Genistein Induces a Protective Immunomodulatory Effect in a Mouse Model of Cervical Cancer
|
|
|
- Nigel Derrick Stevens
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Genistein Induces a Protective Immunomodulatory Effect in a Mouse Model of Cervical Cancer Amir Ghaemi 1,2*, Hoorieh Soleimanjahi 3, Soodeh Razeghi 4, Ali Gorji 2,5, Alijan Tabaraei 1, Abdolvahab Moradi 1, Akram Alizadeh 6, Mohammad Ali Vakili 7 1 Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Infectious Diseases research Centre, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, 2 Shefa Neuroscience Research Centre, 3 Department of Virology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, 4 Sina Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, 5 Institut für Physiologie I, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Robert- Koch-Strasse Münster, Germany, 6 Department of Advanced Technology, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, 7 Department of Health and Social Sciences, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran ABSTRACT Background: Genistein (GEN), a naturally occurring flavonoid present in soy bean, has attracted scientific interest for its possible benefits in cancer. Objective: The potential immunomodulatory effects of genistein on the immune system and against TC-1 tumor cell line were evaluated in adult female C57BL/6 mice. Methods: Mice were treated with GEN 10 days before to 10 days after the tumor induction. Thirty days after the last GEN treatment, lymphocyte proliferation, Lactase Dehydrogenase (LDH) cytolytic activity and cytokine secretion were analyzed in GEN and control groups. Results: The results showed that ingestion of genistein significantly increased lymphocyte proliferation and LDH release. Furthermore, the treatment with genistein also caused a significant increment in interferon gamma (IFN-γ). In addition, the treatment achieved significant therapeutic effect in tumor models compared to the control group. These results indicated that the effect of GEN on tumor growth may be attributed to its effect on lymphocyte proliferation, cytolytic activity and IFN-γ production. Conclusion: These results demonstrate that GEN exerts an immunomodulatory effect in a mouse model of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) associated-cervical cancer. Keywords: Cervical Cancer, Genistein, Human Papillomavirus, Imunomodulation, TC *Corresponding author: Dr. Amir Ghaemi, Faculty of Medicine, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran, Tel: (+) ; Fax: (+) , Ghaem_amir@yahoo.com Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
2 Protective effect of Genistein in cancer INTRODUCTION Human papillomavirus (HPV) has been identified as the etiological agent of cervical carcinoma, the second most common malignancy in women worldwide. Moreover, HPVs are suspected to be also involved in the induction of other tumors, and the development of treatment against HPV remains of utmost priority (1). Chemoprevention is an important strategy to control the process of carcinogenesis. The potential of using medicinal herbs as cancer chemopreventive nutraceuticals and functional foods is promising. Thus, there is a need for exploring drugs/agents which act as chemopreventive agents. Genistein (GEN) (4, 7, 4 -trihydroxyisoflavone) is a phytoestrogen found in high levels in soy bean products (2). Phytostrogens comprise a family of biologically active plant agents called isoflavones, possessing an estrogenic effect (3). GEN-containing dietary supplements and soy bean food ingestion has been linked through epidemiological studies, with a range of potential health effects. These include prevention of breast, colon, and prostate cancers and cardiovascular disease (4-5). The potential beneficial effects of GEN in the human population are supported by similar findings in experimental animals (6). Although GEN has been shown to inhibit cancer cell growth by inhibiting the activity of some enzymes in vitro, this effect of GEN has not been associated with an antitumor effect in vivo (7). One possible mechanism for GEN to prevent tumor development may involve its effect on the immune system and the modulation of the immune response (8). In contrast, it has been shown that GEN has phytosteroid and estrogen-like activity. Therefore, there has been concern that the estrogenic effects of these compounds might have side effects in some situations (9). Due to controversial reports on chemopreventive potential of genistein, the antitumor and immune induced responses of genistein in HPV-associated tumor was investigated in this study. MATERIALS AND METHODS Mice and Cells. C57BL/6 mice (6-8 weeks old) were purchased from the Pasteur Institute (Karaj, Iran). Mice were housed for 1 week before the experiment, given free access to food and water, and maintained in a light/dark cycle with lights on from 6: 00 to 18: 00 h. All experiments were done according to the guidelines for the care and use and the guidelines of the laboratory animal ethical commission of shefa neuroscience research center. TC-1, (Part of the Johns Hopkins Special Collection) was derived from primary epithelial cells of C57BL/6 mice cotransformed with HPV16 E6 and E7 and activated c- Ha-ras oncogene. TC-1 cell line which is HPV-16 E7+ was used as a tumor model in an H-2b murine system.tc-1 cell line was grown in Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium (RPMI 1640) (Gibco-BRL) supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal calf serum (FCS), penicillin/ streptomycin 50 U/ml, 2 mm glutamine, 1 mm sodium pyruvate, 2mM nonessential amino acids, and G mg/ml at 37 C with 5% CO2. Tumor Therapy Assay. For in vivo tumor experiments, C57BL/6 mice (ten per group) were challenged by subcutaneous injection in the right flank with TC-1 cells Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
