Early detection saves lives
|
|
|
- Johnathan Tucker
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging (DITI) used for adjunctive Breast Disease Screening Can Enhance Early Detection : Early detection saves lives DITI's role in breast cancer and other breast disorders is one of early detection and monitoring of abnormal physiology and the establishment of risk factors for the development or existence of cancer. When used adjunctively with other laboratory and outcome assessment tools, the best possible evaluation of breast health is made. This fifteen-minute non invasive test, is a valuable adjunctive tool for alerting gynecologists and primary care physicians to the possibility of underlying breast disease. This test is designed to improve chances for detection of fast-growing, active tumors in the intervals between mammographic screenings or when mammography is not indicated by screening guidelines for women under 50 years of age. DITI may be especially appropriate for younger women under 50 whose denser breast tissue makes it more difficult for mammography to pick up suspicious lesions. This test can provide a 'clinical marker' to the physician just before clinical breast examination as well as to the mammographer before the mammogram is performed, that a specific area of the breast needs particularly close examination." Breast cancers tend to grow significantly faster in younger women under age 50: AGE Under 50 Age Over Age 70 Cancer 71: , 1993 AVERAGE TUMOR DOUBLING TIME 80 Days 157 Days 188 days Source: The faster a malignant tumor grows, the more heat it generates. For younger women in particular, results from DITI screening can lead to earlier detection and ultimately, longer life. More than 90 percent of women diagnosed with early stage, localized cancer are alive five years later, yet only 58% of cancers are diagnosed at this stage according to the American Cancer Society. During a clinical breast examination, a physician must rely on fingers (or palpation) and eyesight to detect tumors in the breast, which for women under age 50 may often occur when cancer is no longer localized or confined to the breast. DITI screening can provide an alert before clinical breast exam or referral to mammography, Sonography, or MRI so as to enhance early detection by the physician. DITI is indicated for women of all ages, particularly in the age group and women of any age in a high risk group. Examination recall is dependant on Thermogram result, age, previous history and risk group and can be 3 monthly, 6 monthly, or 12 monthly.
2 Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging (D.I.T.I.) as a Breast Exam DITI of the breast offers the opportunity of earlier detection of breast disease than has been possible with breast self examination, physician palpation, or mammography alone. DITI is a non invasive test. This means that there is no contact with the body of any kind, no radiation and the procedure is painless. DITI is performed using sophisticated medical infra-red cameras, a clinician simply captures infra-red images, or thermograms of the breasts. The digitized images are stored on a computer and can be sent electronically to a central data-base where a physician, such as a Radiologist or Thermologist (thermal imaging specialist), can perform statistical analysis. Significant asymmetries of the breast can indicate a physiological abnormality. This may be pathological (a disease) or it might indicate an anatomical variant. When a Thermogram is positive, the job of differential diagnosis begins. Reports are colour printed and sent to the patients physician / specialist. DITI detects the subtle physiologic changes that accompany breast pathology, whether it is cancer, fibrocystic disease, an infection or a vascular disease, then the physician can plan accordingly and lay out a careful clinical program to further diagnose and or MONITOR the patient until other standard testing becomes positive, thus allowing for the earliest possible treatment. If a suspicious (positive) DITI breast examination is performed, the appropriate follow-up diagnostic and clinical testing can be ordered. This would include mammography and other imaging tests, clinical laboratory procedures, and nutritional and lifestyle evaluation. All patients thermograms (breast images) are kept on record and form a baseline for all future routine evaluations. DITI is a very sensitive and objective physiological test of abnormalities in the breast and as such is an extremely valuable and important adjunctive test with regard to early detection of breast disease.
