2. A decrease in ambient air temperature will cause the level of cremaster muscle contraction to:
|
|
|
- Edwina Butler
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. The vagina a. Contains skeletal muscle b. Has ridges called rugae c. Is lined by stratified squamous epithelium d. All of the above 2. A decrease in ambient air temperature will cause the level of cremaster muscle contraction to: 3. As a spermatid is converted into a sperm cell, the number of chromosomes it contains in its nucleus will: 4. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The longest portion of the male urethra is located in the corpus spongiosum. b. The glans penis is the distal portion of the corpus cavernosa. c. The prepuce is removed during a circumcision. d. There are 3 erectile bodies within the penis. e. The male external genitalia are the penis and scrotum. 5. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The acrosome is found in the head of the sperm and contains digestive enzymes. b. Fructose and citrate are 2 nutrients found in semen. c. The seminal vesicles are on the posterior surface of the urinary bladder. d. The bulbourethral glands are found just superior to the prostate gland. e. The membranous urethra passes through the urogenital diaphragm 6. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Spermatogenesis consists of meiosis and spermiogenesis. b. A primary spermatocyte is a diploid cell. c. Sertoli cells are large cells within the seminiferous tubules that help regulate sperm synthesis. d. Spermatids are haploid and contain long flagella. e. FSH stimulates the production of androgen binding protein by interstitial cells. 7. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. A male contraceptive pill that blocked hypothalamic release of gonadotropin releasing hormone would have undesirable side effects. b. A rise in plasma levels of LH will cause a rise in plasma levels of testosterone. c. Spermatogonia are found in the outer rim of the seminiferous tubules. d. The end result of the meiosis of 1 type B spermatogonium is 4 spermatids. e. FSH and LH are released by the posterior pituitary in response to rising levels of GnRH. 8. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. As plasma levels of testosterone increase, plasma levels of LH will decrease. b. The prostatic urethra transports semen but does not convey urine. c. Seminal fluid contains a coagulating enzyme that thickens semen. d. Ejaculation is caused by an increase in sympathetic output to the penis. e. The midpiece of the sperm cell is packed with mitochondria. 9. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The layer of the uterus that contains the most actin is the myometrium. b. The external os is the junction between the cervical canal and the uterine cavity. c. The stratum basalis is unresponsive to the cyclic changes in ovarian hormone levels. d. The uterus is posterosuperior to the bladder and anterior to the rectum. e. The normal uterus is in an anteverted position.
2 10. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. In the uterine tubes, the fimbriae are distal to the infundibulum. b. The oviducts are lined by a ciliated epithelium. c. The external urethral orifice is anterior to the external vaginal orifice. d. Secondary follicles contain secondary oocytes. e. Lactiferous ducts convey milk from the alveoli towards the body exterior. 11. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The pelvic diaphragm supports the uterus inferiorly. b. The erectile tissue of the clitoris is homologous to the corpora cavernosa of the penis. c. The fetal ovary will contain oogonia and primary oocytes. d. The first menstrual period is known as menarche. e. The secondary oocyte is a haploid cell that is produced just before ovulation. 12. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The typical site of fertilization is the ampulla of the uterine tube. b. The first polar body and the primary oocyte are both haploid cells. c. The formation of the corpus luteum is stimulated by LH. d. The corpus luteum is maintained during the initial months of pregnancy by HCG. e. The corpus luteum eventually turns into a corpus albicans. 13. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Normally 1 graafian follicle is produced during each menstrual cycle. b. Progesterone causes a slight rise in body temperature. c. In females, meiosis II occurs if and only if fertilization occurs. d. Typically around 5000 oocytes are ovulated in a lifetime. e. A primary follicle does not have an antrum Fix the false statement questions 14. The major secretory product of the Graafian follicle is progesterone. estrogen 15. In the average female ovulation occurs on day 21 of the menstrual cycle The ovary is firmly attached to the uterus by the round ligament. ovarian 17. Contraction of the cremaster muscle will cause an increase in testicular temperature. true 18. Sustentacular cells secrete testosterone. interstitial 19. The prostatic urethra is the shortest portion of the male urethra. membranous 20. Explain how oral contraceptives consisting of high doses of progesterone can prevent fertilization. check your answer w your instructor 21. Compare and contrast oogenesis and spermatogenesis. How are they similar? How are they different? check your answer w your instructor 22. What 2 pituitary hormones are present in both males and females? What are their primary functions in males? What are their primary functions in females? check your answer w your instructor