3 Ghaemi A, et al suspended in 100 µl PBS. PBS- treated mice were used as background control group in all experiments. Experimental Design. Mice were separated in three experimental groups. The mice were gavaged daily with genistein (20 mg/kg) (LC laboratories, USA) dissolved in 4% DMSO (Sigma Aldrich, USA) (Group 1-test group), 4% DMSO (Group 2-Vehicle control). For healthy control group, the mice were mock-infected and PBS-treated (Group 3). All the treatments were done 10 days before to 10 days after the tumor induction. Subcutaneous tumor volume was estimated according to Carlsson s formula (11); hence, the largest (a) and the smallest (b) superficial diameters of the tumor were measured twice a week and then the volume (V) of the tumor was calculated by the formula: (V=a b ) Statistical analysis was performed using Student s t test. All values were expressed as means ± S.D. Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay (LPA). For assessing lymphocyte proliferation, LPA test was performed. Twenty four hours after the last gavage, spleens from the immunized mice were removed and red blood cells were cleared by incubation in lysis buffer (0.15 M NH4Cl, 1 mm KHCO3, 0.1 mm Na2EDTA, ph 7.2) for 5 min at 37 C. Obtained mononuclear cells (2x10 5 cells/well) were grown in each 96-well plate (Nunc, Denmark).The preparations were cultured with RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 1% L-glutamine, 1% HEPES, 0.1% 2ME, 0.1% penicillin/streptomycin and induced in the presence of 10 µg/ml genistein. T cell mitogen PHA (phytohemaglutenin, Sigma chemicals) at a concentration of 5 µg/ml was used as a positive control. Unstimulated splenocytes were used as a negative control. After 3 days, MTT (3-(4,5-dimethyl tetrazolyl-2) 2,5 diphenyl) tetrazolyumbromide (Sigma chemicals) in a concentration of 5 µg/ml was added per well and incubated for 5 h at 37 C in 5% CO2. DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) (100 µl) was added to dissolve the formazan crystals produced. Plates were read at 540 nm, and the results were expressed as stimulation index (SI). The SI was determined as follows: OD values of stimulated cells (Cs) minus the relative cell number of the unstimulated cells (Cu) multiplied or divided by relative OD values of unstimulated cells. All tests were performed in triplicate for each mouse. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay. In order to assess cell cytotoxicity, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level was determined in splenocytes. Twenty-four hours after the final administration, mice were sacrificed and their splenocytes were isolated. For each sample obtained from individual mouse, single cell suspension of mononuclear cells (used as the effecter cells) were cocultured in RPMI 1640 medium with washed EL4 target cells at various effector-to-target cell ratios (E/T ratios) for 4h in phenol red-free RPMI 1640 containing 3% FCS. For preparation of the target cells, EL-4 cells were stimulated with genistein antigen (5 µg/ml). After centrifugation, the supernatants (50 µl/well) were transferred to the 96-well flatbottom plates, and lysis of target cells were determined by measuring LDH release using Cytotoxicity Detection Kit (LDH) according to the procedures stated by the manufacturer (Takara Company). Several controls were used for the cytotoxicity assay. Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
4 Protective effect of Genistein in cancer High control was the total LDH released from the target cells, and all EL4 cells were lysed by a medium containing 1% Triton X-100. Low control was the natural release of LDH from the target cells which was obtained by adding only EL4 cells in the assay medium. T-cell control was used to measure the natural release of LDH from T cells, obtained by only adding the different ratios of T cells in the assay medium. The assay for all samples, including the controls, was performed in triplicate (10). The LDH-mediated conversion of the tetrazolium salt into red formazan product was measured at 490 nm after incubation at room temperature for 30 min. The percentage of specific cytolysis was determined by the following formula: % Cytotoxicity = [(experimental value effector cell control) low control high control low control ] 100 Cytokine Assay. Twenty- four hours after the last oral administration, mice were sacrificed and their splenocytes were isolated. Mononuclear cells from spleens of immunized mice at a concentration of cells/well were incubated in 24-well plates (Nunc, Denmark) for 2 days in a total volume of 1.5 ml of RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% FCS, 1% L-glutamine, 1% HEPES, 0.1% 2ME, 0.1% penicillin/streptomycin and pulsed with 10 µg/ml genistein. The cell supernatants were collected and assayed for the presence of cytokines using commercially available sandwich-based ELISA kits (ebioscience, USA) following manufacturer s instruction. All tests were performed in triplicate for each mouse. Data Analysis. To compare results among different groups, one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with scheffe post hoc comparison was performed. SPSS statistical software version 11.0 was utilized for statistical analyses. Differences were considered statistically significant when p values were <0.05. RESULTS Lymphocyte Proliferation Response. In order to evaluate the effect of GEN treatment on the proliferation of T lymphocytes, three mice per group were used for this experiment. The mice were gavaged daily with GEN or DMSO. The animals were sacrificed and the spleen cells were harvested. The lymphocytes were activated in vitro by GEN and evaluated by MTT methods. A significant increase (p<0.01) in the lymphocyte proliferation was evident in GEN treated groups over those of negative control ones, following stimulation of the spleen cells with antigen, as shown in Figure 1. In order to assess the effect of GEN on the lactate dehydrogenase release, 3 mice/group were used. E/T ratio of 50:1 demonstrated the most significant results among different groups and was selected for further analysis. As shown in Figure 2, lymphocytes in immunized mice with GEN (29.4 ± 1.2%) increased specific cytolytic activity at an E/T ratio of 50:1 significantly as compared to that of DMSO (vehicle control) group (18.5 ± 1.9%) or the healthy control group (13.5 ± 2.9) (p<0.01). However, no statistically significant difference in cytolytic activity was found between the DMSO (vehicle control) group and the healthy control group (p>0.05). Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
5 Ghaemi A, et al The most significant difference among all these groups was at an E/T ratio of 50:1 (data not shown). Based on the results, the CTL activities in immunized mice with GEN group was stronger than those in the control ones. Lymphocyte proliferation stimulation index Genistein DMSO Control Groups Figure 1. Splenocyte proliferation levels after in vitro stimulation with GEN antigen. C57BL/6 mice were challenged by subcutaneous injection of TC-1 cells. Twenty-four hours after final immunization, spleens of mice (three per group) were removed and lymphocyte proliferation was evaluated with MTT method. Formazan crystal formation after incubation of MTT was determined by solving the crystals in DMSO and optical density (OD) was read at 540 nm. Values are mean ± standard error of the mean for the experiments. Lymphocyte proliferation of GEN group was significantly higher than those in control ones (p 0.01). 35 Cytotoxicity % Genistein DMSO Control Groups Figure 2. CTL assays to demonstrate lymphocytes in mice vaccinated with GEN using quantitative measurement of LDH release assay. After mice were immunized with GEN for 20 days, spleens were harvested as described in Materials and Methods. Data were collected from LDH results at various E/T ratios (E/T=25:1, 50:1, 100:1) and expressed as cytotoxicity percentage ± SD. Data shown here are from three independent experiments performed in triplicate (p<0.01). Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
