Basic Knowledge of LDO Voltage Regulator CMOS LINEAR REGULATOR (rev. 2 Feb. 2, 2010)
|
|
|
- Austin Dean
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMOS LINEAR REGULATOR (rev. 2 Feb. 2, 2010) CMOS Linear Regulator Overview The history of CMOS linear regulators is relatively new. They have developed with battery-powered portable electronics devices. Since CMOS processes have been used in large-scale integrated circuits like LSI and microprocessors, they have been miniaturized constantly. Taking full advantage of the miniaturization technology, CMOS linear regulators have become the power management ICs that are widely used in portable electronics products to realize low profile, low dropout, and low supply current. How Are They Different from Bipolar Linear Regulators? In general, a CMOS linear regulator offers lower supply current compare to a bipolar linear regulator. This is because bipolar process is current-driven, while CMOS process is voltage-driven. [See Figure 1] [Figure 1] Current-Driven Device and Voltage-Driven Device Bipolar Transistor MOS Transistor Collector Drain Base Current Base Emitter Current runs between the emitter and the collector when base current is on. Base current must be on to get output current. Gate Voltage Gate Source Current runs between the source and drain when voltage is charged at the gate. Once electric charge is charged, current is not needed to turn on. Linear regulators, which do not require clock operation, are especially suitable to attain low supply current because the operating current of the regulators can be nearly zero in the circuits other than analog operating circuits. One example of bipolar linear regulators is 78 series, multipurpose 3-pin regulators. Since the input voltage range of the series is as high as 30V ~ 40V and the series can pull more than 1A of current, the series are used in various white goods and industrial equipment. Nevertheless, the series are not low dropout because the series output structure is NPN Darlington Output. Table 1 shows some main characteristics of the series. [Table 1] The Major Characteristics of Multipurpose 78 series Regulators Product Maximum Rated Input Operating Dropout Voltage Series Voltage Current 78xx 1A 35V, 40V 4~8mA 2V@1A 78Mxx 500mA 35V, 40V 6~7mA 2V@350mA 78Nxx 300mA 35V, 40V 5~6mA 1.7V@200mA 2V@300mA 78Lxx 100mA 30V, 35V, 40V 6~6.5mA 1.7V@ 40mA Still, the number of process needed for bipolar linear regulators is about a half or two thirds of CMOS process, and therefore a bipolar linear regulator is more cost-effective than a CMOS regulator even if its die-size is larger. Thus, a bipolar linear regulator is better suited for large current or high voltage use. On the other hand, CMOS process s miniaturization technologies are well developed and have advantages such as low voltage, low dropout, small size, and low power consumption. 1
2 Where and How Is CMOS Used? CMOS linear regulators are widely used in battery-powered portable electronics devices because of their low dropout and low supply current characteristics. LDO (Low Dropout) regulators enable battery to be used up to the limit, and therefore the regulators are now essential power management ICs for the devices like mobile phones, digital cameras, and laptop PCs to have long battery life. Because LDO regulators feature to pull large current with small input-output voltage differential while minimizing heat losses, they can meet the wide range of current requirements of each device. Some low supply current types of regulators use lower than 1μA of self-supply current. Because of this feature, those types of regulators can maintain supply current of the electronics devices and wireless applications like mobile phones as low as possible when these devices are in sleep mode. Since these regulators can also provide the benefit of the CMOS miniaturization technology, they offer a great potential to mobile electronics devices that require low profile and high precision. Packages Standard packages used for CMOS linear regulators are SOT-23 and SOT-89. Recently, ultra small packages like CSP (chip scale package) have also become available. Because the development of the power management ICs is led by the progress of mobile devices, they are typically sealed in surface-mount small packages. Picture 1 shows the representative packages. [Picture 1] Examples of CMOS Regulator Packages USP-6: Ultra Small Package USP-4: Ultra Small Package USP-3: Ultra Small Package SOT-89: Standard Mini Power Mold Package SOT-23: Standard Mini Mold Package 2
3 Features: What Can CMOS Do? The premise of linear regulators as the power management ICs is that they are directly connected to a battery or an AC adapter, so you must pay attention to the maximum input voltage. The ICs design rules of CMOS processes vary depending on maximum input voltage, and maximum input voltage and microminiaturization technology are in an inverse relationship; they do not mutually act like the greater serves for the lesser. If you choose high input voltage, then the ICs size will be bigger and its performance diminishes, and if you choose small sized ICs then you need to be careful about maximum input voltage. There are various CMOS regulators with various maximum input voltages for different applications. You should choose the most appropriate ones by carefully examining the types of power source and desired performances of your device [See Table 2]. [Table 2] Product Categories by Operating Voltage (Three-terminal voltage regulators) Operating Product Package Voltage Series USP-3 SOT-23 SOT-89 SOT223 TO V ~ 6V XC V ~ 6V XC6206 2V ~ 10V XC6201 2V ~ 20V XC6202 2V~28V XC6216 3
4 CMOS linear regulators can be categorized as low supply current, large current, high voltage, high-speed, LDO, and so on. There is no strict definition for these categories, but usually low supply current are the ones with the supply current of a few μa, large current are the ones that can pull 500mA or more, high voltage are the ones with the voltage of 15V to 20V or more, and high-speed are the ones with the ripple rejection rate of approximately 60dB@1kHz. LDO does not have an exact definition either. Originally it referred to the low dropout output of PNP output and P-ch MOSFET output, in comparison to the dropout of NPN emitter follower output and NPN Darlington output of a bipolar linear regulator. Figure 3 shows the types of output transistors. These days, the value of less than in on-resistance conversion is becoming one standard of definition. [Figure 3] Output Driver Models NPN Emitter Follower Output Input Power Source NPN Darlington Output Input Power Source Control Circuit Control Circuit Predriver Base Voltage: 0.6V Base Voltage: 0.6V Output Transistor Output Pin Base Voltage: 0.6V Output Pin Control circuit must be higher by 0.6V (base voltage) than the output pin, in order to flow base current. The control circuit is operated by input power source, so dropout voltage of 0.6V is needed. PNP Transistor Output Input Power Source 1.2V or more dropout voltage is needed as the circuit consists of 2 emitter follower circuits. The circuit can output large current because the base current of load transistor can be amplified by the predriver. PMOS Transistor Output Input Power Source Base Voltage: 0.6V Gate Voltage: 0.7V Control Circuit Control Circuit Output Pin Output Pin A transistor turns on when input voltage is lower than base voltage and/or gate voltage is applied. There is no limit on input power source voltage in relative to output pin voltage. The dropout voltage is small because the circuit operates if there is the base voltage or gate voltage, and input power voltage that can operate control circuit. 4
5 Other than the above types of regulators, there are regulators with an ON/OFF function by Chip Enable pin according to need, composite regulators with 2 or 3 channels, regulators with a build-in voltage detector, and more. Such wide variety is another feature of CMOS. This is attributed to the fact that CMOS process can easily scale up circuits and lower supply current because it can completely shut down specific blocks of ICs when circuits are turned off separately. Figure 2 shows the block diagram of XC6415 series, 2-channel output regulators. This product can turn on and off VR1 and VR2 independently. [Figure 2] Block Diagram of 2-Channel Regulator (XC6415 Series) 5
6 Internal Circuit and Basic Structure An internal circuit consists of a reference voltage source, an error amplifier, an output voltage preset resistor, and an output P-ch MOSFET transistor. Some circuits also have a constant current limiter, a foldback circuit and a thermal shutdown function for protection purpose. Since it is difficult to build bandgap reference circuits that are used for bipolar processes as a reference voltage source, usually the reference voltage sources used are unique to CMOS process. For this reason, the output voltage temperature characteristics tend to be slightly inferior compare to bipolar linear regulators. Also, internal phase compensation and circuitries vary depending on the regulator types such as low supply current, high-speed, and low ESR capacitor compatible. For instance, while a low supply current regulator normally uses two amplifiers, a high-speed regulator sometimes contains three amplifiers. Figure 4 indicates the basic circuitry block diagram of the high-speed regulator. By adding a buffer amplifier between a preamplifier and an output P-ch MOSFET transistor, the buffer amplifier can drive the load P-ch MOSFET transistor in higher speed despite the large gate capacity. The output voltage can be determined by the values of divided resistors, R1 and R2, and the current limit value is determined by the values of divided resistors, R3 and R4. Each value is precisely set by trimming. Many high-speed type regulators are compatible with low ESR type capacitors, such as ceramic capacitors, because they are mostly used for wireless applications and portable electronics devices and therefore downsizing is necessary. [Figure 4] Basic Circuitry Block Diagram of High-Speed Type Regulator Current Limit Circuit VIN P-ch MOSFET Output Current Monitor P-ch MOSFET Output Transistor R3 R4 + - Current Limit Circuit Current Limit Comparator Buffer - + Error Amplifier CFB R1 R2 VOUT Output ESR CL Reference Voltage Source VSS 6
