THE STUDY OF THE AFFECTS OF BACKGROUND MUSIC OF SHORT-TERM MEMORY
|
|
|
- Walter Griffin
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE STUDY OF THE AFFECTS OF BACKGROUND MUSIC OF SHORT-TERM MEMORY Liz Jones Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of these experiments was to determine if background music affects shortterm memory. Short-term memory processes information by repeating, grouping and summarizing it to aid its storage in long-term memory and sound is when vibrations of air molecules move through the air, get received, and then translate them into messages that the brain recognizes as sound by the ear. In the method, the test suspects listened to background music while hearing a recording twice, the test suspects then repeated it back after 30 secs. It was found that the test suspects did better while listening to music rather than not listening to music. This is because information in short-term memory is stronger when constantly thought about, when the test suspects are listening to the background music the test suspects are trying hard to remember the recording of information. INTRODUCTION Short-term memory processes information by repeating, grouping and summarizing it to aid its storage in long-term memory. Information only stays in short-term memory for a short amount of time before it is moved to long-term memory or is discarded. The only way for information to be moved to long-term memory is to be repeated multiple times when it is in short-term memory. Short-term memory can only hold 5-7 units of information every secs. Short-term memory only holds information if it is actively thought about. New information can force information out of short-term memory too. If information is not repeated or practiced often, it will be lost from the memory. Units of information are single pieces and information like a person s name. There are many factors of how information gets into long-term memory. One strong factor is repetition
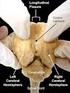
2 and repeating information. If things are repeated often then they will move into longterm memory. Another strong factor is emotion. Like getting in an accident or falling in love. Those kinds of things are hard to forget. The whole world is filled with sound. It allows communication through speak. When strings on a guitar vibrate, it presses on molecules in the surrounding air. Normally the molecules are spread out but the vibration compresses them or pushes them close together. The molecules bump into other ones around it, which is the vibration. Then the vibration is transmitted outward from the guitar strings. That creates waves in the air molecules. Once all that vibrating air hits an eardrum, sound is heard. The only way to hear sound is through vibration. Without it, nothing would be heard. To test this, feel a throat while talking. The vocal cords are making vibration. Sound travels in sound waves. They can be called compression waves also because the air molecules are compressed when they vibrate. Vibration objects send out sound waves in every direction. When sound travel s it has to travel through a medium. That means it has to travel through a gas, liquid, or solid. If sound travels through a liquid or a solid, it travels a lot faster than going through a gas. Molecules cannot vibrate through a gas as fast as they could through a liquid or solid. The speed of sound is four times faster in water than in air and fifteen times faster through steel. The brain is an amazing thing. It is an organ in the body. It controls thought, judgment, personal identity, memory, and other aspects called mind. The brain also controls the body, like body temperature, blood pressure, and the activity of internal Figure 1 - this diagram shows the six main parts of the brain.
3 organs. This helps the body respond to its environment and maintain its health. There are 6 main parts to the brain, the parietal lobe, frontal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, cerebellum, and the spinal cord. The frontal lobe is located at the top of the brain and controls: Problem solving Attention Creative thought Some emotion Intellect Reflection Judgment Initiative Inhibition Coordination of movements Generalized and mass movements Some eye movements Sense of smell Muscle movements Skilled movements Some motor skills Physical reaction Libido (sexual urges) Abstract thought processes Behavior The parietal lobe controls: Appreciation of form through touch (stereognosis) Response to internal stimuli (proprioception) Sensory combination and comprehension Some language and reading functions
4 Some visual functions Sense of touch (tactile sensation) The temporal lobe controls: Some hearing Visual memories Some vision pathways Other memory Music Fear Some language Some speech Some behavior and emotions Sense of identity Auditory memories The occipital lobe controls: Vision Reading The cerebellum controls: Balance Posture Cardiac, respiratory, and vasomotor centers The spinal cord controls: Conduit and source of sensation and movement When vibrations of air molecules move through the air, get received, and then translate them into messages that the brain recognizes as sound by the ear. The ear has 2 different functions. Both are important and different. There is hearing and sensing the
5 body s equilibrium, or balance. The mechanisms for these processes are in the skull's temporal bone located in a hollow space. Memory is all about remembering and forgetting. Information is stored in memory and it can be tapped a bunch of different ways. The ability to retrieve learned material is called memory recall or retrieval. The brain does something called recognition. That is the ability to identify material that has been encountered before. The recognition of a person s face is a good example of good recognition. Being able to not recall the person s name is a good example of faulty recall. When something is learned and then forgotten, it can be relearned a lot quicker than before. Katie Shy tested to see if the age of people affect their memory. She tested this by showing different ages of people 40 pictures for 1 min and then let them sit there for 30 secs. After doing her experiment, she found out that people in their 20s have the best memories. She also learned that male and females both averaged 12 pictures in her experiment. Another thing she found was that shoe size and years of education do not have an exact pattern. The height of the person did matter though. It was learned that the taller the person the better memory they had. MATERIALS AND METHOD A phone, computer, timer, test suspects, music, and seven recordings were used in this experiment. Test suspects were placed in front of a computer. The test suspects listened to background music while hearing a recording twice of 8 words. Once the recording was finished a timer was set for thirty secs and the test suspects waited there quietly. Once the timer was done, the test suspects repeated what was heard in the recording. The same thing happened to the same test suspect but without listening to background music. With no music a different recording was used. The scores were calculated and recorded.