6 Protective effect of Genistein in cancer Cytokine Assay. To determine whether treatment with GEN could modulate cytokine secretion and increase specific immune responses, we measured IL-4 and IFN-γ levels in the supernatants of mononuclear cells from treated mice re-stimulated in vitro with GEN antigen. ELISA results obtained from culture supernatants harvested at 72 h showed that, in response to GEN, spleen cells from the GEN group produced higher level of T helper cell type 1 (Th1)-associated cytokine IFN-γ and lower level of the T helper cell type 2 (Th2)-associated cytokine IL-4 (p<0.001), compared to the control groups, as shown in Figure 3. The results indicate that GEN regimen predominantly displays a Th1 cytokine profile. Figure 3. Determination of the production of IFN-γ and IL-4 cytokines. Collected supernatants were screened for the presence of IFN-γ and IL-4 to determine the type (Th1 versus Th2) of the immune response. Concentration of cytokines was determined by comparison to a standard curve of serially diluted positive control samples. The data is represented as mean ± S.D. Each sample was examined in triplicate and results are representative of two experiments (p< 00.05). Tumor Protection. To determine whether the observed enhancement in the number of GEN-specific cellular immune responses after treatment with GEN could be correlated to a GEN-specific anti-tumor effect, we performed an in vivo tumor treatment experiment using a previously characterized E7-expressing tumor model, TC-1 (11). Mice were injected with TC-1 cells/mouse subcutaneously on the right flank, and then gavaged daily with GEN from 10 days before to 10 days after the tumor induction. Tumors were measured twice a week once they became palpable. Controls consisted of vehicle control group mice challenged with tumors. The tumor volume was monitored up to 30 days after the last GEN treatment (10 days after tumor induction). Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
7 Ghaemi A, et al As shown in figure 4, mice treated with GEN significantly reduced both tumor growth (as measured by volume) and tumor weights when compared to the control mice (p<0.05). These results indicate that vaccination with GEN could induce therapeutic anti-tumor effects. Figure 4. Therapeutic vaccination against TC-1-induced tumors. Mice were inoculated with TC-1 tumor into the right flank and were monitored for the evidence of tumor growth by palpation and inspection twice a week up to 30 days after the last GEN treatment. For the determination of tumor volume, each individual tumor size was measured. Line and scatter plot graphs depicting the tumor volume (mm 3 ) are presented. The data presented is a representative of two independent experiments. DISCUSSION Immune system plays an important role in protection against tumor growth. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes constitute the major antitumor effector population against tumor growth and dissemination (10,12). Consistent with the reported chemopreventive effect of GEN, the present study demonstrated that administration of GEN by gavage for 20 days at physiologically relevant doses in adult female C57BL/6 mice significantly increased antitumor and immune modulating effects to TC-1 tumor cells in vivo models. For evaluating the GEN antitumor responses, we examined its effects on different aspects of immune response using three immunoassay experiments, including LDH cytotoxicity test, interferon-γ and lymphocyte proliferation assay. Cytotoxicity and lymphocyte proliferation assays were carried out to test the specific cellular immune response generated by genistein treatment. The capacity to elicit an effective T cell immunity can be shown by the stimulation of lymphocyte proliferation response. Interferon-γ assay was carried out to examine whether the immune response to TC-1 tumor was in a cell-mediated pathway or not. Interferon-γ is a cytokine involved in cell mediated immune response, especially for Cytotoxic T cells and TH1 cells (13). Primed T cells usually respond quickly and strongly when they come in contact with antigens Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
8 Protective effect of Genistein in cancer that they have previously encountered. In the present paper, we demonstrated that GEN administration stimulates Cytotoxic T lymphocytes, T cell immunity and interferon gamma responses compared to controls. Consistent with the tumor inhibitory effect of GEN reported in humans, increased resistance against cervical cancer was observed after exposure of mice to GEN by gavage for 20 d. This is also in agreement with previous studies that oral administration of GEN inhibited B16F10 lung-tumor nodule formation (14) and decreased B16 tumor volume (15). In another study, Gue et al. showed that at dosages of 6 and 20 mg/kg for 28 d by gavage, GEN significantly decreased B16F10 lung tumor nodule formation (16). In the present study, we used 20 mg/kg GEN for 20 days by gavage based on previous studies which have shown that this dose induces maximum immunomodulation in the mice (16). There are several possible mechanisms that may be responsible for the inhibitory effect of GEN on cervical cancer tumor growth. Some in vitro studies have demonstrated that GEN can directly inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells (17). However, these mechanisms may not play an important role in our in vivo tumor model. In general agreement with previous in vivo studies, our results confirm that the chemopreventive effects of GEN may be related to its immunomodulatory effects. Immunomodulatory effects of GEN have been shown in previous studies. Gue et al. demonstrated significantly increased activities of cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) and natural killer cells by GEN in C57BL/6 mice. The authors conclude that the effect of GEN on CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells might be responsible in part for its stimulatory effect on T cells (18). In line with these findings, our results show increased CTL and lymphocyte proliferation responses. Another study showed that the oral administration of 20 mg/kg genistein increased IFNγ from T cells in response to ovalbumin in female DO11.10 mice. In contrast to the female mice, genistein did not increase cytokine production in male mice, suggesting that the effect of genistein on cytokine production is gender-dependent (19). Accordingly, our present findings verify that GEN treatment induces the increased secretion of IFN-γ from the T cells of GEN- treated female mice. One of the important mechanisms by which GEN exerts its immune response effect is to interact with Estrogen Receptors (ERs) and compete with estrogen for binding (20). ERα is required for 17 β-estradiol-induced increases in IFN-γ expression and Th1 responses. It is possible that binding of GEN to ERβ would leave more free 17 β- estradiol to interact with ERα, thus enhancing T cell activity (21).The main constituent responsible for the immunomodulatory effect of genistein is an isoflavone (4, 7, 4- trihydroxyisoflavone) (22). These results suggest that orally administrated GEN exerts its immunomodulatory effects in female mouse model of cervical cancer in part by increasing proliferation of splenic lymphocytes, elevating cytolytic activity and IFN-γ production, thereby inducing protective anti-tumor immunity. In conclusion, GEN simulates and modulates the immune response to a desired level against HPV-16 tumor-bearing mice. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This research has been financially supported by Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran. Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
