Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2013 preliminary estimates)
|
|
|
- Elfreda Jackson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2013 preliminary estimates) Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley January 25, 2015 What s new for recent years? : Higher top tax rates temporarily depress top incomes In 2013, top income shares have fallen relative to For example, the top 10% income share falls from 50.6% to 48.9%, the top 1% income share falls from 22.8% to 20.1% (Figures 1 and 2). Indeed, top 1% real incomes fell by 14.9% from 2012 to 2013 while bottom 99% average real incomes increased very modestly by 0.2% (Table 1). The very modest increase in bottom 99% incomes in 2013 is consistent with Census measures of Household income, which stagnated in By the end of 2013, the incomes of most American families are still far from having recovered from the losses of the Great Recession. Conceivably, the stronger economic growth in 2014 will translate into larger gains for the bottom 99% in The fall in top incomes in 2013 is due to the 2013 increase in top tax rates (top tax rates increased by about 6.5 percentage points for labor income and about 9.5 percentage points for capital income). 2 The tax change created strong incentives to retime income to take advantage of the lower top tax rates in 2012 relative to 2013 and after. For high income earners, shifting an extra $100 of labor income from 2013 to 2012 saves about $6.5 in taxes and shifting an extra $100 of capital income from 2013 to 2012 saves about $10 in taxes. Realized capital gains are particularly easy to retime, explaining why the drop in top income shares in 2013 is more pronounced for series including capital gains than for series excluding capital gains (Figure 1). University of California, Department of Economics, 530 Evans Hall #3880, Berkeley, CA This is an updated version of Striking It Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States, Pathways Magazine, Stanford Center for the Study of Poverty and Inequality, Winter 2008, 6-7. Much of the discussion in this note is based on previous work joint with Thomas Piketty. All the series described here are available in excel format at 1 See Table A-2 in the official report Income and Poverty in the United States: 2013, series P60-249, US Census Bureau Current Population Report at 2 Top ordinary income marginal tax rates increased from 35 to 39.6% and top income tax rates on realized capital gains and dividends increased from 15 to 20% in In addition, the Affordable Care Act surtax at marginal rate of 3.8% on top capital incomes and 0.9% on top labor incomes was added in 2013 (the surtax is only 0.9% on labor income due to the pre-existing Medicare tax of 2.9% on labor income). The Pease limitation on itemized deductions also increases marginal tax rates by about 1 percentage point for ordinary income and 0.5 percentage points for realized capital gains and dividends in These higher marginal tax rates affect approximately the top 1%.
2 1 This retiming inflates 2012 top income shares and depresses 2013 top income shares. 3 Hence, it is likely that top income shares will rebound in 2014, although they will probably not be quite as high as in Even depressed by income retiming, the top 1% income share in 2013 remains above 20%, more than twice as high as in the 1970s. Hence, it seems very unlikely that the current top tax rate increases will be sufficient to curb the dramatic ascent of top 1% income shares. To cast light on this, we will try to post preliminary estimates for 2014 in June : Uneven recovery from the Great Recession From 2009 to 2012, average real income per family grew modestly by 6.9% (Table 1). However, the gains were very uneven. Top 1% incomes grew by 34.7% while bottom 99% incomes grew only by 0.8% from 2009 to Hence, the top 1% captured 91% of the income gains in the first three years of the recovery. Overall, these results suggest that the Great Recession has only depressed top income shares temporarily and will not undo any of the dramatic increase in top income shares that has taken place since the 1970s. Looking further ahead, based on the US historical record, falls in income concentration due to economic downturns are temporary unless drastic regulation and tax policy changes are implemented and prevent income concentration from bouncing back. Such policy changes took place after the Great Depression during the New Deal and permanently reduced income concentration until the 1970s (Figures 2, 3). In contrast, recent downturns, such as the 2001 recession, lead to only very temporary drops in income concentration (Figures 2, 3). The policy changes that took place coming out of the Great Recession (financial regulation and top tax rate increase in 2013) are not negligible but they are modest relative to the policy changes that took place coming out of the Great Depression. Therefore, it seems unlikely that US income concentration will fall much in the coming years. Great Recession During the Great Recession, from 2007 to 2009, average real income per family declined dramatically by 17.4% (Table 1), 4 the largest two-year 3 Indeed, previous expected top tax rate increases (such as in 1993 for ordinary income and in 1987 for realized capital gains) also produced significant retiming. 4 This decline is much larger than the real official GDP decline of 3.1% from for several reasons. First, our income measure includes realized capital gains while realized capital gains are not included in GDP. Our average real income measure excluding capital gains decreased by 10.8% (instead of 17.4%). Second, the total number of US families increased by 2.5% from 2007 to 2009 mechanically reducing income growth per family relative to aggregate income growth. Third, nominal GDP decreased by 0.6% while the total market nominal income aggregate we use (when excluding realized capital gains) decreased by 5.5%. This discrepancy is due to several factors: (a) nominal GDP decreased only by 0.4% while nominal National Income (conceptually closer to our measure) decreased by 2%. In net, income items included in National Income but excluded from our income measure grew over the period. The main items are supplements to wages and salaries (mostly employer provided benefits), rental income of persons (which imputes rents for homeowners), and undistributed profits of corporations (see National Income by Type of Income, Table 1.12,
3 2 drop since the Great Depression. Average real income for the top percentile fell even faster (36.3 percent decline, Table 1), which lead to a decrease in the top percentile income share from 23.5 to 18.1 percent (Figure 2). Average real income for the bottom 99% also fell sharply by 11.6%, also by far the largest two-year decline since the Great Depression. This drop of 11.6% more than erases the 6.8% income gain from 2002 to 2007 for the bottom 99%. The fall in top decile income share from 2007 to 2009 is actually less than during the 2001 recession from 2000 to 2002, in part because the Great recession has hit bottom 99% incomes much harder than the 2001 recession (Table 1), and in part because upper incomes excluding realized capital gains have resisted relatively well during the Great Recession. New Filing Season Distributional Statistics Timely distributional statistics are central to enlighten the public policy debate. Distributional statistics used to estimate our series are produced by the Statistics of Income Division of the Internal Revenue Service ( Those statistics are extremely high quality and final, but come with an almost 2-year lag (statistics for year 2011 incomes have just been published in the summer of year 2013). In 2012, the Statistics of Income division has started publishing filing season statistics by size of income at These statistics can be used to project the distribution of incomes for the fullyear. It is possible to project reliable full-year statistics by June of the following year when most of the returns filed before the regular April 15 deadline have been processed by IRS. 5 We have used filing season statistics for 2013 incomes to produce preliminary 2013 estimates. The projection assumes that, in each income bracket, the fraction of tax returns processed by July 2014 for 2013 returns is the same as the fraction of tax returns processed by July 2013 for 2012 returns. Because 2013 statistics are based on a projection, they are preliminary and will be updated when more complete statistics for year 2013 become available. Text of Striking it Richer updated with 2013 estimates The recent dramatic rise in income inequality in the United States is well documented. But we know less about which groups are winners and which are losers, or how this may have changed over time. Is most of the income growth being captured by an extremely small income elite? Or is a broader upper middle class profiting? And are capitalists or salaried managers and professionals the main winners? I explore these questions with a uniquely long-term historical view that allows me to place current developments in deeper context than is typically the case. Efforts at analyzing long-term trends are often hampered by a lack of good data. In the United States, and most other countries, household income surveys virtually did not exist prior to The only data source consistently available on a long-run basis is tax data. The U.S. government has published 5 Taxpayers who request a 6-month filing extension generally do not file until October 15. Their tax returns are therefore not processed by IRS until the month of November. A substantial fraction of very high income returns use the filing extension. Hence, estimates based on filing season statistics are not exactly equal to final statistics.
