3-LEAD ECG CRASH COURSE. Mrs Dagmar Muhlbauer NDip AET; BTech EMC; MTech EMC August 2016
|
|
|
- Ada Stephens
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3-LEAD ECG CRASH COURSE Mrs Dagmar Muhlbauer NDip AET; BTech EMC; MTech EMC August 2016
2 Anatomy & Physiology Recap: Heart sits in middle of chest at a slight angle pointing downward, to the left and slightly anterior. RV dominates the anterior view RV dominates visual view LV dominates electrical view CO = HR x SV HR is the most important variable in maintaining CO
3 Anatomy & Physiology Recap: AV septum is non-conductive tissue between the atria and ventricles Acts like a firewall The only electrical communication between the atria and ventricles is the AV node.
4 Anatomy & Physiology Recap: Main pacemaker of the heart is the SA node found in RA (60-100bpm) Internodal pathways AV node (RA) slows down conduction from atria to ventricles to allow for atrial contraction to occur (45-50bpm) Bundle of His gives rise to left and right bundle branches in RA and intraventricular septum Left and right bundle branches (40-45bpm) Purkinje system initiate ventricular depolarization (35-40bpm)
5 Components of the ECG: P wave: Atrial depolarization Wave starts when SA node fires Includes transmission through three internodal pathways, Bachman bundle and atrial myocytes 0.06 to 0.12 seconds
6 Components of the ECG: Tp wave: Atrial repolarization Not seen as occurs at the same time as the QRS
7 Components of the ECG: PR segment: End of P wave to the start of the QRS
8 Components of the ECG: PR interval: Time period from start of P wave to QRS Includes P wave and PR segment Covers all events from initiation of electrical impulse in SA node up to ventricular depolarisation seconds
9 Components of the ECG: QRS complex: Ventricular depolarization Q = first negative deflection R = first positive deflection after P S = first negative deflection after R seconds or half of the PR interval Pathological Q wave: Height is equal to or greater than ⅓ the height of the R wave
10 Components of the ECG: ST segment: End of QRS to beginning of T wave Electrically neutral time for heart between ventricular depolarization and repolarization J-Point: Point where QRS ends and ST begins
11 Components of the ECG: T wave: Ventricular depolarization
12 Components of the ECG: QT interval: QRS complex + ST segment + T wave Ventricular depolarization to ventricular repolarization
13 ECG paper: Little box = 0.04 seconds Big box = 0.20 seconds (5 x little boxes) Big boxes x 5 = 1 second Small marks along bottom of strip every 3 seconds
14 ECG tools: Calipers ECG ruler Straight edge (paper)
15 Calculating rate: Remember that the P wave rate (atrial) may be different to QRS rate (ventricular). Find a QRS that starts on a thick line which is the starting point Then go to exact spot of next QRS (end point). Count the thick lines between the 2 spots.
16 Calculating rate: Print a 6 second strip 30 large boxes = 6 seconds Count the number of complexes x 10 = rate/min
17 Terminology recap: Chronotrope: Change in HR Positive chronotrope causes increase in HR Negative chronotrope causes decrease in HR Dromotrope: Change in speed of conduction through AV junction Positive dromotrope causes increase in AV node conduct velocity Negative dromotrope causes decrease in AV node conduct velocity Inotrope: Change in myocardial contractility Positive inotrope causes increase in myocardial contractility Negative inotrope causes decrease in myocardial contractility
18 ECG Leads: Lead I: +ve L clavicle -ve R clavicle Provides info about left lateral wall of heart Lead II: +ve electrode just below L pectoral muscle -ve R clavicle Provides info about inferior wall of heart Lead III: +ve electrode just below L pectoral muscle -ve L clavicle
19 ECG Leads: Lead II commonly used for cardiac monitoring The positioning of the +ve and ve electrodes in this lead most closely resembles the pathway of current flow in normal atrial and ventricular depolarization.