9 Ghaemi A, et al REFERENCES 1 Zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses in human cancers. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999; 111: Guo TL, Chi RP, Hernandez DM, Auttachoat W, Zheng JF. Decreased 7,12-dimethylbenz [a]anthracene-induced carcinogenesis coincides with the induction of antitumor immunities in adult female B6C3F1 mice pretreated with genistein. Carcinogenesis. 2007; 28: Hsieh CY, Santell RC, Haslam SZ, Helferich WG. Estrogenic effects of genistein on the growth of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells in vitro and in vivo. cancer res. 1998; 59: Messina MJ, Persky V, Setchell KD, Barnes S. Soy intake and cancer risk: a review of the in vitro and in vivo data. Nutr Cancer. 1994; 21: Chang MJ, Nam HK, Myong N, Kim SH. Age-related uterotrophic response of soy isoflavone intake in rats. J Med Food. 2007; 10: Sakai T, Koqiso M. Soy isoflavones and immunity. J Med Invest. 2008; 55: Wang SY, Yang KW, Hsu YT, Chang CL, Yang YC. The differential inhibitory effects of genistein on the growth of cervical cancer cells in vitro. Neoplasma. 2001; 48: Ravindranath MH, Muthuqounder S, Presser N, Viswanathan S. Anticancer therapeutic potential of soy isoflavone, genistein. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004; 546: Goldwyn S, Lazinsky A, Wei H. Promotion of health by soy isoflavones: efficacy, benefit and safety concerns. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 2000; 17: Ghaemi A, Soleimanjahi H, Gill P, Hassan ZM, Razeghi S, Fazeli M, et al. Protection of mice by a λ-based therapeutic vaccine against cancer associated with human papillomavirus type 16. Intervirology. 2011; 54: Ghaemi A, Soleimanjahi H, Gill P, Hassan Z, Jahromi SR, Roohvand F. Recombinant lambda-phage nanobioparticles for tumor therapy in mice models. Genet Vaccines Ther. 2010; 8:3. 12 Grangeon C, Cormary C, Douin-Echinard V, Favre G, Couderc B, Tilkin-Mariamé AF. In vivo induction of antitumor immunity and protection against tumor growth by injection of CD154-expressing tumor cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002; 9: Ghaemi A, Soleimanjahi H, Bamdad T, Soudi S, Arefeian E, Hashemi SM, et al. Induction of humoral and cellular immunity against latent HSV-1 infections by DNA immunization in BALB/c mice. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007; 30: Menon LG, Kuttan R, Nair MG, Chang, YC, Kuttan G. Effect of isoflavones genistein and daidzein in the inhibition of lung metastasis in mice induced by B16F-10 melanoma cells. Nutr Cancer. 1998; 30: Record IR, Broadbent JL, King RA, Dreosti IE, Head RJ, Tonkin AL. Genistein inhibits growth of B16 melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro and promotes differentiation in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1997; 72: Guo TL, McCay JA, Zhang LX, Brown RD, You L, Karrow NA, et al. Genistein modulates immune responses and increases host resistance to B16F10 tumor in adult female B6C3F1 mice. J Nutr. 2001; 131: Kim SH, Kim SH, Kim YB, Jeon YT, Lee SC, Song YS. Genistein inhibits cell growth by modulating various mitogenactivated protein kinases and AKT in cervical cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009; 1171: Guo TL, Chi RP, Germolec DR, White KL. Stimulation of the immune response in B6C3F1 mice by genistein is affected by exposure duration, gender, and litter order. J Nutr. 2005; 135: Sakai T, Koqiso M, Mitsuya K, Komatsu T, Yamamoto S. Genistein enhances antigen-specific cytokine production in female DO11.10 transgenic mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2006; 52: Kurzer MS, Xu X. Dietary phytoestrogens. Annu Rev Nutr. 1997;17: Kuiper GG, Lemmen JG, Carlsson B, Corton JC, Safe SH, van der Saag PT, et al. Interaction of estrogeni chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta. Endocrinology. 1998; 139: Valsecchi AE, Franchi S, Panerai AE, Sacerdote P, Trovato AE, Colleoni M. Genistein, a natural phytoestrogen from soy, relieves neuropathic pain following chronic constriction sciatic nerve injury in mice: anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity. J Neurochem. 2008; 107: Iran.J.Immunol. VOL.9 NO.2 June
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Identification of T-cell epitopes of SARS-coronavirus for development of peptide-based vaccines and cellular immunity assessment methods
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES PKS Chan 陳 基 湘 S Ma 文 子 光 SM Ngai 倪 世 明 Key Messages 1. Subjects recovered from SARS-CoV infection retain memory of cellular immune response to epitopes
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES PKS Chan 陳 基 湘 S Ma 文 子 光 SM Ngai 倪 世 明 Key Messages 1. Subjects recovered from SARS-CoV infection retain memory of cellular immune response to epitopes
Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit
 Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit
 Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600450 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Glycolysis Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 600450 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
CytoSelect LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 Product Manual CytoSelect LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-241 960 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement and monitoring of cell cytotoxicity
Product Manual CytoSelect LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-241 960 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement and monitoring of cell cytotoxicity
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay
 Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 Title: Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay (LPA) Using 3 H- Thymidine Incorporation Assay Core Name: Lloyd Mayer, Mount Sinai Medical Center Effective Date: 02/16/2012 Trial Number: ITN047AI SOP # ITN2800 SOP
