bonded ligands (# 2)
|
|
|
- Jonas McLaughlin
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 bonded ligands (# 2) alkene complexes alkyne complexes allyl complexes diene complexes cyclopentadienyl complexes arene complexes metallacycles M
2 Metal Hydride Y X H Hydride Metal Z or Y X H Z dz 2 Metal dx 2 -dy 2 Hydride H Z H * Metal Dihydrogen H Y X H Metal dx 2 -dy 2 complex dihydrogen back-donation Metal dyz dihydrogen Metal Carbonyl Z * C O Y C O sp X Metal dx 2 -dy 2 bond carbonyl Metal dyz back-donation carbonyl R Z * R Metal Phosphine sp P R R Y X P R R Metal dx 2 -dy 2 bond phosphine Metal dyz back-donation phosphine CR 2 Z * CR2 Metal Alkene CR 2 Y X CR 2 Metal dx 2 -y 2 complex alkene Metal dyz back-donation alkene
3 Transition metal allyl complexes The allyl group, commonly a spectator ligand, binds in one of two ways. In the form it is a simple X type ligand like Me In the form it acts as a LX enyl ligand. It is often useful to think in terms of the resonance forms (2e + 1e donor)
4 allyl anion (ionic model) allyl radical (covalent model) Energy As the number of nodes on the allyl ligand increase the MOs of the free ligand increase in energy, ie i.e. become less stable.
5 Z Z Y Y M X X bond Metal dx 2 -dy 2 3 -allyl l bond Metal dz 2 3 -allyl l Z Z Y Y X X Metal dxy bond 3 -allyl Metal dxy bond 3 -allyl Frontier molecular orbitals of the metal allyl fragment: 1 is occupied by 2 electrons and has appropriate symmetry, energy and orientation to overlap with a suitable metal d orbital. 2 is also occupied by 2 electrons (ionic model) and has appropriate symmetry, energy and orientation to overlap with a suitable metal d orbital. 3 is unoccupied and has appropriate symmetry, energy and orientation to overlap with a suitable metal d orbital for back donation.
6 The plane of the allyl is canted at an angle with respect to the coordination polyhedron around the metal ( is usually 5 10 ). The extent of orbital overlap between 2 and the d xy orbital on the metal is improved if the allyl group moves in this way.
7 The terminal CH 2 groups of the allyl are twisted about the C C vector so as to rotate the anti hydrogens (H a ) away from the metal, and the syn hydrogens (H s ) toward the metal. This allows the bonding p orbital on these carbons to point more directly toward the metal, thus further improving the M L overlap. The 3 allyl group often shows exchange of the syn and anti substituents. One mechanism goes through an 1 allyl intermediate. This kind of exchange can affect the appearance of the 1 H NMR spectrum and also g pp p means that an allyl complex of a given stereochemistry may rearrange with time.
8 Numata et al. Inorg. Chem., 1977, 16, 1737.
9 Synthesis of metal allyl complexes 1. From an alkene via oxidative addition: 2. Nucleophilic attack by an allyl compound (transmetallation): 3. Electrophilic attack by an allyl compound: the metal attacks at the least hindered terminal CH 2 group
10 4. From diene complexes:
11 In the cationic complex the Cr(CO) 2 plane is tilted fully 10 closer to the plane of the ring than it is in neutral complex. This substantial relaxation of the roughly square pyramidal coordination sphere may be attributed to the reduction in d back donation from the oxidized metal center to the ancillary carbonyl and allyl ligand.
12 Transition metal diene complexes The diene ligand usually acts as a 4e donor in its cisoid conformation. This L 2 form is analogous to the Dewar Chatt Duncanson extreme for alkenes. Analogous to metal alkene systems the LX 2 (enediyl or σ2π) form to the metalacyclopropane extreme. The L 2 form is rarely seen with the LX 2 form becoming more important as the back donation increases.
13 The frontier orbitals of the butadiene, 2 (HOMO) and 3 (LUMO), are the most important in bonding to the metal. Depletion of electron density in 2 by donation to the metal and population of 3 by back donation from the metal lengthens the C1 C2 bond and shortens the C2 C3 bond because 2 is C1 C2 antibonding and 3 is C2 C3 bonding. Binding to a metal usually depletes the ligand HOMO and fills the ligand LUMO. This is the main reason why binding has such a profound effect on the chemical character of a ligand. The structure of the bound form of a ligand is often similar to that of the first excited state of the free ligand because to reach this state we promote an electron from the HOMO to the LUMO.
14 Depletion of electron density in by donation to the metal and population of Depletion of electron density in 2 by donation to the metal and population of 3 by back donation from the metal lengthens the C1 C2 bond and shortens the C2 C3 bond because 2 is C1 C2 antibonding and 3 is C2 C3 bonding.
15 The binding of butadiene in the transoid form is much rarer. It is found in the osmium cluster Os 3 (CO) 10 (C 4 H 6 ) in which the diene is 2 bound to two different Os centers. In Cp 2 Zr(C 4 H 6 ) and Cp * (CO)Cr(C 4 H 6 ) the diene is bound to a single metal centre as the transoid form. The cisoid isomer also exists here but it rearranges to give a 1 : 1 thermodynamic mixture of the two forms on standing photolysis leads to the trans form.
