Parasitology Exam (wet mount images) Answers will be found at the end.
|
|
|
- Gervase Boone
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
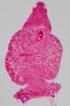
1 Parasitology Exam (wet mount images) Answers will be found at the end. ***Reminder: Slides and examination questions are copyrighted and cannot be copied for publication. 1. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Chilomastix mesnili trophozoites, cysts B. Pentatrichomonas hominis trophozoites C. Giardia lamblia (duodenalis, intestinalis) trophozoites, cysts D. Trichomonas vaginalis trophozoites 2. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Entamoeba coli cysts and trophozoite B. Entamoeba hartmanni cysts and trophozoite C. Iodamoeba bütschlii cysts and trophozoite D. Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar cysts and trophozoite 1 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
2 3. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Entamoeba coli cysts and precyst B. Entamoeba hartmanni cysts and precyst C. Iodamoeba bütschlii cysts and precyst D. Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar cysts and precyst 4. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Pentatrichomonas hominis cysts B. Dientamoeba fragilis cysts C. Chilomastix mesnili cysts D. Retortamonas intestinalis cysts 5. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry 2 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
3 A. Iodamoeba bütschlii cysts B. Entamoeba hartmanni cysts C. Dientamoeba fragilis cysts D. Entamoeba polecki cysts 6. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Algae B. Plant spikes C. Charcot-Leyden crystals D. String artifacts 7. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Hookworm eggs B. Ascaris lumbricoides fertilized eggs C. Trichostrongylus spp. eggs D. Diphyllobothrium latum eggs 8. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry 3 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
4 A. Trichuris trichiura eggs B. Ascaris lumbricoides fertilized eggs C. Ascaris lumbricoides unfertilized eggs D. Hookworm eggs 9. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Taenia spp. eggs B. Hymenolepis nana eggs C. Artifacts, probably pollen D. Hymenolepis diminuta eggs 10. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Ascaris lumbricoides unfertilized eggs 4 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
5 B. Trichuris trichiura eggs C. Hookworm unfertilized eggs D. Ascaris lumbricoides fertilized eggs 11. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Taenia spp. eggs B. Taenia saginata eggs C. Taenia solium eggs D. None of the above 12. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Clonorchis sinensis eggs B. Ascaris lumbricoides decorticate eggs C. Paragonimus spp. eggs D. Diphyllobothrium latum eggs 13. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry 5 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
6 A. Paragonimus spp. eggs B. Trichuris trichiura eggs C. Pollen grains D. Baylisascaris procyonis eggs 14. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry These eggs measure 140 microns. A. Fasciolopsis buski eggs B. Diphyllobothrium latum eggs C. Paragonimus spp. eggs D. Clonorchis sinensis eggs 15. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry 6 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
7 A. Diphyllobothrium latum eggs B. Fasciola hepatica eggs C. Paragonimus spp. eggs D. Clonorchis sinensis eggs 16. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Paragonimus spp. eggs B. Sarcocystis oocysts C. Isospora belli oocysts D. Clonorchis (Opisthorchis) sinensis eggs 17. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Taenia spp. eggs B. Hymenolepis nana eggs C. Hymenolepis diminuta eggs D. Diphyllobothrium latum eggs 18. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry 7 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
8 A. Schistosoma haematobium eggs B. Schistosoma mansoni eggs C. Schistosoma japonicum eggs D. Schistosoma mekongi eggs 19. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Schistosoma japonicum eggs B. Schistosoma haematobium eggs C. Decorticate Ascaris lumbricoides eggs D. Taenia solium eggs 20. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Taenia spp. eggs B. Taenia solium eggs C. Schistosoma japonicum eggs 8 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
9 D. Hymenolepis diminuta eggs 21. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Red blood cells (RBCs) B. Giardia lamblia cysts C. Human tissue and blood cells D. Plant artifacts 22. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites B. Entamoeba coli cysts C. Entamoeba hartmanni cysts D. Endolimax nana trophozoite and cysts 23. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry power, 400x) (the image on the left is seen at 100x/low power): 9 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
10 A. Plant spirals B. Hookworm larvae C. Strongyloides stercoralis rhabditiform larvae D. Strongyloides stercoralis filariform larvae 24. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Balantidium coli B. Fasciola hepatica eggs C. Entamoeba coli D. Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar 25. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Strongyloides stercoralis larvae B. Hookworm larvae 10 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
11 C. Root hairs D. Ascaris lumbricoides larvae 26. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Sarcocystis oocysts B. Microsporidia spores C. Schistosoma haematobium eggs D. Isospora belli oocysts 27. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry power, 400x) (the large object on the left was seen on the surface of the stool) (the image on the far right was seen in a cellulose tape preparation): A. Enterobius vermicularis female worm and eggs B. Hookworm female worm and eggs C. Plant cells D. Unknown artifacts 28. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry 11 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