6 In the follow up experiment the same thing was tested, how many words each suspect could remember after listening to background music. In this experiment, different types of music were used. The test suspect listened to three different types of music, pop, country, classical, and no music also. Each type of music had a different recording to go with it. The test suspect listened and waited like said before in the first experiment. The scores were calculated and recorded. In the next follow up experiment the same thing was tested, how many words each suspect could remember after listening to background music. This time the amount of letters in the 8 words were being determined. A set of 4 different recordings had different amount of letters in them, 3-4, 5-6,7, 9-10, and random letters with no music. A different recording was used for each experiment or set of numbers. The test suspects listened and waited like the first experiment. The scores were calculated and recorded. The next follow up experiment was just like the first one. The same test suspects were used for the first experiment. This experiment was testing the amount of times the test suspects heard the recording set (which was twice). The same test suspects heard it 3 more times using the same method as the first. The results were calculated and recorded. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In this experiment the results were surprising (see figure 1). Test suspects remembered more with background music (5) that without background music (3). This is because information in short-term memory is stronger when constantly thought about. When the test suspects are listening to the background music the test suspects are trying really hard to remember the recording of information. Therefor the information is thought about more and the memory of it is stronger. The high of this data was music and the low was no music.
7 # Correct music Background Sound no music Figure 2 - this graph shows the average number of word memorized by the test suspects with and without music. In this experiment different types of music were tested to see if it would change the data at all from no music (see figure 2). Rock (3) and country (3) made it easier for the test suspect to remember the recording. However the classical (2) made the test suspect worse at remembering the recoding. This happened because the classical music through the test suspects off. The test suspects were used to listening to upbeat music like rock and country. That is why the classical music made the scores wrong. The high of this data was fast music and the low was slow music.
8 Average Change of Words Remembered rock classical country no music Type of Music Figure 3 - this graph shows how many words each test suspects could remember with different types of background music and no music. In this experiment the results were very surprising (see figure 3). The length of words were tested and the lower number of letters were harder to remember like 3-4 letters (3). 5-6 and 7 letters both remembered the same amount of letters (4) letters was the easiest set of words to remember. This is because the smaller letters are harder to remember in short-term memory. Since they are so small, they are easily forgotten. That is why the longer words were easier to remember. The high of this experiment was long letters and the low was short letters.
9 # Correct Length of Words (# of letters) Figure 4 - this graph shows how many words each test suspects could remember. Each recording had a different length for the words. This experiment tested the affects how many times the test suspects heard the same recording (see figure 4). The 1 st and 2 nd time it was heard the same amount was remembered and the test suspects were still getting the recoding into their head (5). The 3 rd time the test suspects heard it, it was almost completely memorized (7). The 4 th time it was heard it stuck in the test suspects head (8). This is because things in shortterm memory get stronger or move to long-term memory when they are actively thought about. The test suspects heard the recording multiply times so the information got stronger. The more times the test suspects heard it, the better it was remembered.