16 Zr Zr Zr slow hv fast Zr Zr
17 Transition metal cyclobutadiene complexes Most of the neutral ligands we have studied (apart from carbenes) have been stable in the free state. Cyclobutadienes on the other hand are highyl reactive when not complexed to a late transition metal. The free molecule, with four π electrons, is antiaromatic and rectangular, but the ligand is square and appears to be aromatic. By populating the LUMO of the free diene the ligand is stabilized by metal back donation. Thus by gaining partial control of two more π electrons the diene attains an electronic structure resembling that of the aromatic six π electron dianion. Ligand to metal σ donation prevents the ligand from accumulating excessive negative charge. This again is a clear example of the free and bound forms of the ligand being substantially different from one another.
18 Preparation
19
20 The Electronic Structure of Ferrocene The two cyclopentadienyl (Cp) rings of ferrocene may be orientated in the two extremes of either an eclipsed (D 5h ) or staggered (D 5d )conformation. The energy of rotation about the Fe Cp axis is very small (~ 4 kjmol 11 ) and ground state structures of ferrocene may show either of these conformations. There is also very little difference in electronic states between the D 5h and D 5d symmetries however the D 5d point group irreducible representations are used here in the description of the electronic structure of ferrocene as they simplify the symmetry matching of ligand molecular orbitals and metal atomic orbitals. The primary orbital interactions that form the metal ligand bonds in ferrocene occur between the Fe orbitals and the orbitals of the Cp ligand. If D 5d symmetry is assumed, so that there is a centre of symmetry in the ferrocene molecule through the Fe atom there will be centro symmetric (g) and antisymmetric (u) combinations. Thefivep orbitals on the planar Cp ring (D 5h symmetry) can be combined to produce five molecular orbitals.
21 The molecular orbitals of the cyclopentadienyl ring (D 5h ) Energy
22 One combination has the full symmetry yof the ring (a 2 ) There are two doubly degenerate combinations (e 1 and e 2 )havingoneandtwo planarnodes at right angles to the plane of the ring. The relative energies of these orbitals increase as the number of nodes increases. The a 2 and e 1 orbitals areboth fully occupied in the electronic configuration of the Cp anion whereas the e 2 orbitals are net anti bonding and are unfilled. For a bis cyclopentadienyl metal complex ( 5 Cp) 2 M, such as ferrocene, the orbitals of the two Cp ligands arecombined pairwise i to form the symmetry adapted t d linear combination of molecular orbitals (SALC s).
23 To do this, the sum and difference of corresponding molecular orbitals on the Cp ligand must be taken, e.g. ( ), ( 1 1 ); ( ), ( 2 2 )etc. For example, ' ' gives rise to a molecular orbital of a 1g symmetry. This gives rise to three sets of ligand molecular orbitals of gerade (g) and ungerade (u) symmetry with respect to the centre of inversion; a low lying filled bonding pair of a 1g and a 2u symmetry a filled weakly bonding pair of e 1g and e 1u symmetry an unfilled anti bonding pair of e 2g and e 2u symmetry. As the two Cp rings are ca. 4Å apart, the in phase and out of phase of combinations are expected to be close in energy.
24 SALC s for a ( 5 Cp) 2 M complex; = A 1g + A 2u + E 1g + E 1u + E 2g + E 2u e 2g e 2u e 1g e 1u Z Y X a 1g a 2u
25 The metal orbitals transform as A 1g (d z2, s) + A 2u (p z ) + E 1u (p x, p y ) + E 1g (d yz, d xz ) + E 2g (d x 2 d y2, d xy ) Irreducible representation of SALC s : = A 1g + A 2u + E 1g + E 1u + E 2g + E 2u By considering these ligand molecular orbitals and how overlap with metal atomic orbitals can be affected the molecular orbital bonding picture of ferrocene can be constructed. For example, the a 1g SALC orbital can in theory overlap with the Fe 4s and 3dz 2 orbitals as they are also of a 1g symmetry. This interaction gives rise to the bonding and anti bonding molecular orbitals of the complex a 1g and a 1g* respectively. Each combination of ligand molecular orbitals and metal molecular orbitals leads to a bonding molecular orbital [( ligand molecular orbital )+( metal atomic orbital )] and a corresponding anti bonding molecular orbital [( ligand molecular orbital ) ( metal atomic orbital)] providing that the energies of the two component sets are sufficiently close for overlap.
26 Symmetry matching of the SALC s with the metal atomic orbitals dxy dx 2 -dy 2 no metal orbital of appropriate symmetry available no metal orbital of appropriate symmetry available e 2g e 2u dyz dxz p y p x e 1g e 1u Z Y X s dz 2 p z a 1g a 2u
27 A qualitative molecular orbital diagram for ferrocene (D 5d ) p z p y p x a 1u e 1u dyz dxz e 1g
28 Due to a difference in energies the a 1g molecular orbital is mainly ligand based with a slight admixture of the Fe 4s and 3dz 2 orbitals. Similarly the a 2u level has little if any metal character due to higher lying Fe 4p z orbital with which it is formally able to combine. The e 1g molecular orbital arises from the bonding combination of the ligand e 1 orbitalswiththefe3dxz and 3dyz orbitals. This is the only symmetry combination of orbitals in the two Cp rings that has appreciable overlap with the metal 3d orbitals to act as an efficient donor and it is thus this interaction which is mainly responsible for the stabilityof the complex. The corresponding anti bonding orbitals, e 1g *, are unfilled in the ground state of ferrocene but they are involved in excited state transitions. The e 1u bonding molecular orbitals are again mainly ligand based but with a small contribution from the higher energy Fe 3 p x,p y orbitals. The a ' molecular orbital mostly consists of the Fe 3dz 2 1g orbital as the ligand a 1g molecular orbital points between the nodes of the metal dz 2 orbital resulting in little or no overlap. The e 2g (dx 2 y 2, dxy) metal orbitals are considered non bonding due to poor 2g ( y, y) g p overlap with the ligand e 2g orbitals.