12 A. Hookworm eggs B. Ascaris lumbricoides eggs C. Artifacts D. Pollen grains 29. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry A. Pollen grains B. Blastocystis spp. C. Iodamoeba bütschlii D. Entamoeba coli 30. The following fecal wet mount images are (iodine stain in some) (high dry 12 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
13 A. Schistosoma haematobium eggs B. Schistosoma mansoni eggs C. Schistosoma japonicum eggs D. Schistosoma intercalatum eggs ANSWERS: ANSWER. 1. C. The flagellate trophozoites and cysts seen would be identified as Giardia lamblia (duodenalis, intestinalis) trophozoites, cysts. Note the teardrop shape of the trophozoite and multiple inclusions in the cysts (multiple nuclei, curved median bodies and linear axonemes). ANSWER. 2. D. Of the organisms seen, the correct identification would be Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar. There are no visible RBCs within the trophozoite; thus the identification of Entamoeba histolytica would be incorrect. Note the chromatoidal bar with rounded ends (arrow). ANSWER 3. A. The amebic cysts seen above would be identified as Entamoeba coli (5 or more nuclei and chromatoidal bars with sharp, pointed ends). Note the precyst at the far right contains the two typical large nuclei, one at each side of the precyst. ANSWER. 4. C. These organisms are Chilomastix mesnili cysts; note the large nucleus and the curved fibril (Shepherd s Crook; two images on the left). ANSWER. 5. A. These organisms are Iodamoeba bütschlii cysts with the large single nuclear karyosome and large glycogen vacuole (may stain intensely with iodine) or may appear clear with no iodine on the wet mount). ANSWER. 6. C. Charcot-Leyden (C-L) crystals are formed from the breakdown products of eosinophils. These crystals are an indication of an immune response, which may or may not be linked to a parasitic infection. Also, there may or may not be eosinophils present in the stool. C-L crystals tend to stain somewhat intensely with iodine, but are easily visible without iodine. There is a large size range of crystals in a single fecal specimen. ANSWER. 7. A. These nematode eggs are hookworm eggs; no genus/species designation is reported since both common human species have the same egg morphology. The eggs usually are seen at about an 8 to 16 ball stage of development. Occasionally, one can see a complete larval worm within the eggshell (see third image from the left). 13 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
14 ANSWER. 8. B. These eggs are fertilized Ascaris lumbricoides eggs. Note the broadly rounded shape, tuberculated (bumpy) shell, and presence of the developing larvae within the eggshells. ANSWER. 9. C. Although these structures very easily mimic helminth eggs in size and shape, they are pollen grains that are often found in fecal specimens. It is sometimes helpful to tap on the coverslip to get the fluid to move under the coverslip; the uneven shape of the pollen grains can often be seen as the structure moves through the fluid. ANSWER 10. A. These structures are unfertilized Ascaris lumbricoides eggs. Note the somewhat elongated shape with highly tuberculated (bumpy) shells. Often these eggs can be seen in the same specimen with fertilized eggs. If unfertilized eggs only are seen, it generally indicates there is no male worm present. The presence of either fertilized or unfertilized eggs is clinically significant and the patient should receive therapy. ANSWER. 11. A. The correct response is Taenia spp. Remember that the Taenia species cannot be identified from the eggs without special staining. Note the broadly oval shape, striated shell, and the presence of the six-hooked oncosphere within the eggshell. ANSWER 12. D. These eggs are Diphyllobothrium latum. Note the smooth shell outline (no opercular shoulders), and the operculum line (arrows) visible in some eggs. If you tap on the coverslip, sometimes you can get the operculum to pop open like the second egg from the left. Also, note the small bump on the end of the egg opposite the operculum (circle). Depending on how the egg is positioned, this small bump may or may not be visible on every egg. ANSWER. 13. B. These structures are Trichuris trichiura eggs. Note the typical oval shape with the two polar plugs (these are not opercula), one at each end of the egg. The overall shell is somewhat thick; however, identification is generally based on the typical shape and presence of the clear polar plugs. ANSWER. 14. A. Based on the size, these eggs could be Fasciolopsis buski or Fasciola hepatica (not given as one of the choices). These eggs are quite large, have a smooth shell with an operculum (can be difficult to see), no opercular shoulders, and a thickening in the shell at the end opposite the operculum. ANSWER 15. C. These structures are Paragonimus spp. eggs. Note the operculum with a swelling at each side (opercular shoulders note ovals) and a thickened shell at the end of the egg opposite the operculum. These eggs can be confused with Diphyllobothrium latum eggs (do not have opercular shoulders). 14 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
