Increase in Vertebral Body Height after Vertebroplasty
|
|
|
- Jeremy Harper
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23: , February 2003 Increase in Vertebral Body Height after Vertebroplasty Akio Hiwatashi, Toshio Moritani, Yuji Numaguchi, and Per-Lennart Westesson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: During clinical work, we have seen increases in vertebral body height associated with vertebroplasty, but our literature search revealed no reports as to how often and to what degree those increases occur. The purpose of this study was to document the frequency and degree of changes in vertebral body height after vertebroplasty. METHODS: The heights of 85 vertebral bodies in 37 patients were measured before and after vertebroplasty. In addition, one adjacent vertebral body was measured in each patient as a control. Twenty-six patients had compression fractures in the thoracic spine, and 24 patients had compression fractures in the lumbar spine. Vertebroplasty was performed with a bilateral transpedicular approach by injecting polymethylmethacrylate, under biplane fluoroscopic control. Measurements were performed on preoperative MR images and on postoperative CT sagittal reformations. Anterior, central, and posterior vertebral body height measurements were obtained in the midsagittal plane. RESULTS: The average increase in vertebral body height was 2.5 mm anteriorly, 2.7 mm centrally, and 1.4 mm posteriorly. Thirteen of 85 treated vertebrae remained unchanged. All control vertebral bodies also remained unchanged. CONCLUSION: Vertebral body height often increases during vertebroplasty. The clinical significance of increasing vertebral body height is unknown. Percutaneous vertebroplasty was described in 1987 (1) for the treatment of aggressive vertebral hemangioma. It was later applied to osteolytic metastasis and osteoporotic compression fractures (2 10). The goal of percutaneous vertebroplasty is to alleviate spinal pain by stabilizing the fracture and strengthening the bone of vertebrae through the percutaneous injection of cement into the vertebral body. Although our literature search revealed no randomized studies, the procedure has been proved to be safe and effective in clinical work, and multiple case studies have documented an approximately 80% success rate for pain relief (1 10). During the clinical use of vertebroplasty, we have seen an increase in the vertebral body height in some patients as the cement is being injected. Our investigation sought to determine the frequency of increases and degree of increase in vertebral body height during vertebroplasty. Received July 3, 2002; accepted after revision September 20. From the Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY Address reprint requests to Akio Hiwatashi, M.D., Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of Rochester Medical Center, 601 Elmwood Ave, Box 648, Rochester, NY American Society of Neuroradiology Methods Patients We performed vertebroplasty in 37 patients (16 men and 21 women; age range, years; mean age, 78 years) because of painful compression fractures. The causes of fractures were osteoporosis (30 patients), metastases (three patients), multiple myeloma (two patients), and lymphoma and myelodysplasia (one patient each). A total of 85 vertebral bodies were treated in these 37 patients. Most of the fractured vertebrae were located around the thoracolumbar junction. The locations and numbers of the treated vertebrae were as follows: T4 (n 1), T5 (n 1), T6 (n 4), T7 (n 4), T8 (n 5), T9 (n 4), T10 (n 9), T11 (n 11), T12 (n 7), L1 (n 12), L2 (n 10), L3 (n 9), L4 (n 6), and L5 (n 2). Vertebroplasty Technique Vertebroplasty was performed through a bipedicular approach by using 13-gauge bone biopsy needles (Osteo-site; Cook, Bloomington, IN) placed into the anterior third of the vertebral body. The procedure was performed under biplane fluoroscopic control with use of moderate conscious sedation and local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. Balloon dilation before cement injection as in kyphoplasty (11) was not performed. Once the two needles were placed in the vertebral body (Fig 1A), the liquid and powder polymethylmethacrylate (Cranioplasty; Codman, Raynham, MA) was mixed with 12 g of barium sulfate (Biotrace; Bryan, Woburn, MA) and 1.2 g of tobramycin (Nebcin; Eli Lilly, Indianapolis, IN) to a doughlike consistency. The cement was thicker than toothpaste and relatively hard to inject through the 13-gauge needle by using the 1-ml syringe. 185
2 186 HIWATASHI AJNR: 23, February 2003 FIG year-old man with osteoporosis. A, Preoperative lateral radiograph of the lumbar spine shows compression fracture of L4 with associated anterior wedging deformity. The transpedicular bone biopsy needle is in place. B, Postoperative lateral radiograph shows considerable increase in vertebral body height, especially in the anterior (3 mm) and central (4 mm) portions. C and D, Schematic drawings of the preoperative (C) and postoperative (D) lateral radiographs. Kyphosis is improved from 25 to 28. Under biplane fluoroscopic guidance (primarily lateral), the cement was injected alternatively through the left and right needles. The injection continued until the vertebral body was filled toward the posterior 20% of the vertebral body (Fig 1B and D) or there was significant leakage. If leakage was suspected, we stopped the injection temporarily and continued when there was no significant leakage into the paraspinal or disk area. If there was epidural extravasation, the injection was stopped and not attempted again. The patient was lying prone on the angiographic table during the injection, but no manipulations of the spinal column were performed before or during the procedure. After cement injection, the patient remained prone on the angiographic table until the cement was completely hard (approximately 15 minutes) and was then transferred to a regular bed. The patient remained in bed until CT had been performed. Thereafter, the patients were discharged to home as tolerated; this usually occurred approximately 2 3 hours after the procedure. Imaging All patients underwent preoperative MR imaging (Signa; GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI) by using precontrast sagittal T1-weighted (600/14/1 [TR/TE/excitations]), fat-suppressed T2-weighted (4000/105/2), and contrast material enhanced (Omniscan; Nycomed, Princeton, NJ) sagittal fat-suppressed T1-weighted (600/14/1) imaging. Imaging matrix was , field of view was cm, and section thickness was 3 mm with intersection gap of 0.2 mm. Immediately after the procedure, CT was performed (Lightspeed; GE Medical Systems) by using a section thickness of 1.25 mm with 0.6-mm overlap. Two-dimensional sagittal reformation of the CT data was performed. If there was motion during scanning, CT was repeated. Measurement The vertical height of the vertebral body was measured on the preoperative MR images and on the postoperative CT scans (Fig 2A-E). Measurements were performed of the anterior, central, and posterior vertebral height in the midsagittal plane by using a magnified image to the nearest 0.1 mm on a distant console (Advantage Windows 4.0; GE Medical Systems). Differences within 1 mm were considered unchanged. One untreated vertebral body adjacent to the treated vertebral body was measured as a control in each patient to evaluate the validity of our measurements. Statistical Analysis The statistical significance of changes in vertebral body height was evaluated with the Student s paired t test in which a P value of less than.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
