Exam 1. Part I Multiple-Choice Questions
|
|
|
- Arron Powers
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exam 1 Name: Date: Part I Multiple-Choice Questions 1. The six dimensions of wellness do NOT include a. Emotional wellness. b. Environmental, or planetary, wellness. c. Spiritual wellness. d. Dietary wellness. 2. Optimism, trust, and self-confidence are components of a. Physical wellness. b. Emotional wellness. c. Spiritual wellness d. Interpersonal wellness. 3. Which of the following best describes spiritual wellness? a. Participation in community work b. Prevention of injuries c. An ability to share feelings with others d. Possession of a set of guiding beliefs that give meaning to life 4. Interpersonal and social wellness a. Involves developing a network of caring people. b. Requires a great degree of self-confidence. c. Is not basic to physical or emotional health. d. Requires an active, creative mind. 5. The most serious threat to one s health in the early 1900s was a. Coronary heart disease. b. Cancer. c. Infectious disease. d. Stroke. 6. In the stages of change model, the precontemplation stage is a. Awareness of the problem. b. Modification of behavior. c. Belief that there is no need for change. d. Planning for change.
2 7. According to the transtheoretical, or stages of change, model for making changes in your behavior, the stage where people may have begun to make small changes in their behavior but are not yet regular or consistent with the changes is the stage. a. Contemplation b. Preparation c. Maintenance d. Action 8. Physical activity can be defined as a. Movement carried out by the skeletal muscles that require energy. b. Any condition that elevates the heart rate. c. Aerobic exercise. d. Strength training. 9. Exercise refers to physical activity that is a. Discontinuous and unplanned b. Planned, structured and repetitive. c. Not a contributor to physical fitness. d. Random or unstructured. 10. The latest version of the Physical Activity and Exercise Guidelines for Americans does NOT recommend a. Getting at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. b. Increasing the volume and intensity of exercise for additional health benefits. c. Getting at least 150 minutes of vigorously intense exercise per day. d. Getting some type of resistance training at least two days per week. 11. The Physical Activity and Exercise Recommendations for Promoting General Health, Fitness, and Weight Management recommend the following for achieving or maintaining weight loss a. Exercising moderately for minutes per day on most days of the week. b. Exercising minutes per day on most days of the week. c. Exercising minutes per day on most days of the week. d. Performing resistance exercise daily. 12. Which of the following is NOT a component of health-related fitness? a. Muscular strength b. Flexibility c. Speed d. Cardiorespiratory endurance
3 13. The ability of the body to perform prolonged, large-muscle, dynamic exercise at moderate to high levels of intensity is a. Anaerobic capacity b. Adaptive capacity c. Cardiorespiratory endurance d. Muscular endurance 14. As a person s cardiorespiratory endurance increases, the a. Amount of blood pumped per heartbeat decreases. b. Resting heart rate decreases. c. Blood volume decreases. d. Resting blood pressure increases. 15. Muscular strength is the a. Ability to sustain a given level of muscular tension over time. b. Ability to move the joints through a full range of motion. c. Amount of force a muscle can produce with a single maximum effort. d. Amount of force a muscle can produce repeatedly over 60 seconds. 16. Muscular endurance is the a. Ability to resist fatigue and to sustain a given level of muscular tension over time. b. Ability to move the joints through a full range of motion. c. Amount of force a muscle can produce with a single maximum effort. d. Amount of time required to contract a muscle completely. 17. Flexibility is best described as a. The ability to move without pain during exercise. b. The ability to move the joints through their full range of motion. c. Sustained motion without resistance. d. The ability to move rapidly during exercise. 18. Which of the following is NOT considered a skill-related fitness component? a. Coordination b. Flexibility c. Balance d. Agility 19. Specificity of training is best shown by which one of the following examples? a. Weight training to develop cardiorespiratory endurance. b. Doing pushups to develop chest and shoulder endurance. c. Running to develop flexibility. d. Bicycling to develop back strength.
4 20. The body adapting to a gradual increase in the amount of exercise is the definition of a. Progressive overload. b. Specificity of exercise. c. The principle of reversibility. d. The principle of assessment. 21. The amount of overload needed to maintain or improve one s fitness level is NOT determined by a. Time (duration). b. Intensity. c. Frequency. d. Specificity. 22. The time component of the FITT principle for overload for a muscular strength program is a. Based on the amount of weight lifted. b. Based on the number of training days per week. c. More than for a cardiorespiratory fitness program. d. Based on the number of sets and repetitions of specific exercises. 23. The recommended time (duration) for cardiorespiratory endurance exercise is minutes. a b c d The Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire (PAR-Q) is designed to a. Establish a proper exercise intensity level. b. Identify potential exercise resources. c. Determine exercise safety. d. Help set exercise goals. 25. An exercise stress test can determine if you have a. Joint problems. b. Excess body fat. c. Excess emotional stress. d. Symptoms of heart disease. 26. The first step in creating a successful fitness program is to a. Determine your training intensity. b. Assess your current fitness goals. c. Set specific fitness goals d. Plan your fitness program.
