The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology
|
|
|
- Clement Jackson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology Bill Smith Clinical Diagnostics Services, London, UK Introduction 3D volumetric ultrasound is shown to be of tremendous value particularly in gynaecology and associated clinical areas. The combination of modern 3D technology and high resolution transvaginal scanning provides increased anatomical and clinical detail. Furthermore it offers considerable benefits from a practical point of view. Nevertheless, its role in gynaecological ultrasound has yet to be fully realised. A single automated sweep of the ultrasound beam through a selected volume of tissue or specific organs produces a wealth of diagnostic information. Rapid acquisition and storage of ultrasound data, speedy retrieval of stored data and easy manipulation of retrieved images considerably reduces examination times. This has obvious positive implications both for the patient as well as the management of busy scan lists. Advances both in transducer design and IT capability have generated high quality 3D imaging particularly when used with transvaginal scan ning (TVS). As a result, 3D technology is now an integral part of gynaecological ultrasound in leading scan units. To date 4D (i.e. real-time 3D) scanning has had little to offer in terms of gynaecological ultrasound. Volumetric facilities are now incorporated within most ultrasound systems. The principal operational controls and functions are similar from system to system, although terminology may obviously vary from one to another.
2 2 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology 3D Image formats The so-called sweep scan produces a volume of ultrasound data. This can be displayed the following formats. Compound Imaging The Compound Image consists of standard x, y and z image components (i.e. parasagittal, transverse and coronal anatomical planes). An additional image is also displayed and is usually in surface rendered or block volume format (see fig. 1a and 2a). The four displays within the Compound Image are quickly assessed and if satisfactory are instantaneously stored at the press of a button. The stored information is transferred to the system memory or hard disc. This data can be retrieved at any stage for further manipulation and evaluation of anatomical planes. viewed simultaneously in three orthogonal planes, i.e. 3D slices at right angles to one another. MPR provides increased anatomical information and greatly improved delineation of pelvic structures within a single image display. The retrieved ultrasound data can then be displayed and recorded in a number of ways or further image formats. Multi-Planar Imaging Multi-Planar Imaging (MPR) comprises of the x, y and z (parasagittal, transverse and coronal) components of a given Compound Image. This allows a specific structure or area within an organ to be Multi View Multi View images (also known as Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging, TUI) consist of tomographic sections through any of the individual MPR image planes. Multi View provides very effective analysis of anatomical details and associated clinical information within any localised region of the pelvis or specific organ. It enhances clinical communication to a considerable extent and offers valuable Fig. 1: 3D imaging formats of a multifollicular ovary containing an endometriotic cyst. Fig. 1a: Compound Image (x, y, z components + BVI) demonstrating antral follicle distribution, ovarian stroma, endometriotic cyst (E) and internal iliac vessel (V). Fig. 1b: Multi View images from the x component of fig. 1a displaying the complete ovarian morphology and associated features. The extent of the endometriotic cyst (E) is completely demonstrated. The ovarian capsule is outlined and para-ovarian structures such as the pelvic vessel (V) are easily separated from ovarian features. Fig. 1c: Block Volume clearly delineating the endometriotic cyst (E) and preservation of normal, healthy ovarian tissue. Fig. 1d: Surface Rendered Image of endometriotic cyst content (E) and cavities of multiple follicles (f). Normal ovarian stroma (ov. strom) is very obvious.
3 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology 3 support to ultrasound scan reporting (see fig. 1b, 3b and 6b). Block Volume Imaging Block Volue Imaging (BVI) displays internal, orthogonal anatomical planes within a given block volume. Its practical and diagnostic value is limited but it can be useful when displaying adjacent features which lie in a random manner in different anatomical planes (see fig. 1c). Surface Rendering Surface Rendered Images (SRI) display anatomical structures with a visual 3D effect. SRI provides greater delineation and increased visual impression of the physical nature of pelvic lesions. It can de monstrate the nature of cavities as well as give an impression of the external features of structures. In addition, it allows the separation of pelvic organs to be visualised with greater clarity (see fig. 1d and 9d). 4D Ultrasound 4D ultrasound utilises advanced IT capability to produce real-time 3D SRI ultrasound imaging. Its role in obstetric scanning and creating image recordings of the baby is well established but its clinical impact to date appears to be relatively limited. This is currently reflected in general pelvic scanning with little application in terms of gynaecological ultrasound to date. 3D Colour Doppler Imaging Advanced 3D technology incorporates colour Doppler (Power Doppler) imaging. 3D reconstruction of imaging planes and volumetric studies demonstrate blood flow within tissues down to the capillary level and the vascular nature of pelvic lesions. The ability to show tissue vascularity is important in the assess ment of diffuse disease and detection of high risk pathological changes in particular. Blood flow indices can provide quantitative measurement of tissue vascularity within a selected volume. Fig. 2: 3D imaging formats of a normal uterus and uterine cavity. Fig. 2a: Compound Image (x, y, z components + SRI) demonstrating a normal endometrial cavity (Endom). Note the interstitial portion of the uterine tube (I) visualised on the rendered image. Fig. 2b: A surface rendered image in Cavity Mode clearly highlights the interstitial tube (I).
