Impact of Model-based Risk Analysis for Liver Surgery Planning
|
|
|
- Kimberly Melton
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact of Model-based Risk Analysis for Liver Surgery Planning C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz 1, B. Preim 2, G. Stavrou 3, K. J. Oldhafer 3, H. K. Hahn 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen, Germany 2 Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Faculty of Computer Science, Magdeburg, Germany 3 Asklepios Hospital Barmbek, Hamburg, Germany Abstract Purpose A model-based risk analysis for oncologic liver surgery was described in previous work [1]. In this paper, we present an evaluation of this method. Methods To prove whether and how the risk analysis facilitates the process of liver surgery planning, an explorative user study with 10 liver experts was conducted. The purpose was to compare and analyze their decision making. Results The results of the study show that model-based risk analysis enhances the awareness of surgical risk in the planning stage. Participants preferred smaller resection volumes and agreed more on the safety margins width in case the risk analysis was available. In addition, time to complete the planning task and confidence of participants was not increased when using the risk analysis. Conclusion This work shows that the applied model-based risk analysis may influence important planning decisions in liver surgery. It lays a basis for further clinical evaluations and points out important fields for future research. Keywords Computer-assisted surgery, Medical visualization, Liver surgery planning, Evaluation 1. Introduction The determination of optimal safety margin widths around liver lesions is a challenging surgical task. Type, number, volume, and location of lesions and their relation to vessels are all important factors when deciding whether a R0 resection can be achieved. Thereby, surgeons have to find a compromise between the safety margin width and the estimated postoperative liver volume.
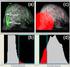
2 To this end, methods for model-based risk analysis in liver surgery were developed [1-4]. We briefly describe the important steps for model-based risk analysis in liver surgery as introduced by Preim et al. (2002) [1]: vascular structures in the liver are segmented semi-automatically using a thresholdbased region-growing technique. Skeletonization with a topology-preserving thinning algorithm yields an exact centerline and vessel radii at each voxel of the skeleton. A graph analysis transforms the vessel skeleton in a directed, acyclic graph where nodes represent bi/tri-furcations. Finally, a 3D model of the vessel graph is calculated and visualized. In addition, all visible lesions and the liver surface are segmented semi-automatically and visualized in 3D. For the visualization of vessels at risk and potentially affected liver parenchyma (territories at risk), the spatial relations between intrahepatic lesions and vessels have to be analyzed. Using an approach by Hansen et al [2], the dependency of territories at risk from safety margins around lesions can be explored interactively. A volume-margin function visualizes the affected liver volume as a function of the safety margins width (Fig. 1, upper right). This visualization also provides information about robustness and sensitivity of vascular risk in the liver. In addition, interactive 3D renderings visualize the impaired liver volume by the portal vein (Fig. 1, upper left), and the hepatic vein (Fig. 1, upper middle). In this work, an explorative user study was conducted to prove whether and how model-based risk analyses facilitate the process of liver surgery planning. In our previous work [1,2], this aspect was not studied in detail. The purpose of the study presented in this paper was to compare and analyze the decision making of liver surgeons and radiologic technicians. Figure 1 Screenshot from a software application for model-based risk analyses in liver surgery. The application was presented in our previous work [2]. The upper-right viewport shows two curves (hepatic vein = green, portal vein = blue) that visualize the remaining functional liver volume as a function of the safety margin width (volume-margin function). Territories at risk for the portal vein (blue) are visualized (red) in the upper left; for the hepatic vein (green) these territories are visualized in the upper middle viewport. The radiologic data and associated overlays of the 3D models can be accessed in the lower viewport.
3 2. Materials and Methods To generate evaluable data during the experiments, clinically relevant reference criteria need to be defined. These criteria should provide the basis for a comparison between the proposed method and a reference system. Three reference criteria were derived from questions that typically arise during the planning of surgical liver interventions: (C1) (C2) (C3) resectability, resection strategy, and safety margins widths around lesions. These criteria are based on subjective assessments by study participants. In addition, reference criteria which can be derived from this decision-making process are defined: (C4) (C5) (C6) total time to analyze a case, amount of user interaction per case, and degree of subjective confidence in decision-making. Experiment Design The study consisted of two separate experiments, called experiment A and experiment B. Each participant completed both experiments. In experiment A, a reference system was presented consisting of a conventional 2D/3D viewer application for planning data. While the 2D viewer visualizes the radiologic slice data, the 3D viewer visualizes the 3D models of vascular structures (hepatic vein, portal vein), the liver surface, and lesions. In addition, the application provides measurement tools for the assessment of distances within the dataset. In experiment B, the utilized software application contained all functionalities that were included in the reference system. In addition, the volume-margin function of the dataset was visualized together with an interactive 3D visualization of vessels at risk and territories at risk as shown in Fig. 1. In each experiment, participants were asked to analyze six CT datasets of the liver. The same six datasets were used in each experiment. For each dataset, participants had to perform specific planning tasks by using the software application. These planning tasks consisted of: determination of a virtual resection surface, selection of critical vessel structures which should be preserved, and selection of potential areas of impaired inflow and outflow. In addition, participants completed a questionnaire for each dataset. The questionnaire directly addresses the criteria (C1-C3) defined above. In the header of each questionnaire, a report on diagnostic findings for the dataset was given and the desired postoperative liver volume was specified (> 35%). Each experiment was conducted as follows. First, participants were informed that the experiment takes between 60 and 90 minutes and that the time is measured during the experiment. Second, the software application was presented and its graphical user interface was explained. Third, a training dataset was loaded and participants conducted the planning tasks for this dataset and filled out a questionnaire. The
4 test supervisor ensured that all questions and planning tasks were understood. Finally, five test datasets were loaded in random order. Participants were informed that the experiment starts and that time is measured from now on. Analogous to the training phase, participants performed surgical planning tasks and filled out a questionnaire for each dataset. Verbal comments were transcribed during the experiment. The experiments were performed in the context of two clinical workshops at Asklepios Clinic Barmbek, Hamburg, Germany. Because not all surgeons could take part at both workshops, several separate meetings took place. The distance between experiment A and B was always at least 3 weeks in order to minimize memory effects. Medical Datasets As shown in Fig. 2, our case database consisted of six abdominal CT datasets (1 training dataset, 5 test datasets). For each dataset, 3D models of the liver, hepatic vein, portal vein, and intrahepatic lesions were generated. The test datasets were selected according to the following criteria: presence of colorectal liver cancer, solitary metastases that are located adjacent to major hepatic vessels, and no presence of cirrhosis. Figure 2 Selected datasets: Case T shows a visualization of the training dataset with a peripherally located metastasis close to the MHV. Case 1, 3, and 4 show datasets with centrally located liver metastases (yellow). In case 2, the metastasis is located in the right liver lobe, while in case 5 it is located in the left liver lobe.
