Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3
|
|
|
- Madeline Golden
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems, given drawings without labels. 2. Recall and pronounce the names of at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems, given descriptions of their functions. Agenda 1. Discuss the purpose of the lesson. 2. Use the blackboard or Transparencies 1-6 to describe the male and female reproductive systems (including the size, shape, location, and function of each part). 3. Hand out Reproductive System Worksheets, filling them out as a whole class. 4. Hand out the Reproductive System Reference Sheet, having volunteers read it aloud if time allows. 5. Assign homework. 3-1
2 Materials Needed Photocopies One transparent copy of: Reproductive System, Transparencies 1-6 One per student of: Reproductive System, Worksheets 1 and 2 Reproductive System, Reference Sheet Individual Homework Exercise: The Reproductive System 3-2
3 Activities 1. Identify the lesson as, primarily, a review of information many students learned in earlier grades. Explain, too, that being well-grounded in knowledge about the reproductive system will help them make sense of discussions later in the unit about birth control, diseases, etc. 2. Use the blackboard (drawing the reproductive systems) and/or Reproductive System Transparencies 1-6 to describe the functions and the sizes/locations/shapes of each part. This should take minutes. These lecture notes will help: Navel PART JOBS / FUNCTION(S) allows passage of oxygen and nourishment, before birth... then it stops working APPROXIMATE ADULT SIZE/LOCATION/SHAPE on the abdomen, it isn t part of the reproductive system Abdomen (also called the belly) Buttocks Pelvis (the pelvic region the lower abdomen) Penis (made up of shaft, glans, and sometimes foreskin) Foreskin Scrotum Testes (singular=testis also called testicles) contains most of our internal organs provides cushion for tail bone; contains muscles for movement supports and protects the internal reproductive organs allows passage of urine; allows passage of semen; provides sensation (has many nerve endings) protects the glans of the penis; provides sensation; males who have been circumcised don t have one holds testes; controls temperature; provides sensation produce sperm; produce sex hormones (androgens, testosterone) JOBS / the part of the body between the rib cage and the pelvis isn t part of the reproductive system Bowl-shaped bone structure 3-5 inches, when not erect 5-7 inches, when erect like a sleeve, covers most of the glans of the penis when it isn t erect muscular sac which is shorter when cold, longer when warm (two) comparable to small plums, each is made of over a mile of tightly coiled tubes, they re parts of both reproductive and endocrine systems APPROXIMATE ADULT 3-3
4 PART FUNCTION(S) SIZE/LOCATION/SHAPE Epididymis (plural=epididymes) allow maturation of sperm (two)more tubes, they form a cap on the back and top of the testes, each leading from one of the testicles Cilia (singular=cilium) Spermatic cords Vas deferens (plural=vasa deferentia also called sperm ducts) sweep an ovum down the fallopian tube; sweep sperm cells through the epididymis suspend the testis; supply blood to the testis; provide sensation; carry sperm from the testis provides storage for sperm; allow passage of sperm (many) hair-like structures which line the fallopian tubes and the epididymes (also line lungs) (two) each one is a multistranded cable, consisting of 2 arteries, 3 groups of veins, some nerve branches, and one vas deferens (two) each is as big around as sewing thread (inside diameter at the end nearest the epididymis) they lead into the abdomen, where (behind the bladder) they widen into storage sacs Bladder provides storage for urine comparable to an orange; it isn t part of the reproductive system Seminal vesicles Semen Prostate gland Cowper s glands (also called bulbourethral glands) contribute fructose (sugar) to semen for nourishing the sperm helps sperm live longer and travel better contributes fluid to semen for sperm s mobility (their ability to travel) produce fluid that cleanses the urethra of acid (from urine) to protect the sperm (two) 2 inch sacs, each opens into a vas deferens (about a teaspoonful per ejaculation) comparable to a grape, it lies below the bladder (two) comparable to pearls, they re below the prostate on either side of the urethra (opening into it) PART JOBS / FUNCTION(S) APPROXIMATE ADULT SIZE/LOCATION/SHAPE 3-4