4 4 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology Principles of 3D Volumetric Imaging A conventional 2D (TVS) ultrasound image or sector is usually generated by electronically steering a narrow ultrasound beam through the body tissues. The size of the 2D image, or anatomical slice, depends upon the 2D sector angle and depth of field of view selected. A 3D volume is created by generating a rapid series of 2D scan sweeps, each very slightly displaced perpendicular to the direction of the scan sweep. A large number of sequential 2D anatomical slices are built up to produce in effect a 3D volume. The size of the volume will be determined by the distance between first and final 2D anatomical slice creating the volume, i.e. 3D sector angle, as well as the 2D sector angle utilised and depth of field selected. The volume information acquired is displayed straight away usually in the form of a stored Compound Image for direct viewing. The ultrasound data stored can then be transferred to the system memory or a server for future inter rogation or simply deleted if not required. Practical aspects Technical Considerations 3D (TVS) ultrasound scanning is both convenient and straight-forward from a practical point of view. The basic technical requirements of a modern 3D system include the following: Uncomplicated, user-friendly controls for acquisition and storage, retrieval, post-scan manipulation and image recording of ultrasound information. Simple initiation of a single, automated 2D scan ning ( survey ) sweep of the area of interest. A stable, high quality grey-scale Fig. 3: Bicornuate uterus. Fig. 3a: Composite Image of a parasagittal 2D section of the uterus and endometrial cavity (Endom) and coronal MPR of an obvious bicornuate cavity (Bicorn Ut). Fig. 3b: MultiView coronal sections outlining the extent of the anatomical malformation.
5 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology 5 image maintained throughout the survey sweep. Rapid acquisition and viewing of stored scan information. Instantaneous transfer of acquired ultra sound data to the system memory or a ser ver or deletion of stored data if not required. Uniform spatial and contrast resolution in the grey-scale image in all anatomical planes within the ultrasound volume. Accurate geometric registration of echo point sources within the 3D volume. Rapid, easy retrieval of stored ultrasound data. It is important to notice that the quality of 3D imaging reflects that of the fundamental 2D grey-scale performance levels of the ultrasound system. Correct utilisation of 2D system controls and grey-scale pre-sets is essential in order to maximise the dia gnostic information provided by 3D ultrasound technology. Utilisation of 3D volumetric technology presents considerable benefits from a practical point of view: Reduces scanning time and length of the ultrasound examination. Reduced examination time for the patient and exposure to ultrasound energy. Promotes the concept of post-scan evaluation. Reduces probe movement as part of TVS in order to acquire ultrasound information and therefore causes less discomfort particularly with patients presenting with pelvic pain. More efficient and cost effective storage and archiving of image material compared to conventional 2D image recording. Scanning Issues 3D ultrasound scanning involves in practice holding the TVS transducer stationary and initiating the single 3D survey sweep. The survey sweep produces the 3D volumetric data which can then be stored once the Compound Image has been assessed. Fig. 4: 3D TVS SIS or fluid ultrasound demonstrating a normal uterine cavity. Fig. 4a and 4b: Composite parasagittal 2D and surface rendered 3D images of the uterine cavity. The SRI reference plane (SR) has been shifted and slightly curved in fig. 4b to accommodate both the uterine cavity and cervical canal. As a result the rendered image clearly demonstrates the complete cavity from the internal os to fundus compared to only the cavity of the uterine body in fig. 4a. Fig. 4c: Multi View coronal sections fully demonstrate the extent and nature of the uterine cavity in a single image.
6 6 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology It is important to ensure the correct use of 2D controls in order to maintain optimal 3D detail. These include selection and utilisation of transducer frequency, focal length and zone, 2D sector angle, frame rate/prf, image size etc. as well as sensitivity controls and greyscale preset functions. The survey sweep allows (2D) visualisation of the area of interest as the system collects the 3D data. This in itself can be of considerable diagnostic and practical value. It is therefore important that a constant level of greyscale imaging is maintained throughout the duration of the 3D sweep. Acquisition and Storage of 3D Volumes The 3D sampling box or sector is superimposed upon the realtime 2D image. The survey or 3D sweep should be adjusted to cover the area of interest only. This involves appropriate selection of both 3D sector angle and the depth of the 3D sample sector or box. The detail obtained from ultrasound images derived from the stored 3D data largely depends upon the following factors: Correct use of 2D greyscale controls 3D sector angle 3D sweep speed Depth of 3D sample sector The selection of 3D sector angle, sweep speed and sampling box size greatly influences frame rates and hence line density within the 3D image volume. These are important considerations in the ability to maximise 3D image quality. The absence of tissue movement problems in general pelvic scanning, certainly compared with ultrasound of the fetus, allows slower sweep speed and improved 3D image definition. 3D sweep scans can typically take 4 8 seconds in gynaecological ultrasound. The acquired ultrasound data is usually immediately displayed in the form of a stored Compound Image. This can be manipulated and/or converted into other forms of 3D imaging if required. Otherwise the volume data can be very quickly trans- Fig. 5: 3D TVS SIS demonstrating an endometrial polyp and submucosal fibroids encroaching on the uterine cavity. Fig. 5a: Compound Image (x, y, z components + BVI) demonstrating the relevant clinical features. Fig. 5b: Multi View coronal sections showing the position and nature of the polyp (P) and indentation of the cavity by the mid-uterine fibroid (M). Fig. 5c: Composite parasagittal 2D and surface rendered 3D sections. Adjustment of the reference plane (SR) produces a localised rendered image of the mid-upper cavity with encroaching fibroids (M) and polyp (P) delineated.
