Objectives. Objectives. What is the concern? Objectives. Approach to Pelvic Pain: The Role of Ultrasound
|
|
|
- Ruby Copeland
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Approach to Pelvic Pain: The Role of Ultrasound Rochelle F. Andreotti M.D. FACR, FSRU, FAIUM Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Vanderbilt University Medical Center I have no financial relationships to disclose. Objectives Objectives Emphasize the importance of sonography the imaging modality of choice for the evaluation of suspected gynecological etiologies of pelvic pain. Illustrate the use of US when a non-gynecological etiology of pain is suspected as an effective substitute to CT for pregnant patients as well as patients in the reproductive age group in view of the lack of ionizing radiation. Objectives What is the concern? Illustrate the use of MRI as a problem solving tool : when the US exam is not adequate in place of computed tomography in pregnant patients with suspected appendicitis Frequency may account for up to 40% of gynecological visits Most common reason for hysterectomies Common reason for laparoscopy Most common reason in United Kingdom 2 nd most common reason in United States
2 Imaging determined by diagnostic considerations Gynecological and obstetrical causes Gastrointestinal and genitourinary causes Imaging? Selection of imaging ACR Appropriateness Criteria on Acute Pelvic Pain in the Reproductive Age Group Determined by clinically suspected differential diagnosis following careful evaluation Sonography the modality of choice for a suspected gynecologic or obstetric abnormality CT more useful for a GI or GU abnormality although MRI is favored over CT in the pregnant patient Sonography as the modality of choice for gynecologic etiologies Non-invasive Radiation free Cost effective Use of both sonographic techniques Transvaginal US (TVS )whenever possible (no contraindications) due to better resolution Sonography gives high resolution anatomic detail of uterus and adnexa! Transabdominal sonography provides more information when structures are beyond field of view of vaginal probe
3 Sonography with abdominal compression Sonography with abdominal compression Displaces bowel Brings structures closer to the transducer Identifies focal areas of tenderness Can use the sliding organ sign to separate structures sliding organ sign Role of Doppler Spectral and color or power Doppler imaging can be used to characterize vascularity to the: ovaries fallopian tubes uterus And narrow the differential considerations Pelvic pain and a normal pelvic sonogram Likely to have improvement or resolution of pain(66 of 86 patients) Further imaging is unlikely to yield positive results(1 of 13 studies) Pelvic pain and MRI Problem-solving tool for specific indications: If further characterization of a disorder is required If the patient s pain fails to resolve, or is more chronic in nature *Harris RD, Holtzman SR, Poppe AM. Clinical Outcome in female patients with pelvic pain and normal pelvic US findings. Radiology 2000; Aug; 216(2):440-3.
4 Approach to imaging of pelvic pain in the female patient Acute pelvic pain Chronic pelvic pain Dysmenorrhea Acute and chronic pelvic pain Definition Acute pain is intense pain characterized by sudden onset. Chronic pain is non-cyclic pelvic pain that lasts 6 months or longer which is severe enough to cause functional disability or the need for medical care. Cyclic pain Pain associated with the menstrual cycle Acute Pelvic Pain Dysmenorrhea Pregnancy status and acute pelvic pain Should ectopic pregnancy be under consideration? Is there concern for fetal exposure to ionizing radiation, making ultrasound the initial imaging modality of choice? Check a serum -hcg! Negative level essentially excludes the diagnosis of an intrauterine pregnancy and ectopic pregnancy. Obstetrical causes of acute pelvic pain in the first trimester Failed intrauterine pregnancy Ectopic pregnancy
5 Gynecologic causes of acute pelvic pain Most common causes Functional ovarian cysts Pelvic inflammatory disease Ovarian torsion Non-neoplastic cysts Simple or hemorrhagic Follicular cyst- abnormal follicular enlargement due to anovulation, commonly associated with hemorrhage with rapid resorption Corpus luteum- normal structure often enlarges with hemorrhage Corpus luteum cysts- associated with pregnancy with resolution usually by 14 weeks gestation Ovarian functional cyst Acute abdominal pain caused by : large size (> cm) hemorrhage rupture or leakage Theca lutein cysts- associated with trophoblastic disease, multiple gestations, usually large and numerous and may persist for weeks after withdrawal of stimulus Hemorrhagic functional cyst Sonographic appearance Hemorrhagic functional cyst Sonographic appearance With hemolysis and retraction of clot a reticular network of stranding Is demonstrated Fluid-fluid level between fluid components and congealed red blood cells Acute hemorrhage is hyperechoic and may be suggestive of a solid mass