10 # Correct Times It Was Heard Figure 5 - this graph shows how well the test suspects remembered the recording after hearing it multiply times. CONCLUSION In the results, the test suspects did better memorizing the recording with music rather without music. This data it important to the world because it is good to know what affects and doesn t affect the brain and mind. The hypothesis was incorrect because the test suspects did better listening to music. In the future, some follow up experiments would be, do distractions affect how well the test suspects do, and do eating and drinking while listening to the recording affect? Citations "brain and spinal cord." Compton's by Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online School Edition. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., Web. 13 Jan "ear." Compton's by Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online School Edition. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., Web. 13 Jan
11 McGrath, Kimberley A. ed. "Memory." The Gale Encyclopedia of Science. Volume 4. Detroit: Gale Group, Print. "memory." Compton's by Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online School Edition. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., Web. 13 Jan Shy, Katie. A STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF AGE ON PEOPLE S MEMORIES. Cary Academy. February 15, Silverstein, Alvin and Virginia Silberstein and Laura Silverstein. Energy. Brookfield: Twenty-First Century Books Print. "The Brain." Enchanted Learning. Enchanted Learning, Web. 22 Feb < >. "Your Brain and Nervous System." Kids Health. Nemours, Web. 22 Feb <
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services
 Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Nikki White Children s Occupational Therapist Barnet Community Services What is Occupational Therapy (OT)? An occupation is anything you do in your daily life. Anything meaningful or purposeful Eg. Getting
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Lecture 2, Human cognition
 Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
Human Cognition An important foundation for the design of interfaces is a basic theory of human cognition The information processing paradigm (in its most simple form). Human Information Processing The
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
It s All in the Brain!
 It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
It s All in the Brain! Presented by: Mari Hubig, M.Ed. 0-3 Outreach Coordinator Educational Resource Center on Deafness What is the Brain? The brain is a muscle In order to grow and flourish, the brain
Homework Help Stroke
 The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
The neurobiology of energy healing...a hands on approach.
 The neurobiology of energy healing...a hands on approach. Have you ever considered why we use our hands for healing? After all it's not called "hands on healing" for nothing. Why do some practitioners
The neurobiology of energy healing...a hands on approach. Have you ever considered why we use our hands for healing? After all it's not called "hands on healing" for nothing. Why do some practitioners
THE STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF DRY ICE ON THE TEMPERATURE OF WATER
 THE STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF DRY ICE ON THE TEMPERATURE OF WATER Justin Tunley Cary Academy ABSTRACT: The purpose of this study was to find out how much the temperature of water would change over time after
THE STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF DRY ICE ON THE TEMPERATURE OF WATER Justin Tunley Cary Academy ABSTRACT: The purpose of this study was to find out how much the temperature of water would change over time after
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.)
 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
1. The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed of atoms and molecules that are in a constant state of constant random motion
 Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
Physical Science Period: Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Practice Test for Unit 3: Ch. 3, and some of 15 and 16: Kinetic Theory of Matter, States of matter, and and thermodynamics, and gas laws. 1. The Kinetic
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Background on Brain Injury
 CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus
 Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Brain Maps The Sensory Homunculus Our brains are maps. This mapping results from the way connections in the brain are ordered and arranged. The ordering of neural pathways between different parts of the
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
THE STUDY OF GUMMY BEARS SOAKED IN DIFFERENT LIQUIDS FOR DIFFERENT AMOUNTS OF TIME
 THE STUDY OF GUMMY BEARS SOAKED IN DIFFERENT LIQUIDS FOR DIFFERENT AMOUNTS OF TIME Emily Grimm Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to determine how much gummy bears grew in different liquids,
THE STUDY OF GUMMY BEARS SOAKED IN DIFFERENT LIQUIDS FOR DIFFERENT AMOUNTS OF TIME Emily Grimm Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to determine how much gummy bears grew in different liquids,
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Chapter 1 Student Reading
 Chapter 1 Student Reading Chemistry is the study of matter You could say that chemistry is the science that studies all the stuff in the entire world. A more scientific term for stuff is matter. So chemistry
Chapter 1 Student Reading Chemistry is the study of matter You could say that chemistry is the science that studies all the stuff in the entire world. A more scientific term for stuff is matter. So chemistry
Brain Injury: Stages of Recovery
 Brain Injury: Stages of Recovery Recovery after brain injury is a process that occurs in stages. Some people move quickly through the stages, while others make slow, but steady gains. The Rancho Los Amigos'
