMD Serrono, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Genzyme, Accorda Therapeutics
Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 THE RHEUMATOID IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL VOL.12, NO. 3,2013 Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahmed A. Al-Hassan*, Mohammed O. Hamzah**,
THE RHEUMATOID IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL VOL.12, NO. 3,2013 Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahmed A. Al-Hassan*, Mohammed O. Hamzah**,
Rheumatoid Arthritis Information
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Information Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs. Alternative
Rheumatoid Arthritis Information Definition Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs. Alternative
Once the immune system is triggered, cells migrate from the blood into the joints and produce substances that cause inflammation.
 HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
Shared care protocol for the management of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
 Tameside Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and NHS Tameside and Glossop Shared care protocol for the management of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
Tameside Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and NHS Tameside and Glossop Shared care protocol for the management of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
BIOLOGICS IN RHEUMATOLOGY 2012
 BIOLOGICS IN RHEUMATOLOGY 2012 13 : 5 Alakendu Ghosh, Kolkata Introduction The term biologics have been used as a collective term for biological therapies. Therapeutic agents with biologic properties,
BIOLOGICS IN RHEUMATOLOGY 2012 13 : 5 Alakendu Ghosh, Kolkata Introduction The term biologics have been used as a collective term for biological therapies. Therapeutic agents with biologic properties,
Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs
 Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs By Rachel A. Burke, Pharm.D., BCACP; and Nicole D. White, Pharm.D. Reviewed by Jessica F. Farrell, Pharm.D.; Benita E. Galloway, Pharm.D., BCPS; and Heather
Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs By Rachel A. Burke, Pharm.D., BCACP; and Nicole D. White, Pharm.D. Reviewed by Jessica F. Farrell, Pharm.D.; Benita E. Galloway, Pharm.D., BCPS; and Heather
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics
 REVIEW Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics Paul P Tak 1 * and Joachim R Kalden 2 Abstract Treatment of inflammatory arthritides including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and
REVIEW Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics Paul P Tak 1 * and Joachim R Kalden 2 Abstract Treatment of inflammatory arthritides including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and
MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Dr Malkit S Riyat. MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nicole Klett,, M.D.
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Nicole Klett,, M.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Primarily targets the synovium of diarthrodial joints Etiology likely combination genetic and environmental Diarthrodial
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital
 Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Dr Sarah Levy Consultant Rheumatology Croydon University Hospital Contents Definition/ epidemiology Diagnosis Importance of early diagnosis/ treatment Guidelines Evidence based treatment protocol Current
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work
 Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
Fabiola Atzeni, Maurizio Benucci, Salvatore Sallì, Sara Bongiovanni, Laura Boccassini, Piercarlo Sarzi-Puttini
 ÔØ Å ÒÙ Ö ÔØ Different effects of biological drugs in rheumatoid arthritis Fabiola Atzeni, Maurizio Benucci, Salvatore Sallì, Sara Bongiovanni, Laura Boccassini, Piercarlo Sarzi-Puttini PII: S1568-9972(12)00278-9
ÔØ Å ÒÙ Ö ÔØ Different effects of biological drugs in rheumatoid arthritis Fabiola Atzeni, Maurizio Benucci, Salvatore Sallì, Sara Bongiovanni, Laura Boccassini, Piercarlo Sarzi-Puttini PII: S1568-9972(12)00278-9
biologics for the treatment of psoriasis
 How to contact us The Psoriasis Association Dick Coles House 2 Queensbridge Northampton NN4 7BF tel: 08456 760 076 (01604) 251 620 fax: (01604) 251 621 email: [email protected] www.psoriasis-association.org.uk
How to contact us The Psoriasis Association Dick Coles House 2 Queensbridge Northampton NN4 7BF tel: 08456 760 076 (01604) 251 620 fax: (01604) 251 621 email: [email protected] www.psoriasis-association.org.uk
Top Down vs. Step Up Therapy Biologics in IBD: Treatment Algorithms. Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago
 Top Down vs. Step Up Therapy Biologics in IBD: Treatment Algorithms Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago Treatment Goals c.2008 Induce and maintain response/remission Prevent complications Disease
Top Down vs. Step Up Therapy Biologics in IBD: Treatment Algorithms Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago Treatment Goals c.2008 Induce and maintain response/remission Prevent complications Disease
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS.
 TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
Treatment trends of rheumatoid arthritis in Japan: Changes toward globalization and its unique innovation
 Inflammation and Regeneration Vol.31 No.1 January 2011 25 Review Article Treatment trends of rheumatoid arthritis in Japan: Changes toward globalization and its unique innovation Nobuyuki Miyasaka* Department
Inflammation and Regeneration Vol.31 No.1 January 2011 25 Review Article Treatment trends of rheumatoid arthritis in Japan: Changes toward globalization and its unique innovation Nobuyuki Miyasaka* Department
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
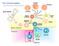 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
REFERENCE CODE GDHC503DFR PUBLICAT ION DATE DECEMBER 2014 METHOTREXATE (RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS) - FORECAST AND MARKET ANALYSIS TO 2023
 REFERENCE CODE GDHC503DFR PUBLICAT ION DATE DECEMBER 2014 METHOTREXATE (RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS) - Executive Summary The table below provides the key metrics for Methotrexate in the 10MM (US, France, Germany,
REFERENCE CODE GDHC503DFR PUBLICAT ION DATE DECEMBER 2014 METHOTREXATE (RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS) - Executive Summary The table below provides the key metrics for Methotrexate in the 10MM (US, France, Germany,
Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis
 Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of Issued: August 2010 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta199 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation at NICE to
Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of Issued: August 2010 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta199 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation at NICE to
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES
 ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HANDBOOK PRIOR AUTHORIZATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL SERVICES `I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Cytokine and CAM Antagonists
 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK `I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Cytokine and CAM Antagonists A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization All prescriptions for Cytokine and CAM Antagonists must
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE HBOOK `I. Requirements for Prior Authorization of Cytokine and CAM Antagonists A. Prescriptions That Require Prior Authorization All prescriptions for Cytokine and CAM Antagonists must
Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit
 Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit Qualitative research proposal to explore factors influencing acceptable risk thresholds used to recommend particular treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit Qualitative research proposal to explore factors influencing acceptable risk thresholds used to recommend particular treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis.
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Infl ectra for rheumatoid arthritis
 Infl ectra for rheumatoid arthritis Some important information to get you started with your treatment This booklet is intended only for use by patients who have been prescribed Inflectra. Introduction
Infl ectra for rheumatoid arthritis Some important information to get you started with your treatment This booklet is intended only for use by patients who have been prescribed Inflectra. Introduction
Pain is the most common complaint for which most patients seek rheumatologic. Chronic Pain From Rheumatoid Arthritis
 PRINTER-FRIENDLY VERSION AVAILABLE AT PAINMEDICINENEWS.COM Chronic Pain From Rheumatoid Arthritis ROLAND STAUD, MD Director, Musculoskeletal Pain Research Professor University of Florida College of Medicine
PRINTER-FRIENDLY VERSION AVAILABLE AT PAINMEDICINENEWS.COM Chronic Pain From Rheumatoid Arthritis ROLAND STAUD, MD Director, Musculoskeletal Pain Research Professor University of Florida College of Medicine
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Treatment of Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Zhanguo Li Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, People s Hospital Beijing University Medical School, China Contents Background Challenges Treatment strategies
Page 1 of 15 Origination Date: 09/14 Revision Date(s): 10/2015, 02/2016 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 10/28/2015
 Moda Health Plan, Inc. Medical Necessity Criteria Subject: Actemra (tocilizumab) Page 1 of 15 Origination Date: 09/14 Revision Date(s): 10/2015, 02/2016 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 10/28/2015
Moda Health Plan, Inc. Medical Necessity Criteria Subject: Actemra (tocilizumab) Page 1 of 15 Origination Date: 09/14 Revision Date(s): 10/2015, 02/2016 Developed By: Medical Criteria Committee 10/28/2015
A Survey of Barriers to Treatment Access in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Survey of Barriers to Treatment Access in Rheumatoid Arthritis in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK October 2009 Funding for this report was provided by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd Carolin Miltenburger,
A Survey of Barriers to Treatment Access in Rheumatoid Arthritis in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK October 2009 Funding for this report was provided by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd Carolin Miltenburger,