3 23. Trace the path that a sperm would travel from the site of its production to the site of fertilization. You should name at least 17 things that the sperm cell would travel through. Then trace the path of a secondary oocyte from its release from the ovary to the site of fertilization. You name at least 3 things the secondary oocyte would travel through. check your answer w your instructor 24. As plasma [testosterone] increases beyond normal values, hypothalamic GnRH release will: 25. As ambient air temperature decreases, the distance between the testes and the abdominopelvic cavity will: 26. The conversion of a corpus luteum to a corpus albicans will cause plasma [progesterone] to: 27. As plasma [estrogen] rises, the thickness of the stratum basalis will: 28. A normal healthy female does NOT produce testosterone false 29. A vasectomy will cause a complete cessation of sperm production false 30. During ovulation, a secondary oocyte is ejected into the peritoneal cavity true 31. The presence of inhibin in the plasma can act as an indicator of pregnancy false 32. Which of the following does NOT secrete hormones involved in the reproductive system? a. Testes b. Hypothalamus c. Anterior Pituitary d. Corpus luteum e. Secondary oocyte 33. Which of the following is TRUE of menstruation? a. It occurs during the last days of the uterine cycle b. It is a sloughing off of the endometrial stratum basalis c. It is an event that is in no way affected by plasma [progesterone] d. Menstrual fluid would most likely contain deoxyribonucleic acid e. 2 of the above are true 34. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The female gametes are called ova b. The male gonads are the testes c. The testes are surrounded by a tunica albuginea and a tunica vaginalis d. The testes interstitial cells function primarily in FSH secretion 35. An adult male with a tumor that caused hypersecretion of testosterone would be expected to have: a. A greater than normal blood concentration of LH b. A lower than normal blood concentration of LH c. Developing ovaries d. Both A and C are TRUE e. Both B and C are TRUE 36. A lack of functioning bulbourethral glands could result in semen that:
4 a. Is more acidic b. Is more basic c. Has a ph of 14 d. Lacks sperm e. Lacks fructose and citrate 37. Which of the following would be the best candidate for a male birth control pill that did not affect male secondary sexual characteristics? a. A chemical that prevented testosterone synthesis b. A chemical that destroyed all testosterone receptors on body cells c. A chemical that blocked LH release d. A chemical that blocked FSH release e. A chemical that destroyed all Leydig and Sertoli cells 38. Which of the following would be farthest from the lumen in a seminiferous tubule? a. Type A spermatogonium b. Sperm c. Spermatid d. Primary spermatocyte e. Secondary spermatocyte 39. Mr. Hasselback discovered a very small, spherical cell that contained 23 chromosomes, lacked a flagellum and contained a Y chromosome. This cell is most likely an: a. Oogonium b. Sperm cell c. Spermatid d. Primary Spermatocyte e. Ovum 40. In a normal male, which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. FSH causes Sertoli cells to release ABP b. LH causes interstitial cells to release testosterone c. GnRH is released from the hypothalamus d. An increase in inhibin release would cause a decrease in LH release 41. Which of the following is TRUE? a. The external urethral orifice is posterior to the vaginal orifice b. The ovarian ligament extends laterally from the ovary to the body wall c. The ovaries, uterine tubes, and uterus comprise the female external genitalia d. The ovaries are kept approximately 3 F cooler than other pelvic organs 42. Which of the following would be present in the ovaries of a 4yr old? a. Secondary oocytes b. Primordial follicles c. Graafian follicles d. Acrosomes e. Seminiferous tubules 43. Which of the following would contain the most nuclei?
5 a. Primary oocyte b. Early primary follicle c. Vesicular follicle d. Type B spermatogonium e. Primordial follicle 44. The morphological change from a spermatid to a sperm cell is known as: a. Spermatogenesis b. Meiosis c. Spermiogenesis d. Mitosis 45. A single sperm cell would travel through the following structures in what order? 1. Seminiferous tubule 2. Penile urethra 3. Epididymis 4. Ejaculatory duct b c d e f. None of the above 46. It is within the that sperm gain the ability to swim. a. Vas deferens b. Epididymis c. Rete testis d. Spongy urethra e. Corpus cavernosa 47. The cells that comprise your cerebellum MUST have been made via: a. Mitosis b. Meiosis 48. If the sympathetic nerves to the penis were severed: a. Erection would be possible but ejaculation would not b. Ejaculation would be possible but erection would not c. Neither erection nor ejaculation would be possible d. Both erection and ejaculation would still be possible 49. Which of the following is the most anterior? a. Anal canal b. Vaginal orifice c. External os d. Internal os e. Urethral orifice 50. Which of the following cells is LEAST likely to be found within a uterine tube?
