Lab 3-4b OSPF over Frame Relay
|
|
|
- Evangeline Carr
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab 3-4b OSPF over Frame Relay Learning Objectives Configure OSPF over Frame Relay Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types Modify default OSPF timers Topology Note on serial interface numbering: Given the diversity of router models and the associated differing naming conventions for serial interfaces (S0, S0/0, S0/0/0), the actual interface numbers on your devices probably differ from those above. The same is true concerning which side of the link is DCE or DTE. You should always draw your own network diagram based upon your specific physical topology. If you are uncertain which side of the connection is DCE, use the show controllers serial interface number command: HQ# show controllers serial0/0/0 Interface Serial0/0/0 Hardware is GT96K DCE V.35, clock rate CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
2 Scenario You are responsible for configuring the new network to connect your company s east branch and west branch through the company headquarters represented by loopback interfaces on each of the three routers. The physical devices have just been installed and connected over Frame Relay hub-and-spoke. Configure OSPF to allow full connectivity between all departments. There will also be an Ethernet connection between East and West. This represents a backup line given by a service provider. This topology may appear again in future labs, so save your configuration when you are done. Step 1: Addressing Set up the Frame Relay switch connecting the routers to have the DLCIs indicated in the diagram between HQ and East and HQ and West. Then configure the router physical interfaces with IP addresses. On the interfaces connected to the Frame Relay switch, configure Frame Relay encapsulation with Inverse ARP disabled and use Frame Relay map statements. Make sure you include the broadcast keyword in your map statements and local Frame Relay maps so that you can ping yourself. Also set up the loopback interfaces. HQ# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. HQ(config)# interface loopback 1 HQ(config-if)# ip address HQ(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# ip address HQ(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay ietf HQ(config-if)# no frame-relay inverse-arp HQ(config-if)# frame-relay map ip HQ(config-if)# frame-relay map ip broadcast HQ(config-if)# frame-relay map ip broadcast HQ(config-if)# no shutdown EAST# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. EAST(config)# interface loopback 2 EAST(config-if)# ip address EAST(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0 EAST(config-if)# ip address EAST(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay ietf EAST(config-if)# no frame-relay inverse-arp EAST(config-if)# frame-relay map ip broadcast EAST(config-if)# frame-relay map ip EAST(config-if)# frame-relay map ip broadcast EAST(config-if)# no shutdown EAST(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0 EAST(config-if)# ip address EAST(config-if)# no shutdown 2-11 CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
3 WEST# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. WEST(config)# interface loopback 2 WEST(config-if)# ip address WEST(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0 WEST(config-if)# ip address WEST(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay ietf WEST(config-if)# no frame-relay inverse-arp WEST(config-if)# frame-relay map ip broadcast WEST(config-if)# frame-relay map ip broadcast WEST(config-if)# frame-relay map ip WEST(config-if)# no shutdown WEST(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0 WEST(config-if)# ip address WEST(config-if)# no shutdown Verify that you have local subnet connectivity with ping. Step 2: Setting Up NMBA OSPF We can set up OSPF for hub-and-spoke over Frame Relay. HQ will be the hub; East and West will be the spokes. Create OSPF process 1, and add the Frame Relay interfaces on each router into area 0 with the network command. Also, add the loopback interfaces on each router into area 0. Then change the network type to allow the correct subnet mask to be advertised. HQ(config)# router ospf 1 HQ(config-router)# network area 0 HQ(config-router)# network area 0 HQ(config-router)# interface loopback 1 HQ(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point EAST(config)# router ospf 1 EAST(config-router)# network area 0 EAST(config-router)# network area 0 EAST(config-router)# interface loopback 2 EAST(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point WEST(config)# router ospf 1 WEST(config-router)# network area 0 WEST(config-router)# network area 0 WEST(config-router)# interface loopback 3 WEST(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point No Frame Relay adjacencies will be established yet, because the default network type is non-broadcast. We can change this by adding neighbor statements. Before that, however, go on East and West and change their Frame Relay interfaces to have OSPF priority 0. This ensures that HQ becomes the DR. Next, configure neighbor statements on HQ pointing toward East and West. Only the router starting the exchange needs neighbor statements (it is HQ in this case). Although it may take a little while because the hello timers are long on non-broadcast, the adjacencies will eventually come up. You can verify adjacency states with the show ip ospf neighbor command. HQ(config)# router ospf 1 HQ(config-router)# neighbor HQ(config-router)# neighbor CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