3 AJNR: 23, February 2003 POSTVERTEBROPLASTY CHANGES 187 FIG year-old woman with osteoporosis. A, Preoperative sagittal T1-weighted MR image shows compression fracture of L2 vertebral body. The inferior aspect of L1 vertebral body shows hypointensity, suggesting edema due to compression. B, Preoperative sagittal T2-weighted MR image shows compression fracture of L2 vertebral body. C, Postoperative CT sagittal reformation shows increased height of L2 vertebral body, especially in the anterior and central portions. D and E, Schematic drawings of preoperative (D) and postoperative (E) measurements of the anterior (A), central (C), and posterior (P) vertebral body heights. The vertebral body height of L2 increases 7 mm anteriorly and 9 mm centrally, whereas the posterior vertebral body height of L2 remains unchanged. The vertebral body height of L1 is also unchanged. Results The vertebral body height increased in 72 of 85 treated vertebral bodies. Thirty-three vertebrae (25 patients) experienced minimal height increase (1 3 mm), whereas 39 vertebrae (24 patients) increased more than 3 mm. The average increase in vertebral body height was 2.2 mm, with a range of 1 15 mm. The average preoperative anterior vertebral body height was 18 mm and increased to 20 mm after the procedure (P.006). The average increase in ante-
4 188 HIWATASHI AJNR: 23, February 2003 rior vertebral body height was 2.5 mm (range, 1 14 mm). The average preoperative central vertebral body height was 13 mm and increased to 16 mm (P.001). The average increase in central vertebral body height was 2.7 mm (range, 1 15 mm). The average preoperative posterior vertebral body height was 21 mm and increased to 23 mm (P.048). The average increase in posterior vertebral body height was 1.4 mm (range, 1 9 mm). The anterior portion of vertebral body height increased in 55 vertebral bodies and remained unchanged in 30. The central portion of vertebral body height increased in 59 vertebral bodies and remained unchanged in 26. The posterior portion of vertebral body height increased in 40 vertebral bodies and remained unchanged in 45. In patients with osteoporosis, the average increase in vertebral body height was 2.7 mm anteriorly, 2.8 mm centrally, and 1.4 mm posteriorly. In patients with neoplasia, the average increase in vertebral body height was 1.6 mm anteriorly, 1.9 mm centrally, and 1.1 mm posteriorly. However, we saw no statistical difference in height increase between these two groups of patients. There was no instance in which we could appreciate a decreased vertebral body height. In no control instance was there a difference larger than 0.6 mm. No significant differences were noted in height of the anterior (P.900), central (P.920), and posterior (P.923) control vertebral heights. The average pre- and postoperative vertebral body heights were the same: 24 mm anteriorly, 22 mm centrally, and 25 mm posteriorly. The average duration between the preoperative MR images and postoperative CT scans was 14 days (range, days). All CT scans were obtained within 4 hours of completion of procedures. No patients with a large increase in vertebral body height showed fluid- or gas-filled clefts on preoperative MR images. The average amount of injected bone cement was 7 ml (range, 2 14 ml). There were no noteworthy complications. Discussion The results of this study demonstrate that vertebroplasty can increase the height of the treated vertebral body. The average increase in height was 2.2 mm (range, 1 15 mm). This confirms our clinical impression that vertebral height can increase during the procedure. Although the results of one study suggest that vertebral body height increases during kyphoplasty (11), we are not aware of any studies of vertebral body heights after vertebroplasty. The mechanism of the increase in vertebral body height is probably related to the injection of the high-viscosity bone cement under pressure. In a few patients, the increase in vertebral body height was so obvious that we could observe it as the cement was injected during the procedure (Fig 1). This seems to occur in patients whose bony walls of the vertebral bodies were intact, thus preventing leakage. Kyphoplasty (11 14) is a variant of vertebroplasty wherein the vertebral body is pretreated with an expandable balloon to create a space where the cement can be injected. The intention and purpose of kyphoplasty is to increase vertebral body height and to avoid injecting cement under pressure. The lack of pressure during the injection of the cement has been thought to be a safety feature to contain the cement in the precreated cavity, rather than injecting it under high pressure as in vertebroplasty. In our clinical experience, the cement injected under pressure tends to spread into preexistent cracks and spaces within the vertebral body. In this way, we believe that the cement fills the available space in the vertebral body and thereby has a better chance of stabilizing a vertebral body fracture than to fill a precreated central space. To our knowledge, no comparison has been made between vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty as to the effectiveness in relieving pain. It may, however, be possible that vertebroplasty with its more diffuse spreading of cement within the fractured vertebral body has a greater chance of stabilizing the fracture than does cement injection into a precreated space in kyphoplasty. This speculation needs to be documented with further studies. We measured the vertebral body height on the preoperative MR images and compared it with the height on postoperative CT scans. This different methodology was prompted by the availability of images. However, measuring an adjacent untreated vertebral body in each patient assured us that the measurements were accurate and comparable. In no control instance was there a difference larger than 0.6 mm. Actually, the measurements were within 0.2 mm in most patients. We were very careful not to accept CT scans with motion since this would make the sagittal reformations unreliable for vertical measurement. The stability of our control measurements adheres to the accuracy of the measurements. Conclusion Vertebroplasty increased vertebral body height in 28 of 37 patients with an average of about 2 mm. Although the clinical significance of restoring some of the vertebral body height is unknown, it may explain the improved stature and amelioration of pain that many patients experience after the procedure. Acknowledgment The authors thank Margaret Kowaluk and Theresa Kubera for images. References 1. Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty [in French]. Neurochiurgie 1987;33: Cortet B, Cotten A, Boutry N, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteolytic metastases or multiple myeloma. Rev Rhum Engl Ed 1997;64: Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiology 1996;200:
5 AJNR: 23, February 2003 POSTVERTEBROPLASTY CHANGES Kaemmerlen P, Thiesse P, Bouvard H, Biron P, Mornex F, Jonas P. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of metastases: technic and results [in French]. J Radiol 1989;70: Cotten A, Boutry N, Cortet B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: state of the art. Radiographics 1998;18: Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Dion JE. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997;18: Cortet B, Cotten A, Boutry N, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: an open prospective study. J Rheumatol 1999;26: Cyteval C, Sarrabere MP, Roux JO, et al. Acute osteoporotic vertebral collapse: open study on percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement in 20 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999;173: Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, McCann RM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine 2000;25: Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME, Deramond H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22: Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Duncan TD, Garfin SR, Wong WH. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures. Clin Imaging 2002;26: Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Deramond H, Jasper LE. An ex vivo biomechanical evaluation of a hydroxyapatite for use with kyphoplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22: Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, Bell G. Initial outcome and efficacy of kyphoplasty in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 2001;26: Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 2001;26:
Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures
 Journal of Clinical Imaging 26 (2002) 1 5 Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures Daphne J. Theodorou a, Stavroula J. Theodorou
Journal of Clinical Imaging 26 (2002) 1 5 Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures Daphne J. Theodorou a, Stavroula J. Theodorou
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty
 Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 10/26/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 10/26/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Despite recent advances in medical
 RADIOLOGIC DECISION-MAKING Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: New Treatment for Vertebral Compression Fractures THOMAS A. PREDEY, M.D., LUKE E. SEWALL, M.D., and STEVEN J. SMITH, M.D. La Grange Memorial Hospital,
RADIOLOGIC DECISION-MAKING Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: New Treatment for Vertebral Compression Fractures THOMAS A. PREDEY, M.D., LUKE E. SEWALL, M.D., and STEVEN J. SMITH, M.D. La Grange Memorial Hospital,
New Technologies in Spine
 New Technologies in Spine Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Compression Fractures Steven R. Garfin, MD,* Hansen A. Yuan, MD, and Mark A. Reiley, MD SPINE Volume 26,
New Technologies in Spine Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Compression Fractures Steven R. Garfin, MD,* Hansen A. Yuan, MD, and Mark A. Reiley, MD SPINE Volume 26,
Minimally Invasive Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
 Original Article 261 Minimally Invasive Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Shang-Won Yu, MD; Tsai-Sheng Fu, MD; Po-Liang Lai, MD; Wen-Jer Chen,
Original Article 261 Minimally Invasive Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Shang-Won Yu, MD; Tsai-Sheng Fu, MD; Po-Liang Lai, MD; Wen-Jer Chen,
Uniextrapedicular Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Thoracic Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
 Uniextrapedicular Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Thoracic Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Zhaohui Ge, MD; Rong Ma, MD; Zhen Chen, MD; Huiyong Zhang, MD; Huiqiang Ding, MD; Siming Liang, MD; Zhigang
Uniextrapedicular Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Thoracic Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Zhaohui Ge, MD; Rong Ma, MD; Zhen Chen, MD; Huiyong Zhang, MD; Huiqiang Ding, MD; Siming Liang, MD; Zhigang
Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty J. Kevin McGraw, MD, John Cardella, MD, John Dean Barr, MD, John M. Mathis, MD, Orestes Sanchez, MD, Marc
Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty J. Kevin McGraw, MD, John Cardella, MD, John Dean Barr, MD, John M. Mathis, MD, Orestes Sanchez, MD, Marc
OVCF of the thoracic and lumbar spine can be a source of
 Published August 26, 2010 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2223 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND
Published August 26, 2010 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2223 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Preliminary Report
 Original Article 306 Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Preliminary Report Jyi-Feng Chen, MD; Shih-Tseng Lee, MD; Tai-Ngar Lui, MD; Chieh-Tsai
Original Article 306 Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Preliminary Report Jyi-Feng Chen, MD; Shih-Tseng Lee, MD; Tai-Ngar Lui, MD; Chieh-Tsai
Percutaneous vertebroplasty, initially conceived and developed
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. McDonald A.T. Trout L.A. Gray A. Dispenzieri K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty in Multiple Myeloma: Outcomes in a Large Patient Series BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Despite the
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. McDonald A.T. Trout L.A. Gray A. Dispenzieri K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty in Multiple Myeloma: Outcomes in a Large Patient Series BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Despite the
Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures
 Yu et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures Chia-Wei Yu, Ming-Kai Hsieh, Lih-Huei Chen *, Chi-Chien
Yu et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures Chia-Wei Yu, Ming-Kai Hsieh, Lih-Huei Chen *, Chi-Chien