15 Diphyllobothrium Paragonimus ANSWER. 16. D. These structures are Clonorchis (Opisthorchis) sinensis eggs. These trematode eggs are characterized by their small size (~30 microns), their dramatic opercular shoulders (see oval), and the small knob at the end opposite the operculum (abopercular end see circle). Clonorchis, Heterophyes, and Metagonimus eggs look almost identical; it can be almost impossible to differentiate one from the other. ANSWER. 17. B. These tapeworm eggs are Hymenolepis nana (the Dwarf Tapeworm). The eggshell is relatively thin, there is a six-hooked oncosphere within the shell, and there are polar filaments between the shell and oncosphere (see arrows). These eggs differ from Hymenolepis diminuta (do not contain polar filaments). ANSWER. 18. B. These blood fluke eggs are Schistosoma mansoni; the eggs tend to be found in the stool; however, occasionally they can be found in the urine. Both urine and stool should be examined for any suspect schistosomiasis patient. Note the large lateral spine (circle); in the egg on the far right the miracidium larva is fully formed. ANSWER. 19. A. These structures are Schistosoma japonicum eggs; note the typical very small lateral spine (within the circles). Often, depending on the way the egg is positioned in the wet mount, the small spine is not visible. Tap on the coverslip and you may see the spine as the egg moves through the fluid. ANSWER. 20. D. These tapeworm eggs belong to the Hymenolepis diminuta (Rat Tapeworm) group. Note they resemble Hymenolepis nana eggs and have the six-hooked oncosphere; however, the H. diminuta eggs do not contain the polar filaments. ANSWER. 21. C. These images represent tissue cells (far left), cell artifact (left), macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (right and far right). Notice how difficult it is to identify these cells without seeing them in a permanent stained smear (1000x magnification). Remember, oil immersion (1000x) is not 15 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
16 recommended for wet mounts, which are viewed using low power (100x) and high dry power (400x) rather than oil immersion (1000x). ANSWER. 22. D. Often, these Endolimax nana organisms are missed on the wet mount due to the low magnification. However, here are two images that represent what can be seen on an iodine wet mount. Notice in the left image there are cysts contain from two to four nuclei, and the cyst shape varies from round to oval, which is typical. The E. nana trophozoite on the right is typical with the very large nuclear karyosome; however, this morphology is an exact overlap of that seen with Iodamoeba bütschlii trophozoites. Consequently no identification could be made without the presence of both trophozoites and cysts. For proficiency testing, these organisms are identified using the permanent stain and oil immersion power (1000x). ANSWER. 23. C. These structures are Strongyloides stercoralis rhabditiform (non-infectious) larvae. In the image on the left, one can see it s a larva, but the actual identification would be difficult. However, in the center image, one can see the genital primordium (packet of genital cells see oval), and in the right image, you can see the short buccal cavity (mouth). These two characteristics provide the morphological details required for the actual identification. ANSWER. 24. A. These images are trophozoites (left) and cysts (right) of Balantidium coli. Note that the large macronucleus can be seen in all four; however, in the center left and right, the macronucleus is quite pale (see arrows). These ciliates are so large, they tend to mimic helminth eggs. In the two images on the left, the cilia can be seen surrounding the trophozoite (particularly in the second from the left trophozoite). Often, the cilia is not visible within the cyst wall. ANSWER. 25. C. These plant root hairs tend to mimic nematode larvae, but there are no actual structural elements present within the root hairs (buccal cavity, genital primordial cells). These artifacts are often used as a proficiency testing challenge to differentiate plant material from actual nematode larvae. ANSWER. 26. D. These coccidian structures are Isospora belli oocysts. The two on the left are less mature (tend to be seen in stool), while the two on the right are much more mature (less commonly seen in human fecal specimens). ANSWER. 27. A. Enterobius vermicularis is diagnosed primarily from cellulose tape preparations from the perianal area. The far left image is a female worm that can occasionally be seen on the surface of the stool specimen. The two center images represent the eggs (center right image contains a fully embryonated egg). The far right image demonstrates pinworm eggs as seen on a cellulose tape preparation. 16 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
17 ANSWER. 28. B. These structures are decorticate fertilized (left) and unfertilized (right) eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides. Rather than the tuberculated (bumpy) shells, the outer coat has been lost (decorticate). Therefore, they may be somewhat more difficult to recognize as Ascaris eggs. Both corticate and decorticate eggs can be seen in a single fecal specimen. Whether the eggs have the bumpy coat or are decorticate has no particular clinical significance; therefore, the report would merely indicate Ascaris lumbricoides eggs present. ANSWER. 29. B. Blastocystis spp. (formerly Blastocystis hominis) is grouped with the Stramenopiles and is the most common parasite found within stool specimens worldwide. There are at least 10 different subtypes/species that we see in clinical specimens; however, they look identical. Since approximately half of the subtypes are pathogenic and half are nonpathogenic, it is important that the physicians know that we can t define pathogenicity from morphology. Report comments are recommended for clarification. Identification is usually confirmed and quantitated (rare, few, moderate, many) from the permanent stained smear. These images are central body forms with the vacuole in the center and the nuclei located around the edges. Comment to be used for reporting Blastocystis spp.: The name Blastocystis spp. contains approximately 10 different subtypes, none of which can be differentiated on the basis of organism morphology; some are pathogenic and some are non-pathogenic. If no other pathogens are found, Blastocystis spp. may be the cause of patient symptoms AND other organisms capable of causing diarrhea should also be ruled out. ANSWER. 30. A. Although Schistosoma haematobium eggs are normally found in urine (adults lie in veins over the bladder), these eggs can occasionally be found in stool specimens. Note the typical terminal spine (circle). Regardless of the suspected species, any patient thought to have schistosomiasis should submit both urine and stool for examination. REFERENCES 1. Garcia, L.S Diagnostic Medical Parasitology, 6th Ed., ASM Press, Washington, D.C. 17 (WET MOUNT IMAGE IDENTIFICATION TEST)