7 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology 7 ferred to the system memory, hard disc or server, or otherwise instantaneously deleted. Retrieval and Manipulation of 3D Volumes Stored volumetric data is usually retrieved in the Composite Image format. All components can be manipulated simultaneously or independent of one another. distance between slices making up the Multi View format can be varied. The greyscale characteristics of the retrieved MPR and/or Multi View can be varied by means of a number of post-processing options. This allows particular features or tissue changes to be visually enhanced in order to highlight diagnostic findings. Cavity Mode: This essentially reverses the grey-scale or selected colour mapping, i.e. making cystic regions lighter and solid regions darker (inversion, see fig. 6). Threshold Control: This is basically a control which determines the level to which ultrasound information is suppressed for surface rendering (mainly low level clutter and noise). MPR images can be rotated in any geometric plane. It is also possible to scroll through the volume thick ness in any one of the anatomical planes. Alternatively, Multi View will generate a series of tomographic images within that plane. The number of image slices as well as the Similarly, the surface rendered image (SRI) can be geometrically manipulated. There are also post-processing options specific to SRI again serving to visually outline structures with greater clarity. These include: A combination of algorithms, typically available in most systems, enables adjustment to be made regarding colour, surface textured appearances, transparency of structures etc. within the rendered volume. Fig. 6: ART stimulated multifollicular ovary. Fig. 6a: Compound Imaging (x, y, z components + BVI) provides immediate visualisation of the number, distribution and relative sizes of stimulated follicles. Fig. 6b: Multi View delineates multiple follicles the facility to scroll through the retrieved tomographic sections enables rapid evaluation and speedy measurements of developing ovarian follicles. This proves to be a considerable asset in terms of the monitoring and measurement of ovarian follicle response to ART stimulation. Fig. 6c: Surface rendered images of the ovary highlighting individual follicles with considerable clarity. Fig. 6d: Cavity Mode further enhances visualisation and provides precise delineation of the multiple follicles.
8 8 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology The SRI reference plane (SR) determines the thick ness or at what depth the rendered image is visualised. The level can be adjusted under visual control and the shape of the SR can be curved in order to demonstrate non-linear anatomical sections (see fig. 4 and fig. 5c). Clincial Aspects Uterus 3D reconstruction of the uterus and uterine cavity in coronal section is a considerable asset particularly with access to Multi View formats. The anatomy of the uterus and presence of uterine lesions prove to be much more recognisable even to the untrained eye in this image plane. The shape and size of the uterine cavity is clearly demonstrated and anatomical malformation readily identified in the coronal plane. The combination of MPR and Multi View formats provide precise location of IUD/IUS devices in-utero and confirms the presence, size, position and nature of intracavital lesions such as polyps, fibroids, adhesions etc. (see fig. 2 and 3). The utilisation of 3D TVS technology as part of Saline Infusion Sonohysterography (SIS), or fluid ultrasound, procedures increases the diagnostic effectiveness of ultrasound examination of the endometrium and uterine cavity. MPR, Multi View and manipulation of SR (coronal) displays present very detailed studies of the distended cavity and any associated pathologies. In a number of clinical units, 3D TVS SIS has proven to be an appropriate alternative to diagnostic hysteroscopy with obvious advantages to both the clinic and patient (see fig. 4 and 5). Fig. 7: Perimenopausal ovary with an intact follicular cyst (C¹) and remnants of a collapsing, clot-filled cyst (C²). Fig. 7a and 7b: Compound Imaging (x, y, z components + BVI) and Multi View sections provides complete details of ovarian morphology and associated lesions. The functional cysts are seen quite separately from one another. The nature of the ovarian stroma can be easily evaluated. The absence of antral follicles remains consistent with patient age.
