Board Review January 6, Electrocardiograms. Brad Sobolewski, MD
|
|
|
- Lynette Hampton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Board Review January 6, 2011 Electrocardiograms Brad Sobolewski, MD
2 Introduction Why did I choose this topic? Most of the EKGs we order are normal We rely on pattern recognition when interpreting them As a diagnostic test EKGs are sensitive, but not specific You don t want to miss a potentially life threatening finding in a healthy appearing patient
3 The focus of this talk Pattern recognition of different EKG findings these common clinical scenarios Chest pain Syncope Toxicology During resuscitation
4 Things I m not discussing A thorough review of EKG interpretation Every type of stable tachycardia Congenital heart disease EKGs including post-op patients and those with pacers All manner of toxicology EKGs In depth management
5 EKG Overview
6 To order or not to order When should you get an EKG? Worrisome history Acute onset Associated with exercise Associated with syncope History of heart disease, connective tissue disorder, rheumatologic disease, sickle cell Cocaine use Abnormal PE with Cardiac findings
7 The normal EKG Rate I won t insult your intelligence here Sinus rhythm a P for every QRS Axis I and avf have mainly positive QRS complexes = normal axis. I is positive and avf is negative = left axis deviation (LAD). I is negative and avf is positive = right axis deviation (RAD). Both leads negative = extreme RAD or extreme LAD
8 Normal values vary by age so check out The Pocket page 13 The normal EKG Criteria for chamber enlargement are found on page 12
9 More about T waves Normally in adults Always upright in leads I, II, V3-6, and always inverted in lead avr Amplitude < 5mm in limb leads, < 15mm in precordial leads Inverted T waves Normal in children (especially V1-3) due to predominance of RV forces Can persist into adulthood, most often in African American/Caribbean women - asymmetric, shallow (<3mm) and usually limited to leads V1-3 Otherwise inverted T waves indicate pathology MI, BBB, RVH/LVH, PE, increased ICP
10 T wave changes at 3 different ages 1 month 3 years 21 years By age 16 T waves should be upright in V2-6 Some normal adults will have a downward V1
11 Normal inverted T waves (V1-V3) in a two year old male
12 Abnormal T wave morphology Prior MI - Inverted T and Q wave Hyperkalemia Acute MI hyperacute T waves
13 Events causing a sudden rise in ICP (e.g. subarachnoid hemorrhage) produce widespread deep T-wave inversions with a bizarre morphology
14 Biphasic T waves Ischemia (up then down) Hypokalemia (down then up)
15 S1 QIII TIII pattern of acute PE
16 What is this J Point Elevation Stuff? Normal variant most commonly seen in young males. Early repolarization of some myocardial fibers may deviate the ST upwards in a concave pattern, especially when R waves high with tall peaked T waves. The J point is frequently elevated where the QRS joins the concave ST elevation Differentiation from MI In J Point you ll see: ST segment elevation is typically less pronounced (equal to or less than 0.05mV) Ventricular surface area is greater (more leads involved)
17 J Point Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction: Anterior Wall
18 There s also J Point depression? Normal depression is 1mm in limb leads and 2mm in precordial leads
19 Chest Pain
20 Ischemia T-waves flat or downsloping The location of the abnormalities are much less clearly correlated with anatomical findings May indicate acute coronary syndrome (e.g. unstable angina)
21 STEMI normal ST elevation min-hours Q waves days Inverted T weeks T normalizes months
22 1. Parent with chest pain Acute Myocardial Infarction: Anterior Wall
23 2. Parent with chest pain Acute Myocardial Infarction: Inferior Wall
24 3. Teenage male with exertional chest pain Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HOCM) LVH Deep T wave inversions in all precordial leads
25 Example 3 A 13 year old female presents with chest pain, tachypnea, and fever Not caused by the 15 year old male seen here
26 4. Pericarditis
27 Chest pain EKG findings summary STEMI - duh, ST segment elevation Ischemia - ST segment depression, flat or downsloping T waves Pericarditis - diffuse ST segment elevation HOCM - LVH, deep T wave inversions in precordial leads
28 Syncope
29 Syncope Cardiac causes of syncope Conduction abnormalities Block, Sick sinus, long QTc Arrhythmias SVT, V Tach, V fib Obstructive lesions arterial stenosis, HOCM, TOF, Anomalous origin of the left coronary artery Acquired lesions tumors, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy
30 Syncope EKG findings in life threatening causes of syncope Prolonged QT Brugada pattern Epsilon waves (arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia) Preexcitation syndrome (Wolff Parkinson White) Nonsinus rhythm Short QT interval ( 0.30 sec) Conduction delay or atrioventricular block Signs of myocardial injury Ventricular hypertrophy or strain patterns
31 5. Wolf Parkinson White
32 6. SVT
33 SVT by originating focus SA node Inappropriate sinus tac SA node reentrant tachycardia Atrial Ectopic atrial tachycardia Multifocal atrial tachycardia A fib with rapid ventricular response A flutter with rapid ventricular response AV Node (Junctional) AV node reentrant tachycardia AV reentrant tachycardia (includes WPW) Junctional ectopic tachycardia Spoiler alert! The key finding of SVT is a Narrow QRS
34 Atrial focus A fib with rapid ventricular response
35 Atrial focus Multifocal atrial tachycardia
36 AV Node AVNRT P is in ST segment, after QRS JET Atrial activity Ventricular activity Short PR waves, P waves fall before and after the narrow QRS
37 7. Atrial Flutter Sawtooth pattern best seen in V1, II and III Atrial rate can be as high as 300
38 A couple more examples of atrial flutter
39 8. Long QT QTc = QT / RR(sec)
40 9. First degree AV block with sinus bradycardia
41 AV Block Disturbance in conduction between sinus impulse and ventricular response 1 st degree PR> upper limit of normal for age 2nd degree Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach) Progressive lengthening of PR until a beat is dropped Mobitz Type II failure at bundle of His, either normal AV conduction or none the ventricle will not contract without a P wave 3 rd degree complete AV dissociation
42 AV Block
43 10. Right Bundle Branch Block
44 Triple B (Right) RBBB Right axis deviation QRS longer than normal for age Terminal slurring of QRS to the right Wide/slurred S in I, V5, V6 Terminal slurred R in V4R, V1, and V2 In adults ST depression and T wave inversion Pro-Tip: You can t reliably diagnose RVH on EKG when RBBB is present
45 Triple B (Left) LBBB Left axis deviation QRS longer than normal for age Loss of Q waves in V5-6 Slurred QRS Complex to the left and posterior Wide R waves in I, avl, V5, and V6 Wide S waves in V1 and V2 ST depression and T wave inversion in V4-6 Pro-Tip: You can t reliably diagnose LVH or ischemia on EKG when LBBB is present
46 Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Idiopathic causes of pulmonary HTN can affect adolescents Older females 3x > males In young children M:F ~ 1:1 Syncope is a common presenting symptom!
47
48 Right ventricular hypertrophy and right axis deviation in a 10-year-old male with primary pulmonary hypertension with tall R waves in V1 and V2 and deep S waves in V5 and V6
49 Syncope EKG findings summary Supraventricular tachycardia narrow QRS Atrial focus A fib with rapid ventricular response irregularly irregular, no P waves Atrial flutter - very fast rate (300), sawtooth pattern Multifocal atrial tachycardia at least 3 P wave morphologies AV Node (junctional) focus AVNRT P is in ST segment, after QRS JET - Short PR waves, P waves fall before and after the narrow QRS #1 cause of SVT in kids are the reentrant mechanisms
50 Syncope EKG findings summary WPW delta wave, sinus rhythm, short PR Long QT >440ms Primary Pulmonary HTN RVH, R axis deviation, RA enlargement (peaked P in II), ST depression V1-3
51 Toxicology
52 Toxicology In general EKGs have low yield in overdoses and accidental ingestions Certain patterns may be seen on the boards however
53 11. 4 year old with altered mental status, tachycardia, dilated pupils and dry mucous membranes TCA Overdose QRS >100 msec predictive of seizures / >160msec predictive of arrhythmias R wave in avr>3mm also predictive of seizure / arrhythmia. Sinus Tachycardia QT prolongation
54 12. A 7 year old cardiac patient has the following EKG. Grandma can t remember what meds he is on Digitalis effects Shortened QT interval Characteristic down-sloping ST depression Dysrhythmias Ventricular / atrial premature beats Paroxysmal A-tac with variable AV block V-tac and V-fib Salvador Dali s moustache
55 EKG findings in cardiac med overdoses
56 Ventricular Dysrhythmias
57 Ventricular dysrhythmias Abnormal rhythms originating in the ventricle (distal to the Bundle of His) are the kind that kill folk In adults #1 cause is CAD In children #1 reentrant mechanism
58 13. Ventricular tachycardia 1. Absence of RS complexes in the precordial ECG leads (V1-V6) RS duration greater than 100 milliseconds in any precordial lead 3. Ventriculoatrial dissociation
59 14. Ventricular fibrillation Chaotic, random, asynchronous electrical activity of the ventricles resulting in rapid, irregular bizarre QRS complexes. Wavy chaotic ventricular depolarization resulting in fibrillatory waves.