6 a. Secondary oocyte b. Polar body c. Primary oocyte d. Sperm e. Ova 51. Which of the following contains the MOST actin and myosin? a. Endometrium b. Perimetrium c. Myometrium d. Muscularis serosa e. Stratum muscularis 52. Days 1-5 of the uterine cycle are known as the proliferative phase. a. The above statement is TRUE b. The above statement is FALSE 53. The acrosome: a. Contains digestive enzymes b. Is NOT found within the midpiece c. Is haploid d. All of the above e. 2 of the above 54. Which of the following is released by the anterior pituitary gland? a. Androgen binding protein b. Gonadotropin releasing hormone c. Insulin d. Interstitial cell stimulating hormone e. Gastrin 55. Cutting the parasympathetic nerves to the penis would: a. Prevent ejaculation only b. Prevent erection only c. Prevent erection and therefore prevent ejaculation d. Prevent neither erection nor ejaculation 56. Sperm are synthesized and then mature in the seminiferous tubules. a. The above statement is TRUE b. The above statement is FALSE because sperm do not need to mature c. The above statement is FALSE because sperm mature in the clavicular recess of the scrotum d. The above statement is FALSE because sperm mature in the epididymis e. The above statement is FALSE because sperm mature in the vas deferens 57. If a spermatogonoium undergoes mitosis, it will yield: a. 4 spermatids b. 2 spermatogonia c. 2 secondary spermatocytes d. 2 primary spermatocytes e. 1 spermatid and 3 polar bodies 58. Ovarian follicles are commonly found within the medulla of the ovary.
7 a. The above statement is TRUE b. The above statement is FALSE 59. A majority (i.e., >50%) of primary follicles will become Graafian follicles. a. The above statement is TRUE b. The above statement is FALSE 60. During days 5-8 of the ovarian cycle, you would expect: a. The corpus luteum to begin secreting progesterone b. Plasma estrogen levels to rise c. The ovarian follicles to decrease in size d. The endometrium to decrease in size 61. The surge of LH release that occurs near the midpoint of the ovarian cycle causes: a. Ovulation b. Mitosis of fertile haploid oogonia c. Reverse peristalsis of the detrusor muscle of the uterus d. All of the above e. 2 of the above 62. A decrease in plasma [LH] will cause plasma [testosterone] to: 63. A decrease in plasma [testosterone] will cause plasma [LH] to: 64. An increase in plasma [inhibin] will cause plasma [FSH] to: 65. During days 5-10 of the ovarian cycle plasma [estrogen] will: 66. During days 1-10 of the ovarian cycle the number of primordial follicles in the ovary will: 67. Progesterone causes plasma [LH] to: 68. Progesterone causes the thickness of the endometrium to: 69. Progesterone causes the viscosity of cervical mucus to: 70. Progesterone causes body temperature to: 71. Estrogen causes the thickness of the endometrium to: 72. Estrogen causes the viscosity of cervical mucus to: 73. Estrogen causes the thickness of the stratum functionalis to: 74. Testosterone causes the body s metabolic rate to: 75. Estrogen causes the rate of bone resorption to: 76. A woman taking synthetic progesterone would expect her plasma estrogen levels to: 77. Which of the following are carried by the components of the spermatic cord?
8 a. Blood b. Lymph c. Sperm d. Action potentials e. All of the above 78. Put the following in the correct path that a sperm would take. a. 1. Ampulla of oviduct b. 2. Internal os of the cervix c. 3. Uterine cavity d. 4. Ductus deferens e. 5. Penile urethra b c d e f Which of the following is the GREATEST? a. Number of sperm produced from a single spermatogonium b. Number of seminiferous tubules in a single testis c. Number of skeletal muscle cells in the internal urethral sphincter d. Length in inches of the membranous urethra e. Number of chromosomes in a spermatid 80. Which of the following is TRUE of the epididymis? a. It is a site of sperm maturation b. Each testis is associated with a single epididymis c. It contains smooth muscle d. All of the above e. 2 of the above 81. Which part of the sperm is responsible for digesting the corona radiata that covers an ovulated oocyte? a. Flagellum b. Cilia c. Acrosome d. Haploid nucleus e. Amphioxus 82. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The spermatic cord passes through the inguinal canal b. 2 ejaculatory ducts empty into the prostate gland c. The penile urethra is found within the corpus cavernosa d. The seminal vesicles secrete fructose as a food source for sperm e. Ejaculation is primarily mediated by the sympathetic nervous system 83. Which of the following is the fewest in number?