5 27. Cardiorespiratory endurance is developed best by activities that a. Involve continuous rhythmic movements of large muscle groups. b. Alternate between brief periods of maximal exertion and rest. c. Gently extend joints beyond their normal range of motion d. Involve working with weights or against resistance. 28. Muscular strength and endurance are developed best by activities that a. Involve continuous rhythmic movements of large muscle groups. b. Gently extend joints beyond their normal range of motion. c. Involve working with resistance such as weights or performing callisthenic exercises. d. Decrease body fat. 29. Flexibility is best developed by a. Stretching only when muscles feel tight. b. Stretching only once a month. c. Stretching only a few muscles. d. Stretching major muscle groups regularly. 30. Which one of the following statements about cooling down is true? a. It restores circulation to its normal resting condition. b. It extends the duration of the cardiorespiratory endurance portion of the workout. c. It increases the chance of overtraining. d. It is most effective for workouts of less than 20 minutes in duration. 31. The two upper chambers of the heart in which blood collects before passing it to the lower chambers are called a. Ventricles. b. Atria. c. Septum. d. Valves. 32. The largest artery in the body is the a. Carotid. b. Atria c. Aorta. d. Coronary. 33. During systole, the heart is a. At rest. b. Contracting. c. Suffering an attack.
6 d. Filling with blood. 34. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is defined as a. The building block of proteins. b. The stored form of glucose. c. The stored form of fats. d. The basic form of energy used by cells. 35. An example of an activity that primarily uses the immediate energy system is a. Running a marathon. b. Weight lifting. c. Walking. d. In line skating. 36. The nonoxidative energy system typically provides energy for a. 3 or fewer seconds. b seconds. c. 3-5 minutes. d minutes. 37. The oxidative energy system produces ATP in structures called a. Alveoli. b. Capillaries. c. Mitochondria. d. Atria. 38. Maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max) is a. The highest rate of oxygen consumption an individual is capable of during maximum physical effort. b. The velocity of oxygen flowing through the blood. c. Solely determined by genetics. d. Very difficult to predict. 39. Which one of the following statements about monitoring exercise heart rate is true? a. Count your pulse for one minute. b. Press firmly on the carotid artery. c. Use your thumb, not one or more of your fingers. d. Count your pulse immediately after stopping exercise. 40. An appropriate exercise heart rate for an average individual is of a. 35%
7 b. 55% c. 75% d. 95% 41. In addition to pulse counting, one may also monitor exercise intensity by using a. Ratings of perceived exertion. b. Time of exercise. c. Heart rate reserve. d. Frequency of training. 42. Which of the following statements about a warm-up session is FALSE? a. It can enhance performance and reduce injuries. b. Warm-up activities are usually of high intensity. c. Muscles work better when their temperature is slightly above resting level. d. It helps spread protective fluid throughout joints and protect joint surfaces. 43. Cooling down after exercise is important to a. Boost oxygen consumption. b. Spread protective fluid within the joints. c. Restore circulation to its normal resting condition. d. Maintain blood flow to the extremities. 44. During the initial phase of an exercise program, a beginner should a. Exercise at the low end of the target heart rate range. b. Exercise at the high end of the target heart rate range. c. Perform short but intense bouts of activity. d. Exercise 5-7 days per week. 45. Muscular strength is assessed by measuring a. The maximum amount of force a muscle can produce in a single maximal effort. b. The maximum amount of force a muscle can produce in 10 repetitions. c. The ability to exert a submaximal force repeatedly over time. d. The ability to exert force rapidly. 46. Muscular endurance is assessed by measuring a. The maximum amount of force a muscle can produce in a s single maximal effort b. The maximum amount of force a muscle can produce in 10 repetitions. c. The ability to exert a submaximal force repeatedly over time. d. The ability to exert force rapidly. 47. A motor unit is made up of a. A tendon and muscle fiber.