60 15. Torsades de pointes Rapid, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia with a characteristic twist of the QRS complex around the isoelectric baseline Can degenerate into V fib
61 Factors associated with torsades Familial long QT syndrome Class IA antiarrhythmics Class III antiarrhythmics Hypomagnesemia Hypokalemia Hypocalcemia Hypoxia Acidosis Heart failure LVH Slow heart rate Female gender Hypothermia Subarachnoid hemorrhage
62 16. V tach Torsades V fib
63 V tach vs. SVT with aberrancy SVT with aberrancy is SVT wide QRS complexes In V tach No P wave association with QRS Preceded by PVC QRS >0.16 sec In SVT with aberrancy QRS sec Preceded by PAC RBBB pattern - rsr in V1 or qrs in V6
64 SVT with aberrancy Pro-Tip: SVT with aberrancy is very rare in kids so a wide complex tachycardia without P waves is probably V tach
65 Seen in young men from South East Asia Pseudo RBBB with J point elevation and concave ST elevation Can lead to paroxysmal V fib and then death UCED attendings like to discuss it Brugada syndrome Normal QRS ST segment elevation and T wave inversion in the right precordial leads V1 and V2 (arrows) Wide S wave in left lateral leads that is characteristic of RBBB is absent
66 Ventricular dysrhythmias EKG findings summary V tach - >3 PVCs, rate V fib rapid irregular rate, bizarre QRS pattern of varying size/morphology Torsades - Rapid, polymorphic ventricular tachycardia with a twist of the QRS complex around the isoelectric baseline Brugada syndrome - Pseudo RBBB with J point elevation and concave ST elevation
67 Other Examples
68 Other examples 17. Pulled from a lake year old with Kawasaki disease Osborn waves Positive deflections between QRS and ST segment - Hypothermia - Hypercalcemia - Head injury - V fib Sinus tachycardia Kawasaki EKGs can show findings consistent with myocarditis such as arrhythmias, prolonged PR/QT intervals, and nonspecific ST changes. Or they can be normal
69 Wrap up EKGs are usually normal when we order them If they re abnormal we have a pretty good idea that they ll be abnormal before we get them (e.g. history) It takes practice and repetition to get good at picking out the abnormal findings Don t miss those findings in the well looking patient Check out these resources How To Read Pediatric EKGs by Park ECG Library Emergency Medicine Education Online
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks
 ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks Cameron Guild, MD Division of Cardiology University of Mississippi Medical Center February 17, 2012 Objectives 1. Describe the electrical
ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks Cameron Guild, MD Division of Cardiology University of Mississippi Medical Center February 17, 2012 Objectives 1. Describe the electrical
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
 Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
EKG Abnormalities. I. Early repolarization abnormality:
 I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal
 How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Mission: Lifeline North Dakota Regional EMS and Hospital Conference Samantha Kapphahn, DO Essentia Health- Interventional Cardiology June 5th, 2014
Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Mission: Lifeline North Dakota Regional EMS and Hospital Conference Samantha Kapphahn, DO Essentia Health- Interventional Cardiology June 5th, 2014
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics. The Myocardial Cell. Chapter 1- Thaler
 Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs
 ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD
 92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
92 Review of Important ECG Findings in Patients with Syncope Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Guidelines recommend 12-lead ECG as an important test to perform in patients with syncope. Though the incidence
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children
 Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Potential Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Children Project S.A.V.E. When sudden death occurs in children, adolescents and younger adults, heart abnormalities are likely causes. These conditions are
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1
 Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL
 Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome
 Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
Acquired, Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers Sudden Arrhythmia Death Syndromes (SADS) Foundation 508 E. South Temple, Suite 202 Salt Lake City, Utah 84102 800-STOP
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians
 Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure ICD-10 Coding for Physicians May 19, 2015 Disclaimer This presentation is intended for educational use. Any duplication is prohibited without written consent
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
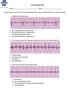 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Lead avr: The Neglected Lead
 Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
An ECG Primer. Quick Look. I saw it, but I did not realize it. Elizabeth Peabody
 4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
Table of Contents Error! Bookmark not defined.
 Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
ECG Measurement and Interpretation
 ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
HOW TO READ AN ECG. Rate = 300 / big squares 1 line = 300 2 line = 150 3 line = 75 4 line = 60 5 line = 50 6 line = 42 7 line = 38
 HOW TO READ AN ECG Pathophysiology Pacemaker Rates: SAN 60-100 AVN 40-60 Ventricle 20-40 Areas of ECG Horizontal scale: 1mm = 0.04s 5mm = 0.2s Calculating Rate Rate = 300 / big squares 1 line = 300 2 line
HOW TO READ AN ECG Pathophysiology Pacemaker Rates: SAN 60-100 AVN 40-60 Ventricle 20-40 Areas of ECG Horizontal scale: 1mm = 0.04s 5mm = 0.2s Calculating Rate Rate = 300 / big squares 1 line = 300 2 line
Adult Cardiac Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks
 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C38.0 Malignant neoplasm of heart 164.1 Malignant neoplasm of heart C45.2 Mesothelioma of pericardium 198.89 Secondary malignant neoplasm of other specified sites C79.89
2 ECG basics. Leads and planes. Leads. Planes. from different perspectives, which are called leads and planes.
 558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
The new generation in ECG interpretation
 The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
Chest Pain in Young Athletes. Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.
 Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
Chest Pain in Young Athletes Christopher Davis, MD, PhD Pediatric Cardiology Rady Children s Hospital San Diego cdavis@rchsd.org 858-966-5855 None Disclosures Chest Pain: the good news and the bad news:
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Basics of EKG Interpretation: A Programmed Study - Barbara Ritter Ed.D, FNP
 Basics of EKG Interpretation: A Programmed Study - Barbara Ritter Ed.D, FNP Acknowledgement is given to Leslie K. Muma, MS, RN, NP for assistance in preparation of this learning module. Description The
Basics of EKG Interpretation: A Programmed Study - Barbara Ritter Ed.D, FNP Acknowledgement is given to Leslie K. Muma, MS, RN, NP for assistance in preparation of this learning module. Description The
ECG Findings. IV Access. 12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI. ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia.
 12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI Presented by Annmarie Keck, RN, BSN, CEN Northwest MedStar Clinical Outreach Educator ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia Immediate Assessment
12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI Presented by Annmarie Keck, RN, BSN, CEN Northwest MedStar Clinical Outreach Educator ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia Immediate Assessment
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol
 Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
The Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed
 Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed Identify the 12-Lead Views Explain the vessels of occlusion Describe the three I s Basic Interpretation of 12-Lead
Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed Identify the 12-Lead Views Explain the vessels of occlusion Describe the three I s Basic Interpretation of 12-Lead
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation DISCLOSURES. Heart Beat Anatomy. I have no financial conflicts to disclose
 Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
Current Management of Atrial Fibrillation Mary Macklin, MSN, APRN Concord Hospital Cardiac Associates DISCLOSURES I have no financial conflicts to disclose Book Women: Fit at Fifty. A Guide to Living Long.
12 Lead ECGs: Ischemia, Injury & Infarction Part 2
 12 Lead ECGs: Ischemia, Injury & Infarction Part 2 McHenry Western Lake County EMS Localization: Left Coronary Artery Right Coronary Artery Right Ventricle Septal Wall Anterior Descending Artery Left Main
12 Lead ECGs: Ischemia, Injury & Infarction Part 2 McHenry Western Lake County EMS Localization: Left Coronary Artery Right Coronary Artery Right Ventricle Septal Wall Anterior Descending Artery Left Main
Electrolyte Physiology. Something in the way she moves
 Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging. Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469)
 Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
Provider Checklist-Outpatient Imaging Checklist: Nuclear Stress Test, Thallium/Technetium/Sestamibi (CPT Code 78451-78454 78469) Medical Review Note: Per InterQual, if any of the following are present,
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle
 Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle Objectives Students will record a six-lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle Objectives Students will record a six-lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
6/5/2014. Objectives. Acute Coronary Syndromes. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology
 Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
Objectives Acute Coronary Syndromes Epidemiology and Health Care Impact Pathophysiology Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Clinical Clues Pre-hospital Spokane County EMS Epidemiology About 600,000 people die
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls
 Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
Palpitations & AF. Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust
 Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
Palpitations & AF Richard Grocott Mason Consultant Cardiologist THH NHS Foundation Trust & Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Foundation Trust Palpitations Frequent symptom Less than 50% associated with arrhythmia
QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers. Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012
 QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012 Agenda ECG ICH E14 Thorough QT/QTc study Role of Statistical Programmer References
QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012 Agenda ECG ICH E14 Thorough QT/QTc study Role of Statistical Programmer References
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier
 Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Episode 20 Atrial fibrillation Prepared by Dr. Lucas Chartier Most common dysrhythmia seen in ED, and incidence increasing with ageing population Presentation Common presentations: younger patients often
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome
 Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Electrocardiographic Issues in Williams Syndrome R. Thomas Collins II, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Internal Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Arkansas Children s Hospital
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS -
 Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Electrophysiology Heart Study - EPS - What is an EPS? EPS is short for ElectroPhysiology heart Study. This procedure looks at the electrical system of your heart. An EPS will show if you have a heart rhythm
Presenter Disclosure Information
 2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
2:15 3 pm Managing Arrhythmias in Primary Care Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Raul Mitrani, MD, FACC, FHRS: Speakers Bureau for Medtronic.