5 Urethra Anus Uterus (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb) Cervix Vagina (also called birth canal...partly covered at birth, in most cases by a hymen) Hymen allows passage of urine in males; allows passage of semen allows passage of bowel movement (feces); provides sensation (has many nerve endings) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby; allows nutrient and waste exchange with placenta; nourishes an embryo, before a placenta grows produces fluids to help sperm travel; produces a mucous plug to keep germs out during pregnancy allows passage of shed endometrium during menstruation; allows passage of sperm; allows passage of baby; produces fluids to cleanse and lubricate itself and to help sperm travel; provides sensation (has many nerve endings) none that we know of for sure, but it may decrease the risk of infection; may be stretched during sexual intercourse or by using a tampon or through physical activities such as sports or riding a bike in female, it s the front of three openings and isn t part of the reproductive system in male, it s the tube inside the penis the opening from the rectum and lower intestines, it isn t part of the reproductive system in female, it s the third of three openings comparable to upside-down pear, when not pregnant, but very stretchy the neck of the uterus, it s opening into the vagina looks like a tiny pink donut, feels like tip of the nose a collapsed tube, like a notblown-up balloon, 2-4 inches long when not sexually aroused and not giving birth, but very stretchy is the middle of female s three openings membrane partly covering vaginal opening PART JOBS / FUNCTION(S) APPROXIMATE ADULT SIZE/LOCATION/SHAPE Ova carry strings of genes called (usually one per cycle) about the 3-5
6 (singular= ovum also called egg cell) Ovaries (singular=ovary) Fallopian tubes Fimbria (plural= fimbriae) Vulva (made up of labia majora, labia minora, and clitoris) Clitoris (made up of shaft, glans and hood) Clitoral hood chromosomes to provide plans for next generation provide storage for ova; allow maturation of ova; produce sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, androgens) allow passage of ova; allow passage of sperm find an ovum and bring it into a fallopian tube protects openings of urethra and vagina, as eyelids protect eyes; provides sensation (has many nerve endings) provides sensation (has many nerve endings) protects the glans of the clitoris; provides sensation (has many nerve endings) size of the period at the end of a sentence (.) (two) comparable to small plums, they re parts of both reproductive and endocrine systems; they are attached by ligaments, to each side of the uterus (two) 4 inches long, trumpetshaped, not much larger than ovum at uterine end... with finger-like fimbriae at loose end, and lined with hair-like cilia (many) fringe-like or finger-like outer ends of the fallopian tube labia are folds of skin; outer labia (labia majora) has pubic hair shaft about 1 inch long, glans comparable to a pearl at front of vulva, where the labia meet like a cap, mostly covers the clitoris, when it isn t erect 3. Hand out Reproductive System Worksheets 1 and 2. Fill them out aloud together, encouraging as much participation by the students as possible. 4. Hand out the Reproductive System Reference Sheet. If time allows, have volunteers take turns reading it aloud. If not, simply explain that people should read it as part of their homework. Homework Make sure students realize that this particular homework is due tomorrow. Answers to the Individual Homework Exercise are as follows: BOX ONE: MALE 1. Cowper s gland (2) 6. scrotum (1) 3-6