8 b. Fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibers. c. A motor nerve connected to muscle fibers. d. A motor nerve connected to a tendon 48. A muscle fiber is a. A motor nerve attached to muscle cells b. A protein structure within muscle cells. c. An enzyme that facilitates metabolism within muscle cells. d. An individual muscle cell. 49. Hypertrophy is defined as a. an increase in muscle fiber size b. a decrease in muscle fiber size c. an increase in muscle fiber number d. a decrease in muscle fiber number 50. Slow twitch muscle fibers are NOT characterized by a. Use in endurance activities b. Fatigue resistance c. Rapid contraction d. Oxidative energy system 51. Fast twitch muscle fibers are NOT characterized by a. Rapid contraction b. Fatigue resistance c. Anaerobic energy system d. Use in sprinting 52. Activities that would predominantly use slow-twitch muscle fibers are a. Walking and jogging b. Jumping and sprinting c. Weight training d. Shot putting 53. Activities that would predominantly use fast-twitch muscle fibers are a. Walking and jogging b. Bike riding c. Sprinting d. Hiking 54. Strength training improves body composition primarily by
9 a. Decreasing body weight b. Increasing muscle mass c. Increasing fat weight d. Decreasing muscle mass 55. Metabolic rate increases if a. Fat mass increases b. Fat mass decreases c. Muscle mass decreases d. Muscle mass increases 56. Isometric exercise is best described as applying force a. With movement b. At a constant speed c. Without a change in length of the muscle d. While a muscle in lengthening 57. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of isometric or static exercises? a. They require no equipment b. They mimic the speed of contraction needed for some sports c. They can be done almost anywhere d. They can overcome weak points in a joint s range of motion 58. Muscular force exerted as a muscle shortens is best classified as a. eccentric. b. isometric. c. concentric. d. isotonic. 59. A muscle lengthens as it contracts during a(n) a. isometric exercise. b. concentric contraction. c. speed-loading exercise. d. eccentric contraction. 60. Isokinetic exercise is best described as applying force a. with movement. b. at a constant speed. c. without movement. d. while a muscle is lengthening.
10 61. The MINIMUM number of training days per week for gaining strength is a. 2. b. 3. c. 5. d Training intensity for weight training is determined by a. number of sets. b. amount of weight lifted. c. number of repetitions. d. amount of time lifting. 63. A recommended amount of resistance and number of repetitions for improving muscular endurance is a % RM and repetitions. b % RM and 1-5 repetitions. c % RM and 1-5 repetitions. d % RM and 5 repetitions. 64. A recommended amount of resistance and number of repetitions for building muscular strength rapidly is a % RM and repetitions. b % RM and 1-5 repetitions c. 80% RM and 1-5 repetitions. d % RM and repetitions. 65. To build individual muscle strength and muscle size, it is best to a. use heavy resistance with few repetitions for multiple sets. b. use medium resistance with a medium number of repetitions. c. use light resistance with many repetitions. d. do resistance exercises for each muscle at least 5 days per week. 66. To improve muscular endurance, it is best to a. use heavy resistance with few repetitions for multiple sets. b. use medium resistance with a medium number of repetitions. c. use light resistance with many repetitions. d. do resistance exercises for each muscle no more than 2 days per week. 67. In weight training, a set is a a. group of exercises followed by a rest period. b. group of repetitions followed by a rest period. c. group of similar exercises followed by a rest period.
11 d. single muscle contraction. 68. Which of the following is an example of an intensive weight training program focused on building muscular strength? a. 1 set, 8-12 repetitions, 70% of 1 RM b. 1 set, 3-5 repetitions, 85% of 1 RM c. 3 sets, repetitions, 60% of 1 RM d. 3 sets, 4-6 repetitions, 90% of 1 RM 69. For overall fitness, you should include different exercises in your weigth training program. a. 2-3 b. 5-6 c d An antagonist muscle is one that a. is stretched when an agonist muscle contracts, opposing the agonist. b. is a contracting muscle. c. is a strong, powerful muscle. d. is a small, weak muscle. Part II True/False Questions 2 points each 71. People in the contemplation stage of change are planning to take action within a month. 72. Coordination is considered a health-related component of fitness. 73. Balance is considered a skill-related component of fitness. 74. Specificity is the principle which states that placing increasing amounts of stress on the body causes adaptations which improves fitness.
12 75. The optimal exercise frequency for improving one s health related cardiorespiratory fitness level is three to five days per week. 76. A person who stops exercising on a regular basis may lose up to 50% of fitness improvements within two months. 77. The three phases of an exercise program are the beginning, progress, and maintenance phases. 78. The vena cava is the largest artery in the body. 79. The nonoxidative (anaerobic) energy system is used for high intensity activities lasting about 10 seconds to 2 minutes. 80. Improved fitness allows you to exercise at higher intensities before the abrupt build-up of metabolic acids referred to as the Lactate Threshold. 81. People who are fit have a higher resting heart rate than people who are unfit. 82. Cardiovascular endurance exercise increases levels of low-density lipoproteins. 83. A fast time and a low heart rate during the 1 mile walk test indicate a high level of cardiorespiratory endurance. 84. The talk test may be used to monitor exercise intensity.