4 EAST(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 EAST(config-if)# ip ospf priority 0 WEST(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 WEST(config-if)# ip ospf priority 0 HQ# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/DROTHER 00:01: Serial0/0/ FULL/DROTHER 00:01: Serial0/0/0 Non-broadcast networks are good for Frame Relay because you have the maximum level of control over neighbor relationships. All OSPF packets are unicast and go only to their intended destination. Non-broadcast saves bandwidth because of the strict control you can have over which router becomes the DR. Step 3: Changing the Network Type to Point-to-Multipoint Point-to-multipoint is an OSPF area type that lends itself very well to a hub-andspoke topology. Point-to-multipoint does not elect DRs or BDRs, so it does not need interface priorities Instead, it treats the network as a collection of point-topoint networks and advertises host routes for any neighbors it has. To configure this, first take off the configuration already there for a nonbroadcast network, meaning the neighbor statements and interface priorities. The adjacencies time out after the dead timer expires. HQ(config)# router ospf 1 HQ(config-router)# no neighbor HQ(config-router)# no neighbor EAST(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 EAST(config-if)# no ip ospf priority 0 WEST(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 WEST(config-if)# no ip ospf priority 0 After removing the old configuration, use the interface-level command ip ospf network point-to-multipoint. Verify that your adjacencies are active with the show ip ospf neighbor command. HQ(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 HQ(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-multipoint EAST(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 EAST(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-multipoint WEST(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 WEST(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-multipoint HQ# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:01: Serial0/0/ FULL/ - 00:01: Serial0/0/ CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
5 Look at the routing table on one of the spoke routers. Notice how the routing table has host routes in it. This is part of point-to-multipoint behavior. EAST# show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set O C O C C O O /8 is variably subnetted, 7 subnets, 2 masks /24 [110/129] via , 00:01:07, Serial0/0/ /24 is directly connected, Loopback /24 [110/65] via , 00:01:07, Serial0/0/ /24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ /24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/ /32 [110/64] via , 00:01:07, Serial0/0/ /32 [110/128] via , 00:01:07, Serial0/0/0 Look at the output of the show ip ospf interface interface command on your routers. Notice that the interface type is point-to-multipoint. EAST# show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address /24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID , Network Type POINT_TO_MULTIPOINT, Cost: 64 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_MULTIPOINT, Timer intervals configured, Hello 30, Dead 120, Wait 120, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 120 Hello due in 00:00:16 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Index 1/1, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) What are some advantages to configuring an NBMA network as point-tomultipoint instead of non-broadcast? What are some disadvantages? Step 4: Changing OSPF Timers Add the Ethernet link connecting East and West to the OSPF process using the network command. EAST(config)# router ospf 1 EAST(config-router)# network area CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
6 WEST(config)# router ospf 1 WEST(config-router)# network area 0 Look at the interface OSPF properties with the show ip ospf interface interface command. EAST# show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/0 FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address /24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID , Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State BDR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) , Interface address Backup Designated router (ID) , Interface address Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:00 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Index 3/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor (Designated Router) Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) Since it is an Ethernet link, it has the default network type of broadcast and the default network timers associated with a broadcast network. Sometimes, you may want to change the default timers to allow for better network convergence, because lower dead timers mean that neighbors that go down are detected more quickly. The disadvantage of this is higher router CPU utilization and more bandwidth being consumed by hello packets. You can change the default hello timer to any time you want with the ip ospf hello-interval seconds command. Change the hello interval to 5 seconds on both sides. Change the dead timer to 15 seconds with the ip ospf deadinterval seconds command. Verify this with the show ip ospf interface interface command. EAST(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0 EAST(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 5 EAST(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval 15 WEST(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0 WEST(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 5 WEST(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval 15 EAST# show ip ospf int f0/0 FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address /24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID , Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State BDR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) , Interface address Backup Designated router (ID) , Interface address Timer intervals configured, Hello 5, Dead 15, Wait 15, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:01 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Index 3/3, flood queue length CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
