FEMALE PELVIC ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION
|
|
|
- Madeleine Shepherd
- 3 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FEMALE PELVIC ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION POLICY: Pelvic ultrasound will be performed with an order from a physician or other qualified clinical practitioner. The examination will be supervised and interpreted by a radiologist or other licensed practitioner who is qualified by reason of training to understand the normal anatomy, pathophysiology of the pelvis, and integration of ultrasound with other imaging techniques to optimize the probability of detecting disease. PURPOSE: To assess the anatomy of the pelvis and document normal and abnormal structures therein. INDICATIONS: Ultrasound of the pelvis is indicated for patients with signs, symptoms, and/or laboratory evidence of disease involving the uterus, endometrium, ovaries and their supporting structures, bladder, or intestine. This examination is an appropriate study for patients with nonspecific pelvic complaints. Patients who, for historical reasons, are at risk for pelvic disease, even without signs, symptoms, or laboratory evidence, are also candidates for ultrasound examination. PATIENT PREPARATION: In most cases, patients will be investigated from a transabdominal approach through the distended urinary bladder. Patients will be instructed to drink ounces of liquid two hours prior to the scheduled examination time and refrain from voiding until instructed by Inland Imaging staff. Patients who do not require a filled bladder need no special preparation. Patients should be instructed to take prescribed oral or injectable medication on their normal schedule. Menstruating women should be scheduled between days 5 and 13 of their menstrual cycle when possible. PROCEDURE: Women who have a history of sexual activity will be examined both transabdominally and endovaginally, unless individual circumstances prohibit one technique. Each organ should be imaged in its entirety (e.g. long and transverse views) before imaging the next organ. The order of organ imaging will be (minimal number of images in parenthesis): Transabdominal Uterus and endometrium (4 images) Right ovary (2 images) Left ovary (2 images) Endovaginal Uterus (5 images, 2 cine sweeps) Endometrium (1 image) Right ovary (2 images, one cine sweep) Left ovary (2 images, one cine sweep) 1
2 TRANSABDOMINAL Transabdominal images are intended to demonstrate the uterine size, contour, and position in the pelvis, and its relationship to other structures (e.g. the bladder, ovaries, vagina, and abnormal structures). Ovaries that are positioned in the superior pelvis and large pelvic masses may be best demonstrated transabdominally and if encountered, additional images will be required to fully document the findings. Minimal stored images should include: Two long axis views of the uterus (oriented along the length of the organ) that include unobstructed views of the fundus and cervix labeled uterus long. One image should be optimized to display measurements of the long and short diameters of the uterus and one image should be optimized to demonstrate the endometrium; One long axis view of the uterus labeled uterus long, to optimize the cervical segment, its relationship to the vagina, and pelvic cul-de-sac (of Douglas); One transverse view of the uterus labeled uterus transverse, to include measurement of it maximal transverse diameter; One view of the right ovary oriented parallel to it longest axis, labeled right ovary long. (In patients who will not receive an endovaginal examination, a second sagittal image of the ovary should be obtained and measured in its longest and orthogonal diameters.) In patients whom the ovary cannot be identified or is absent, a sagittal image of the pelvis shall be obtained and labeled right adnexa long; One view of the right ovary perpendicular to its long axis, labeled right ovary transverse, to include its relationship to the uterus or pelvic sidewall. (In patients who will not receive an endovaginal examination, a second transverse image of the ovary should be obtained and measured in its transverse dimension.) In patients whom the ovary cannot be identified or is absent, a transverse image of the pelvis shall be obtained and labeled right adnexa transverse; One view of the left ovary oriented parallel to its longest axis, labeled left ovary long. (In patients who will not receive an endovaginal examination, a second sagittal image of the ovary should be obtained and measured in its longest and orthogonal diameters.) In patients whom the ovary cannot be identified or is absent, a sagittal image of the pelvis shall be obtained and labeled left adnexa long; One view of the left ovary perpendicular to its long axis, labeled left ovary transverse, to include its relationship to the uterus or pelvic sidewall. (In patients who will not receive an endovaginal examination, a second transverse image of the ovary should be obtained and measured in its transverse dimension.) In patients whom the ovary 2