13 85. The development of large muscle fibers is referred to as atrophy. 86. Myofibrils are made up of groups of muscle fibers. 87. Slow twitch muscle fibers do not fatigue as rapidly as fast twitch muscle fibers and are used primarily during endurance activities. 88. Weight training improves body composition by increasing fat free mass and raising metabolism. 89. Muscular strength can be assessed by measuring the maximum amount of weight a person can lift during one repetition (1 RM). 90. During a strength training exercise, the agonist muscle contracts and the antagonist muscle stretched to allow the contraction. Part III 91. Calculate your target heart rate using the Karvonen method (heart rate reserve (50% - 85%). 92. Calculate your target heart rate using the Maximum Heart Rate method (70% - 85%). Exam 1 Redacted
5TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
Interval Training. Interval Training
 Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA
 Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA Benefits of Starting an Exercise Program 1. Helps build and maintain healthy bones, muscles and joints 2. Reduces feelings
Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA Benefits of Starting an Exercise Program 1. Helps build and maintain healthy bones, muscles and joints 2. Reduces feelings
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Chapter 9: Strength Training Program Design. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 9: Strength Training Program Design ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction There are six (6) types of resistance training: 1. Isometric force development 2. Concentric force development
Chapter 9: Strength Training Program Design ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction There are six (6) types of resistance training: 1. Isometric force development 2. Concentric force development
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines
 USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
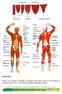 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form
 IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE. Content Title: Methods of training. Practical Application/Explanation. Fartlek training. Continuous training
 Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness. To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical
 Chapter 1 Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Chapter objectives: To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical fitness. To describe different
Chapter 1 Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Chapter objectives: To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical fitness. To describe different
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas
 Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
What is Physical Fitness?
 What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
Chapter 6. Components of Elasticity. Musculotendinous Unit. Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit. Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT
 THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
How To Train For Flexibility
 FLEXIBILITY It has been proven that participating in a flexibility program will have numerous benefits. A flexibility-training program is a planned and deliberate program of specific stretching exercises
FLEXIBILITY It has been proven that participating in a flexibility program will have numerous benefits. A flexibility-training program is a planned and deliberate program of specific stretching exercises
UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 [email protected] FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS
 UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 [email protected] FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS Universal Fitness Network, Inc. specializes in physical
UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 [email protected] FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS Universal Fitness Network, Inc. specializes in physical
Weight Room Rules. 7. A towel is recommended for use in the Weight Room to use as a barrier when working on the benches and mats.
 Weight Room Rules 1. The Weight Room and Recreation Facilities are for the use of Barnard students, Barnard faculty & staff, Barnard alumnae (with Sport Pass) and Columbia undergraduate students (CC, SEAS).
Weight Room Rules 1. The Weight Room and Recreation Facilities are for the use of Barnard students, Barnard faculty & staff, Barnard alumnae (with Sport Pass) and Columbia undergraduate students (CC, SEAS).
Exercise Prescription Case Studies
 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies 14 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies Case 1 Risk Stratification CY CHAN is a 43-year-old man with known history of hypertension on medication under good control.
14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies 14 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies Case 1 Risk Stratification CY CHAN is a 43-year-old man with known history of hypertension on medication under good control.
Plyometric Training. Plyometric Training. chapter
 chapter 16 Plyometric Training Plyometric Training David H. Potach, PT; MS; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D Donald A. Chu, PhD; PT; ATC; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D; FNSCA Chapter Objectives Explain the physiology of plyometric
chapter 16 Plyometric Training Plyometric Training David H. Potach, PT; MS; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D Donald A. Chu, PhD; PT; ATC; CSCS,*D; NSCA-CPT,*D; FNSCA Chapter Objectives Explain the physiology of plyometric
What Are the Health Benefits Associated with Strength Training?
 Strength Training Program Necessary Basic information to obtain results. -- Most of the information contained in this handout is based on information gathered, researched, and presented by the National
Strength Training Program Necessary Basic information to obtain results. -- Most of the information contained in this handout is based on information gathered, researched, and presented by the National
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Rehabilitation. Modalities and Rehabilitation. Basics of Injury Rehabilitation. Injury Rehabilitation. Vocabulary. Vocabulary
 Modalities and Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Chapter 12: Basics of Injury Rehabilitation Vocabulary Balance: ability to maintain our center of gravity over a base of support Kinesthesia: the ability to
Modalities and Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Chapter 12: Basics of Injury Rehabilitation Vocabulary Balance: ability to maintain our center of gravity over a base of support Kinesthesia: the ability to
Clinical Care Program
 Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice
 Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Fit for Flight. Developing a Personal Fitness Program
 Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
Teppe Treppe: A staircase increase in tension production after repeated simulation, even though the muscle is allowed to relax between twitches.
 Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Part II, Muscle: Mechanisms of Contraction and Neural Control, Chapter 12 Outline of class notes Objectives: After studying part II of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Discuss how contractile force
Chapter 4. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 4 Vocabulary physical activity anaerobic exercise anabolic steroids physical fitness overload health screening sedentary lifestyle progression overexertion osteoporosis specificity heat cramps
Chapter 4 Vocabulary physical activity anaerobic exercise anabolic steroids physical fitness overload health screening sedentary lifestyle progression overexertion osteoporosis specificity heat cramps
GA-3 Disaster Medical Assistance Team. Physical Fitness Guide
 GA-3 Disaster Medical Assistance Team Physical Fitness Guide PURPOSE: The purpose of this Physical Fitness Guide is to provide physical fitness training information to the members of the GA-3 Disaster
GA-3 Disaster Medical Assistance Team Physical Fitness Guide PURPOSE: The purpose of this Physical Fitness Guide is to provide physical fitness training information to the members of the GA-3 Disaster
CARDIORESPIRATORY ENDURANCE
 LOOKING AHEAD>>>>> AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Describe how the body produces the energy it needs for exercise List the major effects and benefits of cardiorespiratory endurance
LOOKING AHEAD>>>>> AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Describe how the body produces the energy it needs for exercise List the major effects and benefits of cardiorespiratory endurance
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program - Home Exercise Program
 Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program - Home Exercise Program Getting Started Regular exercise should be a part of life for everyone. Exercise improves the body's tolerance to activity and work, and strengthens
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program - Home Exercise Program Getting Started Regular exercise should be a part of life for everyone. Exercise improves the body's tolerance to activity and work, and strengthens
BASIC PROPERTIES OF MUSCLE
 BASIC PROPERTIES OF MUSCLE 18-1 Lecture Overview Muscles and motion Muscles Muscle structure Relevant properties Force-length properties Muscle states Force-velocity relationship Muscle fiber types Isometric
BASIC PROPERTIES OF MUSCLE 18-1 Lecture Overview Muscles and motion Muscles Muscle structure Relevant properties Force-length properties Muscle states Force-velocity relationship Muscle fiber types Isometric
CPT. Content Outline and Domain Weightings
 Appendix J CPT Content Outline and Domain Weightings National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM) Page 147 National Academy of Sports Medicine - Certified Personal Trainer (CPT) Content Outline Domain I:
Appendix J CPT Content Outline and Domain Weightings National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM) Page 147 National Academy of Sports Medicine - Certified Personal Trainer (CPT) Content Outline Domain I:
Strength Training For Runners
 Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
Training our energy systems
 Training our energy systems By: Kelly Mackenzie, MSC, BPE, AFLCA trainer Regardless of what mode of exercise we are using, we can train all three of our energy systems. There are physiological adaptations
Training our energy systems By: Kelly Mackenzie, MSC, BPE, AFLCA trainer Regardless of what mode of exercise we are using, we can train all three of our energy systems. There are physiological adaptations
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Target Heart Rate and Estimated Maximum Heart Rate
 Target Heart Rate and Estimated Maximum Heart Rate One way of monitoring physical activity intensity is to determine whether a person's pulse or heart rate is within the target zone during physical activity.
Target Heart Rate and Estimated Maximum Heart Rate One way of monitoring physical activity intensity is to determine whether a person's pulse or heart rate is within the target zone during physical activity.
9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework. Revised 2011
 9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework Revised 2011 Course Title: Physical Education and Leisure Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: 485000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course
9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework Revised 2011 Course Title: Physical Education and Leisure Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: 485000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course
BACKPACKING TRIP DIFFICULTY SNAPSHOT
 BACKPACKING TRIP DIFFICULTY SNAPSHOT Of course these ratings are only an indicator of hike difficulty - every hike has its variables beyond elevation gain and distance including weather, experience/fitness,
BACKPACKING TRIP DIFFICULTY SNAPSHOT Of course these ratings are only an indicator of hike difficulty - every hike has its variables beyond elevation gain and distance including weather, experience/fitness,
Personal Fitness Plan
 Personal Fitness Plan 7 th Grade 1 week plan/1 week food log Name Period 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date When you complete this project, you will accomplish the following: Set specific short-term and long-term personal
Personal Fitness Plan 7 th Grade 1 week plan/1 week food log Name Period 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date When you complete this project, you will accomplish the following: Set specific short-term and long-term personal
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR BARIATRIC SURGERY PATIENTS
 PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR BARIATRIC SURGERY PATIENTS The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment of Obesity (March 2005) BENEFITS OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY In order
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY & EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR BARIATRIC SURGERY PATIENTS The University of Chicago Hospitals Center for the Surgical Treatment of Obesity (March 2005) BENEFITS OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY In order
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes.