3 Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging (D.I.T.I.) as a Breast Exam Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among Australian women between the ages of 30 and 60. The average woman has 1 chance in 9 (or about 11 percent) of developing breast cancer during her lifetime. Two-thirds of these women will be over 50 years old, but breast cancer can and does occur in younger women (about 1% of breast cancer cases occure in men). It takes years for a tumor to grow, and the earliest possible indication of abnormality is needed to allow for the earliest possible treatment and intervention. Evidence of disease must be detected long before the intervention stage has passed. Doctors do not yet know how to prevent breast cancer. But you can increase your chances of detecting breast cancer in its earliest stages by understanding the need for, and participating in an early detection programme that will help you increase your chances of detecting breast cancer in its earliest stages. Only about 20 percent of biopsied breast lumps are cancerous. And, if cancer is found early, there are choices for treatment. With prompt treatment, the outlook is good. In fact, most women treated for early breast cancer will be free from breast cancer for the rest of their lives. Risk factors Women who delay having children until their 30 s or who don t have children at all are at higher risk of developing breast cancer. If you have a mother, sister or relative who has had breast cancer this increases the risk for you as does a personal history of non-malignant cystic breast disease. Women whose periods started before the age of 12 or finished after the age of 50 also incur a greater risk of breast cancer. The link between the contraceptive pill and/or Hormone Replacement Therapy after menopause and breast cancer has not been satisfactorily confirmed or disproved at this stage of scientific research. Finally, if you have suffered from cancer of the womb there appears to be an increased risk of cancer of the breast. Current Early Detection Guidelines One day there may be a single method for the early detection of breast cancer. Until then, using a combination of methods will increase your chances of detecting cancer in an early stage. Mammography for all women who are age 40 or older. Regular DITI screening for women of all ages. A regular breast exam by a health professional. Monthly breast self-examination. Personal alertness for changes in the breasts. Readiness to discuss quickly any such changes with a doctor. These guidelines should be considered along with your background and medical history. These guidelines may change as new scientific information becomes available. The final decision regarding all tests, of course, should be made on an individual basis.
4 MAMMOGRAPHY is essential to detecting breast cancer at its earliest stage Beginning at age 40, all women should be encouraged to have a mammogram every 1 to 2 years until age 50. After 50, mammography should be done annually. A mammogram is an x-ray of the breast. It can reveal tumors too small to be felt and can show other changes in the breast that doctors believe may suggest cancer. In mammography, the breast is pressed between two plates; some pressure is applied to get a clear picture. Usually, two x-rays are taken of each breast, one from the top and one from the side. Although some women are concerned about radiation exposure, the risk is very small. A doctor also may suggest a mammogram if a symptom of breast cancer is found, whether through Thermography, BSE, the annual exam, or by chance. If you have a symptom of breast cancer, you should not hesitate to have a mammogram if your doctor recommends it. Other Methods Used For Early Detection Needle biopsies Needle biopsies are less physically traumatic than surgical biopsy and leave little or no scarring on the breast. They cost much less than surgical biopsies and can be evaluated faster. Two types of procedures are currently employed. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy,(fna), requires no anesthesia and offers fast results, sometimes in less than 15 minutes. But FNA requires that a specially trained pathologist be on hand to evaluate the cells removed, and since the technique harvests few cells, it may produce ambiguous results. For those reasons, FNA is most effective for larger lesions that can be felt. The other procedure, core needle biopsy, requires a local anesthetic and takes up to an hour to perform. A springloaded "gun" is used to insert the needle into the breast. The physician guides the needle to its target using either mammography or ultrasound. This type of biopsy removes a larger amount of tissue, and results are available in two or three days. Ultrasound detects breast changes by sending high-frequency sound waves into the breast. The pattern of echoes from these sound waves is converted into an image of the breast's interior. Ultrasound may be helpful in distinguishing between solid masses and cysts (fluid-filled sacs). Unlike mammography, ultrasound cannot detect small calcium deposits that may be present in the breast and that sometimes indicate cancer, nor does it identify small tumors. Recent technical improvements with ultrasound can often make us more confident in diagnosing benign conditions and can reduce the need for an immediate biopsy. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) An MRI machine can take cross-sectional images through different parts of the body, and may be a very sensitive imaging tool for finding breast cancers. MRI might prove to be better than either mammography or ultrasound in determining the extent of cancer in the breast and where it's located. Breast implants can interfere with conventional mammography MRI is the best tool we have for looking at women with silicone implants. While most diagnostic imaging centers have MRI units, relatively few of them have used the technology for detecting breast cancers. Studies now under way, are evaluating whether MRI should join mammography, thermography and ultrasound as part of a standard regimen. Digital Mammography Instead of the image appearing on film, a digital mammogram is stored on a computer disk or tape. This allows manipulation of the image to increase the contrast. A digital mammogram lends itself to computeraided diagnosis. Studies are under way at several medical centers. If those trials are successful, digital mammograms may be widely available in about five years. Diaphanography, or transillumination, shines a bright light through the breast. Transillumination can show the difference between a solid tumor and a cyst. Current studies indicate that this method does not identify the very small cancers that can be detected by mammography. The technique remains experimental.