9 a. Total number of primordial follicles a woman has in her lifetime. b. Total number of primary follicles a woman has in her lifetime. c. Total number of secondary follicles a woman has in her lifetime. d. Total number of Graafian follicles a woman has in her lifetime. e. It cannot be determined 84. Which of the following is CORRECT? a. # of chromosomes in a spermatogonium > # of chromosomes in an oogonium b. # of chromosomes in a secondary spermatocyte = # of chromosomes in a secondary oocyte c. # of vas deferentia in a male = # of ova produced by meiosis of one oogonium d. Size of a polar body > size of an ovum e. All of the above 85. is the primary hormone secreted by the ovary during the follicular phase. a. HCG b. Progesterone c. Estrogen d. Aldosterone 86. What hormone causes ovulation? a. GnRH b. LH c. FSH d. Estrogen e. Progesterone 87. Which of the following hormones is found in both males and females? a. LH b. FSH c. Aldosterone d. GnRH e. All of the above 88. Sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea are more likely to cause peritonitis in females than in males. Which of the following is the most likely reason for this difference? a. Males do not perform meiosis, whereas females do. b. The male urethra performs both urinary and reproductive functions. c. The Fallopian tube is open to the peritoneal cavity d. Male orgasm is usually accompanied by ejaculation of semen e. Females secrete progesterone almost continuously 89. Which of the following cells is haploid? a. Cardiac muscle cell b. Oogonium c. Spermatogonium d. Spermatid e. 2 of the above 90. Which phase of the uterine cycle would coincide with high levels of progesterone?
10 a. Menstrual b. Follicular c. Secretory d. Proliferative e. Ovarian 91. Which of the following does NOT belong? a. Ovary b. Prostate c. Fallopian tube d. Uterus e. Clitoris 92. A leiomyoma is a very common benign tumor that originates within uterine smooth muscle. Based on this, you could assume that a leiomyoma would most likely be found in the: a. Parietal biliary peritoneum b. Labia minora c. Epididymis d. Lactiferous ductule e. Myometrium 93. Which of the following is INCORRECT? a. Primary follicle contains a primary oocyte b. Secondary follicle contains a primary oocyte c. Primordial follicle only found in individuals who have gone through puberty d. Graafian follicle largest, most mature follicle type, which is distinguished by its large antrum. 94. Following ovulation, the remaining follicle cells are transformed into a: a. Corpus albicans b. Vesicular follicle c. Secondary hemorrhagicum d. Corpus luteum e. Bulbospongiosum 95. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The fimbriae of the uterine tube contain cilia. b. The opening between the cervical canal and the vagina is the external os. c. The lumen of the fallopian tube is continuous with the peritoneal cavity d. In most women the uterus is retroverted and flexed anteriorly e. The cervical mucosa contains mucus-secreting glands 96. Which of the following is closest to the liver? a. Stratum functionalis of the endometrium b. Stratum basalis of the endometrium c. Myometrium d. Perimetrium e. External vaginal orifice 97. In terms of chromosome number, which of the following is most similar to a spermatid?
11 a. Spermatogonium b. Primary spermatocyte c. Oogonium d. Detrusor cell e. Second polar body 98. Which of the following is TRUE? a. The seminiferous tubules are the major sites of FSH secretion in the male body. b. Erectile tissues are only found in males. c. Ciliated cells are in greater abundance in the male reproductive ducts than in the female reproductive ducts. d. The prepuce is a common term for the glans penis Which of the following is TRUE? a. A zygote is an example of a haploid cell. b. Spermiogenesis is the process by which a spermatid develops into a sperm. c. Type A spermatogonia only divide meiotically. d. Sustentacular cells are primarily found within the medial glans penis. e. A primary spermatocyte will have half as much DNA as a diploid cell. 100.Which of the following is TRUE? a. Both sperm and PCT cells contain multiple mitochondria. b. The acrosome is found within the flagellum of the sperm and primarily contains digestive enzymes. c. During meiosis, one haploid cell divides twice to form four diploid cells. d. Most spermatids are not found within seminiferous tubules. e. Both A and B are true.