Laboratory No. 3 General Stool Examination (GSE) Collection of samples
 Laboratory No. 3 General Stool Examination (GSE) Collection of samples If a faecal sample is not properly collected and taken care of before examination, they will be of little or no value for accurate
Laboratory No. 3 General Stool Examination (GSE) Collection of samples If a faecal sample is not properly collected and taken care of before examination, they will be of little or no value for accurate
Lynne S. Garcia MS, MT(ASCP), CLS(NCA), BLM(AAB), F(AAM) 051811ti. Diagnostic Medical Parasitology. FAQ s
 Lynne S. Garcia MS, MT(ASCP), CLS(NCA), BLM(AAB), F(AAM) 051811ti Diagnostic Medical Parasitology FAQ s Diagnostic Medical Parasitology FAQ s Santa Maria, CA 93455 Sprinboro, Ohio 45066 A Culture of Service
Lynne S. Garcia MS, MT(ASCP), CLS(NCA), BLM(AAB), F(AAM) 051811ti Diagnostic Medical Parasitology FAQ s Diagnostic Medical Parasitology FAQ s Santa Maria, CA 93455 Sprinboro, Ohio 45066 A Culture of Service
INTESTINAL PROTOZOA. monoxenous vs heteroxenous
 Flagellates: Giardia lamblia Dientamoeba fragilis Chilomastix mesnili Trichomonas hominis Enteromonas hominis Retortamonas intestinalis Ameba: Entamoeba histolytica Entamoeba dispar Entamoeba coli Entamoeba
Flagellates: Giardia lamblia Dientamoeba fragilis Chilomastix mesnili Trichomonas hominis Enteromonas hominis Retortamonas intestinalis Ameba: Entamoeba histolytica Entamoeba dispar Entamoeba coli Entamoeba
Intestinal and Luminal protozoa
 Intestinal and Luminal protozoa Bushehr University of Medical Sciences Department: Microbiology and Parasitology Module: Medical Parasitology Instructor: Mohammad Rayani, PhD 1 Flagellates: Giardia lamblia
Intestinal and Luminal protozoa Bushehr University of Medical Sciences Department: Microbiology and Parasitology Module: Medical Parasitology Instructor: Mohammad Rayani, PhD 1 Flagellates: Giardia lamblia
The Intestinal Protozoa
 The Intestinal Protozoa A. Introduction 1. The Phylum Protozoa is classified into four major subdivisions according to the methods of locomotion and reproduction. a. The amoebae (Superclass Sarcodina,
The Intestinal Protozoa A. Introduction 1. The Phylum Protozoa is classified into four major subdivisions according to the methods of locomotion and reproduction. a. The amoebae (Superclass Sarcodina,
The Helminths. A. Introduction. 1. Phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms) - includes the tapeworms & flukes. a. General Characteristics
 The Helminths A. Introduction 1. Phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms) - includes the tapeworms & flukes a. General Characteristics (1) Multicellular animals characterized by a flat, bilaterally symmetric
The Helminths A. Introduction 1. Phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms) - includes the tapeworms & flukes a. General Characteristics (1) Multicellular animals characterized by a flat, bilaterally symmetric
Intestinal and Luminal protozoa
 Intestinal and Luminal protozoa Bushehr University of Medical Sciences Department: Microbiology and Parasitology Module: Medical Parasitology Instructor: Mohammad Rayani, PhD Flagellates: Giardia lamblia
Intestinal and Luminal protozoa Bushehr University of Medical Sciences Department: Microbiology and Parasitology Module: Medical Parasitology Instructor: Mohammad Rayani, PhD Flagellates: Giardia lamblia
Organisms of Concern. Roundworms (nematodes) Anisakis spp., Pseudoterranova spp., Eustrongylides spp. and Gnathostoma spp.
 Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
Parasites in Fish Parasites are a natural occurrence The parasites do not make the fish sick Thorough cooking of fish will make parasites harmless to humans Organisms of Concern Roundworms (nematodes)
Exercise 2. The Compound Light Microscope
 6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
DIAGNOSING MEDICAL PARASITES: A Public Health Officers Guide to Assisting Laboratory and Medical Officers
 DIAGNOSING MEDICAL PARASITES: A Public Health Officers Guide to Assisting Laboratory and Medical Officers Compiled and edited by: Michael J. Cuomo, Maj, USAF, BSC (PH) Lawrence B. Noel, Maj, USAF, BSC
DIAGNOSING MEDICAL PARASITES: A Public Health Officers Guide to Assisting Laboratory and Medical Officers Compiled and edited by: Michael J. Cuomo, Maj, USAF, BSC (PH) Lawrence B. Noel, Maj, USAF, BSC
COMUNICACIONES REPORTS
 COMUNICACIONES REPORTS COMUNICAÇÕES EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY OF INTESTINAL PARASITIC INFECTIONS IN A RURAL AREA FROM ZULIA STATE, VENEZUELA L. CHACIN-BONILLA, N. GUANIPA, G. CANO, A.M. PARRA, J. ESTEVEZ and
COMUNICACIONES REPORTS COMUNICAÇÕES EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY OF INTESTINAL PARASITIC INFECTIONS IN A RURAL AREA FROM ZULIA STATE, VENEZUELA L. CHACIN-BONILLA, N. GUANIPA, G. CANO, A.M. PARRA, J. ESTEVEZ and
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Cells. Introduction WSBCTC 1
 Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Examinations regarding the prevalence of intestinal parasitic diseases in Polish soldiers contingents assigned to missions abroad
 ORIGINAL PAPER Int Marit Health 2011; 62, 1: 31 36 Copyright 2011 Via Medica ISSN 1641 9251 Examinations regarding the prevalence of intestinal parasitic diseases in Polish soldiers contingents assigned
