Spinal Cord Physiology & Anatomy Class 3 Monday, September 30, 2013 Robinson
|
|
|
- Wilfred Gordon
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Objectives Spinal Cord Physiology & Anatomy Class 3 Monday, September 30, 2013 Robinson -Be able to concisely describe the gross anatomy of the spinal cord including its position inside the vertebral column and the spaces and membranes between the vertebral column and the cord.. -Be able to explain the naming convention of spinal roots relative to the vertebrae in the cervical cord and more caudally. -Be able to explain why there is not C1 dermatome and the general locations of the muscles receiving input from the C1 spinal nerve. -Be able to describe the structure, organization, and basic function of the cord in cross-section, including the difference between a spinal root and a spinal nerve. -Be able to describe the motor somatotopy in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. -Be able to explain the general differences in the gray and white matter at different levels of the spinal cord and why the cord is bigger in the cervical and lumbar regions. -Be able to name the 3 major fasciculi in the cord. -Be able to explain the basic organization of the stretch and withdrawal reflexes. -Be able to describe what a central pattern generator is. -Be able to describe, examples of descending and sensory inputs to CPGs regulating movement. I. Overview As the drawing to the right shows, the spinal cord is the long extension of the brain running down the middle of the back. In some ways the spinal cord looks and functions like a cable bringing sensory information from the body to the brain and sending movement commands from the brain to the body. It is also a complicated processor of sensory and motor information that regulates sensory inflow and contributes to the control of effective movements. Note that for everything discussed in sections III - VI below, there are analogous structures and functions for the head and face, mediated by cranial nuclei and other brainstem neurons. There are 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, and 5 sacral spinal nerves. Note that the most rostral nerve, C1 exits rostral of the C1 vertebra and the last cervical nerve exits below the C7 vertebra. Thus there are 8 cervical spinal nerves but only 7 cervical vertebrae. Thoracic, lumbar, and sacral roots all exit below their associated vertebrae so that there are the same number of roots and vertebrae in these parts of the spine. -Class 3, page 1-
2 II. Spinal Cord Anatomy A. Gross anatomy 1. As illustrated in the cross section to the right through the cord and vertebral column, the spinal cord rests in the spinal canal inside the vertebral column. Spinal nerves extend outward from the cord. Moving from the outside in we see that the large mechanically supportive part of the vertebral column is anterior (or ventral) to the spinal cord. A relatively thin layer of bone covers the lateral surface of the spinal canal which contains the cord. On the posterior (or dorsal) side of the spinal canal, there are boney protrusions or, including the spine on the midline to which axial muscles attach. The epidural space outside the dura containing the cord is filled with fat that cushions the cord. This is the area into which anesthesiologists inject drugs that block axon conduction to block sensation below the injection, a so called epidural. Within the fat padding, the three meninges membranes cover the cord just as they cover the brain. The dura encloses the cord and the dorsal root ganglia which contain the cell bodies of sensory axons carrying somatosensory information into the cord (see below). The arachnoid is under the dura. As in the brain, there is a space under the arachnoid, the subarachnoid space, in which CSF circulates. The pia lines the cord under the subarachnoid space. 2. Spinal nerves exit the vertebral column between two vertebrae, one above and one below. There is an inconsistent convention for naming spinal nerves for the vertebrae associated with it. In the most rostral part of the cord, the cervical segments (cervix means neck; these are the vertebrae of the neck), there are 7 cervical vertebrae and 8 cervical spinal nerves. As the picture below and to the right shows, we name each of the top 7 cervical nerves the vertebra immediately caudal to it (C 1- C 7 ). There are 8 cervical roots for 7 cervical vertebrae because we name the nerve immediately caudal to (below) the most caudal (7 th ) cervical vertebra C 8. Caudal to thec 8 root, we name each spinal root for the vertebra immediately rostral (above) it. -Class 3, page 2-
3 3. The spinal nerve at each level of the cord carries somatic sensory information from a specific region of skin at that level into the cord. Each spinal nerve also sends motor commands to specific muscles at the level of the nerve. The region of the skin from which somatosensory information enters the cord through one spinal nerve is called a dermatome. The region of the body that receives motor commands from one spinal root is called a myotome. Dermatomes and myotomes represent skin and muscles in the same parts of the body, respectively. The drawing to the left shows the dermatomes associated with spinal nerves at each spinal segment. The arrangement of dermatomes makes some sense in that cervical segments (C 2 - C 8 ) carry information from the upper part of the body while lumbar and sacral segments carry information from lower parts of the body. Still, the arrangement of dermatomes in the limbs seems different from that in the trunk. In the drawing above of a standing man, the borders of the dermatomes in the limbs are approximately vertical while those in the trunk are approximately horizontal. A sensible way to understand the arrangement of dermatomes is to imagine our bodies on all fours, as in the drawing to the right. In this posture the borders of all of the dermatomes run approximately vertically and are roughly parallel. Further, the progression from lumbar dermatomes on the front of the legs to sacral dermatome, on the back of the legs and on the buttocks, now looks orderly. -Class 3, page 3-