4 3 detailed statistics on income reported for tax purposes since 1913, when the modern federal income tax started. These statistics report the number of taxpayers and their total income and tax liability for a large number of income brackets. Combining these data with population census data and aggregate income sources, one can estimate the share of total personal income accruing to various upper-income groups, such as the top 10 percent or top 1 percent. We define income as the sum of all income components reported on tax returns (wages and salaries, pensions received, profits from businesses, capital income such as dividends, interest, or rents, and realized capital gains) before individual income taxes. We exclude government transfers such as Social Security retirement benefits or unemployment compensation benefits from our income definition. Non-taxable fringe benefits such as employer provided health insurance is also excluded from our income definition. Therefore, our income measure is defined as cash market income before individual income taxes. Evidence on U.S. top income shares Figure 1 presents the pre-tax income share of the top decile since 1917 in the United States. In 2013, the top decile includes all families with market income above $116,500. The overall pattern of the top decile share over the century is U-shaped. The share of the top decile is around 45 percent from the mid-1920s to It declines substantially to just above 32.5 percent in four years during World War II and stays fairly stable around 33 percent until the 1970s. Such an abrupt decline, concentrated exactly during the war years, cannot easily be reconciled with slow technological changes and suggests instead that the shock of the war played a key and lasting role in shaping income concentration in the United States. After decades of stability in the post-war period, the top decile share has increased dramatically over the last twenty-five years and has now regained its pre-war level. Indeed, the top decile share in 2012 is equal to 50.6 percent, a level higher than any other year since 1917 and even surpasses 1928, the peak of stock market bubble in the roaring 1920s. Figure 2 decomposes the top decile into the top percentile (families with income above $394,000 in 2012) and the next 4 percent (families with income between $161,000 and $394,000), and the bottom half of the top decile (families with income between $114,000 and $161,000). Interestingly, most of the fluctuations of the top decile are due to fluctuations within the top percentile. The drop in the next two groups during World War II is far less dramatic, and they recover from the WWII shock relatively quickly. Finally, their shares do not increase much during the recent decades. In contrast, the top percentile has gone through enormous fluctuations along the course of the twentieth century, from about 18 percent before WWI, to a peak to almost 24 percent in the late 1920s, to only about 9 percent during the 1960s-1970s, and back to almost 23.5 percent by Those at the very top of the income distribution therefore play a central role in the evolution of U.S. inequality over the course of the twentieth century. The implications of these fluctuations at the very top can also be seen when we examine trends in real income growth per family between the top 1
5 4 percent and the bottom 99 percent in recent years as illustrated on Table 1. From 1993 to 2013, for example, average real incomes per family grew by only 15.1% over this 20 year period (implying an annual growth rate of.71%). However, if one excludes the top 1 percent, average real incomes of the bottom 99% grew only by 7.3% from 1993 to 2013 (implying an annual growth rate of.35%). Top 1 percent incomes grew by 62.4% from 1993 to 2013 (implying a 2.45% annual growth rate). This implies that top 1 percent incomes captured almost 60% of the overall economic growth of real incomes per family over the period The period encompasses, however, a dramatic shift in how the bottom 99 percent of the income distribution fared. Table 1 next distinguishes between five sub-periods: (1) the expansion of the Clinton administrations, (2) the recession, (3) the expansion of the Bush administrations, (4) the Great Recession, (5) and During both expansions, the incomes of the top 1 percent grew extremely quickly by 98.7% and 61.8% respectively. However, while the bottom 99 percent of incomes grew at a solid pace of 20.3% from 1993 to 2000, these incomes grew only 6.8% percent from 2002 to As a result, in the economic expansion of , the top 1 percent captured two thirds of income growth. Those results may help explain the disconnect between the economic experiences of the public and the solid macroeconomic growth posted by the U.S. economy from 2002 to Those results may also help explain why the dramatic growth in top incomes during the Clinton administration did not generate much public outcry while there has been a great level of attention to top incomes in the press and in the public debate since During both recessions, the top 1 percent incomes fell sharply, by 30.8% from 2000 to 2002, and by 36.3% from 2007 to The primary driver of the fall in top incomes during those recessions is the stock market crash which reduces dramatically realized capital gains, and, especially in the period, the value of executive stock-options. However, bottom 99 percent incomes fell by 11.6% from 2007 to 2009 while they fell only by 6.5 percent from 2000 to Therefore, the top 1 percent absorbed a larger fraction of losses in the recession (57%) than in the Great recession (49%). The 11.6 percent fall in bottom 99 percent incomes is the largest fall on record in any two year period since the Great Depression of From 2009 to 2012, average real income per family grew modestly by 6.9% (Table 1) but the gains were very uneven. Top 1% incomes grew by 34.7% while bottom 99% incomes grew only by 0.8%. Hence, the top 1% captured 91% of the income gains in the first three years of the recovery. From 2009 to 2010, top 1% grew fast and then stagnated from 2010 to Bottom 99% stagnated both from 2009 to 2010 and from 2010 to Top 1% incomes increased sharply from 2011 to 2012 while bottom 99% incomes grew only modestly. 6 Top 1% incomes fell in 2013, likely due to a retiming of 6 The exact percentage 91% is sensitive to measurement error, especially the growth in the total number of families from 2009 to 2012, estimated from the Current Population Survey. However, the conclusion that most of the gains from economic growth was captured by the top 1% is not in doubt.
6 5 income from 2013 to 2012 to take advantage of the low top tax rates of 2012 before the top tax rates increase in The top percentile share declined during WWI, recovered during the 1920s boom, and declined again during the great depression and WWII. This very specific timing, together with the fact that very high incomes account for a disproportionate share of the total decline in inequality, strongly suggests that the shocks incurred by capital owners during 1914 to 1945 (depression and wars) played a key role. 7 Indeed, from 1913 and up to the 1970s, very top incomes were mostly composed of capital income (mostly dividend income) and to a smaller extent business income, the wage income share being very modest. Therefore, the large decline of top incomes observed during the period is predominantly a capital income phenomenon. Interestingly, the income composition pattern at the very top has changed considerably over the century. The share of wage and salary income has increased sharply from the 1920s to the present, and especially since the 1970s. Therefore, a significant fraction of the surge in top incomes since 1970 is due to an explosion of top wages and salaries. Indeed, estimates based purely on wages and salaries show that the share of total wages and salaries earned by the top 1 percent wage income earners has jumped from 5.1 percent in 1970 to 12.4 percent in Evidence based on the wealth distribution is consistent with those facts. Estimates of wealth concentration, measured by the share of total wealth accruing to top 1 percent wealth holders, constructed by Wojciech Kopczuk and myself from estate tax returns for the period in the United States show a precipitous decline in the first part of the century with only fairly modest increases in recent decades. The evidence suggests that top incomes earners today are not rentiers deriving their incomes from past wealth but rather are working rich, highly paid employees or new entrepreneurs who have not yet accumulated fortunes comparable to those accumulated during the Gilded Age. Such a pattern might not last for very long. The drastic cuts of the federal tax on large estates could certainly accelerate the path toward the reconstitution of the great wealth concentration that existed in the U.S. economy before the Great Depression. The labor market has been creating much more inequality over the last thirty years, with the very top earners capturing a large fraction of macroeconomic productivity gains. A number of factors may help explain this increase in inequality, not only underlying technological changes but also the retreat of institutions developed during the New Deal and World War II - such as progressive tax policies, powerful unions, corporate provision of health and retirement benefits, and changing social norms regarding pay inequality. We need to decide as a society whether this increase in income inequality is efficient and acceptable and, if not, what mix of institutional and tax reforms should be developed to counter it. 7 The negative effect of the wars on top incomes can be explained in part by the large tax increases enacted to finance the wars. During both wars, the corporate income tax was drastically increased and this reduced mechanically the distributions to stockholders. 8 Interestingly, this dramatic increase in top wage incomes has not been mitigated by an increase in mobility at the top of the wage distribution. As Wojciech Kopczuk, myself, and Jae Song have shown in a separate paper, the probability of staying in the top 1 percent wage income group from one year to the next has remained remarkably stable since the 1970s.
