BIOLOGICS IN RHEUMATOLOGY 2012
|
|
|
- Silvia White
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOLOGICS IN RHEUMATOLOGY : 5 Alakendu Ghosh, Kolkata Introduction The term biologics have been used as a collective term for biological therapies. Therapeutic agents with biologic properties, including monoclonal antibodies and soluble cytokine receptors have been in use against rheumatic diseases for some time now. Treatment of rheumatic diseases has undergone a remarkable change over the last 10 years. This can be credited to an increased understanding of the immune system and the mechanisms and causes of rheumatic diseases which has enabled us to treat the underlying cause aggressively and early. The use of biologics has become essential along with DMARDs in treatment of autoimmune diseases. The success of early biologics, especially etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, has strongly influenced researcher and manufacturers to develop a new generation of biologic agents that inhibit cytokine behavior, cellular activation and inflammatory gene transcription by various means. Some of these novel therapies in development are not antibodies, soluble receptors or natural antagonists, but are rather small molecules that specifically inhibit intracellular, cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions intrinsic to systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Therefore, the term biologic therapies may better be replaced with a more accurate term, such as biologic response modifier or targeted therapy that differentiates these finely tuned immunomodulators and anti-inflammatory agents from less specific immunosuppressive drugs such as cytotoxic agents and corticosteroids. Till date with biologics The use of biologic agents has revolutionized the treatment of rheumatic diseases overall. Early aggressive therapy and tight control seem to produce significant positive outcomes in patients. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: The introduction of agents that inhibited the key proinflammatory cytokine, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), ushered in a new era in the treatment of RA in the late 1990s. TNF inhibitors and B-cell inhibitors are approved in many other countries for the treatment of RA and a number of other autoimmune systemic inflammatory conditions: (1) etanercept, which is a soluble TNF receptorimmunoglobulin IgG Fc fusion construct; (2) infliximab, which is a chimeric anti-tnf monoclonal antibody (mab); (3) adalimumab, which is a human anti-tnf mab; (4) certolizumab pegol, which is a PEGylated Fab fragment of a humanized mab; and (5) golimumab, which is a human anti-tnf mab and (6) rituximab, a CD-20 receptor inhibitor mab. Recently, IL-6 inhibitor (Tocilizumab) and CTLA 4 blockers (Abatacept) have been also quite successfully being used in RA. The success of these agents has not only provided an opportunity to achieve better outcomes for patients with RA, but it also has had a dramatic impact on the overall approach to the treatment of RA and the goals of therapy. However, approximately 30-40% of patients with established disease fail to respond to TNF-α antagonists and the majority of those that respond initially do not achieve complete remission. 1 Concerns have also been raised about the short- and long-term tolerability of these agents. 659
2 Medicine Update 2012 Vol. 22 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) involves aberrancy in multiple components of the immune system including B cells, T cells, cytokines and growth factors. Therapeutic agents targeting these mediators selectively have been tested for the treatment of SLE. The two large phase 3 trials of belimumab, the monoclonal antibody against B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), showed significant clinical benefit. Response rates were 57.6 and 43.2% for 10 mg/kg belimumab, compared with 43.6 and 33.8% for placebo in BLISS-52 and BLISS-76, respectively. On the contrary, large phase 2/3 randomized placebo-controlled trials of B-cell depletion, using anti-cd20 antibody, rituximab, in SLE, reported unexpected negative results. Studies of a costimulation blocker (abatacept), tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (infliximab), and interleukin-6 inhibitor (tocilizumab) also showed either negative results or were associated with high rates of adverse events. Studies of T cell and interferon inhibition remain in the early developmental phase. However, a recent multicenter double blind placebo controlled study was conducted using a fully human anti-ifn α monoclonal antibody, sifalimumab, with fairly positive non-adverse results. 2 SPONDYLOARTHRITIS The spondyloarthritis (SpAs) have five subtypes: ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, and major parts of the arthritis and spondylitis spectrum associated with psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, undifferentiated SpA. Ankylosing spondylitis is the most frequent subtype of SpA, more prevalent than undifferentiated SpA. Based on the high prevalence of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis is also quite frequent, whereas reactive arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease are relatively rare. Therapeutic options for more severe forms of spondyloarthritis have been rather limited in the last decade. From accumulating evidences it is evident that anti-tnf therapy is the most suitable for treating spondyloarthritis. Unlike rheumatoid arthritis, where DMARDs are an effective measure for treatment, in spondyloarthritis specially in Ankylosing spondylitis DMARDs can offer no remedy to severely affected patients. Therefore, anti-tnf could be the first line of defence in such patients. ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS The TNF-α blockers are biologic medications that have shown great promise in treating ankylosing spondylitis. They have been shown to be highly effective in treating not only the arthritis of the joints but the spinal arthritis associated with ankylosing spondylitis and related diseases. In the open pilot study performed in Berlin, Germany, infliximab in a dosage of 5 mg/kg improved the disease activity of patients with severe ankylosing spondylitis, with short mean disease duration of 5 years. Nine of 10 patients showed an improvement of greater than 50% in disease activity as measured by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI); the median improvement of the BASDAI after 4 weeks was 70%. The efficacy of infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis has been proved from a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial performed in Germany, a highly significant effect of infliximab treatment (5 mg/kg body weight given at weeks 0, 2, and 6), with the primary outcome parameter of a 50% improvement of disease activity (BASDAI), was achieved in 53% of the patients treated with infliximab compared with 8% on placebo. Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with the soluble TNFα receptor, etanercept, has now been studied to a larger extent. The primary outcome parameter was a 50% or greater improvement of the BASDAI. Treatment with etanercept resulted in a 50% regression of disease activity in 57% of these patients, versus 6% on placebo at week 6 (P = 0.004). Large trials with this drug are in progress. PSORIASIS Currently six biologics are approved for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis treatment and are being used regularly, viz., etarnercept, adalimumab, infliximab, alefacept, golimumab and ustekinumab. There are strong evidences that both etanercept and infliximab work in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. At the end of 12 weeks, 87% of patients in the etanercept group had achieved a Psoriatic Arthritis Response Criteria response, compared with 26% in the placebo group. In another study with infliximab, patients achieved a 20% improvement according to the American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20) in all patients by week 2, 8 patients improved 70% (ACR70) at week 10; 6 patients maintained this level of improvement after week 54. At week 10, MRI revealed an 82.5% mean reduction in inflammation from baseline. Taken together, both agents seem to work favorably in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Even as these biologics transform many lives, others continue to suffer. Some patients cannot access these treatments due to their high cost and/or insurance coverage issues; some are precluded from using them due to preexisting conditions (TB, HIV, cancer, etc.); some are concerned about side effects or long term uncertainties; and some are simply not aware of these new treatments. For still others, their first try with a biologic does not work. After all, no biologic can work in 100% of cases. New emergences In the past, any improvement with treatment was considered good; however, now there is a growing interest in maintaining a tight control and achieving as low a disease state as possible. Most of the above discussed biologics rarely result in disease 660
3 Biologics in Rheumatology 2012 remission and provide clinical benefits in some sporadic cases of rheumatic diseases. Therefore, alternative therapies are needed and inhibitions of small molecules like kinases, transcription factors, chemokines etc were the most suitable targets. However, issues remain in regard to how to predict who will respond to which agents and how to monitor disease activity while using these agents. Looking to the future, biosimilars (or generic biologics) and a number of new small molecules are being developed that may have an important impact on the treatment. BIOSMILARS Biosimilars is the term used for generic versions of biologic agents. These biologic agents are often manufactured in cell lines, and thus are subject to modifications -- such as glycosylation -- that may potentially alter the efficacy and safety of the product. There are examples of biologic agents with identical primary sequences in which changes in the manufacturing processes have led to important differences in safety and efficacy. A multicenter observational before-after study with Etanar, a recombinant TNF receptor: Fc fusion protein has been shown to be effective in suppressing disease activity in patients with RA who fail to respond to DMARDs. 3 Etanar can effectively control disease activity in real-life patients with active RA and poor responses to not only MTX but also other DMARDs. Introduction of biosimilars requires a specifically designed pharmacovigilance plan. In order to be released to the public, biosimilars must be shown to be as close to identical to the parent biological product based on data compiled through clinical, animal and analytical studies. Moreover, it is difficult and costly to recreate biologics because the complex proteins are derived from living organisms that are genetically modified. In contrast, small molecule drugs made up of a chemically based compound can be easily replicated, orally administered to patients and are considerably less expensive to reproduce. Therefore, research and development of small molecule therapeutic targets was the need of the hour. SMALL MOLECULES Inhibition of T-Cell Co stimulatory Pathways Binding of a T-cell surface co stimulatory molecule with its ligand expressed on the surface of an antigen-presenting cell (APC) provides a second signal to the T cell in addition to the signal generated from T cell receptor (TCR) recognition of antigen-mhc complex. The second, co stimulatory signal promotes T cell activation in response to antigen recognition. In the absence of co stimulatory signals, T-cell responsiveness is impaired. The possible roles of the various co stimulatory pathways like including the CD40-CD40 ligand (CD-40L), CD28- CTLA4-B7, CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1)-intracellular adhesion molecule-1, OX40 (CD134)-OX40L and CD2-LFA3 pathways has been reviewed in autoimmune disease. CTLA4 Immunoglobulin The B7 family of cell surface molecules delivers stimulatory signals to T cells through interaction with a common ligand, CD28, present on T-cell surfaces and suppressive signals through binding with T-cell surfaceexpressed CTLA4 (CD154). A soluble chimeric molecule, CTLA4 immunoglobulin has been developed to inhibit T-cell costimulation by B7-family molecules. CTLA4 immunoglobulin consists of the extracellular component of CTLA4 fused to human IgG Fc. The affinity of CTLA4 for B7 molecules is greater than the affinity of CD28, permitting CTLA4 immunoglobulin to prevent B7-mediated CD28 signaling. Costimulatory blockade has also been considered in the management of chronic plaque psoriasis, RA and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Anti-CD40 Ligand Monoclonal Interaction between CD40 on APC surfaces and its ligand on T-cell surfaces, CD40L, generates c-stimulatory signals for T-cell activation. This ligand-receptor pair also induces B-cell proliferation and formation of germinal centers when CD40L present on activated T cells binds CD40 expressed on B cells. Two monoclonal antibodies against CD40L have been developed and tested in patients but have failed to demonstrate the same success in human subjects with RA and SLE as has been observed in animal models of arthritis and autoimmune disease. However, a mechanistic study of B cells obtained from five patients with SLE who participated in an open-label study of this anti-cd40l antibody, found that anti-cd40l treatment induced a persistent reduction in the frequency of anti-dsdna antibody-producing B cells. 4 Anti-CD11a Monoclonal The T-cell surface complex CD11a/CD18 (also termed LFA-1) interacts with its ligand, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), as part of a costimulatory pathway for T-cell activation. LFA-1-ICAM-1 interaction also serves to form a tight junction adjacent to the TCR that enhances the interaction between the TCR and antigen/mhc complex on APCs. Efalizumab, a humanized, monoclonal antibody against CD11a, has been developed to disrupt this interaction. Efalizumab treatment of psoriasis has resulted in consistent clinical and histologic improvement in several clinical trials. 5 A phase II, 661