7 2. epididymis (2) 3. foreskin (1) * 4. penis (1) 5. prostate gland (1) BOX TWO: FEMALE 1. cervix (1) 2. clitoral hood (1) * 3. clitoris (1) * 4. fallopian tube (2) 5. fimbria (M) 7. seminal vesicle (2) 8. spermatic cord (2) 9. testicle (2) 10. vas deferens (2) 6. hymen (1) * 7. ovary (2) 8. uterus (1) 9. vagina (1) 10. vulva (1) BOX THREE: PARTS THAT PEOPLE OF ANY SEX HAVE 1. abdomen (1) 5. cilia (M) 2. anus (1) 6. navel (1) 3. bladder (1) 7. pelvis (1) 4. buttocks (1) 8. urethra (1) Each correct answer is worth 2 points, if spelled correctly (only 1 point, if misspelled). Each answer in parentheses is worth another point. Thus, the total possible so far is 84 (28 X 3). FILL IN THE BLANKS: A) ovum B) ova C) sperm D) semen E) ejaculation F) menstruation G) nocturnal emission Each correct word is worth 2 points ( nocturnal emission counts as two separate words, each worth 2 points) if spelled correctly (1 point, if misspelled). Thus, the total possible for the fill-inthe-blanks section is 16 (8 X 2). So the exercise is worth 100 points, altogether. * Give the student 5 bonus points if they thought to mention that some people do not have the asterisked (*) parts. For example, if a female has experienced ritual genital mutilation, she may no longer have a clitoris or clitoral hood. If a male has been circumcised, he will no longer have a foreskin. If a female has had vaginal intercourse, masturbated with a finger or sex toy, used tampons, or ridden a bike or a horse, she may have less hymen or none at all. Thus, the most accurate answer for clitoris would be (0-1), for foreskin (0-1) and for hymen (0-1). 3-7
8 Reproductive System Transparency 1 NAVEL ABDOMEN PELVIS FEMALE MALE NOTE: The illustrations on these transparencies do not represent all people s bodies, including people who haven t reached puberty, heavier people, and some people who are trans and/or intersex. 3-8
9 Reproductive System Transparency 2 SHAFT OF PENIS SCROTUM GLANS OF PENIS FORESKIN PENIS BUTTOCKS SCROTUM 3-9
10 Reproductive System Transparency 3 BLADDER SEMINAL VESICLE PROSTATE GLAND VAS DEFERENS COWPER S GLAND URETHRA EPIDIDYMIS TESTIS SPERMATIC CORD VAS DEFERENS VEINS and ARTERIES EPIDIDYMIS TESTIS Cilia line each vas deferens. SCROTUM 3-10
11 Reproductive System Transparency 4 FALLOPIAN TUBE UTERUS BLADDER OVARY URETHRA SHAFT of CLITORIS GLANS of CLITORIS ANUS VAGINA Cilia line each fallopian tube. 3-11
12 Reproductive System Transparency 5 UTERUS OVARY CERVIX FIMBRIA VAGINA 3-12
13 Reproductive System Transparency 6 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE GENITALS TWO OR THREE MONTHS GESTATION LABIO-SCROTAL SWELLING GLANS AREA URETHRAL GROOVE ANAL PIT TAIL (CUT AWAY) FULLY DEVELOPED GLANS of PENIS FORESKIN SHAFT of CLITORIS CLITORAL HOOD GLANS of CLITORIS URETHRA SHAFT of PENIS LABIA MAJORA LABIA MINORA VAGINA HYMEN SCROTUM ANUS 3-13
14 Reproductive System Worksheet CILIA LINE EACH VAS DEFERENS NOTE: The illustrations on these worksheets do not represent all people s bodies, including people who haven t reached puberty, heavier people, and some people who are trans and/or intersex. 3-14
15
16 Reproductive System Worksheet
17 Reproductive System Worksheet 3 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE GENITALS TWO OR THREE MONTHS GESTATION LABIO-SCROTAL SWELLING GLANS AREA URETHRAL GROOVE ANAL PIT TAIL (CUT AWAY) FULLY DEVELOPED * This does not represent all bodies, inlcuding trans and/or intersex folks. 3-17
18 Reproductive System Reference Sheet: Glossary ABSTINENCE Choosing not to do something. In this context, it means choosing not to have sexual intercourse. Most people abstain from intercourse at some times during their lives. DISCHARGE Fluid. Urine and semen are kinds of discharge, but the word is usually used to describe either the normal wetness of the vagina or the abnormal wetness that may come from an infection in the penis or the vagina. EJACULATION The release of semen from the penis. ERECTION The penis or clitoris filling with blood and becoming larger and harder. FECES Solid waste that is made in the intestines (the bowels). It is sometimes called a bowel movement or poop. It is released through the anus when we go to the bathroom. GENITALS The parts of the reproductive system located on the outside of a person s body. The female genitals may also be called the vulva. MASTURBATION A person massaging their own genitals or other parts of the body for pleasure or comfort. Most people masturbate at some times during their lives; some choose not to. It is safe; it can t cause pregnancy, spread disease, or lead to a broken heart. Each culture, religion, and family has its own beliefs about whether or when it is OK to masturbate. MENSTRUATION The lining of the uterus (the endometrium) emptying out. It is sometimes called having a period. NOCTURNAL EMISSION Ejaculation of semen during sleep. It is sometimes called having a wet dream, although it doesn t mean the person was necessarily dreaming. ORGASM Very pleasurable sensation. It is a series of muscular contractions of the reproductive organs, followed by muscular relaxation and a sense of relief. Masturbation and sexual intercourse often lead to orgasm. In males ejaculation usually happens at the same time. 3-18