7 Table 1. Real Income Growth by Groups Average Income Real Growth Top 1% Incomes Real Growth Bottom 99% Incomes Real Growth Fraction of total growth (or loss) captured by top 1% (1) (2) (3) (4) Full period % 62.4% 7.3% 59% Clinton Expansion % 98.7% 20.3% 45% 2001 Recession % -30.8% -6.5% 57% Bush Expansion % 61.8% 6.8% 65% Great Recession % -36.3% -11.6% 49% Recovery % 34.7% 0.8% 91% Top tax increase % -14.9% 0.2% 106% Computations based on family market income including realized capital gains (before individual taxes). Incomes exclude government transfers (such as unemployment insurance and social security) and non-taxable fringe benefits. Incomes are deflated using the Consumer Price Index. Column (4) reports the fraction of total real family income growth (or loss) captured by the top 1%. For example, from 2002 to 2007, average real family incomes grew by 16.1% but 65% of that growth accrued to the top 1% while only 35% of that growth accrued to the bottom 99% of US families. Source: Piketty and Saez (2003), series updated to 2013.
8 50% Top 10% Income Share 45% 40% 35% 30% Including capital gains Excluding capital gains 25% FIGURE 1 The Top Decile Income Share, Source: Table A1 and Table A3, col. P Income is defined as market income (and excludes government transfers). In 2013, top decile includes all families with annual income above $116,500.
9 Share of total income accruing to each group 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% Top 1% (incomes above $392,000 in 2013) Top 5-1% (incomes between $165,500 and $392,000) Top 10-5% (incomes between $116,500 and $165,500) 0% FIGURE 2 Decomposing the Top Decile US Income Share into 3 Groups, Source: Table A3, cols. P90-95, P95-99, P Income is defined as market income including capital gains. Top 1% denotes the top percentile (families with annual income above $392,000 in 2013) Top 5-1% denotes the next 4% (families with annual income between $165,500 and $392,000 in 2013) Top 10-5% denotes the next 5% (bottom half of the top decile, families with annual income between $116,500 and $165,500 in 2013).
10 Top 0.01% Income Share 6% 5% 4% 3% 2% Including capital gains Excluding capital gains 1% 0% FIGURE 3 The Top 0.01% Income Share, Source: Table A1 and Table A3, col. P Income is defined as market income including (or excluding) capital gains. In 2013, top.01% includes the 16,300 top families with annual income above $8.5m.
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2012 preliminary estimates)
 Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2012 preliminary estimates) Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley September 3, 2013 What s new for recent years? 2009-2012: Uneven
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2012 preliminary estimates) Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley September 3, 2013 What s new for recent years? 2009-2012: Uneven
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2009 and 2010 estimates)
 Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2009 and 2010 estimates) Emmanuel Saez March 2, 2012 What s new for recent years? Great Recession 2007-2009 During the
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2009 and 2010 estimates) Emmanuel Saez March 2, 2012 What s new for recent years? Great Recession 2007-2009 During the
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Update using 2006 preliminary estimates)
 Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Update using 2006 preliminary estimates) Emmanuel Saez March 15, 2008 The recent dramatic rise in income inequality in the United
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Update using 2006 preliminary estimates) Emmanuel Saez March 15, 2008 The recent dramatic rise in income inequality in the United
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2015 preliminary estimates)
 Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2015 preliminary estimates) Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley June 30, 2016 What s new for recent years? 2013-2015: Robust income
Striking it Richer: The Evolution of Top Incomes in the United States (Updated with 2015 preliminary estimates) Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley June 30, 2016 What s new for recent years? 2013-2015: Robust income
Top Incomes throughout the Great Recession
 Top Incomes throughout the Great Recession Emmanuel Saez UC Berkeley Rodolfo Debenedetti Lecture December 2012 1 INTRODUCTION Free market economies generate substantial inequality Main criticism of capitalism
Top Incomes throughout the Great Recession Emmanuel Saez UC Berkeley Rodolfo Debenedetti Lecture December 2012 1 INTRODUCTION Free market economies generate substantial inequality Main criticism of capitalism
Income and Wealth Inequality: Evidence and Policy Implications
 Income and Wealth Inequality: Evidence and Policy Implications Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley Neubauer Collegium Lecture University of Chicago October 2014 1 MEASURING INEQUALITY Inequality matters because
Income and Wealth Inequality: Evidence and Policy Implications Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley Neubauer Collegium Lecture University of Chicago October 2014 1 MEASURING INEQUALITY Inequality matters because
Income Inequality and the Great Recession
 Income Inequality and the Great Recession September 2010 Report by the U.S. Congress Joint Economic Committee Representative Carolyn B. Maloney, Chair Senator Charles E. Schumer, Vice Chairman EXECUTIVE
Income Inequality and the Great Recession September 2010 Report by the U.S. Congress Joint Economic Committee Representative Carolyn B. Maloney, Chair Senator Charles E. Schumer, Vice Chairman EXECUTIVE
The pattern of wealth and income inequality during the. Top Wealth Shares in the United States, 1916 2000: Evidence from Estate Tax Returns
 Top Wealth Shares in the United States, 1916 2000 Top Wealth Shares in the United States, 1916 2000: Evidence from Estate Tax Returns Abstract - This paper presents new homogeneous series on top wealth
Top Wealth Shares in the United States, 1916 2000 Top Wealth Shares in the United States, 1916 2000: Evidence from Estate Tax Returns Abstract - This paper presents new homogeneous series on top wealth
DATA AND CHART PACK February 2016
 DATA AND CHART PACK February 2016 Income Inequality Income includes the revenue streams from wages, salaries, interest on a savings account, dividends from shares of stock, rent, and profits from selling
DATA AND CHART PACK February 2016 Income Inequality Income includes the revenue streams from wages, salaries, interest on a savings account, dividends from shares of stock, rent, and profits from selling
Income and Wealth Concentration in a Historical and International Perspective
 Income and Wealth Concentration in a Historical and International Perspective Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley and NBER February 21, 2004 Abstract This paper summarizes the main findings of the recent studies
Income and Wealth Concentration in a Historical and International Perspective Emmanuel Saez, UC Berkeley and NBER February 21, 2004 Abstract This paper summarizes the main findings of the recent studies
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TOP WEALTH SHARES IN THE UNITED STATES, 1916-2000: EVIDENCE FROM ESTATE TAX RETURNS. Wojciech Kopczuk Emmanuel Saez
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TOP WEALTH SHARES IN THE UNITED STATES, 1916-2000: EVIDENCE FROM ESTATE TAX RETURNS Wojciech Kopczuk Emmanuel Saez Working Paper 10399 http://www.nber.org/papers/w10399 NATIONAL
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TOP WEALTH SHARES IN THE UNITED STATES, 1916-2000: EVIDENCE FROM ESTATE TAX RETURNS Wojciech Kopczuk Emmanuel Saez Working Paper 10399 http://www.nber.org/papers/w10399 NATIONAL
THE BUFFETT RULE: A BASIC PRINCIPLE OF TAX FAIRNESS. The National Economic Council
 THE BUFFETT RULE: A BASIC PRINCIPLE OF TAX FAIRNESS The National Economic Council April 2012 The Buffett Rule: A Basic Principle of Tax Fairness The Buffett Rule is the basic principle that no household
THE BUFFETT RULE: A BASIC PRINCIPLE OF TAX FAIRNESS The National Economic Council April 2012 The Buffett Rule: A Basic Principle of Tax Fairness The Buffett Rule is the basic principle that no household
Average Federal Income Tax Rates for Median-Income Four-Person Families
 820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 center@cbpp.org http://www.cbpp.org April 10, 2002 OVERALL FEDERAL TAX BURDEN ON MOST FAMILIES INCLUDING MIDDLE-
820 First Street, NE, Suite 510, Washington, DC 20002 Tel: 202-408-1080 Fax: 202-408-1056 center@cbpp.org http://www.cbpp.org April 10, 2002 OVERALL FEDERAL TAX BURDEN ON MOST FAMILIES INCLUDING MIDDLE-
Over the last 40 years, the U.S. federal tax system has undergone three
 Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 21, Number 1 Winter 2007 Pages 3 24 How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez Over
Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 21, Number 1 Winter 2007 Pages 3 24 How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez Over
CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE CBO. The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009
 CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE Percent 70 The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009 60 50 Before-Tax Income Federal Taxes Top 1 Percent 40 30 20 81st
CONGRESS OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESSIONAL BUDGET OFFICE Percent 70 The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2008 and 2009 60 50 Before-Tax Income Federal Taxes Top 1 Percent 40 30 20 81st
Gloomy Days, But a Ray of Hope, for Oregon Workers
 Executive Summary September 3, 2010 Gloomy Days, But a Ray of Hope, for Oregon Workers Labor Day is an appropriate moment to reflect on the state of Oregon workers. This year s holiday takes place as the
Executive Summary September 3, 2010 Gloomy Days, But a Ray of Hope, for Oregon Workers Labor Day is an appropriate moment to reflect on the state of Oregon workers. This year s holiday takes place as the
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES HOW PROGRESSIVE IS THE U.S. FEDERAL TAX SYSTEM? A HISTORICAL AND INTERNATIONAL PERSPECTIVE. Thomas Piketty Emmanuel Saez
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES HOW PROGRESSIVE IS THE U.S. FEDERAL TAX SYSTEM? A HISTORICAL AND INTERNATIONAL PERSPECTIVE Thomas Piketty Emmanuel Saez Working Paper 12404 http://www.nber.org/papers/w12404 NATIONAL
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES HOW PROGRESSIVE IS THE U.S. FEDERAL TAX SYSTEM? A HISTORICAL AND INTERNATIONAL PERSPECTIVE Thomas Piketty Emmanuel Saez Working Paper 12404 http://www.nber.org/papers/w12404 NATIONAL
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS
 THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS Vol. CXVIII February 2003 Issue 1 INCOME INEQUALITY IN THE UNITED STATES, 1913 1998* THOMAS PIKETTY AND EMMANUEL SAEZ This paper presents new homogeneous series on top
THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS Vol. CXVIII February 2003 Issue 1 INCOME INEQUALITY IN THE UNITED STATES, 1913 1998* THOMAS PIKETTY AND EMMANUEL SAEZ This paper presents new homogeneous series on top
New York State Employment Trends
 New York State Employment Trends August 2015 Thomas P. DiNapoli New York State Comptroller Prepared by the Office of Budget and Policy Analysis Additional copies of this report may be obtained from: Office
New York State Employment Trends August 2015 Thomas P. DiNapoli New York State Comptroller Prepared by the Office of Budget and Policy Analysis Additional copies of this report may be obtained from: Office
Growing Wealth, Inequality, and Housing in the United States Zhu Xiao Di February 2007 W07-1
 Joint Center for Housing Studies Harvard University Growing Wealth, Inequality, and Housing in the United States Zhu Xiao Di February 2007 W07-1 by Zhu Xiao Di. All rights reserved. Short sections of text,
Joint Center for Housing Studies Harvard University Growing Wealth, Inequality, and Housing in the United States Zhu Xiao Di February 2007 W07-1 by Zhu Xiao Di. All rights reserved. Short sections of text,
To: Debt, Equity, and Capital Tax Reform Working Group From: Small Business Investor Alliance Date: April 12, 2013
 To: Debt, Equity, and Capital Tax Reform Working Group From: Small Business Investor Alliance Date: April 12, 2013 On behalf of the Small Business Investor Alliance 1 (SBIA), we commend the committee on
To: Debt, Equity, and Capital Tax Reform Working Group From: Small Business Investor Alliance Date: April 12, 2013 On behalf of the Small Business Investor Alliance 1 (SBIA), we commend the committee on
Top MTR. Threshold/Averag e Income. US Top Marginal Tax Rate and Top Bracket Threshold. Top MTR (Federal Individual Income Tax)
 Source: IRS, Statistics of Income Division, Historical Table 23 Top Marginal Tax Rate and Top Bracket Threshold Top MTR (Federal Individual Income Tax) 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% Top MTR
Source: IRS, Statistics of Income Division, Historical Table 23 Top Marginal Tax Rate and Top Bracket Threshold Top MTR (Federal Individual Income Tax) 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% Top MTR
Chapter 12: Gross Domestic Product and Growth Section 1
 Chapter 12: Gross Domestic Product and Growth Section 1 Key Terms national income accounting: a system economists use to collect and organize macroeconomic statistics on production, income, investment,
Chapter 12: Gross Domestic Product and Growth Section 1 Key Terms national income accounting: a system economists use to collect and organize macroeconomic statistics on production, income, investment,
Poverty, Inequality and Trends in the Labor Market. Hilary Hoynes, University of California Berkeley
 Poverty, Inequality and Trends in the Labor Market Hilary Hoynes, University of California Berkeley Overview Since the 1980s we have seen little improvement in poverty despite steady economic growth At
Poverty, Inequality and Trends in the Labor Market Hilary Hoynes, University of California Berkeley Overview Since the 1980s we have seen little improvement in poverty despite steady economic growth At
Non Farm Payroll Employment Developments among States during the Great Recession and Jobless Recovery
 Non Farm Payroll Employment Developments among States during the Great Recession and Jobless Recovery Prepared by: Paul E. Harrington and Neeta P. Fogg Center for Labor Markets and Policy, Drexel University
Non Farm Payroll Employment Developments among States during the Great Recession and Jobless Recovery Prepared by: Paul E. Harrington and Neeta P. Fogg Center for Labor Markets and Policy, Drexel University
R e a l i t y C h e c k
 The New American Economy A Rising Tide that Lifts Only Yachts T he United States is the richest country on earth; the income of the average American household substantially exceeds that of the average
The New American Economy A Rising Tide that Lifts Only Yachts T he United States is the richest country on earth; the income of the average American household substantially exceeds that of the average
Chapter 10 Fiscal Policy Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.)
 Chapter 10 Fiscal Policy Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter introduces you to a formal analysis of fiscal policy, and puts it in context with real-world data and
Chapter 10 Fiscal Policy Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter introduces you to a formal analysis of fiscal policy, and puts it in context with real-world data and
The Wealth of Households: An Analysis of the 2013 Survey of Consumer Finances
 November 214 The Wealth of Households: An Analysis of the 213 Survey of Consumer Finances By David Rosnick and Dean Baker* Center for Economic and Policy Research 1611 Connecticut Ave. NW Suite 4 Washington,
November 214 The Wealth of Households: An Analysis of the 213 Survey of Consumer Finances By David Rosnick and Dean Baker* Center for Economic and Policy Research 1611 Connecticut Ave. NW Suite 4 Washington,
The Great Depression is often cast as the
 A Great Recession Brief Income, Wealth, and Debt and the Great Recession The Russell Sage Foundation and The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality October 212 Timothy Smeeding, University of Wisconsin,
A Great Recession Brief Income, Wealth, and Debt and the Great Recession The Russell Sage Foundation and The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality October 212 Timothy Smeeding, University of Wisconsin,
wealth inequality The last three decades have witnessed The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality
 national report card wealth inequality The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality By Edward N. Wolff Key findings After two decades of robust growth in middle class wealth, median net worth plummeted
national report card wealth inequality The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality By Edward N. Wolff Key findings After two decades of robust growth in middle class wealth, median net worth plummeted
Income Tax Liabilities Statistics 2012-13 to 2014-15
 Coverage: United Kingdom Theme: The Economy Released: 13 February 2015 Next Release: May 2015 Frequency of release: Twice yearly (Jan/Feb and Apr/May) Income Tax Liabilities Statistics 2012-13 to 2014-15
Coverage: United Kingdom Theme: The Economy Released: 13 February 2015 Next Release: May 2015 Frequency of release: Twice yearly (Jan/Feb and Apr/May) Income Tax Liabilities Statistics 2012-13 to 2014-15
State of Working Britain
 State of Working Britain Aim is to Gives an up to date assessment of the performance of UK labour market, to highlight recent important developments seeks to describe and understand the major long-term
State of Working Britain Aim is to Gives an up to date assessment of the performance of UK labour market, to highlight recent important developments seeks to describe and understand the major long-term
THE STATE OF THE ECONOMY
 THE STATE OF THE ECONOMY CARLY HARRISON Portland State University Following data revisions, the economy continues to grow steadily, but slowly, in line with expectations. Gross domestic product has increased,
THE STATE OF THE ECONOMY CARLY HARRISON Portland State University Following data revisions, the economy continues to grow steadily, but slowly, in line with expectations. Gross domestic product has increased,
Volume URL: http://www.nber.org/books/lutz45-1. Chapter Title: Liquidity Ratios and Cash Balances. Chapter URL: http://www.nber.