7 Basic Performance Basic Electrical Characteristics Table 3 shows general electrical characteristics of a CMOS regulator. [Table 3] General Characteristics of CMOS Regulators by Types Type Low Supply Current High Voltage Large Current Super High Speed High speed Ultra High speed XC6201 XC6216 XC6220 XC6204/05 XC6221 XC6222 Unit Output Voltage Range 1.3~6 2.0~23 0.8~5 0.9~6 0.8~5 0.8~5 V Output Voltage Accuracy ±2 ±2 ±1 ±2 ±2 ±1 % Output Voltage Temp.Stability ±100 ±100 ±100 ±100 ±100 ±100 ppm/ Max ma Dropout Voltage@100mA V Supply Current 2 5 8(PS mode) μa Standby Current μa Line Regulation %/V Input Voltage 2~10 2~28 1.6~6 2~10 1.6~6 1.7~6 V Output Noise - 30 μvrms PSRR@1 khz db Note: The values shown are typical values. 7
8 Ripple Rejection Rate The basic performances of CMOS linear regulators include output voltage accuracy, supply current, line regulation, load regulation, dropout voltage, and output voltage temperature characteristics. Because these parameters are fundamental characteristics of series regulators, there is no major difference between CMOS regulators and bipolar linear regulators. There are various types of CMOS linear regulators depending on applications, but they can be roughly subdivided into two categories according to their performance; regulators that feature low supply current and high-speed LDO regulators that focus on transient response characteristics. This categorization is based on the differences of the following capability to the changes of input voltage or output current, and therefore this feature is hard to be indicated by conventional DC characteristics. Hence, these days ripple rejection rate is included in the basic characteristics in order to indicate the basic performance of CMOS linear regulators. The formula of Ripple Rejection Rate is as shown below. Ripple Rejection Rate =20*Log (change in output voltage / change in input voltage) Graph 1 indicates the ripple rejection rate of XC6209 series, high-speed regulators. Also, the actual waveform is shown in Figure 4. Using the input voltage with the peak-to-peak voltage of 1V and changing frequency, you can see the changes in the ripple value of output voltage. In Graph 1, the ripple rejection rate is -80dB when frequency is 1 khz. So the output voltage will change approximately 0.1mV as input voltage changes 1V, and therefore we cannot identify major change in the oscilloscope in Figure 5. But when frequency is 100 khz the ripple rejection rate will be 50dB, so the output ripple becomes a few mv and the changes become visible on the oscilloscope. [Graph 1] Ripple Rejection Rate Characteristics (XC6209B302) Ripple Rejection Rate:RR (db) XC6209(3V) VIN=4VDC+1Vp-pAC IOUT=30mA, CL=1μF(Ceramic) Ripple Frequency: f (khz) [Figure 5] Ripple Rejection Rate: Actual Input Voltage and Output Voltage Waveform (IOUT=30mA) Input Voltage: Input Ripple Frequency:1 khz Input Voltage: Input Ripple Frequency: 100 khz Output Voltage: Vpp: 1V Output Voltage: Vpp: 1V 8
9 Dropout Voltage Another basic characteristic of linear regulators is dropout voltage, but most CMOS regulators are low dropout types that have very small dropout voltage. This trait derives from the fact that the regulators have been developed to achieve long-time use of battery life. Graph 2 shows the relationship between input voltage and output voltage. You can tell that the dropout voltage is remarkably small. [Graph 2] The Relationship between Input Voltage and Output Voltage (XC6209B302: Output Current=30mA) Input Voltage OUTPUT 100mV/div Small dropout voltage (Approx, 50mV) Input-output dropout voltage literally means the voltage difference between input and output voltage, but it also suggests the amount of available current. The dropout voltage characteristics of XC6209B302 are shown in Graph 3 for your reference. For example, if you need the output current of 150mA using a regulator with the output voltage of 3V, then needed dropout voltage is 300mV, and therefore needed input voltage is 3.3V. [Graph 3] Dropout Voltage vs. Output Current (XC6209B302) Dropout Voltage: Vdif [V] CIN=1μF(Ceramic), CL=1μF(Ceramic) Topr=85 o C(Top) =25 o C(Middle) =-40 o C(Bottom) Recent LDO has the improved drivability of a P-ch MOSFET driver, so you are likely able to get output current up to the current limit almost without dropout, if there is certain dropout voltage : IOUT [ma] 9
10 Transient Response Characteristics: Compliance Capability When Input Voltage or Load Current Changes Stepwise These days burst mode is commonly used for the digital signal processing of electronics devices, and therefore the change of load current on LSI and memory is getting larger than ever. Hence, transient response characteristics that can be compliant with the changes are now an essential quality of regulators. Transient response characteristics can be categorized as line-transient response and load transient response, and these characteristics are completely depending on the supply current of a circuit. Let us focus attention on the error amplifier and gate capacitance value of the P-ch MOSFET load switching transistor shown in Figure 3, a basic internal circuit block diagram. A CMOS linear regulator contains a large P-ch MOSFET transistor as a load switch, and the response speed is determined almost entirely by the output impedance of the error amplifier to drive the MOSFET transistor and the MOSFET transistor gate capacitance value. The factor that determines the output impedance of the error amplifier is the supply current of a circuit; as supply current increases, the impedance becomes lower and response becomes higher speed. As previously described, the drivability of a high-speed regulator is improved by adding a buffer. Because the buffer functions as an amplifier as well, there will be 3 sets of amplification: a preamplifier error amplifier (40dB), a buffer amplifier (20dB), and a load P-ch MOSFET transistor (20dB). They form a feedback circuit with the open-loop gain of 80dB or more sensitivity and can respond to the change of output voltage in sensitive and high-speed manner. Observing the actual waveform of the load transient response in Graph 4, the voltage recovery starts within a few micro seconds after the output voltage changes, which are caused by the change of the load current. [Graph 4] Load Transient Response of High-Speed LDO (XC6209B302) VIN=VCE=4.0V,tr=tf =5usec CIN= CL=1.0 uf (ceramic) Output Voltage: VOUT (V) Output Voltage Voltage recovery starts w hile output current is changing : IOUT (ma Time (20usec/div) 10
11 Graph 5 compares the load transient responses between XC6201 series and XC6209 series, a low supply current type and a high-speed type. The size of P-ch MOSFET transistors in both series is just about the same because both ICs are as small as to be assembled in SOT-25 package, but the waveform is apparently different. [Graph 5] Load Transient Response Comparison Low Supply Current Regulator: XC6201x302 High Speed Regulator: XC6209x VIN=VCE=4.0V, tr=tf=5usec CIN= CL=1.0 uf(tantalum) VIN=VCE=4.0V, tr=tf=5usec CIN= CL=1.0 uf(ceramic) 250 Output Voltage: VOUT (V) Output Voltage : IOUT (ma) Output Voltage: VOUT (V) Output Voltage : IOUT (ma) Time (200uS/div) Time (200uS/div) Generally speaking, P-silicon substrate can improve line-transient response time and ripple rejection rate. This is because P- silicon substrate is grounded to the VSS, and therefore circuits on the silicon substrate are less affected by input power source. Figure 6 shows the inverter circuit on P-silicon substrate. Reference voltage sources inside of ICs are often designed using this characteristic. [Figure 6] Inverter Formed on P-Silicon Substrate Power Input Inverter Input Inverter Output As P Silicon substrate equal to VSS electronic potential, it is less affected by noise from the substrate. N+ P+ P+ N+ N+ P+ P-ch MOSFET N-ch MOSFET N Well P Well VSS P Silicon Substrate Twin-Tub Structure Recent LDO regulators response in extremely high-speed, and have good compliance capability to load transient response. Yet at the same time this high-speed response can make the power line unstable, and it may not only worsen the performance as a high-speed regulator but also can affect output of other linear regulators when there is impedance from connecters and wires at a power line. Wiring on PC board must be designed carefully in order to avoid impedance from the power line. 11
12 Output Noise Characteristics White noise is one of the output noises, which occurs when thermal noise arising in an output-voltage preset resistor is amplified by an error amplifier. Thermal noise can get larger when impedance is high, so there is ultra high-speed, low noise CMOS regulators of which supply current is 70μA. The noise characteristic of the regulator is shown in Graph 6. [Graph 6] Output Noise Density (XC6204B302) 10 VIN=4.0V, Iout=10mA CL=1uF(Ceramic), Ta=25 o C Output Noice Density (uv/ Hz] Integrated Range: 30uVrms Frequency:f (khz) 12
13 Protection Function/Power Saving Function Overcurrent Protection and Heat Protection Since linear regulators are power ICs, they normally have some kinds of protection functions. Commonly used protections are current limiter circuits and foldback circuits for overcurrent protection, and thermal shutdown circuits for heat protection. Graph 7 shows the operational characteristics example of a constant current limiter and a foldback circuit. When output current is going to get higher than 300mA, the constant current limiter operates and the output voltage descends almost vertically in the graph. As the descent continues, the foldback circuit operates and reduces the output current. Eventually the output current is decreased to 10 or 20mA, so the heat loss can be reduced as low as about 100mW in the case input voltage is 4.0V. [Graph 7] Current Limit and Foldback Operation (XC6209B302) CE/CL Discharge Some of recent CMOS linear regulators can automatically discharge the charge remained in load capacitors, synchronizing the regulators ON/OFF switch. This power management function is often used to improve the efficiency of the batteries in portable electronic devices. Since each block discharges the charge remained in capacitors at the moment of power off, the time to wait discharging is shortened and thus it is easy to program ON/OFF sequence of each block. Graph 8 shows an output voltage waveform of the high-speed discharge, XC6221B series when the CE pin is OFF. You can see the remained charge in a load capacitor is discharged in high speed when the CE pin voltage reaches to 0V. [Graph 8] High Speed Discharge Waveform (XC6221B Series) XC6221A 高 With 速 ディスチャージなし high speed discharge Output Voltage: VOUT (V) Foldback VIN=4.0V CIN=1μF(Ceramic), CL=1μF(Cerami c) Current Limiting Operation : IOUT (ma) XC6221B 高 Without 速 ディスチャージあり High speed discharge 13