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Revised Spring 2006 1
 It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
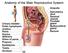 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Chapter 28: The Reproductive System
 Chapter 28: The Reproductive System Chapter Objectives MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. List the major components of the male reproductive system and their general functions. 2. Explain the structure of the
Chapter 28: The Reproductive System Chapter Objectives MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. List the major components of the male reproductive system and their general functions. 2. Explain the structure of the
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Chapter 28: Reproductive System
 I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Reproductive System (Chapter 28) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College. Eastern Campus
 Reproductive System (Chapter 28) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Reproductive System (Chapter 28) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
CHAPTER 22: THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS. 3. Define the terms meiosis, DNA, somatic cells, gametes, diploid, haploid and zygote.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones
 Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones Fertilization Gametes Oocyte, Sperm Acrosomal reaction
Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones Fertilization Gametes Oocyte, Sperm Acrosomal reaction
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System. Major Organs. Function: producing offspring. External Reproductive Organs
 Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar. W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C.
 Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C. 27695-7621 Introduction The boar has a tremendous impact on the reproductive efficiency
Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C. 27695-7621 Introduction The boar has a tremendous impact on the reproductive efficiency
The cry of a cat in heat, insects chirping outside the window,
 59 Sex and Reproduction Concept Outline 59.1 Animals employ both sexual and asexual reproductive strategies. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction. Some animals reproduce asexually, but most reproduce sexually;
59 Sex and Reproduction Concept Outline 59.1 Animals employ both sexual and asexual reproductive strategies. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction. Some animals reproduce asexually, but most reproduce sexually;
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3
 Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 3 The first steps to forming a new organism Descriptive embryology I Germ cell formation / gametogenesis And Fertilisation Why bother with sex? In terms of
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
The Endocrine System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012
 Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services
 For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services FAMILY PLANNING AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH In July 2011, FHI became FHI 360. FHI 360 is a nonprofit human development organization dedicated to improving lives
For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services FAMILY PLANNING AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH In July 2011, FHI became FHI 360. FHI 360 is a nonprofit human development organization dedicated to improving lives
Course Syllabus National College of Midwifery 2012 08/2012
 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Credits: 4.0 Course Description: This course provides a thorough survey of human anatomy and physiology, including proper identification of body planes and sections
Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Credits: 4.0 Course Description: This course provides a thorough survey of human anatomy and physiology, including proper identification of body planes and sections
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
BIOL2020 Human Anatomy and Physiology II RSCC. Prepared microscope slides of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue
 Lab 1 Muscle tissue overview Structure and function of skeletal muscles Muscles of facial expression Prepared microscope slides of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue Muscle models and cadaver
Lab 1 Muscle tissue overview Structure and function of skeletal muscles Muscles of facial expression Prepared microscope slides of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue Muscle models and cadaver
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
regulation of ECF composition and volume regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon
 Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
1. AMOUNT OF FSH PRESENT
 The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Hormonal regulation of gonad function overview
 Hormonal regulation of gonad function overview Role of hormones in reproductive functions production and maintenance of mature gametes optimization of the circumstances of impregnation support of pregnancy,
Hormonal regulation of gonad function overview Role of hormones in reproductive functions production and maintenance of mature gametes optimization of the circumstances of impregnation support of pregnancy,
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
Reproductive Anatomy and Fertility
 Describe the functions of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems. Analyze factors that affect male and female fertility. Outline the process of estrous and estrus. UNIT Objectives 4 Discuss
Describe the functions of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems. Analyze factors that affect male and female fertility. Outline the process of estrous and estrus. UNIT Objectives 4 Discuss
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
Course: AG 534 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction
 Course: AG 53 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction Unit Objective CAERT Lesson Plan Library Unit Problem Area Les son Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 1,2, 3 Introduction to Animal Science Match terms
Course: AG 53 Zoology - Science of Animal Reproduction Unit Objective CAERT Lesson Plan Library Unit Problem Area Les son Animal. Plant & Soil Science 1 1,2, 3 Introduction to Animal Science Match terms
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Understand the organization of the ovary. 2. Understand the arrangement of cells that make up an
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Dr. Paul W. L. Kwan Tufts University School of Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Understand the organization of the ovary. 2. Understand the arrangement of cells that make up an
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Unit #5 Human Growth and Development 6 th Grade - Chapter 7, 8 7 th Grade - Chapter 12 8 th Grade - Chapter 16, 17
 8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
PART 3: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 PART 3: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONTENTS 1. Normal female reproductive tract histology 2. Endocrine control of the oestrous cycle 3. Morphological changes during the oestrous cycle 4. Normal background
PART 3: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONTENTS 1. Normal female reproductive tract histology 2. Endocrine control of the oestrous cycle 3. Morphological changes during the oestrous cycle 4. Normal background
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 15. The Urinary System. Slides 15.1 15.20. Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM
 UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM 1 UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM Reading Gray s Anatomy for Students (GAFS), Chapters 4-5 Gray s Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy (GDGHA), Labs 10-17 Unit
UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM 1 UNIT #2 - ABDOMEN, PELVIS AND PERINEUM Reading Gray s Anatomy for Students (GAFS), Chapters 4-5 Gray s Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy (GDGHA), Labs 10-17 Unit
What is artificial insemination (AI)?