20 Steps to analyse a strip: 1. Rate (atrial & ventricular)? 2. Regular / irregular? If irregular, is it regularly irregular or irregularly irregular? 3. P waves? Present? Uniform? P wave before each QRS? 4. PR interval? Within normal limits? Constant?
21 Steps to analyse a strip: 5. QRS complexes? P waves and QRS associated with each other? Narrow? 0.10 seconds (supraventricular) Wide? > 0.12 seconds (ventricular) QRS uniform throughout? Any dropped beats?
22 Arrhythmia zones of the heart: Sinus Node Arrhythmias: Supraventricular When the heart functions normally, SA node acts as a primary pacemaker The autonomic nervous system innervates the SA node through the vagus nerve Stimulation of vagus: firing of SA node Stimulation of SNS it
23 Arrhythmia zones of the heart: Atrial Arrhythmias: Supraventricular Result from impulses originating in areas outside the SA node
24 Arrhythmia zones of the heart: Junctional Arrhythmias: Supraventricular Originate in the AV junction (area around AV node and bundle of His) Occurs when SA node is suppressed and fails to conduct impulses or when a block in conduction occurs
25 Arrhythmia zones of the heart: Ventricular Arrhythmias: Originate in the ventricles below the bundle of His Occur when electrical impulses depolarize the myocardium using a different pathway from normal impulses QRS complex will be wider because of prolonged conduction through ventricles
26 Normal Sinus Rhythm: Impulse starts in SA node & progresses to ventricles through normal conduction pathway Rhythm: Regular Rate: Normal P wave: P wave for every QRS; similar in size and shape QRS complexes: Similar in size and shape ( seconds) PR interval: Normal ( seconds) QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
27 Sinus Bradycardia: Normal response to demand for blood flow. Vagal stimulation & sympathetic stimulation Automaticity in SA node Rhythm: Regular Rate: <60bpm P wave: P wave for every QRS; similar in size and shape QRS complexes: Similar in size and shape ( seconds) PR interval: Normal ( seconds) QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
28 Sinus Tachycardia: Results in reduced CO Rhythm: Regular Rate: >100 but <160bpm (except during exercise) P wave: P wave for every QRS; similar in size and shape QRS complexes: Similar in size and shape ( seconds) PR interval: Normal ( seconds) QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
29 Sinus Arrhythmia: Pacemaker cells of SA node fire irregularly Rhythm is irregular & corresponds with respiratory cycle During inspiration: An increase in the flow of blood back to the heart reduces vagal tone which HR P-P interval shortens During expiration: VR decreases which increases vagal tone and HR P-P interval lengthens Cyclic irregular rhythm that varies with respiratory cycle
30 Sinus Arrest: Disorder of impulse formation Due to lack of electrical activity in the atrium (atrial standstill) Atria aren t stimulated and an entire PQRST complex is missing Sinus pause: Atrial standstill when 1 or 2 beats aren t formed Sinus arrest: When 3 or more beats aren t formed SA node fails to generate an impulse Causes: Acute infection Heart disease Vagal stimulation
31 Premature Atrial Contraction: Originate outside the SA node Result from irritable focus in the atria that takes over as pacemaker for one or more beats SA node fires an impulse but then irritable focus jumps in, firing its own impulse before SA node fires again Baseline rhythm is regular Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Depends P wave: Present but abnormal QRS complexes: Normal. Similar in size and shape ( seconds) PR interval: Normal ( seconds) QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal or abnormal with some embedded P waves
32 Atrial Tachycardia: Supraventricular tachycardia Rhythm originates above the ventricles Rhythm: Regular Rate: Atrial rate of bpm P wave: Almost hidden in T wave QRS complexes: Normal. Similar in size and shape ( seconds) PR interval: Normal ( seconds) QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Distorted by P wave
33 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia: Supraventricular tachycardia Numerous atrial foci firing intermittently Produces varying P waves Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Atrial rate of bpm P wave: Configuration varies QRS complexes: Normal. Similar in size and shape ( seconds) PR interval: Varies QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Distorted by P wave