4 randomized, controlled trial of efalizumab for the treatment of subjects with RA on concurrent methotrexate is underway. Intracellular Targets Signal transduction pathways provide an intracellular mechanism by which cells respond and adapt to environmental stress. Inflammatory mediators including TNF and IL-1 activate numerous intracellular signaling cascades, resulting in transcription of various mediators of the inflammatory process including chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines. Pro-inflammatory stimuli engage these pathways to direct a response that can either be physiologic, as with exposure to pathogens, or harmful to the host, as in chronic autoimmune diseases. Thus studying these signal transduction mechanisms have led us to a greater understanding and identification of potential therapeutic targets. All these cascades have been subjected to intense investigational efforts to develop pathway-specific inhibitors. Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases The mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are members of a highly conserved serine/threonine protein kinase family that regulate gene expression, cell survival, proliferation, cytokine expression, and metalloproteinase production. These kinases phosphorylate serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues on intracellular proteins and are divided into three major classes in mammals, the c-jun N terminal kinase (JNK), extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK), and p38 MAPKs. p38 MAPK The p38 MAPK pathway has attracted considerable attention as a potential therapeutic target because of its ability to regulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in vitro as well as in vivo. Four isoforms of p38-mapk (α, β, γ, and ) have been identified, and p38α appears to be a critical factor for cytokine expression and regulation in macrophages and other cell types in the joint. Inhibition of p38 MAPK by p38 MAPK inhibitor such as RWJ blocked the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), TNF-α, IL-1 and IL-8 in cultured macrophages. More recently, the potent p38 MAPK inhibitor FR prevented CIA from developing in rats and also suppressed joint destruction when treatment was initiated after the onset of arthritis. 6 As the p38 MAPK inhibitors such as RWJ-67657, BIBB- 796, VX- 745, VX-702, SCIO-469 etc. were also effective when tested in a therapeutic protocol, these data suggest that p38-mapk inhibitors may have therapeutic potential and have been developed and tested in clinical trials. 7 Extracellular Signal Related Kinases Medicine Update 2012 Vol Extracellular Signal Related Kinases (ERKs) have critical role in cell proliferation, induction of proinflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6 and MMPs thus promoting inflammation, lymphocyte activation and tissue destruction. Thus this signaling cascade is an important target for therapy where inflammatory diseases are concerned. Several small-molecule inhibitors of MEK (MAPK- ERK Kinase) 1 and 2 like PD and ARRY-162 have shown efficiency in controlling ERK in animal models. Oral administration of PD to mice with CIA suppressed synovitis, pannus formation and cartilage and bone destruction 8 whereas ARRY-162 significantly reduced inflammation in CIA and AIA rats. 9 Administration of ERK 1 and 2 inhibitors (FR180204) to mice reduced clinical signs of arthritis. 10 c-jun N-Terminal Kinase The development of small molecule inhibitors of c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is also underway. JNKs play an important role in the transcriptional activation of some matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that degrade articular cartilage and promote joint destruction in RA. This is supported by the studies showing that the broad spectrum JNK inhibitor SP suppressed the IL-1 induced MMP-1 expression in vitro as well as bone erosion in a mouse model of arthritis in vivo. 11 In preclinical studies, a c-jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor reduced clinical synovitis and blocked radiographic joint damage in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. 12 Janus kinases Janus kinases (Jaks) play a very important role in innate and adaptive immunity. Though Jak1 and Jak2 both are ubiquitously expressed, it is Jak3 which is primarily involves in cells of immune system and is critical in lymphocyte activation, function and proliferation. Given this multifactorial role in innate and adaptive immunity, it was expected that Jaks are involved in pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. It was first observed that Jak3 reduced clinical signs of inflammatory arthritis by more than 90% and protected against joint damage in mice models of RA. Thus small molecule Jak inhibitors CP and INCB18424 were therapeutically tested and found to effacious and well tolerated in phase II trial in RA patients with considerably reducing ACR 20, ACR 50 and ACR 70 when compared to placebo. 13,14 Infact Tofacitinib (CP690550) has gone under a large phase III monotherapy trial as reported in EULAR Thus, Jak inhibitors are arguably, at this moment, the bestperforming small-molecules drugs under investigations and are also being tried against other rheumatic diseases than RA.
5 Biologics in Rheumatology 2012 Table 1 Type Molecule Agent Chemokines Cytokines Adhesion molecules CCR1 CXCL 12/13 Inhibitors IL-17/IL-17R Secukinumab IL-18 IL-12/23 VCAM-1 E-selectin Antibodies or recombinant proteins Ustekinumab Briakinimab Transcription factor NF-κB Mechanism or development Increased ACR 20 responses in treated patients in phase Ib trial. 19 Potential role in decreasing inflammation in RA synovium 20 and CIA 21 respectively. Targets IL-17A; preliminary efficacies in RA and psoriasis, now being tried in Ankylosing spondilytis. 22 Effectively reduce inflammation in preclinical studies in animal models. 23 Inhibits Th17 differentiation, thus blocks secretion of IL-17. PHOENIX trial in psoriatic arthritis (phase III) and plaque psoriasis (approved). Reduced the number of inflamed joints in CIA models. Trial on chronic plaque psoriasis but failed to reduce the PASI score in patients. 24 NF-κB is considered the master regulator of inflammation and immunity. It plays a pivotal role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Several drugs primarily corticosteroids has been successfully controlling inflammation by depending largely on inhibition of NF-κB transcriptional activity. The NF-κB transcription factor is regulated by the upstream IKK complex, consisting of the kinases IKK1 and IKK 2 and the regulatory component NEMO (NF-κB essential modulator). IKK2 is dominant kinase in the activation NFκB pathway, thus its selective inhibition can be explored as potential future therapeutic targets. Some orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitors of IKK2 have been shown to suppress development and progression of inflammation in animal models. 16,17 Another approach to inhibit NF-κB pathway could be the use of a cell-permeable peptide similar to NEMO-binding protein (NBD) of IKK2 thus disrupting the interaction of IKK2 with NEMO, thereby blocking the formation of IKK complex. This inhibitory peptide has been shown to suppress inflammation and bone destruction in joints of mice with collagen-induced arthritis not causing any toxicity. 