9 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology 9 3D TVS provides more elaborate evaluation of endometrial changes. The introduction of 3D colour Doppler is shown to be extremely useful in terms of identifying high risk changes as well as gauging the extent of endometrial malignancy. Volumetric assessment of blood flow changes within the myometrium also demonstrates diffuse benign disease. This has increased our ability to confirm the likelihood of adenomyosis in particular and has been an important element in the early detection of endometriosis. 3D volumetric ultrasound has had a major clinical impact in other areas of gynaecology. More comprehensive examination of the myometrium, uterine cavity and endometrium greatly assists investigation of fertility issues and possible causes of recurrent miscarriage. Ovaries 3D volumetric ultrasound presents the ideal imaging modality for examining ovarian morphology. MPR, Multi View and a choice of surface rendered displays offer very precise imaging of follicle patterns and stromal distribution within the ovary. This has proved invaluable both in the assessment of gynae cological disease as well as the investigation of fertility and ovulatory issues (see fig. 6 and 7). Improved delineation and interrogation of ovarian lesions provides a more reliable diagnostic impression of their nature. 3D imaging formats accurately gauge the preservation of normal, functional ovarian tissue in the presence of large lesions. This remains crucial in terms of clinical management and choice of surgical techniques if indicated. The introduction of 3D colour Doppler differentiates between high and low risk lesions with far greater diagnostic confidence. The additional use of SRI facilities not only outlines pelvic structures with greater clarity but can distinguish between ovarian and adjacent para-ovarian features with more certainty. This is particularly useful in examination of the adnexal regions and associated pathologies involving the Fallopian tube. Fig. 8: Adherent ovary with extensive adnexal/pelvic adhesions and loculated fluid collections. Fig. 8a: Localised 2D image of the adnexal region shows a complex mass. Fig. 8b: Multi View sections through the area outlined in fig. 8a clearly demonstrate the ovary (Ov) adherent to the pelvic sidewall with numerous, extensive bands of adhesions. Associated loculated fluid contains clot which has probably resulted from spill from the collapsed corpus luteum (CL) just visible within the ovary. Fig. 8c: Composite image of 2D and SRI 3D images. The rendered image highlights remnants of the corpus luteum (CL) and visualises the fluid cavities (c) resulting from the multiple bands of adhesions clearly evident.
10 10 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology Pelvis (General) Complex, diffuse gynaecological disease affecting adjacent organs or structures within the pelvic cavity are very often difficult to evaluate by conventional 2D TVS ultrasound scanning. This might include for example chronic PID, extensive pelvic endometriosis or the spread of malignancy. The facility to retrieve 3D ultrasound data and carefully examine different anatomical planes using a choice of 3D imaging formats is a tremendous benefit in these cases. Individual, neighbouring structures involved with the spread of disease can be recognised more easily and the extent of the disease estimated with greater diagnostic accuracy (see fig. 8 and 9). 3D volumetric ultrasound is a particular asset for those patients presenting with moderate to severe endometriosis. These patients experience considerable discomfort during a conventional TVS ultrasound examination. The ability to restrict probe movement to a minimum is a major consideration especially in these cases and also for any patient experiencing significant pelvic discomfort. The TVS probe is held still in order to carry out 3D scan sweeps and gently repositioned in only a selected number of locations in order to interrogate all areas of interest. Post scan evaluation Scan Reporting Modern 3D volumetric ultrasound promotes the possibility of post-scan evaluation. The speed of system operation and quality of stored images makes it convenient and reliable to consider reporting of ultrasound examinations at a later time after the scan has been completed. The survey sweep itself should be adequate to serve as an initial evaluation of relevant structures or areas of interest in a large number of cases. Minimal scanning only is sometimes required to view the pelvic structures and select relevant Fig. 9: Early tubal ectopic pregnancy (5+ weeks gestation) and associated haematosalpinx. Fig. 9a: Multi View coronal sections confirm an obvious decidual response but no intra-uterine pregnancy sac was identified. Fig. 9b: Compound Imaging (x, y, z + SRI) identifies the ovary (Ov), a para-ovarian mass (T), a fimbrial cyst (F) with an early extra-uterine pregnancy sac (G) outlined on the rendered image. Manipulation of the anatomical planes allows more effective examination and recognition of relevant structures.
11 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology 11 areas for speedy acquisition and storage of scan details. As a result, scanning times are considerably reduced certainly in more straightforward, non-complex cases. The facility to connect the ultrasound system to a suitable IT workstation means reporting of scans can be easily carried out remotely and at anytime following completion of the scan or scan list. This has practical advantage certainly in the management of busy scan lists and regarding efficiency of patient throughput. In addition, it has been shown that post-scan evaluation of 3D images in more complex clinical cases, especially those involving extensive, diffuse pelvic change, is extremely useful in terms of accuracy of diagnosis. Clinical Communication Ultrasound images remain an essential part of ultrasound scan reporting. Standard 2D greyscale images can be difficult to interpret both in terms of the anatomy and clinical features shown, particularly to the untrained eye. 3D reconstruction, especially the use of MPR, Multi View and volume rendering, can make the content of the ultrasound image much more apparent. Multi View coronal sections of the uterus or SRI of the adnexal region for example result in much more obvious detail as part of the images used to support written texts. Volumetric imaging formats produced from the retrieved data can be of value to referring clinicians in terms of pre-surgical planning. 3D volumetric ultrasound reconstruction in modern systems can be utilised in a similar manner to MRI regarding image interpretation and clinical communication. Fig. 9c: Localised Multi View sections show the distended, blood-filled uterine tube (UT) immediately adjacent and probably adherent to the ovary (Ov). The fimbrial cyst (F) is again well seen and free fluid (clot) present within the pelvic/adnexal region. Fig. 9d: Composite image of an individual MPR section showing the tubal mass (T), fimbrial cyst (F) and ovary (Ov) and surface renderung of the adnexal structures. The rendered image shows the convoluted nature of the tube (UT) and its attachment to the ovary (Ov).
12 Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2011 all rights reserved. Design and specifications subject to change without notice. 01/2011 TWPUS0012EC.EU Printed in Europe ULTRASOUND CT MRI X-RAY SERVICES
13
Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering
 Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
3D in Gynecology: Luxury or necessity?