3 cannot be identified or is absent, a transverse image of the pelvis shall be obtained and labeled left adnexa transverse. ENDOVAGINAL Endovaginal images are intended to demonstrate the details of myometrial architecture, endometrial texture and thickness, and ovarian structure. Most abnormalities of female pelvic organs can be demonstrated to better advantage with endovaginal imaging and adequate documentation is required to allow accurate characterization and follow-up of pathologic findings. All endovaginal examinations performed on female patients by a male sonographer will be chaperoned by a female Inland Imaging staff. The endovaginal examination should be performed with the urinary bladder empty with the patient in the supine position on an elevated foam pad to allow movement of the transducer in all planes. All transducers shall be covered with a clean protective sheath prior to use and all transducers shall be cleaned after each use in an approved antimicrobial solution or automated disinfection device, such as the Trophon EPR unit. The sonographer or patient may insert the transducer. Minimal stored images should include: three long axis views of the uterus, labeled uterus long. One image should optimize display of the fundus and mid body, one image should optimize the cervix, and one image document the endometrium in its maximal thickness. When the endometrial/myometrial interface is conspicuous, the double layer endometrial thickness should be measured at its maximal dimension perpendicular to the plane of the endometrial cavity; one cine sweep of the uterus in sagittal plane from right to left and labeled uterus long right to left; three transverse images of the uterus labeled uterus transverse, to include the cervix, mid body, and fundus; one cine sweep of the uterus in transverse plane from the cervix to fundus and labeled uterus transverse fundus to cervix; one image of the right ovary oriented parallel to its long axis labeled right ovary long to include measurements of its longest and orthogonal diameters. In patients whom the ovary cannot be identified or is absent, an image of the right adnexal region shall be obtained and labeled right adnexa long; one image of the right ovary perpendicular to it long axis labeled right ovary transverse to include measurement of the maximal transverse diameter. In patients whom the ovary cannot be identified or is absent, an image of the right adnexal region shall be obtained and labeled right adnexa transverse; one cine sweep of the right ovary in the plane that optimizes its visualization labeled right ovary; 3
4 one image of the left ovary oriented parallel to its long axis labeled left ovary long to include measurements of its longest and orthogonal diameters. In patients whom the ovary cannot be identified or is absent, an image of the left adnexal region shall be obtained and labeled left adnexa; one image of the left ovary perpendicular to its long axis labeled left ovary transverse to include measurement of the maximal transverse diameter. In patients whom the ovary cannot be identified or is absent, an image of the left adnexal region shall be obtained and labeled left adnexa transverse; one cine sweep of the left ovary in the plane that optimizes its visualization labeled left ovary. PATHOLOGIC CONDITIONS: When pathologic processes are detected during the course of the examination, extra images are necessary to characterize the abnormality. One or more cine clips should be obtained of any detected pathology. The following is a description of commonly encountered abnormalities, or conditions that should be considered during the examination and the minimum additional stored images expected for each circumstance. The list is not intended to be comprehensive, and sonographers are expected to apply their knowledge of pathophysiology to provide clear images of the abnormalities they encounter. Many pathologic conditions will be imaged with both transabdominal and endovaginal techniques, but the sonographer shall focus his/her efforts on the technique that optimizes pathologic details and information. Uterine Mass: It is the purpose of the examination to document the number, position, and size of uterine masses. Transabdominal ultrasound is best suited to image large uterine masses that extend beyond the field of view of endovaginal transducers. If the uterus can be imaged in its entirety with the endovaginal probe, uterine masses are usually best characterized with an endovaginal examination. Uterine masses, whether imaged best with transabdominal or endovaginal probes, with conspicuous margins should be individually imaged in two orthogonal planes and labeled with their respective position (i.e. uterus right, uterus left, uterus anterior, uterus posterior, uterus midline, uterus fundus, uterus cervix). If more than one mass is present, labels A, B, C, etc, shall be included on the center of the mass in the stored image in two planes, for up to a maximum of 5 masses. Three orthogonal dimensions of the largest mass with conspicuous, reproducible margins shall be stored, with its appropriate label (e.g. uterus posterior A ). Endometrial Mass/Thickening: Whenever possible, the endometrium should be examined between the conclusion of menses and the subsequent ovulation (days 5-13 in a normally menstruating patient) to avoid over estimation of endometrial thickness late in the cycle, and to optimize the opportunity to visualize endometrial masses (e.g. polyps, cancer). If a mass with conspicuous and reproducible margins is identified, it should be imaged in two orthogonal planes, 4