5 Participants Medical knowledge and experience in liver surgery planning are necessary to perform the planning tasks and to give meaningful answers in the questionnaire. For that reason, the subject pool consisted of 10 liver experts (three females, seven males), including four chief physicians, one senior physician, two assistant physicians, three radiology technicians. The radiology technicians were part of an expert team for liver surgery planning at MeVis Medical Solutions, Bremen, Germany. They are quite familiar in analyzing CT data of the liver and prepare virtual resection proposals for clinical customers frequently. The mean age of the participants was years (± 4.7). The mean number of years of surgical experience were 15.6 (±5.3), excluding the radiology technicians. 3. Results Comparison of given assessments concerning patient resectability (C1) revealed that participants showed better agreement of answers in experiment B (cf. Fig. 3). In addition, the results show that participant's decisions were much more cautious and less optimistic when using the risk analysis. For example, in case 1, two surgeons who rated a patient as resectable in experiment A changed their decision to non-resectable in experiment B. Furthermore, all participants who rated a patient as resectable with a large safety margin > 5mm in case 1, 3 and 5 changed their decision to resectable with a small safety margin < 5mm. Although there exist no significant differences between experiment A and B (p>0.05, Wilcoxon test), the results indicate that the proposed vascular risk analysis enhances the awareness of surgical risk in the planning stage. (Experiment A) (Experiment B) Figure 3 Assessed respectability for cases 1-5 in experiments A and B (white = resectable with a large safety margin (> 5mm), light grey = resectable with a small safety margin (< 5mm), dark grey = not resectable ). Figures 4-6 illustrate the changes in the resection strategy (C2) that were made in the study. The amount and direction of changes reveal that the risk analysis has different magnitudes of influence on surgical decision-making that depend, among other factors, on the selected medical dataset. For cases 1 and 2, the changes show a clear trend towards the choice of smaller resection volumes when using the risk analysis. The same trend, to a lesser extent, can also be observed for cases 4 and 5. For case 3, the majority of subjects did not change their resection strategy when using the risk analysis. The analysis shows that subjects changed their resection strategy in many cases. This is unsurprising, because it can be expected that when repeating experiment A (or B) several times with the same
6 participants, the preferred resection strategy will not be constant (test-retest variability). However, the changes observed in this study follow a clear trend towards the choice of smaller resection volumes in case the risk analysis is available. This supports the above statement that the proposed methods enhance the awareness of surgical risk. (a) (b) Figure 4 (a) Changes in resection strategy for case 1: While a right hemihepatectomy was the most frequently chosen resection strategy in experiment A, 6 participants changed their strategy in experiment B. The trend favors local resections (0/4) and rejecting surgical resection (0/2). These changes indicate that participants underestimated risk in experiment A and prefer a smaller resection volume in experiment B. (b) Changes in resection strategy for case 2: Participants show a similar trend such as in case 1. Right hemihepatectomy and extended right hemihepatectomy were found to be the most appropriate resection strategies in experiment A. However, whereas local resections were not taken into account in experiment A, five subjects chose a local resection. Analogously to case 1, these changes indicate that participants underestimated risk in experiment A and prefer a smaller resection volume in experiment B. (a) (b) Figure 5 (a) Changes in resection strategy for case 3: The majority of subjects did not change their resection strategy. No significant trend can be observed for this case. (b) Changes in resection strategy for case 4: Several trends can be observed. First, the extended left hemihepatectomy (2/5) is the strategy most subjects preferred in experiment B, in contrast to experiment A. Second, all subjects who chose a right hemihepatectomy in experiment A changed their opinion in B. Overall, the changes indicate a trend towards smaller resection (right lobe left lobe, central local) when using the risk analysis.
7 Figure 6 Changes in resection strategy for case 5: Although the strategy selections and changes of subjects seem to be inconsistent at first glance, there is a clear trend towards smaller resection volumes. 5 subjects choose a resection with a smaller resection volume than in experiment B. The analysis of selected safety margins widths (C3) showed that the variation of values was lower for all cases in experiment B (cf. Fig. 7). Thus, subjects agree more when the safety margin is chosen with the proposed risk analysis (experiment B) than with 3D measurement tools (experiment A). A selected safety margin width depends on the chosen resection strategy. Thus, the measured trend to choose smaller resection volumes in experiment B seems to have an influence on the width of safety margins, or vice versa. Statistically significant differences were not found (p>0.05, Wilcoxon test). Figure 7 Selected safety margin widths for cases 1-5 in experiments A and B. The comparison of times (C4) taken to complete the test tasks (cf. Fig. 8) revealed that there are no significant differences between experiments A and B (p > 0.05, Wilcoxon test). However, the way surgeons used the provided 2D/3D visualization techniques was different in each experiment. In experiment A, the CT slices were more often accessed than in experiment B (cf. Fig. 9). The numbers are many times higher in experiment A, especially for cases 1 and 2. An analysis of user interaction (C5) during the experiments also showed that the amount of interaction with the volume margin function was highest in cases 1 and 2 (cf. Fig. 10). This relation
8 indicates that interaction with the 2D slice data is required less when the risk analysis is extensively used. Figure 8 Time needed by participants for the completion of test tasks in experiment A and experiment B. The antennas in the box plot visualize maximum and minimum values. Data points that exceed the interquartile range more than one and a half time are defined as outliers. Figure 9 Number of values from the volume-margin function that were accessed in experiment B. Figure 10 Total number of CT slices that were accessed by participants in experiment A (light grey) and experiment B (dark grey) for datasets 1-5.