Title: Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay (LPA) Using 3 H- Thymidine Incorporation Assay Core Name: Lloyd Mayer, Mount Sinai Medical Center Effective Date: 02/16/2012 Trial Number: ITN047AI SOP # ITN2800 SOP
The Evaluation of Interferon-beta Levels in HPV-positive Cervical Cancer Cell Lines
 The Evaluation of Interferon-beta Levels in HPV-positive Cervical Cancer Cell Lines Olivia M. Ford and Jennifer T. Thomas, Ph.D. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common viral sexually transmitted
The Evaluation of Interferon-beta Levels in HPV-positive Cervical Cancer Cell Lines Olivia M. Ford and Jennifer T. Thomas, Ph.D. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common viral sexually transmitted
EFFECT OF PREDATED VACCINATION AND CHINESE HERBAL ADJUVANT RABBIT HEMORRHAGIC DISEASE VACCINE ON IMMUNE RESPONSE IN YOUNG RABBITS
 Pathology and Hygiene EFFECT OF PREDATED VACCINATION AND CHINESE HERBAL ADJUVANT RABBIT HEMORRHAGIC DISEASE VACCINE ON IMMUNE RESPONSE IN YOUNG RABBITS Longsheng Yang*, Jiabin Xue, Fang Wang, Yuanliang
Pathology and Hygiene EFFECT OF PREDATED VACCINATION AND CHINESE HERBAL ADJUVANT RABBIT HEMORRHAGIC DISEASE VACCINE ON IMMUNE RESPONSE IN YOUNG RABBITS Longsheng Yang*, Jiabin Xue, Fang Wang, Yuanliang
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
Immunomodulatory Effects of Mycobacteria. Toh S.S. 1 and Seah G.T. 2
 Immunomodulatory Effects of Mycobacteria Toh S.S. 1 and Seah G.T. 2 Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, National University of Singapore MD4, 5 Science Drive 2, Singapore 117597 ABSTRACT It
Immunomodulatory Effects of Mycobacteria Toh S.S. 1 and Seah G.T. 2 Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, National University of Singapore MD4, 5 Science Drive 2, Singapore 117597 ABSTRACT It
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS
 EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECT OF THE COMPOUND RIBOXYL ON THE ATP LEVEL AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM HUMAN DERMAL FIBROBLASTS FINAL REPORT OF THE STUDY GT050923 Study promoter: LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS ZA Les
NCL Method ITA-6. Leukocyte Proliferation Assay
 NCL Method ITA-6 Leukocyte Proliferation Assay Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory National Cancer Institute-Frederick SAIC-Frederick Frederick, MD 21702 (301) 846-6939 ncl@mail.nih.gov December
NCL Method ITA-6 Leukocyte Proliferation Assay Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory National Cancer Institute-Frederick SAIC-Frederick Frederick, MD 21702 (301) 846-6939 ncl@mail.nih.gov December
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
 ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
ATCC 30-1010K Store at 4 C This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for use in humans, animals or for diagnostics. Introduction Measurement of cell viability and
Comparison of whole blood and PBMC assays for T-cell functional analysis
 Deenadayalan et al. BMC Research Notes 213, 6:12 SHORT REPORT Open Access Comparison of whole blood and assays for T-cell functional analysis Anbarasu Deenadayalan, Prabhavathi Maddineni and Alamelu Raja
Deenadayalan et al. BMC Research Notes 213, 6:12 SHORT REPORT Open Access Comparison of whole blood and assays for T-cell functional analysis Anbarasu Deenadayalan, Prabhavathi Maddineni and Alamelu Raja
CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Product Manual CytoSelect Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number CBA-240 96 assays (96-well plate) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The measurement
Basic Science in Medicine
 Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
Medical Journal of th e Islamic Republic of Iran Volume 18 Number 3 Fall 1383 November 2004 Basic Science in Medicine ] EXPANSION OF HUMAN CORD BLOOD PRIMITIVE PROGENITORS IN SERUM-FREE MEDIA USING HUMAN
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma
 The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
Gene Silencing Oligos (GSOs) Third Generation Antisense
 Gene Silencing Oligos (GSOs) Third Generation Antisense Walter R. Strapps, Ph.D. Executive Director, RNA Therapeutics Idera Pharmaceuticals Cambridge, MA NASDAQ: IDRA www.iderapharma.com Idera is a leader
Gene Silencing Oligos (GSOs) Third Generation Antisense Walter R. Strapps, Ph.D. Executive Director, RNA Therapeutics Idera Pharmaceuticals Cambridge, MA NASDAQ: IDRA www.iderapharma.com Idera is a leader
Generation of EBV-immortalized B cell lines
 UCANU 0014 Version November 01, 2011 Page 1 van 6 Generation of EBVimmortalized B cell lines CMCI (Center for molecular and Cellular Intervention) University Medical Center Utrecht Written by Name Function
UCANU 0014 Version November 01, 2011 Page 1 van 6 Generation of EBVimmortalized B cell lines CMCI (Center for molecular and Cellular Intervention) University Medical Center Utrecht Written by Name Function
Immunogenicity Evaluation of a DNA Vaccine Expressing the Hepatitis C Virus Non-Structural Protein 2 Gene in C57BL/6 Mice
 Iranian Biomedical Journal 18 (1): 1-7 (January 2014) DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1231.2013 Immunogenicity Evaluation of a DNA Vaccine Expressing the Hepatitis C Virus Non-Structural Protein 2 Gene in C57BL/6 Mice
Iranian Biomedical Journal 18 (1): 1-7 (January 2014) DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1231.2013 Immunogenicity Evaluation of a DNA Vaccine Expressing the Hepatitis C Virus Non-Structural Protein 2 Gene in C57BL/6 Mice
2.1.2 Characterization of antiviral effect of cytokine expression on HBV replication in transduced mouse hepatocytes line
 i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Determination of specificity of intracellular detection of IL-7Rα by flow cytometry
 CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
Cytotoxic properties of Acorus calamus in MCF -7 breast cancer cells
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 1 Number 1 (2013) pp. 106-111 www.ijcrar.com Cytotoxic properties of Acorus calamus in MCF -7 breast cancer cells S.B. Sreejaya and K.S. Santhy* Department of Zoology, Avinashilingam
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 1 Number 1 (2013) pp. 106-111 www.ijcrar.com Cytotoxic properties of Acorus calamus in MCF -7 breast cancer cells S.B. Sreejaya and K.S. Santhy* Department of Zoology, Avinashilingam
Anti-CD38 anti-cd3 bispecific antibody in multiple myeloma
 Anti-CD38 anti-cd3 bispecific antibody in multiple myeloma David E. Szymkowski Senior Director, Biotherapeutics Proteins by Design 1960s...1980s...2000s... Where are the bispecific antibody drugs? J Exp.
Anti-CD38 anti-cd3 bispecific antibody in multiple myeloma David E. Szymkowski Senior Director, Biotherapeutics Proteins by Design 1960s...1980s...2000s... Where are the bispecific antibody drugs? J Exp.