4 Note on the drawing at the top of the previous page, that there is no C 1 dermatome marked on the skin above the C 2 dermatome, though, as the drawing on the bottom of page 2 shows, there is a C 1 spinal root. The sensory fibers entering the cord via the C 1 spinal nerve bring in information from the meninges around the cerebellum and medulla, not from the skin. As we will learn when we study cranial nerves, somatosensory information from the skin rostral to the C 2 dermatome enters the brain through the trigeminal nerve. Since, as noted on the previous page, dermatomes and myotomes represent skin and muscles in the same parts of the body, and there is no C 1 dermatome, it is fair to ask where muscles are that receive the motor signals from the C 1 spinal nerve. The C 1 spinal nerve sends motor axons to a few muscles in 3 locations, the mouth, the front of the neck and the back of the skull. I show you the muscles in each location but you do not need to name them or even know exactly where they are. Just be able to describe their 3 general locations. Mouth - The geniohyoid muscle, highlighted in red in the drawing to the left (of the left side of the tongue) lies deep under the tongue. Front of neck - The infrahyoid muscles highlighted in pink in the drawing below and to the left (of the front of the neck) are on the front of the neck. Back of skull - The suboccipital muscles, highlighted in pink on the bottom drawing on the left (of the back of the neck) are on the bottom of the skull. -Class 3, page 4-
5 4. The spinal cord stops growing earlier in development than the rest of the body so the cord is shorter than the vertebral column. As you can see in the drawing to the right, in adults the cord ends at ~L1 (1 st lumbar vertebra). Below L1 the vertebral canal contains only dorsal and ventral roots. (Anesthesiologists exploit this anatomy when they inject drugs to produce a spinal block. They inject below L1 so that their needle does not enter, and damage, the spinal cord. Below L1 the needle enters the spinal canal in the vertebral column and pushes aside the roots there without damaging them.) 5. As we see in the drawing below and to the right, a spinal nerve is composed of two components, a dorsal root and a ventral root. The dorsal root carries sensory information into the cord. The ventral root carries motor commands out of the cord. The two roots join peripheral to the dorsal root ganglion to form a spinal nerve that exits the vertebral column at the associated vertebral level. As noted above the cord is shorter than the vertebral column. Thus as we move caudally in the cord, there is an increasingly large offset between the where roots exit the cord and where joined dorsal and ventral roots, i.e., spinal nerves, exit the vertebral column. As apparent in the drawing above and to the right, below the cervical segments, the nerve roots travel more and more caudally to reach their exit points. 6. Once outside the vertebral column spinal nerves branch to form peripheral nerves. B. Cross sectional anatomy 1. As the drawing to the right shows, spinal gray matter (cell bodies) forms a roughly H-shaped pattern inside white matter (axons). This H is functionally arranged in the sensory-dorsal, motorventral organization that is a consequence of development. 2. This drawing also shows that somatosensory information enters the cord through primary afferent axons in White matter (axons) Gray matter (cell bodies) Intermediate spinal gray matter interneurons Dorsal Horn (posterior horn) sensory Ventral Horn (anterior horn) motor Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Ventral Root motor Spinal Root Dorsal Root sensory Spinal Nerve dorsal (sensory) roots. All axons need cell bodies to support them. The cell bodies of the axons in the dorsal root are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG; a ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside the CNS). As we will describe in more detail when we study the somatosensory system, after the sensory axons in the dorsal root enter the cord they branch. Some of the branches synapse on neurons in the ipsilateral dorsal horn of the spinal gray matter (the top arms of the H). -Class 3, page 5-