5 A Physical Breast Exam Is A Must Women should have breast examinations during their routine checkups. You may find it convenient to schedule this exam during your routine physical checkup. If a breast exam is not done during that checkup, you should ask for one. During the exam, the health professional feels the breast and underarm with the fingers, checking for lumps. This is called palpation. The breasts also are checked for other changes such as dimpling, scaling, or puckering of the skin or a discharge from the nipples. Women 40 and older should have breast examinations annually. Breast Self Exam (BSE) Women should do breast self-examination monthly. Breasts come in all sizes and shapes, just as women do. Your own breasts will even change throughout your life. Your monthly menstrual cycle, menopause, childbirth, breast-feeding, age, weight changes, and birth control pills or other hormones may change the shape, size. and feel of your breasts. It is important to learn what is normal for you. This can be done by using BSE. It is easy to do, and, as the name implies, you do it yourself. Women taking charge of their own health are doing BSE regularly. They are also eating healthy foods, exercising regularly, and avoiding tobacco use. BSE is done once a month so that you become familiar with the usual appearance and feel of your own breasts. Familiarity makes it easier to notice any changes in your breasts from one month to another. In fact, some health professionals suggest that, at first, women do BSE every day for a month so that they really know the "geography" of their breasts. Early discovery of a change from what is normal is the whole idea behind BSE. The best time to do BSE is 2 or 3 days after the end of your period, when your breasts are least likely to be tender or swollen. A woman who no longer has periods may find it helpful to pick a particular day, such as the first day of the month, to remind herself that it is time to do BSE. If you discover anything unusual, such as a lump, a discharge from the nipple, or dimpling or puckering of the skin, you should see your doctor at once. Remember, 8 out of 10 biopsied breast lumps are not cancer. Many women have irregular or "lumpy" breasts. The term "benign breast condition" refers to those changes in a woman's breasts that are not cancerous. Many doctors believe that nearly all women have some benign breast changes after age 30. But any change is best diagnosed by your doctor. Discussing BSE with your doctor will help you understand the procedure better. Ask your doctor or other health professional to review with you the steps of BSE, as well as to explain what you are feeling in your breasts. This will assure you that you are doing your BSE correctly and thoroughly, and you will gain more confidence in examining your breasts. Remember every part of the breast cancer detection plan: Regular Mammograms. Regular Digital infrared thermogram screening Routine breast examination by a health professional. Monthly breast self-examination.
6 BREAST SELF-EXAMINATION ( BSE ) REMEMBER, BSE IS NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR ROUTINE THERMOGRAMS, MAMMOGRAMS OR REGULAR BREAST EXAMS BY A DOCTOR. Breast self-examination should be done once a month so you become familiar with the usual appearance and feel of your breasts. Familiarity makes it easier to notice any changes in the breast from one month to another. Early discovery of a change from what is "normal" is the main idea behind BSE. The outlook is much better if you detect cancer in an early stage. If you menstruate, the best time to do BSE is 2 or 3 days after your period ends, when your breasts are least likely to be tender or swollen. If you no longer menstruate, pick a day such as the first day of the month, to remind yourself it is time to do BSE. Here is one way to do BSE: Stand before a mirror. Inspect both breasts for anything unusual such as any discharge from the nipples or puckering, dimpling, or scaling of the skin. The next two steps are designed to emphasize any change in the shape or contour of your breasts. As you do them, you should be able to feel your chest muscles tighten. Watching closely in the mirror, clasp your hands behind your head and press your hands forward. Next, press your hands firmly on your hips and bow slightly toward your mirror as you pull your shoulders and elbows forward.