34 Wandering Atrial Pacemaker: Irregular rhythm Pacemaker changes its focus from the SA node to another area above the ventricles Origin of impulse wanders beat-to-beat from the SA node to other atrial sites or to AV junction Multifocal atrial tachycardia is a tachycardic version of Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Normal P wave: Configuration varies QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Varies QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
35 Atrial Flutter: Supraventricular tachycardia Originates in a single atrial focus. AV node fails to allow conduction of all the impulses to the ventricles Due to this, the ventricular rate is slower Rhythm: Atrial is regular and Ventricular is irregular Rate: Atrial rate of bpm & Ventricular rate is slower P wave: Classic saw-toothed experience QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: Unidentifiable ST segment: Normal T waves: Unidentifiable
36 Atrial Fibrillation: Chaotic, asynchronous, electrical activity in atrial tissue Stems from the firing of a number of impulses in re-entry pathways Ectopic impulses may fire at a rate of bpm, causing atria to quiver instead of contract Ventricles only respond to those impulses that make it through AV node Rhythm: Irregularly irregular Rate: Atrial rate is indiscernible & ventricular rate is slower P wave: Absent, replaced with fine fibrillatory waves QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Indiscernible QT interval: Unmeasurable ST segment: Normal T waves: Indiscernible
37 Premature Junctional Contraction: An ectopic beat occurs when an irritable location within the AV junction acts as a pacemaker and fires prematurely or out of sequence The atria are depolarized in retrograde fashion causing an inverted P wave Ventricles depolarized normally PJC appears as an early beat Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Depends on underlying rhythm P wave: Inverted and precedes the QRS complex with PJC, otherwise normal QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Normal for underlying rhythm and 0.06secs for PJC QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
38 Junctional Escape Beat: A beat that occurs after a conduction delay from the atria Normal intrinsic firing rate of cells in AV junction is 40-60bpm AV junction can take over as the pacemaker if the SA node slows down or fails to conduct Prevents ventricular standstill Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Depends on underlying rhythm but usually slow P wave: Underlying rhythm may be normal but JEB has inverted or no P wave QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Normal QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
39 Junctional: String of beats that occurs after a conduction delay from the atria Normal intrinsic firing rate of cells in AV junction is 40-60bpm AV junction can take over as the pacemaker if the SA node slows down or fails to conduct Prevents ventricular standstill Rhythm: Regular Rate: 40-60bpm P wave: Absent or inverted and preceding each QRS QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Not present or normal QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
40 Accelerated Junctional: Irritable focus in the AV junction that speeds up to take over as the heart s pacemaker The atria are depolarized by means of a retrograde conduction and the ventricles function normally Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: Absent QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
41 Junctional Tachycardia: 3 or more PJCs occur in a row An irritable focus from the AV junction has enhanced automaticity, overriding the SA node to function as the pacemaker Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: Inverted or absent QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Unmeasurable or normal if present and inverted QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
42 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Ectopic beat Electrical irritability in the ventricular conduction system or muscle tissue Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Depends on underlying rhythm P wave: Absent with PVC but present with other QRS complexes QRS complexes: Wide & bizarre for PVC; normal for underlying rhythm PR interval: None in PVC; normal in underlying rhythm QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
43 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Couplets: 2 PVCs in a row Salvo: 3 or more PVCs in a row Considered a run of VT (dangerous) Multiform: PVCs that look different from one another Arise from different sites Bigeminy / Trigeminy: PVC every other beat = bigeminy PVC every third beat = trigeminy