6 Hemorrhagic functional cyst Sonographic appearance A diffuse pattern of low level echoes More commonly associated with an endometrioma Internal echoes and septations Hemorrhagic functional cyst Sonographic appearance Leakage of hemorrhagic fluid with associated peritoneal irritation is common Hemorrhagic functional cyst Evolution Hemorrhagic functional cyst Evolution 10 days later Hemorrhagic functional cyst Doppler evaluation Hemorrhagic functional cyst Doppler evaluation Peripheral color Doppler signal No central vascularity Low impedance arterial flow
7 Pelvic inflammatory disease Consists of inflammation of the endometrium, fallopian tubes, pelvic peritoneum and adjacent structures causing fever, leucocytosis and cervical motion tenderness. Ascending infection usually by N. Gonorrhea, Chlamydia and super infecting organisms from the vagina Manifested by tubo-ovarian complexes, peritonitis and abscess formation Usually bilateral but may be unilateral in patients with IUD s No simple diagnostic test Imaging diagnosis of PID Transvaginal sonography Salpingitis Can usually only detect complications of PID Early changes are often subtle although color Doppler may enhance our capabilities Difficulty visualizing tubal wall without fluid
8 Imaging diagnosis of PID Transvaginal sonography Salpingitis In the presence of fluid, common findings include: wall thickness > 5 mm incomplete septa thickening of endosalpingeal folds (cogwheel sign) Nonspecific findings: fluid in the endometrial cavity and /or cul-de-sac ovarian enlargement often with numerous small cysts ( polycystic ovary appearance) Salpingitis Tubo-ovarian complex Progression of disease with exudation of pus from the distal fallopian tube An inflammatory mass including the tube and adjacent ovary is formed Increased vascularity within fallopian tube wall The ovary is still visualized as a separate structure Incomplete septa Tubo-ovarian complex Tubo-ovarian abscess Imaging definition consists of a complete breakdown of architecture so that separate structures are no longer identified ovary Fallopian tube
9 Tubo-ovarian abscess Tubo-ovarian abscess Breakdown of architecture Incomplete septa Cogwheel sign Ovarian Torsion Diagnosis strongly considered with abrupt onset of severe unilateral pain Most commonly seen with associated nausea and vomiting Pain constant or intermittent (with partial or intermittent torsion) However: Symptoms may be variable The diagnosis of adnexal torsion has remained a clinical and imaging enigma Due to: Vague clinical presentation Abdominal pain being the only consistent symptom Common denominator: Enlarged abnormal appearing ovary Ovarian torsion Vascular supply to the ovary Commonly benign ovarian tumors or cysts (50-80%) may act as a fulcrum to potentiate torsion due to increased ovarian volume or weight. Ovarian hormone induction leading to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome and enlargement Hemorrhagic corpus luteum of pregnancy Hyper mobile adnexa 0varian artery & vein Uterine Artery & vein Pampiniform plexus Infundibulo-pelvic ligament Utero-ovarian ligament
10 Complete Ovarian Torsion Pathophysiology Can progress rapidly to occlusion of the arterial circulation. The organ may quickly become very dark black in color due to hemorrhage, necrosis and gangrenous changes Early intervention is key! Decreases the incidence of complications and improves ovarian salvage rates The use of pelvic sonography has enhanced our ability to determine when intervention is advisable Sonographic findings of ovarian torsion Enlarged ovary or ovarian complex Sonographic findings of ovarian torsion Irregular internal texture suggesting hemorrhage and edema Non-specific findings of ovarian torsion Peripherally placed follicles Ground glass pattern centrally consistent with edema Doppler evaluation of ovarian torsion Assumption: Color and spectral Doppler would prove to be an accurate tool for the evaluation of ovarian torsion. In actuality: Doppler findings vary depending on degree of torsion and its chronicity
11 Doppler evaluation of ovarian torsion Paratubal cyst as fulcrum for torsion Lack of arterial and venous signal should enable confident diagnosis False positive diagnoses may be obtained Depth of penetration greater than beam capabilities Improper Doppler or grayscale settings (ie. PRF setting) Doppler evaluation of ovarian torsion Ovarian color Doppler signal has been frequently reported in cases of surgically proven torsion! Presence of Doppler signal and ovarian torsion Patients with pathologically proven ovarian torsion 1/2 have been shown to have documented ovarian arterial Doppler signal only 1/3 have been shown to have documented ovarian venous and arterial signal *Shadinger, Andreotti and Kurian. Preoperative sonographic and clinical characteristics as predictors of ovarian torsion, J Ultrasound in Med 27: 7-13, Presence of arterial and venous Doppler signal The diagnosis of ovarian torsion An enlarged edematous ovary or ovarian complex is the most consistent finding Doppler findings vary likely depending on degree and chronicity. Lack of Doppler flow enables fairly confident diagnosis but ovarian arterial and venous Doppler signal has been reported in a third of surgically proven cases of ovarian torsion.