Brain Injury: Stages of Recovery Recovery after brain injury is a process that occurs in stages. Some people move quickly through the stages, while others make slow, but steady gains. The Rancho Los Amigos'
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Lecture One: Brain Basics
 Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
HEARING. With Your Brain
 HEARING With Your Brain Better Hearing with Both Ears Experience A NEW FREEDOM Your brain is responsible for processing everything you hear and needs accurate sound information from both ears. When you
HEARING With Your Brain Better Hearing with Both Ears Experience A NEW FREEDOM Your brain is responsible for processing everything you hear and needs accurate sound information from both ears. When you
The Adolescent Brain Learning Strategies & Teaching Tips
 The Adolescent Brain & Teaching Tips The adolescent brain is still developing and therefore requires different brain compatible strategies for learning. This section describes the adolescent brain, details
The Adolescent Brain & Teaching Tips The adolescent brain is still developing and therefore requires different brain compatible strategies for learning. This section describes the adolescent brain, details
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych
 Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Most people living with epilepsy do not experience serious problems with their thinking. However, there are aspects of thinking that can be affected
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Most people living with epilepsy do not experience serious problems with their thinking. However, there are aspects of thinking that can be affected
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI)
 Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
TESTING DRY ICE IN DIFFERENT LIQUIDS. Aditya S. Cary Academy ABSTRACT
 TESTING DRY ICE IN DIFFERENT LIQUIDS Aditya S Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this experiment was to see how dropping dry ice into different liquids affect the mass and temperature of the dry ice.
TESTING DRY ICE IN DIFFERENT LIQUIDS Aditya S Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this experiment was to see how dropping dry ice into different liquids affect the mass and temperature of the dry ice.
The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software
 Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Chapter 10 Auditory Content The Design and Implementation of Multimedia Software David Bernstein Jones and Bartlett Publishers www.jbpub.com David Bernstein (jbpub.com) Multimedia Software Jones and Bartlett
Approaching the End of Life. A Guide for Family & Friends
 Approaching the End of Life A Guide for Family & Friends Approaching the End of Life A Guide for Family & Friends Patrice Villars, MS, GNP and Eric Widera, MD Introduction In this booklet you will find
Approaching the End of Life A Guide for Family & Friends Approaching the End of Life A Guide for Family & Friends Patrice Villars, MS, GNP and Eric Widera, MD Introduction In this booklet you will find
Parkinson s Disease (PD)
 Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Problem-Based Group Activities for a Sensation & Perception Course. David S. Kreiner. University of Central Missouri
 -Based Group Activities for a Course David S. Kreiner University of Central Missouri Author contact information: David Kreiner Professor of Psychology University of Central Missouri Lovinger 1111 Warrensburg
-Based Group Activities for a Course David S. Kreiner University of Central Missouri Author contact information: David Kreiner Professor of Psychology University of Central Missouri Lovinger 1111 Warrensburg
xxx Lesson 19 how memory works and techniques to improve it, and (2) appreciate the importance of memory skills in education and in his or her life.
 xxx Lesson 19 Memory Skills! Overview: This lesson provides a basic look at how our memory works and how it can be improved by using some simple techniques. Objectives: The objective of this lesson is
xxx Lesson 19 Memory Skills! Overview: This lesson provides a basic look at how our memory works and how it can be improved by using some simple techniques. Objectives: The objective of this lesson is
Amazing AmMy Brain! DID YOU KNOW..
 My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
My Amazing Brain! DID YOU KNOW... 3 Your Amazing Brain 4-5 How your Amazing Brain Works 6 7 Left Brain, Right Brain 8 Brain Facts 9 Senses 10 Look after your Brain 11 What Does a Brain Scientist Do? MY
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
How To Write A Checkbook
 ThisPersonal checking account lesson is designed to be for grades 9-12 Financial Literacy classes. Financial Literacy is a state graduation requirement. 1 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES: The objective of this lesson
ThisPersonal checking account lesson is designed to be for grades 9-12 Financial Literacy classes. Financial Literacy is a state graduation requirement. 1 GOALS AND OBJECTIVES: The objective of this lesson
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 12, December-2011 1 Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 12, December-2011 1 Cerebral Hemispheres and Learning: A Study of the Correlation between Brain Dominations and Learning Styles
Memory: The Long and Short of It
 Memory: The Long and Short of It Memory s Beginnings Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) Encoding Converting information into a form that can be entered into memory Storage Retaining information over varying
Memory: The Long and Short of It Memory s Beginnings Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) Encoding Converting information into a form that can be entered into memory Storage Retaining information over varying
This is how quickly your brain forgets things
 Brain gym starters This is how quickly your brain forgets things Your brain is a muscle Like every other muscle it needs exercise Brain gym is one way to exercise your mind so that you can learn better.