29 Since the occupied orbitals are of either a, e 1 or e 2 type symmetry no intrinsic barrier to 1 2 internal rotation is predicted as each of these molecular orbitals are symmetric about the axis of rotation. The very low values observed for this rotation (~ 4 kjmol 1 ) may be attributed to van der Waals forces bt between the two Cp rings. The attachment of additional groups or ligands destroys the D 5d /D 5h symmetry of ferrocene thus altering the molecular orbital diagram. 1. S. Barlow, H. E. Bunting, C. Ringham, J. C. Green, G. U. Bublitz, S. G. Boxer, J. W. Perry, S. R. Marder, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, J. C. Calabrese, L. T. Cheng, J. C. Green, S. R. Marder, W. Tam, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, D. R. Kanis, M. A. Ratner, T. J. Marks, Chem. Rev. 1994, 94,
30
31
32
Electron Counting in Organometallic Chemistry
 Electron Counting in Organometallic Chemistry 1. The 18-Electron Rule; definition & rationalisation The constitution and structure of main group element complexes can be predicted and rationalised by a
Electron Counting in Organometallic Chemistry 1. The 18-Electron Rule; definition & rationalisation The constitution and structure of main group element complexes can be predicted and rationalised by a
Organometallics Study Seminar Chapter 13: Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds
 Organometallics Study Seminar Chapter 13: Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds Contents 1. Carbene Complexes 2. Silylene Complexes 3. Metal-Heteroatom Multiple Bonds 1. Carbene Complexes 1.1 Classes of Carbene
Organometallics Study Seminar Chapter 13: Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds Contents 1. Carbene Complexes 2. Silylene Complexes 3. Metal-Heteroatom Multiple Bonds 1. Carbene Complexes 1.1 Classes of Carbene
18 electron rule : How to count electrons
 18 electron rule : How to count electrons The rule states that thermodynamically stable transition metal organometallic compounds are formed when the sum of the metal d electrons and the electrons conventionally
18 electron rule : How to count electrons The rule states that thermodynamically stable transition metal organometallic compounds are formed when the sum of the metal d electrons and the electrons conventionally
Covalent Bonding & Molecular Orbital Theory
 Covalent Bonding & Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry 754 Solid State Chemistry Dr. Patrick Woodward Lecture #16 References - MO Theory Molecular orbital theory is covered in many places including most
Covalent Bonding & Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry 754 Solid State Chemistry Dr. Patrick Woodward Lecture #16 References - MO Theory Molecular orbital theory is covered in many places including most
CHAPTER 5: MOLECULAR ORBITALS
 Chapter 5 Molecular Orbitals 5 CHAPTER 5: MOLECULAR ORBITALS 5. There are three possible bonding interactions: p z d z p y d yz p x d xz 5. a. Li has a bond order of. (two electrons in a bonding orbital;
Chapter 5 Molecular Orbitals 5 CHAPTER 5: MOLECULAR ORBITALS 5. There are three possible bonding interactions: p z d z p y d yz p x d xz 5. a. Li has a bond order of. (two electrons in a bonding orbital;
Conjugation is broken completely by the introduction of saturated (sp3) carbon:
 Chapter 16 Conjugation, resonance, and dienes Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. A common conjugated system involves 1,3-dienes, such as 1,3-butadiene.
Chapter 16 Conjugation, resonance, and dienes Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. A common conjugated system involves 1,3-dienes, such as 1,3-butadiene.