MagExtractor -Genome-
 Instruction manual MagExtractor-Genome-0810 F0981K MagExtractor -Genome- NPK-101 100 preparations Store at 4 C Contents [1] Introduction [2] Components [3] Materials required [4] Protocol 1. Purification
Instruction manual MagExtractor-Genome-0810 F0981K MagExtractor -Genome- NPK-101 100 preparations Store at 4 C Contents [1] Introduction [2] Components [3] Materials required [4] Protocol 1. Purification
QuickTiter FeLV Core Antigen ELISA Kit (FeLV p27)
 Product Manual QuickTiter FeLV Core Antigen ELISA Kit (FeLV p27) Catalog Numbers VPK-155 96 wells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) is
Product Manual QuickTiter FeLV Core Antigen ELISA Kit (FeLV p27) Catalog Numbers VPK-155 96 wells FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) is
TABLE OF CONTENT. Page ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. iii ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT. vii LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES. xvi ABBREVIATIONS.
 x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
Summary and conclusion 2013
 The work presented in the thesis is focused on the problems related to the prostate gland. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) are the two major problems associated with prostate.
The work presented in the thesis is focused on the problems related to the prostate gland. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) are the two major problems associated with prostate.
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 10 October 2007 Doc. Ref. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON POTENCY TESTING OF CELL BASED IMMUNOTHERAPY
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 10 October 2007 Doc. Ref. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON POTENCY TESTING OF CELL BASED IMMUNOTHERAPY
Oncos Therapeutics: ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy. March 2015. Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder
 Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit
 Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation A) Prepare a yeast culture (see the Galactose Induction Protocol for details). 1) Start a small culture (e.g. 2 ml) in YEPD or selective media from a single colony. 2) Spin
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation A) Prepare a yeast culture (see the Galactose Induction Protocol for details). 1) Start a small culture (e.g. 2 ml) in YEPD or selective media from a single colony. 2) Spin
Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit
 Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0479r 96 Tests Operating instructions www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0479r 96 Tests Operating instructions www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
Effectively Exploiting Big Data with Semantics
 Effectively Exploiting Big Data with Semantics Thomas C. Rindflesch, Ph.D. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health Digital Government Institute s Government Big Data Conference, October
Effectively Exploiting Big Data with Semantics Thomas C. Rindflesch, Ph.D. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health Digital Government Institute s Government Big Data Conference, October
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Antibody Production at Strategic Diagnostics Inc. SOP#: M-119 Version #: 1 Date Approved: August 6, 2009 Author: Strategic Diagnostic Inc. Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Antibody Production at Strategic Diagnostics Inc. SOP#: M-119 Version #: 1 Date Approved: August 6, 2009 Author: Strategic Diagnostic Inc. Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE
Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1
 9/8/2015 Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1 Stefan Eichmüller, PhD GMP & T Cell Therapy Unit, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
9/8/2015 Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1 Stefan Eichmüller, PhD GMP & T Cell Therapy Unit, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
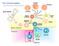 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
Custom Antibody Services
 prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy
 CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
CD22 Antigen Is Broadly Expressed on Lung Cancer Cells and Is a Target for Antibody-Based Therapy Joseph M. Tuscano, Jason Kato, David Pearson, Chengyi Xiong, Laura Newell, Yunpeng Ma, David R. Gandara,
MALIGNANT PLEURAL FLUIDS AID MESOTHELIOMA CELL GROWTH AND PROPAGATION
 MALIGNANT PLEURAL FLUIDS AID MESOTHELIOMA CELL GROWTH AND PROPAGATION HUI MIN CHEAH PhD Candidate School of Medicine and Pharmacology University of Western Australia Lung Institute of Western Australia
MALIGNANT PLEURAL FLUIDS AID MESOTHELIOMA CELL GROWTH AND PROPAGATION HUI MIN CHEAH PhD Candidate School of Medicine and Pharmacology University of Western Australia Lung Institute of Western Australia
GenScript Antibody Services
 GenScript Antibody Services Scientific experts, innovative technologies, proven performance We specialize in custom antibody production to empower your research Custom Polyclonal Antibody Production Custom
GenScript Antibody Services Scientific experts, innovative technologies, proven performance We specialize in custom antibody production to empower your research Custom Polyclonal Antibody Production Custom
Prospects for Vaccines against Hepatitis C Viruses. T. Jake Liang. M.D. Liver Diseases Branch NIDDK, NIH, HHS
 Prospects for Vaccines against Hepatitis C Viruses T. Jake Liang. M.D. Liver Diseases Branch NIDDK, NIH, HHS HCV Vaccine Prevention strategies Protective immunity Barriers and solutions Vaccine candidates
Prospects for Vaccines against Hepatitis C Viruses T. Jake Liang. M.D. Liver Diseases Branch NIDDK, NIH, HHS HCV Vaccine Prevention strategies Protective immunity Barriers and solutions Vaccine candidates
Clonal Analysis of Cancer Cells that Survived Anticancer Drug Treatment
 Osaka City Medical Journal Vol. 43, No.2 259-265, 1997 Clonal Analysis of Cancer Cells that Survived Anticancer Drug Treatment TETSUJI TANAKA, LING CHANG, NAOHIKO UMESAKI and SACHIO OGITA Department of
Osaka City Medical Journal Vol. 43, No.2 259-265, 1997 Clonal Analysis of Cancer Cells that Survived Anticancer Drug Treatment TETSUJI TANAKA, LING CHANG, NAOHIKO UMESAKI and SACHIO OGITA Department of
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Basic Overview of Preclinical Toxicology Animal Models
 Basic Overview of Preclinical Toxicology Animal Models Charles D. Hebert, Ph.D., D.A.B.T. December 5, 2013 Outline Background In Vitro Toxicology In Vivo Toxicology Animal Models What is Toxicology? Background
Basic Overview of Preclinical Toxicology Animal Models Charles D. Hebert, Ph.D., D.A.B.T. December 5, 2013 Outline Background In Vitro Toxicology In Vivo Toxicology Animal Models What is Toxicology? Background
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Colorimetric Format)
 Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Colorimetric Format) Catalog Number CBA-070 CBA-070-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual CytoSelect 48-Well Cell Adhesion Assay (ECM Array, Colorimetric Format) Catalog Number CBA-070 CBA-070-5 48 assays 5 x 48 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Mouse krebs von den lungen 6 (KL-6) ELISA
 KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse krebs von den lungen 6 (KL-6) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse KL-6 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants, body fluid and tissue homogenate Cat. No.
KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse krebs von den lungen 6 (KL-6) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse KL-6 in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants, body fluid and tissue homogenate Cat. No.
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) ELISA Kit
 Rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. CSB-E14405r For the quantitative determination of rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) concentrations in serum, plasma and tissue
Rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. CSB-E14405r For the quantitative determination of rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) concentrations in serum, plasma and tissue
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit
 Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Amaxa Mouse T Cell Nucleofector Kit For T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice Evaluated for murine T cells isolated from C57BL/6 & BALB/c mice This protocol is designed for murine lymphocytes or
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012. Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation. System
 Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Biochemistry
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Biochemistry The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences /Clinical Biochemistry, is awarded by the Faculty of Graduate Studies
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Biochemistry The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences /Clinical Biochemistry, is awarded by the Faculty of Graduate Studies
Rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) ELISA Kit
 Rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. CSB-E14405r For the quantitative determination of rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) concentrations in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates.
Rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. CSB-E14405r For the quantitative determination of rat creatine kinase MM isoenzyme (CK-MM) concentrations in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates.
OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone.
 Title of the poster Authors Sheffield Cancer Research Centre University of Sheffield OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone. Dr Penelope Ottewell Background
Title of the poster Authors Sheffield Cancer Research Centre University of Sheffield OPG-Fc inhibits ovariectomy-induced growth of disseminated breast cancer cells in bone. Dr Penelope Ottewell Background
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual
 Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics
 The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
QuickTiter Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg) ELISA Kit
 Product Manual QuickTiter Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg) ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers VPK-5004 VPK-5004-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
Product Manual QuickTiter Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg) ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers VPK-5004 VPK-5004-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary GeneBLAzer RAR alpha DA Assay Kit GeneBLAzer RAR alpha-uas-bla GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1387, K1685 Target Description The retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha)
Validation & Assay Performance Summary GeneBLAzer RAR alpha DA Assay Kit GeneBLAzer RAR alpha-uas-bla GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1387, K1685 Target Description The retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha)
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer, Trevigen, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD For further infomation, please contact: William Booth, Ph.D. Tel: +44 (0)1235
NCL Method ITA-14. Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro
 NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
NCL Method ITA-14 Analysis of Nanoparticle Effects on Maturation of Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells In Vitro Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Immunophenotyping peripheral blood cells
 IMMUNOPHENOTYPING Attune Accoustic Focusing Cytometer Immunophenotyping peripheral blood cells A no-lyse, no-wash, no cell loss method for immunophenotyping nucleated peripheral blood cells using the Attune
IMMUNOPHENOTYPING Attune Accoustic Focusing Cytometer Immunophenotyping peripheral blood cells A no-lyse, no-wash, no cell loss method for immunophenotyping nucleated peripheral blood cells using the Attune
OKT3. ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody. used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~
 g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
g944202 潘 怡 心 OKT3 ~ The first mouse monoclonal antibody used in clinical practice in the field of transplantation ~ As everybody knows, OKT3 is the first mouse monoclonal antibody produced for the treatment
Immunomodulatory Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino on Human Immune Cells
 Immunomodulatory Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino on Human Immune Cells Busarawan Sriwanthana, Weena Threesangsri and Walailuk Wanavichet National Institute of Health Department of Medical Sciences
Immunomodulatory Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino on Human Immune Cells Busarawan Sriwanthana, Weena Threesangsri and Walailuk Wanavichet National Institute of Health Department of Medical Sciences
cause harmful and unwanted toxicity to normal cells. The therapeutic index of chemotherapy is
 Using Viruses to Kill Cancer: Investigating the role of in vitro cell differentiation in HSV-1 double-mutant KM110red infection of hfob and U2OS cells Natalie Raso Background In the successful development
Using Viruses to Kill Cancer: Investigating the role of in vitro cell differentiation in HSV-1 double-mutant KM110red infection of hfob and U2OS cells Natalie Raso Background In the successful development
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity. Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands
 Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands CBER/NIAID/WHO, Bethesda MD, December 11 2007 A working model of an antiviral
Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands CBER/NIAID/WHO, Bethesda MD, December 11 2007 A working model of an antiviral
PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens
 www.iqproducts.nl PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens IFN- γ PURE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160P s 50 tests FITC [RUO] [REF] IQP-160F s 50 tests R-PE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160R s 50
www.iqproducts.nl PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens IFN- γ PURE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160P s 50 tests FITC [RUO] [REF] IQP-160F s 50 tests R-PE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160R s 50
Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi
 Author Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi Zhu Judy Wei Biological Sciences Though she hopes to attend medical school, Judy Wei
Author Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi Zhu Judy Wei Biological Sciences Though she hopes to attend medical school, Judy Wei
Anticancer Effects of and Direction of Research on Hippophae
 Anticancer Effects of and Direction of Research on Hippophae Xu Mingyu (Xiyuan Hospital, Institute of Chinese Medicine, China, Beijing 100091) Seabuckthorn, Hippophae rhamnoides L., belongs to genus Hippophae
Anticancer Effects of and Direction of Research on Hippophae Xu Mingyu (Xiyuan Hospital, Institute of Chinese Medicine, China, Beijing 100091) Seabuckthorn, Hippophae rhamnoides L., belongs to genus Hippophae
TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0010 TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael W. Fannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0010 TITLE: Treatment of Prostate Cancer with a DBP-MAF-Vitamin D Complex to Target Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael W. Fannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit ABE5487 100 assays; Store at -20 C
 Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit ABE5487 100 assays; Store at -20 C I. Introduction: Creatine Kinase (CK) also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and ATP: creatine N- phosphotransferase
Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit ABE5487 100 assays; Store at -20 C I. Introduction: Creatine Kinase (CK) also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and ATP: creatine N- phosphotransferase
Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory
 Immunology and Cell Biology (1999) 77, 559 564 Special Feature Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory DA FULCHER
Immunology and Cell Biology (1999) 77, 559 564 Special Feature Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory DA FULCHER
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual
 Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Fulfilling the Promise
 Fulfilling the Promise Advancing the Fight Against Cancer: America s Medical Schools and Teaching Hospitals For more than a century, the nation s medical schools and teaching hospitals have worked to understand,
Fulfilling the Promise Advancing the Fight Against Cancer: America s Medical Schools and Teaching Hospitals For more than a century, the nation s medical schools and teaching hospitals have worked to understand,
lung cancer targeted photodynamic therapy and imaging
 99m Tc-Hematoporphyrin linked albumin nanoparticles for lung cancer targeted photodynamic therapy and imaging Su-Geun Yang, Ji-Eun Chang, Byungchul Shin, Sanghyun Park, Kun Na and Chang-Koo Shim* *Corresponding
99m Tc-Hematoporphyrin linked albumin nanoparticles for lung cancer targeted photodynamic therapy and imaging Su-Geun Yang, Ji-Eun Chang, Byungchul Shin, Sanghyun Park, Kun Na and Chang-Koo Shim* *Corresponding
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit
 Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E15852c (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of canine CK-MB concentrations in serum and plasma.
Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E15852c (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of canine CK-MB concentrations in serum and plasma.
Use of Mycobacterium vaccae (SRL172) as an Immunomodulating Agent in Association with Murine Melanoma Model B16-FIO
 Arch. Rnzi Ins. (2) 51 47 Use of Mycobacterium vaccae (SRL172) as an Immunomodulating Agent in Association with Murine Melanoma Model B16-FIO Baban, B.,* Souberbielle, B., Sharafi, J., Mohaghegh Hazrati,
Arch. Rnzi Ins. (2) 51 47 Use of Mycobacterium vaccae (SRL172) as an Immunomodulating Agent in Association with Murine Melanoma Model B16-FIO Baban, B.,* Souberbielle, B., Sharafi, J., Mohaghegh Hazrati,
RayBio Creatine Kinase (CK) Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit
 RayBio Creatine Kinase (CK) Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 28, 2014 RayBio Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay (Cat#: 68CL-CK-S100) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You
RayBio Creatine Kinase (CK) Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 28, 2014 RayBio Creatine Kinase Activity Colorimetric Assay (Cat#: 68CL-CK-S100) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You
Inc. Wuhan. Quantity Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate 1 Plate sealer for 96 wells 4 Standard (liquid) 2
 Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: uscnk@uscnk.com ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: uscnk@uscnk.com ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
protocol handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel
 handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
handbook 3D cell culture mimsys G hydrogel supporting real discovery handbook Index 01 Cell encapsulation in hydrogels 02 Cell viability by MTS assay 03 Live/Dead assay to assess cell viability 04 Fluorescent
Analysis of Factors Influencing Clinical Types of Psoriasis Vulgaris
 대 한 건 선 학 회 지 제 5 권, 제 1 호 Journal of the Korean Society for Psoriasis Vol. 5, No. 1, 43-47, 2008 Analysis of Factors Influencing Clinical Types of Psoriasis Vulgaris Sang Eun Lee, M.D., Jung Eun Lee,
대 한 건 선 학 회 지 제 5 권, 제 1 호 Journal of the Korean Society for Psoriasis Vol. 5, No. 1, 43-47, 2008 Analysis of Factors Influencing Clinical Types of Psoriasis Vulgaris Sang Eun Lee, M.D., Jung Eun Lee,
A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery
 A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery Björn Frendéus, PhD VP, Preclinical research Presenter: Björn Frendéus Date: 2011-11-08 1 Antibodies have revolutionized Cancer Treatment!
A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery Björn Frendéus, PhD VP, Preclinical research Presenter: Björn Frendéus Date: 2011-11-08 1 Antibodies have revolutionized Cancer Treatment!
Canine Creatine Kinase MM isoenzyme(ck-mm) ELISA. kit
 BlueGene Biotech. Tel: 0086-21-61471242 Fax: 0086-21-61471242 ext 806 E-mail: sales@bluegene.cc tech@bluegene.cc www.elisakit.cc www.bluegene.cc Canine Creatine Kinase MM isoenzyme(ck-mm) ELISA kit 96
BlueGene Biotech. Tel: 0086-21-61471242 Fax: 0086-21-61471242 ext 806 E-mail: sales@bluegene.cc tech@bluegene.cc www.elisakit.cc www.bluegene.cc Canine Creatine Kinase MM isoenzyme(ck-mm) ELISA kit 96
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Health benefits of isoflavones
 Intake of Fermented Soybeans, Natto, Is Associated with Reduced Bone Loss in Postmenopausal Women: Japanese Population- Based Osteoporosis (JPOS) Study Author: Yukihiro Ikeda, Masayuki Iki, Akemi Morita,
Intake of Fermented Soybeans, Natto, Is Associated with Reduced Bone Loss in Postmenopausal Women: Japanese Population- Based Osteoporosis (JPOS) Study Author: Yukihiro Ikeda, Masayuki Iki, Akemi Morita,
International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005
 Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
 Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Mary E. Kopechek Honor s Research Thesis May 17, 2007 Research Advisor: Dr. Jeff Lakritz, DVM, PhD The Ohio State
Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Mary E. Kopechek Honor s Research Thesis May 17, 2007 Research Advisor: Dr. Jeff Lakritz, DVM, PhD The Ohio State
How To Make A Tri Reagent
 TRI Reagent For processing tissues, cells cultured in monolayer or cell pellets Catalog Number T9424 Store at room temperature. TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description TRI Reagent is a quick and convenient
TRI Reagent For processing tissues, cells cultured in monolayer or cell pellets Catalog Number T9424 Store at room temperature. TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description TRI Reagent is a quick and convenient
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay. Introduction
 Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million deaths
Routine Assessment of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity in a Novel Three Dimensional Culture Assay Application Note Introduction Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for around 7.6 million deaths
Summary & Conclusion
 The prognostic value of angiogenesis markers in patients with non-hodgkin lymphoma. Summary & Conclusion The current study aims to asses the prognostic value of some angiogenesis markers in patients with
The prognostic value of angiogenesis markers in patients with non-hodgkin lymphoma. Summary & Conclusion The current study aims to asses the prognostic value of some angiogenesis markers in patients with