 This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
Personal Trainer Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities (1/01/12)
 1. Core Knowledge A. Kinesiology: Anatomy and Biomechanics B. Exercise Physiology C. Basic Nutrition and Weight Management D. Human Behavior 2. Health and Medical Review; and Fitness Assessment A. Health
1. Core Knowledge A. Kinesiology: Anatomy and Biomechanics B. Exercise Physiology C. Basic Nutrition and Weight Management D. Human Behavior 2. Health and Medical Review; and Fitness Assessment A. Health
National Academy of Sports Medicine. Cardiorespiratory Training for Fitness
 National Academy of Sports Medicine Cardiorespiratory Training Copyright 2008 National Academy of Sports Medicine Printed in the United States of America All rights reserved. Except for use in a review,
National Academy of Sports Medicine Cardiorespiratory Training Copyright 2008 National Academy of Sports Medicine Printed in the United States of America All rights reserved. Except for use in a review,
Chapter 4 Exercise Metabolism and Bioenergetics:
 CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders
 Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders INTRODUCTION: Health and well being are the result of many factors: Physical activity is one of these factors.
Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders INTRODUCTION: Health and well being are the result of many factors: Physical activity is one of these factors.
Preparing for the Washington State Criminal Justice Training Commission Physical Ability Test
 Preparing for the Washington State Criminal Justice Training Commission Physical Ability Test Whereas many training routines can be used to improve performance in the Physical Ability Test (PAT), participants
Preparing for the Washington State Criminal Justice Training Commission Physical Ability Test Whereas many training routines can be used to improve performance in the Physical Ability Test (PAT), participants
In structured sports programs, participation and enjoyment should be emphasized rather than competition and winning.
 Preschool Children The California Department of Health Services Physical Activity for Children, Youth, and Adults All preschool children should participate every in a form of physical activity appropriate
Preschool Children The California Department of Health Services Physical Activity for Children, Youth, and Adults All preschool children should participate every in a form of physical activity appropriate
LEVEL II DEVELOPING FITNESS PHYSIOLOGY. January 2008 Page 1
 DEVELOPING FITNESS January 2008 Page 1 DEVELOPING FITNESS There are many reasons why young hockey players should develop high levels of fitness; they will be less prone to injury; they will recover faster
DEVELOPING FITNESS January 2008 Page 1 DEVELOPING FITNESS There are many reasons why young hockey players should develop high levels of fitness; they will be less prone to injury; they will recover faster
Tests For Predicting VO2max
 Tests For Predicting VO2max Maximal Tests 1.5 Mile Run. Test Population. This test was developed on college age males and females. It has not been validated on other age groups. Test Procedures. A 1.5
Tests For Predicting VO2max Maximal Tests 1.5 Mile Run. Test Population. This test was developed on college age males and females. It has not been validated on other age groups. Test Procedures. A 1.5
2014-2015 Curriculum Blueprint Grade: 6/7 Course: M/J Comprehensive P.E. 6 th and 7 th Grade Unit 1: Safety and Fitness
 Unit 1: Safety and Fitness 15 days 1 Heat exhaustion, heat stroke, dehydration, frostbite, warm up, cool down, aerobic, anaerobic, resting heart rate, target heart rate, cardiovascular fitness, strength,
Unit 1: Safety and Fitness 15 days 1 Heat exhaustion, heat stroke, dehydration, frostbite, warm up, cool down, aerobic, anaerobic, resting heart rate, target heart rate, cardiovascular fitness, strength,
9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS
 Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
ABOUT US. Why train using the ACTIV8 Program? - Restoration of movement. Performance Enhancement & Injury Prevention
 ABOUT US Mission Statement - ACTIV8 Strength and Conditioning Program is committed to providing training experience for each participant. Our focus is on building a strong and functionally fit human being
ABOUT US Mission Statement - ACTIV8 Strength and Conditioning Program is committed to providing training experience for each participant. Our focus is on building a strong and functionally fit human being
Educational Innovation
 Educational Innovation July, 2013 Dear Educators, On behalf of all of MCESA, we are excited that you are using our content specific assessments in your school or district. We sincerely hope that the assessments
Educational Innovation July, 2013 Dear Educators, On behalf of all of MCESA, we are excited that you are using our content specific assessments in your school or district. We sincerely hope that the assessments
Strength and Conditioning Program
 Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness
 Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
12 Week Do-it-Yourself Fitness Program
 12 Week Do-it-Yourself Fitness Program Created by Brad Awalt, MS, ACSM Assistant Manager, Health Plus [email protected] January 2011 Do you have a goal to begin an exercise routine, but not sure
12 Week Do-it-Yourself Fitness Program Created by Brad Awalt, MS, ACSM Assistant Manager, Health Plus [email protected] January 2011 Do you have a goal to begin an exercise routine, but not sure
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down
 Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training
 Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training Baechle Chapter 4, pp. 143-151, 151, Powers & Howley pp. 253-255 255 Lecture Overview Neural Adaptations Skeletal Muscle Adaptations Connective Tissue Anatomy Connective
Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training Baechle Chapter 4, pp. 143-151, 151, Powers & Howley pp. 253-255 255 Lecture Overview Neural Adaptations Skeletal Muscle Adaptations Connective Tissue Anatomy Connective
Strength, Size, or Power?