14 G.O(Green Operation) Basic Knowledge of XC6217 series are the CMOS linear regulators with Green Operation function that can switch between HS (high-speed mode) and PS (power-save mode) depending on output current. The regulator s internal supply current will automatically be changed to 25μA and will change to high-speed transient response mode when output current goes over 8mA(Max.) and internal supply current will be 4.5μA and becomes low supply current mode when output current goes 0.5mμA(MIN.). By automatically switching supply current, the series avoids consuming extra current and can ensure both efficiency and high-speed transient response. When the GO pin is high level, the series can be fixed to high-speed transient response, so you can select the operation mode according to need. Also, the XC6217B series have high-speed discharge function of an output capacitor in addition to the Green Operation function. The function is useful for portable electronics applications that require precise power management, like cellular phones. [Figure 7] Operational circuits of XC6217 [Graph 9] Supply current in of Green Operation. [Graph 10] Example of Load transient response using GO pin [Figure 7] Operational Circuit of XC6217 ceramic ceramic [Graph 9] Supply Current of Green Operation 30 XC6217 Series (GO Mode) 3.1 XC6217x302 V IN =CE=4.0V, GO=V SS (A/B Type), Tr=Tf=5μs Ta=25, C IN =C L =1μF(ceramic) GO mode 300 Supply Current :ISS (ua) PS Mode HS Mode PS Mode to HS Mode HS Mode to PS Mode : IOUT (ma) Output Voltage: VOUT (V) mA 0.1mA Output Voltage Time (500μs/div) : IOUT (ma) At the moment of load current change, the Supply current of the ICs become larger and are switched to high speed mode, so transient response is fast. When load current becomes small, supply current will be 5μA after delay time and will be in power save mode. 14
15 3.1 Basic Knowledge of [Graph 10] Load Transient Response Using GO Pin HighSpeed mode XC6217x302 V IN =CE=4.0V, GO=V IN (A/B Type), Tr=Tf=5μs Ta=25, C IN =C L =1μF(ceramic) Output Voltage 250 Output Voltage: VOUT (V) mA 10mA Time (500μs/div) : IOUT (ma) By having GO pin H level before load current change, the ICs can be high speed mode at the moment of the change. This function can make dropout voltage even smaller and is effective when strict output voltage transient response is needed. 15
16 Types and Application Examples Increasing Power Dissipation Capacity by a Package The power dissipation of a linear regulator is determined by the relationship among input voltage, output voltage, and output current. Power Dissipation (pd) = (Input Voltage Output Voltage) x It is important how effectively the package can release heat and prevent from heating in actual devices. USP package is one of the packages that can effectively release heat. On the backside of the package, the metal die which the ICs silicon is on is exposed, and heat is released to the PC board through the die. [See Photo 2] [Photo 2] Heat Dissipation Pad on the Backside of USP-6C Bared Metal Surface The amount of heat release is determined by the metal area dimension of a PC board. An example of USP-6C power dissipation characteristics is shown in Graph 11. If the power dissipation of an USP-6C itself is 120mW, it can be increased to 1W if the IC is mounted on the board shown in Figure 11. [Graph 11] Heat Dissipation Characteristics: USP-6C Package 1200 Power Dissipation Pd(mW) Ambient Temperature Ta( ) 16
17 [Figure 11] PC Board used for the Evaluation of Heat Dissipation Mounting Area Laser Trimming The output voltage is fixed in the most of CMOS linear regulators, and is not adjustable by external components such as a resistor [See Figure 12]. [Figure 12] The Image of Tolerance Compensation by Lazar Trimming Technology Trimming size is determined based on the measured value of each chip to improve accuracy. Laser Trimming Before Trimming: There is tolerance arisen in wafer manufacturing process. After Trimming: Centering on the target value, tolerance is narrowed down. 17
18 Instead, in most cases, the output voltages are set in 0.1 or 0.05V increments precisely by laser-trimming technology. This is because CMOS process cannot generate a stable reference voltage source in its structure like a bandgap reference for bipolar transistors [See Note 1]. Voltage is set freely and voltage accuracy is stabilized by trimming off tolerance of the internal reference voltage source and the output voltage preset resistor [See Figure 12]. The output voltage accuracy is generally ±2%, and ±1% for high-precision versions. There are also products of which output voltage accuracy within their operating temperature range is strictly defined. [Note 1] Bandgap Reference The circuit to obtain stable voltage in certain temperature by using energy bandgaps and resistance of a bipolar transistor, utilizing the antithetic nature of the voltage temperature coefficient relative to the rated temperature. Which Voltage Is Accessible When Small Quantity Is Needed? Since most CMOS regulators cannot adjust their output voltage externally, you need to check stock availability before buying it. Popular output voltages such as 5.0V, 3.3V, 3.0V, 2.8V, 1.8V should be more accessible than other. The Trend of Development in Future The miniaturization of CMOS process LSI is evolving year by year, and recently even 90nm rule is about to be mass produced. Extreme miniaturization is not always effective for power ICs like linear regulators, as a certain level of input power source voltage is necessary. Still, miniaturization is what CMOS is good at. Utilizing the technology, for instance, a new regulator that can output 1.2V/1A with the input voltage of 1.5V using 0.35μm or 0.5μm should be available in near future. Further improvements of high voltage regulators using various CMOS technologies are also expected. Such positive prediction is possible because CMOS process have a large accumulation of technologies and experiences in the development of LSI and memories. In future, CMOS linear regulators are expected to be used in a wider range of fields including automotives. 18
19 ~Introduction to XC6601~ Examples of Use The efficiency of a CMOS regulator can be improved by combining with a switching regulator, as described in Figure 13. [Figure 13] Improving Efficiency by Combining with DC/DC Converter V IN =3.6V VIN VOUT V OUT =1.5V XC9235 XC9236 XC9237 ( 降 Step 圧 DC/DC down コンバータ) DC/DC converter V IN =1.5V VIN XC6601 高 速 VR VOUT High speed LDO V OUT =1.2V Because recent CMOS linear regulators can operate with extremely low voltage and their dropout voltage is getting smaller [Graph11], the regulator can be used after decreasing voltage efficiently by step-down DC/DC converters. For instance, the regulator can obtain 1.2V output voltage from 3.6V power source with the efficiency of 68%, after stepping down the voltage to 1.5V by DC/DC with efficiency of 85%. If the regulator generates 1.2V of output voltage directly from the power source then the efficiency would be 33%, so it is the improvement of 35%. Also, the regulator functions as a filter and can reduce output ripple. Combining DC/DC converter is especially useful when multiple power sources are needed. [Graph11] Dropout Voltage Comparing Dropout Voltage (XC6601/XC6210) VOUT=1.2V 19
Understanding the Terms and Definitions of LDO Voltage Regulators
 Application Report SLVA79 - October 1999 Understanding the Terms and Definitions of ltage Regulators Bang S. Lee Mixed Signal Products ABSTRACT This report provides an understanding of the terms and definitions
Application Report SLVA79 - October 1999 Understanding the Terms and Definitions of ltage Regulators Bang S. Lee Mixed Signal Products ABSTRACT This report provides an understanding of the terms and definitions
LM1084 5A Low Dropout Positive Regulators
 5A Low Dropout Positive Regulators General Description The LM1084 is a series of low dropout voltage positive regulators with a maximum dropout of 1.5 at 5A of load current. It has the same pin-out as
5A Low Dropout Positive Regulators General Description The LM1084 is a series of low dropout voltage positive regulators with a maximum dropout of 1.5 at 5A of load current. It has the same pin-out as
High Accuracy, Ultralow IQ, 1 A, anycap Low Dropout Regulator ADP3338
 High Accuracy, Ultralow IQ, 1 A, anycap Low Dropout Regulator ADP3338 FEATURES High accuracy over line and load: ±.8% @ 25 C, ±1.4% over temperature Ultralow dropout voltage: 19 mv (typ) @ 1 A Requires
High Accuracy, Ultralow IQ, 1 A, anycap Low Dropout Regulator ADP3338 FEATURES High accuracy over line and load: ±.8% @ 25 C, ±1.4% over temperature Ultralow dropout voltage: 19 mv (typ) @ 1 A Requires
NTE923 & NTE923D Integrated Circuit Precision Voltage Regulator
 NTE923 & NTE923D Integrated Circuit Precision Voltage Regulator Description: The NTE923 and NTE923D are voltage regulators designed primarily for series regulator applications. By themselves, these devices
NTE923 & NTE923D Integrated Circuit Precision Voltage Regulator Description: The NTE923 and NTE923D are voltage regulators designed primarily for series regulator applications. By themselves, these devices
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong SAE 800
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Preliminary Data SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone, 2 tones, 3 tones
CE8301 Series. Introduction. Features. Ordering Information. Applications SMALL PACKAGE PFM CONTROL STEP-UP DC/DC CONVERTER
 SMALL PACKAGE PFM CONTROL STEP-UP DC/DC CONVERTER Introduction The is a CMOS PFM-control step-up switching DC/DC converter that mainly consists of a reference voltage source, an oscillator, and a comparator.