6 3. Motoneurons, i.e., those whose axons terminate on muscles, are in the ventral horn of spinal gray matter. The axons of these motoneurons leave the cord through ventral (motor) roots to terminate on ipsilateral muscles. As the drawing to the right shows, there is a relationship between the position of a motoneuron in the ventral horn and the position of the muscle that it contacts in the body. Motoneurons for axial (trunk) muscles are in the medial part of the ventral horn while the motoneurons for distal (limb) muscles are in the lateral ventral horn. The more lateral a motoneuron in the ventral horn, the more distal the muscle that the motoneuron contacts. 4. Further, as the drawing to the right shows there is a dorsal-ventral (posterior-anterior) organization in which the motoneurons of flexor muscles lie more dorsally in the ventral horn than the motoneurons of extensor muscles. 5. We call an arrangement like this, in which there is an orderly spatial representation of the body inside the CNS, a somatotopy. 6. Note in the drawing in the middle of the previous page that between the dorsal and ventral horns of the spinal gray matter there is a region called the intermediate gray. Neurons in this region are interneurons that process sensory information entering the cord from nearby spinal roots as well as motor signals descending from the brain. These neurons then send their output to motoneurons in the ventral horn. -Class 3, page 6-
7 7. The size and shape of the spinal gray matter and white matter in cross-sections of different levels of the cord, as well as of the whole section, are different depending on the cord level. a. The gray matter in the cervical and lumbar segments is enlarged because these parts of the cord contain sensory neurons, motoneurons, and interneurons related to the arms and legs, respectively. This makes cervical and lumbar segments bulge a little producing the cervical and lumbar enlargements. You can see the cervical and lumbar enlargements in the cord pictured in the drawing on the top right of page 5 above. The drawing to the right shows the gray matter of all spinal segments. Note the larger ventral and dorsal horns in the cervical and lumbar enlargements. b. There is a rostral-to-caudal decrease in the amount of white matter because each level of the cord contains the fibers ascending from, and descending to, all of the more caudal segments. On the right you can see that cord cross sections at different levels have different shapes and sizes of both white matter and gray matter. The drawing of the cord to the left of the cross sections shows the level of each of the 4 sections on the right. In brief summary, the distinctive features of sections at different levels are: S2 smallest white matter; biggest gray/white matter ratio L2 more white matter, particularly dorsal and medial; still large gray/white matter ratio T4 smallest gray matter; smallest gray/white matter ratio C6 - largest cross section; larger lateral extension of ventral horn; large white matter Please learn to identify the level of a section from its appearance. -Class 3, page 7-
8 8. We divide the white matter of the cord into three major structures, funiculi or ropes. These are labeled in the right side of the drawing to the right. 9. Within these funiculi run axons carrying sensory information to the brain and axons carrying motor information from the brain to motoneurons in the spinal cord. In subsequent lectures we will learn about the major sensory and motor tracts in the cord. III. Spinal Reflexes Stimulating somatosensory nerves entering the cord elicits stereotyped, short latency movements via reflex pathways through the spinal cord. Some examples are: Stretch (or monosynaptic or deep tendon) reflex As the drawing below and to the right shows, stretch of a receptor in a muscle (a muscle spindle) activates sensory axons that synapse directly onto and excite motoneurons for the same (homonymous) muscle and for muscles with similar action (synergists). They also activate inhibitory interneurons in the intermediate gray matter. These, in turn, synapse onto and inhibit the motoneurons of muscles with the opposite action as the stretched muscle (antagonists). Thus, stretching a muscle makes it contract very quickly. This contraction is unopposed by contraction of antagonist muscles neurons for antagonist muscles are because antagonist motoneurons are inhibited. Note that even this simple reflex involves both agonist and antagonist muscles. This is the reflex that physicians test when they use a reflex hammer to tap a tendon in your elbow or knee. The tap stretches muscle spindles in a muscle and that muscle contracts. This reflex resists muscle stretching by unexpected increase in loads. -Class 3, page 8-
9 Flexion (or withdrawal) and cross-extension reflex - The drawing to the right illustrates a more complex reflex that excites and inhibits motoneurons on both sides of the cord. the spinal pathway via which stretching a tendon in the biceps muscle stretches a muscle spindle and contracts the muscle containing the spindle and its agonists while relaxing its antagonists. A painful stimulus on the skin of the lower leg activates a pathway to the ipsilateral side of the cord that excites the motoneurons of flexor muscles (and their synergists, not shown) and inhibits the motoneurons for extensor muscles. The same sensory input also activates a sensory pathway in the dorsal horn of the spinal gray matter that sends axons across the midline to excite the motoneuron for extensor muscles and inhibit those for flexor muscles on the other side. Thus, a painful stimulus on your right foot, for example, will withdraw your right leg and extend your left leg to support you as your right leg supports you less. Reflexes like this can involve neurons in multiple spinal cord segments that control multiple joints. V1. Central Pattern Generators and Descending Control Networks of neurons in the spinal cord, called central