Chapter 16. Human Circulatory System
|
|
|
- Theodora Cain
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 16 Human Circulatory System
2 Transport Involves the absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
3 Human Circulatory System Closed circulatory system- blood is always in blood vessels. Heart which pumps blood. Network of blood vessels which carry blood to and from all cells of the body.
4 Human Circulatory System
5 (I) Three Kinds of Blood Vessels 1. Arteries 2. Veins 3. Capillaries
6 Arteries Thick-walled Smooth muscle Transports blood away from heart Carries oxygenated blood (high levels of O2) Arteries divide into smaller vessels known as arterioles
7 Arteries Thick-walled Smooth muscle Transports blood away from heart Carries oxygenated blood (high levels of O2) Arteries divide into smaller vessels known as arterioles
8 Thin-walled Veins Transports blood to the heart Carries deoxygenated blood Contain valves which help prevent the backflow of blood Divide into smaller vessels known as venules
9 Very thin-walled (one cell thick) Site for the exchange of materials between the blood and body tissue (cells) Arterioles and venules are connected by capillaries Capillaries
10 Very thin-walled (one cell thick) Site for the exchange of materials between the blood and body tissue (cells) Arterioles and venules are connected by capillaries Capillaries
11 Very thin-walled (one cell thick) Site for the exchange of materials between the blood and body tissue (cells) Arterioles and venules are connected by capillaries Capillaries
12 (II) Heart Composed of cardiac muscle It is a 4-chambered pump composed of 2 atria and 2 ventricles The ventricles have thicker walls than the atria The heart pumps blood through the arteries creating a blood pressure
13 Human Heart
14 Human Heart
15 Superior Vena Cava Brings deoxygenated blood from the upper portion of the body and into the right atrium
16 Inferior Vena Cava Brings deoxygenated blood from the lower portion of the body and into the right atrium
17 Right Atrium Receives blood from the inferior and superior vena cava and pumps it into the right atrium
18 Valves A-V valve- separates the atrium from the ventricle Semi-lunar valve- separates ventricles from the arteries
19 Right Ventricle Receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it into the pulmonary artery
20 Pulmonary Artery Receives blood from the right ventricle and transports it to the lungs
21 Pulmonary Vein Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and transports it to the left atrium
22 Left Atrium Receives blood from the pulmonary vein and pumps it into the left ventricle
23 Left Ventricle Receives blood from the left atrium and pumps it into the aorta
24 Aorta Major artery of the body Receives blood from the left ventricle and transports it to the rest of the body
25 Septum Separates the heart into a left side and a right side Left side contains oxygenated blood Right side contains deoxygenated blood
26 (III) Types of Circulation
27 Sphygmomanometer Instrument used to measure the pressure of the blood in the artery of the arm Ex: 120/ = systolic pressure 80 = diastolic pressure
28 (IV) Heartbeat Cycle Diastole (relaxation)- is the period when the ventricles are filling with blood. The A-V valve is open and blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle Systole (contraction)- is the period when the ventricle pumps blood out of the heart. A-V valve closes and the semi-lunar valve opens
29 1. Pulmonary Circulation The pathway from which blood flows from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart ( R.V. Pulm. Artery Lungs Pulm. Vein L.A.)
30 2. Systemic Circulation The pathway that carries blood from the heart to all parts of the body with the exception of the lungs
31 3. Coronary Circulation Muscle tissue of the heart is supplied with blood through a system of coronary blood vessels Coronary arteries- supply oxygenated blood to the muscle tissue of the heart
32 Disorders of the Circulatory System
33 Cardiovascular Diseases Are diseases of the heart and blood vessels
34 High Blood Pressure Increased pressure in the arteries due to stress, diet, cigarette smoking, and aging Can lead to damage of the lining of arteries and weakening of the heart muscle
35 Heart Attacks Two Types 1. Coronary Thrombosis 2. Angina Pectoris
36 Coronary Thrombosis Blockage of the coronary artery resulting in oxygen deficiency in the heart muscle
37 Coronary Thrombosis
38 Angina Pectoris Narrowing of the coronary artery causing an inadequate supply of oxygen to the heart muscle
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
 Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
Overview of the Cardiovascular System 2 vascular (blood vessel) loops: Pulmonary circulation: from heart to lungs and back) Systemic circulation: from heart to other organs and back Flow through systemic
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes.
 Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Note: The left and right sides of the heart must pump exactly the same volume of blood when averaged over a period of time
 page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
page 1 HEART AS A PUMP A. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1. Two pumps, arranged in series a. right heart: receives blood from the systemic circulation (via the great veins and vena cava) and pumps blood
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
CHAPTER 6: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM and the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Most of the cells in the human body are not in direct contact with the external environment, so rely on the circulatory
Circulatory system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 3.2 Organisation and the Vascular Structures 3.2.2 Organisational complexity of the human - Human Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems 3.2.3.H Blood Cells extended study 3.2.4.H Heartbeat control Objectives
Name: 3.2 Organisation and the Vascular Structures 3.2.2 Organisational complexity of the human - Human Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems 3.2.3.H Blood Cells extended study 3.2.4.H Heartbeat control Objectives
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Comparing Organs BIOLOGY SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS
 BIOLOGY SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS Comparing Organs Grade-Level Expectations The exercises in these instructional tasks address content related to the following science grade-level expectation: Contents
BIOLOGY SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS Comparing Organs Grade-Level Expectations The exercises in these instructional tasks address content related to the following science grade-level expectation: Contents
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
Cardiology. Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart.
 Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart. Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart Page 1 CONTENT Introduction Page 3 How to use the ECG Self Learning package.page
Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart. Module 1: Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart Page 1 CONTENT Introduction Page 3 How to use the ECG Self Learning package.page
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
2.2.1 Pressure and flow rate along a pipe: a few fundamental concepts
 1.1 INTRODUCTION Single-cell organisms live in direct contact with the environment from where they derive nutrients and into where they dispose of their waste. For living systems containing multiple cells,
1.1 INTRODUCTION Single-cell organisms live in direct contact with the environment from where they derive nutrients and into where they dispose of their waste. For living systems containing multiple cells,
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
the Cardiovascular System
 5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
5 Chapter Anatomy Jones and & Physiology Bartlett Learning, LLC of the Cardiovascular System OUTLINE Introduction The Heart Structures of the Heart Conduction System Functions of the Heart The Blood Vessels
THE HEART AND CIRCULATION HENRY S. CABIN, M.D.
 CHAPTER 1 THE HEART AND CIRCULATION HENRY S. CABIN, M.D. INTRODUCTION The cardiovascular system is an elaborate network that performs two major tasks: It delivers oxygen and nutrients to body organs and
CHAPTER 1 THE HEART AND CIRCULATION HENRY S. CABIN, M.D. INTRODUCTION The cardiovascular system is an elaborate network that performs two major tasks: It delivers oxygen and nutrients to body organs and
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Circulation Stations
 Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Paper 1 Answer all questions. Each question is followed by four options, A, B, C and D. For each question, choose one answer only
 hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
hapter 19 lood irculation and Transport Paper 1 nswer all questions. Each question is followed by four options,,, and. For each question, choose one answer only 1. Type of blood cell P Q R Function Protects
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Exam #1 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question answered correctly is worth one point, and the
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Normal & Abnormal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
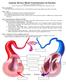 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Normal Intracardiac Pressures. Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network
 Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
Normal Intracardiac Pressures Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network Principle Pressures recorded from catheter tip Electrical transducer - wheatstone bridge mechanical to electrical waveform display
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
How To Treat A Single Ventricle And Fontan
 COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
COACH Columbus Ohio Adult Congenital Heart Disease Program The Heart Center at Nationwide Children s Hospital & The Ohio State University Single Ventricle Defects Normal Heart Structure The heart normally
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Using Blood-Thinning (Anticoagulant) Drugs
 A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
A Patient s Guide to Primary and Secondary Prevention of PATIENT EDUCATION GUIDE What Is Cardiovascular Disease? Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that covers any disease of the heart and circulatory
Heart Diseases and their Complications
 Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness
 Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
Cardiovascular System
 Topics to Review Diffusion Skeletal muscle fiber (cell) anatomy Membrane potential and action potentials Action potential propagation Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle skeletal muscle
Topics to Review Diffusion Skeletal muscle fiber (cell) anatomy Membrane potential and action potentials Action potential propagation Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle skeletal muscle
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems
 Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
S.M.A.R.T.box. Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP. Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers
 CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
Cardiovascular Biomechanics
 Cardiovascular Biomechanics Instructor Robin Shandas, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Pediatric Cardiology and Mechanical Engineering Robin.shandas@colorado.edu (303) 837-2586 (MWF) / (303) 492-0553 (T,Th)
Cardiovascular Biomechanics Instructor Robin Shandas, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Pediatric Cardiology and Mechanical Engineering Robin.shandas@colorado.edu (303) 837-2586 (MWF) / (303) 492-0553 (T,Th)
CardiacAdvantage. Catheterization. Patient Guide. Cardiac
 Cardiac Catheterization Patient Guide CardiacAdvantage CardiacAdvantage Cardiac Catheterization For more information, please visit: stjoeshealth.org/cardiovascular Understanding Your Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac Catheterization Patient Guide CardiacAdvantage CardiacAdvantage Cardiac Catheterization For more information, please visit: stjoeshealth.org/cardiovascular Understanding Your Cardiac Catheterization
How To Treat Heart Valve Disease
 The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville The Valve Clinic at Baptist Health Madisonville Welcome to the Baptist Health Madisonville Valve Clinic at the Jack L. Hamman Heart & Vascular Center. We
Understanding Varicose Veins
 Understanding Varicose Veins Professor Bruce Campbell Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as a
Understanding Varicose Veins Professor Bruce Campbell Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as a
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect
 Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
Understanding your child s heart Atrial septal defect About this factsheet This factsheet is for the parents of babies and children who have an atrial septal defect (ASD). It explains, what an atrial septal
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter
 Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Atrial Fibrillation: The heart of the matter This booklet has been written especially for people with atrial fibrillation (AF), a heart condition often described as an irregular heartbeat (also known
Cardiac Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
Cardiac Rehabilitation Introduction Experiencing heart disease should be the beginning of a new, healthier lifestyle. Cardiac rehabilitation helps you in two ways. First, it helps your heart recover through
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Have a Heart: Cardiology Coding. Agenda
 Have a Heart: Cardiology Coding AAPC Regional Conference October 25-27, 2012 Chicago Presented by: Betty A Hovey, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CPC-H, CPCD Director, ICD-10 Development and Training AAPC Agenda Anatomy
Have a Heart: Cardiology Coding AAPC Regional Conference October 25-27, 2012 Chicago Presented by: Betty A Hovey, CPC, CPMA, CPC-I, CPC-H, CPCD Director, ICD-10 Development and Training AAPC Agenda Anatomy
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
LECTURE 3: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - BLOOD VESSELS
 LECTURE 3: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - BLOOD VESSELS INTRODUCTION To fully grasp the circulatory system and the processes that may progress to heart disease, it is vital that one comprehend the functioning
LECTURE 3: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - BLOOD VESSELS INTRODUCTION To fully grasp the circulatory system and the processes that may progress to heart disease, it is vital that one comprehend the functioning
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly email worldanaesthesia@mac.com
 INTRODUCTION TO CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 125 16 TH MARCH 2009 Toby Elkington, Specialist Registrar Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Salford Royal NHS
INTRODUCTION TO CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 125 16 TH MARCH 2009 Toby Elkington, Specialist Registrar Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Salford Royal NHS
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Heart information. Children with heart problems
 Heart information Children with heart problems Contents 2 Your heart 2 Structure 3 How your heart pumps blood 4 Development 5 What are heart problems 5 Congenital heart defects 6 Heart murmurs 6 Congestive
Heart information Children with heart problems Contents 2 Your heart 2 Structure 3 How your heart pumps blood 4 Development 5 What are heart problems 5 Congenital heart defects 6 Heart murmurs 6 Congestive
Questions FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008
 FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
FOETAL CIRCULATION ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 91 18 TH MAY 2008 Dr. S. Mathieu, Specialist Registrar in Anaesthesia Dr. D. J. Dalgleish, Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch
Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques
 Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Taking patients blood pressure during dental examinations is critical to their overall
Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Taking patients blood pressure during dental examinations is critical to their overall
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
CHAPTER 15: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. 2. Describe the location, size, and orientation of the human heart.
 CHAPTER 15: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs that compose the cardiovascular system and discuss the general functions of this system. 2. Describe the location, size, and orientation
CHAPTER 15: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs that compose the cardiovascular system and discuss the general functions of this system. 2. Describe the location, size, and orientation
Every cell in the animal body must acquire the energy
 52 Circulation Concept Outline 52.1 The circulatory systems of animals may be open or closed. Open and Closed Circulatory Systems. All vertebrates have a closed circulation, while many invertebrate animals
52 Circulation Concept Outline 52.1 The circulatory systems of animals may be open or closed. Open and Closed Circulatory Systems. All vertebrates have a closed circulation, while many invertebrate animals
What Will You Learn From This Module?
 What Is This Module About? Have you ever cut yourself accidentally? What came out of the wound? The fluid that came out of your wound is blood. Blood is red and quite viscous (thick). Blood is called the
What Is This Module About? Have you ever cut yourself accidentally? What came out of the wound? The fluid that came out of your wound is blood. Blood is red and quite viscous (thick). Blood is called the
Cardiac Masses and Tumors
 Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
Cardiac Masses and Tumors Question: What is the diagnosis? A. Aortic valve myxoma B. Papillary fibroelastoma C. Vegetation from Infective endocarditis D. Thrombus in transit E. None of the above Answer:
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
High Blood Pressure (Essential Hypertension)
 Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Sacramento Heart & Vascular Medical Associates February 18, 2012 500 University Ave. Sacramento, CA 95825 Page 1 916-830-2000 Fax: 916-830-2001 What is essential hypertension? Blood pressure is the force
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects
 Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
Facts about Congenital Heart Defects Joseph A. Sweatlock, Ph.D., DABT New Jersey Department of Health Early Identification & Monitoring Program Congenital heart defects are conditions that are present
INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE
 Hughes Undergraduate Biological Science Education Initiative HHMI INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE Learn how to measure heart rate and blood pressure. Learn the normal values for heart rate
Hughes Undergraduate Biological Science Education Initiative HHMI INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE Learn how to measure heart rate and blood pressure. Learn the normal values for heart rate
The Pumping Heart LESSON
 14 LESSON The Pumping Heart WOOD RIVER GALLERY/PNI INTRODUCTION You now know the ingredients that cells need to release energy oxygen and nutrients. How do these essential ingredients get to the cells?
14 LESSON The Pumping Heart WOOD RIVER GALLERY/PNI INTRODUCTION You now know the ingredients that cells need to release energy oxygen and nutrients. How do these essential ingredients get to the cells?