SMALL PACKAGE PFM CONTROL STEP-UP DC/DC CONVERTER Introduction The is a CMOS PFM-control step-up switching DC/DC converter that mainly consists of a reference voltage source, an oscillator, and a comparator.
1.5A Very L.D.O Voltage Regulator LM29150/29151/29152
 FEATURES High Current Capability 1.5A Low Dropout Voltage 350mV Low Ground Current Accurate 1% Guaranteed Initial Tolerance Extremely Fast Transient Response Reverse-Battery and "Load Dump" Protection
FEATURES High Current Capability 1.5A Low Dropout Voltage 350mV Low Ground Current Accurate 1% Guaranteed Initial Tolerance Extremely Fast Transient Response Reverse-Battery and "Load Dump" Protection
TOSHIBA Bipolar Linear Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TAR5SB15~TAR5SB50
 TOSHIBA Bipolar Linear Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TARSB~TARSB Point Regulators (Low-Dropout Regulator) TARSB~TARSB The TARSBxx Series is comprised of general-purpose bipolar single-power-supply
TOSHIBA Bipolar Linear Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic TARSB~TARSB Point Regulators (Low-Dropout Regulator) TARSB~TARSB The TARSBxx Series is comprised of general-purpose bipolar single-power-supply
High Accuracy, Ultralow IQ, 1.5 A, anycap Low Dropout Regulator ADP3339
 Data Sheet High Accuracy, Ultralow IQ,.5 A, anycap Low Dropout Regulator FEATURES FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM High accuracy over line and load: ±.9% at 5 C, ±.5% over temperature Ultralow dropout voltage:
Data Sheet High Accuracy, Ultralow IQ,.5 A, anycap Low Dropout Regulator FEATURES FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM High accuracy over line and load: ±.9% at 5 C, ±.5% over temperature Ultralow dropout voltage:
Advanced Monolithic Systems
 Advanced Monolithic Systems FEATURES Three Terminal Adjustable or Fixed oltages* 1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 2.85, 3.3 and 5. Output Current of 1A Operates Down to 1 Dropout Line Regulation:.2% Max. Load Regulation:.4%
Advanced Monolithic Systems FEATURES Three Terminal Adjustable or Fixed oltages* 1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 2.85, 3.3 and 5. Output Current of 1A Operates Down to 1 Dropout Line Regulation:.2% Max. Load Regulation:.4%
Series AMLDL-Z Up to 1000mA LED Driver
 FEATURES: Click on Series name for product info on aimtec.com Series Up to ma LED Driver Models Single output Model Input Voltage (V) Step Down DC/DC LED driver Operating Temperature range 4ºC to 85ºC
FEATURES: Click on Series name for product info on aimtec.com Series Up to ma LED Driver Models Single output Model Input Voltage (V) Step Down DC/DC LED driver Operating Temperature range 4ºC to 85ºC
AAT3238 DATA SHEET. 300mA MicroPower TM High Performance LDO Linear Regulator. Applications. Features. General Description. Typical Application
 General Description The MicroPower low dropout (LDO) linear regulator is ideally suited for portable applications where very fast transient response, extended battery life, and small size are critical.
General Description The MicroPower low dropout (LDO) linear regulator is ideally suited for portable applications where very fast transient response, extended battery life, and small size are critical.
AS2815. 1.5A Low Dropout Voltage Regulator Adjustable & Fixed Output, Fast Response
 1.5A Low Dropout oltage Regulator Adjustable & Fixed Output, Fast Response FEATURES Adjustable Output Down To 1.2 Fixed Output oltages 1.5, 2.5, 3.3, 5.0 Output Current of 1.5A Low Dropout oltage 1.1 Typ.
1.5A Low Dropout oltage Regulator Adjustable & Fixed Output, Fast Response FEATURES Adjustable Output Down To 1.2 Fixed Output oltages 1.5, 2.5, 3.3, 5.0 Output Current of 1.5A Low Dropout oltage 1.1 Typ.
LM2941/LM2941C 1A Low Dropout Adjustable Regulator
 LM2941/LM2941C 1A Low Dropout Adjustable Regulator General Description The LM2941 positive voltage regulator features the ability to source 1A of output current with a typical dropout voltage of 0.5V and
LM2941/LM2941C 1A Low Dropout Adjustable Regulator General Description The LM2941 positive voltage regulator features the ability to source 1A of output current with a typical dropout voltage of 0.5V and
Preliminary Datasheet
 Features Macroblock Preliminary Datasheet 1.2A Constant Output Current 93% Efficiency @ input voltage 13V, 350mA, 9~36V Input Voltage Range Hysteretic PFM Improves Efficiency at Light Loads Settable Output
Features Macroblock Preliminary Datasheet 1.2A Constant Output Current 93% Efficiency @ input voltage 13V, 350mA, 9~36V Input Voltage Range Hysteretic PFM Improves Efficiency at Light Loads Settable Output
CA723, CA723C. Voltage Regulators Adjustable from 2V to 37V at Output Currents Up to 150mA without External Pass Transistors. Features.
 CA73, CA73C Data Sheet April 1999 File Number 788. Voltage Regulators Adjustable from V to 37V at Output Currents Up to 1mA without External Pass Transistors The CA73 and CA73C are silicon monolithic integrated
CA73, CA73C Data Sheet April 1999 File Number 788. Voltage Regulators Adjustable from V to 37V at Output Currents Up to 1mA without External Pass Transistors The CA73 and CA73C are silicon monolithic integrated
NCP707. 200 ma, Very-Low Quiescent Current, I Q 25 A, Low Noise, Low Dropout Regulator
 NCP77 2 ma, Very-Low Quiescent Current, I Q 25 A, Low Noise, Low Dropout Regulator The NCP77 is 2 ma LDO that provides the engineer with a very stable, accurate voltage with very low noise suitable for
NCP77 2 ma, Very-Low Quiescent Current, I Q 25 A, Low Noise, Low Dropout Regulator The NCP77 is 2 ma LDO that provides the engineer with a very stable, accurate voltage with very low noise suitable for
Chip Diode Application Note
 Chip Diode Application Note Introduction The markets of portable communications, computing and video equipment are challenging the semiconductor industry to develop increasingly smaller electronic components.
Chip Diode Application Note Introduction The markets of portable communications, computing and video equipment are challenging the semiconductor industry to develop increasingly smaller electronic components.
LM139/LM239/LM339/LM2901/LM3302 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Quad Comparators
 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Quad Comparators General Description The LM139 series consists of four independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification as low as 2 mv max for
Low Power Low Offset Voltage Quad Comparators General Description The LM139 series consists of four independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification as low as 2 mv max for
400KHz 60V 4A Switching Current Boost / Buck-Boost / Inverting DC/DC Converter
 Features Wide 5V to 32V Input Voltage Range Positive or Negative Output Voltage Programming with a Single Feedback Pin Current Mode Control Provides Excellent Transient Response 1.25V reference adjustable
Features Wide 5V to 32V Input Voltage Range Positive or Negative Output Voltage Programming with a Single Feedback Pin Current Mode Control Provides Excellent Transient Response 1.25V reference adjustable
AAT4280 Slew Rate Controlled Load Switch
 General Description Features SmartSwitch The AAT4280 SmartSwitch is a P-channel MOSFET power switch designed for high-side load switching applications. The P-channel MOSFET device has a typical R DS(ON)
General Description Features SmartSwitch The AAT4280 SmartSwitch is a P-channel MOSFET power switch designed for high-side load switching applications. The P-channel MOSFET device has a typical R DS(ON)
NCT3941S/S-A Nuvoton 4 Times Linear Fan Driver NCT3941S/S-A
 Nuvoton 4 Times Linear Fan Driver NCT3941S/S-A -I- Revision A4 Table of Content- 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION...1 2. FEATURES...1 3. APPLICATION...1 4. BLOCK DIAGRAM...2 5. PIN CONFIGURATION AND TYPICAL APPLICATION
Nuvoton 4 Times Linear Fan Driver NCT3941S/S-A -I- Revision A4 Table of Content- 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION...1 2. FEATURES...1 3. APPLICATION...1 4. BLOCK DIAGRAM...2 5. PIN CONFIGURATION AND TYPICAL APPLICATION
DATA SHEET. TDA8560Q 2 40 W/2 Ω stereo BTL car radio power amplifier with diagnostic facility INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. 1996 Jan 08
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET power amplifier with diagnostic facility Supersedes data of March 1994 File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 1996 Jan 08 FEATURES Requires very few external components High
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET power amplifier with diagnostic facility Supersedes data of March 1994 File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 1996 Jan 08 FEATURES Requires very few external components High
S-1702 Series. SUPER-LOW CURRENT CONSUMPTION 150 ma VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH BUILT-IN HIGH-ACCURACY VOLTAGE DETECTOR AND RESET INPUT FUNCTION.