19 OVULATION The release of an ovum from the ovary. OVUM The cell from a woman (called, in English, an egg ) which carries strings of genes (called chromosomes) to provide the plans for the next generation. The plural of ovum is ova. REPRODUCTION Making more of something. In this context, it means humans making babies... more humans. SEMEN The fluid which helps sperm live longer and travel more easily. SEX Sex can mean the biological differences in people s brains and bodies that make them male or female. It can also mean a wide range of activities, including oral, anal or vaginal intercourse; putting fingers, hands or sex toys into the vagina or the anus; masturbating; and rubbing bodies together, with or without clothes on. SEXUAL INTERCOURSE Some specific kinds of sex. It is called vaginal intercourse when a penis is inside the vagina. Most pregnancies begin this way. It is called oral intercourse when the mouth touches the genitals. It is called anal intercourse when a penis is inside the anus. Each culture, religion, and family has its own beliefs about when sexual intercourse is OK and about which kinds are OK. SEXUALITY The part of all human beings which has to do with being male or female, being able to trust and love, needing and enjoying touch and closeness, liking and respecting ourselves and others, and reproducing (making babies). SMEGMA The paste-like discharge that collects between the glans of the penis and the foreskin, or between the glans of the clitoris and the clitoral hood. It provides lubrication, but it can collect bacteria and have a strong odor if it isn t washed away regularly. SPERMATAZOON The cell from a man (usually called sperm, for short) which carries strings of genes (called chromosomes ) to provide the plans for the next generation. The plural of spermatazoon is spermatazoa. URINE Liquid waste, sometimes called pee, that is made in the kidneys and stored in the bladder. It is released through the urethra, when we go to the bathroom. Urine is not the same as semen. 3-19
20 Individual Homework Exercise: The Reproductive System NAME NOTE: DUE TOMORROW! DIRECTIONS: 1. Put each part in the proper box. Box One is for parts that only males have. Box Two is for parts that only females have. Box Three is for parts that all people have. have. 2. Then, in the parentheses, write 1 if each person has one of that part. Write 2 if a person has two of them. Write M if a person has many of them. YOU WILL USE ALL OF THE FOLLOWING TERMS: abdomen anus bladder buttocks cervix cilium clitoral hood clitoris Cowper s gland epididymis fallopian tube fimbria foreskin hymen navel ovary pelvis penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle spermatic cord testicle urethra uterus vagina vas deferens vulva BOX ONE: MALE PARTS 1. ( ) 2. ( ) 3. ( ) 4. ( ) 5. ( ) 6. ( ) 7. ( ) 8. ( ) 9. ( ) 10. ( ) 3-20
21 BOX TWO: FEMALE PARTS 1. ( ) 2. ( ) 3. ( ) 4. ( ) 5. ( ) 6. ( ) 7. ( ) 8. ( ) 9. ( ) 10. ( ) BOX THREE: PARTS THAT PEOPLE OF ANY SEX HAVE 1. ( ) 2. ( ) 3. ( ) 4. ( ) 5. ( ) 6. ( ) 7. ( ) 8. ( ) 9. ( ) 10. ( ) 3-21
22 MORE DIRECTIONS: Answer the questions below. (The answers are not on the list above. You will find them, though, on the Reproductive System Reference Sheet.) Spelling counts. A. What is the Latin word for an egg cell? B. What is the plural for that? C. What is the common word for spermatazoa? D. What fluid carries and nourishes them? E. When this fluid comes out of the penis, what is that called? F. What is the medical word for period? G. What is the medical term for wet dream? 3-22
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Unit #5 Human Growth and Development 6 th Grade - Chapter 7, 8 7 th Grade - Chapter 12 8 th Grade - Chapter 16, 17
 8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Here we will talk about:
 Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Agenda: 1. Help students learn about health and major body systems. 2. Introduce the reproductive system
 FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE
 Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
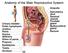 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
Growing up what s it all about?