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Wilfred C. G. Peh 1,2 Michael S. Gelbart 2 Louis. Gilula 2 Dallas D. Peck 2,3 Received January 17, 2002; accepted after revision October 22, 2002. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General
Wilfred C. G. Peh 1,2 Michael S. Gelbart 2 Louis. Gilula 2 Dallas D. Peck 2,3 Received January 17, 2002; accepted after revision October 22, 2002. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General
MRI and Bone Scan Imaging in the Preoperative Evaluation of Painful Vertebral Fractures Treated with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
 MRI and Bone Scan Imaging in the Preoperative Evaluation of Painful Vertebral Fractures Treated with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty SALVATORE MASALA 1, ORAZIO SCHILLACI 2, FRANCESCO MASSARI 1, ROBERTA
MRI and Bone Scan Imaging in the Preoperative Evaluation of Painful Vertebral Fractures Treated with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty SALVATORE MASALA 1, ORAZIO SCHILLACI 2, FRANCESCO MASSARI 1, ROBERTA
Osteoporosis and Vertebral Compression (Spinal) Fractures Fact Sheet
 Osteoporosis and Vertebral Compression (Spinal) Fractures Fact Sheet About Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is estimated to affect 200 million women worldwide. 1 Worldwide, osteoporosis causes more than nine
Osteoporosis and Vertebral Compression (Spinal) Fractures Fact Sheet About Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is estimated to affect 200 million women worldwide. 1 Worldwide, osteoporosis causes more than nine
Comparing Pain Reduction Following Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:583-590 ISSN 1533-3159 Meta-analysis Comparing Pain Reduction Following Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures J. Brian Gill, MD, Mark Kuper,
Pain Physician 2007; 10:583-590 ISSN 1533-3159 Meta-analysis Comparing Pain Reduction Following Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures J. Brian Gill, MD, Mark Kuper,
visualized. The correct level is then identified again. With the use of a microscope and
 SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
SURGERY FOR SPINAL STENOSIS Laminectomy A one inch (or longer for extensive stenosis) incision is made in the middle of the back over the effected region of the spine. The muscles over the bone are moved
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary
 X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
Percutaneous Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Percutaneous Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures A Meta-analysis of Complications Michael J. Lee, MD, Mark Dumonski, MD, Patrick Cahill, MD, Tom Stanley, MD, Daniel Park, MD, and Kern Singh, MD
Percutaneous Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures A Meta-analysis of Complications Michael J. Lee, MD, Mark Dumonski, MD, Patrick Cahill, MD, Tom Stanley, MD, Daniel Park, MD, and Kern Singh, MD
Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures
 Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Vesselplasty: A New Technical Approach to Treat Symptomatic Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Flors et al. Vesselplasty to Treat Symptomatic VCFs Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Vesselplasty: A New Technical Approach
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Flors et al. Vesselplasty to Treat Symptomatic VCFs Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Vesselplasty: A New Technical Approach
Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures
 Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures Kook Jin Chung Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University Korea 2 1. Introduction As the number
Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures Kook Jin Chung Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University Korea 2 1. Introduction As the number
Axial Loading during MR Imaging Can Influence Treatment Decision for Symptomatic Spinal Stenosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:170 174, February 2004 Axial Loading during MR Imaging Can Influence Treatment Decision for Symptomatic Spinal Stenosis Akio Hiwatashi, Barbro Danielson, Toshio Moritani, Robert
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:170 174, February 2004 Axial Loading during MR Imaging Can Influence Treatment Decision for Symptomatic Spinal Stenosis Akio Hiwatashi, Barbro Danielson, Toshio Moritani, Robert
The Risk of New Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in the Year after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 The Risk of New Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in the Year after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Maurits H.J. Voormolen, MD, Paul N.M. Lohle, MD, PhD, Job R. Juttmann, MD, PhD, Yolanda van der
The Risk of New Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in the Year after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Maurits H.J. Voormolen, MD, Paul N.M. Lohle, MD, PhD, Job R. Juttmann, MD, PhD, Yolanda van der
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine
 Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
National Medical Policy
 National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Kyphoplasty NMP62 Effective Date*: October 2003 Updated: August 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT NOTICE at the
National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Kyphoplasty NMP62 Effective Date*: October 2003 Updated: August 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT NOTICE at the
62 M.J.B. Stallmeyer and G.H. Zoarski
 5 Patient Evaluation and Selection M.J.B. Stallmeyer and Gregg H. Zoarski Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) can occur as a result of osteoporosis, malignant primary bone tumors, osteolytic metastases,
5 Patient Evaluation and Selection M.J.B. Stallmeyer and Gregg H. Zoarski Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) can occur as a result of osteoporosis, malignant primary bone tumors, osteolytic metastases,
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Compression Fractures: Quantitative Prospective Evaluation of Long-term Outcomes
 Clinical Studies Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Compression Fractures: Quantitative Prospective Evaluation of Long-term Outcomes Gregg H. Zoarski, MD, 1 Paige Snow, PA, MSHS, Wayne J. Olan,
Clinical Studies Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Compression Fractures: Quantitative Prospective Evaluation of Long-term Outcomes Gregg H. Zoarski, MD, 1 Paige Snow, PA, MSHS, Wayne J. Olan,
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16287-16293 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0011602
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16287-16293 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0011602 Original Article Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty under local