18 And the others... Chemokines: Chemokines and chemokine receptors control the recruitment of leukocytes to sites of inflammation. In animal models of arthritis, various chemokine antagonists have effectively reduced synovial inflammation and leukocyte infiltration. As a result, novel therapeutic agents for rheumatic diseases have begun to target chemokine function. Cytokines: Several other cytokines like IL-17, IL-18 and IL-12/23 have been found to have role in initiating inflammation and immune defects and thus their inhibition could be and needed to be addressed. Adhesion molecules: Inhibiting the interaction of various pairs of adhesion molecules and their respective ligands has been proposed as a useful therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases such as RA & other autoimmune diseases. Small molecules inhibitors and biologics such as monoclonal antibodies are in development for this purpose. The details of the above new developing targets are summarized in Table 1. Strengths The availability of several well-established and broadly applicable methods for antibody generation and development. A growing repertoire of technologies to redesign antibodies with modified or new properties to enhance their clinical potential. A high success rate compared to other drugs: 17% for humanized antibodies from the first human trial to regulatory approval [*]. Well-established and broadly applicable production technologies [*]. Often, but not invariably, well tolerated by patients. Limitations Expensive, reflecting high production costs and commonly large doses [*], potentially limiting patient access or clinical applications. Clinical applications currently limited to cell surface or extracellular targets. Cannot be orally administered. 663
6 Conclusion Biologics have revolutionized the treatment of autoimmune diseases due to their efficacy, speed of onset and tolerability. A careful dissection of a targeted pathway is needed so that novel therapeutic interventions designed to specifically block inflammatory signaling may be developed. The development of new agents and expanded use of existing agents continues to be a highly active area of investigation among the rheumatic diseases with a multitude of innovative therapeutic strategies in various stages of development. Although development of treatments continues at a rapid pace, therapeutic research in some diseases is hindered by the rarity of the disease, variation in phenotype, and concerns about toxicity. These issues make trial design challenging. In the coming years developments in this area are going to be exciting and will influence the therapeutic approaches for the effective suppression of rheumatic diseases. However, overall, biologic therapies represent an exciting advance in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. For millions of patients, treatment success may translate to rapid suppression of inflammation, prevention of disability, improved quality of life and the goal of complete disease remission something unthinkable a decade ago. REFERENCES 1. Voll RE, Kalden JR. Do we need new treatment that goes beyond tumor necrosis factor blockers for rheumatoid arthritis? Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005; 1051: Xu W, Zhang Y, Pan H, Ye D. Is sifalimumab a human anti-ifn alpha monoclonal antibody with a potential therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus? Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70(Suppl 3): Rondon F. Etanar therapy in real-life patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Program and abstracts of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2010 Annual Scientific Meeting; November 7-11, 2010; Atlanta, Georgia. Abstract Huang W, Sinha J, Newman J, et al.: The effect of anti-cd40 ligand antibody on B cells in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2002, 46: Gottlieb AB, Krueger JG, Wittkowski K, et al.: Psoriasis as a model for T-cell-mediated disease: immunobiologic and clinical effects of treatment with multiple doses of efalizumab, an anti- CD11a antibody. Arch Dermatol 2002, 138: Nishikawa M, Myoui A, Tomita T, et al. Prevention of the onset and progression of collagen-induced arthritis in rats by the potent p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor FR Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: Smit RJ. Therapies for rheumatoid arthritis; hope springs eternal. Drug Discov Today 2005; 10: Thiel MJ, Schaefer CJ, Lesch ME, et al. Central role of the MEK/ ERK MAP kinase pathway in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis: potential proinflammatory mechanisms. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: Winkler J, Wright D, Phenegar J, et al. ARRY-162, a potent and Medicine Update 2012 Vol selective inhibitor of Mek1/2: preclinical and clinical evidence of activity in arthritis. Proceeding of 9 th World Congresson Inflammation Ohori M, Takeuchi M, Maruki R, et al. FR180204, a novel and selective inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Naunyn Schmeidebergs Arch Pharmacol 2007; 374: Han Z, Boyle DL, Chang L, et al.: c-jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest 2001;108: Han Z, Chang L, Yamanishi Y, et al. Joint damage and inflammation in c-jun N-terminal kinase 2 knockout mice with passive murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46: Murphy PM. Incyte s JAK Inhibitor Demonstrates Marked Clinical Benefits in Phase IIa Rheumatoid Arthritis Study. Incyte press release at the EULAR 2008 Congress 14. Kremer JM, Bloom BJ, Breedveld FC, et al. The safety and efficacy of a JAK inhibitor in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa trial of three dosage levels of CP-690,550 versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: McInnes I, et al. Phase 2 study of the effects of open-label tofacitinib (CP-690,550) and double-blind atorvastatin on lipids in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. EULAR 2011; Abstract LB Gillooly KM, Pattoli MA, Taylor TL, et al. Periodic, partial inhibition of IkappaB kinase beta-mediated signaling yields therapeutic benefit in preclinical models of rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2009; 331: Schopf L, Savinainen A, Anderson K, et al. IKKbeta inhibition protects against bone and cartilage destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: Jimi E, Aoki K, Saito H, et al. Selective inhibition of NF-kappa B blocks osteoclastogenesis and prevents inflammatory bone destruction in vivo. Nat Med 2004; 10: Haringman JJ, Kraan MC, Smeets TJM, et al.: Chemokine blockade and chronic inflammatory disease: proof of concept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46 (suppl): s Zheng B, Ozen Z, Zhang X, et al. CXCL 13 neutralization reduces the severity of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: Tamamura H, Tsutsumi H, Masuno H, et al. development of low molecular weight CXCR4 antagonists by exploratory structural tuning of cyclic tetra- and penta-peptide scaffolds towards the treatment of HIV infection, cancer metastasis and rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Med Chem 2007; 14: Baeten D, et al. The anti-il17a monoclonal antibody secukinumab (AIN457) showed good safety and efficacy in the treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis. ACR 2010; Abstract L Plater-Zyberk C, Joosten LA, Helsen MM, et al.: Therapeutic effect of neutralizing endogenous IL-18 activity in the collageninduced model of arthritis. J Clin Invest 2001;108: Bhushan M, Bleiker TO, Ballsdon AE, et al.: Anti-E-selectin is ineffective in the treatment of psoriasis: a randomized trial. Br J Dermatol 2002;146:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Health Technology Appraisal Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure
Immune modulation in rheumatology. Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association
 Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
Immune modulation in rheumatology Geoff McColl University of Melbourne/Australian Rheumatology Association A traditional start to a presentation on biological agents in rheumatic disease is Plasma cell