7 Some women do the next part of the exam in the shower because fingers glide over soapy skin, making it easy to concentrate on the texture underneath. Raise your left arm. Use three or four fingers of your right hand to explore your left breast firmly, carefully, and thoroughly. Beginning at the outer edge, press the flat part of your fingers in small circles, moving the circles slowly around the breast. Gradually work toward the nipple. Be sure to cover the entire breast. Pay special attention to the area between the breast and the underarm, including the underarm itself. Feel for any unusual lump or mass under the skin. Gently squeeze the nipple and look for a discharge. (If you have any discharge during the month - whether or not it is during BSE - see your doctor.) Repeat steps 4 and 5 on your right breast. Steps 4 and 5 should be repeated lying down. Lie flat on your back with your left arm over your head and a pillow or folded towel under your left shoulder. This position flattens the breast and makes it easier to examine. Use the same circular motion described earlier. Repeat the exam on your right breast. The earliest sign of breast cancer is a single painless firm to hard lump. The edges of the lump are not sharp and stretch out gradually into the surrounding tissue if felt between the fingers. Erosion of the nipple or discharge may indicate an early cancer. Late signs of cancer include an inability to move the lump which appears attached to the skin or to the deeper breast tissue. There may be puckering of the skin above the cancer or retraction of the nipple. Eventually there will be breast enlargement, hardness, inflammation and pain. Almost half of breast cancers begin in the nipple or outer and upper quarter of the breast. The earlier a cancer of the breast is discovered, the better the chances of a complete recovery.
Mammography AND CLINICAL BREAST EXAMS. joytolife.org WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT BREAST CANCER HOW TO DO A BREAST SELF-EXAM EARLY DETECTION SAVES LIVES
 Mammography AND CLINICAL BREAST EXAMS WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT BREAST CANCER HOW TO DO A BREAST SELF-EXAM joytolife.org EARLY DETECTION SAVES LIVES As a woman, you face many special concerns that call
Mammography AND CLINICAL BREAST EXAMS WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT BREAST CANCER HOW TO DO A BREAST SELF-EXAM joytolife.org EARLY DETECTION SAVES LIVES As a woman, you face many special concerns that call
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast. September 2012
 Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Feeling Your Way To Healthy Breast. Lisa Barnes, BSN, RN Ruth Fay,B.A.,M.B.A.,RN Mary Grady, BSN, RN Margaret Richmond, MA, RN
 Feeling Your Way To Healthy Breast Lisa Barnes, BSN, RN Ruth Fay,B.A.,M.B.A.,RN Mary Grady, BSN, RN Margaret Richmond, MA, RN WHAT ARE MY BREASTS MADE OF? A breast is made of three main parts: glands,
Feeling Your Way To Healthy Breast Lisa Barnes, BSN, RN Ruth Fay,B.A.,M.B.A.,RN Mary Grady, BSN, RN Margaret Richmond, MA, RN WHAT ARE MY BREASTS MADE OF? A breast is made of three main parts: glands,
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate Patient information: Breast cancer screening (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is breast cancer screening? Breast
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2013 UpToDate Patient information: Breast cancer screening (The Basics) Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate What is breast cancer screening? Breast
Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer
 Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer There was no history in my family. But the test was positive and it was breast cancer. I was so shocked, I couldn t believe it. ~ Colette
Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer Reduce Your Risk of Breast Cancer There was no history in my family. But the test was positive and it was breast cancer. I was so shocked, I couldn t believe it. ~ Colette
Breast Cancer Screening
 Breast Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team October Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Breast Cancer Screening The American Cancer Society and Congregational Health Ministry Team October Module To access this module via the Web, visit www.cancer.org and type in congregational health ministry
Mammograms & Breast Health. An Information Guide for Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mammograms & Breast Health An Information Guide for Women This booklet was developed by the Centers for Disease Control
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mammograms & Breast Health An Information Guide for Women This booklet was developed by the Centers for Disease Control
Breast cancer affects one in eight Australian women. It is the most common cancer for Victorian women, with almost 3,700 diagnoses in 2012.