7 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor (Designated Router) Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) What are some downsides to changing the timers if they are not tuned correctly? Challenge: Minimal Hello Intervals Configure the serial link to have even lower convergence time in case of a failure. To configure this, use the variant of the dead-interval command ip ospf dead-interval minimal hello-multiplier multiplier. This command sets the dead interval to one second. The hello rate is the multiplier number of hellos per second. Configure the routers to send five hellos a second. Look at the dead time column of the show ip ospf neighbor command. Is it a different format than before for that connection? Appendix A: TCL Connectivity Verification tclsh foreach address { } { ping $address } HQ# tclsh HQ(tcl)# HQ(tcl)#foreach address { +>(tcl)# >(tcl)# >(tcl)# >(tcl)# >(tcl)# CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
8 +>(tcl)# >(tcl)# >(tcl)# >(tcl)#} { +>(tcl)#ping $address } Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: EAST# tclsh EAST(tcl)# EAST(tcl)#foreach address { +> > > > > > > > >} { +>ping $address } Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: 8-11 CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
9 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms WEST# tclsh WEST(tcl)# WEST(tcl)#foreach address { +> > > > > > > > >} { +>ping $address } Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/4/4 ms Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: 9-11 CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
10 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: HQ# show run hostname HQ interface Loopback1 ip address ip ospf network point-to-point interface Serial0/0/0 ip address encapsulation frame-relay ietf ip ospf network point-to-multipoint frame-relay map ip frame-relay map ip broadcast frame-relay map ip broadcast no frame-relay inverse-arp no shutdown router ospf 1 network area 0 network area 0 end EAST# show run hostname EAST interface Loopback2 ip address ip ospf network point-to-point interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address ip ospf hello-interval 5 ip ospf dead-interval 15 no shutdown interface Serial0/0/0 ip address encapsulation frame-relay ietf ip ospf network point-to-multipoint clock rate frame-relay map ip broadcast frame-relay map ip frame-relay map ip broadcast no frame-relay inverse-arp no shutdown router ospf 1 network area 0 network area 0 network area 0 end CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
11 WEST# show run hostname WEST interface Loopback3 ip address ip ospf network point-to-point interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address ip ospf hello-interval 5 ip ospf dead-interval 15 no shutdown interface Serial0/0/0 ip address encapsulation frame-relay ietf ip ospf network point-to-multipoint clock rate frame-relay map ip broadcast frame-relay map ip broadcast frame-relay map ip no frame-relay inverse-arp no shutdown router ospf 1 network area 0 network area 0 network area 0 end CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 - Lab 3-4b Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF
 OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice
 CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice Two neighbouring routers are configured for OSPF, but they have different hello and dead intervals. What will happen? They will become adjacent as long as they are configured
CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice Two neighbouring routers are configured for OSPF, but they have different hello and dead intervals. What will happen? They will become adjacent as long as they are configured
CCNP CISCO CERTIFIED NETWORK PROFESSIONAL LAB MANUAL
 CCNP CISCO CERTIFIED NETWORK PROFESSIONAL LAB MANUAL VER 2.0 Page 1 of 315 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We can write a 1000 page book, but we can t find enough words to describe the credit Mr. Siddiq Ahmed deserves
CCNP CISCO CERTIFIED NETWORK PROFESSIONAL LAB MANUAL VER 2.0 Page 1 of 315 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We can write a 1000 page book, but we can t find enough words to describe the credit Mr. Siddiq Ahmed deserves
Link-State Routing Protocols
 Link-State Routing Protocols Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Link-state routing protocol Single-area OSPF concepts Single-area OSPF
Link-State Routing Protocols Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Link-state routing protocol Single-area OSPF concepts Single-area OSPF
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Table of Contents. Cisco Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN
 Table of Contents Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Related Products...2 Conventions...2 Configure...3 Network Diagram...3 Configuration
Table of Contents Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...2 Related Products...2 Conventions...2 Configure...3 Network Diagram...3 Configuration
Frame Mode MPLS Implementation
 CHAPTER 4 Frame Mode MPLS Implementation Lab 4-1: Configuring Frame Mode MPLS (4.5.1) In this lab, you learn how to do the following: Configure EIGRP on a router. Configure LDP on a router. Change the
CHAPTER 4 Frame Mode MPLS Implementation Lab 4-1: Configuring Frame Mode MPLS (4.5.1) In this lab, you learn how to do the following: Configure EIGRP on a router. Configure LDP on a router. Change the
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