44 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Treatment: Lignocaine Hydrochloride: Control of haemodynamically compromising PVCs, i.e. complex ventricular ectopy (symptomatic / unstable patient) associated with AMI / ACS: Multiform (multifocal) Repetitive (couplets, salvos, or > 3) R on T pattern Complex ventricular ectopy in the setting of myocardial ischemia or causing haemodynamic instability should be suppressed. (Only in the setting of symptomatic, complex ectopy is lignocaine likely to benefit a patient having an AMI / ACS). Loading dose: 1mg/kg slowly IVI Repeat loading dose: 0.5mg/kg every 5 minutes Maximum dose: 3mg/kg Follow with maintenance infusion of 1-4mg/min upon restoration of a stable rhythm 100mg/5ml (2%) ampoule
45 Ventricular Escape Beat: Ventricular escape beats occur when the rate of electrical discharge reaching the ventricles falls below the rate of ventricular depolarisation Escape beat usually occurs 2-3 seconds after an electrical impulse has failed to reach the ventricles Acts to prevent cardiac arrest Rhythm: Irregular Rate: Depends on underlying rhythm but usually bradycardic P wave: Absent with PVC but present with other QRS complexes QRS complexes: Wide & bizarre for PVC; normal for underlying rhythm PR interval: None in PVC; normal in underlying rhythm QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
46 Idioventricular: Rhythms of last resort Act as safety mechanism to prevent ventricular standstill when no impulses are conducted to the ventricles from above the bundle of His The cells of the His-Purkinje system take over and act as the heart s pacemaker Rhythm: Regular Rate: 20-40bpm P wave: Absent QRS complexes: Wide & bizarre PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: 0.60 seconds ST segment: Absent T waves: Normal
47 Accelerated Idioventricular: Same characteristics as idioventricular, just faster Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: Absent QRS complexes: Wide & bizarre PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: 0.60 seconds ST segment: Absent T waves: Normal
48 Ventricular Tachycardia: Three or more PVCs occur in a row Ventricular rate exceeds 100bpm Results from increased myocardial irritability Monomorphic or Polymorphic Rhythm: Regular Rate: bpm P wave: Absent QRS complexes: Wide & bizarre PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: Unmeasurable ST segment: Absent T waves: Opposite direction of QRS
49 Torsades de Pointes: Twisting about the points Special form of polymorphic VT QRS complexes rotate about the baseline deflecting downward and upward for several beats Rhythm: Irregular Rate: bpm P wave: Absent QRS complexes: Wide with changing amplitude PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: 0.60 seconds ST segment: Absent T waves: Normal
50 Torsades de Pointes: Treatment: Pulseless = Defibrillation & CPR Pulse: Magnesium Sulphate 1 2g (2 to 4 ml of a 50% solution) Dilute 1g/2ml vial to 10ml with sterile water = 10% solution. Give slowly, not exceeding 1.5ml/min, with continuous careful monitoring. Lignocaine hydrochloride if Magnesium not available or ineffective Cardioversion
51 Ventricular Fibrillation: Chaotic pattern of electrical activity in the ventricles in which electrical impulses arise from many different foci Produces no effective muscular contraction and no CO Rhythm: Irregulary irregular Rate: Undetermined P wave: Absent QRS complexes: Indiscernible PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: N/A ST segment: Absent T waves: Indiscernible
52 AV Blocks: Interruption in the conduction of impulses between the atria and ventricles Block can occur at AV node, bundle of His or bundle branches
53 1 st Degree AV Block: Impulses from the atria are consistently delayed during conduction through AV node Conduction eventually occurs, it just takes longer than normal E.g. people walking in line through a doorway, but each person hesitates before crossing the threshold Rhythm: Regular Rate: Based on underlying rhythm P wave: Normal QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: >0.20 seconds QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
54 2 nd Degree Type I AV Block: Occurs when each successive impulse from the SA node is delayed slightly longer than the previous impulse Pattern continues until an impulse fails to be conducted to the ventricles Then cycle repeats E.g. line of people trying to get through a doorway, each one taking longer and longer until finally one cant get through Rhythm: Atrial regular and ventricular irregular Rate: Atrial rate and ventricular rate will differ with atrial rate being faster P wave: Normal QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Gradually longer with each successive beat until a P wave fails to conduct to ventricles QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