 Breast cancer Summary Breast cancer affects one in nine Australian women. It is important for all women to get to know the normal look and feel of their breasts. Although most breast changes aren t caused
Breast cancer Summary Breast cancer affects one in nine Australian women. It is important for all women to get to know the normal look and feel of their breasts. Although most breast changes aren t caused
Nicole Kounalakis, MD
 Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Management Nicole Kounalakis, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery Goal of Breast Evaluation The goal of breast evaluation is to classify findings as: normal physiologic variations
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
BREAST CANCER. How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk. cruk.org
 BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader. Two years ago, I was working as a bedside nurse. One of my colleagues felt
 Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Ali A. Kader, S. (2010). Breast cancer awareness for women and men. UCQ Nursing Journal of Academic Writing, Winter 2010, 70 76. BREAST CANCER AWARENESS FOR WOMEN AND MEN by Samar Ali A. Kader Two years
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Breast Cancer. Presentation by Dr Mafunga
 Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Breast Cancer Presentation by Dr Mafunga Breast cancer in the UK Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women. Around 1 in 9 women will develop breast cancer It most commonly affects women over
Breast cancer in the family
 Birmingham Women's NHS Foundation Trust Breast cancer in the family Information for women with a slightly increased risk of breast cancer This is a no smoking hospital Breast cancer in the family what
Birmingham Women's NHS Foundation Trust Breast cancer in the family Information for women with a slightly increased risk of breast cancer This is a no smoking hospital Breast cancer in the family what
PART TWO: DIAGNOSING BREAST CANCER
 PART TWO: DIAGNOSING BREAST CANCER What is Breast Cancer? Normal cells can turn into cancer because of genetic inheritance or repeated exposure to a cancer-related substance in the environment, such as
PART TWO: DIAGNOSING BREAST CANCER What is Breast Cancer? Normal cells can turn into cancer because of genetic inheritance or repeated exposure to a cancer-related substance in the environment, such as
Guide to Understanding Breast Cancer
 An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
An estimated 220,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, and one in eight will be diagnosed during their lifetime. While breast cancer is a serious disease, most patients
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
DIAGNOSIS: DCIS Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) This factsheet gives information on an early form of breast cancer called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It explains what it is, how your breast is made
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy
 Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Breast Cancer Toolkit. Marion DePuit, MSN, Faith Community Nurse. Leslie Brown, BA, Community Advocate 9/2014. Understanding Breast Cancer
 GENERAL: Breast Cancer Toolkit Marion DePuit, MSN, Faith Community Nurse Leslie Brown, BA, Community Advocate 9/2014 Understanding Breast Cancer (Adapted from the American Cancer Society and Breast Cancer.org)
GENERAL: Breast Cancer Toolkit Marion DePuit, MSN, Faith Community Nurse Leslie Brown, BA, Community Advocate 9/2014 Understanding Breast Cancer (Adapted from the American Cancer Society and Breast Cancer.org)
Breast Imaging Made Brief and Simple. Jane Clayton MD Associate Professor Department of Radiology LSUHSC New Orleans, LA
 Breast Imaging Made Brief and Simple Jane Clayton MD Associate Professor Department of Radiology LSUHSC New Orleans, LA What women are referred for breast imaging? Two groups of women are referred for
Breast Imaging Made Brief and Simple Jane Clayton MD Associate Professor Department of Radiology LSUHSC New Orleans, LA What women are referred for breast imaging? Two groups of women are referred for
Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Breast Cancer Awareness Month Issue 12 October 2015 In this Issue 2 Cancer Statistics in Kenya 3 What is Breast Cancer? 4 Symptoms of Breast