 This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Corporate Cash Balances, 1914-43: Manufacturing and Trade Volume Author/Editor: Friedrich
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Corporate Cash Balances, 1914-43: Manufacturing and Trade Volume Author/Editor: Friedrich
After a severe slowdown in the early 1990s, General Fund
 Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States: Current Challenges in California Abstract - General Fund revenue growth in California has been quite strong in recent
Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States Forecasting Revenue Receipts in the States: Current Challenges in California Abstract - General Fund revenue growth in California has been quite strong in recent
The U.S. and Midwest Economy in 2016: Implications for Supply Chain Firms
 The U.S. and Midwest Economy in 2016: Implications for Supply Chain Firms Rick Mattoon Senior Economist and Economic Advisor Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago Right Place Supply Chain Management Conference
The U.S. and Midwest Economy in 2016: Implications for Supply Chain Firms Rick Mattoon Senior Economist and Economic Advisor Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago Right Place Supply Chain Management Conference
Estonia and the European Debt Crisis Juhan Parts
 Estonia and the European Debt Crisis Juhan Parts Estonia has had a quick recovery from the recent recession and its economy is in better shape than before the crisis. It is now much leaner and significantly
Estonia and the European Debt Crisis Juhan Parts Estonia has had a quick recovery from the recent recession and its economy is in better shape than before the crisis. It is now much leaner and significantly
West Bank and Gaza: Labor Market Trends, Growth and Unemployment 1
 West Bank and Gaza: Labor Market Trends, Growth and Unemployment 1 Labor market developments in the West Bank and Gaza (WBG) since the 1994 Oslo accords have reflected relatively sluggish growth performance.
West Bank and Gaza: Labor Market Trends, Growth and Unemployment 1 Labor market developments in the West Bank and Gaza (WBG) since the 1994 Oslo accords have reflected relatively sluggish growth performance.
Details and Analysis of Dr. Ben Carson s Tax Plan
 FISCAL FACT Jan. 2016 No. 493 Details and Analysis of Dr. Ben Carson s Tax Plan By Kyle Pomerleau Director of Federal Projects Key Findings Dr. Ben Carson s tax plan would replace the federal income tax
FISCAL FACT Jan. 2016 No. 493 Details and Analysis of Dr. Ben Carson s Tax Plan By Kyle Pomerleau Director of Federal Projects Key Findings Dr. Ben Carson s tax plan would replace the federal income tax
Women and Men in the Recovery: Where the Jobs Are Women Recover Jobs Lost in Recession in Year Five
 IWPR #C426 November 2014 Women and Men in the Recovery: Where the Jobs Are Women Recover Jobs Lost in Recession in Year Five Heidi Hartmann, Ph.D., Elyse Shaw, and Rachel O Connor Overview While the number
IWPR #C426 November 2014 Women and Men in the Recovery: Where the Jobs Are Women Recover Jobs Lost in Recession in Year Five Heidi Hartmann, Ph.D., Elyse Shaw, and Rachel O Connor Overview While the number
The Economic Impact of the Senior Population on a State s Economy: The Case of North Dakota
 The Economic Impact of the Senior Population on a State s Economy: The Case of North Dakota RICHARD RATHGE January 2007 NORTH DAKOTA STATE DATA CENTER North Dakota State University, an Equal Opportunity
The Economic Impact of the Senior Population on a State s Economy: The Case of North Dakota RICHARD RATHGE January 2007 NORTH DAKOTA STATE DATA CENTER North Dakota State University, an Equal Opportunity
Lars Osberg. Department of Economics Dalhousie University 6214 University Avenue Halifax, Nova Scotia B3H 3J5 CANADA Email: Lars.Osberg@dal.
 Not Good Enough to be Average? Comments on The Weak Jobs recovery: whatever happened to the great American jobs machine? by Freeman and Rodgers Lars Osberg Department of Economics Dalhousie University
Not Good Enough to be Average? Comments on The Weak Jobs recovery: whatever happened to the great American jobs machine? by Freeman and Rodgers Lars Osberg Department of Economics Dalhousie University
Quarterly Economics Briefing
 Quarterly Economics Briefing March June 2015 2016 Review of Current Conditions: The Economic Outlook and Its Impact on Workers Compensation The exhibits below are updated to reflect the current economic
Quarterly Economics Briefing March June 2015 2016 Review of Current Conditions: The Economic Outlook and Its Impact on Workers Compensation The exhibits below are updated to reflect the current economic
Is there a revolution in American saving?
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Is there a revolution in American saving? John Tatom Networks Financial institute at Indiana State University May 2009 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/16139/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Is there a revolution in American saving? John Tatom Networks Financial institute at Indiana State University May 2009 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/16139/
Long Island is rapidly losing its lead in private health care coverage. That distinctive mark of middle class success - private
 RESEARCH REPORT Regional Labor Review Fall 1998 Long Island s Ailing Health Care Benefits by Niev Duffy Long Island is rapidly losing its lead in private health care coverage. That distinctive mark of
RESEARCH REPORT Regional Labor Review Fall 1998 Long Island s Ailing Health Care Benefits by Niev Duffy Long Island is rapidly losing its lead in private health care coverage. That distinctive mark of
A Strong Housing Recovery Fuels Growth
 Chapman University A. Gary Anderson Center for Economic Research FOR RELEASE: ONLINE: June 12, 2013; 10:00 a.m. PRINT: June 13, 2013 CONTACT: James Doti, President and Donald Bren Distinguished Chair of
Chapman University A. Gary Anderson Center for Economic Research FOR RELEASE: ONLINE: June 12, 2013; 10:00 a.m. PRINT: June 13, 2013 CONTACT: James Doti, President and Donald Bren Distinguished Chair of
Uneven Progress: Upstate Employment Trends Since the Great Recession
 Uneven Progress: Upstate Employment Trends Since the Great Recession OFFICE OF THE NEW YORK STATE COMPTROLLER Thomas P. DiNapoli, State Comptroller AUGUST 2016 Message from the Comptroller August 2016
Uneven Progress: Upstate Employment Trends Since the Great Recession OFFICE OF THE NEW YORK STATE COMPTROLLER Thomas P. DiNapoli, State Comptroller AUGUST 2016 Message from the Comptroller August 2016
Do Commodity Price Spikes Cause Long-Term Inflation?