 ISUOG 2011 Los Angeles September 16-22 3D in Gynecology: Luxury or necessity? Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch Educational objectives To describe the 3D US tools available to complement 2D US To apply these tools
ISUOG 2011 Los Angeles September 16-22 3D in Gynecology: Luxury or necessity? Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch Educational objectives To describe the 3D US tools available to complement 2D US To apply these tools
TISSUE MIMICKING GEL QUALITY LE PHANTOM SERIES DESIGN. performance the ultrasound labs ofand. icking material has the same attenuation mim-
 QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
QUALITY Tissue Benefits Mimicking of s RMI recognized RMI as the ultrasound standard phantoms for quality are performance the ultrasound labs ofand hospitals, manufacturers. clinics Sophisticated and ultrasound
How To Use A Voluson Compact Ultrasound System
 Voluson i Extraordinary vision Compact series Extraordinary vision to care for your patients. Your needs shape the future of ultrasound. It s your feedback that drives every technological advancement that
Voluson i Extraordinary vision Compact series Extraordinary vision to care for your patients. Your needs shape the future of ultrasound. It s your feedback that drives every technological advancement that
The following chapter is called The Role of Endoscopy, Laparoscopy, and Hysteroscopy in Infertility.
 Welcome to Chapter 14. The following chapter is called The Role of Endoscopy, Laparoscopy, and Hysteroscopy in Infertility. The authors are Dr. Jose Remohi and Dr. Jaime Ferro. 1 There are several tools
Welcome to Chapter 14. The following chapter is called The Role of Endoscopy, Laparoscopy, and Hysteroscopy in Infertility. The authors are Dr. Jose Remohi and Dr. Jaime Ferro. 1 There are several tools
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Twelve. Figure 12.1: 3D Curved MPR Viewer Window
 Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
Twelve The 3D Curved MPR Viewer This Chapter describes how to visualize and reformat a 3D dataset in a Curved MPR plane: Curved Planar Reformation (CPR). The 3D Curved MPR Viewer is a window opened from
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Ultrasound Scanning on the IVF Unit
 Saint Mary s Hospital Department of Reproductive Medicine Ultrasound Scanning on the IVF Unit Information For Patients INS/DRM/CLI/014 V4/01/11/2013 1 The ultrasound scan is an important part of the programme.
Saint Mary s Hospital Department of Reproductive Medicine Ultrasound Scanning on the IVF Unit Information For Patients INS/DRM/CLI/014 V4/01/11/2013 1 The ultrasound scan is an important part of the programme.
Objective. Indications for IUDs. IUDs 3 types. ParaGard IUD. Mirena IUD. Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Inert
 Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and Adjacent Myometrium
 Technical dvance Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and djacent Myometrium Preliminary Observations Rochelle F. ndreotti, MD, rthur C. Fleischer, MD, Lawrence E. Mason, Jr, MD Objective. y
Technical dvance Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and djacent Myometrium Preliminary Observations Rochelle F. ndreotti, MD, rthur C. Fleischer, MD, Lawrence E. Mason, Jr, MD Objective. y
GE Healthcare. Vivid 7 Dimension Cardiovascular Ultrasound System
 GE Healthcare Vivid 7 Dimension Cardiovascular Ultrasound System New dime Introducing multi-dimensional and 4D imaging. The ability to incorporate multi-dimensional and 4D imaging into your clinical routine
GE Healthcare Vivid 7 Dimension Cardiovascular Ultrasound System New dime Introducing multi-dimensional and 4D imaging. The ability to incorporate multi-dimensional and 4D imaging into your clinical routine
Benign Ovarian Masses
 Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Why would you need a hysterectomy?
 Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Why would you need a hysterectomy? Removal of the uterus is performed to prevent, alleviate, or treat pain, pressure, bleeding, or cancer. Each reason is described in detail in the following pages. Benign
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries. Simple Cystic Masses
 Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
GE Healthcare VOLUSON 730 PRO The Diamond Release
 GE Healthcare VOLUSON 730 PRO The Diamond Release imagination at work VOLUSON 730 PRO The Standard in Women's Healthcare 4D Dedication Dimensional Diagnostic Digital GE Healthcare continues to elevate
GE Healthcare VOLUSON 730 PRO The Diamond Release imagination at work VOLUSON 730 PRO The Standard in Women's Healthcare 4D Dedication Dimensional Diagnostic Digital GE Healthcare continues to elevate
K Raja/N Varol FPA 2013. FPA Sydney August 31 2013
 FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Voluson E8 Extraordinary vision
 Voluson E8 Extraordinary vision Innovation for early detection Throughout the years, your feedback has driven all our technological advancements, helping to make GE Healthcare a leader in women s health
Voluson E8 Extraordinary vision Innovation for early detection Throughout the years, your feedback has driven all our technological advancements, helping to make GE Healthcare a leader in women s health
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao.
 Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Implementation of hysteroscopy in an infertility clinic: The one-stop uterine diagnosis and treatment
 Facts Views Vis Obgyn, 2014, 6 (4): 235-239 Short communication Implementation of hysteroscopy in an infertility clinic: The one-stop uterine diagnosis and treatment R. Campo 1,2,3, R. Meier,2, N. Dhont
Facts Views Vis Obgyn, 2014, 6 (4): 235-239 Short communication Implementation of hysteroscopy in an infertility clinic: The one-stop uterine diagnosis and treatment R. Campo 1,2,3, R. Meier,2, N. Dhont
Reproductive Health Group
 Gynaecology Services & Treatments 2015 Fee Schedule Consultations - Assessment Initial gynaecology consultation 200-250 Follow-up gynaecology consultation 150-175 Initial fertility consultation *Harley
Gynaecology Services & Treatments 2015 Fee Schedule Consultations - Assessment Initial gynaecology consultation 200-250 Follow-up gynaecology consultation 150-175 Initial fertility consultation *Harley
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Company profile. Quote from the analyst of. Company Milestone. Feel the Difference. Tel: +86-755-26722860 Fax: +86-755-26722850
 Company profile Since the establishment, SonoScape has committed to provide high standard medical equipments for healthcare of human beings. SonoScape specializes in the development and production of diagnostic
Company profile Since the establishment, SonoScape has committed to provide high standard medical equipments for healthcare of human beings. SonoScape specializes in the development and production of diagnostic
GYNAECOLOGY. Ahmed Mohamed Abbas*, Mohamed Khalaf*, Abd El-Aziz E. Tammam**, Ahmed H. Abdellah**, Ahmed Mwafy**. Introduction ABSTRACT
 Thai Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 2015, Vol. 23, pp. 113-117 GYNAECOLOGY The Diagnostic Value of Saline Infusion Sonohysterography Versus Hysteroscopy in Evaluation of Uterine Cavity in
Thai Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology April 2015, Vol. 23, pp. 113-117 GYNAECOLOGY The Diagnostic Value of Saline Infusion Sonohysterography Versus Hysteroscopy in Evaluation of Uterine Cavity in
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy
 Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management
 Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Voxar 3D TM. A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools
 Voxar 3D TM A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools The power to deliver advanced visualization throughout the enterprise To effectively manage the rapid growth of large volumetric
Voxar 3D TM A suite of advanced visualization and analysis software tools The power to deliver advanced visualization throughout the enterprise To effectively manage the rapid growth of large volumetric
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Three-dimensional Ultrasound Imaging
 NELSON - 3D/4D ULTRASOUND IMAGING - UIA ANNUAL MEETING, 3/2006 1 Three-dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Thomas R. Nelson, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego La Jolla, California Abstract Three-dimensional
NELSON - 3D/4D ULTRASOUND IMAGING - UIA ANNUAL MEETING, 3/2006 1 Three-dimensional Ultrasound Imaging Thomas R. Nelson, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego La Jolla, California Abstract Three-dimensional
The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate.
 The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate. The procedure is well tolerated. No consensus on effectiveness of HSC in improving prognosis of subfertile women. systematic
The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate. The procedure is well tolerated. No consensus on effectiveness of HSC in improving prognosis of subfertile women. systematic
ViewPoint 6. Clarify your View
 ViewPoint 6 Clarify your View Clear information helps you see the bigger picture Using over 20 years of experience and feedback from customers across the globe, we ve simplified ultrasound reporting and
ViewPoint 6 Clarify your View Clear information helps you see the bigger picture Using over 20 years of experience and feedback from customers across the globe, we ve simplified ultrasound reporting and
1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound
 Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations. Bruce Thomadsen. University of Wisconsin -Madison
 Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations Bruce Thomadsen University of Wisconsin -Madison Conflicts of Interest The author has no known conflicts involving this presentation Learning
Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations Bruce Thomadsen University of Wisconsin -Madison Conflicts of Interest The author has no known conflicts involving this presentation Learning
Fact sheet 9. Screening for ovarian cancer
 Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
It understands your everyday
 Ultrasound Affiniti It understands your everyday Philips Affiniti ultrasound system for women s health care Affiniti ultrasound for women s health care Designed to set you ahead and help you stay ahead,
Ultrasound Affiniti It understands your everyday Philips Affiniti ultrasound system for women s health care Affiniti ultrasound for women s health care Designed to set you ahead and help you stay ahead,
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
More than a Portable System
 More than a Portable System General Imaging More than Mobile Setting a new standard: the Premium-performance Mobile A new class of systems: the Gold Standard in terms of quality and solutions meets the
More than a Portable System General Imaging More than Mobile Setting a new standard: the Premium-performance Mobile A new class of systems: the Gold Standard in terms of quality and solutions meets the
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Ultrasound. Your versatile performer to depend on. Philips ClearVue ultrasound family for women s health care
 Ultrasound ClearVue Your versatile performer to depend on Philips ClearVue ultrasound family for women s health care Over 70 countries More than 5,000 systems Touching 25 million lives every year For one
Ultrasound ClearVue Your versatile performer to depend on Philips ClearVue ultrasound family for women s health care Over 70 countries More than 5,000 systems Touching 25 million lives every year For one
Vivid S6. Cardiovascular ultrasound system. imagination at work. GE Healthcare
 GE Healthcare Vivid S6 Cardiovascular ultrasound system imagination at work Taking care of everyone. Strong performance and innovative miniaturization make the Vivid S6 a highly desirable system for a
GE Healthcare Vivid S6 Cardiovascular ultrasound system imagination at work Taking care of everyone. Strong performance and innovative miniaturization make the Vivid S6 a highly desirable system for a
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
ParaVision 6. Innovation with Integrity. The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research.
 ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
ParaVision 6 The Next Generation of MR Acquisition and Processing for Preclinical and Material Research Innovation with Integrity Preclinical MRI A new standard in Preclinical Imaging ParaVision sets a
Cornual ruptured pregnancy with placenta increta CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE
 142 CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE Agarwal NR 1, Rani A 1 *, Batra S 1 1. Department of Obststetrics and Gynaecology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banares Hindu Univarsity.
142 CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE Agarwal NR 1, Rani A 1 *, Batra S 1 1. Department of Obststetrics and Gynaecology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banares Hindu Univarsity.
A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding
 TRUCLEAR System A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding Do You Suffer from Abnormal Uterine Bleeding? What is a Hysteroscopy? What is the TRUCLEAR Procedure? What Happens Before Your
TRUCLEAR System A potential treatment for your abnormal uterine bleeding Do You Suffer from Abnormal Uterine Bleeding? What is a Hysteroscopy? What is the TRUCLEAR Procedure? What Happens Before Your
UGEO H60 PERFORMANCE IN STYLE
 CT-UGEO-H60-CWW-MCI-0731-EN 2012 Samsung Electronics All Rights Reserved. Samsung Electronics Reserves The Right To Modify The Design, Packaging, Specifications And Features Shown Herein, Without Prior
CT-UGEO-H60-CWW-MCI-0731-EN 2012 Samsung Electronics All Rights Reserved. Samsung Electronics Reserves The Right To Modify The Design, Packaging, Specifications And Features Shown Herein, Without Prior
Samsung Ultrasound H60
 Samsung Medison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer around
Samsung Medison is a global leading medical devices company. Founded in 1985, the company now sells cutting-edge medical devices including diagnostic ultrasound, digital X-ray and blood analyzer around
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL
 Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Thinking ahead. Focused on life. REALIZED: GROUNDBREAKING RESOLUTION OF 80 µm VOXEL X-ray ZOOM RECONSTRUCTION Flat Panel Detector (FPD) Automatic Positioning Function For ø 40 x H 40 mm, ø 60 x H 60 mm,
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps
 Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
SAMSUNG ULTRASOUND RS80A
 Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
Samsung Medison is a global leading medical device company. Founded in 1985, the company sells cutting-edge diagnostic ultrasound devices around the world in various medical fields. The company has attracted
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
Ultrasound and Hysteroscopy in Infertility
 Ultrasound and Hysteroscopy in Infertility James M. Shwayder, M.D., J.D. Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, Mississippi Ultrasound
Ultrasound and Hysteroscopy in Infertility James M. Shwayder, M.D., J.D. Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, Mississippi Ultrasound
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
SUBSEROSAL FIBROIDS TREATMENT
 INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A.
 Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Role of Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy in Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy in Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Jyotsana, Kamlesh Manhas, Sudha Sharma Abstract Abnormal uterine poses a real challenge for the gynecologists
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy in Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Jyotsana, Kamlesh Manhas, Sudha Sharma Abstract Abnormal uterine poses a real challenge for the gynecologists
BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND
 BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND Goals: To become familiar with: Ultrasound wave Wave propagation and Scattering Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Biomedical Ultrasound Transducers Biomedical Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasonic
BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND Goals: To become familiar with: Ultrasound wave Wave propagation and Scattering Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Biomedical Ultrasound Transducers Biomedical Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasonic
Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy. Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III
 Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III First Trimester Sonography Localization of Gestational Sac Intrauterine vs. ectopic Identification of abnormalities Embryonic demise
Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III First Trimester Sonography Localization of Gestational Sac Intrauterine vs. ectopic Identification of abnormalities Embryonic demise
What are the differences between fibroid and ovarian cyst?
 DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
DR LEE KEEN WHYE MBBS (Singapore), FRCOG (U.K), FAMS (Singapore) Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Advisor, Endometriosis Association, Singapore KW Lee Clinic & Surgery For Women No. 6 Napier Road,
Screening for ovarian cancer Page 1 of 5 Ovacome
 Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
Fact sheet 9 Screening for ovarian cancer Ovacome is a national charity providing advice and support to women with ovarian cancer. We give information about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, research and
Changing The World One Hospital At a Time
 Changing The World One Hospital At a Time miplatform Integrated Medical Image and Information Management Platform PACS/RIS System Mobile Imaging System Image-based Conferencing System TeleMed/TeleRad System
Changing The World One Hospital At a Time miplatform Integrated Medical Image and Information Management Platform PACS/RIS System Mobile Imaging System Image-based Conferencing System TeleMed/TeleRad System
The Benign Endometrial Hyperplasia Sequence
 Page 1 Slide 1 Introduction A mini lecture from www.endometrium endometrium.org The Benign Endometrial Hyperplasia Sequence This is Dr. George Mutter, I am a gynecologic pathologist at Harvard Medical
Page 1 Slide 1 Introduction A mini lecture from www.endometrium endometrium.org The Benign Endometrial Hyperplasia Sequence This is Dr. George Mutter, I am a gynecologic pathologist at Harvard Medical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids?
 da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
3 Summary of clinical applications and limitations of measurements
 CA125 (serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cancer Antigen 125 (CA125) 1.2 Alternative names Mucin 16 1.3 NLMC code To follow 1.4 Description of analyte CA125 is an antigenic determinant
CA125 (serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cancer Antigen 125 (CA125) 1.2 Alternative names Mucin 16 1.3 NLMC code To follow 1.4 Description of analyte CA125 is an antigenic determinant
VFI Technology to Change the Way You Work
 Technology to Change the Way You Work Vascular Ultrasound Made Easier Vector Flow Imaging VFI VFI is a ground-breaking technology that can revolutionize the workflow for many Doppler ultrasound applications.