Aon Kenya Insurance Brokers Ltd Aon Hewitt Healthcare Division Breast Cancer Awareness Month Issue 12 October 2015 In this Issue 2 Cancer Statistics in Kenya 3 What is Breast Cancer? 4 Symptoms of Breast
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Oxford Regional Genetic Department Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer What
APGO Clinical Skills Curriculum. The Breast Exam
 APGO Clinical Skills Curriculum The Breast Exam Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO) Undergraduate Medical Education Committee 2008 The Breast Exam Table of Contents Intended Learning
APGO Clinical Skills Curriculum The Breast Exam Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO) Undergraduate Medical Education Committee 2008 The Breast Exam Table of Contents Intended Learning
Breast Augmentation. If you are dissatisfied with your breast size, augmentation surgery is a choice to consider. Breast augmentation can:
 Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass. Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003
 Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003 Common Presentations of Breast Disease Breast Mass Abnormal
Evaluation and Management of the Breast Mass Gary Dunnington,, M.D. Department of Surgery Internal Medicine Ambulatory Conference December 4, 2003 Common Presentations of Breast Disease Breast Mass Abnormal
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Infrared Thermography Not a Useful Breast Cancer Screening Tool
 Contact: Jeanne-Marie Phillips Sharon Grutman HealthFlash Marketing The American Society of Breast Surgeons 203-977-3333 877-992-5470 Infrared Thermography Not a Useful Breast Cancer Screening Tool Mammography
Contact: Jeanne-Marie Phillips Sharon Grutman HealthFlash Marketing The American Society of Breast Surgeons 203-977-3333 877-992-5470 Infrared Thermography Not a Useful Breast Cancer Screening Tool Mammography
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Patient information leaflet
 BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
Having a Breast Biopsy. A Guide for Women and Their Families
 Having a Breast Biopsy A Guide for Women and Their Families Fast Facts n n Most women who have a breast biopsy do not have breast cancer. About 4 out of every 5 breast biopsies are negative for cancer.
Having a Breast Biopsy A Guide for Women and Their Families Fast Facts n n Most women who have a breast biopsy do not have breast cancer. About 4 out of every 5 breast biopsies are negative for cancer.
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Tell a Friend, Save a Life: The Breast Cancer Prevention & Detection Kit
 Tell a Friend, Save a Life: The Breast Cancer Prevention & Detection Kit About the Tell a Friend, Save a Life Breast Cancer Prevention and Detection Kit Breast cancer affects us all, because we all have
Tell a Friend, Save a Life: The Breast Cancer Prevention & Detection Kit About the Tell a Friend, Save a Life Breast Cancer Prevention and Detection Kit Breast cancer affects us all, because we all have
Understanding. Breast Changes. National Cancer Institute. A Health Guide for Women. National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute Understanding Breast Changes A Health Guide for Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health It was easier to talk with my doctor after reading
National Cancer Institute Understanding Breast Changes A Health Guide for Women U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health It was easier to talk with my doctor after reading
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Michael A. Boss, M.D. FMH Plastic, Reconstructive und Aesthetic Surgery
 Michael A. Boss, M.D. FMH Plastic, Reconstructive und Aesthetic Surgery Boss Aesthetic Center Schauplatzgasse 23 CH-3011 Bern Switzerland +41 31 311 7691 www.aesthetic-center.com B r e a s t A u g m e
Michael A. Boss, M.D. FMH Plastic, Reconstructive und Aesthetic Surgery Boss Aesthetic Center Schauplatzgasse 23 CH-3011 Bern Switzerland +41 31 311 7691 www.aesthetic-center.com B r e a s t A u g m e
Breast Pain. National Cancer Helpline 1800 200 700
 General information Breast Pain Breast Pain This factsheet gives information on breast pain in women. It explains the different types and causes of breast pain and how it can be diagnosed and treated.
General information Breast Pain Breast Pain This factsheet gives information on breast pain in women. It explains the different types and causes of breast pain and how it can be diagnosed and treated.