9 Several surgeons stated verbally that the risk analysis is especially helpful in case 1 (five surgeons), case 2 (three surgeons), and case 5 (two surgeons), because the potential areas of risk are hard to identify with 3D planning models or 2D slices. However, three surgeons noted that the territories of risk visualized for the first branching of the left portal vein in case 5 are misleading, because this part of the vessel could be saved intraoperatively by applying a special cutting approach and would therefore not represent a risk for the patient. Similar comments were also made for the inferior vena cava (extrahepatic vein with inflow of the hepatic vein). Participants suggested integrating a function that allows excluding specific vessels from the risk analyses. The questionnaire asked participants to rank their confidence (C6) in decision-making concerning questions 2, 3, 5, and 6 on an ordinal scale from 1 to 4 (1 = very sure, 2 sure, 3 = less sure, 4 = not sure). An analysis of the data revealed that there exist no significant differences between experiment A and B (p>0.05, Wilcoxon test). However, the mean values indicate that participants felt more confidence in experiment A (cf. Table 1). An interesting observation in this context was that several participants mentioned that it is even more difficult to make a final decision when considering the additional information provided by the risk analysis. Two surgeons mentioned that they selected less sure or not sure in experiment B because they would prefer to discuss the resection strategy with colleagues before making a final decision. Such verbal comments were not made in experiment A. Table 1 Subjective confidence of participants based on a scale from 1 to 4 (1 = very sure, 2 sure, 3 = less sure, 4 = not sure). The results of the user study can be summarized as follows: The applied model-based risk analysis enhances the awareness of surgical risk in the planning stage (assessment of resectability, determination of resection strategy) Subjects prefer smaller resection volumes in case the risk analysis is available Subjects agree more on the safety margins width in case the risk analysis is utilized Subjects do not take more time when analyzing a dataset using the risk analysis. In this context, 2D slices were less accessed in case the risk analyses were available Confidence in decision-making is not higher when using the risk analyses In conclusion, the results show that the methods proposed in this work facilitate the process of liver surgery planning. 4. Discussion Previous studies in the field of liver surgery planning evaluated only the impact of 3D visualization [5] and virtual resection planning [6]. Thereby, the planning data was always compared with a presentation of 2D CT images. The study performed in this work investigated the usefulness of modelbased risk analysis for liver surgery planning. The results of the study show that the proposed risk analysis may influence important planning decisions for liver surgery.
10 An interesting result of the study is that confidence in decision-making was not higher when using the risk analysis. The mean confidence values are even higher without the risk analysis. There are several possible explanations for this result. First, all participants were quite familiar with the 3D planning models and the exploration of 2D slice data available in experiment A. Thus, the level of trust in the new risk analyses was probably lower than in the established 2D/3D exploration techniques. This might have had an effect on the level of confidence. It is expected that the level of confidence will increase after subjects are more familiar with the approach. Second, the additional information in experiment B enhanced the awareness of surgical risk and could explain why participants rated this as less confident. Thus, the subjective confidence in decision-making might correlate with risk awareness of subjects. The mean time to complete the planning tasks was not significantly lower when using the risk analysis. Because experiment A always took place before experiment B, a potential bias in favor of experiment B in terms of time was introduced. Thus, the results should be interpreted by taking these circumstances into account. It would be interesting to measure what happens if participants would receive more training. We assume that training has a significant effect on the time users require to complete a planning task. Another reason for this result could be the increase in risk awareness that raised up new questions during the planning process. Thus, additional time was required. It is also assumed that the high difficulty of the selected cases influenced the confidence of participants and the measured time. For the future, it would be desirable to prove the benefit of the proposed risk analysis by evaluating them in clinical routine. This would require a clinical study with a randomized decision regarding the utilization of the results of the risk analysis and the subsequent evaluation of clinical criteria, such as complication rate, tumor recurrence, and blood loss [7]. The participants could be divided in different groups depending on their level of training (surgical experience, experience with 3D planning software and experience with model-based risk analysis) to evaluate how this affects the outcome of surgical decisions. Such separate assessments were not meaningful in the recent study due to the small number of participants. In addition, it would be important to compare preoperative resection plans with intraoperative performed resection surfaces quantitatively. Therefore, the performed resection needs to be measured intraoperatively, e.g., by using a surgical navigation system, or acquired using postoperative imaging. In conclusion, this work contributes to computer-assisted liver surgery planning. It lays a basis for further developments and evaluations in the context of model-based risk analyses and points out promising fields for further research. References [1] Preim, B., Bourqain, H., Selle, D., Peitgen, H.-O., and Oldhafer, K. Resection Proposals for Oncologic Liver Surgery based on Vascular Territories. Proceedings of International Symposium on Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (CARS). Elsevier, pp , 2002 [2] Hansen, C., Zidowitz, S., Hindennach, M., Schenk, A., Hahn, H., and Peitgen, H.-O. Interactive Determination of Robust Safety Margins for Oncologic Liver Surgery. In: International Journal of Computer-Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 4(5), pp , 2009 [3] Schwaiger J, Markert M, Seidl B, Shevchenko N, Doerfler N, Lueth TC. Risk analysis for intraoperative liver surgery. In: Proceedings of IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc., pp , 2010 [4] Lamata P, Lamata F, Sojar V, Makowski P, Massoptier L, Casciaro S, Ali W, Stüdeli T, Declerck J, Elle OJ,Edwin B. Use of the Resection Map system as guidance during hepatectomy. In: Surg Endosc., 24(9), pp , 2010 [5] Lamade, W., Glombitza, G., Fischer, L., Chiu, P., Cardenas, C. E., Thorn, M., Meinzer, H. P., et al. The impact of 3-dimensional reconstructions on operation planning in liver surgery. In: Arch Surg, 135, pp.