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16287-16293 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0011602 Original Article Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty under local
Compression Fractures
 September 2006 Compression Fractures Eleanor Adams Harvard Medical School Year IV Overview Spine Anatomy Thoracolumbar Fractures Cases Compression Fractures, Ddx Radiologic Tests of Choice Treatment Options
September 2006 Compression Fractures Eleanor Adams Harvard Medical School Year IV Overview Spine Anatomy Thoracolumbar Fractures Cases Compression Fractures, Ddx Radiologic Tests of Choice Treatment Options
Department of Orthopedics, Wuhu No. 2 People s Hospital, Wannan Medical College, Anhui, China
 Treatment of vertebral body compression fractures using percutaneous kyphoplasty guided by a combination of computed tomography and C-arm fluoroscopy with finger-touch guidance to determine the needle
Treatment of vertebral body compression fractures using percutaneous kyphoplasty guided by a combination of computed tomography and C-arm fluoroscopy with finger-touch guidance to determine the needle
Cement augmentation for vertebral fractures in patients with multiple myeloma
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 551-557 ORIGINAL STUDY Cement augmentation for vertebral fractures in patients with multiple myeloma Haroon Majeed, Rajendranath Bommireddy, Zdenek Klezl From Royal Derby
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 551-557 ORIGINAL STUDY Cement augmentation for vertebral fractures in patients with multiple myeloma Haroon Majeed, Rajendranath Bommireddy, Zdenek Klezl From Royal Derby
Management of Painful Vertebral Hemangiomas with Kyphoplasty: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review
 Pain Physician 2009; 12:E297-E303 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Reports Management of Painful Vertebral Hemangiomas with Kyphoplasty: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review Jonathan O. Jones, MD 1, Brian
Pain Physician 2009; 12:E297-E303 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Reports Management of Painful Vertebral Hemangiomas with Kyphoplasty: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review Jonathan O. Jones, MD 1, Brian
The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize
 SPRING 2013 Robot-Guided Spine Surgery Christopher R. Good, M.D., F.A.C.S. and Blair K. Snyder, P.A.-C. The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize patient function and accelerate a return to a
SPRING 2013 Robot-Guided Spine Surgery Christopher R. Good, M.D., F.A.C.S. and Blair K. Snyder, P.A.-C. The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize patient function and accelerate a return to a
Spinal Compression Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
were assessed using a subset of patients who had responded to the Brief Pain Inventory and the Edmonton Symptom Assessment Scale.
 Pain Medicine 2011; *: ** ** Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Vertebral Compression Fracture Treatment with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Experience in 407 Patients with 1,156 Fractures in a Tertiary Cancer Centerpme_1278
Pain Medicine 2011; *: ** ** Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Vertebral Compression Fracture Treatment with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Experience in 407 Patients with 1,156 Fractures in a Tertiary Cancer Centerpme_1278
Balloon Kyphoplasty. Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures.
 Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures. Outline. Outline. Holmes Criteria. Disclosure:
 Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Department of Radiology Virginia Mason Medical Center Affiliate Professor, University of Washington Disclosure: Book Royalties, Springer-Verlag
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Department of Radiology Virginia Mason Medical Center Affiliate Professor, University of Washington Disclosure: Book Royalties, Springer-Verlag
Discover a new approach to vertebral augmentation
 Discover a new approach to vertebral augmentation AVAmax Advanced Vertebral Augmentation system The AVAmax vertebral balloon and AVAflex curved needle allowed a uniform cement fill during this pictured
Discover a new approach to vertebral augmentation AVAmax Advanced Vertebral Augmentation system The AVAmax vertebral balloon and AVAflex curved needle allowed a uniform cement fill during this pictured
But My Back Hurts Only When I m Standing!
 But My Back Hurts Only When I m Standing! Axial Loading for Spinal Canal Stenosis Matthew Cham, MD; Akio Hiwatashi, MD; Per-Lennart Westesson, MD, PhD, DDS Division of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology,
But My Back Hurts Only When I m Standing! Axial Loading for Spinal Canal Stenosis Matthew Cham, MD; Akio Hiwatashi, MD; Per-Lennart Westesson, MD, PhD, DDS Division of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology,
A Thesis. entitled. Biomechanical Evaluation of Vertebral Augmentation to Compare Biocure Cement with PMMA. Devdatt D. Mhatre
 A Thesis entitled Biomechanical Evaluation of Vertebral Augmentation to Compare Biocure Cement with PMMA by Devdatt D. Mhatre Submitted to the Graduate Faculty as partial fulfillment of the requirements
A Thesis entitled Biomechanical Evaluation of Vertebral Augmentation to Compare Biocure Cement with PMMA by Devdatt D. Mhatre Submitted to the Graduate Faculty as partial fulfillment of the requirements
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery
 Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer. Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU
 Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Sohag Faculty of Medicine, Sohag University, Sohag, Egypt
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(2):145-50 Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating vertebral compression caused by malignancy, osteoporosis, and infections
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(2):145-50 Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating vertebral compression caused by malignancy, osteoporosis, and infections
Objectives. Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment. Level of Fracture. Neuro exam Muscle Grading
 Objectives Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment Johannes Bernbeck,, MD Review and apply the understanding of incidence and etiology of VCF. Examine conservative and operative management
Objectives Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment Johannes Bernbeck,, MD Review and apply the understanding of incidence and etiology of VCF. Examine conservative and operative management
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE. CP57 Version: V3
 GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