Conjugation is broken completely by the introduction of saturated (sp 3 ) carbon:
 Conjugation. Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. ne of the simplest conjugated molecules is 1,3-butadiene. Conjugation comes in three flavors, the
Conjugation. Conjugation relies on the partial overlap of p-orbitals on adjacent double or triple bonds. ne of the simplest conjugated molecules is 1,3-butadiene. Conjugation comes in three flavors, the
Chapter 9. Chemical reactivity of molecules depends on the nature of the bonds between the atoms as well on its 3D structure
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry & Bonding Theories I) Molecular Geometry (Shapes) Chemical reactivity of molecules depends on the nature of the bonds between the atoms as well on its 3D structure Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry & Bonding Theories I) Molecular Geometry (Shapes) Chemical reactivity of molecules depends on the nature of the bonds between the atoms as well on its 3D structure Molecular
Hybrid Molecular Orbitals
 Hybrid Molecular Orbitals Last time you learned how to construct molecule orbital diagrams for simple molecules based on the symmetry of the atomic orbitals. Molecular orbitals extend over the entire molecule
Hybrid Molecular Orbitals Last time you learned how to construct molecule orbital diagrams for simple molecules based on the symmetry of the atomic orbitals. Molecular orbitals extend over the entire molecule
Molecular-Orbital Theory
 Molecular-Orbital Theory 1 Introduction Orbitals in molecules are not necessarily localized on atoms or between atoms as suggested in the valence bond theory. Molecular orbitals can also be formed the
Molecular-Orbital Theory 1 Introduction Orbitals in molecules are not necessarily localized on atoms or between atoms as suggested in the valence bond theory. Molecular orbitals can also be formed the
methyl RX example primary RX example secondary RX example secondary RX example tertiary RX example
 ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 eginning patterns to knowfor S and E eactions - horizontal and vertical templates for practice Example 1 - two possible perspectives (deuterium and tritium
ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 eginning patterns to knowfor S and E eactions - horizontal and vertical templates for practice Example 1 - two possible perspectives (deuterium and tritium
Theoretical Methods Laboratory (Second Year) Molecular Symmetry
 Theoretical Methods Laboratory (Second Year) DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Molecular Symmetry (Staff contacts: M A Robb, M J Bearpark) A template/guide to the write-up required and points for discussion are
Theoretical Methods Laboratory (Second Year) DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Molecular Symmetry (Staff contacts: M A Robb, M J Bearpark) A template/guide to the write-up required and points for discussion are
CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway
 CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway "Organic Chemistry" by Maitland Jones, 4th edition Chapter 12 Homework: 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 15, 16, 17, 19, 21, 24, 26, 28, 29, 30, 38, 39, 44,
CHEM 322 Organic Chemistry II - Professor Kathleen V. Kilway "Organic Chemistry" by Maitland Jones, 4th edition Chapter 12 Homework: 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 15, 16, 17, 19, 21, 24, 26, 28, 29, 30, 38, 39, 44,
Symmetry and group theory
 Symmetry and group theory or How to Describe the Shape of a Molecule with two or three letters Natural symmetry in plants Symmetry in animals 1 Symmetry in the human body The platonic solids Symmetry in
Symmetry and group theory or How to Describe the Shape of a Molecule with two or three letters Natural symmetry in plants Symmetry in animals 1 Symmetry in the human body The platonic solids Symmetry in
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas unsaturated
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas unsaturated
Benzene Benzene is best represented as a resonance hybrid:
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) is a substitution reaction usually involving the benzene ring; more specifically it is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) is a substitution reaction usually involving the benzene ring; more specifically it is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
TRANSITION METALS AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY
 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE TRANSITION METALS AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY For Review 1. Chromium ([Ar]:4s 0 3d 5 ) and copper [Ar]:4s 1 3d 10 ) have electron configurations which are different from that predicted
CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE TRANSITION METALS AND COORDINATION CHEMISTRY For Review 1. Chromium ([Ar]:4s 0 3d 5 ) and copper [Ar]:4s 1 3d 10 ) have electron configurations which are different from that predicted
Chapter 10 Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems
 . 0 onjugated Systems hapter 0 onjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems onjugated systems are those in which a π-bond is connected or conjugated (from the Latin conjugare which means to link r yoke
. 0 onjugated Systems hapter 0 onjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems onjugated systems are those in which a π-bond is connected or conjugated (from the Latin conjugare which means to link r yoke
Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound
 Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound The analysis of the outcome of a reaction requires that we know the full structure of the products as well as the reactants In the 19 th and early 20 th
Determining the Structure of an Organic Compound The analysis of the outcome of a reaction requires that we know the full structure of the products as well as the reactants In the 19 th and early 20 th
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson
 Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
Suggested solutions for Chapter 7
 s for Chapter 7 7 PRBLEM 1 Are these molecules conjugated? Explain your answer in any reasonable way. C Et C Et C Et Revision of the basic kinds of conjugation and how to show conjugation with curly arrows.
s for Chapter 7 7 PRBLEM 1 Are these molecules conjugated? Explain your answer in any reasonable way. C Et C Et C Et Revision of the basic kinds of conjugation and how to show conjugation with curly arrows.
Chapter 10. Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems. Class Notes. B. The allyl group is both a common name and an accepted IUPAC name
 Chapter 10 Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems Chapter 10 suggested problems: I. The allyl group Class Notes A. B. The allyl group is both a common name and an accepted IUPAC name 1. Allyl alcohol
Chapter 10 Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems Chapter 10 suggested problems: I. The allyl group Class Notes A. B. The allyl group is both a common name and an accepted IUPAC name 1. Allyl alcohol
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life Name Period This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you
Chapter 9 - Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Chapter 9 - Covalent Bonding: Orbitals 9.1 Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model A. Hybridization 1. The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new
Chapter 9 - Covalent Bonding: Orbitals 9.1 Hybridization and the Localized Electron Model A. Hybridization 1. The mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Concept Check 10.1 An atom in a molecule is surrounded by four pairs of electrons, one lone pair and three bonding pairs. Describe how the four
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Concept Check 10.1 An atom in a molecule is surrounded by four pairs of electrons, one lone pair and three bonding pairs. Describe how the four
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Chem 1: Chapter 10 Page 1 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory I) VSEPR Model Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Model A) Model predicts Predicts electron arrangement and molecular
Chem 1: Chapter 10 Page 1 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory I) VSEPR Model Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Model A) Model predicts Predicts electron arrangement and molecular
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
 Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models The goal in this laboratory experience is to get you so you can easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed formulas,
The Synthesis of trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) Chloride
 CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) Chloride To learn about Coordination Compounds and Complex Ions. To learn about Isomerism.
CHEM 122L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(iii) Chloride To learn about Coordination Compounds and Complex Ions. To learn about Isomerism.