12 The Role of CT and MRI Sonography is initial exam of choice CT features Thickening of fallopian tube Target sign Computed tomography is being used more frequently Appendicitis most common reason! Deviation of uterus Infiltration of fat MRI ovarian torsion Is there a role at this time? MRI of ovarian torsion Role in the diagnosis of ovarian torsion has not been established Rha and colleagues* have shown similar diagnostic findings both on MR and CT *Rha SE et al. CT and MR imaging features of adnexal torsion. Radiographics 2002; 22(2) MRI of ovarian torsion T2 Images courtesy of Dr. Susanna Lee, Dept of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Mass. Marked ovarian enlargement Heterogeneous, hyperintense pattern due to edema and hemorrhage Peripherally displaced follicles Non-gynecologic causes of acute pelvic pain
13 Common gastrointestinal and genitourinary causes where imaging plays a role Most commonly appendicitis Diverticulitis Intestinal obstruction Inflammatory bowel disease Ureteral calculi Common gastrointestinal and genitourinary causes where sonography plays a role Appendicitis Ureteral calculi Inflammatory bowel disease? Appendicitis Most common GI cause of pelvic pain in women Diffuse or periumbilical pain that migrates to the right lower quadrant Appendicitis CT with contrast imaging modality of choice to confirm diagnosis in non-pregnant female (sensitivity 95%-100% and specificity 87%-98%) But US may be an effective substitute with a sensitivity (67%-100%) and specificity (83%- 96%) Appendicitis US with graded compression initial imaging test in pregnant females but often inconclusive due to large uterus MRI next appropriate imaging modality due to lack of ionizing radiation Sonographic features of appendicitis Blind ended thick walled, tubular, noncompressible, aperistaltic structure At least 3 mm single wall thickness Appendicolith highly specific Surrounding echogenic fat
14 Sonographic features of appendicitis Increased color Doppler vascularity within wall CT features of appendicitis Enlarged appendix (>6mm) with thickened enhancing wall (>2mm) Pericecal fat stranding MR features of appendicitis Similar to CT A negative oral contrast agent (Gastromark) may be used to demonstrate low signal in bowel and in a normal appendix Enlarged edematous appendix on T2 weighted MRI saggital image Urinary tract Ureteral calculi Ureteral calculi Costovertebral angle pain that radiates to groin rather than true pelvic pain Best detected by non-contrast CT (sensitivity of 96% and specificity of 93%- 98%) Alternative for evaluation of distal ureter is TAS or TVS, especially in pregnant females (sensitivities 34%-95%)
15 Inflammatory bowel disease Monitoring activity of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease with CE US. Valette, European radiology. 2001,11:10 pg Wilson S R, Burns P N Radiology 2010;257: by Radiological Society of North America Approach to Pelvic Pain Acute pain Suspect Ob or gyn cause Suspect non-gyn cause Chronic pelvic pain US + -hcg - -hcg US or MRI CT or US Chronic pelvic pain Disabling condition which may have more than one cause Often goes undiagnosed (up to 60%) Gyn, GI, GU and MSK abnormalities involved Common etiologies with imaging findings Endometriosis Adenomyosis Pelvic varices Malpositioned IUD s
16 Endometriosis Most common benign gynecological disorder Functional endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity and musculature Cysts (endometriomas), plaques, implants or nodules Endometriosis: Sites involved Ovary Uterine ligament Pouch of Douglas Pelvic peritoneum Abdominal scars Symptoms of endometriosis Dysmenorrhea Dyspareunia Abnormal bleeding Severity of pain may not correlate with the extent of disease! Role of ultrasound Historically the endometrioma is only form of disease readily diagnosed and confirmation obtained with time. Majority of implants and adhesions not detectable Sonographic features of endometriomas Single or multiple thick walled cystic masses with diffuse low level homogeneous echoes Hyperechoic foci adjacent to the wall are commonly demonstrated Internal vascularity only with decidualization due to pregnancy
17 The role of MRI as a problem solving tool High sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing deep and nodular endometriosis in addition to cystic type Plaque-like lesions may go undetected until laparoscopy Hemorrhagic cyst or endometrioma? Hemorrhagic cyst or endometrioma? MRI appearance Cystic endometriosis T1 increased signal or heterogeneous, or homogeneous increased signal Nodular endometriosis T1 intermediate signal T2 variable signal characteristics NRI and cystic endometriosis MRI and cystic endometriosis T1 fat sat T2 T1 T1 with fat sat T2 Images courtesy of Dr. Susanna Lee, Dept of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Mass.