 4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up. (for boys and girls)
 What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury
 Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-6.3:
 GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Revised Spring 2006 1
 It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Boys and Puberty. about body changes and other stuff!
 Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! In this booklet, we ve got together a heap of information so that you can be informed about the important stuff.
Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! In this booklet, we ve got together a heap of information so that you can be informed about the important stuff.
identify the physical, interpersonal, and emotional aspects of healthy human beings
 Lesson Four Title: Theme: Time: Materials: You, Your Body and Puberty Puberty for Boys and Girls 110 minutes External Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz External
Lesson Four Title: Theme: Time: Materials: You, Your Body and Puberty Puberty for Boys and Girls 110 minutes External Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy - Quiz External
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Gonorrhoea. Looking after your sexual health
 Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
Boys and. about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM
 Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 2 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM In
Boys and Puberty Everything boys will ever need to know about body changes and other stuff! 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 1 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM 10368 Boys & Puberty 23260.indd 2 8/4/09 11:12:17 AM In
Vaginal corona. Myths surrounding virginity your questions answered
 Vaginal corona Myths surrounding virginity your questions answered RFSU wish to thank translator Jonas Hartelius for valuable comments, and not at least, for the term vaginal corona. Content Anna Knöfel
Vaginal corona Myths surrounding virginity your questions answered RFSU wish to thank translator Jonas Hartelius for valuable comments, and not at least, for the term vaginal corona. Content Anna Knöfel
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
That being said, consider the following as you decide whether or not a vasectomy is your best option for birth control.
 Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Since you re reading this, you are probably strongly considering a vasectomy as a way to enjoy sex without the risk of pregnancy. You may feel nervous or hesitant to get one or have questions and concerns
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Leader's Resource. Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms.
 Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
Leader's Resource Information on Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Signs and Symptoms of STDs Note: Both men and women can have an STD without physical symptoms. Any of the following can indicate to
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
Questions, Questions, Questions
 1 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and your
1 2 Puberty! Puberty is the biological transition from childhood to adulthood. Your body is changing to make it possible to have a baby in the future. Puberty affects your body, your thoughts and your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
Chlamydia THE FACTS. How do people get Chlamydia?
 What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
What is Chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection that is sexually transmitted and often causes no symptoms. If not treated, chlamydia can damage reproductive organs and make it difficult for
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Some activities need additional guidance, or can be expanded: These are your testicles, this is where semen and sperm is made.