 S-172 Series www.sii-ic.com SUPER-LOW CURRENT CONSUMPTION 15 ma VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH BUILT-IN HIGH-ACCURACY VOLTAGE DETECTOR AND RESET INPUT FUNCTION Seiko Instruments Inc., 28-212 Rev.2.1_ The S-172
S-172 Series www.sii-ic.com SUPER-LOW CURRENT CONSUMPTION 15 ma VOLTAGE REGULATOR WITH BUILT-IN HIGH-ACCURACY VOLTAGE DETECTOR AND RESET INPUT FUNCTION Seiko Instruments Inc., 28-212 Rev.2.1_ The S-172
CS8481. 3.3 V/250 ma, 5.0 V/100 ma Micropower Low Dropout Regulator with ENABLE
 3.3 /250 ma, 5.0 /100 ma Micropower Low Dropout Regulator with The CS8481 is a precision, dual Micropower linear voltage regulator. The switched 3.3 primary output ( OUT1 ) supplies up to 250 ma while
3.3 /250 ma, 5.0 /100 ma Micropower Low Dropout Regulator with The CS8481 is a precision, dual Micropower linear voltage regulator. The switched 3.3 primary output ( OUT1 ) supplies up to 250 ma while
LM138 LM338 5-Amp Adjustable Regulators
 LM138 LM338 5-Amp Adjustable Regulators General Description The LM138 series of adjustable 3-terminal positive voltage regulators is capable of supplying in excess of 5A over a 1 2V to 32V output range
LM138 LM338 5-Amp Adjustable Regulators General Description The LM138 series of adjustable 3-terminal positive voltage regulators is capable of supplying in excess of 5A over a 1 2V to 32V output range
LM2704 Micropower Step-up DC/DC Converter with 550mA Peak Current Limit
 Micropower Step-up DC/DC Converter with 550mA Peak Current Limit General Description The LM2704 is a micropower step-up DC/DC in a small 5-lead SOT-23 package. A current limited, fixed off-time control
Micropower Step-up DC/DC Converter with 550mA Peak Current Limit General Description The LM2704 is a micropower step-up DC/DC in a small 5-lead SOT-23 package. A current limited, fixed off-time control
unit : mm With heat sink (see Pd Ta characteristics)
 Ordering number: EN1321E Monolithic Linear IC LA4261 3.5 W 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier for Home Stereos and Music Centers Features. Minimum number of external parts required (No input capacitor, bootstrap
Ordering number: EN1321E Monolithic Linear IC LA4261 3.5 W 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier for Home Stereos and Music Centers Features. Minimum number of external parts required (No input capacitor, bootstrap
STLQ015. 150 ma, ultra low quiescent current linear voltage regulator. Description. Features. Application
 150 ma, ultra low quiescent current linear voltage regulator Description Datasheet - production data Features SOT23-5L Input voltage from 1.5 to 5.5 V Very low quiescent current: 1.0 µa (typ.) at no load
150 ma, ultra low quiescent current linear voltage regulator Description Datasheet - production data Features SOT23-5L Input voltage from 1.5 to 5.5 V Very low quiescent current: 1.0 µa (typ.) at no load
R-78xx-0.5 INNOLINE. Features. 0.5 AMP SIP3 Single Output. Derating-Graph (Ambient Temperature) DC/DC-Converter
 Features Description Efficiency up to 97%,Non isolated, no need for heatsinks Pin-out compatible with LM78XX Linears Very low profile( L*W*H=11.5*7.5*10.2 ) Wide input range.(4.75v ~ 32V) Short circuit
Features Description Efficiency up to 97%,Non isolated, no need for heatsinks Pin-out compatible with LM78XX Linears Very low profile( L*W*H=11.5*7.5*10.2 ) Wide input range.(4.75v ~ 32V) Short circuit
1.0A LOW DROPOUT LINEAR REGULATOR
 1.0A LOW DROPOUT LINEAR REGULATOR Description Pin Assignments The is a low dropout three-terminal regulator with 1.0A output current ability, and the dropout voltage is specified at typical 1.1V at 1.0A
1.0A LOW DROPOUT LINEAR REGULATOR Description Pin Assignments The is a low dropout three-terminal regulator with 1.0A output current ability, and the dropout voltage is specified at typical 1.1V at 1.0A
AP1509. 150KHz, 2A PWM BUCK DC/DC CONVERTER. Description. Pin Assignments V IN. Applications. Features. (Top View) GND GND. Output AP1509 GND GND
 Description Pin Assignments The series are monolithic IC designed for a stepdown DC/DC converter, and own the ability of driving a 2A load without additional transistor. It saves board space. The external
Description Pin Assignments The series are monolithic IC designed for a stepdown DC/DC converter, and own the ability of driving a 2A load without additional transistor. It saves board space. The external
LM79XX Series 3-Terminal Negative Regulators
 LM79XX Series 3-Terminal Negative Regulators General Description The LM79XX series of 3-terminal regulators is available with fixed output voltages of b5v b8v b12v and b15v These devices need only one
LM79XX Series 3-Terminal Negative Regulators General Description The LM79XX series of 3-terminal regulators is available with fixed output voltages of b5v b8v b12v and b15v These devices need only one
AP331A XX G - 7. Lead Free G : Green. Packaging (Note 2)
 Features General Description Wide supply Voltage range: 2.0V to 36V Single or dual supplies: ±1.0V to ±18V Very low supply current drain (0.4mA) independent of supply voltage Low input biasing current:
Features General Description Wide supply Voltage range: 2.0V to 36V Single or dual supplies: ±1.0V to ±18V Very low supply current drain (0.4mA) independent of supply voltage Low input biasing current:
SPI-8001TW. Switching Regulators. Dual 1.5 A, DC/DC Step-Down Converter. SANKEN ELECTRIC CO., LTD. http://www.sanken-ele.co.jp/en/
 Data Sheet 27469.301.1 Designed to meet high-current requirements at high efficiency in industrial and consumer applications; embedded core, memory, or logic supplies; TVs, VCRs, and office equipment,
Data Sheet 27469.301.1 Designed to meet high-current requirements at high efficiency in industrial and consumer applications; embedded core, memory, or logic supplies; TVs, VCRs, and office equipment,
LM3940 1A Low Dropout Regulator for 5V to 3.3V Conversion
 1A Low Dropout Regulator for 5V to 3.3V Conversion General Description The LM3940 is a 1A low dropout regulator designed to provide 3.3V from a 5V supply. The LM3940 is ideally suited for systems which
1A Low Dropout Regulator for 5V to 3.3V Conversion General Description The LM3940 is a 1A low dropout regulator designed to provide 3.3V from a 5V supply. The LM3940 is ideally suited for systems which
L78MxxAB L78MxxAC. Precision 500 ma regulators. Features. Description
 L78MxxAB L78MxxAC Precision 500 ma regulators Features Output current to 0.5 A Output voltages of 5; 6; 8; 9; 10; 12; 15; 18; 24 V Thermal overload protection Short circuit protection Output transition
L78MxxAB L78MxxAC Precision 500 ma regulators Features Output current to 0.5 A Output voltages of 5; 6; 8; 9; 10; 12; 15; 18; 24 V Thermal overload protection Short circuit protection Output transition
Application Note TMA Series
 1W, SIP, Single & Dual Output DC/DC Converters Features SIP Package with Industry Standard Pinout Package Dimension: 19.5 x 10.2 x 6.1 mm (0.77 x 0.4 x 0.24 ) 5V&12V Models 19.5 x 10.2 x 7.1 mm (0.77 x
1W, SIP, Single & Dual Output DC/DC Converters Features SIP Package with Industry Standard Pinout Package Dimension: 19.5 x 10.2 x 6.1 mm (0.77 x 0.4 x 0.24 ) 5V&12V Models 19.5 x 10.2 x 7.1 mm (0.77 x
1A L.D.O VOLTAGE REGULATOR
 FEATURES Output Current up to 1 A Low Dropout Voltage (1.2V at 1A Output current) Three Terminal Adjustable(ADJ) or Fixed 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.85V, 5.0V Line Regulation typically at 0.1% max. Load
FEATURES Output Current up to 1 A Low Dropout Voltage (1.2V at 1A Output current) Three Terminal Adjustable(ADJ) or Fixed 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.85V, 5.0V Line Regulation typically at 0.1% max. Load
High Voltage Current Shunt Monitor AD8212
 High Voltage Current Shunt Monitor AD822 FEATURES Adjustable gain High common-mode voltage range 7 V to 65 V typical 7 V to >500 V with external pass transistor Current output Integrated 5 V series regulator
High Voltage Current Shunt Monitor AD822 FEATURES Adjustable gain High common-mode voltage range 7 V to 65 V typical 7 V to >500 V with external pass transistor Current output Integrated 5 V series regulator
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part count
SC339. Ultra Low Output Voltage Linear FET Controller POWER MANAGEMENT. Applications. Typical Application Circuit
 Description The SC339 is an ultra-low output voltage, linear power supply controller designed to simplify power management for notebook PCs. It is part of Semtech s Smart LDO TM family of products. The
Description The SC339 is an ultra-low output voltage, linear power supply controller designed to simplify power management for notebook PCs. It is part of Semtech s Smart LDO TM family of products. The
Power management for handheld and portable applications. A tradition of leadership in power management is now mobile
 Power management for handheld and portable applications A tradition of leadership in power management is now mobile Leaders in PM for Mobile Advanced analog power management ICs Integrated devices with
Power management for handheld and portable applications A tradition of leadership in power management is now mobile Leaders in PM for Mobile Advanced analog power management ICs Integrated devices with
www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LF411 Low Offset, Low Drift JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description
LM 358 Op Amp. If you have small signals and need a more useful reading we could amplify it using the op amp, this is commonly used in sensors.