18 MRI and cystic endometriosis MRI features Nodular endometriosis T1 fat sat T2 Hemorrhagic cyst Endometriomas Images courtesy of Dr. Susanna Lee, Dept of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Mass. Adenomyosis The Tender Uterus Adenomyosis Pelvic congestion A gynecological condition characterized by the presence of ectopic endometrial glands and hyperplastic stroma in the myometrium Commonly incorrectly labeled as fibroids Usually in the older reproductive age group Symptoms Uterine tenderness Dysmenorrhea Menorrhagia Abnormal myometrial echogenicity Hypoechoic areas corresponding to smooth muscle hyperplasia Echogenic heterotopic endometrial tissue
19 Abnormal Myometrial Echogenicity Myometrial cysts Heterogeneous Myometrial Echotecture Linear Striations Myometrial cysts corresponding to dilated glands or hemorrhagic foci Abnormal Myometrial Echogenicity Echogenic nodules Heterogeneous Myometrial Echotexture Ectopic glands Focal or diffuse Endometrial myometrial junction Poor definition Endometrium Pseudo-widening
20 Mass Effect Elliptical myometrial abnormality Uterine contour unchanged Adenomyosis and Fibroids Mass Effect with Leiomyomas with change in uterine contour Color Doppler Is not present peripherally as with leiomyomas May be present or increased throughout the area in question Optimized for low flow may be the most valuable technique for differentiation of the two processes. MR Imaging of Adenomyosis MRI as a problem solving tool in the diagnosis of adenomyosis Highly accurate with sensitivity and specificity of % and an overall accuracy of % Accuracies of sonography and MRI similar MR may give additional information when TVS is indeterminate
21 MR Imaging Signs Abnormal myometrial signal intensity low signal intensity (hyperplastic smooth muscle) areas of high signal intensity (heterotopic glands) Thickening of the junctional zone >11mm Linear striations of high signal intensity (associated with pseudowidening of the endometrium) Poor definition of the endometrial- myometrial junction Pelvic congestion syndrome Chronic pelvic pain that is associated with dilatation of pelvic veins (i.e. pelvic varices) and reduced venous return Dull chronic pain exacerbated by prolonged standing and relieved by lying down and elevating the legs Sonography and pelvic congestion Used in the initial assessment to rule out other pelvic etiologies with similar symptoms Shown to be of value in the diagnosis Pelvic congestion: sonographic criteria Presence of tortuous and dilated pelvic venous plexuses Dilated arcuate veins crossing the uterine myometrium Pelvic congestion: sonographic signs --47-year-old woman with pelvic congestion syndrome Dilatation of the left ovarian vein with reversed caudal flow Polycystic-like changes of the ovary Variable spectral Doppler waveforms in the veins during the Valsalva maneuver Park, S. J. et al. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004;182: Copyright 2007 by the American Roentgen Ray Society
22 Ovarian remnant syndrome Other causes of chronic pelvic pain Uncommon condition occurring after unilateral or bilateral oophorectomy, with or without a hysterectomy A fragment of ovarian tissue is left behind encased in adhesions and becomes functional and cystic Ovarian remnant syndrome Imaging findings Cystic or multiseptated ovarian masses Masses contain a rim of ovarian tissue Intrauterine contraceptive devices Easily visualized by transvaginal sonography due to their increased echogenicity and marked attenuation of the sound beam Abnormal position may cause chronic pain IUD visualization Satisfactory IUD location TVS with 3D reconstructions in the coronal plane can confirm the position of the entire IUD in the uterus When abnormally located, may show that part of the IUD is imbedded in the myometrium
23 Unsatisfactory IUD location Approach to Pelvic Pain Chronic pain US MRI Dysmenorrhea Cyclic pain Dysmenorrhea Cyclic pain during menstruation Primary dysmenorrhea if there is no underlying pelvic pathology and no direct imaging findings but imaging may be useful to exclude other causes Secondary dysmenorrhea due to underlying pelvic pathology
24 Secondary dysmenorrhea Common causes Endometriosis Adenomyosis Intrauterine devices Less common causes mullerian anomalies of the uterus or vagina with obstruction of menstrual flow intrauterine synechia fibroids pelvic congestion syndrome Primary dysmenorrhea No imaging findings to Pelvic Pain Cyclic Pain Secondary dysmenorrhea US MRI Approach to Pelvic Pain Acute pain Chronic pain Cyclic Pain Thank you! Suspect Ob or gyn cause Suspect non-gyn cause US Primary dysmenorrhea Secondary dysmenorrhea US + -hcg - -hcg MRI No imaging findings US US or MRI CT or US MRI
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: Cervix. Cervix. Nabothian cysts. cervical polyps. leiomyomas. Cervical stenosis
 Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
Gynecology Abnormal Pelvic Anatomy and Physiology: (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Cervix Nabothian cysts result from chronic cervicitis most
ProSono Copyright 2006. Ovarian Pathology
 Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Ovarian Pathology Physiologic cysts: Functional cysts Pathology: A simple cyst is a sac containing fluid or semi-solid material. Physiologic cysts are generic types of hormonally active cysts that result
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries. Simple Cystic Masses
 Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
Gynecology Abnormal Physiology of the ovaries (Effective February 2007) pediatric, reproductive, and perimenopausal/postmenopausal (24-28 %) Simple Cystic Masses ovary s function is to mature oocytes until
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation
 J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
J Clin Ultrasound 17:327-332, June 1989 Ovarian Torsion: Sonographic Evaluation Mark A. Helvie, MD,* and Terry M. Silver, MDI Abstract: The sonographic and clinical findings of 13 patients with surgically
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
BELIEVE MIDWIFERY SERVICES, LLC