11 , 2000 [6] Lang, H., Radtke, A., Hindennach, M., Schroeder, T., Fruhauf, N. R., Malago, M., Bourquain, H., Peitgen, H.-O., Oldhafer, K. J., and Broelsch, C. E. Impact of virtual tumor resection and computer-assisted risk analysis on operation planning and intraoperative strategy in major hepatic resection. In: Arch Surg, 140(7), pp , 2005 [7] Schenk, A., Zidowitz, S., Bourquain, H., Hindennach, M., Hansen, C., Hahn, H. K., and Peitgen, H.-O. Clinical relevance of model based computer-assisted diagnosis and therapy." In: Proceedings of SPIE Medical Imaging. Vol. 6915, pp , 2008
Risk Maps for Liver Surgery
 Risk Maps for Liver Surgery Christian Hansen 1, Stephan Zidowitz 1, Felix Ritter 1, Christoph Lange 1, Karl Oldhafer 2, Horst K. Hahn 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Insitute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
Risk Maps for Liver Surgery Christian Hansen 1, Stephan Zidowitz 1, Felix Ritter 1, Christoph Lange 1, Karl Oldhafer 2, Horst K. Hahn 1 1 Fraunhofer MEVIS, Insitute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
Computer Aided Liver Surgery Planning Based on Augmented Reality Techniques
 Computer Aided Liver Surgery Planning Based on Augmented Reality Techniques Alexander Bornik 1, Reinhard Beichel 1, Bernhard Reitinger 1, Georg Gotschuli 2, Erich Sorantin 2, Franz Leberl 1 and Milan Sonka
Computer Aided Liver Surgery Planning Based on Augmented Reality Techniques Alexander Bornik 1, Reinhard Beichel 1, Bernhard Reitinger 1, Georg Gotschuli 2, Erich Sorantin 2, Franz Leberl 1 and Milan Sonka
Virtual Resection with a Deformable Cutting Plane
 Virtual Resection with a Deformable Cutting Plane Olaf Konrad-Verse 1, Bernhard Preim 2, Arne Littmann 1 1 Center for Medical Diagnostic Systems and Visualization, Universitaetsallee 29, 28359 Bremen,
Virtual Resection with a Deformable Cutting Plane Olaf Konrad-Verse 1, Bernhard Preim 2, Arne Littmann 1 1 Center for Medical Diagnostic Systems and Visualization, Universitaetsallee 29, 28359 Bremen,
The LiverSurgeryTrainer - Training of Computer-Based Planning in Liver Resection Surgery
 The LiverSurgeryTrainer - Training of Computer-Based Planning in Liver Resection Surgery Jeanette Mönch 1, Konrad Mühler 2, Christian Hansen 3, Karl-Jürgen Oldhafer 4, Gregor Stavrou 4, Christian Hillert
The LiverSurgeryTrainer - Training of Computer-Based Planning in Liver Resection Surgery Jeanette Mönch 1, Konrad Mühler 2, Christian Hansen 3, Karl-Jürgen Oldhafer 4, Gregor Stavrou 4, Christian Hillert
Intraoperative Adaptation and Visualization of Preoperative Risk Analyses for Oncologic Liver Surgery
 Intraoperative Adaptation and Visualization of Preoperative Risk Analyses for Oncologic Liver Surgery Christian Hansen *a, Stefan Schlichting b, Stephan Zidowitz a, Alexander Köhn a, Milo Hindennach a,
Intraoperative Adaptation and Visualization of Preoperative Risk Analyses for Oncologic Liver Surgery Christian Hansen *a, Stefan Schlichting b, Stephan Zidowitz a, Alexander Köhn a, Milo Hindennach a,
Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments
 PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
PICTORIL ESSY Sonographic Demonstration of Couinaud s Liver Segments Dean Smith, MD, FRCPC, Donal Downey, M, Ch, FRCPC, lison Spouge, MD, FRCPC, Sue Soney, RT, RDMS, RCMS The segmental localization of
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye
 Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye 8 Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye Kazutoshi Kan Michio Oikawa Takashi Azuma Shio Miyamoto OVERVIEW: A surgery support
Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye 8 Surgery Support System as a Surgeon s Advanced Hand and Eye Kazutoshi Kan Michio Oikawa Takashi Azuma Shio Miyamoto OVERVIEW: A surgery support
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
PANCREATIC AND PERIAMPULLARY TUMORS: PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY. Dr. Shailesh V. Shrikhande
 PANCREATIC AND PERIAMPULLARY TUMORS: PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY Dr. Shailesh V. Shrikhande Associate Professor & Consultant Surgeon GI and HPB Surgical Oncology Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai INDIA HELICAL
PANCREATIC AND PERIAMPULLARY TUMORS: PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY Dr. Shailesh V. Shrikhande Associate Professor & Consultant Surgeon GI and HPB Surgical Oncology Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai INDIA HELICAL
Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases
 I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest
 Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
Liver Surgery Planning Using Virtual Reality
 Virtual and Augmented Reality Supported Simulators Liver Surgery Planning Using Virtual Reality Bernhard Reitinger, Alexander Bornik, Reinhard Beichel, and Dieter Schmalstieg Graz University of Technology
Virtual and Augmented Reality Supported Simulators Liver Surgery Planning Using Virtual Reality Bernhard Reitinger, Alexander Bornik, Reinhard Beichel, and Dieter Schmalstieg Graz University of Technology
A novel Real-Time Web3D Surgical Teaching Tool based on WebGL
 A novel Real-Time Web3D Surgical Teaching Tool based on WebGL Steven Birr 1, Jeanette Mönch 1, Dirk Sommerfeld 1, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Institut für Simulation und Graphik, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg
A novel Real-Time Web3D Surgical Teaching Tool based on WebGL Steven Birr 1, Jeanette Mönch 1, Dirk Sommerfeld 1, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Institut für Simulation und Graphik, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg
Adaptive script based animations for intervention planning
 Adaptive script based animations for intervention planning Konrad Muehler, Ragnar Bade, and Bernhard Preim Department of Simulation and Graphics, Department of Computer Science, Otto-von-Guericke University
Adaptive script based animations for intervention planning Konrad Muehler, Ragnar Bade, and Bernhard Preim Department of Simulation and Graphics, Department of Computer Science, Otto-von-Guericke University
Results reported refer to the mesh-based refinement (MBR) method described in the paper attached.
 Results reported refer to the mesh-based refinement (MBR) method described in the paper attached. Liver Segmentation in CT Data: A Segmentation Refinement Approach Reinhard Beichel 12, Christian Bauer
Results reported refer to the mesh-based refinement (MBR) method described in the paper attached. Liver Segmentation in CT Data: A Segmentation Refinement Approach Reinhard Beichel 12, Christian Bauer
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations. Chapter. Grade. CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
How To Develop An Image Guided Software Toolkit
 IGSTK: a software toolkit for image-guided surgery applications Kevin Cleary a,*, Luis Ibanez b, Sohan Ranjan a, Brian Blake c a Imaging Science and Information Systems (ISIS) Center, Department of Radiology,
IGSTK: a software toolkit for image-guided surgery applications Kevin Cleary a,*, Luis Ibanez b, Sohan Ranjan a, Brian Blake c a Imaging Science and Information Systems (ISIS) Center, Department of Radiology,
The Medical Exploration Toolkit - An efficient support for visual computing in surgical planning and training
 Nr.: FIN-004-2008 The Medical Exploration Toolkit - An efficient support for visual computing in surgical planning and training Konrad Mühler, Christian Tietjen, Felix Ritter, Bernhard Preim Arbeitsgruppe
Nr.: FIN-004-2008 The Medical Exploration Toolkit - An efficient support for visual computing in surgical planning and training Konrad Mühler, Christian Tietjen, Felix Ritter, Bernhard Preim Arbeitsgruppe
The Whipple Procedure. Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain
 The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
Case Number: RT2009-124(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor, Oncology Special Nurse, Resident Doctor
 Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
Objectives. Mylene T. Truong, MD. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Background
 Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Imaging of Pleural Tumors Mylene T. Truong, MD Imaging of Pleural Tumours Mylene T. Truong, M. D. University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Objectives To review tumors involving the
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives
 Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Lenox Hill Hospital Department of Surgery General Surgery Goals and Objectives Medical Knowledge and Patient Care: Residents must demonstrate knowledge and application of the pathophysiology and epidemiology
Piattaforma Avanzata per la Pianificazione Pre-Operatoria nella Chirurgia Laparoscopica Pediatrica
 Department of Innovation Engineering Salento University Lecce, Italy Piattaforma Avanzata per la Pianificazione Pre-Operatoria nella Chirurgia Laparoscopica Pediatrica Lucio Tommaso De Paolis, Giovanni
Department of Innovation Engineering Salento University Lecce, Italy Piattaforma Avanzata per la Pianificazione Pre-Operatoria nella Chirurgia Laparoscopica Pediatrica Lucio Tommaso De Paolis, Giovanni
Cancer Care Delivered Locally by Physicians You Know and Trust