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Breast Cancer. Your right to know. Illinois Department of Public Health
 Breast Cancer Your right to know Illinois Department of Public Health The information contained in this brochure regarding recommendations for the early detection, diagnosis and treatment of breast disease
Breast Cancer Your right to know Illinois Department of Public Health The information contained in this brochure regarding recommendations for the early detection, diagnosis and treatment of breast disease
Common Breast Complaints:
 : Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
: Palpable mass Abnormal mammogram with normal physical exam Vague thickening or nodularity Nipple Discharge Breast pain Breast infection or inflammation The physician s goal is to determine whether the
Breast Implants: Local Complications and Adverse Outcomes
 Breast Implants: Local Complications and Adverse Outcomes This booklet highlights the most common problems associated with silicone gel-filled and saline-filled breast implants: those that occur in the
Breast Implants: Local Complications and Adverse Outcomes This booklet highlights the most common problems associated with silicone gel-filled and saline-filled breast implants: those that occur in the
A Guide to Breast Screening
 A Guide to Breast Screening Contents Information for Carers, Family, Friends and Medical Guardians of Care Introduction Information on BreastCheck Information on Attending Screening The Screening Story
A Guide to Breast Screening Contents Information for Carers, Family, Friends and Medical Guardians of Care Introduction Information on BreastCheck Information on Attending Screening The Screening Story
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer
 Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
Guideline for the Imaging of Patients Presenting with Breast Symptoms incorporating the guideline for the use of MRI in breast cancer Version History Version Date Summary of Change/Process 0.1 09.01.11
What You Need to Know Before Treatment About: Breast Cancer
 What You Need to Know Before Treatment About: Breast Cancer Publication MDCH-1234 Revised: September 2008 Authority: Public Act 368 of 1978, as amended by Public Act 195 of 1986 and Public Act 15 of 1989.
What You Need to Know Before Treatment About: Breast Cancer Publication MDCH-1234 Revised: September 2008 Authority: Public Act 368 of 1978, as amended by Public Act 195 of 1986 and Public Act 15 of 1989.
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant
 Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Phyllodes tumours: borderline malignant and malignant This booklet is for people who would like more information on borderline malignant or malignant phyllodes tumours. It describes what they are, the
Invasive lobular breast cancer
 Invasive lobular breast cancer This booklet is about invasive lobular breast cancer. It describes what invasive lobular breast cancer is, the symptoms, how it s diagnosed and possible treatments. Diagnosed
Invasive lobular breast cancer This booklet is about invasive lobular breast cancer. It describes what invasive lobular breast cancer is, the symptoms, how it s diagnosed and possible treatments. Diagnosed
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
 Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Understanding Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer A WOMAN S GUIDE This brochure is made possible through partnership support from Project Hope for Ovarian Cancer Research and Education. Project HOPE FOR OVARIAN
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Early Prostate Cancer: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Early Prostate Cancer:
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are the
NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are the
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer begins in our cells. Cells are the building blocks of our tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body.
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Prevention and Screening for Breast Cancer
 Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Prevention and Screening for Breast Cancer Information for women and their families 1 What is breast cancer? The female breast is mainly consisted
Cancer Expert Working Group on Cancer Prevention and Screening Prevention and Screening for Breast Cancer Information for women and their families 1 What is breast cancer? The female breast is mainly consisted
Questions and answers on breast cancer A guide for women and their physicians
 Canadian Breast Cancer Initiative Questions and answers on breast cancer A guide for women and their physicians 2nd edition Based on The Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Care and Treatment
Canadian Breast Cancer Initiative Questions and answers on breast cancer A guide for women and their physicians 2nd edition Based on The Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Care and Treatment
D. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 ACR BI-RADS ATLAS D. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Under MQSA, is it necessary to include a numeric assessment code (i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6) in addition to the assessment category in all mammography
ACR BI-RADS ATLAS D. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Under MQSA, is it necessary to include a numeric assessment code (i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6) in addition to the assessment category in all mammography
There are many different types of cancer and sometimes cancer is diagnosed when in fact you are not suffering from the disease at all.
 About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
About Cancer Cancer is a disease where there is a disturbance in the normal pattern of cell replacement. The cells mutate and become abnormal or grow uncontrollably. Not all tumours are cancerous (i.e.