55 2 nd Degree Type II AV Block: Occasional impulses from the SA node fail to conduct to the ventricles You wont see the PR interval lengthen before the impulse fails to conduct E.g. people passing through a doorway at the same speed, except that, periodically, one of them just cant get through Rhythm: Atrial regular and ventricular irregular Rate: Atrial rate and ventricular rate will differ with atrial rate being faster P wave: Normal, but some not followed by a QRS QRS complexes: Normal PR interval: Constant but may be normal or prolonged QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
56 3 rd Degree AV Block: Impulses from atria are completely blocked at the AV node and cant be conducted to the ventricles E.g. line of people waiting to go through a doorway but no one can go through Atria and ventricles act independently Atria remain under control of SA node (60-100bpm) Ventricles originate from AV node (40-60bpm) Rhythm: Regular Rate: Atrial rate and ventricular rate will differ P wave: Normal QRS complexes: Normal / Wide PR interval: Varies QT interval: Normal ST segment: Normal T waves: Normal
57 Agonal Rhythm: Similar in appearance to an idioventricular rhythm But occurs at a rate of < 20bpm Dying heart Basically asystole with an occasional P wave or QRS complex QRS complexes are very wide and very bizarre Treat as asystole
58 Asystole: Ventricular standstill No electrical activity in the heart and no CO Rhythm: N/A Rate: Undetermined P wave: Absent QRS complexes: Absent PR interval: Unmeasurable QT interval: N/A ST segment: Absent T waves: Absent
59 Pacemakers: Atrial Pacemakers: Ventricular Pacemakers: Loss of capture:
60 References: 1. ECGs Made Easy; B Aehlert, RN; Mosby Lifeline; Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation; TB Garcia, MD, FACEP & GT Miller, NREMT-P; Jones & Bartlett; ECG Interpretation Made Incredibly Easy, 5 th Edition; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Wolters Kluwer; 2011.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
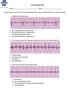 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
School of Health Sciences
 School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics. The Myocardial Cell. Chapter 1- Thaler
 Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response
 Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
Electrolyte Physiology. Something in the way she moves
 Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
ECG Filtering. Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903
 ECG Filtering Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903 ECG Filtering Three common noise sources q Baseline wander q Power line interference q Muscle noise When filtering any biomedical signal care should be
ECG Filtering Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903 ECG Filtering Three common noise sources q Baseline wander q Power line interference q Muscle noise When filtering any biomedical signal care should be
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
For more information about the use of the Propaq monitor, refer to the Propaq Directions For Use.
 Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Lecture Outline. Cardiovascular Physiology. Cardiovascular System Function. Functional Anatomy of the Heart
 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
 Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide
 Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias
 Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
TOP 5. The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac. Arrhythmias in Dogs & Cats. Sinus Arrhythmia. TOP 5 Arrhythmias Seen in Dogs & Cats
 Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Top 5 ardiology Peer reviewed TOP 5 rrhythmias in Dogs & ats shley Jones, DVM mara Estrada, DVM, DVIM (ardiology) University of Florida The term cardiac arrhythmia encompasses all cardiac rhythms other
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR. Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University
 Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
Crash Cart Drugs Drugs used in CPR Dr. Layla Borham Professor of Clinical Pharmacology Umm Al Qura University Introduction A list of the drugs kept in the crash carts. This list has been approved by the