In the last decade, there have been major changes in the
 233 Promising New Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis The Kinase Inhibitors Yusuf Yazici, M.D., and Alexandra L. Regens, B.A. Abstract Three major advances over the last decade have impacted the way we
233 Promising New Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis The Kinase Inhibitors Yusuf Yazici, M.D., and Alexandra L. Regens, B.A. Abstract Three major advances over the last decade have impacted the way we
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the New Millennium. Neal I. Shparago, D.O., FACP, FACR
 Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the New Millennium Neal I. Shparago, D.O., FACP, FACR What is RA? Symmetric inflammatory polyarthritis Rheumatoid factor positive in 80% Anti-CCP positive in approximately
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the New Millennium Neal I. Shparago, D.O., FACP, FACR What is RA? Symmetric inflammatory polyarthritis Rheumatoid factor positive in 80% Anti-CCP positive in approximately
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bonita S. Libman, M.D.
 The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped?
 Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped? Robert L. DiGiovanni, DO, FACOI Program Director Largo Medical Center Rheumatology Fellowship [email protected] Do not pour strange medicines
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment ever be stopped? Robert L. DiGiovanni, DO, FACOI Program Director Largo Medical Center Rheumatology Fellowship [email protected] Do not pour strange medicines
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC)
 BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) September 2014 Review date: September 2017 Bulletin 203: Tocilizumab (subcutaneous) in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy for the treatment
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) September 2014 Review date: September 2017 Bulletin 203: Tocilizumab (subcutaneous) in combination with methotrexate or as monotherapy for the treatment
Biologic Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Biologic Treatments Rheumatoid Arthritis (also known as cytokine inhibitors, TNF inhibitors, IL 1 inhibitor, or Biologic Response Modifiers) Description Biologics are new class of drugs that have been
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
REFERENCE CODE GDHC503DFR PUBLICAT ION DATE DECEMBER 2014 METHOTREXATE (RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS) - FORECAST AND MARKET ANALYSIS TO 2023
 REFERENCE CODE GDHC503DFR PUBLICAT ION DATE DECEMBER 2014 METHOTREXATE (RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS) - Executive Summary The table below provides the key metrics for Methotrexate in the 10MM (US, France, Germany,
REFERENCE CODE GDHC503DFR PUBLICAT ION DATE DECEMBER 2014 METHOTREXATE (RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS) - Executive Summary The table below provides the key metrics for Methotrexate in the 10MM (US, France, Germany,
subcutaneous initially every 4 weeks then every 12 weeks Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 02/24/2010
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Humira (adalimumab subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Humira (adalimumab subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
Speaking Plainly. Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis
 in association with Plain English Campaign Speaking Plainly Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis A guide to help healthcare professionals talking to patients with rheumatoid arthritis Foreword
in association with Plain English Campaign Speaking Plainly Biologic treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis A guide to help healthcare professionals talking to patients with rheumatoid arthritis Foreword
Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists
 Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists 1. Which of the following matches of biologic targets that contribute to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and
Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options: Update for Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacists 1. Which of the following matches of biologic targets that contribute to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and
Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept Effective Against Plaque Psoriasis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2011 Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2011 Is Monotherapy Treatment of Etanercept
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Update 2014 Mark Hulsey, MD FACR Rheumatoid Arthritis Key Features Symptoms >6 weeks duration Often lasts the remainder of the patient s life Inflammatory synovitis Palpable synovial
Rheumatoid Arthritis Update 2014 Mark Hulsey, MD FACR Rheumatoid Arthritis Key Features Symptoms >6 weeks duration Often lasts the remainder of the patient s life Inflammatory synovitis Palpable synovial
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd
 ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd 07 February 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
ustekinumab 45mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe (Stelara ) SMC No. (944/14) Janssen-Cilag Ltd 07 February 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Evidence-based Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (2009)
 CPLD reviews its distance learning programmes every twelve months to ensure currency. This update has been produced by an expert and should be read in conjunction with the Evidencebased Management of distance
CPLD reviews its distance learning programmes every twelve months to ensure currency. This update has been produced by an expert and should be read in conjunction with the Evidencebased Management of distance
Welcome to the Launch of Biocon s Breakthrough Innovation. For Psoriasis. Treatment
 Welcome to the Launch of Biocon s Breakthrough Innovation For Psoriasis Treatment PRESS MEET Bangalore, August 10, 2013 Autoimmune Diseases are on the Rise Globally Autoimmune Disease Segment includes
Welcome to the Launch of Biocon s Breakthrough Innovation For Psoriasis Treatment PRESS MEET Bangalore, August 10, 2013 Autoimmune Diseases are on the Rise Globally Autoimmune Disease Segment includes
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
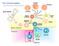 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER ABOUT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of arthritis (chronic inflammatory polyarthritis) that typically affects hands and feet, although any joint in the body
Immunosuppressive drugs
 Immunosuppressive drugs RJM ten Berge Afd. Inw. Geneeskunde AMC contents overview targets mechanism of action Effects on immune capacity measured by responses to vaccination Immune response 1 calcineurin
Immunosuppressive drugs RJM ten Berge Afd. Inw. Geneeskunde AMC contents overview targets mechanism of action Effects on immune capacity measured by responses to vaccination Immune response 1 calcineurin
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation. B cell maturation
 B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies. Biochemistry Journal. August 1, 2007 405, pp.
 Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies 1 Biochemistry Journal August 1, 2007 405, pp. 559 568 Joseph Friedman, Sarah Kraus, Yirmi Hauptman, Yoni Schiff
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Outline. Treatment Goal 4/10/2013. Clinical evaluation New treatment options Future research Discussion
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Rheumatoid Arthritis Robert L. Talbert, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Outline Clinical evaluation New treatment
Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis
 Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery
 A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery Björn Frendéus, PhD VP, Preclinical research Presenter: Björn Frendéus Date: 2011-11-08 1 Antibodies have revolutionized Cancer Treatment!
A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery Björn Frendéus, PhD VP, Preclinical research Presenter: Björn Frendéus Date: 2011-11-08 1 Antibodies have revolutionized Cancer Treatment!
DU maladies systémiques Biothérapies des maladies systémiques Le 25 mai 2012
 DU maladies systémiques Biothérapies des maladies systémiques Le 25 mai 2012 10h-10h10 10h10-10h40 10h40-11h10 11h10-11h40 11h40-12h10 12h10-12h40 -Introduction : Luc Mouthon -Immunoglobulines intraveineuses
DU maladies systémiques Biothérapies des maladies systémiques Le 25 mai 2012 10h-10h10 10h10-10h40 10h40-11h10 11h10-11h40 11h40-12h10 12h10-12h40 -Introduction : Luc Mouthon -Immunoglobulines intraveineuses
Company Presentation June 2011 Biotest AG 0
 Company Presentation June 2011 0 Disclaimer This document contains forward-looking statements on overall economic development as well as on the business, earnings, financial and asset situation of and
Company Presentation June 2011 0 Disclaimer This document contains forward-looking statements on overall economic development as well as on the business, earnings, financial and asset situation of and
Let s talk about Arthritis
 Let s talk about Arthritis Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis Kam Shojania, MD, FRCPC Clinical Professor and Head, St. Paul s, UBC and VGH Divisions of Rheumatology Slides with thanks to: Cheryl Koehn
Let s talk about Arthritis Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis Kam Shojania, MD, FRCPC Clinical Professor and Head, St. Paul s, UBC and VGH Divisions of Rheumatology Slides with thanks to: Cheryl Koehn
Biologic Therapies in Clinical Development for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Biologic Therapies in Clinical Development for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Mark C. Genovese, MD Abstract: The therapeutic objective in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Biologic Therapies in Clinical Development for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Mark C. Genovese, MD Abstract: The therapeutic objective in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
biologics for the treatment of psoriasis
 How to contact us The Psoriasis Association Dick Coles House 2 Queensbridge Northampton NN4 7BF tel: 08456 760 076 (01604) 251 620 fax: (01604) 251 621 email: [email protected] www.psoriasis-association.org.uk
How to contact us The Psoriasis Association Dick Coles House 2 Queensbridge Northampton NN4 7BF tel: 08456 760 076 (01604) 251 620 fax: (01604) 251 621 email: [email protected] www.psoriasis-association.org.uk
Patient Input Information Clinical Trials Outcomes Common Drug Review
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION USTEKINUMAB (Stelara Janssen Inc.) Indication: Psoriatic Arthritis Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that ustekinumab not be listed at the submitted
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION USTEKINUMAB (Stelara Janssen Inc.) Indication: Psoriatic Arthritis Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends that ustekinumab not be listed at the submitted
Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. Genetic Contributions to Autoimmunity. Targets of Autoimmunity
 Autoimmunity Factors predisposing an individual to autoimmune disease Mechanisms of initiation of autoimmunity Pathogenesis of particular autoimmune disease Animal models of autoimmune disease Treatment
Autoimmunity Factors predisposing an individual to autoimmune disease Mechanisms of initiation of autoimmunity Pathogenesis of particular autoimmune disease Animal models of autoimmune disease Treatment
Methotrexate (Rheumatoid Arthritis) - Forecast and Market Analysis to 2023
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3128342/ Methotrexate (Rheumatoid Arthritis) - Forecast and Market Analysis to 2023 Description: Methotrexate (Rheumatoid Arthritis)
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3128342/ Methotrexate (Rheumatoid Arthritis) - Forecast and Market Analysis to 2023 Description: Methotrexate (Rheumatoid Arthritis)
Drug Development Services
 Drug Development Services USING BLOOD AND BONE MARROW PRIMARY CELL SYSTEMS Clinically Relevant In Vitro Assays Broad Spectrum of Drug Classes Multi-Species Platforms Enhancing Drug Development through
Drug Development Services USING BLOOD AND BONE MARROW PRIMARY CELL SYSTEMS Clinically Relevant In Vitro Assays Broad Spectrum of Drug Classes Multi-Species Platforms Enhancing Drug Development through
Spondyloarthritis is a general term for a group of rheumatic
 Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America Supplement 1 11 Current Treatment for Psoriatic Arthritis and Other Spondyloarthritides Spondyloarthritis is a general term for a group of rheumatic diseases,
Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America Supplement 1 11 Current Treatment for Psoriatic Arthritis and Other Spondyloarthritides Spondyloarthritis is a general term for a group of rheumatic diseases,
Inflammation, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cytokines
 Inflammation, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cytokines Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the commonest inflammatory joint disease with considerable morbidity and mortality. Conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic
Inflammation, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cytokines Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the commonest inflammatory joint disease with considerable morbidity and mortality. Conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic
A Case for Cure: Drug Portfolio Analysis. Team: PharmaKings Anirvan Chaudhuri Neha Madan Xiao Huang Jason Park Anjai Lal
 A Case for Cure: Drug Portfolio Analysis Team: PharmaKings Anirvan Chaudhuri Neha Madan Xiao Huang Jason Park Anjai Lal Executive Summary Our team recommends. A Recombinant Protein for treatment of Multiple
A Case for Cure: Drug Portfolio Analysis Team: PharmaKings Anirvan Chaudhuri Neha Madan Xiao Huang Jason Park Anjai Lal Executive Summary Our team recommends. A Recombinant Protein for treatment of Multiple
17 : 2. Arup Kumar Kundu, Kolkata ABSTRACT
 17 : 2 Targets of Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder of unknown aetiology characterized by joint erosion and destruction. It is the most common