 P UBERTY This section includes: Teachers Notes changes - Female changes - Male Inside a boys body Inside a girls body Inside our bodies Boys growing up Girls growing up Hormones Coping with emotions Being
P UBERTY This section includes: Teachers Notes changes - Female changes - Male Inside a boys body Inside a girls body Inside our bodies Boys growing up Girls growing up Hormones Coping with emotions Being
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
II. III. 2004 Core Knowledge National Conference, Grade Level, (Unit Name Here) 1
 Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
Teaching A Touchy Topic: Life Cycles and Reproduction Grade Level: Fifth Grade Written by: Kimberly Ruckh, Linda Cambra, Dallas Bankston; Challenge Charter School, Glendale, Az. Length of Unit: Five Lessons
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING
 NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING 1 MODULE 1: SEX AND SEXUALITY Unit 1: The Concepts of Sex and Sexuality Unit 2: Human
NATIONAL OPEN UNIVERSITY OF NIGERIA SCHOOL OF EDUCATION COURSE CODE: EGC 903 COURSE TITLE: SEX AND FAMILY COUNSELLING 1 MODULE 1: SEX AND SEXUALITY Unit 1: The Concepts of Sex and Sexuality Unit 2: Human
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse. Your Body s Design for Bladder Control
 National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse Your Body s Design for Bladder Control BLADDER Let s talk about bladder control for women. There s treatment that works. CONTROL Let s Talk
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse Your Body s Design for Bladder Control BLADDER Let s talk about bladder control for women. There s treatment that works. CONTROL Let s Talk
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
There are four areas where you can expect changes to occur as your hormone therapy progresses.
 You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
Chlamydia. Looking after your sexual health
 Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
How To Choose Between A Vaginal Birth Or A Cesarean Section
 Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Bowel Control Problems
 Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Bowel Control Problems WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Bowel control problems affect at least 1 million people in the United States. Loss of normal control of the bowels is
Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood.
 Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood. Puberty can start as early as 8 or 9 years old or as late as 18 or 19 years old. The average age for girls is 10.5 years old. The average age for
Puberty is the bridge between childhood and adulthood. Puberty can start as early as 8 or 9 years old or as late as 18 or 19 years old. The average age for girls is 10.5 years old. The average age for
Chapter 28: Reproductive System
 I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
FAMILY LIFE EDUCATION ACPS Fifth Grade
 Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
Table of Contents UNIT I FAMILY...2 Relatives and Family Friends...2 Similarities and Differences among Families...2 UNIT II PERSONAL AND SEXUAL SAFETY... 3 Sexual Safety Good and Bad Touching... 3 UNIT
CHAPTER 22: THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS. 3. Define the terms meiosis, DNA, somatic cells, gametes, diploid, haploid and zygote.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
OBJECTIVES: 1. Briefly explain why human reproduction is significant, and how sexual reproduction always results in a unique zygote. 2. List the functions of the reproductive systems. 3. Define the terms
Syphilis. Looking after your sexual health
 Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology
 Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Lesson 251c Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology Core Area. Animal Science Unit 250. Genetics and Breeding Topic 251. Fertilization California Academic Standard. Science Grades 9 through 12 Biology/Life
Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1
 Mary Wenstrom Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1 Health Education Grade 10 Content Area: Sexuality Education Health Literacy: Effective Communicator and Critical Thinker Life Skills: Understanding Adolescence,
Mary Wenstrom Sexuality Education Lesson Plan #1 Health Education Grade 10 Content Area: Sexuality Education Health Literacy: Effective Communicator and Critical Thinker Life Skills: Understanding Adolescence,
Vasectomy Services Patient Information
 Vasectomy Services Patient Information Vasectomy Vasectomy Please read this information leaflet and consent form carefully, and bring it with you to your appointment. Please ask the doctor any questions
Vasectomy Services Patient Information Vasectomy Vasectomy Please read this information leaflet and consent form carefully, and bring it with you to your appointment. Please ask the doctor any questions
Human Embryonic Development. Human fetal development
 Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Human Embryonic Development Day 1: 1 st cleavage 1 cell becomes 2 (2-cell stage) Day 2: 2 nd cleavage 4-cell stage Day 3: 6-12 cell stage can test at this stage for genetic diseases if done by IVF Day
Vasectomy: Patient Information. Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon
 Vasectomy: Patient Information by Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon An educational service provided by: bergen Urological associates Stuart H. Levey, M.D. Andrew L.
Vasectomy: Patient Information by Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon An educational service provided by: bergen Urological associates Stuart H. Levey, M.D. Andrew L.