 No. 11-1 Do Commodity Price Spikes Cause Long-Term Inflation? Geoffrey M.B. Tootell Abstract: This public policy brief examines the relationship between trend inflation and commodity price increases and
No. 11-1 Do Commodity Price Spikes Cause Long-Term Inflation? Geoffrey M.B. Tootell Abstract: This public policy brief examines the relationship between trend inflation and commodity price increases and
For Immediate Release
 Household Income Trends May 2015 Issued July 2015 Gordon Green and John Coder Sentier Research, LLC For Immediate Release 1 Household Income Trends May 2015 Note This report on median household income
Household Income Trends May 2015 Issued July 2015 Gordon Green and John Coder Sentier Research, LLC For Immediate Release 1 Household Income Trends May 2015 Note This report on median household income
Wealth and Demographics: Demographics by Wealth and Wealth by Demographics using the Survey of Consumer Finances. *** DRAFT March 11, 2013 ***
 Wealth and Demographics: Demographics by Wealth and Wealth by Demographics using the Survey of Consumer Finances *** DRAFT March 11, 2013 *** Jeff Thompson* Economist Microeconomic Surveys Federal Reserve
Wealth and Demographics: Demographics by Wealth and Wealth by Demographics using the Survey of Consumer Finances *** DRAFT March 11, 2013 *** Jeff Thompson* Economist Microeconomic Surveys Federal Reserve
Social Security Administration Continuous Work History Sample - A Review
 Working Paper Series Congressional Budget Office Washington, D.C. EARNINGS INEQUALITY AND HIGH EARNERS: CHANGES DURING AND AFTER THE STOCK MARKET BOOM OF THE 1990s Jonathan A. Schwabish (e-mail: jonathan.schwabish@cbo.gov)
Working Paper Series Congressional Budget Office Washington, D.C. EARNINGS INEQUALITY AND HIGH EARNERS: CHANGES DURING AND AFTER THE STOCK MARKET BOOM OF THE 1990s Jonathan A. Schwabish (e-mail: jonathan.schwabish@cbo.gov)
Effects on pensioners from leaving the EU
 Effects on pensioners from leaving the EU Summary 1.1 HM Treasury s short-term document presented two scenarios for the immediate impact of leaving the EU on the UK economy: the shock scenario and severe
Effects on pensioners from leaving the EU Summary 1.1 HM Treasury s short-term document presented two scenarios for the immediate impact of leaving the EU on the UK economy: the shock scenario and severe
Pew Study: American Middle Class is Steadily Shrinking
 Pew Study: American Middle Class is Steadily Shrinking December 23, 2015 by Gary D. Halbert of ProFutures Investments IN THIS ISSUE: 1. Pew Research: American Middle Class is Steadily Shrinking 2. Pew
Pew Study: American Middle Class is Steadily Shrinking December 23, 2015 by Gary D. Halbert of ProFutures Investments IN THIS ISSUE: 1. Pew Research: American Middle Class is Steadily Shrinking 2. Pew
The labour market, I: real wages, productivity and unemployment 7.1 INTRODUCTION
 7 The labour market, I: real wages, productivity and unemployment 7.1 INTRODUCTION Since the 1970s one of the major issues in macroeconomics has been the extent to which low output and high unemployment
7 The labour market, I: real wages, productivity and unemployment 7.1 INTRODUCTION Since the 1970s one of the major issues in macroeconomics has been the extent to which low output and high unemployment
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D.
 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Economic fluctuations, also called business cycles, are movements of GDP away from potential
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Ing. Mansoor Maitah Ph.D. et Ph.D. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Economic fluctuations, also called business cycles, are movements of GDP away from potential
Q&A on tax relief for individuals & families
 Q&A on tax relief for individuals & families A. Tax cuts individuals What are the new tax rates? The table below shows the new tax rates being rolled out from 1 October 2008, 1 April 2010 and 1 April 2011,
Q&A on tax relief for individuals & families A. Tax cuts individuals What are the new tax rates? The table below shows the new tax rates being rolled out from 1 October 2008, 1 April 2010 and 1 April 2011,
 The Credit Card Report May 4 The Credit Card Report May 4 Contents Visa makes no representations or warranties about the accuracy or suitability of the information or advice provided. You use the information
The Credit Card Report May 4 The Credit Card Report May 4 Contents Visa makes no representations or warranties about the accuracy or suitability of the information or advice provided. You use the information
Why is California s Unemployment Rate so High and what does it Mean for the State s Economic Future?
 September 2010 Why is California s Unemployment Rate so High and what does it Mean for the State s Economic Future? The state s unemployment rate is now nearly 3% higher than the national rate. In August
September 2010 Why is California s Unemployment Rate so High and what does it Mean for the State s Economic Future? The state s unemployment rate is now nearly 3% higher than the national rate. In August
income inequality The takeoff in income inequality over the By Jeffrey Thompson and Timothy Smeeding January 2014
 national report card 30 income inequality income inequality January 2014 The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality By Jeffrey Thompson and Timothy Smeeding Key findings The Great Recession had a mixed
national report card 30 income inequality income inequality January 2014 The Stanford Center on Poverty and Inequality By Jeffrey Thompson and Timothy Smeeding Key findings The Great Recession had a mixed
Wealth Inequality in the United States since 1913
 Wealth Inequality in the United States since 1913 Emmanuel Saez (UC Berkeley) Gabriel Zucman (LSE) October 2014 Introduction US Income inequality has increased sharply since the 1970s Mixed existing evidence
Wealth Inequality in the United States since 1913 Emmanuel Saez (UC Berkeley) Gabriel Zucman (LSE) October 2014 Introduction US Income inequality has increased sharply since the 1970s Mixed existing evidence
Chapter 4 Consumption, Saving, and Investment
 Chapter 4 Consumption, Saving, and Investment Multiple Choice Questions 1. Desired national saving equals (a) Y C d G. (b) C d + I d + G. (c) I d + G. (d) Y I d G. 2. With no inflation and a nominal interest
Chapter 4 Consumption, Saving, and Investment Multiple Choice Questions 1. Desired national saving equals (a) Y C d G. (b) C d + I d + G. (c) I d + G. (d) Y I d G. 2. With no inflation and a nominal interest
Top Incomes in the Long Run of History. Anthony B. Atkinson, Thomas Piketty, and Emmanuel Saez*
 Journal of Economic Literature 2011, 49:1, 3 71 http:www.aeaweb.org/articles.php?doi=10.1257/jel.49.1.3 Top Incomes in the Long Run of History Anthony B. Atkinson, Thomas Piketty, and Emmanuel Saez* A
Journal of Economic Literature 2011, 49:1, 3 71 http:www.aeaweb.org/articles.php?doi=10.1257/jel.49.1.3 Top Incomes in the Long Run of History Anthony B. Atkinson, Thomas Piketty, and Emmanuel Saez* A
ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES
 ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES Prepared by Quantria Strategies, LLC for the National Federation of Independent Business and the S Corporation Association ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES CONTENTS
ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES Prepared by Quantria Strategies, LLC for the National Federation of Independent Business and the S Corporation Association ENTITY CHOICE AND EFFECTIVE TAX RATES CONTENTS
I. Introduction to Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model
 University of California-Davis Economics 1B-Intro to Macro Handout 8 TA: Jason Lee Email: jawlee@ucdavis.edu I. Introduction to Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model In this chapter we develop a model
University of California-Davis Economics 1B-Intro to Macro Handout 8 TA: Jason Lee Email: jawlee@ucdavis.edu I. Introduction to Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model In this chapter we develop a model
Special Report. December 16, 2009. pace of household borrowing.
 December 16, 29 HIGHLIGHTS Consumer credit is an important indicator of the level of household borrowing. Since peaking in 28, U.S. consumer credit has fallen by 3.8%, its largest decline since World War
December 16, 29 HIGHLIGHTS Consumer credit is an important indicator of the level of household borrowing. Since peaking in 28, U.S. consumer credit has fallen by 3.8%, its largest decline since World War
FISCAL POLICY* Chapter. Key Concepts
 Chapter 11 FISCAL POLICY* Key Concepts The Federal Budget The federal budget is an annual statement of the government s expenditures and tax revenues. Using the federal budget to achieve macroeconomic
Chapter 11 FISCAL POLICY* Key Concepts The Federal Budget The federal budget is an annual statement of the government s expenditures and tax revenues. Using the federal budget to achieve macroeconomic
Determination of the December 2007 Peak in Economic Activity
 Page 1 of 6 This report is also available as a PDF file. Determination of the December 2007 Peak in Economic Activity The Business Cycle Dating Committee of the National Bureau of Economic Research met
Page 1 of 6 This report is also available as a PDF file. Determination of the December 2007 Peak in Economic Activity The Business Cycle Dating Committee of the National Bureau of Economic Research met
Levy Economics Institute of Bard College. Policy Note A DECADE OF FLAT WAGES?