17 : 2 Targets of Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis ABSTRACT Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder of unknown aetiology characterized by joint erosion and destruction. It is the most common
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY. Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds
 NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy
 Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
Making the switch to a safer CAR-T cell therapy HaemaLogiX 2015 Technical Journal Club May 24 th 2016 Christina Müller - chimeric antigen receptor = CAR - CAR T cells are generated by lentiviral transduction
Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics
 REVIEW Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics Paul P Tak 1 * and Joachim R Kalden 2 Abstract Treatment of inflammatory arthritides including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and
REVIEW Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics Paul P Tak 1 * and Joachim R Kalden 2 Abstract Treatment of inflammatory arthritides including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and
Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Swedish Society of Rheumatology, April 14, 2011
 Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Swedish Society of Rheumatology, April 14, 2011 Working party: Eva Baecklund, Helena Forsblad d Elia, Carl Turesson Background Our purpose
Guidelines for the Pharmaceutical Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Swedish Society of Rheumatology, April 14, 2011 Working party: Eva Baecklund, Helena Forsblad d Elia, Carl Turesson Background Our purpose
Commercial Insight: Disease Modification in Rheumatoid Arthritis - Market awaits game changing therapies and strategies
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1504775/ Commercial Insight: Disease Modification in Rheumatoid Arthritis - Market awaits game changing therapies and strategies
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1504775/ Commercial Insight: Disease Modification in Rheumatoid Arthritis - Market awaits game changing therapies and strategies
påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã==
 påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã== adalimumab 40mg pre-filled syringe for subcutaneous injection (Humira ) No. (218/05) Abbott New indication: treatment of active and progressive psoriatic arthritis in adults
påçííáëü=jéçáåáåéë=`çåëçêíáìã== adalimumab 40mg pre-filled syringe for subcutaneous injection (Humira ) No. (218/05) Abbott New indication: treatment of active and progressive psoriatic arthritis in adults
Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab)
 Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab) Effective Date: 5/1/08 Committee Review Date: 1/6/01, 9/18/01, 1/15/02, 1/7/03, 1/20/04, 1/18/05, 12/7/05, 10/15/06, 7/2/07, 11/5/07, 3/25/08 Policy Statements:
Drug Therapy Guidelines: Humira (adalimumab) Effective Date: 5/1/08 Committee Review Date: 1/6/01, 9/18/01, 1/15/02, 1/7/03, 1/20/04, 1/18/05, 12/7/05, 10/15/06, 7/2/07, 11/5/07, 3/25/08 Policy Statements:
Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy
 Media Release Basel, 6 June 2012 Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy Roche (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY) today announced
Media Release Basel, 6 June 2012 Roche s RoACTEMRA improved rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms significantly more than adalimumab as single-agent therapy Roche (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY) today announced
Biologics: Specific Drug Safety Challenges. Violetta B. Kyburz
 Biologics: Specific Drug Safety Challenges Violetta B. Kyburz 2012 2013 2014 Biologics: Specific Drug Safety Challenges Topics for discussion Particular issues in the preclinical development of biologics
Biologics: Specific Drug Safety Challenges Violetta B. Kyburz 2012 2013 2014 Biologics: Specific Drug Safety Challenges Topics for discussion Particular issues in the preclinical development of biologics
Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 THE RHEUMATOID IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL VOL.12, NO. 3,2013 Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahmed A. Al-Hassan*, Mohammed O. Hamzah**,
THE RHEUMATOID IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL VOL.12, NO. 3,2013 Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of IL-1α and IL-8 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahmed A. Al-Hassan*, Mohammed O. Hamzah**,
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist
 Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis, treatment and prognosis Dr David D Cruz MD FRCP Consultant Rheumatologist The Louise Coote Lupus Unit St Thomas Hospital London AMUS meeting London 7 th March 2012 Disclosures
BRIEFING DOCUMENT FOR ABATACEPT (BMS-188667) BIOLOGICAL LICENSE APPLICATION 125118 FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE
 BRIEFING DOCUMENT FOR ABATACEPT () BIOLOGICAL LICENSE APPLICATION 125118 FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE 6 SEPTEMBER 2005 Applicant: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company Pharmaceutical
BRIEFING DOCUMENT FOR ABATACEPT () BIOLOGICAL LICENSE APPLICATION 125118 FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE 6 SEPTEMBER 2005 Applicant: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company Pharmaceutical
DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view. Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London
 DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London History: NICE (E&W) guidelines for starting anti-tnf agents April 2001
DAS28 criteria for initiation of biologics in early RA: a clinician s view Dr Patrick Kiely St George s Healthcare NHS Trust, London History: NICE (E&W) guidelines for starting anti-tnf agents April 2001
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES
 ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
Staph Protein A, Immune Complexes, Cryoglobulins, and the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
 Staph Protein A, Immune Complexes, Cryoglobulins, and the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Immunomodulation, not Immunosuppression Written by Craig Wiesenhutter, M.D. January 2016 This paper has been
Staph Protein A, Immune Complexes, Cryoglobulins, and the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Immunomodulation, not Immunosuppression Written by Craig Wiesenhutter, M.D. January 2016 This paper has been
OKT3. ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody. used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~
 g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 White Paper March 2013 Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Catherine Augustyn, Brigham Walker, and Thomas F. Goss, PharmD Boston Healthcare Associates, Inc., Boston,
White Paper March 2013 Recognizing the Value of Innovation in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Catherine Augustyn, Brigham Walker, and Thomas F. Goss, PharmD Boston Healthcare Associates, Inc., Boston,
Therapeutic Class Overview : Psoriasis Plaque Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis - Novel Oral Drugs And Biologics To Change Future Treatment Paradigm