5 measured in its greatest diameter, and labeled endometrium long or coronal or transverse. In cases where the margins are inconspicuous (e.g. retained products of conception, endometrial polyps in the secretory phase of the cycle), only the maximal double layer endometrial thickness should be measured. Color (or power) Doppler ultrasound should be applied to endometrial masses/thickening to identify the relative quantity and source (e.g. anterior or posterior uterine wall) of blood flow. Spectral Doppler measurement of flow within a mass should be attempted to characterize its maximal systolic velocity and Resistive Index. Representative images of color and spectral Doppler should be stored and labeled endometrium long or coronal or transverse. Ovarian Mass: Ovarian masses should be examined for the purpose of confirming their ovarian origin, documenting their size, and identifying features that permit characterization of benignity or malignancy. In addition to documentation of the ovaries in (see minimum stored images above), ovarian masses (and simple ovarian cysts greater than 3cm) must be separately imaged in two orthogonal planes, labeled right ovary long or transverse and left ovary long or transverse. One image in each plane should be free of measurements and one image should include measurements. Cysts should be measured to include the cyst wall. Images of ovarian masses should be obtained to accurately demonstrate their contour (e.g. smooth, irregular, inconspicuous), wall thickness, presence or absence of internal septa, solid elements, or suspended echoes. Color (or power) Doppler ultrasound should be applied to ovarian masses (with the exception of thin, smooth walled cysts with no septa or solid elements) to identify flow within their margins/septa/solid elements. Spectral Doppler flow of the mass should be attempted to characterize the maximal systolic velocity and Resistive Index of internal septa or solid elements. Representative images of color and spectral Doppler should be stored and labeled right ovary or left ovary. Adnexal (extraovarian) Mass: The purpose of the examination is to document a mass that is separate from the ovary by identifying and documenting normal ovaries, localizing its position in the pelvis, measuring its size, and characterizing its sonographic features. Extraovarian masses, encountered both transabdominally and endovaginally, should be imaged in two orthogonal planes and labeled right, midline, or left long and right, midline, or left transverse. One image in each plane should be free of measurements and one image should include measurements. Images of extraovarian masses should be selected to accurately demonstrate their contour (e.g. smooth, irregular, inconspicuous), wall thickness, presence or absence of internal septa, solid elements, or suspended echoes. Color (or power) Doppler ultrasound should be applied to extraovarian masses to identify flow within their margins/septa/solid elements. Spectral Doppler flow of the mass should be attempted to characterize the maximal systolic velocity and Resistive Index. Representative images of color and spectral Doppler should be stored and labeled right or left. The extraovarian position of a mass that lies adjacent to the ovary may be best demonstrated with 5
6 a cine clip that simultaneously demonstrates the mass and ovary while gentle transducer pressure is applied to record discordant movement of the two structures. Post Hysterectomy/Oophorectomy: An examination may be requested for pelvic symptoms (e.g. pain) in patients with a history of prior hysterectomy and/or oophorectomy. If the patient has had a hysterectomy and bilateral oophorectomy, a transabdominal examination through the distended urinary bladder with three representatives sagittal (labeled right, midline, and left long) and three axial images (labeled transverse) should be performed. Normal structures that should be documented are the vagina and vaginal cuff in a sagittal view labeled midline long and both pelvic sidewalls including a long axis view of the common/external iliac artery on each side. In patients with a hysterectomy without oophorectomy, unilateral oophorectomy, partial hysterectomy, or pelvic pathology, an endovaginal examination should be performed if the structures of interest will be better characterized. Right Lower Quadrant Pain: Patients with right lower quadrant symptoms (e.g. pain) may be imaged under the Pelvic or Abdominal Ultrasound protocols. If evaluation of the right lower quadrant is requested as part of a Pelvic Ultrasound, the routine pelvic protocol should be performed in addition to a focused examination directed at the cecum/appendix. The cecum is identified by first locating the ascending colon, and following it inferiorly to its blind end. Tissue between the skin and cecum can be displaced by slowly applying pressure with the examining hand and transducer to the patient s tolerance. If the appendix cannot be located, representative images of the right lower quadrant obtained in sagittal and axial planes should be obtained and labeled RLQ long and transverse. If the appendix is identified, it should be imaged in two planes labeled RLQ long and transverse, measured in its maximal outer-to-outer diameter in long axis images, and representative power or color Doppler images obtained. Ovarian Torsion: Patients who are referred to consider ( rule out ) ovarian and/or adnexal torsion and patients with symptoms of torsion (i.e. sudden onset, severe, unilateral lower abdominal pain that worsens intermittently over many hours) shall be imaged with both color (or