2 ECG basics. Leads and planes. Leads. Planes. from different perspectives, which are called leads and planes.
 558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
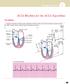 ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms The Basics 1. Anatomy of the cardiac conduction system: relationship to the ECG cardiac cycle. A, Heart: anatomy of conduction system. B, P-QRS-T complex: lines to
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation
 Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Detecting Atrial-ventricular blocks Arrhythmia based on RR-intervals on ECG Signals
 Detecting Atrial-ventricular blocks Arrhythmia based on -intervals on ECG Signals Makki Akasha abikier, Ibrahim Musa Ishag, Mohammed Izzeldin, Dong Gyu Lee, Gyoyong shon, Keun Ho Ryu Database/ioinformatics
Detecting Atrial-ventricular blocks Arrhythmia based on -intervals on ECG Signals Makki Akasha abikier, Ibrahim Musa Ishag, Mohammed Izzeldin, Dong Gyu Lee, Gyoyong shon, Keun Ho Ryu Database/ioinformatics
The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s
 EMS Solutions Presents The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s NOTICE: You DO NOT Have the Right to Reprint or Resell this Publication. However, you MAY give this report away, provided you do not change or alter the
EMS Solutions Presents The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s NOTICE: You DO NOT Have the Right to Reprint or Resell this Publication. However, you MAY give this report away, provided you do not change or alter the
Table of Contents Error! Bookmark not defined.
 Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
PSIO 603/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 2007 MRB 422; 626-6833 jburt@u.arizona.edu. MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle
 SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
DEFIBRILLATION AND THE AUTOMATIC EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR A GUIDE
 DEFIBRILLATION AND THE AUTOMATIC EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR A GUIDE Defibrillation and the AED, A guide Revised February 2012 Page 1 of 22 Original document complied by Pat Standen, Grampians Trauma, Emergency
DEFIBRILLATION AND THE AUTOMATIC EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR A GUIDE Defibrillation and the AED, A guide Revised February 2012 Page 1 of 22 Original document complied by Pat Standen, Grampians Trauma, Emergency
Basics of Pacing. Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN
 Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
Basics of Pacing Ruth Hickling, RN-BSN Tasha Conley, RN-BSN The Cardiac Conduction System Cardiac Conduction System Review Normal Conduction Conduction QRS QRS Complex Complex RR PP ST ST segment segment
GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS. (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support)
 AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
AUSTRALIAN RESUSCITATION COUNCIL GUIDELINE 11.9 MANAGING ACUTE DYSRHYTHMIAS (To be read in conjunction with Guideline 11.7 Post-Resuscitation Therapy in Adult Advanced Life Support) The term cardiac arrhythmia
What Are Arrhythmias?
 What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
What Are Arrhythmias? Many people have questions about what the word arrhythmia means, and arrhythmias can be a difficult subject to understand. The text below should give you a better understanding of
Electrophysiology study (EPS)
 Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Electrophysiology study (EPS) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Key Medical Terms Associated with the Cardiovascular System
 1 Key Medical Terms Associated with the Cardiovascular System Aneurysm: A thin, weakened section of the wall of an artery or vein that bulges outward, forming a balloon-like sac. Common causes are atherosclerosis,
1 Key Medical Terms Associated with the Cardiovascular System Aneurysm: A thin, weakened section of the wall of an artery or vein that bulges outward, forming a balloon-like sac. Common causes are atherosclerosis,
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
An ECG Primer. Quick Look. I saw it, but I did not realize it. Elizabeth Peabody
 4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
Signal-averaged electrocardiography late potentials
 SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL
 Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109
 Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109 Interventions to prevent cardiac arrest + Airway management + Ventilation support + Treatment of bradyarrhythmias & Tachyarrhythmias Treat cardiac arrest
Present : PGY 王 淳 峻 Supervisor: F1 王 德 皓 991109 Interventions to prevent cardiac arrest + Airway management + Ventilation support + Treatment of bradyarrhythmias & Tachyarrhythmias Treat cardiac arrest
Lethal Arrhythmias: Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130
 Lethal Arrhythmias: Advanced Rhythm Interpretation Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for five (5.0) contact hours. This course expires January 24,