IOS NAT Load Balancing with Optimized Edge Routing for Two Internet Connections Document ID: 99427 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1
![O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1 O 10.16.1.0/27 [110/129] via 192.168.1.5, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/1](/thumbs/39/20242582.jpg) 1 Which two statements are true regarding the advantages of the use of static routes? (Choose increased security reduced effort in configuring routes the administrator maintains control over routing easier
1 Which two statements are true regarding the advantages of the use of static routes? (Choose increased security reduced effort in configuring routes the administrator maintains control over routing easier
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs
 Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs Learning Objectives Configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router Enable MPLS on a router Verify
Lab 4.2 Challenge Lab: Implementing MPLS VPNs Learning Objectives Configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) on a router Enable MPLS on a router Verify
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections
 IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
IOS NAT Load Balancing for Two ISP Connections Document ID: 100658 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing
 Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 4, 2007 Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing Akram Al-Rawi College of CS & IT, King Faisal University, Al-Hassa,
Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology Volume 4, 2007 Effect of Windows XP Firewall on Network Simulation and Testing Akram Al-Rawi College of CS & IT, King Faisal University, Al-Hassa,
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
 Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Router and Routing Basics
 Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
How To Configure A Cisco Router With A Cio Router
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
Monitoring Routing. Monitoring OSPF LSAs. Type 1 CHAPTER
 44 CHAPTER You can use ASDM to monitor OSPF LSAs, OSPF and EIGRP neighbors, and the routing table. To access the routing monitoring screens, go to Monitoring > Routing in the ASDM interface. This section
44 CHAPTER You can use ASDM to monitor OSPF LSAs, OSPF and EIGRP neighbors, and the routing table. To access the routing monitoring screens, go to Monitoring > Routing in the ASDM interface. This section
CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0
 Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
CertificationKits.com EIGRP Sample CCNA Lab. EIGRP Routing. The purpose of this lab is to explore the functionality of the EIGRP routing protocol.
 EIGRP Routing The purpose of this lab is to explore the functionality of the EIGRP routing protocol. Hardware & Configuration Required for this Lab Two Cisco routers with two Fast Ethernet interfaces and
EIGRP Routing The purpose of this lab is to explore the functionality of the EIGRP routing protocol. Hardware & Configuration Required for this Lab Two Cisco routers with two Fast Ethernet interfaces and
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
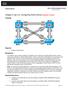 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Introduction about cisco company and its products (network devices) Tell about cisco offered courses and its salary benefits (ccna ccnp ccie )
 CCNA Introduction about cisco company and its products (network devices) Tell about cisco offered courses and its salary benefits (ccna ccnp ccie ) Inform about ccna its basic course of networking Emergence
CCNA Introduction about cisco company and its products (network devices) Tell about cisco offered courses and its salary benefits (ccna ccnp ccie ) Inform about ccna its basic course of networking Emergence
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite
 Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
Laboratorio 3 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
How To Lower Data Rate On A Network On A 2Ghz Network On An Ipnet 2 (Net 2) On A Pnet 2 On A Router On A Gbnet 2.5 (Net 1) On An Uniden Network On
 Lab 8.1.10.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Lab 8.1.10.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands
 Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
CCNA 2 v5.0 Routing Protocols Final Exam Answers
 CCNA 2 v5.0 Routing Protocols Final Exam Answers 1 Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded about network 192.168.1.0 in the R2 routing table? This network was learned through summary LSAs from an ABR.*
CCNA 2 v5.0 Routing Protocols Final Exam Answers 1 Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded about network 192.168.1.0 in the R2 routing table? This network was learned through summary LSAs from an ABR.*
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
GregSowell.com. Mikrotik Routing
 Mikrotik Routing Static Dynamic Routing To Be Discussed RIP Quick Discussion OSPF BGP What is Routing Wikipedia has a very lengthy explanation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/routing In the context of this
Mikrotik Routing Static Dynamic Routing To Be Discussed RIP Quick Discussion OSPF BGP What is Routing Wikipedia has a very lengthy explanation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/routing In the context of this
DYNAMIC MULTIPOINT VPN HUB AND SPOKE INTRODUCTION
 DYNAMIC MULTIPOINT VPN HUB AND SPOKE INTRODUCTION NOVEMBER 2004 1 INTRODUCTION Spoke, Presentation_ID 11/04 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 What is Dynamic Multipoint VPN? Dynamic Multipoint
DYNAMIC MULTIPOINT VPN HUB AND SPOKE INTRODUCTION NOVEMBER 2004 1 INTRODUCTION Spoke, Presentation_ID 11/04 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 What is Dynamic Multipoint VPN? Dynamic Multipoint