 West Florida Physician Office Building Johnson Ave. University Pkwy. Olive Road N. Davis Hwy. For more information on West Florida Cancer Center: 850-494-5404 2130 East Johnson Avenue Pensacola, Florida
West Florida Physician Office Building Johnson Ave. University Pkwy. Olive Road N. Davis Hwy. For more information on West Florida Cancer Center: 850-494-5404 2130 East Johnson Avenue Pensacola, Florida
Uitgangsvraag 3: Welke prognostische factoren moeten er beschreven worden in het pa-verslag van het resectiepreparaat
 Uitgangsvraag 3: Welke prognostische factoren moeten er beschreven worden in het pa-verslag van het resectiepreparaat van HCC patiënten? Primaire studies I Study ID II Method III Patient characteristics
Uitgangsvraag 3: Welke prognostische factoren moeten er beschreven worden in het pa-verslag van het resectiepreparaat van HCC patiënten? Primaire studies I Study ID II Method III Patient characteristics
WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS
 WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS Nguyen Dinh Duong Department of Environmental Information Study and Analysis, Institute of Geography, 18 Hoang Quoc Viet Rd.,
WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS Nguyen Dinh Duong Department of Environmental Information Study and Analysis, Institute of Geography, 18 Hoang Quoc Viet Rd.,
Low-dose CT Imaging. Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital
 Lung Cancer Screening with Low-dose CT Imaging Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital Despite recent declines in the incidence of lung cancer related to the
Lung Cancer Screening with Low-dose CT Imaging Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital Despite recent declines in the incidence of lung cancer related to the
TEXT-FILLED STACKED AREA GRAPHS Martin Kraus
 Martin Kraus Text can add a significant amount of detail and value to an information visualization. In particular, it can integrate more of the data that a visualization is based on, and it can also integrate
Martin Kraus Text can add a significant amount of detail and value to an information visualization. In particular, it can integrate more of the data that a visualization is based on, and it can also integrate
VIRTUAL REALITY, AUGMENTED REALITY AND ROBOTICS IN SURGICAL PROCEDURES OF THE LIVER
 VIRTUAL REALITY, AUGMENTED REALITY AND ROBOTICS IN SURGICAL PROCEDURES OF THE LIVER Luc SOLER 1, Nicholas AYACHE 2, Stéphane NICOLAU 1,2, Xavier PENNEC 2, Clément FOREST 1,2, Hervé DELINGETTE 2, Didier
VIRTUAL REALITY, AUGMENTED REALITY AND ROBOTICS IN SURGICAL PROCEDURES OF THE LIVER Luc SOLER 1, Nicholas AYACHE 2, Stéphane NICOLAU 1,2, Xavier PENNEC 2, Clément FOREST 1,2, Hervé DELINGETTE 2, Didier
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL
 Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery Melvin J Silverstein C H A P T E R 5 Introduction Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery combines oncologic principles with plastic surgical techniques. But it
Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery Melvin J Silverstein C H A P T E R 5 Introduction Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery combines oncologic principles with plastic surgical techniques. But it
Hepatic resection (Removal of part of the liver)
 Hepatic resection (Removal of part of the liver) The liver is the largest solid organ in the body and is located in the upper right-quadrant of the abdomen under the rib cage. Functionally it is a major
Hepatic resection (Removal of part of the liver) The liver is the largest solid organ in the body and is located in the upper right-quadrant of the abdomen under the rib cage. Functionally it is a major
Oftentimes, as implant surgeons, we are
 CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
CLINICAL AVOIDING INJURY TO THE INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BY ROUTINE USE OF INTRAOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHS DURING IMPLANT PLACEMENT Jeffrey Burstein, DDS, MD; Chris Mastin, DMD; Bach Le, DDS, MD Injury to the
Medical Marijuana Use in Patients with History of SCCHN Treated with Radiotherapy
 HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH Assessment the Impact of Real-time Tumor Tracking & Reduced Planning Target Volume Margins on Quality-of-Life in Prostate Cancer Patients Treatment with Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy
HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH Assessment the Impact of Real-time Tumor Tracking & Reduced Planning Target Volume Margins on Quality-of-Life in Prostate Cancer Patients Treatment with Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy
Whiplash injuries can be visible by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Pain Research and Management Autumn 2006; Vol. 11, No. 3, pp.
 Whiplash injuries can be visible by functional magnetic resonance imaging 1 Bengt H Johansson, MD FROM ABSTRACT: Pain Research and Management Autumn 2006; Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 197-199 Whiplash trauma can
Whiplash injuries can be visible by functional magnetic resonance imaging 1 Bengt H Johansson, MD FROM ABSTRACT: Pain Research and Management Autumn 2006; Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 197-199 Whiplash trauma can
Lip Cancer: Treatment & Reconstruction
 Lip Cancer: Treatment & Reconstruction GBMC - Head & Neck Cancer Grand Rounds Elizabeth E. Redd, M.D. With the assistance of Ira Papel, M.D. Patrick Byrne, M.D. Lip Cancer: Treatment & Reconstruction Anatomic
Lip Cancer: Treatment & Reconstruction GBMC - Head & Neck Cancer Grand Rounds Elizabeth E. Redd, M.D. With the assistance of Ira Papel, M.D. Patrick Byrne, M.D. Lip Cancer: Treatment & Reconstruction Anatomic
Twelve. Figure 12.1: 3D Curved MPR Viewer Window
 Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
AnatomyBrowser: A Framework for Integration of Medical Information
 In Proc. First International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 98), Cambridge, MA, 1998, pp. 720-731. AnatomyBrowser: A Framework for Integration of Medical
In Proc. First International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 98), Cambridge, MA, 1998, pp. 720-731. AnatomyBrowser: A Framework for Integration of Medical
Electronic health records to study population health: opportunities and challenges
 Electronic health records to study population health: opportunities and challenges Caroline A. Thompson, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor of Epidemiology San Diego State University Caroline.Thompson@mail.sdsu.edu
Electronic health records to study population health: opportunities and challenges Caroline A. Thompson, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor of Epidemiology San Diego State University Caroline.Thompson@mail.sdsu.edu
Bridging Techniques. What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS
 Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
Bridging Techniques What s between EMR and Traditional Surgery? Elisabeth C. McLemore, MD, FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Surgery Assistant Program Director, General Surgery Residency Disclosures
Introduction. Case History
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Case Report of Renal Cell Carcino Shimajiri, Shouhei; Shingaki, Yoshi Masaya; Tamamoto, Tooru; Toda, Taka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Case Report of Renal Cell Carcino Shimajiri, Shouhei; Shingaki, Yoshi Masaya; Tamamoto, Tooru; Toda, Taka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科
 Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科 Papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid Definition latent aberrant thyroid occult thyroid carcinoma latent papillary carcinoma)
Surgical Management of Papillary Microcarcinoma 趙 子 傑 長 庚 紀 念 醫 院 林 口 總 院 一 般 外 科 Papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid Definition latent aberrant thyroid occult thyroid carcinoma latent papillary carcinoma)
BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader. Two years ago, I was working as a bedside nurse. One of my colleagues felt
 Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. John P. Roberts, MD Chief, Division of Transplant Service University of California, San Francisco
 Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma John P. Roberts, MD Chief, Division of Transplant Service University of California, San Francisco Hepatocellular Carcinoma HCC is the 5th most common
Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma John P. Roberts, MD Chief, Division of Transplant Service University of California, San Francisco Hepatocellular Carcinoma HCC is the 5th most common
Authors: Masahiro Watanabe*, Motoi Okuda**, Teruo Matsuzawa*** Speaker: Masahiro Watanabe**
 Visualization of the Blood flow and the Stress distribution with the Diagnostic Support System for Circulatory Disease in the Volume Communications Environment Authors: Masahiro Watanabe*, Motoi Okuda**,
Visualization of the Blood flow and the Stress distribution with the Diagnostic Support System for Circulatory Disease in the Volume Communications Environment Authors: Masahiro Watanabe*, Motoi Okuda**,
DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA.
 DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA. Juan Antonio Martínez Mera Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías da Información Universidade de Santiago de Compostela
DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMAGING SYSTEM FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE THORACIC AORTA. Juan Antonio Martínez Mera Centro Singular de Investigación en Tecnoloxías da Información Universidade de Santiago de Compostela
Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer
 Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer Guest Expert: Sukru, MD Professor of Transplant Surgery Mario Strazzabosco, MD Professor of Internal Medicine www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
Leading the Way to Treat Liver Cancer Guest Expert: Sukru, MD Professor of Transplant Surgery Mario Strazzabosco, MD Professor of Internal Medicine www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
COMMISSIONING. for ULTRA-RADICAL SURGERY ADVANCED OVARIAN CANCER
 COMMISSIONING for ULTRA-RADICAL SURGERY in ADVANCED OVARIAN CANCER WHY THIS MUST HAPPEN PERSPECTIVE COMMISSIONING FOR WHO, FOR WHAT? Biological Basis Surgical Basis International and national standards
COMMISSIONING for ULTRA-RADICAL SURGERY in ADVANCED OVARIAN CANCER WHY THIS MUST HAPPEN PERSPECTIVE COMMISSIONING FOR WHO, FOR WHAT? Biological Basis Surgical Basis International and national standards
SBRT (Elekta), 45 Gy in fractions of 3 Gy 3x/week for 5 weeks (N=22) vs.
 Uitgangsvraag 6: Wat is de plaats van stereotactische radiotherapiebehandeling (SBRT) bij HCC patiënten? Primaire studies I Study ID II Method III Patient characteristics IV Intervention(s) V Results primary
Uitgangsvraag 6: Wat is de plaats van stereotactische radiotherapiebehandeling (SBRT) bij HCC patiënten? Primaire studies I Study ID II Method III Patient characteristics IV Intervention(s) V Results primary
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
PLASTIC SURGERY RESIDENTS HANDBOOK
 PLASTIC SURGERY RESIDENTS HANDBOOK I. PLASTIC SURGERY REQUIREMENTS a. AACPS Post Interview Communication Guidelines b. General Competencies c. Plastic Surgery Goals & Objectives d. ACGME Required Index
PLASTIC SURGERY RESIDENTS HANDBOOK I. PLASTIC SURGERY REQUIREMENTS a. AACPS Post Interview Communication Guidelines b. General Competencies c. Plastic Surgery Goals & Objectives d. ACGME Required Index
Breast. Patient information. cancer clinical pathway
 Breast Patient information cancer clinical pathway This leaflet was written to properly inform people following breast cancer treatment plan. It doesn t replace the dialogue with healthcare staff; it rather
Breast Patient information cancer clinical pathway This leaflet was written to properly inform people following breast cancer treatment plan. It doesn t replace the dialogue with healthcare staff; it rather
Arkansas Medicaid Physician/Independent Lab/CRNA/Radiation Therapy Center Providers
 Arkansas Department of Human Services Division of Medical Services Donaghey Plaza South P.O. Box 1437 Little Rock, Arkansas 72203-1437 Internet Website: www.medicaid.state.ar.us Telephone (501) 682-8292
Arkansas Department of Human Services Division of Medical Services Donaghey Plaza South P.O. Box 1437 Little Rock, Arkansas 72203-1437 Internet Website: www.medicaid.state.ar.us Telephone (501) 682-8292
restricted to certain centers and certain patients, preferably in some sort of experimental trial format.
 Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Managing Pancreatic Cancer, Part 4: Pancreatic Cancer Surgery, Complications, & the Importance of Surgical Volume Dr. Matthew Katz, Surgeon, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX I m going to talk a little
Bernice E. Rogowitz and Holly E. Rushmeier IBM TJ Watson Research Center, P.O. Box 704, Yorktown Heights, NY USA
 Are Image Quality Metrics Adequate to Evaluate the Quality of Geometric Objects? Bernice E. Rogowitz and Holly E. Rushmeier IBM TJ Watson Research Center, P.O. Box 704, Yorktown Heights, NY USA ABSTRACT
Are Image Quality Metrics Adequate to Evaluate the Quality of Geometric Objects? Bernice E. Rogowitz and Holly E. Rushmeier IBM TJ Watson Research Center, P.O. Box 704, Yorktown Heights, NY USA ABSTRACT
Voxar 3D TM. A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools
 Voxar 3D TM A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools The power to deliver advanced visualization throughout the enterprise To effectively manage the rapid growth of large volumetric
Voxar 3D TM A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools The power to deliver advanced visualization throughout the enterprise To effectively manage the rapid growth of large volumetric
CASE OF THE MONTH AUGUST-2015 DR. GURUDUTT GUPTA HEAD HISTOPATHOLOGY
 CASE OF THE MONTH AUGUST-2015 DR. GURUDUTT GUPTA HEAD HISTOPATHOLOGY CASE HISTORY 52Y MALE RIGHT RADICAL NEPHERECTOMY Case of right renal mass with IVC thrombus. History of surgery and RT for right occipital
CASE OF THE MONTH AUGUST-2015 DR. GURUDUTT GUPTA HEAD HISTOPATHOLOGY CASE HISTORY 52Y MALE RIGHT RADICAL NEPHERECTOMY Case of right renal mass with IVC thrombus. History of surgery and RT for right occipital
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Proteomics-based Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: proteomics_based_testing_related_to_ovarian_cancer 7/2010
Corporate Medical Policy Proteomics-based Testing Related to Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: proteomics_based_testing_related_to_ovarian_cancer 7/2010
Exploratory data analysis (Chapter 2) Fall 2011
 Exploratory data analysis (Chapter 2) Fall 2011 Data Examples Example 1: Survey Data 1 Data collected from a Stat 371 class in Fall 2005 2 They answered questions about their: gender, major, year in school,
Exploratory data analysis (Chapter 2) Fall 2011 Data Examples Example 1: Survey Data 1 Data collected from a Stat 371 class in Fall 2005 2 They answered questions about their: gender, major, year in school,
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What the hepatologist wants to know
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What the hepatologist wants to know Hélène Castel, MD Liver Unit Hôpital St-Luc CHUM? CAR Annual Scientific Meeting Saturday, April 27 th 2013 Disclosure statement I do not have
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What the hepatologist wants to know Hélène Castel, MD Liver Unit Hôpital St-Luc CHUM? CAR Annual Scientific Meeting Saturday, April 27 th 2013 Disclosure statement I do not have
Clinical Training for Visage 7 Cardiac. Visage 7
 Clinical Training for Visage 7 Cardiac Visage 7 Overview Example Usage 3 Cardiac Workflow Examples 4 Remove Chest Wall 5 Edit Chest Wall Removal 6 Object Display Popup 7 Selecting Optimal Phase 8 Thick
Clinical Training for Visage 7 Cardiac Visage 7 Overview Example Usage 3 Cardiac Workflow Examples 4 Remove Chest Wall 5 Edit Chest Wall Removal 6 Object Display Popup 7 Selecting Optimal Phase 8 Thick
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA GI Site Group Hepatocellular Carcinoma Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA GI Site Group Hepatocellular Carcinoma Authors: Dr. Jennifer Knox, Dr. Mairead McNamara 1. INTRODUCTION
Treatment of Hepatic Neoplasm
 I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for treatment of hepatic neoplasm outside of systemic chemotherapy alone when determined to be medically necessary and within the medical criteria
The Global Surgery Package Part I. Riva Lee Asbell
 The Global Surgery Package Part I Riva Lee Asbell Introduction One of the least understood concepts in surgical coding concerns the details involved in the Global Surgery Package. Some of the rules were
The Global Surgery Package Part I Riva Lee Asbell Introduction One of the least understood concepts in surgical coding concerns the details involved in the Global Surgery Package. Some of the rules were
Medical Diagnosis and Visual Perception - An Evaluation of Usability
 How Useful is Computer Graphics for Medical Diagnoses? G. Domik 1, S. Arens 1, I. Scharlau 2, F. Hilkenmeier 2 1 Computer Graphics, Visualization, Image Processing 2 Cognitive Psychology University of
How Useful is Computer Graphics for Medical Diagnoses? G. Domik 1, S. Arens 1, I. Scharlau 2, F. Hilkenmeier 2 1 Computer Graphics, Visualization, Image Processing 2 Cognitive Psychology University of
An Interactive Visualization Tool for the Analysis of Multi-Objective Embedded Systems Design Space Exploration
 An Interactive Visualization Tool for the Analysis of Multi-Objective Embedded Systems Design Space Exploration Toktam Taghavi, Andy D. Pimentel Computer Systems Architecture Group, Informatics Institute
An Interactive Visualization Tool for the Analysis of Multi-Objective Embedded Systems Design Space Exploration Toktam Taghavi, Andy D. Pimentel Computer Systems Architecture Group, Informatics Institute
UCLA Asian Liver Program
 CLA Program Update Program Faculty Myron J. Tong, PhD, MD Professor of Medicine Hepatology Director, Asian Liver Program Surgery Ronald W. Busuttil, MD, PhD Executive Chair Department of Surgery Director,
CLA Program Update Program Faculty Myron J. Tong, PhD, MD Professor of Medicine Hepatology Director, Asian Liver Program Surgery Ronald W. Busuttil, MD, PhD Executive Chair Department of Surgery Director,
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment Decision Tree
 Treatment Decision Tree Derek DuBay, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Liver Transplant and Hepatobiliary Surgery UAB Department of Surgery 1 UAB Liver Tumor Clinic Referrals: 205 996 5970 (phone) 205
Treatment Decision Tree Derek DuBay, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Liver Transplant and Hepatobiliary Surgery UAB Department of Surgery 1 UAB Liver Tumor Clinic Referrals: 205 996 5970 (phone) 205
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET
 LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
LIVER TUMORS PROFF. S.FLORET NEOPLASM OF LIVER PRIMARY 1)BENIGN 2)MALIGNANT METASTATIC/SECONDARY LIVER Primary Liver Cancer the Second Killer among tumors high morbidity and mortality(20.40/100,000) etiology
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD
 SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
Tricia Cox on 7/18/2012 at Oncology Center. Sarah Randolf. Female
 SAMPLE This Survivorship Care Plan will facilitate cancer care following active treatment. It may include important contact information, a treatment summary, recommendations for follow-up care testing,
SAMPLE This Survivorship Care Plan will facilitate cancer care following active treatment. It may include important contact information, a treatment summary, recommendations for follow-up care testing,
New Methods for Guidance of Light-Based Treatments Using Objective Melanin Measurements
 New Methods for Guidance of Light-Based Treatments Using Objective Melanin Measurements Sean Doherty, MD, 1 Richard Cohen, PhD, 2 Felicia Whitney, RN, 2 Oksana Bradley, MD, 2 (Ukraine) Brooke Seckel, MD
New Methods for Guidance of Light-Based Treatments Using Objective Melanin Measurements Sean Doherty, MD, 1 Richard Cohen, PhD, 2 Felicia Whitney, RN, 2 Oksana Bradley, MD, 2 (Ukraine) Brooke Seckel, MD
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
SAMSUNG ULTRASOUND RS80A
 Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Visualizing Data: Scalable Interactivity
 Visualizing Data: Scalable Interactivity The best data visualizations illustrate hidden information and structure contained in a data set. As access to large data sets has grown, so has the need for interactive
Visualizing Data: Scalable Interactivity The best data visualizations illustrate hidden information and structure contained in a data set. As access to large data sets has grown, so has the need for interactive
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis. A. Criminisi & the InnerEye team @ MSRC
 Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi & the InnerEye team @ MSRC Medical image analysis the goal Automatic, semantic analysis and quantification of what observed in medical scans Brain
Machine Learning for Medical Image Analysis A. Criminisi & the InnerEye team @ MSRC Medical image analysis the goal Automatic, semantic analysis and quantification of what observed in medical scans Brain
Advanced Volume Rendering Techniques for Medical Applications
 Advanced Volume Rendering Techniques for Medical Applications Verbesserte Darstellungsmethoden für Volumendaten in medizinischen Anwendungen J. Georgii 1, J. Schneider 1, J. Krüger 1, R. Westermann 1,
Advanced Volume Rendering Techniques for Medical Applications Verbesserte Darstellungsmethoden für Volumendaten in medizinischen Anwendungen J. Georgii 1, J. Schneider 1, J. Krüger 1, R. Westermann 1,
Clustering & Visualization
 Chapter 5 Clustering & Visualization Clustering in high-dimensional databases is an important problem and there are a number of different clustering paradigms which are applicable to high-dimensional data.