 LM 358 Op Amp S k i l l L e v e l : I n t e r m e d i a t e OVERVIEW The LM 358 is a duel single supply operational amplifier. As it is a single supply it eliminates the need for a duel power supply, thus
LM 358 Op Amp S k i l l L e v e l : I n t e r m e d i a t e OVERVIEW The LM 358 is a duel single supply operational amplifier. As it is a single supply it eliminates the need for a duel power supply, thus
Content Map For Career & Technology
 Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
Content Strand: Applied Academics CT-ET1-1 analysis of electronic A. Fractions and decimals B. Powers of 10 and engineering notation C. Formula based problem solutions D. Powers and roots E. Linear equations
Application Report SLVA072
 Application Report August 1999 Mixed Signal Products SLVA72 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product
Application Report August 1999 Mixed Signal Products SLVA72 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product
100V - 100W DMOS AUDIO AMPLIFIER WITH MUTE/ST-BY THERMAL SHUTDOWN STBY-GND
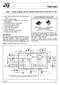 TDA7294 100V - 100W DMOS AUDIO AMPLIFIER WITH MUTE/ST-BY VERY HIGH OPERATING VOLTAGE RANGE (±40V) DMOS POWER STAGE HIGH OUTPUT POWER (UP TO 100W MU- SIC POWER) MUTING/STAND-BY FUNCTIONS NO SWITCH ON/OFF
TDA7294 100V - 100W DMOS AUDIO AMPLIFIER WITH MUTE/ST-BY VERY HIGH OPERATING VOLTAGE RANGE (±40V) DMOS POWER STAGE HIGH OUTPUT POWER (UP TO 100W MU- SIC POWER) MUTING/STAND-BY FUNCTIONS NO SWITCH ON/OFF
LM2941 LM2941C 1A Low Dropout Adjustable Regulator
 June 1994 LM2941 LM2941C 1A Low Dropout Adjustable Regulator General Description The LM2941 positive voltage regulator features the ability to source 1A of output current with a typical dropout voltage
June 1994 LM2941 LM2941C 1A Low Dropout Adjustable Regulator General Description The LM2941 positive voltage regulator features the ability to source 1A of output current with a typical dropout voltage
Rail-to-Rail, High Output Current Amplifier AD8397
 Rail-to-Rail, High Output Current Amplifier AD8397 FEATURES Dual operational amplifier Voltage feedback Wide supply range from 3 V to 24 V Rail-to-rail output Output swing to within.5 V of supply rails
Rail-to-Rail, High Output Current Amplifier AD8397 FEATURES Dual operational amplifier Voltage feedback Wide supply range from 3 V to 24 V Rail-to-rail output Output swing to within.5 V of supply rails
MP2259 1A, 16V, 1.4MHz Step-Down Converter
 MP59 1A, 1V, 1.MHz Step-Down Converter TM The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP59 is a monolithic integrated stepdown switch mode converter with an internal power MOSFET. It achieves 1A
MP59 1A, 1V, 1.MHz Step-Down Converter TM The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP59 is a monolithic integrated stepdown switch mode converter with an internal power MOSFET. It achieves 1A
POWER FORUM, BOLOGNA 20-09-2012
 POWER FORUM, BOLOGNA 20-09-2012 Convertitori DC/DC ad alta densità di potenza e bassa impedenza termica. Massimo GAVIOLI. Senior Field Application Engineer. Intersil SIMPLY SMARTER Challenges when Designing
POWER FORUM, BOLOGNA 20-09-2012 Convertitori DC/DC ad alta densità di potenza e bassa impedenza termica. Massimo GAVIOLI. Senior Field Application Engineer. Intersil SIMPLY SMARTER Challenges when Designing
unit:mm 3022A-DIP12F 0.5 0.81 2.54
 Ordering number:enn1718b Monolithic Linear IC LA4550 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier for Radio, Tape Recorder Use Features Low quiescent current. On-chip 2 channels permitting use in stereo and bridge amplifier
Ordering number:enn1718b Monolithic Linear IC LA4550 2-Channel AF Power Amplifier for Radio, Tape Recorder Use Features Low quiescent current. On-chip 2 channels permitting use in stereo and bridge amplifier
Datasheet. 2A 380KHZ 20V PWM Buck DC/DC Converter. Features
 General Description Features The is a 380 KHz fixed frequency monolithic step down switch mode regulator with a built in internal Power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input
General Description Features The is a 380 KHz fixed frequency monolithic step down switch mode regulator with a built in internal Power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input
1.5A L.D.O. VOLTAGE REGULATOR (Adjustable & Fixed) LM1086
 FEATURES Output Current of 1.5A Fast Transient Response 0.04% Line Regulation 0.2% Load Regulation Internal Thermal and Current Limiting Adjustable or Fixed Output oltage(1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 3.3, 5.0) Surface
FEATURES Output Current of 1.5A Fast Transient Response 0.04% Line Regulation 0.2% Load Regulation Internal Thermal and Current Limiting Adjustable or Fixed Output oltage(1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 3.3, 5.0) Surface
TS321 Low Power Single Operational Amplifier
 SOT-25 Pin Definition: 1. Input + 2. Ground 3. Input - 4. Output 5. Vcc General Description The TS321 brings performance and economy to low power systems. With high unity gain frequency and a guaranteed
SOT-25 Pin Definition: 1. Input + 2. Ground 3. Input - 4. Output 5. Vcc General Description The TS321 brings performance and economy to low power systems. With high unity gain frequency and a guaranteed
LM117 LM317A LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator
 LM117 LM317A LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator General Description The LM117 series of adjustable 3-terminal positive voltage regulators is capable of supplying in excess of 1 5A over a 1 2V to 37V
LM117 LM317A LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator General Description The LM117 series of adjustable 3-terminal positive voltage regulators is capable of supplying in excess of 1 5A over a 1 2V to 37V
MC34063A MC34063E DC-DC CONVERTER CONTROL CIRCUITS
 MC34063A MC34063E DC-DC CONVERTER CONTROL CIRCUITS OUTPUT SWITCH CURRENT IN EXCESS OF 1.5A 2% REFERENCE ACCURACY LOW QUIESCENT CURRENT: 2.5mA (TYP.) OPERATING FROM 3V TO 40V FREQUENCY OPERATION TO 100KHz
MC34063A MC34063E DC-DC CONVERTER CONTROL CIRCUITS OUTPUT SWITCH CURRENT IN EXCESS OF 1.5A 2% REFERENCE ACCURACY LOW QUIESCENT CURRENT: 2.5mA (TYP.) OPERATING FROM 3V TO 40V FREQUENCY OPERATION TO 100KHz
LDO03C/LDO06C/LDO10C
 NEW LDO03C/LDO06C/LDO10C A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e 1 8 6 1. Introduction 2 2. Models Features 2 3. General Description Electrical Description 2 Physical Construction 2 4. Features and Functions Wide
NEW LDO03C/LDO06C/LDO10C A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e 1 8 6 1. Introduction 2 2. Models Features 2 3. General Description Electrical Description 2 Physical Construction 2 4. Features and Functions Wide
TDA4605 CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR SWITCH MODE POWER SUPPLIES USING MOS TRANSISTORS
 CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR SWITCH MODE POWER SUPPLIES USING MOS TRANSISTORS Fold-Back Characteristic provides Overload Protection for External Diodes Burst Operation under Short-Circuit and no Load Conditions
CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR SWITCH MODE POWER SUPPLIES USING MOS TRANSISTORS Fold-Back Characteristic provides Overload Protection for External Diodes Burst Operation under Short-Circuit and no Load Conditions
Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V. Huan Lin
 Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V Huan Lin 4/2/2010 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Objective... Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Implementation...
Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V Huan Lin 4/2/2010 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Objective... Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Implementation...