 Levy Economics Institute of Bard College Levy Economics Institute of Bard College Policy Note 14 / 4 A DECADE OF FLAT WAGES? FERNANDO RIOS-AVILA and JULIE L. HOTCHKISS Workers wages are the most important
Levy Economics Institute of Bard College Levy Economics Institute of Bard College Policy Note 14 / 4 A DECADE OF FLAT WAGES? FERNANDO RIOS-AVILA and JULIE L. HOTCHKISS Workers wages are the most important
Executive summary. Global Wage Report 2014 / 15 Wages and income inequality
 Executive summary Global Wage Report 2014 / 15 Wages and income inequality Global Wage Report 2014/15 Wages and income inequality Executive summary INTERNATIONAL LABOUR OFFICE GENEVA Copyright International
Executive summary Global Wage Report 2014 / 15 Wages and income inequality Global Wage Report 2014/15 Wages and income inequality Executive summary INTERNATIONAL LABOUR OFFICE GENEVA Copyright International
Housing finance in Italy
 Housing finance in Italy Defining characteristics One of the salient features of the Italian housing market is the high rate of ownership. According to data from the 2001 census, 71% of Italian households
Housing finance in Italy Defining characteristics One of the salient features of the Italian housing market is the high rate of ownership. According to data from the 2001 census, 71% of Italian households
Solutions to Problem Set #2 Spring, 2013. 1.a) Units of Price of Nominal GDP Real Year Stuff Produced Stuff GDP Deflator GDP
 Economics 1021, Section 1 Prof. Steve Fazzari Solutions to Problem Set #2 Spring, 2013 1.a) Units of Price of Nominal GDP Real Year Stuff Produced Stuff GDP Deflator GDP 2003 500 $20 $10,000 95.2 $10,504
Economics 1021, Section 1 Prof. Steve Fazzari Solutions to Problem Set #2 Spring, 2013 1.a) Units of Price of Nominal GDP Real Year Stuff Produced Stuff GDP Deflator GDP 2003 500 $20 $10,000 95.2 $10,504
Jarle Bergo: Monetary policy and the outlook for the Norwegian economy
 Jarle Bergo: Monetary policy and the outlook for the Norwegian economy Speech by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank, at the Capital markets seminar, hosted by Terra-Gruppen AS, Gardermoen,
Jarle Bergo: Monetary policy and the outlook for the Norwegian economy Speech by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank, at the Capital markets seminar, hosted by Terra-Gruppen AS, Gardermoen,
Economic Policy Challenges for the 'Social Market Economy' in a Globalized World: Old wine in new skins?
 Economic Policy Challenges for the 'Social Market Economy' in a Globalized World: Old wine in new skins? Dr. Bodo Herzog ESB Business School, Reutlingen University, Germany ESB Business School Social Market
Economic Policy Challenges for the 'Social Market Economy' in a Globalized World: Old wine in new skins? Dr. Bodo Herzog ESB Business School, Reutlingen University, Germany ESB Business School Social Market
CHAPTER 7: AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY
 CHAPTER 7: AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY Learning goals of this chapter: What forces bring persistent and rapid expansion of real GDP? What causes inflation? Why do we have business cycles? How
CHAPTER 7: AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY Learning goals of this chapter: What forces bring persistent and rapid expansion of real GDP? What causes inflation? Why do we have business cycles? How
Svein Gjedrem: The economic situation in Norway
 Svein Gjedrem: The economic situation in Norway Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, 21 March 2002. Please
Svein Gjedrem: The economic situation in Norway Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, 21 March 2002. Please
Perspective. Economic and Market. A Productivity Problem?
 James W. Paulsen, Ph.D. Perspective Bringing you national and global economic trends for more than 30 years Economic and Market March 20, 2015 A Productivity Problem? In the post-war era, U.S. productivity
James W. Paulsen, Ph.D. Perspective Bringing you national and global economic trends for more than 30 years Economic and Market March 20, 2015 A Productivity Problem? In the post-war era, U.S. productivity
THE ECONOMIC IMPACT OF CORPORATE TAX RATE REDUCTIONS
 THE ECONOMIC IMPACT OF CORPORATE TAX RATE REDUCTIONS Leadership makes the difference January 211 The Economic Impact of Corporate Tax Rate Reductions January 211 Canadian Manufacturers & Exporters Author:
THE ECONOMIC IMPACT OF CORPORATE TAX RATE REDUCTIONS Leadership makes the difference January 211 The Economic Impact of Corporate Tax Rate Reductions January 211 Canadian Manufacturers & Exporters Author:
A LIFE-CYCLE AND GENERATIONAL PERSPECTIVE ON THE WEALTH AND INCOME OF MILLENNIALS
 A LIFE-CYCLE AND GENERATIONAL PERSPECTIVE ON THE WEALTH AND INCOME OF MILLENNIALS William R. Emmons and Ray Boshara Young adulthood is the life stage when the greatest increases in income and wealth typically
A LIFE-CYCLE AND GENERATIONAL PERSPECTIVE ON THE WEALTH AND INCOME OF MILLENNIALS William R. Emmons and Ray Boshara Young adulthood is the life stage when the greatest increases in income and wealth typically
Notes - Gruber, Public Finance Chapter 20.3 A calculation that finds the optimal income tax in a simple model: Gruber and Saez (2002).
 Notes - Gruber, Public Finance Chapter 20.3 A calculation that finds the optimal income tax in a simple model: Gruber and Saez (2002). Description of the model. This is a special case of a Mirrlees model.
Notes - Gruber, Public Finance Chapter 20.3 A calculation that finds the optimal income tax in a simple model: Gruber and Saez (2002). Description of the model. This is a special case of a Mirrlees model.
Capital Gains Taxes: An Overview
 Order Code 96-769 Updated January 24, 2007 Summary Capital Gains Taxes: An Overview Jane G. Gravelle Senior Specialist in Economic Policy Government and Finance Division Tax legislation in 1997 reduced
Order Code 96-769 Updated January 24, 2007 Summary Capital Gains Taxes: An Overview Jane G. Gravelle Senior Specialist in Economic Policy Government and Finance Division Tax legislation in 1997 reduced
USES OF CONSUMER PRICE INDICES
 USES OF CONSUMER PRICE INDICES 2 2.1 The consumer price index (CPI) is treated as a key indicator of economic performance in most countries. The purpose of this chapter is to explain why CPIs are compiled
USES OF CONSUMER PRICE INDICES 2 2.1 The consumer price index (CPI) is treated as a key indicator of economic performance in most countries. The purpose of this chapter is to explain why CPIs are compiled
Adecade into the 21st century, Michigan s longbruised
 Michigan League FOR Human Services December 2010 Michigan's Economy Continues to Cause Pain: Communities of Color Take a Harder Hit Adecade into the 21st century, Michigan s longbruised economy continues
Michigan League FOR Human Services December 2010 Michigan's Economy Continues to Cause Pain: Communities of Color Take a Harder Hit Adecade into the 21st century, Michigan s longbruised economy continues
LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES
 LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Peter Ireland Department of Economics Boston College peter.ireland@bc.edu http://www2.bc.edu/peter-ireland/ec132.html Copyright (c) 2013 by Peter Ireland. Redistribution
LECTURE NOTES ON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Peter Ireland Department of Economics Boston College peter.ireland@bc.edu http://www2.bc.edu/peter-ireland/ec132.html Copyright (c) 2013 by Peter Ireland. Redistribution
How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far?