OSPF Routing Protocol
 OSPF Routing Protocol Contents Introduction Network Architecture Campus Design Architecture Building Block Design Server Farm Design Core Block Design WAN Design Architecture Protocol Design Campus Design
OSPF Routing Protocol Contents Introduction Network Architecture Campus Design Architecture Building Block Design Server Farm Design Core Block Design WAN Design Architecture Protocol Design Campus Design
Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching
 CCNP3 v5 - Chapter 5 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing High Availability in a Campus Environment Routing issues Hosts rely on a router to find the best path Issues with established
CCNP3 v5 - Chapter 5 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing High Availability in a Campus Environment Routing issues Hosts rely on a router to find the best path Issues with established
Lab 8.9.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR
 Lab 8.9.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
Lab 8.9.3 QoS Classification and Policing Using CAR Objective Scenario Step 1 This lab uses Committed Access Rate (CAR) to classify and police traffic. Although the classification and policing actions
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
GLBP Gateway Load Balancing Protocol By MEDDANE Redouane Cisco Instructor 1 How GLBP Works. GLBP works by making use of a single virtual IP address, which is configured as the default gateway on the hosts.
Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection
 Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: Can you describe the role of dynamic routing protocols
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to answer the following questions: Can you describe the role of dynamic routing protocols
Cisco CCNP 642 901 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT)
 Cisco CCNP 642 901 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Course Number: 642 901 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exams: Cisco CCNP Exam 642 901:
Cisco CCNP 642 901 Optimizing Converged Cisco Networks (ONT) Course Number: 642 901 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exams: Cisco CCNP Exam 642 901:
Network Simulator Lab Study Plan
 The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
Table of Contents. Cisco How Does Load Balancing Work?
 Table of Contents How Does Load Balancing Work?...1 Document ID: 5212...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Load Balancing...1 Per Destination and
Table of Contents How Does Load Balancing Work?...1 Document ID: 5212...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Load Balancing...1 Per Destination and
Example: Advertised Distance (AD) Example: Feasible Distance (FD) Example: Successor and Feasible Successor Example: Successor and Feasible Successor
 642-902 Route: Implementing Cisco IP Routing Course Introduction Course Introduction Module 01 - Planning Routing Services Lesson: Assessing Complex Enterprise Network Requirements Cisco Enterprise Architectures
642-902 Route: Implementing Cisco IP Routing Course Introduction Course Introduction Module 01 - Planning Routing Services Lesson: Assessing Complex Enterprise Network Requirements Cisco Enterprise Architectures
Lab 10: Confi guring Basic Border Gateway Protocol
 Lab 10: Objective Confi gure P1R1 for basic Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP). Confi gure P1R1 and P1R2 for Interior Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP). Confi rm BGP connectivity. Lab Topology For this
Lab 10: Objective Confi gure P1R1 for basic Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP). Confi gure P1R1 and P1R2 for Interior Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP). Confi rm BGP connectivity. Lab Topology For this
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Troubleshooting IP Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN
 Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN Help us help you. Please rate this document. Contents Introduction Conventions Hardware and Software Versions Network Diagram Configuration Procedures Enabling Configuring
Configuring a Basic MPLS VPN Help us help you. Please rate this document. Contents Introduction Conventions Hardware and Software Versions Network Diagram Configuration Procedures Enabling Configuring
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging
 Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
PT Activity 8.1.2: Network Discovery and Documentation Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Cisco s OSPF Implementation P1C-107
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example
 ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example Document ID: 91264 Contributed by Dinkar Sharma, Magnus Mortensen, and Prashant Joshi, Cisco TAC Engineers. May 13, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example Document ID: 91264 Contributed by Dinkar Sharma, Magnus Mortensen, and Prashant Joshi, Cisco TAC Engineers. May 13, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Configuring Denial of Service Protection
 24 CHAPTER This chapter contains information on how to protect your system against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The information covered in this chapter is unique to the Catalyst 6500 series switches,
24 CHAPTER This chapter contains information on how to protect your system against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The information covered in this chapter is unique to the Catalyst 6500 series switches,
Chapter 1 Implement EIGRP operations... 2. Chapter 2 Implement multiarea OSPF operations... 18. Chapter 4 Implement Cisco IOS routing features...