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
A Girlfriend s Guide. Breast Augmentation WWW.RPSMD.COM
 A Girlfriend s Guide to Breast Augmentation 1 Your Breast Augmentation Surgery: This is an important decision that you are considering. Have you always thought about increasing the size of your breasts,
A Girlfriend s Guide to Breast Augmentation 1 Your Breast Augmentation Surgery: This is an important decision that you are considering. Have you always thought about increasing the size of your breasts,
BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK
 BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK BRCA1 & BRCA2 What is hereditary breast cancer? Cancer is unfortunately very common, with 1 in 3 people developing cancer at some point in their lifetime. Breast cancer occurs
BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK BRCA1 & BRCA2 What is hereditary breast cancer? Cancer is unfortunately very common, with 1 in 3 people developing cancer at some point in their lifetime. Breast cancer occurs
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
The best treatment Your guide to breast cancer treatment in England and Wales
 The best treatment Your guide to breast cancer treatment in England and Wales If you are looking for information on the treatment of secondary breast cancer (also known as advanced or metastatic breast
The best treatment Your guide to breast cancer treatment in England and Wales If you are looking for information on the treatment of secondary breast cancer (also known as advanced or metastatic breast
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
CONTENTS: WHAT S IN THIS BOOKLET
 Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
Q Questions & A & Answers About Your Prostate Having a biopsy test to find out if you may have prostate cancer can bring up a lot of questions. This booklet will help answer those questions. CONTENTS:
BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
 BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre December 2014 Contents About this booklet 1 Your First Oncology Consultation
BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Cancer Care Pathways Directorate Tailored Information in Cancer Care (TICC) Sir Anthony Mamo Oncology Centre December 2014 Contents About this booklet 1 Your First Oncology Consultation
Medicare Part B. Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests
 Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests This article from Medicare B News Issue 223 dated October 21, 2005 is being updated and reprinted to ensure that the Noridian Administrative
Mammograms - Updated Billing Guide for Screening and Diagnostic Tests This article from Medicare B News Issue 223 dated October 21, 2005 is being updated and reprinted to ensure that the Noridian Administrative
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer
 A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
A Patient s Guide Follow-Up Care for Breast Cancer Recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) is a nonprofit organization which represents
Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions
 Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions Q: What is the thyroid gland? A: The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It is one of the
Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions Q: What is the thyroid gland? A: The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It is one of the
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer?
 Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Are You at Risk for Ovarian Cancer? A Woman s Guide Read this brochure to learn more about ovarian cancer symptoms, risk factors and what you can do to reduce your risk. ALL WOMEN HAVE SOME RISK OF OVARIAN
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body
 How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
How to Do Self Lymphatic Massage on your Upper Body UHN For patients who were treated for breast cancer on one side of their body. For example: Lumpectomy Mastectomy Lymph node removal from an underarm
Test Your Breast Cancer Knowledge
 Test Your Breast Cancer Knowledge Regular exams and a good understanding can help defend against breast cancer, yet many women hold outdated ideas about their own breast cancer risk. Take this quiz to
Test Your Breast Cancer Knowledge Regular exams and a good understanding can help defend against breast cancer, yet many women hold outdated ideas about their own breast cancer risk. Take this quiz to
A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain
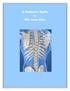 A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain Anatomy Where are the rib joints? Your rib cage is made up of twelve pairs of ribs. The ribs attach to the spine in the back, and to the breastbone in the front. The
A Patient s Guide to Rib Joint Pain Anatomy Where are the rib joints? Your rib cage is made up of twelve pairs of ribs. The ribs attach to the spine in the back, and to the breastbone in the front. The
Prostate Cancer Guide. A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
Prostate Cancer Guide A resource to help answer your questions about prostate cancer Thank you for downloading this guide to prostate cancer treatment. We know that all the information provided online
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet
 U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
U.K. Familial Ovarian Cancer Screening Study (UK FOCSS) Phase 2 Patient Information Sheet 1. Invitation You are being invited to take part in a research study. Before you decide it is important for you
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Inflammatory breast cancer
 april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
april 2007 information about Inflammatory breast cancer What is inflammatory breast cancer? Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and rapidly growing form of breast cancer. Unlike other breast cancers which
Allegheny Health Network. Breast Care Center
 Allegheny Health Network Breast Care Center Breast health is a top priority of every woman. At Allegheny Health Network, you ll find a full array of breast care services designed with your needs in mind.
Allegheny Health Network Breast Care Center Breast health is a top priority of every woman. At Allegheny Health Network, you ll find a full array of breast care services designed with your needs in mind.
Goiter. This reference summary explains goiters. It covers symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
Goiter Introduction The thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck. If the gland becomes abnormally enlarged, it is called a goiter. Goiters usually do not cause pain. But a large goiter could cause