Chapter 5 Clustering & Visualization Clustering in high-dimensional databases is an important problem and there are a number of different clustering paradigms which are applicable to high-dimensional data.
Decision Trees What Are They?
 Decision Trees What Are They? Introduction...1 Using Decision Trees with Other Modeling Approaches...5 Why Are Decision Trees So Useful?...8 Level of Measurement... 11 Introduction Decision trees are a
Decision Trees What Are They? Introduction...1 Using Decision Trees with Other Modeling Approaches...5 Why Are Decision Trees So Useful?...8 Level of Measurement... 11 Introduction Decision trees are a
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION. Francis Yao, M.D.
 UCSF TRANSPLANT CONFERENCE - 9/28/2012 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION Francis Yao, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine and Surgery Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
UCSF TRANSPLANT CONFERENCE - 9/28/2012 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION Francis Yao, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine and Surgery Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
Yttrium-90 Radioembolization
 Yttrium-90 Radioembolization Yttrium-90 radioembolization is generally used as a palliative therapy for selected patients with unresectable tumors of the liver including: Metastatic tumors from colorectal
Yttrium-90 Radioembolization Yttrium-90 radioembolization is generally used as a palliative therapy for selected patients with unresectable tumors of the liver including: Metastatic tumors from colorectal
CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION
 CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION CINDY WEILAND AND SANDRA L. KATANICK Continued innovations in noninvasive testing equipment provide skilled sonographers and physicians with the technology
CHAPTER 4 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TEST VALIDATION CINDY WEILAND AND SANDRA L. KATANICK Continued innovations in noninvasive testing equipment provide skilled sonographers and physicians with the technology
By James D. Gould, MD FACS
 By James D. Gould, MD FACS BACKGROUND Balloon devices enlarge narrowed sinus ostia and outflow tracts by remodeling the surrounding bone and paranasal sinus structures. Multiple studies have demonstrated
By James D. Gould, MD FACS BACKGROUND Balloon devices enlarge narrowed sinus ostia and outflow tracts by remodeling the surrounding bone and paranasal sinus structures. Multiple studies have demonstrated
Challenge of FUJIFILM in Medical ICT
 Challenge of FUJIFILM in Medical ICT Sep.10, 2014 FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS Forward-looking statements, such as those relating to earnings forecasts and other projections contained in this material, are
Challenge of FUJIFILM in Medical ICT Sep.10, 2014 FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS Forward-looking statements, such as those relating to earnings forecasts and other projections contained in this material, are
Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC): Now and the Future
 Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC): Now and the Future Mazin Al-kasspooles, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Surgical Oncology Director, Regional Therapy
Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC): Now and the Future Mazin Al-kasspooles, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Surgical Oncology Director, Regional Therapy
Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed Tomography (CT) Scan of the Chest Performed for Reasons Other than Thyroid Disease
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2011, 2, 264-268 doi:10.4236/ijcm.2011.23042 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Incidence of Incidental Thyroid Nodules on Computed
R/F. Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening. 3. Utility of Chest Tomosynthesis. 1.
 R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
R/F Efforts to Reduce Exposure Dose in Chest Tomosynthesis Targeting Lung Cancer Screening Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East Kaoru Shimizu Ms. Kaoru Shimizu 1. Introduction
Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery
 Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery Background: Surgery is by nature invasive. Efforts have been made over time to reduce complications and the trauma inherently associated with surgery through
Clinical Practice Assessment Robotic surgery Background: Surgery is by nature invasive. Efforts have been made over time to reduce complications and the trauma inherently associated with surgery through
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
ERBEJET 2. The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY
 ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
ERBEJET 2 The versatility of waterjet surgery: ERBEJET 2 with hybrid instruments WATERJET SURGERY Gentle interventions in surgery and endoscopy Waterjet surgery with hybrid technology Waterjet surgery
journal of surgical research 191 (2014) 74e83 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect
 journal of surgical research 191 (2014) 74e83 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.journalofsurgicalresearch.com Visualizing surgical quality data with treemaps
journal of surgical research 191 (2014) 74e83 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.journalofsurgicalresearch.com Visualizing surgical quality data with treemaps
IntelliSpace PACS 4.4. Image Enabled EMR Workflow and Enterprise Overview. Learning Objectives
 IntelliSpace PACS 4.4 Image Enabled EMR Workflow and Enterprise Overview Learning Objectives Use the Cerner EMR to view images and reports via IntelliSpace PACS: Image Launch Workflow (SUBI Image Viewer)
IntelliSpace PACS 4.4 Image Enabled EMR Workflow and Enterprise Overview Learning Objectives Use the Cerner EMR to view images and reports via IntelliSpace PACS: Image Launch Workflow (SUBI Image Viewer)
XIV ANNUAL MEETING OF NURSING
 Archive of Oncology 2000;8(Suppl 1):69. SESSION 5 XIV ANNUAL MEETING OF NURSING 69 Archive of Oncology 2000;8(Suppl 1):70. 70 UDC: 616.34-007.272:616-089.8:614.39 I. GAJI M. ULAFI Æ. MIHAJLOVI R. NE I
Archive of Oncology 2000;8(Suppl 1):69. SESSION 5 XIV ANNUAL MEETING OF NURSING 69 Archive of Oncology 2000;8(Suppl 1):70. 70 UDC: 616.34-007.272:616-089.8:614.39 I. GAJI M. ULAFI Æ. MIHAJLOVI R. NE I