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2763286/ Therapeutic Class Overview : Psoriasis Plaque Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis - Novel Oral Drugs And Biologics To Change
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2763286/ Therapeutic Class Overview : Psoriasis Plaque Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis - Novel Oral Drugs And Biologics To Change
How will we prevent rheumatoid arthritis? Kevin Deane, MD/PhD Division of Rheumatology University of Colorado
 How will we prevent rheumatoid arthritis? Kevin Deane, MD/PhD Division of Rheumatology University of Colorado Outline 1) Brief overview of natural history of RA and how current understanding of disease
How will we prevent rheumatoid arthritis? Kevin Deane, MD/PhD Division of Rheumatology University of Colorado Outline 1) Brief overview of natural history of RA and how current understanding of disease
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center
 Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Media Release. Basel, 11 June 2009. RA patients with enhanced response identified
 Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
Media Release Basel, 11 June 2009 New data demonstrate the ability of MabThera to reduce the progression of joint damage when used as a first-line biologic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis RA patients
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit
 Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit Qualitative research proposal to explore factors influencing acceptable risk thresholds used to recommend particular treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit Qualitative research proposal to explore factors influencing acceptable risk thresholds used to recommend particular treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis.
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry Interpreting Sameness of Monoclonal Antibody Products Under the Orphan Drug Regulations U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation
Guidance for Industry Interpreting Sameness of Monoclonal Antibody Products Under the Orphan Drug Regulations U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 Review Article ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS M JOSHI* Our understanding of the pathology and management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has evolved significantly over last two decades.
Review Article ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS M JOSHI* Our understanding of the pathology and management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has evolved significantly over last two decades.
Original Policy Date
 MP 5.01.20 Tysabri (natalizumab) Medical Policy Section Prescription Drug Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Local Policy/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 5.01.20 Tysabri (natalizumab) Medical Policy Section Prescription Drug Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Local Policy/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies. Mark Holguin
 Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies Mark Holguin 25 years ago Why I chose oncology People How to help people with possibly the most difficult thing they may have to deal with Science Turning
Update in Hematology Oncology Targeted Therapies Mark Holguin 25 years ago Why I chose oncology People How to help people with possibly the most difficult thing they may have to deal with Science Turning
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS.
 TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
TEMA 10. REACCIONES INMUNITARIAS MEDIADAS POR CÉLULAS. The nomenclature of cytokines partly reflects their first-described function and also the order of their discovery. There is no single unified nomenclature,
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Despite remarkable advances in therapy, rheumatoid
 Use of Biological Agents in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Richard J. Misischia, MD, and Larry W. Moreland, MD Despite remarkable advances in therapy, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) still results in
Use of Biological Agents in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Richard J. Misischia, MD, and Larry W. Moreland, MD Despite remarkable advances in therapy, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) still results in
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Winter 2013. Changing landscapes, pipeline products and plan sponsor impact
 Winter 2013 Changing landscapes, pipeline products and plan sponsor impact Changing landscapes, pipeline products and plan sponsor impact The pharmaceutical landscape is changing as is the profile of blockbuster
Winter 2013 Changing landscapes, pipeline products and plan sponsor impact Changing landscapes, pipeline products and plan sponsor impact The pharmaceutical landscape is changing as is the profile of blockbuster
Week 12 study results
 Week 12 study results 15 April 2015 Copyright 2015 Galapagos NV Disclaimer This document may contain certain statements, including forward-looking statements, such as statements concerning the safety and
Week 12 study results 15 April 2015 Copyright 2015 Galapagos NV Disclaimer This document may contain certain statements, including forward-looking statements, such as statements concerning the safety and
Top Down vs. Step Up Therapy Biologics in IBD: Treatment Algorithms. Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago
 Top Down vs. Step Up Therapy Biologics in IBD: Treatment Algorithms Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago Treatment Goals c.2008 Induce and maintain response/remission Prevent complications Disease
Top Down vs. Step Up Therapy Biologics in IBD: Treatment Algorithms Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago Treatment Goals c.2008 Induce and maintain response/remission Prevent complications Disease
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE
 ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
ANTIBODIES AGAINST CITRULLINATED PEPTIDES IN EARLY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE Principal investigators: Dr Raimon Sanmartí Sala Hospital Clínic i Provincial de Barcelona
Immune Basis of New MS Therapies
 Immune Basis of New MS Therapies Samia J Khoury, MD Director of Abou-Haidar Neuroscience Institute Director of Multiple Sclerosis Center Professor of Neurology AUBMC MS Center & Harvard Medical School
Immune Basis of New MS Therapies Samia J Khoury, MD Director of Abou-Haidar Neuroscience Institute Director of Multiple Sclerosis Center Professor of Neurology AUBMC MS Center & Harvard Medical School
Giant Spondylitis and Its Effect on Globlogical Therapy
 Cytokine and CAM Antagonists and Related Agents Review 01/22/2010 Copyright 2005-2010 by Provider Synergies, L.L.C. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. All rights reserved. No
Cytokine and CAM Antagonists and Related Agents Review 01/22/2010 Copyright 2005-2010 by Provider Synergies, L.L.C. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. All rights reserved. No
How To Choose A Biologic Drug
 North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