Radiology. Abbreviations: ADL activities of daily living PMMA polymethylmethacrylate
 Avery J. Evans, MD Mary E. Jensen, MD Kevin E. Kip, PhD 2 Andrew J. DeNardo, MD Gregory J. Lawler, MD 3 Geoffrey A. Negin, MD Kent B. Remley, MD 4 Selene M. Boutin, MSN, ARN Steven A. Dunnagan, MD 5 Index
Avery J. Evans, MD Mary E. Jensen, MD Kevin E. Kip, PhD 2 Andrew J. DeNardo, MD Gregory J. Lawler, MD 3 Geoffrey A. Negin, MD Kent B. Remley, MD 4 Selene M. Boutin, MSN, ARN Steven A. Dunnagan, MD 5 Index
Comparison of High-Viscosity Cement Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Pain Physician 2015; 18:E187-E194 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Assessment Comparison of High-Viscosity Cement Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Pain Physician 2015; 18:E187-E194 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Assessment Comparison of High-Viscosity Cement Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
Acute Osteoporotic and Neoplastic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Fluid Sign at MR Imaging 1
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Andrea Baur, MD Axel Stäbler, MD Susanne Arbogast, MD Hans Roland Duerr, MD Reiner Bartl, MD Maximilian Reiser, MD Index terms: Osteoporosis, 30.56 Spine, fractures, 30.411
Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Andrea Baur, MD Axel Stäbler, MD Susanne Arbogast, MD Hans Roland Duerr, MD Reiner Bartl, MD Maximilian Reiser, MD Index terms: Osteoporosis, 30.56 Spine, fractures, 30.411
Open Access. Jun Takahashi *,1, Mikio Kamimura 2, Yohei Yuzawa 1, Tetsuya Kinoshita 1 and Hiroyuki Kato 1. 390-8621, Japan. Nagano, 399-0021, Japan
 The Open Spine Journal, 2010, 2, 29-34 29 Open Access Anterior Vertebral Reconstruction Surgery using Polymethylmethacrylate and Posterior Spinal Short Fusion through the Posterior Approach for Osteoporotic
The Open Spine Journal, 2010, 2, 29-34 29 Open Access Anterior Vertebral Reconstruction Surgery using Polymethylmethacrylate and Posterior Spinal Short Fusion through the Posterior Approach for Osteoporotic
А А А дламая АмАяАяАсАяАя АК А АВдлАмАК АКАВАК
 Аядл АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК 2 АяАяА АВА АсдлАя А А А длая АяАяАсАяАя АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК Ас. apple apple АУ fi applefi АвАвАУ- fi applefi - АУapple applefi apple fi fi fi applefi-. (. 2-184, 2-185) АУ apple
Аядл АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК 2 АяАяА АВА АсдлАя А А А длая АяАяАсАяАя АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК Ас. apple apple АУ fi applefi АвАвАУ- fi applefi - АУapple applefi apple fi fi fi applefi-. (. 2-184, 2-185) АУ apple
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression
 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression 1 Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine November 2009, Volume 11, pp.
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression 1 Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine November 2009, Volume 11, pp.
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
MINIMAL ACCESS SPINE SURGERY
 MINIMAL ACCESS SPINE SURGERY Spinal ailments are amongst the most common ailments that afflict mankind. Back pain, for example, has achieved epidemic proportions worldwide in the last two decades and is
MINIMAL ACCESS SPINE SURGERY Spinal ailments are amongst the most common ailments that afflict mankind. Back pain, for example, has achieved epidemic proportions worldwide in the last two decades and is
ICD 9 Codes: Osteoporosis 733. 0, Vertebral Fracture closed 805.8, Pathological fracture of Vertebrae 733.13
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy ICD 9 Codes: Osteoporosis 733. 0, Vertebral Fracture closed 805.8, Pathological fracture of Vertebrae 733.13 Vertebral
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy ICD 9 Codes: Osteoporosis 733. 0, Vertebral Fracture closed 805.8, Pathological fracture of Vertebrae 733.13 Vertebral
SPINAL FRACTURES OUR TREATMENT GUIDE
 SPINAL FRACTURES OUR TREATMENT GUIDE 7 Cervical Spinal fractures are common around the world and can have a major impact on your quality of life. If not treated soon enough, they can even make carrying
SPINAL FRACTURES OUR TREATMENT GUIDE 7 Cervical Spinal fractures are common around the world and can have a major impact on your quality of life. If not treated soon enough, they can even make carrying
POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY
 POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY Postoperative spine imaging, either by surgery or by mini-invasive procedures, is a complex tool and depends
POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY Postoperative spine imaging, either by surgery or by mini-invasive procedures, is a complex tool and depends
Health Quality Ontario The provincial advisor on the quality of health care in Ontario
 Health Quality Ontario The provincial advisor on the quality of health care in Ontario ONTARIO HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT SERIES Vertebral Augmentation Involving Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty for Cancer-Related
Health Quality Ontario The provincial advisor on the quality of health care in Ontario ONTARIO HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT SERIES Vertebral Augmentation Involving Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty for Cancer-Related
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging
 Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Vertebral body stenting / stentoplasty
 Published 6 August 2012, doi:10.4414/smw.2012.13658 Cite this as: Vertebral body stenting / stentoplasty Paul F. Heini, Regula Teuscher Spine Service, Orthopaedic Hospital Sonnenhof, Bern, Switzerland
Published 6 August 2012, doi:10.4414/smw.2012.13658 Cite this as: Vertebral body stenting / stentoplasty Paul F. Heini, Regula Teuscher Spine Service, Orthopaedic Hospital Sonnenhof, Bern, Switzerland
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
APSS YANGON OPERATIVE SPINE COURSE. Local Organizing Chairman: Prof Myint Thaung. Venue: Yangon Orthopaedic Hospital
 5 th - 8 th Feb 2015 Pls insert Hospital Logo here Local Organizing Chairman: Prof Myint Thaung Venue: Yangon Orthopaedic Hospital Invited International and Local Faculties Arvind Jayaswal (India) Chung-Chek
5 th - 8 th Feb 2015 Pls insert Hospital Logo here Local Organizing Chairman: Prof Myint Thaung Venue: Yangon Orthopaedic Hospital Invited International and Local Faculties Arvind Jayaswal (India) Chung-Chek
CHARACTERSTIC RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
 OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
Spinal Arthrodesis Group Exercises
 Spinal Arthrodesis Group Exercises 1. Two surgeons work together to perform an arthrodesis. Dr. Bonet, a general surgeon, makes the anterior incision to gain access to the spine for the arthrodesis procedure.