Application Note 142 August 2013. New Linear Regulators Solve Old Problems AN142-1
 August 2013 New Linear Regulators Solve Old Problems Bob Dobkin, Vice President, Engineering and CTO, Linear Technology Corp. Regulators regulate but are capable of doing much more. The architecture of
August 2013 New Linear Regulators Solve Old Problems Bob Dobkin, Vice President, Engineering and CTO, Linear Technology Corp. Regulators regulate but are capable of doing much more. The architecture of
AP1506. 150KHz, 3A PWM BUCK DC/DC CONVERTER. Pin Assignments. Description. Features. Applications. ( Top View ) 5 SD 4 FB 3 Gnd 2 Output 1 V IN
 Description Pin Assignments The series are monolithic IC designed for a stepdown DC/DC converter, and own the ability of driving a 3A load without external transistor. Due to reducing the number of external
Description Pin Assignments The series are monolithic IC designed for a stepdown DC/DC converter, and own the ability of driving a 3A load without external transistor. Due to reducing the number of external
High Common-Mode Rejection. Differential Line Receiver SSM2141. Fax: 781/461-3113 FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM FEATURES. High Common-Mode Rejection
 a FEATURES High Common-Mode Rejection DC: 00 db typ 60 Hz: 00 db typ 20 khz: 70 db typ 40 khz: 62 db typ Low Distortion: 0.00% typ Fast Slew Rate: 9.5 V/ s typ Wide Bandwidth: 3 MHz typ Low Cost Complements
a FEATURES High Common-Mode Rejection DC: 00 db typ 60 Hz: 00 db typ 20 khz: 70 db typ 40 khz: 62 db typ Low Distortion: 0.00% typ Fast Slew Rate: 9.5 V/ s typ Wide Bandwidth: 3 MHz typ Low Cost Complements
LM2576R. 3.0A, 52kHz, Step-Down Switching Regulator FEATURES. Applications DESCRIPTION TO-220 PKG TO-220V PKG TO-263 PKG ORDERING INFORMATION
 LM2576 FEATURES 3.3, 5.0, 12, 15, and Adjustable Output ersions Adjustable ersion Output oltage Range, 1.23 to 37 +/- 4% AG10Maximum Over Line and Load Conditions Guaranteed 3.0A Output Current Wide Input
LM2576 FEATURES 3.3, 5.0, 12, 15, and Adjustable Output ersions Adjustable ersion Output oltage Range, 1.23 to 37 +/- 4% AG10Maximum Over Line and Load Conditions Guaranteed 3.0A Output Current Wide Input
LDS8720. 184 WLED Matrix Driver with Boost Converter FEATURES APPLICATION DESCRIPTION TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
 184 WLED Matrix Driver with Boost Converter FEATURES High efficiency boost converter with the input voltage range from 2.7 to 5.5 V No external Schottky Required (Internal synchronous rectifier) 250 mv
184 WLED Matrix Driver with Boost Converter FEATURES High efficiency boost converter with the input voltage range from 2.7 to 5.5 V No external Schottky Required (Internal synchronous rectifier) 250 mv
MIC33050. General Description. Features. Applications. Typical Application. 4MHz Internal Inductor PWM Buck Regulator with HyperLight Load
 4MHz Internal Inductor PWM Buck Regulator with HyperLight Load General Description The Micrel is a high-efficiency 600mA PWM synchronous buck (step-down) regulator with internal inductor featuring HyperLight
4MHz Internal Inductor PWM Buck Regulator with HyperLight Load General Description The Micrel is a high-efficiency 600mA PWM synchronous buck (step-down) regulator with internal inductor featuring HyperLight
2.996/6.971 Biomedical Devices Design Laboratory Lecture 4: Power Supplies
 2.996/6.971 Biomedical Devices Design Laboratory Lecture 4: Power Supplies Instructor: Dr. Hong Ma Sept. 19, 2007 Key Problem Ideal voltage sources do not exist! Voltage regulators use feedback to reduce
2.996/6.971 Biomedical Devices Design Laboratory Lecture 4: Power Supplies Instructor: Dr. Hong Ma Sept. 19, 2007 Key Problem Ideal voltage sources do not exist! Voltage regulators use feedback to reduce
5.5 V Input, 300 ma, Low Quiescent Current, CMOS Linear Regulator ADP122/ADP123
 Data Sheet 5.5 V Input, 3 ma, Low Quiescent Current, CMOS Linear Regulator ADP/ADP3 FEATURES Input voltage supply range:.3 V to 5.5 V 3 ma maximum output current Fixed and adjustable output voltage versions
Data Sheet 5.5 V Input, 3 ma, Low Quiescent Current, CMOS Linear Regulator ADP/ADP3 FEATURES Input voltage supply range:.3 V to 5.5 V 3 ma maximum output current Fixed and adjustable output voltage versions
SELECTION GUIDE. Nominal Input
 www.murata-ps.com NKE Series FEATURES RoHS Compliant Sub-Miniature SIP & DIP Styles 3kVDC Isolation UL Recognised Wide Temperature performance at full 1 Watt load, 40 C to 85 C Increased Power Density
www.murata-ps.com NKE Series FEATURES RoHS Compliant Sub-Miniature SIP & DIP Styles 3kVDC Isolation UL Recognised Wide Temperature performance at full 1 Watt load, 40 C to 85 C Increased Power Density
Reading: HH Sections 4.11 4.13, 4.19 4.20 (pgs. 189-212, 222 224)
 6 OP AMPS II 6 Op Amps II In the previous lab, you explored several applications of op amps. In this exercise, you will look at some of their limitations. You will also examine the op amp integrator and
6 OP AMPS II 6 Op Amps II In the previous lab, you explored several applications of op amps. In this exercise, you will look at some of their limitations. You will also examine the op amp integrator and
Maintenance/ Discontinued
 DATA SHEET Part Package Code AN12946A HQFP048-P-0707 includes following four Product lifecycle stage. planed Publication date: August 2008 1 Contents Overview.. 3 Features.. 3 Applications. 3 Package.
DATA SHEET Part Package Code AN12946A HQFP048-P-0707 includes following four Product lifecycle stage. planed Publication date: August 2008 1 Contents Overview.. 3 Features.. 3 Applications. 3 Package.
Low Noise, Matched Dual PNP Transistor MAT03
 a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
a FEATURES Dual Matched PNP Transistor Low Offset Voltage: 100 V Max Low Noise: 1 nv/ Hz @ 1 khz Max High Gain: 100 Min High Gain Bandwidth: 190 MHz Typ Tight Gain Matching: 3% Max Excellent Logarithmic
TS34119 Low Power Audio Amplifier
 SOP-8 DIP-8 Pin assignment: 1. CD 8. VO2 2. FC2 7. Gnd 3. FC1 6. Vcc 4. Vin 5. VO1 General Description The TS34119 is a low power audio amplifier, it integrated circuit intended (primarily) for telephone
SOP-8 DIP-8 Pin assignment: 1. CD 8. VO2 2. FC2 7. Gnd 3. FC1 6. Vcc 4. Vin 5. VO1 General Description The TS34119 is a low power audio amplifier, it integrated circuit intended (primarily) for telephone
650W Single Output Power Supply
 AK-650 series Features : Universal AC input with active PFC Programmable output Voltage ( 0% ~ 05% ) Programmable output Current ( % ~ 05% ) High efficiency up to 9% + / 0.5A auxiliary output Intelligent
AK-650 series Features : Universal AC input with active PFC Programmable output Voltage ( 0% ~ 05% ) Programmable output Current ( % ~ 05% ) High efficiency up to 9% + / 0.5A auxiliary output Intelligent
PS323. Precision, Single-Supply SPST Analog Switch. Features. Description. Block Diagram, Pin Configuration, and Truth Table. Applications PS323 PS323
 Features ÎÎLow On-Resistance (33-ohm typ.) Minimizes Distortion and Error Voltages ÎÎLow Glitching Reduces Step Errors in Sample-and-Holds. Charge Injection, 2pC typ. ÎÎSingle-Supply Operation (+2.5V to
Features ÎÎLow On-Resistance (33-ohm typ.) Minimizes Distortion and Error Voltages ÎÎLow Glitching Reduces Step Errors in Sample-and-Holds. Charge Injection, 2pC typ. ÎÎSingle-Supply Operation (+2.5V to
Simple PWM Boost Converter with I/O Disconnect Solves Malfunctions Caused when V OUT <V IN
 Simple PWM Boost Converter with I/O Disconnect Solves Malfunctions Caused when V OUT
Simple PWM Boost Converter with I/O Disconnect Solves Malfunctions Caused when V OUT
Precision, Unity-Gain Differential Amplifier AMP03
 a FEATURES High CMRR: db Typ Low Nonlinearity:.% Max Low Distortion:.% Typ Wide Bandwidth: MHz Typ Fast Slew Rate: 9.5 V/ s Typ Fast Settling (.%): s Typ Low Cost APPLICATIONS Summing Amplifiers Instrumentation
a FEATURES High CMRR: db Typ Low Nonlinearity:.% Max Low Distortion:.% Typ Wide Bandwidth: MHz Typ Fast Slew Rate: 9.5 V/ s Typ Fast Settling (.%): s Typ Low Cost APPLICATIONS Summing Amplifiers Instrumentation
High Speed, Low Cost, Triple Op Amp ADA4861-3
 High Speed, Low Cost, Triple Op Amp ADA486-3 FEATURES High speed 73 MHz, 3 db bandwidth 625 V/μs slew rate 3 ns settling time to.5% Wide supply range: 5 V to 2 V Low power: 6 ma/amplifier. db flatness:
High Speed, Low Cost, Triple Op Amp ADA486-3 FEATURES High speed 73 MHz, 3 db bandwidth 625 V/μs slew rate 3 ns settling time to.5% Wide supply range: 5 V to 2 V Low power: 6 ma/amplifier. db flatness:
Understanding Low Drop Out (LDO) Regulators
 Understanding Low Drop Out (LDO) Regulators Michael Day, Texas Instruments ABSTRACT This paper provides a basic understanding of the dropout performance of a low dropout linear regulator (LDO). It shows
Understanding Low Drop Out (LDO) Regulators Michael Day, Texas Instruments ABSTRACT This paper provides a basic understanding of the dropout performance of a low dropout linear regulator (LDO). It shows
1.5A Ultra Low Dropout Linear Regulator TJ3965
 FEATURES Ultra Low Dropout Voltage Low Ground Pin Current Excellent Line and Load Regulation Guaranteed Output Current of 1.5A Available in MSOP8, SOP8, SOP8PP, SOT223, TO252, TO263, TO220, and SOT89 Packages
FEATURES Ultra Low Dropout Voltage Low Ground Pin Current Excellent Line and Load Regulation Guaranteed Output Current of 1.5A Available in MSOP8, SOP8, SOP8PP, SOT223, TO252, TO263, TO220, and SOT89 Packages
CLASS-D VERTICAL DEFLECTION AMPLIFIER FOR TV AND MONITOR APPLICATION OUT CFLY + CFLY - BOOT VREG FEEDCAP FREQ. July 2001 1/8
 CLASS-D VERTICAL DEFLECTION AMPLIFIER FOR TV AND MONITOR APPLICATION FEATURES PRELIMINARY DATA HIGH EFFICIENCY POWER AMPLIFIER NO HEATSINK SPLIT SUPPLY INTERNAL FLYBACK GENERATOR OUTPUT CURRENT UP TO.5
CLASS-D VERTICAL DEFLECTION AMPLIFIER FOR TV AND MONITOR APPLICATION FEATURES PRELIMINARY DATA HIGH EFFICIENCY POWER AMPLIFIER NO HEATSINK SPLIT SUPPLY INTERNAL FLYBACK GENERATOR OUTPUT CURRENT UP TO.5
PS25202 EPIC Ultra High Impedance ECG Sensor Advance Information
 EPIC Ultra High Impedance ECG Sensor Advance Information Data Sheet 291498 issue 2 FEATURES Ultra high input resistance, typically 20GΩ. Dry-contact capacitive coupling. Input capacitance as low as 15pF.