power) and spectral Doppler, in addition to standard gray scale images. Doppler imaging of both the affected and contra lateral ovary is necessary to demonstrate variations in vascularity, and labeled right ovary and left ovary as appropriate. Spectral images shall include at least one intraovarian (not capsular) arterial signal to include measurement of the Resistive Index. Images of intraovarian (not capsular) spectral venous flow should be sought (with machine settings of low PRF and low wall filter) and recorded. If arterial and/or venous spectral signals cannot be detected, representative color and spectral images without flow shall be recorded and labeled right ovary or left ovary. The presence of arterial or venous flow does not rule out ovarian torsion. The ovaries should be evaluated for additional findings 6
7 which may be seen in the presence of ovarian torsion. These may include an ovarian mass, ascites, abnormal ovarian location, an enlarged ovary with or without peripheral follicles and the sonographic whirlpool sign. The sonographic whirlpool sign is a twisting of the vascular pedicle demonstrated in both gray scale and color Doppler imaging. It is sometimes best demonstrated transabdominally. Uterine Anomaly and IUD: Patients with suspected developmental uterine anomalies (e.g. bicornuate uterus) and patients with an IUD should be imaged with a volume acquisition (manual or automated) and a coronal rendering of the endometrium recorded. For uterine anomalies, the coronal rendering shall include the serosal surface of the uterine fundus. For patients with an IUD, the rendered image(s) should include the entire IUD (e.g. both arms and body of a T shaped IUD) and its relationship to the endometrium. Note whether the IUD is normally placed within the fundal end of the endometrial cavity, is imbedded within the myometrium, has perforated the serosal lining, or is located completely outside the uterus. 7
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Uterine Fibroids. More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth.
 Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
Uterine Fibroids More than half of all women have fibroids. They are a common, benign, uterine growth. Fibroids are not a disease. Much like the genetic blueprint that determines the color of your eyes
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations. Bruce Thomadsen. University of Wisconsin -Madison
 Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations Bruce Thomadsen University of Wisconsin -Madison Conflicts of Interest The author has no known conflicts involving this presentation Learning
Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations Bruce Thomadsen University of Wisconsin -Madison Conflicts of Interest The author has no known conflicts involving this presentation Learning
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology
 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology Bill Smith Clinical Diagnostics Services, London, UK Introduction 3D volumetric ultrasound is shown to be of
The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology Bill Smith Clinical Diagnostics Services, London, UK Introduction 3D volumetric ultrasound is shown to be of
ProSono Copyright 2006. Ovarian Pathology
 Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps
 Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
3D in Gynecology: Luxury or necessity?
 ISUOG 2011 Los Angeles September 16-22 3D in Gynecology: Luxury or necessity? Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch Educational objectives To describe the 3D US tools available to complement 2D US To apply these tools
ISUOG 2011 Los Angeles September 16-22 3D in Gynecology: Luxury or necessity? Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch Educational objectives To describe the 3D US tools available to complement 2D US To apply these tools
Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering
 Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization
 September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries. Simple Cystic Masses
 Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Use of Ultrasound in the Provision of Abortion. Juan E. Vargas, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology and Radiology, UCSF
 Use of Ultrasound in the Provision of Abortion Juan E. Vargas, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology and Radiology, UCSF Overview Uses and indications of ultrasound in the provision
Use of Ultrasound in the Provision of Abortion Juan E. Vargas, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology and Radiology, UCSF Overview Uses and indications of ultrasound in the provision
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and Adjacent Myometrium
 Technical dvance Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and djacent Myometrium Preliminary Observations Rochelle F. ndreotti, MD, rthur C. Fleischer, MD, Lawrence E. Mason, Jr, MD Objective. y
Technical dvance Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and djacent Myometrium Preliminary Observations Rochelle F. ndreotti, MD, rthur C. Fleischer, MD, Lawrence E. Mason, Jr, MD Objective. y
Ultrasound Scanning on the IVF Unit
 Saint Mary s Hospital Department of Reproductive Medicine Ultrasound Scanning on the IVF Unit Information For Patients INS/DRM/CLI/014 V4/01/11/2013 1 The ultrasound scan is an important part of the programme.