Spinal Arthrodesis Group Exercises 1. Two surgeons work together to perform an arthrodesis. Dr. Bonet, a general surgeon, makes the anterior incision to gain access to the spine for the arthrodesis procedure.
Long-Term Benefits of Percutaneous Anatomical Restoration of Vertebral Compression Fractures Linked to Malignancy
 DOI: DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.12294-14.1 Received: 16.11.2014 / Accepted: 17.2.2015 Published Online: 24.02.2016 Original Investigation Long-Term Benefits of Percutaneous Anatomical Restoration of Vertebral
DOI: DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.12294-14.1 Received: 16.11.2014 / Accepted: 17.2.2015 Published Online: 24.02.2016 Original Investigation Long-Term Benefits of Percutaneous Anatomical Restoration of Vertebral
VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURE AND KIENBOCK S DISEASE TREATMENTS
 TREATMENTS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be
TREATMENTS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be
Metastatic Bone Disease and Multiple Myeloma 16000122-01
 Metastatic Bone Disease and Multiple Myeloma 16000122-01 1 Southwest Spine Institute Douglas S. Won, MD Spine Surgery Specialist Director of Southwest Spine Institute Clinical Asst. Professor, UT Southwestern
Metastatic Bone Disease and Multiple Myeloma 16000122-01 1 Southwest Spine Institute Douglas S. Won, MD Spine Surgery Specialist Director of Southwest Spine Institute Clinical Asst. Professor, UT Southwestern
Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases
 September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Bone Disease in Myeloma
 Bone Disease in Myeloma Washington, DC August 8, 2009 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma Vascular Cytokines
Bone Disease in Myeloma Washington, DC August 8, 2009 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma Vascular Cytokines
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING
 CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
CERVICAL PROCEDURES PHYSICIAN CODING Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Interbody Fusion (ACDF) Anterior interbody fusion, with discectomy and decompression; cervical below C2 22551 first interspace 22552
Surgical Spine Care Center
 OUTCOMES DIVISION OF MEDICINE Surgical Spine Care Center About Cleveland Clinic Florida Cleveland Clinic Florida s medical staff are dedicated physicians who have joined the clinic as salaried doctors
OUTCOMES DIVISION OF MEDICINE Surgical Spine Care Center About Cleveland Clinic Florida Cleveland Clinic Florida s medical staff are dedicated physicians who have joined the clinic as salaried doctors
KYPHON. Reimbursement Guide. Physician Reimbursement. Balloon Kyphoplasty Procedure. ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes. CPT Codes and Payment
 KYPHON Balloon Kyphoplasty Procedure Reimbursement Guide ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes Providers should report the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code that most accurately describes the patient s condition. Please refer
KYPHON Balloon Kyphoplasty Procedure Reimbursement Guide ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes Providers should report the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code that most accurately describes the patient s condition. Please refer
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R.
 Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
Title: Interspinous Process Decompression with the X-Stop Device for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Review. Authors: Jennifer R. Madonia-Barr, MS, PA-C and David L. Kramer, MD Institution: Connecticut
Image-guided Spine Procedures for Relief of Severe Lower Back Pain:
 Image-guided Spine Procedures for Relief of Severe Lower Back Pain: A Guide to Epidural Steroid Injection, Facet Joint Injection, and Selective Nerve Root Block. PETER H TAKEYAMA MD HENRY WANG MD PhD SVEN
Image-guided Spine Procedures for Relief of Severe Lower Back Pain: A Guide to Epidural Steroid Injection, Facet Joint Injection, and Selective Nerve Root Block. PETER H TAKEYAMA MD HENRY WANG MD PhD SVEN
Instability concept. Symposium- Cervical Spine. Barcelona, February 2014
 Instability concept Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd AOSpine Principles Symposium- Cervical Spine Orthopaedic Depatment. Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor UAB Barcelona, February 2014
Instability concept Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd AOSpine Principles Symposium- Cervical Spine Orthopaedic Depatment. Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor UAB Barcelona, February 2014
Burst fracture of the fifth lumbar vertebra: results of posterior internal fixation and transpedicular bone grafting
 Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :435 440 DOI 10.1007/s00586-002-0390-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A. Kaminski E. J. Müller G. Muhr Burst fracture of the fifth lumbar vertebra: results of posterior internal fixation and transpedicular
Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :435 440 DOI 10.1007/s00586-002-0390-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A. Kaminski E. J. Müller G. Muhr Burst fracture of the fifth lumbar vertebra: results of posterior internal fixation and transpedicular
Understanding. Balloon Kyphoplasty and Myeloma-Induced Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Understanding Balloon Kyphoplasty and Myeloma-Induced Vertebral Compression Fractures International Myeloma Foundation 12650 Riverside Drive, Suite 206 North Hollywood, CA 91607 USA Telephone: 800-452-CURE
Understanding Balloon Kyphoplasty and Myeloma-Induced Vertebral Compression Fractures International Myeloma Foundation 12650 Riverside Drive, Suite 206 North Hollywood, CA 91607 USA Telephone: 800-452-CURE
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Corporate Medical Policy Spinal Manipulation under Anesthesia
 Corporate Medical Policy Spinal Manipulation under Anesthesia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: spinal_manipulation_under_anesthesia 5/1998 1/2015 1/2016 1/2015 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Spinal Manipulation under Anesthesia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: spinal_manipulation_under_anesthesia 5/1998 1/2015 1/2016 1/2015 Description