Brain gym starters This is how quickly your brain forgets things Your brain is a muscle Like every other muscle it needs exercise Brain gym is one way to exercise your mind so that you can learn better.
What is Energy? What is the relationship between energy and work?
 What is Energy? What is the relationship between energy and work? Compare kinetic and potential energy What are the different types of energy? What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Great, but
What is Energy? What is the relationship between energy and work? Compare kinetic and potential energy What are the different types of energy? What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Great, but
Functions of the Brain
 Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
A diagram of the ear s structure. The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal.
 A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
A diagram of the ear s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear includes the portion of the ear that we see the pinna/auricle and the ear canal. The pinna or auricle is a concave cartilaginous structure,
Songwriting. Geniuses. for. 25 Tips for the Genius in Everyone. By Gene Burnett
 Songwriting for Geniuses 25 Tips for the Genius in Everyone By Gene Burnett Songwriting for Geniuses iii Introduction This little book is entitled Songwriting For Geniuses and is comprised of various tips
Songwriting for Geniuses 25 Tips for the Genius in Everyone By Gene Burnett Songwriting for Geniuses iii Introduction This little book is entitled Songwriting For Geniuses and is comprised of various tips
VAK Learning Styles. Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions:
 What is Your Learning Preference? VAK Learning Styles Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions: Some people like to see what you
What is Your Learning Preference? VAK Learning Styles Whether you realise it or not, we all have preferences for how we absorb information, analyse it and make decisions: Some people like to see what you
Skill acquisition. Skill acquisition: Closed loop theory Feedback guides learning a motor skill. Problems. Motor learning practice
 Motor learning theories closed loop theory schema theory hierarchical theory Skill acquisition Motor learning practice Fitt s three stages motor imagery physical changes Skill acquisition: Closed loop
Motor learning theories closed loop theory schema theory hierarchical theory Skill acquisition Motor learning practice Fitt s three stages motor imagery physical changes Skill acquisition: Closed loop
Basic brain information
 Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Writing Learning Objectives
 Writing Learning Objectives Faculty Development Program Office of Medical Education Boston University School of Medicine All Rights Reserved 2004 No copying or duplication of this presentation without
Writing Learning Objectives Faculty Development Program Office of Medical Education Boston University School of Medicine All Rights Reserved 2004 No copying or duplication of this presentation without
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Chapter 7: Memory. Memory
 Chapter 7: Memory Case Study: H.M. and His Missing Memories Section 1: Memory Classifications and Processes Section 2: Three Stages of Memory Section 3: Forgetting and Memory Improvement Experiment: Applying
Chapter 7: Memory Case Study: H.M. and His Missing Memories Section 1: Memory Classifications and Processes Section 2: Three Stages of Memory Section 3: Forgetting and Memory Improvement Experiment: Applying
FREE CHORD BOOK Introduction
 FREE CHORD BOOK Introduction Hi, I m Andy and welcome to my chord book for beginners! Most chord books are packed full hundreds of chord diagrams, so many in fact it could take literally years to play
FREE CHORD BOOK Introduction Hi, I m Andy and welcome to my chord book for beginners! Most chord books are packed full hundreds of chord diagrams, so many in fact it could take literally years to play
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
THE STUDY OF HELIUM AND BALLOONS. Will Barbrey. Cary Academy ABSTRACT
 THE STUDY OF HELIUM AND BALLOONS Will Barbrey Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to determine how strong helium was against air and weights. Helium weighs one gram less than air therefore
THE STUDY OF HELIUM AND BALLOONS Will Barbrey Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to determine how strong helium was against air and weights. Helium weighs one gram less than air therefore
Advanced Techniques for the Walkingbass
 Advanced Techniques for the Walkingbass I have seen guys with 5 string basses who can t get half the sounds that you are getting out of just three. -Buddy Fo of the Invitations If you have read the Beginners
Advanced Techniques for the Walkingbass I have seen guys with 5 string basses who can t get half the sounds that you are getting out of just three. -Buddy Fo of the Invitations If you have read the Beginners
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Music Theory: Explanation and Basic Principles
 Music Theory: Explanation and Basic Principles Musical Scales Musical scales have developed in all cultures throughout the world to provide a basis for music to be played on instruments or sung by the
Music Theory: Explanation and Basic Principles Musical Scales Musical scales have developed in all cultures throughout the world to provide a basis for music to be played on instruments or sung by the
The Effects of Moderate Aerobic Exercise on Memory Retention and Recall
 The Effects of Moderate Aerobic Exercise on Memory Retention and Recall Lab 603 Group 1 Kailey Fritz, Emily Drakas, Naureen Rashid, Terry Schmitt, Graham King Medical Sciences Center University of Wisconsin-Madison
The Effects of Moderate Aerobic Exercise on Memory Retention and Recall Lab 603 Group 1 Kailey Fritz, Emily Drakas, Naureen Rashid, Terry Schmitt, Graham King Medical Sciences Center University of Wisconsin-Madison
How to make more money in forex trading. 2003 W. R. Booker & Co. All rights reserved worldwide, forever and ever and ever.