 Table of Contents Chapter 1... 2 94 106 Chapter 2 Implement multiarea OSPF operations... 18 96 120 Chapter 3 Describe integrated IS-IS... 30 97 130 Chapter 4 Implement Cisco IOS routing features... 48
Table of Contents Chapter 1... 2 94 106 Chapter 2 Implement multiarea OSPF operations... 18 96 120 Chapter 3 Describe integrated IS-IS... 30 97 130 Chapter 4 Implement Cisco IOS routing features... 48
Distance Vector Routing Protocols. Routing Protocols and Concepts Ola Lundh
 Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Ola Lundh Objectives The characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. The network discovery process of distance vector routing
Distance Vector Routing Protocols Routing Protocols and Concepts Ola Lundh Objectives The characteristics of distance vector routing protocols. The network discovery process of distance vector routing
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional)
 Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional) CCNP Route (642-902) EIGRP Chapter: EIGRP Overview and Neighbor Relationships EIGRP Neighborships Neighborship over WANs EIGRP Topology, Routes,
Course Contents CCNP (CISco certified network professional) CCNP Route (642-902) EIGRP Chapter: EIGRP Overview and Neighbor Relationships EIGRP Neighborships Neighborship over WANs EIGRP Topology, Routes,
Zarząd (7 osób) F inanse (13 osób) M arketing (7 osób) S przedaż (16 osób) K adry (15 osób)
 QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
QUESTION NO: 8 David, your TestKing trainee, asks you about basic characteristics of switches and hubs for network connectivity. What should you tell him? A. Switches take less time to process frames than
Cisco Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs
 Table of Contents Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...2 Hardware and Software Versions...3 Configuration Examples...3 Allow a Select Host to Access the Network...3 Allow
Table of Contents Configuring Commonly Used IP ACLs...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...2 Hardware and Software Versions...3 Configuration Examples...3 Allow a Select Host to Access the Network...3 Allow
Chapter 4. Distance Vector Routing Protocols
 Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 4 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Chapter 4 Distance Vector Routing Protocols CCNA2-1 Chapter 4 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Seminar Seite 1 von 10
 Seminar Seite 1 von 10 CISCO - Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Dauer: 5 Tage Kosten: 2.490,00 EUR (pro Person / zzgl. MwSt) Ziele: Der Kurs Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) vermittelt den Teilnehmern
Seminar Seite 1 von 10 CISCO - Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Dauer: 5 Tage Kosten: 2.490,00 EUR (pro Person / zzgl. MwSt) Ziele: Der Kurs Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) vermittelt den Teilnehmern
CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts. Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding
 Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
IPv6 over MPLS VPN. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: 112085. Requirements
 IPv6 over MPLS VPN Document ID: 112085 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram VRF Configuration Multiprotocol BGP (MP BGP) Configuration
IPv6 over MPLS VPN Document ID: 112085 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram VRF Configuration Multiprotocol BGP (MP BGP) Configuration
Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 Conceitos de protocolos de Encaminhamento Cap 2
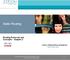 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
Cisco Configuring Basic MPLS Using OSPF
 Table of Contents Configuring Basic MPLS Using OSPF...1 Introduction...1 Mechanism...1 Hardware and Software Versions...2 Network Diagram...2 Configurations...2 Quick Configuration Guide...2 Configuration
Table of Contents Configuring Basic MPLS Using OSPF...1 Introduction...1 Mechanism...1 Hardware and Software Versions...2 Network Diagram...2 Configurations...2 Quick Configuration Guide...2 Configuration
IPv6 Diagnostic and Troubleshooting
 8 IPv6 Diagnostic and Troubleshooting Contents Introduction.................................................. 8-2 ICMP Rate-Limiting........................................... 8-2 Ping for IPv6 (Ping6)..........................................