ORIGINAL PAPER Int Marit Health 2011; 62, 1: 31 36 Copyright 2011 Via Medica ISSN 1641 9251 Examinations regarding the prevalence of intestinal parasitic diseases in Polish soldiers contingents assigned
OBJECTIVES PROCEDURE. Lab 2- Bio 160. Name:
 Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY RED BLOOD CELLS AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS IN URINALYSIS
 URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
MODIFIED TRICHROME STAIN
 MODIFIED TRICHROME STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Modified trichrome stain for the microsporidia (Ryan-Blue). The diagnosis of intestinal microsporidiosis (Brachiola spp., Enterocytozoon
MODIFIED TRICHROME STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Modified trichrome stain for the microsporidia (Ryan-Blue). The diagnosis of intestinal microsporidiosis (Brachiola spp., Enterocytozoon
Copyright 1995 by Dr. Hulda Regehr Clark. khz 177, 188 77, 91 295 288 277 88, 96, 133, 126 100
 Mold, Mold Toxin Frequencies Copyright 1995 by Dr. Hulda Regehr Clark Other molds and mold toxins Aflatoxin Cytochalasin B Ergot Griseovulvin Sorghum syrup Sterigmatocystin Zearalenone Slime molds Argyria
Mold, Mold Toxin Frequencies Copyright 1995 by Dr. Hulda Regehr Clark Other molds and mold toxins Aflatoxin Cytochalasin B Ergot Griseovulvin Sorghum syrup Sterigmatocystin Zearalenone Slime molds Argyria
CONTENTS NEWS WORLD DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTICS CLOSE UP STAY HEALTHY KNOWING MORE
 CONTENTS NEWS Another company acquisition by Cormay Chemistry days Our Participation in Clinical Lab Expo 2011 in Atlanta 4 5 5 WORLD DIAGNOSTICS Critical Evaluation of Faecal Parasite Concentrators 6
CONTENTS NEWS Another company acquisition by Cormay Chemistry days Our Participation in Clinical Lab Expo 2011 in Atlanta 4 5 5 WORLD DIAGNOSTICS Critical Evaluation of Faecal Parasite Concentrators 6
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology
 Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
Microscopy and Cellular Morphology As we discussed in class, many organisms on the planet exist as single cells and are referred to as microorganisms bacteria, protozoans, among others. When a single microorganism
ZENTEL (Albendazole) PRODUCT INFORMATION
 ZENTEL (Albendazole) PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION ZENTEL contains albendazole, which is methyl [5-(propylthio)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl] carbamate. It is a member of the benzimidazole group of anthelmintic
ZENTEL (Albendazole) PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION ZENTEL contains albendazole, which is methyl [5-(propylthio)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl] carbamate. It is a member of the benzimidazole group of anthelmintic
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains)
 LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
Exercise 9: Blood. Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826.
 Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Students will identify these animal cell structures: Students should properly answer the pre-activity cell membrane, nucleus. questions.
 WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
TEST UPDATE: Ova and Parasites Effective: September 2008
 TEST UPDATE: Ova and Parasites Effective: September 2008 Related Information CPT Cryptosporidium by FA Giardia by FA 87177 (ova and parasite exam); 87209 (complex special stain) Synonyms Fecal Parasite
TEST UPDATE: Ova and Parasites Effective: September 2008 Related Information CPT Cryptosporidium by FA Giardia by FA 87177 (ova and parasite exam); 87209 (complex special stain) Synonyms Fecal Parasite
AMEBAS AND CILIATES. Parasites can be studied by one being aware of the following relevant aspects of their parasite biology:
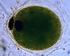 1 LABORATORY 2 PARASITOLOGY NOTES AMEBAS AND CILIATES EUKARYOTIC PARASITES: Parasites can be studied by one being aware of the following relevant aspects of their parasite biology: 1. Distribution (where
1 LABORATORY 2 PARASITOLOGY NOTES AMEBAS AND CILIATES EUKARYOTIC PARASITES: Parasites can be studied by one being aware of the following relevant aspects of their parasite biology: 1. Distribution (where
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
For Medical Laboratory Technology Students. Parasitology. Girma Mekete Mohamed Awole Adem. Jimma University
 LECTURE NOTES For Medical Laboratory Technology Students Parasitology Girma Mekete Mohamed Awole Adem Jimma University In collaboration with the Ethiopia Public Health Training Initiative, The Carter Center,
LECTURE NOTES For Medical Laboratory Technology Students Parasitology Girma Mekete Mohamed Awole Adem Jimma University In collaboration with the Ethiopia Public Health Training Initiative, The Carter Center,
Gram Staining. The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain. Advantages:
 Gram Staining The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain Advantages: Can observe size and morphology (like other staining) Can find out additional information about the organism- primarily what type of
Gram Staining The Most Commonly Used Differential Stain Advantages: Can observe size and morphology (like other staining) Can find out additional information about the organism- primarily what type of
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells
 Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
PARASITIC CONTAMINATION OF WELLS DRINKING WATER IN MAZANDARAN PROVINCE
 Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 2009, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 241-246 PARASITIC CONTAMINATION OF WELLS DRINKING WATER IN MAZANDARAN PROVINCE 1 Z. Yousefi, * 2 H. Ziaei hezarjaribi, 1 A. A. Enayati, 1 R.
Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 2009, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 241-246 PARASITIC CONTAMINATION OF WELLS DRINKING WATER IN MAZANDARAN PROVINCE 1 Z. Yousefi, * 2 H. Ziaei hezarjaribi, 1 A. A. Enayati, 1 R.
Microbiological Stool Examination: Overview
 ID: JCDR/2012/4003:2073 Microbiology Section Review Microbiological Stool Examination: Overview Kotgire Santosh A., Introduction Stool (faeces) is an important body substance which has to be checked for
ID: JCDR/2012/4003:2073 Microbiology Section Review Microbiological Stool Examination: Overview Kotgire Santosh A., Introduction Stool (faeces) is an important body substance which has to be checked for
Microscopes and the Metric System
 Microscopes and the Metric System BIO162 Fall 2007 Sizes of Microorganisms: -Viruses: 0.01 0.3 um -Bacteria: 1 3 um -Fungi: 3 30 um -Protozoa: 5 1000 um 1 Measuring Microorganisms Ocular Micrometer The
Microscopes and the Metric System BIO162 Fall 2007 Sizes of Microorganisms: -Viruses: 0.01 0.3 um -Bacteria: 1 3 um -Fungi: 3 30 um -Protozoa: 5 1000 um 1 Measuring Microorganisms Ocular Micrometer The
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns
 Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Living things: Cells Living things:
 unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
Eosinophilia in returning travellers and migrants from the tropics: UK recommendations for investigation and initial management
 Journal of Infection (2010) 60, 1e20 www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/jinf CLINICAL GUIDELINES OF THE BRITISH INFECTION SOCIETY Eosinophilia in returning travellers and migrants from the tropics: UK recommendations
Journal of Infection (2010) 60, 1e20 www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/jinf CLINICAL GUIDELINES OF THE BRITISH INFECTION SOCIETY Eosinophilia in returning travellers and migrants from the tropics: UK recommendations
CHAPTER 8 Freshwater snails
 BIOLOGY 337 CHAPTER 8 Freshwater snails Intermediate hosts of schistosomiasis and foodborne trematode infections Many species of freshwater snail belonging to the family Planorbidae are intermediate hosts
BIOLOGY 337 CHAPTER 8 Freshwater snails Intermediate hosts of schistosomiasis and foodborne trematode infections Many species of freshwater snail belonging to the family Planorbidae are intermediate hosts
3.1 Cells and cell function
 BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
AURAMINE O STAIN. Preanalytical Considerations
 AURAMINE O STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Acid-fast mycobacteria resist decolorization by acid-alcohol after primary staining owing to the high lipid (mycolic acid) content in their cell
AURAMINE O STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Acid-fast mycobacteria resist decolorization by acid-alcohol after primary staining owing to the high lipid (mycolic acid) content in their cell
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Rooting for Mitosis Overview Students will fix, stain, and make slides of onion root tips. These slides will be examined for the presence
Continued. Overhead 1. Overhead 2. Chap 2 - Hazards - Biological, Chemical, and Physical. Chapter 2: Hazards - Biological, Chemical and Physical
 Chapter 2: Hazards - Biological, Chemical and Physical Overhead 1 Objective: Awareness of: Biological hazards Chemical hazards Physical hazards Characteristics of certain microorganisms To perform a hazard
Chapter 2: Hazards - Biological, Chemical and Physical Overhead 1 Objective: Awareness of: Biological hazards Chemical hazards Physical hazards Characteristics of certain microorganisms To perform a hazard
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD
 ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
 1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
G-H. Haloperidol, Serum or Plasma. Haptoglobin (Hp), Serum. Analytik. Gonococcus see Neisseria gonorrhoeae
 137 Gonococcus see Neisseria gonorrhoeae GPT see Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Serum Growth Hormone (HGH, STH) see Somatotropin Haloperidol, Serum or Plasma Related Information: Lithium (Li), Serum Synonyms:
137 Gonococcus see Neisseria gonorrhoeae GPT see Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Serum Growth Hormone (HGH, STH) see Somatotropin Haloperidol, Serum or Plasma Related Information: Lithium (Li), Serum Synonyms:
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia.
 Hemophilia Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia. Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Hemophilia Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia. Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Internal Parasites Donna K. Carver, DVM, PhD, ACPV
 Internal Parasites Donna K. Carver, DVM, PhD, ACPV Parasites are organisms that live in or on another organism (host) and gain an advantage at the expense of the host. Internal parasites live inside their
Internal Parasites Donna K. Carver, DVM, PhD, ACPV Parasites are organisms that live in or on another organism (host) and gain an advantage at the expense of the host. Internal parasites live inside their
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - GRANULOCYTE FORMATION AND CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
Discovering cells. The fi rst drawing of cells
 Discovering cells Living things are made of cells. Just as bricks and planks of wood are the building blocks for houses, cells are the building blocks of living things. Cells, although they are very small,
Discovering cells Living things are made of cells. Just as bricks and planks of wood are the building blocks for houses, cells are the building blocks of living things. Cells, although they are very small,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB)
 Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
GRADE 7: Life science 1. UNIT 7L.1 7 hours. Specialised cells. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Key vocabulary and technical terms
 GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
Protists and Fungi. What color are the cells in the living culture?
 Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
Protists and Fungi Objectives 1. Recognize and identify (to genus) the organisms covered in lab. 2. Describe the characteristics of each organism. 3. Correctly classify the organisms. I. Protists The protists
Animal & Plant Cell Slides
 Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
Animal & Plant Cell Slides Category: Biology Type: Class Experiment, 60 min class Materials: 2 Glass Slides 2 Cover Slips 1 Bottle of methylene blue (optional) 1 Plastic tray 1 Bottle of iodine 1 Plastic
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
A Retrospective Evaluation of the Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites in Istanbul, Turkey
 Türkiye Parazitoloji Dergisi, 34 (3): 166 171, 2010 Türkiye Parazitol Derg. Türkiye Parazitoloji Derneği Turkish Society for Parasitology A Retrospective Evaluation of the Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites
Türkiye Parazitoloji Dergisi, 34 (3): 166 171, 2010 Türkiye Parazitol Derg. Türkiye Parazitoloji Derneği Turkish Society for Parasitology A Retrospective Evaluation of the Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites
MICROSCOPY. To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope.
 MICROSCOPY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope. To demonstrate skill in the use of ocular and stage micrometers for measurements of cell size. To recognize
MICROSCOPY I. OBJECTIVES To demonstrate skill in the proper utilization of a light microscope. To demonstrate skill in the use of ocular and stage micrometers for measurements of cell size. To recognize
Chapter 3. Cell Division. Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.
 Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Chapter 3 Cell Division Laboratory Activities Activity 3.1: Mock Mitosis Activity 3.2: Mitosis in Onion Cells Activity 3.3: Mock Meiosis Goals Following this exercise students should be able to Recognize
Life Cycle of a Butterfly
 Name: Date: Life Cycle of a Butterfly Life cycle refers to the stages of development, growth and reproduction that a living thing goes through. The butterfly's life cycle is made up of four stages: egg,
Name: Date: Life Cycle of a Butterfly Life cycle refers to the stages of development, growth and reproduction that a living thing goes through. The butterfly's life cycle is made up of four stages: egg,
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
A single FLOTAC is more sensitive than triplicate Kato Katz for the diagnosis of low-intensity soil-transmitted helminth infections
 Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2009) 103, 347 354 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst A single FLOTAC is more
Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2009) 103, 347 354 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/trst A single FLOTAC is more
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Note Students are expected to review the corresponding information in the course textbook(s) as well as the classroom notes in preparation for this lab and to aid in
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Note Students are expected to review the corresponding information in the course textbook(s) as well as the classroom notes in preparation for this lab and to aid in
B2 1 Cells, Tissues and Organs
 B2 Cells, Tissues and Organs 5 minutes 5 marks Page of 7 Q. The diagram shows a bacterium. On the drawing, name the structures labelled A, B, C and D. (Total 4 marks) Q2. (a) The diagrams show cells containing
B2 Cells, Tissues and Organs 5 minutes 5 marks Page of 7 Q. The diagram shows a bacterium. On the drawing, name the structures labelled A, B, C and D. (Total 4 marks) Q2. (a) The diagrams show cells containing
MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES
 EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
EXPERIMENT 1 MICROSCOPY OF LIVING MICROBES Many students taking microbiology for the first time feel that they are going to have a hard time with the microscope. This lab as an experiment is intended to
Hematology Morphology Critique
 Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
The illustrations below reflect other scientists results in identifying and counting the stages of the onion root tip and the whitefish blastula.
 Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Abstract: The purpose of this laboratory experiment was to identify in what stage of mitosis viewed cells were in. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Although the
Common Avian Parasites Introduction Diagnosis of Parasites Protozoa
 Common Avian Parasites Peter S. Sakas DVM, MS Niles Animal Hospital and Bird Medical Center 7278 N. Milwaukee Ave. Niles IL 60714 (847) 647-9325 FAX (847) 647 8498 www.nilesanimalhospital.com Introduction
Common Avian Parasites Peter S. Sakas DVM, MS Niles Animal Hospital and Bird Medical Center 7278 N. Milwaukee Ave. Niles IL 60714 (847) 647-9325 FAX (847) 647 8498 www.nilesanimalhospital.com Introduction
PROGRAM DRIVERS FREQUENCY LIST
 PROGRAM DRIVERS FREQUENCY LIST Ref: CFAD = Book Cure for All Diseases CFAC = Book Cure for All Cancers CFAAC= Book Cure for All Advanced Cancers HIV = Book The Cure for HIV/AIDS POAC = Book Prevention
PROGRAM DRIVERS FREQUENCY LIST Ref: CFAD = Book Cure for All Diseases CFAC = Book Cure for All Cancers CFAAC= Book Cure for All Advanced Cancers HIV = Book The Cure for HIV/AIDS POAC = Book Prevention
Cytology of Lymph Nodes
 Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
CERVICAL CANCER What every woman should know What is a cervix?