 The 10 Rules How to make more money in forex trading. 2003 W. R. Booker & Co. All rights reserved worldwide, forever and ever and ever. 2 10 Rules Page 2 Rule #1: Never lie to anyone. Never lie to yourself
The 10 Rules How to make more money in forex trading. 2003 W. R. Booker & Co. All rights reserved worldwide, forever and ever and ever. 2 10 Rules Page 2 Rule #1: Never lie to anyone. Never lie to yourself
Executive. Presented by Patti Jenks Principal, ASSETS High School
 Executive Function Presented by Patti Jenks Principal, ASSETS High School 4 Major Lobes of the Brain Another look inside. How does the brain work? Parietal Lobe - orientation, calculation, certain types
Executive Function Presented by Patti Jenks Principal, ASSETS High School 4 Major Lobes of the Brain Another look inside. How does the brain work? Parietal Lobe - orientation, calculation, certain types
Tune Up Your Memory. Overview of course. A Few Statistics 2/3/2015
 Tune Up Your Memory Michelle Swantek Certified Geriatric Wellness Instructor MorningStar Senior Living Boise Overview of course How Memory Works How the Brain Works Use It or Lose It Nutrition and Exercise
Tune Up Your Memory Michelle Swantek Certified Geriatric Wellness Instructor MorningStar Senior Living Boise Overview of course How Memory Works How the Brain Works Use It or Lose It Nutrition and Exercise
Taking Hold of Your Mind: What Skills:
 Taking Hold of Your Mind: What Skills: Observing, Describing, and Participating Core mindfulness skills are the foundation of all Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) skills training. The problems addressed
Taking Hold of Your Mind: What Skills: Observing, Describing, and Participating Core mindfulness skills are the foundation of all Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) skills training. The problems addressed
Perceptual Motor Development
 Perceptual Motor Development Characteristic Involves children during preschool to primary grades; usually ages 21/2 to 6. Combines movement abilities with academics (reading,writing,language, math) Engages
Perceptual Motor Development Characteristic Involves children during preschool to primary grades; usually ages 21/2 to 6. Combines movement abilities with academics (reading,writing,language, math) Engages
Playing By Ear Who Can Play By Ear?... 2 How To Play By Ear... 3 Happy Birthday To You (By Ear)... 4 Match Tones... 5 Add Chords...
 Playing By Ear Who Can Play By Ear?... 2 How To Play By Ear... 3 Happy Birthday To You (By Ear)... 4 Match Tones... 5 Add Chords... 6 Allcanplay TM Piano * MaxLearning.Net 2009 * Playing By Ear * 4/6/2009
Playing By Ear Who Can Play By Ear?... 2 How To Play By Ear... 3 Happy Birthday To You (By Ear)... 4 Match Tones... 5 Add Chords... 6 Allcanplay TM Piano * MaxLearning.Net 2009 * Playing By Ear * 4/6/2009
Alcohol and the Adolescent Brain. Ruth Bowles. BS, CPP Executive Director The Rockland Council on Alcoholism and other Drug Dependence, Inc.