Lesson 3. Chemical Bonding. Molecular Orbital Theory
 Lesson 3 Chemical Bonding Molecular Orbital Theory 1 Why Do Bonds Form? An energy diagram shows that a bond forms between two atoms if the overall energy of the system is lowered when the two atoms approach
Lesson 3 Chemical Bonding Molecular Orbital Theory 1 Why Do Bonds Form? An energy diagram shows that a bond forms between two atoms if the overall energy of the system is lowered when the two atoms approach
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Javier E. Horta, M.D., Ph.D. University of Massachusetts Lowell Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Javier E. Horta, M.D., Ph.D. University of Massachusetts Lowell Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties
 324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
324 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 6.5 Periodic Variations in Element Properties By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe and explain the observed trends
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
A. Essentially the order of Pt II affinity for these ligands (their Lewis basicity or nucleophilicity)
 (c) Entering Ligand Effects 284 The second order rate constant k 2 in square planar complexes in the rate law below that we just discussed is strongly dependent on the nature of Y, the entering ligand
(c) Entering Ligand Effects 284 The second order rate constant k 2 in square planar complexes in the rate law below that we just discussed is strongly dependent on the nature of Y, the entering ligand
Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions Why this chapter? To understand organic and/or biochemistry, it is necessary to know: -What occurs -Why and
A pure covalent bond is an equal sharing of shared electron pair(s) in a bond. A polar covalent bond is an unequal sharing.
 CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
CHAPTER EIGHT BNDING: GENERAL CNCEPT or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the
Crystalline solids. A solid crystal consists of different atoms arranged in a periodic structure.
 Crystalline solids A solid crystal consists of different atoms arranged in a periodic structure. Crystals can be formed via various bonding mechanisms: Ionic bonding Covalent bonding Metallic bonding Van
Crystalline solids A solid crystal consists of different atoms arranged in a periodic structure. Crystals can be formed via various bonding mechanisms: Ionic bonding Covalent bonding Metallic bonding Van
4/18/2011. 9.8 Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions. Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions
 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic ring Some substituents activate the ring, making it more reactive than benzene
9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic ring Some substituents activate the ring, making it more reactive than benzene
CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13. Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software http://www.foxitsoftware.com For evaluation only.
 Generated by Foxit PDF reator Foxit Software Pd- AND f-blk RGANETALLIS PAn organometallic compound must contain P a carbon-metal bond. PBook, p. 459, gives list of common ligands P An over-view of organometallics
Generated by Foxit PDF reator Foxit Software Pd- AND f-blk RGANETALLIS PAn organometallic compound must contain P a carbon-metal bond. PBook, p. 459, gives list of common ligands P An over-view of organometallics
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic substitution is the typical reaction type for aromatic rings. Generalized electrophilic aromatic substitution: E E Electrophile Lewis acid: may be or neutral.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic substitution is the typical reaction type for aromatic rings. Generalized electrophilic aromatic substitution: E E Electrophile Lewis acid: may be or neutral.
LCAO-MO Correlation Diagrams
 LCAO-MO Correlation Diagrams (Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals to yield Molecular Orbitals) For (Second Row) Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules (X 2 ) - the following LCAO-MO s are generated: LCAO MO
LCAO-MO Correlation Diagrams (Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals to yield Molecular Orbitals) For (Second Row) Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules (X 2 ) - the following LCAO-MO s are generated: LCAO MO
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models Introduction: The goal in this laboratory experience is for you to easily and quickly move between empirical formulas, molecular formulas, condensed
Section Activity #1: Fill out the following table for biology s most common elements assuming that each atom is neutrally charged.
 LS1a Fall 2014 Section Week #1 I. Valence Electrons and Bonding The number of valence (outer shell) electrons in an atom determines how many bonds it can form. Knowing the number of valence electrons present
LS1a Fall 2014 Section Week #1 I. Valence Electrons and Bonding The number of valence (outer shell) electrons in an atom determines how many bonds it can form. Knowing the number of valence electrons present
The Unshifted Atom-A Simpler Method of Deriving Vibrational Modes of Molecular Symmetries
 Est. 1984 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-020 X CODEN: OJCHEG 2012, Vol. 28, No. (1): Pg. 189-202 The Unshifted
Est. 1984 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-020 X CODEN: OJCHEG 2012, Vol. 28, No. (1): Pg. 189-202 The Unshifted
CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW
 Answer the following questions. CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW 1. What are the three kinds of bonds which can form between atoms? The three types of Bonds are Covalent, Ionic and Metallic. Name Date Block 2.
Answer the following questions. CHEMISTRY BONDING REVIEW 1. What are the three kinds of bonds which can form between atoms? The three types of Bonds are Covalent, Ionic and Metallic. Name Date Block 2.
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life
 Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life Multiple-Choice Questions 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living
A REVIEW OF GENERAL CHEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES
 A REVIEW OF GENERAL CEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Draw Lewis (electron dot and line) structural formulas for simple compounds and ions from molecular
A REVIEW OF GENERAL CEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Draw Lewis (electron dot and line) structural formulas for simple compounds and ions from molecular
Resonance Structures Arrow Pushing Practice
 Resonance Structures Arrow Pushing Practice The following is a collection of ions and neutral molecules for which several resonance structures can be drawn. For the ions, the charges can be delocalized
Resonance Structures Arrow Pushing Practice The following is a collection of ions and neutral molecules for which several resonance structures can be drawn. For the ions, the charges can be delocalized
CHEM 101 Exam 4. Page 1
 CEM 101 Exam 4 Form 1 (White) November 30, 2001 Page 1 Section This exam consists of 8 pages. When the exam begins make sure you have one of each. Print your name at the top of each page now. Show your
CEM 101 Exam 4 Form 1 (White) November 30, 2001 Page 1 Section This exam consists of 8 pages. When the exam begins make sure you have one of each. Print your name at the top of each page now. Show your
Molecular Geometry and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland Community College for the use of this experiment.