 Strength, Size, or Power? Helen M. Binkley, Ph.D., CSCS*D, NSCA-CPT Which one are you training for strength, size, or power? First, let s identify what each of these are. Strength is the ability to produce
Strength, Size, or Power? Helen M. Binkley, Ph.D., CSCS*D, NSCA-CPT Which one are you training for strength, size, or power? First, let s identify what each of these are. Strength is the ability to produce
Exercise Metabolism II
 Exercise Metabolism II Oxygen debt & deficit Lactate threshold --------------------------------------------------------------- VO2max, VO2max and Lactate threshold CHO and fat metabolism during exercise
Exercise Metabolism II Oxygen debt & deficit Lactate threshold --------------------------------------------------------------- VO2max, VO2max and Lactate threshold CHO and fat metabolism during exercise
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
IMGPT: Exercise After a Heart Attack 610 944 8140 805 N. RICHMOND ST (Located next to Fleetwood HS) Why is exercise important following a heart
 Why is exercise important following a heart attack? Slow progression back into daily activity is important to strengthen the heart muscle and return blood flow to normal. By adding aerobic exercises, your
Why is exercise important following a heart attack? Slow progression back into daily activity is important to strengthen the heart muscle and return blood flow to normal. By adding aerobic exercises, your
Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM. Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD
 Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD PURPOSE The purpose of the Cardinals strength and conditioning manual is to provide the athlete with a general overview of
Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD PURPOSE The purpose of the Cardinals strength and conditioning manual is to provide the athlete with a general overview of
1.1.1 To include: Body language - facial expressions, gestures, eye contact and posture
 Unit 415 Delivering Personal Training Sessions Recommended Guided Learning Hours: 58 Credit value 9 QCF Unit Number J/600/9053 1. Understand how to instruct exercise during personal training sessions 1.1
Unit 415 Delivering Personal Training Sessions Recommended Guided Learning Hours: 58 Credit value 9 QCF Unit Number J/600/9053 1. Understand how to instruct exercise during personal training sessions 1.1
Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise
 Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise Suggestions for Teachers Background Static exercise involves the contraction of skeletal muscle without a change in muscle length, hence the alternative term, isometric
Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise Suggestions for Teachers Background Static exercise involves the contraction of skeletal muscle without a change in muscle length, hence the alternative term, isometric
Certificate in Personal Training Case-Study Marking Checklist Unit Number: 500/8259/0of 2
 Candidate Name: Assessor Name: IV Name: Certificate in Personal Training Case-Study Marking Checklist Unit Number: 500/8259/0of 2 Date: Date: NB: Candidates must achieve enough passes to show competency
Candidate Name: Assessor Name: IV Name: Certificate in Personal Training Case-Study Marking Checklist Unit Number: 500/8259/0of 2 Date: Date: NB: Candidates must achieve enough passes to show competency
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8
 Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 3 Notes- Muscular System Ch. 8 Functions of the muscular system: movement of body or body parts and materials within the body maintain posture and body position
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Accreditation Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
About the health benefits of walking, march and Nording Walking.
 About the health benefits of walking, march and Nording Walking. Project and realization: Marta Szymańska, Kl. I F Walking is the most natural and the simplest form of physical activity. It doesn t require
About the health benefits of walking, march and Nording Walking. Project and realization: Marta Szymańska, Kl. I F Walking is the most natural and the simplest form of physical activity. It doesn t require
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Lesson 6: Planning for Physical Fitness
 Lesson 6: Planning for Physical Fitness Introduction In this lesson students review the basics of physical fitness, including definitions of physical fitness health- and skill-related fitness components
Lesson 6: Planning for Physical Fitness Introduction In this lesson students review the basics of physical fitness, including definitions of physical fitness health- and skill-related fitness components
Physical Fitness Training. 12 Week Preparation Program
 OVERVIEW Physical Fitness Training 12 Week Preparation Program To help prepare you for a career in law enforcement, the Recruitment Team of the Las Vegas Metropolitan Police Department has instituted a
OVERVIEW Physical Fitness Training 12 Week Preparation Program To help prepare you for a career in law enforcement, the Recruitment Team of the Las Vegas Metropolitan Police Department has instituted a
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
Once the immune system is triggered, cells migrate from the blood into the joints and produce substances that cause inflammation.
 HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
A1 Reasons for taking part in activity. A2 Health, fitness, exercise and performance
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
8th Grade Personal Fitness Plan
 8th Grade Personal Fitness Plan 2 Week Activity Log & 1 week Food Log Name: Period: Date: Personal Fitness Contract I,, am going to make a commitment to helping build my lifelong fitness and nutrition
8th Grade Personal Fitness Plan 2 Week Activity Log & 1 week Food Log Name: Period: Date: Personal Fitness Contract I,, am going to make a commitment to helping build my lifelong fitness and nutrition
Progression Models in Resistance Training for Healthy Adults
 POSITION STAND Progression Models in Resistance Training for Healthy Adults SUMMARY American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand on Progression Models in Resistance Training for Healthy Adults. Med.
POSITION STAND Progression Models in Resistance Training for Healthy Adults SUMMARY American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand on Progression Models in Resistance Training for Healthy Adults. Med.
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
GCSE P.E. REVISION BOOKLET
 GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Blood Pressure. Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls. Blood Pressure. Blood Pressure
 Blood Pressure Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls Systolic pressure exerted on arteries during systole Diastolic pressure in arteries during diastole 120/80 Borderline
Blood Pressure Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls Systolic pressure exerted on arteries during systole Diastolic pressure in arteries during diastole 120/80 Borderline
Exercise and FES cycle fact sheet
 Exercise and FES cycle fact sheet FES = Functional Electrical Stimulation. An electrical current is passed through paralysed muscle causing it to contract. The electrical current uses the peripheral nerves
Exercise and FES cycle fact sheet FES = Functional Electrical Stimulation. An electrical current is passed through paralysed muscle causing it to contract. The electrical current uses the peripheral nerves
Welcome to. Get Fit!
 Welcome to Get Fit! UC Wellness and Fitness Program October 15, 2005 April 30, 2006 Congratulations! You re taking an important step to leading a healthier lifestyle. By enrolling in Get Fit!, you are
Welcome to Get Fit! UC Wellness and Fitness Program October 15, 2005 April 30, 2006 Congratulations! You re taking an important step to leading a healthier lifestyle. By enrolling in Get Fit!, you are
Functional Firefighter Fitness
 Functional Firefighter Fitness The information provided is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for the advice of, or treatment that may be prescribed by your physician.
Functional Firefighter Fitness The information provided is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for the advice of, or treatment that may be prescribed by your physician.
Department of Defense DIRECTIVE
 Department of Defense DIRECTIVE NUMBER 1308.1 June 30, 2004 PDUSD(P&R) SUBJECT: DoD Physical Fitness and Body Fat Program References: (a) DoD Directive 1308.1, "DoD Physical Fitness and Body Fat Program,"
Department of Defense DIRECTIVE NUMBER 1308.1 June 30, 2004 PDUSD(P&R) SUBJECT: DoD Physical Fitness and Body Fat Program References: (a) DoD Directive 1308.1, "DoD Physical Fitness and Body Fat Program,"
PREPARATION AND TRAINING SCHEDULES FOR YOUR CAREER IN THE ROYAL NAVY LIFE WITHOUT LIMITS
 PREPARATION AND TRAINING SCHEDULES FOR YOUR CAREER IN THE ROYAL NAVY LIFE WITHOUT LIMITS ROYAL NAVY FITNESS PROGRAMME Now that you are considering a career in the Royal Navy, you should be aware of the
PREPARATION AND TRAINING SCHEDULES FOR YOUR CAREER IN THE ROYAL NAVY LIFE WITHOUT LIMITS ROYAL NAVY FITNESS PROGRAMME Now that you are considering a career in the Royal Navy, you should be aware of the
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
The Rehabilitation Team
 Considerations in Designing a Rehab Program Philosophy of Sports Medicine Healing Process Pathomechanics of Injury Psychological Aspects Goals of Rehab Chapter 1 Group effort The Rehabilitation Team AEP/Athletic
Considerations in Designing a Rehab Program Philosophy of Sports Medicine Healing Process Pathomechanics of Injury Psychological Aspects Goals of Rehab Chapter 1 Group effort The Rehabilitation Team AEP/Athletic
DIABETES MELLITUS. By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria
 DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy or DMD? Muscular Dystrophy is a group of inherited muscle disorders, in which muscles weaken over time. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy or DMD? Muscular Dystrophy is a group of inherited muscle disorders, in which muscles weaken over time. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Overtraining with Resistance Exercise
 ACSM CURRENT COMMENT Overtraining with Resistance Exercise One of the fastest growing and most popular types of exercise in recent years is resistance exercise, whether used for the purpose of general
ACSM CURRENT COMMENT Overtraining with Resistance Exercise One of the fastest growing and most popular types of exercise in recent years is resistance exercise, whether used for the purpose of general
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