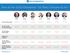 How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far? 10-Year GDP Growth 10.0% 16.0% -1.0% 13.9% 15.0% -9.5% 11.5% 10-Year Capital Investment Growth 28.8% 46.6% -2.8% 43.9% 48.9% -18.6% 29% 10-Year Wage
How do the 2016 Presidential Tax Plans Compare So Far? 10-Year GDP Growth 10.0% 16.0% -1.0% 13.9% 15.0% -9.5% 11.5% 10-Year Capital Investment Growth 28.8% 46.6% -2.8% 43.9% 48.9% -18.6% 29% 10-Year Wage
Economic Outlook, November 2013 November 21, 2013. Jeffrey M. Lacker President Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond
 Economic Outlook, November 2013 November 21, 2013 Jeffrey M. Lacker President Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Asheboro SCORE Asheboro, North Carolina It's a pleasure to be with you today to discuss the
Economic Outlook, November 2013 November 21, 2013 Jeffrey M. Lacker President Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Asheboro SCORE Asheboro, North Carolina It's a pleasure to be with you today to discuss the
Strategy Document 1/03
 Strategy Document / Monetary policy in the period 5 March to 5 June Discussed by the Executive Board at its meeting of 5 February. Approved by the Executive Board at its meeting of 5 March Background Norges
Strategy Document / Monetary policy in the period 5 March to 5 June Discussed by the Executive Board at its meeting of 5 February. Approved by the Executive Board at its meeting of 5 March Background Norges
Living Standard Trends in Australia: Report for Anglicare Australia. BEN PHILLIPS NATSEM UNIVERSITY OF CANBERRA, September 2015
 Living Standard Trends in Australia: Report for Anglicare Australia BEN PHILLIPS NATSEM UNIVERSITY OF CANBERRA, September 2015 2 Contents 1 Executive Sumary 3 2 Introduction 5 3 Methodology 6 4 Results
Living Standard Trends in Australia: Report for Anglicare Australia BEN PHILLIPS NATSEM UNIVERSITY OF CANBERRA, September 2015 2 Contents 1 Executive Sumary 3 2 Introduction 5 3 Methodology 6 4 Results
The Aftermath of the Housing Bubble
 The Aftermath of the Housing Bubble James Bullard President and CEO, FRB-St. Louis Housing in America: Innovative Solutions to Address the Needs of Tomorrow 5 June 2012 The Bipartisan Policy Center St.
The Aftermath of the Housing Bubble James Bullard President and CEO, FRB-St. Louis Housing in America: Innovative Solutions to Address the Needs of Tomorrow 5 June 2012 The Bipartisan Policy Center St.
The State of Working America 12th Edition
 The State of Working America 12th Edition LAWRENCE MISHEL JOSH BIVENS ELISE GOULD HEIDI SHIERHOLZ Wages EPI DIGITAL EDITION This chapter is from The State of Working America, 12th Edition, an Economic
The State of Working America 12th Edition LAWRENCE MISHEL JOSH BIVENS ELISE GOULD HEIDI SHIERHOLZ Wages EPI DIGITAL EDITION This chapter is from The State of Working America, 12th Edition, an Economic
cepr briefing paper Defaulting on The Social Security Trust Fund Bonds: Winner and Losers CENTER FOR ECONOMIC AND POLICY RESEARCH SUMMARY Dean Baker 1
 cepr CENTER FOR ECONOMIC AND POLICY RESEARCH briefing paper Defaulting on The Social Security Trust Fund Bonds: Winner and Losers Dean Baker 1 July 23, 2001 SUMMARY The United States government has never
cepr CENTER FOR ECONOMIC AND POLICY RESEARCH briefing paper Defaulting on The Social Security Trust Fund Bonds: Winner and Losers Dean Baker 1 July 23, 2001 SUMMARY The United States government has never
Objectives for Chapter 9 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 1 Objectives for Chapter 9 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply At the end of Chapter 9, you will be able to answer the following: 1. Explain what is meant by aggregate demand? 2. Name the four categories
1 Objectives for Chapter 9 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply At the end of Chapter 9, you will be able to answer the following: 1. Explain what is meant by aggregate demand? 2. Name the four categories
AN EXAMINATION OF THE EQUITY RISK PREMIUM ASSUMED BY CANADIAN PENSION PLAN SPONSORS
 TITLE: AN EXAMINATION OF THE EQUITY RISK PREMIUM ASSUMED BY CANADIAN PENSION PLAN SPONSORS Authored by: Andrews, Doug, MBA, FCIA, FSA, CFA Vice President Aon Consulting 145 Wellington Street West Suite
TITLE: AN EXAMINATION OF THE EQUITY RISK PREMIUM ASSUMED BY CANADIAN PENSION PLAN SPONSORS Authored by: Andrews, Doug, MBA, FCIA, FSA, CFA Vice President Aon Consulting 145 Wellington Street West Suite
Agenda. Business Cycles. What Is a Business Cycle? What Is a Business Cycle? What is a Business Cycle? Business Cycle Facts.
 Agenda What is a Business Cycle? Business Cycles.. 11-1 11-2 Business cycles are the short-run fluctuations in aggregate economic activity around its long-run growth path. Y Time 11-3 11-4 1 Components
Agenda What is a Business Cycle? Business Cycles.. 11-1 11-2 Business cycles are the short-run fluctuations in aggregate economic activity around its long-run growth path. Y Time 11-3 11-4 1 Components
Tax: Are we paying our fair share?
 Australian Council of Social Service Tax: Are we paying our fair share? The effects of the current tax mix on contributions to the tax system ACOSS Tax Talk No 1 January 2015 1 Who we are ACOSS is the
Australian Council of Social Service Tax: Are we paying our fair share? The effects of the current tax mix on contributions to the tax system ACOSS Tax Talk No 1 January 2015 1 Who we are ACOSS is the
The impact of the recession on the labour market
 The impact of the recession on the labour market 14 May 2009 Chapter 4: Pensioner income and expenditure Pension Trends Impact of the recession on the labour market Introduction Chapter 1: Recent changes
The impact of the recession on the labour market 14 May 2009 Chapter 4: Pensioner income and expenditure Pension Trends Impact of the recession on the labour market Introduction Chapter 1: Recent changes
The Problem with Structural Unemployment in the U.S.
 Issue Brief October 2012 The Problem with Structural Unemployment in the U.S. BY DEAN BAKER* It took centuries worth of research and evidence for astronomers to convince the world, including their fellow
Issue Brief October 2012 The Problem with Structural Unemployment in the U.S. BY DEAN BAKER* It took centuries worth of research and evidence for astronomers to convince the world, including their fellow
12.1 Introduction. 12.2 The MP Curve: Monetary Policy and the Interest Rates 1/24/2013. Monetary Policy and the Phillips Curve
 Chapter 12 Monetary Policy and the Phillips Curve By Charles I. Jones Media Slides Created By Dave Brown Penn State University The short-run model summary: Through the MP curve the nominal interest rate
Chapter 12 Monetary Policy and the Phillips Curve By Charles I. Jones Media Slides Created By Dave Brown Penn State University The short-run model summary: Through the MP curve the nominal interest rate
Crunch or Crucible? Upcoming Changes in the Federal Tax Law A Special Edition Tax Guide for Friends and Alumni of Pomona College
 Upcoming Changes in the Federal Tax Law A Special Edition Tax Guide for Friends and Alumni of Pomona College Pomona College, Office of Trusts & Estates, 550 N. College Ave., Claremont, CA 91711 www.pomona.planyourlegacy.org
Upcoming Changes in the Federal Tax Law A Special Edition Tax Guide for Friends and Alumni of Pomona College Pomona College, Office of Trusts & Estates, 550 N. College Ave., Claremont, CA 91711 www.pomona.planyourlegacy.org
The Employment Crisis in Spain 1
 The Employment Crisis in Spain 1 Juan F Jimeno (Research Division, Banco de España) May 2011 1 Paper prepared for presentation at the United Nations Expert Meeting The Challenge of Building Employment
The Employment Crisis in Spain 1 Juan F Jimeno (Research Division, Banco de España) May 2011 1 Paper prepared for presentation at the United Nations Expert Meeting The Challenge of Building Employment
APPENDIX TO: Top Incomes in Korea, 1933-2010: Evidence from Income Tax Statistics
 TOP INCOMES IN KOREA, 1933-2010: EV Title INCOME TAX STATISTICS Author(s) KIM, NAK NYEON; KIM, JONGIL Citation Hitotsubashi Journal of Economics, Issue 2015-06 Date Type Departmental Bulletin Paper Text
TOP INCOMES IN KOREA, 1933-2010: EV Title INCOME TAX STATISTICS Author(s) KIM, NAK NYEON; KIM, JONGIL Citation Hitotsubashi Journal of Economics, Issue 2015-06 Date Type Departmental Bulletin Paper Text