8 IPv6 Diagnostic and Troubleshooting Contents Introduction.................................................. 8-2 ICMP Rate-Limiting........................................... 8-2 Ping for IPv6 (Ping6)..........................................
IP Addressing and Subnetting. 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
IP Addressing and Subnetting 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Objectives Upon completion, you will be able to: Discuss the Types of Network Addressing Explain the Form of an IP Address
Cisco Site-to-Site VPN Lab 3 / GRE over IPSec VPNs by Michael T. Durham
 Cisco Site-to-Site VPN Lab 3 / GRE over IPSec VPNs by Michael T. Durham In part two of NetCertLabs Cisco CCNA Security VPN lab series, we explored setting up a site-to-site VPN connection where one side
Cisco Site-to-Site VPN Lab 3 / GRE over IPSec VPNs by Michael T. Durham In part two of NetCertLabs Cisco CCNA Security VPN lab series, we explored setting up a site-to-site VPN connection where one side
IPv6 Hands-on Lab. Faraz Shamim, Technical Leader Harold Ritter, Technical Leader. Toronto, Canada May 30, 2013
 Toronto, Canada May 30, 2013 IPv6 Hands-on Lab Faraz Shamim, Technical Leader Harold Ritter, Technical Leader 2011 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Connect 1 Prerequisites:
Toronto, Canada May 30, 2013 IPv6 Hands-on Lab Faraz Shamim, Technical Leader Harold Ritter, Technical Leader 2011 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Connect 1 Prerequisites:
Working knowledge of TCP/IP protocol Suite IPX/SPX protocols Suite, MCSE or CNE or experienced in supporting a LAN environment.
 Cisco Certified Network Associate (640-802) Overview & Objectives This course will lead to a CISCO Certification (CCNA). This is the CISCO: Fundamental of Internetworking and WAN Configuration but with
Cisco Certified Network Associate (640-802) Overview & Objectives This course will lead to a CISCO Certification (CCNA). This is the CISCO: Fundamental of Internetworking and WAN Configuration but with
Laboratorio 4. Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite
 Laboratorio 4 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
Laboratorio 4 Comunicación sincrónica Vía Satélite Esquema de la Red WAN 192.168.0.0 /30 192.168.0.1 Router 1 Router 2 10.0.1.1 192.168.0.1 10.0.2.1 Ethernet Ethernet 10.0.1.20 LAN 1 10.0.1.0 /24 LAN 2
640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1
 640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1 Course Introduction Course Introduction Chapter 01 - Small Network Implementation Introducing the Review Lab Cisco IOS User Interface Functions
640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1 Course Introduction Course Introduction Chapter 01 - Small Network Implementation Introducing the Review Lab Cisco IOS User Interface Functions
CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI
 CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI Gökhan AKIN İTÜ 2003 TOPOLOJİ: İSTENENLER: 1. Topolojiyi Legacy DDR tekniği ile kurunuz. 2. Aynõ Topolojiyi Dialer Profile tekniğini kullanarak
CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI Gökhan AKIN İTÜ 2003 TOPOLOJİ: İSTENENLER: 1. Topolojiyi Legacy DDR tekniği ile kurunuz. 2. Aynõ Topolojiyi Dialer Profile tekniğini kullanarak
Cisco 12 CCNA Certification
 Cisco 12 CCNA Certification Application for Board Authorization of Courses District: Chilliwack School District 33 Developed by: John Murtha Date: May7, 2004 School: Sardis Secondary Principal: Bob Patterson
Cisco 12 CCNA Certification Application for Board Authorization of Courses District: Chilliwack School District 33 Developed by: John Murtha Date: May7, 2004 School: Sardis Secondary Principal: Bob Patterson
ITRI CCL. IP Routing Primer. Paul C. Huang, Ph.D. ITRI / CCL / N300. CCL/N300; Paul Huang 1999/6/2 1
 IP Routing Primer Paul C. Huang, Ph.D. ITRI / / N300 /N300; Paul Huang 1999/6/2 1 Basic Addressing / Subnetting Class A 0 Network Host Host Host 127 networks / 16,777,216 hosts Class A natural mask 255.0.0.0