pattern generators (CPGs), can generate repeating patterns of muscle contraction and relaxation. Examples of behaviors mediated by CPGs are rhythmic scratching, shaking (think of dogs getting rid of water on their coats), and locomotion. CPGs can produce patterned muscle activity without outside input but both descending signals from the brain and sensory input can influence them. Using locomotion as an example, you can walk without thinking about the movements you make partly because of spinal CPGs producing these movements. Still, you can change the speed and direction of your walking movements voluntarily. The drawing below shows the back end of a cat whose spinal cord is severed at b---b. Despite the fact that descending commands do not reach the cord caudal to the cut, the CPG in the lumbar cord can generate alternating contractions of muscles appropriate to creating walking movements in the hind legs. Further, if we suspend the cat over a treadmill the sensory input generated by the feet on the moving surface can slow or speed the walking movements to match the speed of the treadmill. -Class 3, page 9-
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28
 The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
The Reflex Arc and Reflexes Laboratory Exercise 28 Background A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the nervous system. This pathway begins with a receptor at the dendrite
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
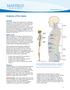 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises
 1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
1 General A&P Nervous Tissues, Nerves, Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
SPINAL CORD CIRCUITS AND MOTOR CONTROL
 OVERVEW The proximate control of movement is provided by neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem. The primary motor neurons located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord gray matter (and the corresponding
OVERVEW The proximate control of movement is provided by neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem. The primary motor neurons located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord gray matter (and the corresponding
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses
 The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses 1 Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy November 2009, 38, pp.
The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses 1 Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy November 2009, 38, pp.
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential
 Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Assessment of spinal anaesthetic block
 Assessment of spinal anaesthetic block Dr Graham Hocking Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Medicine John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford UK Email: ghocking@btinternet.com Spinal anaesthesia has the advantage
Assessment of spinal anaesthetic block Dr Graham Hocking Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Medicine John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford UK Email: ghocking@btinternet.com Spinal anaesthesia has the advantage
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Reflex Response (Patellar Tendon) Using BIOPAC Reflex Hammer Transducer SS36L
 Updated 7.31.06 BSL PRO Lesson H28: Reflex Response (Patellar Tendon) Using BIOPAC Reflex Hammer Transducer SS36L This PRO lesson describes basic reflex exercises and details hardware and software setup
Updated 7.31.06 BSL PRO Lesson H28: Reflex Response (Patellar Tendon) Using BIOPAC Reflex Hammer Transducer SS36L This PRO lesson describes basic reflex exercises and details hardware and software setup
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
The Motor System: Lecture 1 Spinal motor system
 The Motor System: Lecture 1 Spinal motor system Reza Shadmehr Traylor 410, School of Medicine, shadmehr@jhu.edu NOTE: All slides and lecture notes for the motor lectures of Dr. Shadmehr are available at:
The Motor System: Lecture 1 Spinal motor system Reza Shadmehr Traylor 410, School of Medicine, shadmehr@jhu.edu NOTE: All slides and lecture notes for the motor lectures of Dr. Shadmehr are available at:
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
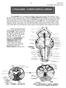 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Meninges of Cord. Spinal Roots and Nerve. 31 Pairs of Spinal Nerves. White Matter Columns 2/24/2014. Book Fig. 8.1. Book Fig. 8.3
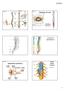 Book Fig. 8.3 Book Fig. 8.1 Meninges of Cord Filum terminale ------- strand connecting end of cord to coccyx to keep cord centered 31 Pairs of Spinal Nerves Book Fig. 8.7 Spinal Roots and Nerve White Matter
Book Fig. 8.3 Book Fig. 8.1 Meninges of Cord Filum terminale ------- strand connecting end of cord to coccyx to keep cord centered 31 Pairs of Spinal Nerves Book Fig. 8.7 Spinal Roots and Nerve White Matter
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Dr. Enas Elsayed. Brunnstrom Approach
 Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab. Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Human Anatomy & Physiology Reflex Physiology lab Objectives: To understand what reflexes are, the processes involved, and purpose of reflexes. Introduction: A reflex is an involuntary neural response to
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
 Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia 1 Contents Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia... 1 Introduction... 3 A brief review of cerebellar anatomy... 4 Basic Circuit... 4 Parallel and climbing fiber input has a very different
Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia 1 Contents Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia... 1 Introduction... 3 A brief review of cerebellar anatomy... 4 Basic Circuit... 4 Parallel and climbing fiber input has a very different
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex
 Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Nursing. Management of Spinal Trauma. Content. Objectives. Objectives
 7 cervical vertebrae Content 12 thoracic vertebrae Nursing 5 sacral vertebrae Management of Spinal Trauma Kwai Fung Betty Siu Ward Manager O&T Dept TKOH Date : 22nd April 2007 5 lumbar vertebrae 4 coccygeal
7 cervical vertebrae Content 12 thoracic vertebrae Nursing 5 sacral vertebrae Management of Spinal Trauma Kwai Fung Betty Siu Ward Manager O&T Dept TKOH Date : 22nd April 2007 5 lumbar vertebrae 4 coccygeal
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Weakness More diffuse More focal Atrophy Mild, general Severe, focal Atrophy versus weakness
 Spinal Cord Disorders (Dr. Merchut) Clinical signs and symptoms in spinal cord lesions 1. Motor signs and symptoms Lower motor neuron (LMN) signs (Table 1) are found in a limb if some of its muscles are
Spinal Cord Disorders (Dr. Merchut) Clinical signs and symptoms in spinal cord lesions 1. Motor signs and symptoms Lower motor neuron (LMN) signs (Table 1) are found in a limb if some of its muscles are
Factors Influencing Human Postures
 Chapter 3 Factors Influencing Human Postures 3.1 Introduction Postures and motions generated by the human body are very difficult to simulate since the human body has so many interrelated muscles that
Chapter 3 Factors Influencing Human Postures 3.1 Introduction Postures and motions generated by the human body are very difficult to simulate since the human body has so many interrelated muscles that
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques
 Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HN-2: Stretch Receptors and Reflexes
 Experiment HN-2: Stretch Receptors and Reflexes Exercise 1: Achilles Tendon Reflex Aim: To determine conduction time from tendon tap to response of the gastrocnemius muscle in the Achilles tendon reflex
Experiment HN-2: Stretch Receptors and Reflexes Exercise 1: Achilles Tendon Reflex Aim: To determine conduction time from tendon tap to response of the gastrocnemius muscle in the Achilles tendon reflex
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function. Skeletal muscles act on bones to produce movement of the limb and to move (lift and carry) objects.
 ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
ELEC 811 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy and Function The primary function of a skeletal muscle is to generate forces, by contracting; these forces allow us to move through and interact with our environment Skeletal
Lu L m u b m a b r a rta T p a Figure 12.30
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Anatomy PHL 212. By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan
 Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Anatomy PHL 212 By Dr Tajdar Husain Khan Overview of Anatomy Anatomy(from the Greek word anatome,"dissection") is a branch of natural science dealing with the structural organization of living things The
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 3: Brain s Building Blocks. Module 3. Brain s Building Blocks
 Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary
 X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary Introduction Exercising your neck can make it stronger, more flexible and reduce neck pain that is caused by stress and fatigue. This reference summary describes
X-Plain Neck Exercises Reference Summary Introduction Exercising your neck can make it stronger, more flexible and reduce neck pain that is caused by stress and fatigue. This reference summary describes
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
POST SURGICAL RETURN OF RIGHT LEG PAIN. TREATED SUCCESSFULLY WITH COX FLEXION DISTRACTION DECOMPRESSION ADJUSTING
 POST SURGICAL RETURN OF RIGHT LEG PAIN. TREATED SUCCESSFULLY WITH COX FLEXION DISTRACTION DECOMPRESSION ADJUSTING A 47 year old white married female was seen for the chief complaint of low back and right
POST SURGICAL RETURN OF RIGHT LEG PAIN. TREATED SUCCESSFULLY WITH COX FLEXION DISTRACTION DECOMPRESSION ADJUSTING A 47 year old white married female was seen for the chief complaint of low back and right
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
McMaster Spikeyball Therapy Drills
 BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
BODY BLOCKS In sequencing Breathing and Tempo Flexibility / Mobility and Proprioception (feel) Upper body segment Middle body segment Lower body segment Extension / Static Posture Office / Computer Travel
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Don t. Hamstrings. Calf Muscles. both legs 2-3 times. stretch is felt in the back of the calf. Repeat with both legs 2-3 times.
 Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching (e.g. stretch after walking). Stretch until you feel mild discomfort, not pain. Never bounce or force a stretch. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