 , LLC TITLE: ADENOMYOSIS EFFECTIVE DATE: May, 2012 POLICY STATEMENT Adenomyosis is a common benign gynecologic disorder that any certified nurse-midwife who provides gynecologic care is likely to see on
, LLC TITLE: ADENOMYOSIS EFFECTIVE DATE: May, 2012 POLICY STATEMENT Adenomyosis is a common benign gynecologic disorder that any certified nurse-midwife who provides gynecologic care is likely to see on
Objective. Indications for IUDs. IUDs 3 types. ParaGard IUD. Mirena IUD. Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Inert
 Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Sonographic Evaluation of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Anna S. Lev-Toaff, MD FACR Department of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Leading Edge in Diagnostic
Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization
 September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
September 2006 Pelvic Pain and In Vitro Fertilization Celeste Lopez, Harvard Medical School Year III September 18, 2006 Mrs. G 37yo with IVF oocyte retrieval the day before presentation to the ED Complains
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Benign Ovarian Masses
 Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Benign Ovarian Masses Anthony Hanbidge Learning Objectives Describe technique for assessment of ovarian masses Explain importance of transvaginal scan List the common benign masses Specify distinguishing
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine
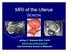 MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
MRI of the Uterus BENIGN Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D. FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine Normal Anatomy M Junctional JZ Zone EE Junctional Zone is the inner layer or the myometrium
良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介. Benign adnexal mass
 良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介 Benign adnexal mass Prepubertal Age Group Adolescent Age Group Reproductive Age Group Postmenopausal Age Group Prepubertal Age Group Differential Diagnosis Diagnosis and Management Prepubertal
良 性 附 屬 器 腫 瘤 簡 介 Benign adnexal mass Prepubertal Age Group Adolescent Age Group Reproductive Age Group Postmenopausal Age Group Prepubertal Age Group Differential Diagnosis Diagnosis and Management Prepubertal
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management
 Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Ovarian cysts Diagnosis and Management Mr P K Athanasias MRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist St Anthony s Hospital pathanasias@gmail.com Introduction ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ located in
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S.
 Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
Kate O Hanlan, M. D. F. A. C. O. G., F. A. C. S. Gynecologic Oncology, Surgery and Endoscopy 4370 Alpine Road Portola Valley, CA 94028-7523 Phone: (650)-851-6669 FAX: (650) 851-9747 Regarding Ovarian Cancer,
K Raja/N Varol FPA 2013. FPA Sydney August 31 2013
 FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
FPA Sydney August 31 2013 Ms wilson 32 year old woman Presents with worsening, heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding and pain for 6 months. Ms Wilson What is the differential diagnosis What are the
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts
 Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
Image Presentation Sonographic Spectrum of Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cysts Kiran A. Jain, MD Objective. To present the spectrum of sonographic findings associated with hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Methods. Experience
SUBSEROSAL FIBROIDS TREATMENT
 INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
INTRODUCTION Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are the most common pelvic mass found in women. Fibroids are benign tumors that arise from the uterine muscular tissue (myometrium). They occur
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound
 Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
Indications/Goals: 1 st Trimester OB Ultrasound Geoffrey E. Hayden, MD Director of Emergency Ultrasonography Vanderbilt Emergency Medicine Primary objective is to identify an intrauterine pregnancy Secondary
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
All you need to know about Endometriosis. Nordica Fertility Centre, Lagos, Asaba, Abuja
 All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
All you need to know about Endometriosis October, 2015 About The Author Nordica Lagos Fertility Centre is one of Nigeria's leading centres for world class Assisted Reproductive Services, with comfort centres
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Medical criteria for IUCD s Based on the WHO MEC (2004- Annexure 3) system a woman s eligibility for IUCD insertion falls in 4 categories. These categ
 CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
CLIENT ASSESSMENT Ensure that the woman is not pregnant Determine the length and direction of uterus. Ensure that she does not have gonorrhea and chlamydia, and is not a high risk case of STI s Identify
Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy. Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III
 Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III First Trimester Sonography Localization of Gestational Sac Intrauterine vs. ectopic Identification of abnormalities Embryonic demise
Ultrasound in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Elizabeth Lipson, HMS III First Trimester Sonography Localization of Gestational Sac Intrauterine vs. ectopic Identification of abnormalities Embryonic demise
Ultrasonography of adnexal causes of acute pelvic pain in pre-menopausal non-pregnant women
 Ultrasonography of adnexal causes of acute pelvic pain in pre-menopausal non-pregnant women Carolyn S. Dupuis, Young H. Kim Department of Radiology, UMass Memorial Medical Center, University of Massachusetts
Ultrasonography of adnexal causes of acute pelvic pain in pre-menopausal non-pregnant women Carolyn S. Dupuis, Young H. Kim Department of Radiology, UMass Memorial Medical Center, University of Massachusetts