IP Routing Primer Paul C. Huang, Ph.D. ITRI / / N300 /N300; Paul Huang 1999/6/2 1 Basic Addressing / Subnetting Class A 0 Network Host Host Host 127 networks / 16,777,216 hosts Class A natural mask 255.0.0.0
IP Routing Configuring RIP, OSPF, BGP, and PBR
 13 IP Routing Configuring RIP, OSPF, BGP, and PBR Contents Overview..................................................... 13-6 Routing Protocols.......................................... 13-6 Dynamic Routing
13 IP Routing Configuring RIP, OSPF, BGP, and PBR Contents Overview..................................................... 13-6 Routing Protocols.......................................... 13-6 Dynamic Routing
Layer 3 Routing User s Manual
 User s Manual Second Edition, July 2011 www.moxa.com/product 2011 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
User s Manual Second Edition, July 2011 www.moxa.com/product 2011 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
How To Understand Bg
 Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
Table of Contents BGP Case Studies...1 BGP4 Case Studies Section 1...3 Contents...3 Introduction...3 How Does BGP Work?...3 ebgp and ibgp...3 Enabling BGP Routing...4 Forming BGP Neighbors...4 BGP and
Chapter 12 Configuring VRRP and VRRPE
 Chapter 12 Configuring VRRP and VRRPE This chapter describes how to configure HP routing switches to configure the following router redundancy protocols: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) The standard
Chapter 12 Configuring VRRP and VRRPE This chapter describes how to configure HP routing switches to configure the following router redundancy protocols: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) The standard
Interconnecting Multiple OSPF Areas
 C H A P T E R 4 Interconnecting Multiple OSPF Areas This chapter introduces readers to the use, operation, configuration, and verification of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) in multiple areas. After completing
C H A P T E R 4 Interconnecting Multiple OSPF Areas This chapter introduces readers to the use, operation, configuration, and verification of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) in multiple areas. After completing
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Textbook Required: Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 Lab Manual.
 Course: NET 251 Building Scalable Internetworks Credits: 3 Textbook Required: Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 Lab Manual. Course Description: In this course,
Course: NET 251 Building Scalable Internetworks Credits: 3 Textbook Required: Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks v5.0 Lab Manual. Course Description: In this course,
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
How To Set Up A Netvanta For A Pc Or Ipad (Netvanta) With A Network Card (Netvina) With An Ipa (Net Vanta) And A Ppl (Netvi) (Netva)
 VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD NetVanta 3200 NetVanta 3200 NetVanta Series (with T1/FT1 or T1/FT1 + DSX-1 Network Interface Module) Quick Configuration Guide
VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD VPN WAN LAN PWR STAT TD RD TD RD TD RD NetVanta 3200 NetVanta 3200 NetVanta Series (with T1/FT1 or T1/FT1 + DSX-1 Network Interface Module) Quick Configuration Guide
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers
 Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
Configuring DNS on Cisco Routers Document ID: 24182 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Setting Up a Router to Use DNS Lookups Troubleshooting You Can Ping a Web
Administrative Distance
 RIP is a distance vector routing protocol. It shares routing information through the local broadcast in every 30 seconds. In this tutorial we will explain RIP routing fundamentals with examples such as
RIP is a distance vector routing protocol. It shares routing information through the local broadcast in every 30 seconds. In this tutorial we will explain RIP routing fundamentals with examples such as
Instructor Notes for Lab 3
 Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