 Alcohol and the Adolescent Brain Ruth Bowles. BS, CPP Executive Director The Rockland Council on Alcoholism and other Drug Dependence, Inc. Freedom is that instant between when someone tells you to do
Alcohol and the Adolescent Brain Ruth Bowles. BS, CPP Executive Director The Rockland Council on Alcoholism and other Drug Dependence, Inc. Freedom is that instant between when someone tells you to do
Lesson Plan in Brief What To Know What To Do What To Say
 Lesson Plan Leader s Guide Lesson Plan in Brief What To Know What To Do What To Say Children and parents need to know about alcohol and its effects to make good decisions about drinking. They need to
Lesson Plan Leader s Guide Lesson Plan in Brief What To Know What To Do What To Say Children and parents need to know about alcohol and its effects to make good decisions about drinking. They need to
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
MEMORY MODULE A Training Module for Parents and Educators of Children with Traumatic Brain Injury.
 MEMORY MODULE A Training Module for Parents and Educators of Children with Traumatic Brain Injury. Funded by an IDEA Discretionary Grant #2007-9911-22 Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction (http://www.dpi.wi.gov)
MEMORY MODULE A Training Module for Parents and Educators of Children with Traumatic Brain Injury. Funded by an IDEA Discretionary Grant #2007-9911-22 Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction (http://www.dpi.wi.gov)
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
THE CHOIR: SING WHILE YOU WORK. THE BASICS OF SINGING bbc.co.uk/thechoir
 THE BASICS OF ING THE BASICS OF ING Gareth Malone Welcome to The Choir: Sing While You Work guide to singing. If you re reading this, congratulations, as you have either already taken that first step and
THE BASICS OF ING THE BASICS OF ING Gareth Malone Welcome to The Choir: Sing While You Work guide to singing. If you re reading this, congratulations, as you have either already taken that first step and
Behavior & Sensory Strategies for Individuals with ASD
 Behavior & Sensory Strategies for Individuals with ASD Kathleen Mo Taylor, OTR/L The Autism Programs Center for Development and Disability University of New Mexico This presentation is made possible, in
Behavior & Sensory Strategies for Individuals with ASD Kathleen Mo Taylor, OTR/L The Autism Programs Center for Development and Disability University of New Mexico This presentation is made possible, in
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Learn How to Revise 1
 Learn How to Revise 1 SCHOOL EXAM DATES 2016 END OF YEAR EXAMS FOR YEARS 7-9 BEGIN ON MONDAY 6 TH JUNE THEY WILL TAKE PLACE IN LESSONS DURING THIS WEEK AND IF NECESSARY THE WEEK AFTER. Some subjects are
Learn How to Revise 1 SCHOOL EXAM DATES 2016 END OF YEAR EXAMS FOR YEARS 7-9 BEGIN ON MONDAY 6 TH JUNE THEY WILL TAKE PLACE IN LESSONS DURING THIS WEEK AND IF NECESSARY THE WEEK AFTER. Some subjects are
A Guide for Enabling Scouts with Cognitive Impairments
 A Guide for Enabling Scouts with Cognitive Impairments What cognitive impairments are discussed in this manual? Autism Spectrum Disorder Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder Depression Down Syndrome
A Guide for Enabling Scouts with Cognitive Impairments What cognitive impairments are discussed in this manual? Autism Spectrum Disorder Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder Depression Down Syndrome
B U R T & D A V I E S PERSONAL INJURY LAWYERS
 TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
Knowledge and Understanding of the World. Early Learning Goals. National Curriculum. (learning objectives) (level 1 descriptors)
 Knowledge and Understanding of the World Knowledge and Understanding of the world Science K&U4 Ask questions about why things happened and how things work To talk about what they see To make recordings
Knowledge and Understanding of the World Knowledge and Understanding of the world Science K&U4 Ask questions about why things happened and how things work To talk about what they see To make recordings
Integrated Skills in English ISE II
 Integrated Skills in English ISE II Reading & Writing exam Sample paper 2 Your full name: (BLOCK CAPITALS) Candidate number: Centre: Time allowed: 2 hours Instructions to candidates 1. Write your name,
Integrated Skills in English ISE II Reading & Writing exam Sample paper 2 Your full name: (BLOCK CAPITALS) Candidate number: Centre: Time allowed: 2 hours Instructions to candidates 1. Write your name,
Arkansas State PIRC/ Center for Effective Parenting
 Strengthening Your Child s Home STUDY SKILLS In addition to participating in class, success in school will require your child to use good work and study habits at home. Your child will need to spend time
Strengthening Your Child s Home STUDY SKILLS In addition to participating in class, success in school will require your child to use good work and study habits at home. Your child will need to spend time
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
 CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS. 6.1. CONNECTIONS AMONG NEURONS Neurons are interconnected with one another to form circuits, much as electronic components are wired together to form a functional
How Does Memory Change With Age? Class Objectives. Think about the importance of your memory 3/22/2011. The retention of information over time
 How Does Memory Change With Age? The retention of information over time Class Objectives What is memory? What factors influence our memory? Think about the importance of your memory It s hard to even attempt
How Does Memory Change With Age? The retention of information over time Class Objectives What is memory? What factors influence our memory? Think about the importance of your memory It s hard to even attempt
1 Characteristics of Living Things
 CHAPTER 2 1 Characteristics of Living Things SECTION It s Alive!! Or Is It? BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are all living things made of?