 Dr. Osama Ibrahim Azawi Department of Surgery and Obstetrics Lecture in Artificial Insemination 1 Preface Today, the artificial insemination has become a normal method of breeding quality cattle. A large
Dr. Osama Ibrahim Azawi Department of Surgery and Obstetrics Lecture in Artificial Insemination 1 Preface Today, the artificial insemination has become a normal method of breeding quality cattle. A large
Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract
 Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract Andrew Healey Contents 1 Introduction... 21 2 Embryology of the Female Genitourinary Tract... 22 2.1 Development of the Gonads... 22 2.2 Relationship Between
Embryology of the Female Reproductive Tract Andrew Healey Contents 1 Introduction... 21 2 Embryology of the Female Genitourinary Tract... 22 2.1 Development of the Gonads... 22 2.2 Relationship Between
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
QI05024 A PRACTICAL GUIDE. Artificial Breeding. of beef cattle
 QI05024 A PRACTICAL GUIDE Artificial Breeding of beef cattle QI05024 A PRACTICAL GUIDE Artificial Breeding of beef cattle Queensland Primary Industries and Fisheries ISSN 0727-6073 ISBN 0 7345 0309 3
QI05024 A PRACTICAL GUIDE Artificial Breeding of beef cattle QI05024 A PRACTICAL GUIDE Artificial Breeding of beef cattle Queensland Primary Industries and Fisheries ISSN 0727-6073 ISBN 0 7345 0309 3
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
PUBERTY. Dr. Valérie M. Schwitzgebel. Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Hôpital des Enfants HUG Genève Valerie.Schwitzgebel@hcuge.
 PUBERTY Dr. Valérie M. Schwitzgebel Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Hôpital des Enfants HUG Genève Valerie.Schwitzgebel@hcuge.ch V. Schwitzgebel 2004 PHYSIOLOGY of PUBERTY DEFINITION
PUBERTY Dr. Valérie M. Schwitzgebel Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Hôpital des Enfants HUG Genève Valerie.Schwitzgebel@hcuge.ch V. Schwitzgebel 2004 PHYSIOLOGY of PUBERTY DEFINITION
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
URINARY and GENITAL SYSTEM: Sylabus for foreign students from microscopic anatomy
 Department of Histology and Embryology, P.J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice URINARY and GENITAL SYSTEM: Sylabus for foreign students from microscopic anatomy Authors: MVDr. Štefan TÓTH, PhD.;
Department of Histology and Embryology, P.J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice URINARY and GENITAL SYSTEM: Sylabus for foreign students from microscopic anatomy Authors: MVDr. Štefan TÓTH, PhD.;
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Timing is everything. Ovulation Tracking. Patient Information Booklet
 Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY
 COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY Policy: Infertility Evaluation and Treatment Number: MM 1306 Date Effective:
COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY Policy: Infertility Evaluation and Treatment Number: MM 1306 Date Effective:
NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING
 NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING 1 MODULE 1: SEX AND SEXUALITY Unit 1: The Concepts of Sex and Sexuality Unit 2: Human
NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING 1 MODULE 1: SEX AND SEXUALITY Unit 1: The Concepts of Sex and Sexuality Unit 2: Human
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models:
 Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Ch16 Endocrine part 2
 Ch16 Endocrine part 2 several separate organs release hormones into capillaries hormones are transported in the blood Hypothalamus Pituitary glands Pineal gland Thyroid Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal Cortex
Ch16 Endocrine part 2 several separate organs release hormones into capillaries hormones are transported in the blood Hypothalamus Pituitary glands Pineal gland Thyroid Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal Cortex
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao.
 Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