Information for the Patient About Surgical
 Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Information for the Patient About Surgical Decompression and Stabilization of the Spine Aging and the Spine Daily wear and tear, along with disc degeneration due to aging and injury, are common causes
Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation
 167 Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation Richard F. Costello, DO a, *, Douglas P. Beall, MD a,b MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N
167 Nomenclature and Standard Reporting Terminology of Intervertebral Disk Herniation Richard F. Costello, DO a, *, Douglas P. Beall, MD a,b MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N
Computed Tomography-guided Percutaneous Transpedicular Biopsy of the Thoracic Spine
 Computed Tomography-guided Percutaneous Transpedicular Biopsy of the Thoracic Spine Wen-Ching Hsu, MD; Kun-Eng Lim, MD Background: Despite the recent, widespread use around the world of computed tomography
Computed Tomography-guided Percutaneous Transpedicular Biopsy of the Thoracic Spine Wen-Ching Hsu, MD; Kun-Eng Lim, MD Background: Despite the recent, widespread use around the world of computed tomography
Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University
 Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University CanMEDS Roles / Competencies Name: PGY Rotation Dates: s s Exceeds N/A Attending Staff:
Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University CanMEDS Roles / Competencies Name: PGY Rotation Dates: s s Exceeds N/A Attending Staff:
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Bakman M, Chan K, Bang C, Basu A, Seo G, Monu JUV Department of Imaging Sciences University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY Introduction
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Bakman M, Chan K, Bang C, Basu A, Seo G, Monu JUV Department of Imaging Sciences University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY Introduction
CT-guided Biopsy of Focal Lesions in Patients with Multiple Myeloma May Reveal New and More Aggressive Cytogenetic Abnormalities
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:781 785, April 2001 CT-guided Biopsy of Focal Lesions in Patients with Multiple Myeloma May Reveal New and More Aggressive Cytogenetic Abnormalities Ramesh Avva, Rudy L. Vanhemert,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:781 785, April 2001 CT-guided Biopsy of Focal Lesions in Patients with Multiple Myeloma May Reveal New and More Aggressive Cytogenetic Abnormalities Ramesh Avva, Rudy L. Vanhemert,
The treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar severe burst fractures with short pedicle screw fixation and vertebroplasty
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 493-500 ORIGINAL STUDY The treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar severe burst fractures with short pedicle screw fixation and vertebroplasty Shaoqi He, Lixing Lin, Xiaojun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 493-500 ORIGINAL STUDY The treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar severe burst fractures with short pedicle screw fixation and vertebroplasty Shaoqi He, Lixing Lin, Xiaojun
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings
 Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES: DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES
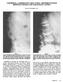 VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES: DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES Kevin D. Harrington, M.D. Figure 1 Lateral radiograph of a sixty-six year old woman with known breast cancer and scintigraphically
VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES: DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES Kevin D. Harrington, M.D. Figure 1 Lateral radiograph of a sixty-six year old woman with known breast cancer and scintigraphically
James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE:
 James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE: 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand
James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE: 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand
Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis
 Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh like structure within bones become thin, causing bones
Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh like structure within bones become thin, causing bones
The Effects of Cox Decompression Technic in the Treatment of Low Back Pain and Sciatica in a Golf Professional
 Cox Technic Email Case Report 72, June 2009, James Schantz DC 1 The Effects of Cox Decompression Technic in the Treatment of Low Back Pain and Sciatica in a Golf Professional James E. Schantz, D.C. Leading
Cox Technic Email Case Report 72, June 2009, James Schantz DC 1 The Effects of Cox Decompression Technic in the Treatment of Low Back Pain and Sciatica in a Golf Professional James E. Schantz, D.C. Leading
Vivian Gonzalez Gillian Lieberman, MD. January 2002. Lumbar Spine Trauma. Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 January 2002 Lumbar Spine Trauma Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Anatomy and Biomechanics of Lumbar Spine Three-Column Concept Classification of Fractures Our Patient Imaging Modalities
January 2002 Lumbar Spine Trauma Vivian Gonzalez, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Anatomy and Biomechanics of Lumbar Spine Three-Column Concept Classification of Fractures Our Patient Imaging Modalities
LONG-TERM CONSEQUENCES OF STABLE FRACTURES OF THE THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAL BODIES
 LONG-TERM CONSEQUENCES OF STABLE FRACTURES OF THE THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAL BODIES M. H. YOUNG, CARDIFF, WALES Senior Lecturer iii Ortliopaedic Surgery, Welsh National School of Medicine I-Jo,zorarv
LONG-TERM CONSEQUENCES OF STABLE FRACTURES OF THE THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAL BODIES M. H. YOUNG, CARDIFF, WALES Senior Lecturer iii Ortliopaedic Surgery, Welsh National School of Medicine I-Jo,zorarv
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging
 Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