CHAPTER 2 1 Characteristics of Living Things SECTION It s Alive!! Or Is It? BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are all living things made of?
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Learning Theories Taught in EDFL 2240: Educational Psychology. Behavioral Learning Theories (Learning is defined as a change in behavior)
 Learning Theories Taught in EDFL 2240: Educational Psychology Behavioral Learning Theories (Learning is defined as a change in behavior) Pavlov & Watson s Classical (Reflexive) Conditioning Definition:
Learning Theories Taught in EDFL 2240: Educational Psychology Behavioral Learning Theories (Learning is defined as a change in behavior) Pavlov & Watson s Classical (Reflexive) Conditioning Definition:
Imagine It! ICEBREAKER:
 ICEBREAKER: Imagine It! FOCUS: To develop creativity and increase participants comfort with acting in front of a group PURPOSE: To help participants relax before working on their public presentation skills
ICEBREAKER: Imagine It! FOCUS: To develop creativity and increase participants comfort with acting in front of a group PURPOSE: To help participants relax before working on their public presentation skills
Standards Alignment Minnesota Science Standards Alignment Matrix www.brainu.org/resources/mnstds
 Lesson Summary: Neurons transfer information by releasing neurotransmitters across the synapse or space between neurons. Students model the chemical communication between pre-synaptic and post-synaptic
Lesson Summary: Neurons transfer information by releasing neurotransmitters across the synapse or space between neurons. Students model the chemical communication between pre-synaptic and post-synaptic
The Physics and Math of Ping-pong and How It Affects Game Play. By: Connor Thompson & Andrew Johnson
 The Physics and Math of Ping-pong and How It Affects Game Play 1 The Physics and Math of Ping-pong and How It Affects Game Play By: Connor Thompson & Andrew Johnson The Practical Applications of Advanced
The Physics and Math of Ping-pong and How It Affects Game Play 1 The Physics and Math of Ping-pong and How It Affects Game Play By: Connor Thompson & Andrew Johnson The Practical Applications of Advanced
Lecture 2. The Development Part of the. The Greenspan Floortime Approach D Part of Model Lecture 2
 Lecture 2 The Development Part of the DIR /Floortime Model The Greenspan Floortime Approach D Part of Model Lecture 2 Functional Emotional Developmental elopmental Capacities Core capacities that integrate
Lecture 2 The Development Part of the DIR /Floortime Model The Greenspan Floortime Approach D Part of Model Lecture 2 Functional Emotional Developmental elopmental Capacities Core capacities that integrate
Brain Basics: A Brain in Sync
 Brain Basics: A Brain in Sync By: Dr. Robert Melillo The idea of a functional relationship between the left and right sides of the brain is hardly new. In 1949, Canadian neuropsychologist Donald O. Hebb,
Brain Basics: A Brain in Sync By: Dr. Robert Melillo The idea of a functional relationship between the left and right sides of the brain is hardly new. In 1949, Canadian neuropsychologist Donald O. Hebb,
Chapter 4 COMMUNICATION SKILLS. The difference between verbal and nonverbal communication. The difference between hearing and listening
 Chapter 4 COMMUNICATION SKILLS What You Will Learn The difference between verbal and nonverbal communication The difference between hearing and listening Factors that promote effective communication Barriers
Chapter 4 COMMUNICATION SKILLS What You Will Learn The difference between verbal and nonverbal communication The difference between hearing and listening Factors that promote effective communication Barriers
Multiple Choice For questions 1-10, circle only one answer.
 Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 1 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 1. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