POSTMENOPAUSAL ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO
 POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
POSTMENOPAUSAL OVARIAN CYSTS:HOW TO ASSESS AND WHAT TO DO Steven R. Goldstein, MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Director of Gynecologic Ultrasound Co-Director, Bone Densitometry New York University
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
 Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Semester 1 Orientation - 101 This class is an introduction to sonography which includes a basic anatomy review, introduction to sonographic scanning techniques and physical principles. This curriculum
Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and Adjacent Myometrium
 Technical dvance Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and djacent Myometrium Preliminary Observations Rochelle F. ndreotti, MD, rthur C. Fleischer, MD, Lawrence E. Mason, Jr, MD Objective. y
Technical dvance Three-Dimensional Sonography of the Endometrium and djacent Myometrium Preliminary Observations Rochelle F. ndreotti, MD, rthur C. Fleischer, MD, Lawrence E. Mason, Jr, MD Objective. y
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion with Color Doppler Sonography: Depiction of Twisted Vascular Pedicle
 Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion with Color Doppler Sonography: Depiction of Twisted Vascular Pedicle Eun Ju Lee, MD, Hyuck Chan Kwon, MD, Hee Jae Joo, MD, Jung Ho Suh, MD, Arthur C. Fleischer, MD The purpose
Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion with Color Doppler Sonography: Depiction of Twisted Vascular Pedicle Eun Ju Lee, MD, Hyuck Chan Kwon, MD, Hee Jae Joo, MD, Jung Ho Suh, MD, Arthur C. Fleischer, MD The purpose
Endometriosis: An Overview
 Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis: An Overview www.bcwomens.ca Welcome to the BC Women s Centre for Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis. This handout will give you some basic information about endometriosis. It will also explain
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group
 Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Endometriosis Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women and Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients
 Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Women s Health Laparoscopy Information for patients This leaflet is for women who have been advised to have a laparoscopy. It outlines the common reasons doctors recommend this operation, what will happen
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM
 DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM NEPHRITIS, NEPHROTIC SYNDROME ANS NEPHROSIS (580 589.9) 580 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.0 WITH LESION OF PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.4 WITH LESION OF RAPIDLY
DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM NEPHRITIS, NEPHROTIC SYNDROME ANS NEPHROSIS (580 589.9) 580 ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.0 WITH LESION OF PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 580.4 WITH LESION OF RAPIDLY
Variations in Appearance of Endometriomas
 CME rticle Variations in ppearance of Endometriomas Elizabeth sch,, Deborah Levine, MD Objective. ecause of the range of patient ages with endometriosis, the persistence of endometriomas, and the degradation
CME rticle Variations in ppearance of Endometriomas Elizabeth sch,, Deborah Levine, MD Objective. ecause of the range of patient ages with endometriosis, the persistence of endometriomas, and the degradation
The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
Uterus myomatosus. 10-May-15. Clinical presentation. Incidence. Causes? 3 out of 4 women. Growth rate vary. Most common solid pelvic tumor in women
 Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Uterus myomatosus A.J. Henriquez March 14, 2015 Uterus myomatosus Definition, incidence, clinical presentation and diagnosis. New FIGO classification for uterine leiomyomas Brief description on treatment
Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering
 Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Image Presentation Three-Dimensional Inversion Rendering New Sonographic Technique and Its Use in Gynecology Ilan E. Timor-Tritsch, MD, RDMS, na Monteagudo, MD, RDMS, Tanya Tsymbal,, RDMS, Irina Strok,
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
10 Common Questions Answers SBO
 10 Common Questions Answers SBO 1 What is Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO)? After food passes through our stomach, it soon arrives in our intestines, starting at the small bowel. This tube-like organ meanders
10 Common Questions Answers SBO 1 What is Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO)? After food passes through our stomach, it soon arrives in our intestines, starting at the small bowel. This tube-like organ meanders
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog
 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Catalog 2 School of Diagnostic Medical Sonography Course Schedule Our program provides a broad base of education and performance- based clinical experience
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding)
 Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Heavy periods (menstrual bleeding) This information sheet has been given to you to help answer some of the questions you may have about heavy periods and the treatments that are available. This leaflet
Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis
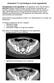 Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis Pathophysiology of acute appendicitis. Acute appendicitis occurs when the lumen is obstructed, leading to fluid accumulation, luminal distention, inflammation
Abdominal CT scan findings in Acute Appendicitis Pathophysiology of acute appendicitis. Acute appendicitis occurs when the lumen is obstructed, leading to fluid accumulation, luminal distention, inflammation
Ectopic Pregnancy. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL
 RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