Technology to Change the Way You Work Vascular Ultrasound Made Easier Vector Flow Imaging VFI VFI is a ground-breaking technology that can revolutionize the workflow for many Doppler ultrasound applications.
3D Ultrasound. Outline. What is 3D US? Volume Sonography. 3D Ultrasound in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential. Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
 in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential Outline What is 3D US? What are obvious advantages of 3D US? What is the future of 3D US? Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 2D US
in Obstetrics: Current Modalities & Future Potential Outline What is 3D US? What are obvious advantages of 3D US? What is the future of 3D US? Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 2D US
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine
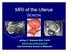 MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
Automated Breast Volume Scanning 3D Ultrasound of the Breast
 Automated Breast Volume Scanning 3D Ultrasound of the Breast Roel Mus, MD Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre (RUNMC), Nijmegen, The Netherlands Matthieu Rutten, MD, PhD Jeroen Bosch Ziekenhuis,
Automated Breast Volume Scanning 3D Ultrasound of the Breast Roel Mus, MD Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre (RUNMC), Nijmegen, The Netherlands Matthieu Rutten, MD, PhD Jeroen Bosch Ziekenhuis,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
Voluson E8. Extraordinary vision
 Voluson E8 Extraordinary vision Voluson E8 Your foundation for extraordinary vision. Throughout the years, your feedback has driven Voluson * technological advancements, helping to make GE Healthcare a
Voluson E8 Extraordinary vision Voluson E8 Your foundation for extraordinary vision. Throughout the years, your feedback has driven Voluson * technological advancements, helping to make GE Healthcare a
Endometriosis, Fertility and Pregnancy
 This leaflet covers endometriosis and fertility. It provides information for women who have been diagnosed with endometriosis who would like to know if and how this can affect their fertility, and for
This leaflet covers endometriosis and fertility. It provides information for women who have been diagnosed with endometriosis who would like to know if and how this can affect their fertility, and for
GYN 56 1.0 11/2015-E. GynTrainer. the virtual platform for diverse and risk-free training of gynecological diagnosis and therapy
 GYN 56 1.0 11/2015-E GynTrainer the virtual platform for diverse and risk-free training of gynecological diagnosis and therapy Virtual Reality (VR) in Medical Training and Further Education at KARL STORZ
GYN 56 1.0 11/2015-E GynTrainer the virtual platform for diverse and risk-free training of gynecological diagnosis and therapy Virtual Reality (VR) in Medical Training and Further Education at KARL STORZ
PICTURE PERFECT Ultrasound
 PICTURE PERFECT Ultrasound Precision, control and an amazingly clear picture Aplio 400 delivers in every way. Ensuring every examination has an optimal result, it provides you with unsurpassed image quality,
PICTURE PERFECT Ultrasound Precision, control and an amazingly clear picture Aplio 400 delivers in every way. Ensuring every examination has an optimal result, it provides you with unsurpassed image quality,
DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with
 VERSATILE INTUITIVE efficient DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with dedicated panoramic imaging With thirty years of experience in designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art dental panoramic and tomographic
VERSATILE INTUITIVE efficient DENTAL Cone beam 3D X-RAY SYSTEM with dedicated panoramic imaging With thirty years of experience in designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art dental panoramic and tomographic
REGISTRATION OF 3D ULTRASOUND IMAGES TO SURFACE MODELS OF THE HEART
 To appear in: Proceedings of the Interface to Real & Virtual Worlds (Montpellier, France, May 28-30, 1997) REGISTRATION OF 3D ULTRASOUND IMAGES TO SURFACE MODELS OF THE HEART Stefan Pieper, Michael Weidenbach*,
To appear in: Proceedings of the Interface to Real & Virtual Worlds (Montpellier, France, May 28-30, 1997) REGISTRATION OF 3D ULTRASOUND IMAGES TO SURFACE MODELS OF THE HEART Stefan Pieper, Michael Weidenbach*,
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
Ectopic Pregnancy. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook
 In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae
 CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae Uterine synechiae are intrauterine adhesions. They may involve small focal areas of the endometrium (Figures 10.1a e), or they can be so extensive that they obliterate the
CHAPTER 10 Uterine Synechiae Uterine synechiae are intrauterine adhesions. They may involve small focal areas of the endometrium (Figures 10.1a e), or they can be so extensive that they obliterate the
Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization
 September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
ProSono Copyright 2006. Ovarian Pathology
 Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result

 details >>> HERE
details >>> HERE