 CERVICAL CANCER What every woman should know What is a cervix? The cervix is the entrance to the womb from the vagina. It is the narrow, lower part of the uterus that is the passageway connecting the uterus
CERVICAL CANCER What every woman should know What is a cervix? The cervix is the entrance to the womb from the vagina. It is the narrow, lower part of the uterus that is the passageway connecting the uterus
Hematology Sequence. Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES. c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral Blood Smear (several parts)
 Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
Agricultural Labor among School Children in Rural Assiut, Egypt
 Agricultural Labor among School Children in Rural Assiut, Egypt Safaa A. M. Kotb *1, Asmaa G. Mohamed 1 Ekram M. Abdel Khalek 2, Doaa A. Yones 3 1 Community Health Nursing, Assiut Faculty of Nursing. 2
Agricultural Labor among School Children in Rural Assiut, Egypt Safaa A. M. Kotb *1, Asmaa G. Mohamed 1 Ekram M. Abdel Khalek 2, Doaa A. Yones 3 1 Community Health Nursing, Assiut Faculty of Nursing. 2
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment
 Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment 1a. All living things are made up of. a. cells b. tissues c. organisms d. systems 1b. All living things are made up of. 1c. Explain what cells are
Fifth Grade Cells: Structures and Processes Assessment 1a. All living things are made up of. a. cells b. tissues c. organisms d. systems 1b. All living things are made up of. 1c. Explain what cells are
Medical Laboratory Technology Program. Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives
 Medical Laboratory Technology Program Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives Medical Laboratory Technology Student Learning Outcomes All Colorado Mesa University associate
Medical Laboratory Technology Program Student Learning Outcomes & Course Descriptions with Learning Objectives Medical Laboratory Technology Student Learning Outcomes All Colorado Mesa University associate
Benzie Leelanau District Health Department
 Benzie Leelanau District Health Department Benzie Leelanau District Health Department Tri county Health Dept. Until 1990. G.T. County H.D. contract until 1996. Environmental Health regulations adopted
Benzie Leelanau District Health Department Benzie Leelanau District Health Department Tri county Health Dept. Until 1990. G.T. County H.D. contract until 1996. Environmental Health regulations adopted
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity
 Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING
 VERSION 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/01/2016 MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING MALARIA MICROSCOPY STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE MM-SOP-09 1. PURPOSE AND SCOPE To describe the procedure for counting malaria parasites on
VERSION 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/01/2016 MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING MALARIA MICROSCOPY STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE MM-SOP-09 1. PURPOSE AND SCOPE To describe the procedure for counting malaria parasites on
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY. Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab
 HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
Cell Division CELL DIVISION. Mitosis. Designation of Number of Chromosomes. Homologous Chromosomes. Meiosis
 Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
Cell Division CELL DIVISION Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial purpose.
UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and the Environment Situations. Cells
 Lesson Summaries HUMAN AND SOCIAL BIOLOGY UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and the Environment Situations Lesson 2 Cells OBJECTIVES At the end of this lesson you will be able to: a) Describe the structure of
Lesson Summaries HUMAN AND SOCIAL BIOLOGY UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and the Environment Situations Lesson 2 Cells OBJECTIVES At the end of this lesson you will be able to: a) Describe the structure of
How To Help Fight Schistosomiasis And Sth
 The book describes an approach in which epidemiological data are used to select the control strategy to be applied to the school-age population and shows how periodic data collection from sentinel sites
The book describes an approach in which epidemiological data are used to select the control strategy to be applied to the school-age population and shows how periodic data collection from sentinel sites
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test
 BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test 1. Why is the microscope in our lab called a compound microscope? 2. How do you calculate total magnification? 3. What is the lowest and the maximal magnification
BIO 10 Lab 1 Introduction Pre Lab Test 1. Why is the microscope in our lab called a compound microscope? 2. How do you calculate total magnification? 3. What is the lowest and the maximal magnification
Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites on Fruits Available in Ibadan Markets, Oyo State, Nigeria
 ISSN 2079-2018 IDOSI Publications, 2011 Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites on Fruits Available in Ibadan Markets, Oyo State, Nigeria 1,3 2 1 1 J.A. Alli, GO Abolade, A.F. Kolade, A.O. Salako, 1 1 2 1 C.J.
ISSN 2079-2018 IDOSI Publications, 2011 Prevalence of Intestinal Parasites on Fruits Available in Ibadan Markets, Oyo State, Nigeria 1,3 2 1 1 J.A. Alli, GO Abolade, A.F. Kolade, A.O. Salako, 1 1 2 1 C.J.
Biology. STANDARD II: Objective 3. Osmosis Inquiry Labs
 Biology STANDARD II: Objective 3 Osmosis Inquiry Labs Background Knowledge: Students should have used a microscope before and be familiar with the parts. They should also know how to make a wet mount slide.
Biology STANDARD II: Objective 3 Osmosis Inquiry Labs Background Knowledge: Students should have used a microscope before and be familiar with the parts. They should also know how to make a wet mount slide.
Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points)
 Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
General Practice Service Willows Information Sheets. Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs
 General Practice Service Willows Information Sheets Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs Flea Tick Mite Louse Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs What types of skin
General Practice Service Willows Information Sheets Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs Flea Tick Mite Louse Ectoparasites (fleas and other skin parasites) in dogs What types of skin
Impressions of a Stoma
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Impressions of a Stoma Overview Students use two different methods to view stomata on the underside of leaves. Introduction Plants exchange the
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES
 SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
SHEEP EYE DISSECTION PROCEDURES The anatomy of the human eye can be better shown and understood by the actual dissection of an eye. One eye of choice for dissection, that closely resembles the human eye,
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