 Molecular and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland ommunity ollege for the use of this experiment. Objectives To construct molecular models for covalently bonded atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions
Molecular and VSEPR We gratefully acknowledge Portland ommunity ollege for the use of this experiment. Objectives To construct molecular models for covalently bonded atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions
2/10/2011. Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain. Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain. 4.3 Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain
 4.3 Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain Angle strain The strain induced in a molecule when bond angles are forced to deviate from the ideal 109º tetrahedral value (Adolf von Baeyer 1885) Stability of
4.3 Stability of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain Angle strain The strain induced in a molecule when bond angles are forced to deviate from the ideal 109º tetrahedral value (Adolf von Baeyer 1885) Stability of
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three types: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms Ionic Bonding
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three types: Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of electrons Metallic Metal atoms bonded to several other atoms Ionic Bonding
Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces
 Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces Not quite the type of Force we re talking about Before we talk about noncovalent molecular forces, let s talk very briefly about covalent bonds. The Illustrated
Use the Force! Noncovalent Molecular Forces Not quite the type of Force we re talking about Before we talk about noncovalent molecular forces, let s talk very briefly about covalent bonds. The Illustrated
Chemistry Workbook 2: Problems For Exam 2
 Chem 1A Dr. White Updated /5/1 1 Chemistry Workbook 2: Problems For Exam 2 Section 2-1: Covalent Bonding 1. On a potential energy diagram, the most stable state has the highest/lowest potential energy.
Chem 1A Dr. White Updated /5/1 1 Chemistry Workbook 2: Problems For Exam 2 Section 2-1: Covalent Bonding 1. On a potential energy diagram, the most stable state has the highest/lowest potential energy.
Molecular Orbital Theory
 Molecular Orbital Theory To date, we have looked at three different theories of molecular boning. They are the VSEPR Theory (with Lewis Dot Structures), the Valence Bond Theory (with hybridization) and
Molecular Orbital Theory To date, we have looked at three different theories of molecular boning. They are the VSEPR Theory (with Lewis Dot Structures), the Valence Bond Theory (with hybridization) and
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ARMATIC CMPUNDS 1. Name benzene derivatives given the structures, and draw the structures given the names. This includes: Monosubstituted benzenes named as derivatives of benzene:
A STUDENT SHULD BE ABLE T: ARMATIC CMPUNDS 1. Name benzene derivatives given the structures, and draw the structures given the names. This includes: Monosubstituted benzenes named as derivatives of benzene:
Laboratory 11: Molecular Compounds and Lewis Structures
 Introduction Laboratory 11: Molecular Compounds and Lewis Structures Molecular compounds are formed by sharing electrons between non-metal atoms. A useful theory for understanding the formation of molecular
Introduction Laboratory 11: Molecular Compounds and Lewis Structures Molecular compounds are formed by sharing electrons between non-metal atoms. A useful theory for understanding the formation of molecular
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding. Modified by Dr. Daniela Radu
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding Modified by Dr. Daniela Radu What is Organic Chemistry? Living things are made of organic chemicals Proteins that make
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding Modified by Dr. Daniela Radu What is Organic Chemistry? Living things are made of organic chemicals Proteins that make
CHEM 101/105 BONDING (continued) Lect-16
 CHEM 0/05 BONDING (continued) Lect6 A Second covalent bonding theory, MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY accounts for covalent bonding by... before looking at MO, return for a moment to the individual unbonded atom
CHEM 0/05 BONDING (continued) Lect6 A Second covalent bonding theory, MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY accounts for covalent bonding by... before looking at MO, return for a moment to the individual unbonded atom
NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e)
 NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e) 1 H NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds Erich Hückel s study of aromaticity in the 1930s produced a set of rules for determining whether a compound is aromatic.
NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e) 1 H NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds Erich Hückel s study of aromaticity in the 1930s produced a set of rules for determining whether a compound is aromatic.
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
 INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR) Theory and Interpretation of IR spectra ASSIGNED READINGS Introduction to technique 25 (p. 833-834 in lab textbook) Uses of the Infrared Spectrum (p. 847-853) Look over pages
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR) Theory and Interpretation of IR spectra ASSIGNED READINGS Introduction to technique 25 (p. 833-834 in lab textbook) Uses of the Infrared Spectrum (p. 847-853) Look over pages
1.15 Bonding in Methane and Orbital Hybridization
 1.15 Bonding in Methane and Orbital Hybridization Structure of Methane tetrahedral bond angles = 109.5 bond distances = 110 pm but structure seems inconsistent with electron configuration of carbon Electron
1.15 Bonding in Methane and Orbital Hybridization Structure of Methane tetrahedral bond angles = 109.5 bond distances = 110 pm but structure seems inconsistent with electron configuration of carbon Electron
Question 4.2: Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements: Mg, Na, B, O, N, Br.
 Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories
Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Modified by Dr. Daniela R. Radu Why This Chapter? Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Modified by Dr. Daniela R. Radu Why This Chapter? Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical
Name: Class: Date: 3) The bond angles marked a, b, and c in the molecule below are about,, and, respectively.
 Name: Class: Date: Unit 9 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The basis of the VSEPR model of molecular bonding is. A) regions of
Name: Class: Date: Unit 9 Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The basis of the VSEPR model of molecular bonding is. A) regions of
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding
 CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding SECTION 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding OBJECTIVES 1. Define Chemical bond. 2. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonding.. 4. Explain
CHAPTER 6 Chemical Bonding SECTION 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding OBJECTIVES 1. Define Chemical bond. 2. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonding.. 4. Explain
Self Assessment_Ochem I
 UTID: 2013 Objective Test Section Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct answer; please carefully bubble your choice on the scantron sheet.
UTID: 2013 Objective Test Section Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct answer; please carefully bubble your choice on the scantron sheet.
Theme 3: Bonding and Molecular Structure. (Chapter 8)
 Theme 3: Bonding and Molecular Structure. (Chapter 8) End of Chapter questions: 5, 7, 9, 12, 15, 18, 23, 27, 28, 32, 33, 39, 43, 46, 67, 77 Chemical reaction valence electrons of atoms rearranged (lost,
Theme 3: Bonding and Molecular Structure. (Chapter 8) End of Chapter questions: 5, 7, 9, 12, 15, 18, 23, 27, 28, 32, 33, 39, 43, 46, 67, 77 Chemical reaction valence electrons of atoms rearranged (lost,
Chapter 15 Radical Reactions. Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by
 Chapter 15 Radical Reactions Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond; a radical contains an atom that does not have an octet of electrons,
Chapter 15 Radical Reactions Radicals are reactive species with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond; a radical contains an atom that does not have an octet of electrons,
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy
 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy Theory behind NMR: In the late 1940 s, physical chemists originally developed NMR spectroscopy to study different properties of atomic nuclei,
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy Theory behind NMR: In the late 1940 s, physical chemists originally developed NMR spectroscopy to study different properties of atomic nuclei,
CHEM 1211K Test IV. MULTIPLE CHOICE (3 points each)
 CEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE COICE (3 points each) 1) ow many single covalent bonds must a silicon atom form to have a complete octet in its valence shell? A) 4 B) 3 C) 1 D) 2 E) 0 2) What is the maximum
CEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE COICE (3 points each) 1) ow many single covalent bonds must a silicon atom form to have a complete octet in its valence shell? A) 4 B) 3 C) 1 D) 2 E) 0 2) What is the maximum
Elements in the periodic table are indicated by SYMBOLS. To the left of the symbol we find the atomic mass (A) at the upper corner, and the atomic num
 . ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
EXPERIMENT 9 Dot Structures and Geometries of Molecules
 EXPERIMENT 9 Dot Structures and Geometries of Molecules INTRODUCTION Lewis dot structures are our first tier in drawing molecules and representing bonds between the atoms. The method was first published
EXPERIMENT 9 Dot Structures and Geometries of Molecules INTRODUCTION Lewis dot structures are our first tier in drawing molecules and representing bonds between the atoms. The method was first published
Section 3: Crystal Binding
 Physics 97 Interatomic forces Section 3: rystal Binding Solids are stable structures, and therefore there exist interactions holding atoms in a crystal together. For example a crystal of sodium chloride
Physics 97 Interatomic forces Section 3: rystal Binding Solids are stable structures, and therefore there exist interactions holding atoms in a crystal together. For example a crystal of sodium chloride
Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds GE 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out some suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Molecular Models in Biology
 Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction
 Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Chemistry 105, Chapter 7 Exercises
 hemistry 15, hapter 7 Exercises Types of Bonds 1. Using the periodic table classify the bonds in the following compounds as ionic or covalent. If covalent, classify the bond as polar or not. Mg2 4 i2 a(3)2
hemistry 15, hapter 7 Exercises Types of Bonds 1. Using the periodic table classify the bonds in the following compounds as ionic or covalent. If covalent, classify the bond as polar or not. Mg2 4 i2 a(3)2
The strength of the interaction
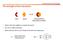 The strength of the interaction Host Guest Supramolecule (host-guest complex) When is the host capable to recognize the guest? How do we define selectivity Which element will we use to design the host
The strength of the interaction Host Guest Supramolecule (host-guest complex) When is the host capable to recognize the guest? How do we define selectivity Which element will we use to design the host
3. Assign these molecules to point groups a. (9) All of the dichlorobenzene isomers Cl
 CE 610 Spring 2007 Problem Set 1 key Total points = 200 1. (10 points) What distinguishes transition metals from the other elements in the periodic table? List five physical or chemical features that are
CE 610 Spring 2007 Problem Set 1 key Total points = 200 1. (10 points) What distinguishes transition metals from the other elements in the periodic table? List five physical or chemical features that are
Chapter 1 Benzene Blues 27
 hapter 1 Benzene Blues 27 The ybridization Model of Atoms in Molecules An important question facing chemists about 80 years ago, was, ow does one go from recently invented atomic orbitals to rationalizing
hapter 1 Benzene Blues 27 The ybridization Model of Atoms in Molecules An important question facing chemists about 80 years ago, was, ow does one go from recently invented atomic orbitals to rationalizing
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction: The NMR Spectrum serves as a great resource in determining the structure of an organic compound by revealing the hydrogen and carbon skeleton.