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response
 Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Advanced EKG Interpretation
 Advanced EKG Interpretation JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS AND NURSING INTERVENTIONS Objectives Identify specific cardiac dysrhythmias Describe appropriate nursing interventions for specific dysrhythmias Junctional
Advanced EKG Interpretation JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS AND NURSING INTERVENTIONS Objectives Identify specific cardiac dysrhythmias Describe appropriate nursing interventions for specific dysrhythmias Junctional
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: May 27, 2016 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI)
 Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Novartis Gilenya FDO Program Clinical Protocol and Highlights from Prescribing Information (PI) Highlights from Prescribing Information - the link to the full text PI is as follows: http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/gilenya.pdf
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Introduction. Sinus Rhythms. Premature Beats. Secondary article. John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
 John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
John A Kastor, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland, USA Cardiac arrhythmias are disturbances in the rhythm of the heart manifested by irregularity or by abnormally fast rates ( tachycardias ) or
NAME OF THE HOSPITAL: 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3
 1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
1. Coronary Balloon Angioplasty: M7F1.1/ Angioplasty with Stent(PTCA with Stent): M7F1.3 1. Name of the Procedure: Coronary Balloon Angioplasty 2. Select the Indication from the drop down of various indications
Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout.
 Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout. TLoC is common huge variation in management range of clinicians
Assessment, diagnosis and specialist referral of adults (>16 years) with an episode of transient loss of consciousness (TLoC) or a blackout. TLoC is common huge variation in management range of clinicians
Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians
 Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians May 2011 Notices These coding suggestions and coverage guidelines do not replace seeking coding advice from the payer and/or your coding staff. The ultimate responsibility
Preparing for ICD-10 for Physicians May 2011 Notices These coding suggestions and coverage guidelines do not replace seeking coding advice from the payer and/or your coding staff. The ultimate responsibility
Signal-averaged electrocardiography late potentials
 SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms
 Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics
 Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation The Basics Family Practice Symposium Tim McAveney, M.D. 10/23/09 Objectives Review the fundamentals of managing afib Discuss the risks for stroke and the indications for anticoagulation
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide
 Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations.
 INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
Premature Ventricular Contractions. Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS
 Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Premature Ventricular Contractions Ralph Augostini, MD FACC FHRS Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Premature Ventricular Contractions: ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for Management of Patients With Ventricular
Cardiac Arrest: General Considerations
 Andrea Gabrielli, MD, FCCM Cardiac Arrest: General Considerations Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is described as a series of assessments and interventions performed during a variety of acute medical
Andrea Gabrielli, MD, FCCM Cardiac Arrest: General Considerations Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is described as a series of assessments and interventions performed during a variety of acute medical
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology
 Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Cardiology ICD-10-CM Coding Tip Sheet Overview of Key Chapter Updates for Cardiology Chapter 4: Endocrine, Nutritional, and Metabolic Diseases (E00-E89) The diabetes mellitus codes are combination codes
Guidelines for the interpretation of the neonatal electrocardiogram
 European Heart Journal (2002) 23, 1329 1344 doi:10.1053/euhj.2002.3274, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Task Force Report Guidelines for the interpretation of the neonatal electrocardiogram
European Heart Journal (2002) 23, 1329 1344 doi:10.1053/euhj.2002.3274, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Task Force Report Guidelines for the interpretation of the neonatal electrocardiogram
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias
 8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
8 Peri-arrest arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmias are relatively common in the peri-arrest period. They are common in the setting of acute myocardial infarction and may precipitate ventricular
38 year old female with mild obesity. She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD.
 Stress Testing: Wael A. Jaber, MD,FACC 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD. You recommend: A. Exercise
Stress Testing: Wael A. Jaber, MD,FACC 38 year old female with mild obesity She is planning an exercise program to loose weight. She has no other known risk factors for CAD. You recommend: A. Exercise