RBH GUIDELINES FOR ULTRASOUND REFERRAL Introduction Ultrasound can be very useful as a first line investigation; it is typically non-invasive and does not involve ionising radiation. However, a significant
The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology
 The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology Bill Smith Clinical Diagnostics Services, London, UK Introduction 3D volumetric ultrasound is shown to be of
The Practical Application and Clinical Use of Modern 3D Ultrasound Technology in Gynaecology Bill Smith Clinical Diagnostics Services, London, UK Introduction 3D volumetric ultrasound is shown to be of
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Lippes Loop intrauterine device left in the uterus for 50 years. Case report
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Lippes Loop intrauterine device left in the uterus for 50 years Case report Background.The first Lippes Loop intrauterine device was distributed in 1962. It was a
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Lippes Loop intrauterine device left in the uterus for 50 years Case report Background.The first Lippes Loop intrauterine device was distributed in 1962. It was a
The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary
 September 2000 The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary Aradhana M. Venkatesan,, Harvard Medical School Year- IV MD 1 Menu of Tests Trans-abdominal pelvic ultrasound Trans-vaginal pelvic ultrasound Pelvic
September 2000 The Radiologic Evaluation of the Ovary Aradhana M. Venkatesan,, Harvard Medical School Year- IV MD 1 Menu of Tests Trans-abdominal pelvic ultrasound Trans-vaginal pelvic ultrasound Pelvic
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A.
 Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Specialists In Reproductive Medicine & Surgery, P.A. Craig R. Sweet, M.D. www.dreamababy.com Fertility@DreamABaby.com Excellence, Experience & Ethics Endometriosis Awareness Week/Month Common Questions
Abdominal Pain in a Pregnant Patient
 January 2007 Abdominal Pain in a Pregnant Patient Megan Browning, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 HPI Ms.O is a 21yo pregnant female (23+6 weeks gestation) Woke with 5/10 crampy abdominal pain followed
January 2007 Abdominal Pain in a Pregnant Patient Megan Browning, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 HPI Ms.O is a 21yo pregnant female (23+6 weeks gestation) Woke with 5/10 crampy abdominal pain followed
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer
 Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Media Contact: Gerri Gomez Howard Cell: 303-748-3933 gerri@gomezhowardgroup.com Frequently Asked Questions About Ovarian Cancer What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in tissues
Abdominal Wall Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of Literature
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 13, No. 4, October 2012 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol13/oct2012/91001.htm Abdominal Wall Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of Literature Jafar Malmir1,
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 13, No. 4, October 2012 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol13/oct2012/91001.htm Abdominal Wall Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of Literature Jafar Malmir1,
Use of Ultrasound in the Provision of Abortion. Juan E. Vargas, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology and Radiology, UCSF
 Use of Ultrasound in the Provision of Abortion Juan E. Vargas, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology and Radiology, UCSF Overview Uses and indications of ultrasound in the provision
Use of Ultrasound in the Provision of Abortion Juan E. Vargas, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology and Radiology, UCSF Overview Uses and indications of ultrasound in the provision
Once a woman has had a hysterectomy, she will no longer have menstrual periods and cannot have a child. She no longer needs to use contraception.
 Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
Hysterectomy Summary Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the womb (uterus), with or without the cervix. Hysterectomy is used to treat a number of conditions, including heavy or painful periods, fibroids
The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate.
 The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate. The procedure is well tolerated. No consensus on effectiveness of HSC in improving prognosis of subfertile women. systematic
The position of hysteroscopy in current fertility practice is under debate. The procedure is well tolerated. No consensus on effectiveness of HSC in improving prognosis of subfertile women. systematic
What could endometriosis mean for me?
 Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA
 Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
Pelvic Floor Relaxation Beverly E Hashimoto, M.D. Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA Disclosures Beverly Hashimoto: GE Medical Systems: research support and consultant (all fees given to Virginia
MHRI IUD Protocol. Migraine with aura Current DVT or PE History of or current breast cancer Active viral hepatitis Severe cirrhosis or liver tumors
 Table of Contents A. Indications B. Contraindications C. Prior to Insertion D. Insertion E. Follow-Up Visit F. Removal G. Re-Insertion H. Complications/Side Effects I. Appendices MHRI IUD Protocol A. Indications
Table of Contents A. Indications B. Contraindications C. Prior to Insertion D. Insertion E. Follow-Up Visit F. Removal G. Re-Insertion H. Complications/Side Effects I. Appendices MHRI IUD Protocol A. Indications
Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East. Oxford Clinic
 Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East Oxford Clinic Objectives of this talk To understand risk of malignancy and thus not fear it Practical advice for follow up of asymptomatic cysts Practical advice
Ovarian Cysts Made Simple Michael East Oxford Clinic Objectives of this talk To understand risk of malignancy and thus not fear it Practical advice for follow up of asymptomatic cysts Practical advice
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer?
 Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN. Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY.
 Ovarian Cancer 2 OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN by Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY Ogden, Utah Instructor s Name Date Ovarian Cancer 2 Background
Ovarian Cancer 2 OVARIAN CANCER IS A MAJOR CAUSE OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN WOMEN by Name of Student HTHSCI 1110 WEBER STATE UNIVERSITY Ogden, Utah Instructor s Name Date Ovarian Cancer 2 Background
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension
 Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Cornual ruptured pregnancy with placenta increta CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE
 142 CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE Agarwal NR 1, Rani A 1 *, Batra S 1 1. Department of Obststetrics and Gynaecology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banares Hindu Univarsity.
142 CORNUAL RUPTURED PREGNANCY WITH PLACENTA INCRETA A RARE CASE Agarwal NR 1, Rani A 1 *, Batra S 1 1. Department of Obststetrics and Gynaecology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banares Hindu Univarsity.
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids?
 da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
da Vinci Myomectomy Changing the Experience of Surgery Are you a candidate for the latest treatment option for uterine fibroids? Your doctor may be able to offer you a new, minimally invasive surgical
WOOD COUNTY SCHOOL OF PRACTICAL NURSING. Medical/Surgical Nursing: Reproductive
 WOOD COUNTY SCHOOL OF PRACTICAL NURSING Medical/Surgical Nursing: Reproductive Time: 19 Hours Theory; 1 Hour Pharmacology IV, (1 Diet Therapy - Integrated.) Placement: Nursing IV. Instructor: Toni Tennant,
WOOD COUNTY SCHOOL OF PRACTICAL NURSING Medical/Surgical Nursing: Reproductive Time: 19 Hours Theory; 1 Hour Pharmacology IV, (1 Diet Therapy - Integrated.) Placement: Nursing IV. Instructor: Toni Tennant,
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
The following chapter is called The Role of Endoscopy, Laparoscopy, and Hysteroscopy in Infertility.
 Welcome to Chapter 14. The following chapter is called The Role of Endoscopy, Laparoscopy, and Hysteroscopy in Infertility. The authors are Dr. Jose Remohi and Dr. Jaime Ferro. 1 There are several tools
Welcome to Chapter 14. The following chapter is called The Role of Endoscopy, Laparoscopy, and Hysteroscopy in Infertility. The authors are Dr. Jose Remohi and Dr. Jaime Ferro. 1 There are several tools
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps
 Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
Treating heavy menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids or polyps With today s medical advances the outlook for successful treatment of fibroids and polyps has never been better. You don t have to live with
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Hysterectomy. The time to take care of yourself
 Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
Hysterectomy The time to take care of yourself The time to take care of yourself Women spend a lot of time taking care of others spouses, children, parents. We often overlook our own needs. But when our
2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide
 2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide Effective January 1, 2014 Medicare National Average Rates and Allowables (Not Adjusted For Geography) CPT * HCPCS Code 58150 58152 58180 58200 58210
2014 OB/GYN Surgery Medicare Reimbursement Coding Guide Effective January 1, 2014 Medicare National Average Rates and Allowables (Not Adjusted For Geography) CPT * HCPCS Code 58150 58152 58180 58200 58210
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 About this information This leaflet is for you if you have a cyst on one or both ovaries and are considering surgery.
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
Ultrasound and Hysteroscopy in Infertility
 Ultrasound and Hysteroscopy in Infertility James M. Shwayder, M.D., J.D. Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, Mississippi Ultrasound
Ultrasound and Hysteroscopy in Infertility James M. Shwayder, M.D., J.D. Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, Mississippi Ultrasound
OB/GYN. Clerkship Learning Objectives. Office for Clinical Affairs Department of OB/GYN (515) 271-1629 (515) 271-1421 FAX (515) 271-1727
 OB/GYN Clerkship Learning Objectives Rebecca Shaw, MD, FACOG Office for Clinical Affairs Department of OB/GYN (515) 271-1629 (515) 271-1421 FAX (515) 271-1727 General Description Required Rotation This
OB/GYN Clerkship Learning Objectives Rebecca Shaw, MD, FACOG Office for Clinical Affairs Department of OB/GYN (515) 271-1629 (515) 271-1421 FAX (515) 271-1727 General Description Required Rotation This

 Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE  Additional information >>> HERE
Additional information >>> HERE