EPIC Ultra High Impedance ECG Sensor Advance Information Data Sheet 291498 issue 2 FEATURES Ultra high input resistance, typically 20GΩ. Dry-contact capacitive coupling. Input capacitance as low as 15pF.
DATA SHEET. TDA1518BQ 24 W BTL or 2 x 12 watt stereo car radio power amplifier INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 July 1994 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is an integrated class-b output amplifier in a 13-lead single-in-line (SIL) plastic power package.
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET File under Integrated Circuits, IC01 July 1994 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is an integrated class-b output amplifier in a 13-lead single-in-line (SIL) plastic power package.
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA07H4047M
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7H7M RoHS Compliance,-7MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7H7M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7H7M RoHS Compliance,-7MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7H7M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the
How To Power A Power Control Microprocessor (Power Control) Microprocessor 2 (Power) (Power Power) (Control) (Repower) Microcontroller (Power/Reflow) (Mini) (Microprocessor) (Wired) (Wire
 PTC NTC for Surface Mounting Application What is a Thermistor? Thermally Sensitive Resistor Thermistor Positive Temperature Coefficient PTC Negative Temperature Coefficient NTC Characteristics of Thermistors
PTC NTC for Surface Mounting Application What is a Thermistor? Thermally Sensitive Resistor Thermistor Positive Temperature Coefficient PTC Negative Temperature Coefficient NTC Characteristics of Thermistors
SC728/SC729. 2A Low Vin, Very Low Ron Load Switch. POWER MANAGEMENT Features. Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit SC728 / SC729
 POWER MANAGEMT Features Input Voltage Range 1.1V to 2A Continuous Output Current Ultra-Low Ron 36mΩ Automatic Output Discharge Circuit Fast Turn-on Option With No Output Discharge Circuit SC728 Extended
POWER MANAGEMT Features Input Voltage Range 1.1V to 2A Continuous Output Current Ultra-Low Ron 36mΩ Automatic Output Discharge Circuit Fast Turn-on Option With No Output Discharge Circuit SC728 Extended
UL/ RAILWAYS Certified Constant Current LED Driver Wide Input and Output Voltage Range Digital PWM and Analogue Voltage Dimming
 Features Regulated Converters Selection Guide UL/ RAILWAYS Certified Constant Current LED Driver Wide Input and Output Voltage Range Digital PWM and Analogue Voltage Dimming Short Circuit Protected Pinned
Features Regulated Converters Selection Guide UL/ RAILWAYS Certified Constant Current LED Driver Wide Input and Output Voltage Range Digital PWM and Analogue Voltage Dimming Short Circuit Protected Pinned
Supply voltage Supervisor TL77xx Series. Author: Eilhard Haseloff
 Supply voltage Supervisor TL77xx Series Author: Eilhard Haseloff Literature Number: SLVAE04 March 1997 i IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products or to
Supply voltage Supervisor TL77xx Series Author: Eilhard Haseloff Literature Number: SLVAE04 March 1997 i IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products or to
PIN CONFIGURATION FEATURES ORDERING INFORMATION ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS. D, F, N Packages
 DESCRIPTION The µa71 is a high performance operational amplifier with high open-loop gain, internal compensation, high common mode range and exceptional temperature stability. The µa71 is short-circuit-protected
DESCRIPTION The µa71 is a high performance operational amplifier with high open-loop gain, internal compensation, high common mode range and exceptional temperature stability. The µa71 is short-circuit-protected
TL783C, TL783Y HIGH-VOLTAGE ADJUSTABLE REGULATOR
 HIGH-VOLTAGE USTABLE REGULATOR SLVS36C SEPTEMBER 1981 REVISED APRIL 1997 Output Adjustable From 1.25 V to 125 V When Used With an External Resistor Divider 7-mA Output Current Full Short-Circuit, Safe-Operating-Area,
HIGH-VOLTAGE USTABLE REGULATOR SLVS36C SEPTEMBER 1981 REVISED APRIL 1997 Output Adjustable From 1.25 V to 125 V When Used With an External Resistor Divider 7-mA Output Current Full Short-Circuit, Safe-Operating-Area,
Current vs. Voltage Feedback Amplifiers
 Current vs. ltage Feedback Amplifiers One question continuously troubles the analog design engineer: Which amplifier topology is better for my application, current feedback or voltage feedback? In most
Current vs. ltage Feedback Amplifiers One question continuously troubles the analog design engineer: Which amplifier topology is better for my application, current feedback or voltage feedback? In most
Push-Pull FET Driver with Integrated Oscillator and Clock Output
 19-3662; Rev 1; 5/7 Push-Pull FET Driver with Integrated Oscillator General Description The is a +4.5V to +15V push-pull, current-fed topology driver subsystem with an integrated oscillator for use in
19-3662; Rev 1; 5/7 Push-Pull FET Driver with Integrated Oscillator General Description The is a +4.5V to +15V push-pull, current-fed topology driver subsystem with an integrated oscillator for use in
Description. Table 1. Device summary
 2 A positive voltage regulator IC Description Datasheet - production data Features TO-220 Output current up to 2 A Output voltages of 5; 7.5; 9; 10; 12; 15; 18; 24 V Thermal protection Short circuit protection
2 A positive voltage regulator IC Description Datasheet - production data Features TO-220 Output current up to 2 A Output voltages of 5; 7.5; 9; 10; 12; 15; 18; 24 V Thermal protection Short circuit protection
APPLICATIONS. Battery chargers. DC motor control. Level translating QUANTITY PER REEL. ZXCT1009FTA 7 8mm 3,000 units 109 SOT23
 HIGH-SIDE CURRENT MONITOR DESCRIPTION The is a high side current sense monitor. Using this device eliminates the need to disrupt the ground plane when sensing a load current. It takes a high side voltage
HIGH-SIDE CURRENT MONITOR DESCRIPTION The is a high side current sense monitor. Using this device eliminates the need to disrupt the ground plane when sensing a load current. It takes a high side voltage
Isolated AC Sine Wave Input 3B42 / 3B43 / 3B44 FEATURES APPLICATIONS PRODUCT OVERVIEW FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
 Isolated AC Sine Wave Input 3B42 / 3B43 / 3B44 FEATURES AC averaging technique used to rectify, amplify, and filter 50 Hz to 400 Hz sine-wave signals. Accepts inputs of between 20 mv to 550 V rms to give
Isolated AC Sine Wave Input 3B42 / 3B43 / 3B44 FEATURES AC averaging technique used to rectify, amplify, and filter 50 Hz to 400 Hz sine-wave signals. Accepts inputs of between 20 mv to 550 V rms to give
Regulated D.C. Power Supply
 442 17 Principles of Electronics Regulated D.C. Power Supply 17.1 Ordinary D.C. Power Supply 17.2 Important Terms 17.3 Regulated Power Supply 17.4 Types of Voltage Regulators 17.5 Zener Diode Voltage Regulator
442 17 Principles of Electronics Regulated D.C. Power Supply 17.1 Ordinary D.C. Power Supply 17.2 Important Terms 17.3 Regulated Power Supply 17.4 Types of Voltage Regulators 17.5 Zener Diode Voltage Regulator
PECL and LVDS Low Phase Noise VCXO (for 65-130MHz Fund Xtal) XIN XOUT N/C N/C CTRL VCON (0,0) OESEL (Pad #25) 1 (default)
 Reserved BUF BUF 62 mil OESEL^ Reserved Reserved PL520-30 FEATURES 65MHz to 130MHz Fundamental Mode Crystals. Output range (no PLL): 65MHz 130MHz (3.3V). 65MHz 105MHz (2.5V). Low Injection Power for crystal
Reserved BUF BUF 62 mil OESEL^ Reserved Reserved PL520-30 FEATURES 65MHz to 130MHz Fundamental Mode Crystals. Output range (no PLL): 65MHz 130MHz (3.3V). 65MHz 105MHz (2.5V). Low Injection Power for crystal
Fundamentals of Power Electronics. Robert W. Erickson University of Colorado, Boulder
 Robert W. Erickson University of Colorado, Boulder 1 1.1. Introduction to power processing 1.2. Some applications of power electronics 1.3. Elements of power electronics Summary of the course 2 1.1 Introduction
Robert W. Erickson University of Colorado, Boulder 1 1.1. Introduction to power processing 1.2. Some applications of power electronics 1.3. Elements of power electronics Summary of the course 2 1.1 Introduction