Lethal Arrhythmias: Advanced Rhythm Interpretation Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for five (5.0) contact hours. This course expires January 24,
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
Premature Ventricular Contractions. Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS
 Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study
 Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
Patient Information Sheet Electrophysiological study Your doctor has recommended performing an electrophysiological study (also called EPS). EPS is a diagnostic procedure designed to test and evaluate
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC. BLS Changes
 ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
ACLS Provider Manual Comparison Sheet Based on 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR and ECC CPR Chest compressions, Airway, Breathing (C-A-B) BLS Changes New Old Rationale New science indicates the following order:
Andrew T. Reisner, Gari D. Clifford, and Roger G. Mark
 CHAPTER 1 The Physiological Basis of the Electrocardiogram Andrew T. Reisner, Gari D. Clifford, and Roger G. Mark Before attempting any signal processing of the electrocardiogram it is important to first
CHAPTER 1 The Physiological Basis of the Electrocardiogram Andrew T. Reisner, Gari D. Clifford, and Roger G. Mark Before attempting any signal processing of the electrocardiogram it is important to first
Trust Guideline for the Management of New-born Babies with abnormal heart rhythm
 A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
A clinical guideline recommended for use In: Blakeney Ward, Delivery Suite, Neonatal Unit By: For: Key words: Written by: Supported by: Approved by: Neonatal Medical Staff (SHOs, registrars, consultants)
ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms
 Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus Rhythm. P-Waves: PRInterval:
 EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus. : 60-100 beats per minute r Rhythrn: Atrial - - o Pwaves: Uniform in appearance Upright w/ normal shape One Preceding each QRS Nor more than.10 second o PR interval:
EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus. : 60-100 beats per minute r Rhythrn: Atrial - - o Pwaves: Uniform in appearance Upright w/ normal shape One Preceding each QRS Nor more than.10 second o PR interval:
The Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
Catheter Ablation. A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias
 Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Catheter Ablation A Guided Approach for Treating Atrial Arrhythmias A P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K This brochure will provide an overview of atrial arrhythmias (heart rhythm problems affecting the upper
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias
 Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
Guideline for the management of arrhythmias The following guideline is approved only for use at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. It is provided as supporting information for the
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
New resuscitation science and American Heart Association treatment guidelines were released October 28, 2010!
 ACLS Study Guide 2010 Bulletin: New resuscitation science and American Heart Association treatment guidelines were released October 28, 2010! The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains
ACLS Study Guide 2010 Bulletin: New resuscitation science and American Heart Association treatment guidelines were released October 28, 2010! The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol
 Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm
 Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
MEDICATIONS USED IN ADULT CODE BLUE EMERGENCIES. Source: ACLS Provider Manual. American Heart Association. 2001, 2002. Updated 2003.
 MEDICATIONS USED IN ADULT CODE BLUE EMERGENCIES Source: ACLS Provider Manual. American Heart Association. 2001, 2002. Updated 2003. 1 ET Administration Atropine o First drug for symptomatic sinus bradycardia
MEDICATIONS USED IN ADULT CODE BLUE EMERGENCIES Source: ACLS Provider Manual. American Heart Association. 2001, 2002. Updated 2003. 1 ET Administration Atropine o First drug for symptomatic sinus bradycardia
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
Rigel 333 Multi Parameter Patient Simulator Version 2.0
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Rigel 333 Multi Parameter Patient Simulator Version 2.0 Rigel Medical Seaward Group 18 Bracken Hill Peterlee, County Durham SR8 2SW England www.rigelmedical.com Dear User: We appreciate
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Rigel 333 Multi Parameter Patient Simulator Version 2.0 Rigel Medical Seaward Group 18 Bracken Hill Peterlee, County Durham SR8 2SW England www.rigelmedical.com Dear User: We appreciate
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1
 Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Normal Intracardiac Pressures. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