Saint Mary s Hospital Department of Reproductive Medicine Ultrasound Scanning on the IVF Unit Information For Patients INS/DRM/CLI/014 V4/01/11/2013 1 The ultrasound scan is an important part of the programme.
How can I be sure it will be performed to a high standard?
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (About ultrasound scans at Derriford) What is an Ultrasound Scan? How does it work? What are the dangers? What are the advantages? Who will perform my scan? How can I be sure
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (About ultrasound scans at Derriford) What is an Ultrasound Scan? How does it work? What are the dangers? What are the advantages? Who will perform my scan? How can I be sure
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy. Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III
 Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III First Trimester Sonography Localization of Gestational Sac Intrauterine vs. ectopic Identification of abnormalities Embryonic demise
Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III First Trimester Sonography Localization of Gestational Sac Intrauterine vs. ectopic Identification of abnormalities Embryonic demise
K Raja/N Varol FPA 2013. FPA Sydney August 31 2013
 FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management
 Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Ultrasound of the Female Pelvis
 AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of Ultrasound of the Female Pelvis Parameter developed in collaboration with the American College of Radiology (ACR), the American College of Obstetricians and
AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of Ultrasound of the Female Pelvis Parameter developed in collaboration with the American College of Radiology (ACR), the American College of Obstetricians and
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
General and Objectives Clinical Skills for. Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology. Nursing Department
 General and Objectives Clinical Skills for Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology Nursing Department Objectives and clinical skills of Antenatal unit Provide antenatal care to woman during normal
General and Objectives Clinical Skills for Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology Nursing Department Objectives and clinical skills of Antenatal unit Provide antenatal care to woman during normal
2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide
 2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide Effective January 1, 2014 Medicare National Average Rates and Allowables (Not Adjusted For Geography) CPT * HCPCS Code 58150 58152 58180 58200 58210
2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide Effective January 1, 2014 Medicare National Average Rates and Allowables (Not Adjusted For Geography) CPT * HCPCS Code 58150 58152 58180 58200 58210
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound
 Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS
 BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
BERGEN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY PROGRAM Division of Health Professions DMS 213 SYLLABUS Course Title: DMS 213 - Abdominal Sonography 2 2 lec. 3 lab. 3 credits (5 hours) Required
Objective. Indications for IUDs. IUDs 3 types. ParaGard IUD. Mirena IUD. Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Inert
 Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
The percentage of women 21-64 years of age who received one or more Pap tests to screen for cervical cancer.
 Measure Name: Cervical Cancer Screen Owner: NCQA (CCS) Measure Code: CER Lab Data: Y Rule Description: General Criteria Summary The percentage of women 21-64 years of age who received one or more Pap tests
Measure Name: Cervical Cancer Screen Owner: NCQA (CCS) Measure Code: CER Lab Data: Y Rule Description: General Criteria Summary The percentage of women 21-64 years of age who received one or more Pap tests
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids?
 da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
Step-by-Step Insertion Instructions
 Step-by-Step Insertion Instructions Please read these instructions carefully and please visit LILETTAHCP.com for the full Prescribing Information. You may also visit LILETTAhcp.com/video for a video demonstration.
Step-by-Step Insertion Instructions Please read these instructions carefully and please visit LILETTAHCP.com for the full Prescribing Information. You may also visit LILETTAhcp.com/video for a video demonstration.
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination
 Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Cervical Cancer The Importance of Cervical Screening and Vaccination Cancer Cells Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Sometimes, this
Comparison of ovarian cyst formation in women using the
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 20: 381 385 Comparison of ovarian cyst formation in women using the Blackwell Science, Ltd levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system vs. hysterectomy P. INKI*, R. HURSKAINEN
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 20: 381 385 Comparison of ovarian cyst formation in women using the Blackwell Science, Ltd levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system vs. hysterectomy P. INKI*, R. HURSKAINEN
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
2016 Hysterectomy Reimbursement Fact Sheet
 2016 Hysterectomy Reimbursement Fact Sheet The information contained in this document is provided for informational purposes only and represents no statement, promise, or guarantee by Ethicon concerning
2016 Hysterectomy Reimbursement Fact Sheet The information contained in this document is provided for informational purposes only and represents no statement, promise, or guarantee by Ethicon concerning
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine
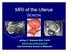 MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook
 In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL
 RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster.
 MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster. Pictured above: UF gynecologists Sharon Byun, MD, Shireen Madani Sims, MD, and Michael Lukowski, MD, with the robotic surgery equipment. Make
MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY FOR WOMEN Back to Life. Faster. Pictured above: UF gynecologists Sharon Byun, MD, Shireen Madani Sims, MD, and Michael Lukowski, MD, with the robotic surgery equipment. Make
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
Endometriosis: An Overview
 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A.
 Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Lippes Loop intrauterine device left in the uterus for 50 years. Case report
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Lippes Loop intrauterine device left in the uterus for 50 years Case report Background.The first Lippes Loop intrauterine device was distributed in 1962. It was a
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Lippes Loop intrauterine device left in the uterus for 50 years Case report Background.The first Lippes Loop intrauterine device was distributed in 1962. It was a
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus
 LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Hysteroscopy. What is a hysteroscopy? When is this surgery used? How do I prepare for surgery?
 What is a hysteroscopy? This is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin tube with a tiny camera to look inside the uterus. There are no incisions. Saline solution is used to expand the uterus in order to
What is a hysteroscopy? This is a procedure where a doctor uses a thin tube with a tiny camera to look inside the uterus. There are no incisions. Saline solution is used to expand the uterus in order to
ASSESSMENT REPORT. Program: AAS Diagnostic Medical Sonography Cardiac Vascular Tract
 ASSESSMENT REPORT Date Submitted: February 9, 2015 School: Engelstad School of Health Sciences Program: AAS Diagnostic Medical Sonography Cardiac Vascular Tract Submitted By: Tracy Lopez, Program Director
ASSESSMENT REPORT Date Submitted: February 9, 2015 School: Engelstad School of Health Sciences Program: AAS Diagnostic Medical Sonography Cardiac Vascular Tract Submitted By: Tracy Lopez, Program Director
Medical criteria for IUCD s Based on the WHO MEC (2004- Annexure 3) system a woman s eligibility for IUCD insertion falls in 4 categories. These categ
 CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
Ovarian cancer. A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment
 Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
Ovarian cancer A guide for journalists on ovarian cancer and its treatment Contents Contents 2 3 Section 1: Ovarian Cancer 4 i. Types of ovarian cancer 4 ii. Causes and risk factors 5 iii. Symptoms and
ULTRASOUND PROTOCOLS
 ULTRASOUND PROTOCOLS Please use and scan in Exam Work Sheets. If exam is negative or there is only one finding, you may write in tech comments, otherwise please use sheet. Abdomen Aorta: Long measure Proximal
ULTRASOUND PROTOCOLS Please use and scan in Exam Work Sheets. If exam is negative or there is only one finding, you may write in tech comments, otherwise please use sheet. Abdomen Aorta: Long measure Proximal
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors
 From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
From this site: http://www.energeticnutrition.com /vitalzym/fibroid_tumors.html Uterine Fibroid Tumors Uterine Fibroid Tumors A woman s fibroisis condition usually associated with estrogen dominance. Uterine
Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion with Color Doppler Sonography: Depiction of Twisted Vascular Pedicle
 Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion with Color Doppler Sonography: Depiction of Twisted Vascular Pedicle Eun Ju Lee, MD, Hyuck Chan Kwon, MD, Hee Jae Joo, MD, Jung Ho Suh, MD, Arthur C. Fleischer, MD The purpose
Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion with Color Doppler Sonography: Depiction of Twisted Vascular Pedicle Eun Ju Lee, MD, Hyuck Chan Kwon, MD, Hee Jae Joo, MD, Jung Ho Suh, MD, Arthur C. Fleischer, MD The purpose
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
Once a woman has had a hysterectomy, she will no longer have menstrual periods and cannot have a child. She no longer needs to use contraception.
 Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary
 September 2000 The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary Aradhana M. Venkatesan,, Harvard Medical School Year- IV MD 1 Menu of Tests Trans-abdominal pelvic ultrasound Trans-vaginal pelvic ultrasound Pelvic
September 2000 The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary Aradhana M. Venkatesan,, Harvard Medical School Year- IV MD 1 Menu of Tests Trans-abdominal pelvic ultrasound Trans-vaginal pelvic ultrasound Pelvic