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction: The NMR Spectrum serves as a great resource in determining the structure of an organic compound by revealing the hydrogen and carbon skeleton.
Molecular Symmetry 1
 Molecular Symmetry 1 I. WHAT IS SYMMETRY AND WHY IT IS IMPORTANT? Some object are more symmetrical than others. A sphere is more symmetrical than a cube because it looks the same after rotation through
Molecular Symmetry 1 I. WHAT IS SYMMETRY AND WHY IT IS IMPORTANT? Some object are more symmetrical than others. A sphere is more symmetrical than a cube because it looks the same after rotation through
Chemistry 111 Laboratory Experiment 4: Visualizing Molecular Orbitals with MacSpartan Pro (This experiment will be conducted in OR341)
 Chemistry 111 Laboratory Experiment 4: Visualizing Molecular Orbitals with MacSpartan Pro (This experiment will be conducted in OR341) Introduction In class we have discussed Lewis structures, resonance,
Chemistry 111 Laboratory Experiment 4: Visualizing Molecular Orbitals with MacSpartan Pro (This experiment will be conducted in OR341) Introduction In class we have discussed Lewis structures, resonance,
5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules
 5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules What you will accomplish in this experiment This experiment will give you an opportunity to draw Lewis structures of covalent compounds, then use those
5. Structure, Geometry, and Polarity of Molecules What you will accomplish in this experiment This experiment will give you an opportunity to draw Lewis structures of covalent compounds, then use those
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition
 Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
Mulliken suggested to split the shared density 50:50. Then the electrons associated with the atom k are given by:
 1 17. Population Analysis Population analysis is the study of charge distribution within molecules. The intention is to accurately model partial charge magnitude and location within a molecule. This can
1 17. Population Analysis Population analysis is the study of charge distribution within molecules. The intention is to accurately model partial charge magnitude and location within a molecule. This can
17.2 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS
 17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
17. REACTINS INVLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC RADICALS 793 As Eq. 17. shows, the products derived from the reaction of water at the ring carbons are not formed. The reason is that these products are not aromatic
Health Science Chemistry I CHEM-1180 Experiment No. 15 Molecular Models (Revised 05/22/2015)
 (Revised 05/22/2015) Introduction In the early 1900s, the chemist G. N. Lewis proposed that bonds between atoms consist of two electrons apiece and that most atoms are able to accommodate eight electrons
(Revised 05/22/2015) Introduction In the early 1900s, the chemist G. N. Lewis proposed that bonds between atoms consist of two electrons apiece and that most atoms are able to accommodate eight electrons
Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 22 Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions The α Position The carbon next to the carbonyl group is designated as being in the α position Electrophilic
PROTEINS THE PEPTIDE BOND. The peptide bond, shown above enclosed in the blue curves, generates the basic structural unit for proteins.
 Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Chapter 7. Comparing Ionic and Covalent Bonds. Ionic Bonds. Types of Bonds. Quick Review of Bond Types. Covalent Bonds
 Comparing Ionic and Covalent Bonds Chapter 7 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure Intermolecular forces (much weaker than bonds) must be broken Ionic bonds must be broken 1 Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds
Comparing Ionic and Covalent Bonds Chapter 7 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Structure Intermolecular forces (much weaker than bonds) must be broken Ionic bonds must be broken 1 Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions, Course Notes Archive, 1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions An organic reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom in an aromatic
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions, Course Notes Archive, 1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions An organic reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom in an aromatic
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Ultraviolet Spectroscopy The wavelength of UV and visible light are substantially shorter than the wavelength of infrared radiation. The UV spectrum ranges from 100 to 400 nm. A UV-Vis spectrophotometer
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy The wavelength of UV and visible light are substantially shorter than the wavelength of infrared radiation. The UV spectrum ranges from 100 to 400 nm. A UV-Vis spectrophotometer
13C NMR Spectroscopy
 13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
Group Theory and Molecular Symmetry
 Group Theory and Molecular Symmetry Molecular Symmetry Symmetry Elements and perations Identity element E - Apply E to object and nothing happens. bject is unmoed. Rotation axis C n - Rotation of object
Group Theory and Molecular Symmetry Molecular Symmetry Symmetry Elements and perations Identity element E - Apply E to object and nothing happens. bject is unmoed. Rotation axis C n - Rotation of object
Electronegativity and Polarity
 and Polarity N Goalby Chemrevise.org Definition: is the relative tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons in a covalent bond to itself. is measured on the Pauling scale (ranges from 0 to
and Polarity N Goalby Chemrevise.org Definition: is the relative tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons in a covalent bond to itself. is measured on the Pauling scale (ranges from 0 to
Chapter 6. Alkenes: Structure and Stability
 hapter 6. Alkenes: Structure and Stability Steric Acid (saturated fatty acid) Linoleic Acid (unsaturated fatty acid) Degrees of unsaturation saturated hydrocarbon n 2n2 cycloalkane (1 ring) n 2n alkene
hapter 6. Alkenes: Structure and Stability Steric Acid (saturated fatty acid) Linoleic Acid (unsaturated fatty acid) Degrees of unsaturation saturated hydrocarbon n 2n2 cycloalkane (1 ring) n 2n alkene
