MRI and Bone Scan Imaging in the Preoperative Evaluation of Painful Vertebral Fractures Treated with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
|
|
|
- Spencer Strickland
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MRI and Bone Scan Imaging in the Preoperative Evaluation of Painful Vertebral Fractures Treated with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty SALVATORE MASALA 1, ORAZIO SCHILLACI 2, FRANCESCO MASSARI 1, ROBERTA DANIELI 2, ANTONIO URSONE 1, ROBERTO FIORI 1 and GIOVANNI SIMONETTI 1 1 Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Radiology and 2 Department of Nuclear Medicine, University of Rome "Tor Vergata", Rome, Italy Abstract. Background: This study compared the role and timing of bone scintigraphy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the evaluation of vertebral compression fractures (VCFs), before treatment with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. To our knowledge, no prior articles have described, in osteoporotic and pathological vertebral fractures, the role of MRI and bone scintigraphy as pre-procedural work up in those patients candidated to undergo spinal interventional procedures. Materials and Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed of thirty patients treated with interventional procedures for painful vertebral fractures at our institution between January 2002 and July Results: In patients, selected after evaluation with MRI and bone scan imaging, both procedures demonstrated swift pain relief associated with vertebral resistance augmentation. Conclusion: MRI revealed itself to be equivalent to bone scan imaging in selecting patients to be treated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the first 3/4 months, while bone scintigraphy was more accurate in the evaluation of elderly fractures (>3/4 months). MRI was superior to bone scintigraphy in vertebral collapses due to multiple myeloma. The vertebral fracture is defined as a reduction in height of the vertebral body beyond 20% of its initial dimensions (1-4). This condition is generated when the combination of the axial and rotational forces on the spine exceed the resistance offered by the vertebral body. Primary osteoporosis is responsible for about 85% of vertebral compression fractures Correspondence to: Salvatore Masala, MD, Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Radiology, "Tor Vergata" University General Hospital, 81 Oxford Street, Rome, Italy. Tel: , Fax: , salva.masala@tiscali.it Key Words: MRI, bone scintigraphy, vertebral compression fracture, interventional radiology, kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty. (VCFs), while secondary osteoporosis and neoplasty determine the remaining 15% (5). Vertebroplasty, the percutaneous injection of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement into the vertebral body, first described by Galibert et al. in 1984, has been applied to the treatment of collapsed vertebrae due to aggressive hemangiomas, osteolytic tumors and osteoporosis (6). Kyphoplasty is a recent treatment for VCF, first employed by Reiley in 1997, which, through the swelling of an inflatable bone tamp (IBT) into the collapsed vertebral body, elevates the endplates, thereby restoring the vertebral body height and creating a void to be filled with cement (7). To obtain these notable results, the patient must be precisely studied with diagnostic imaging. Patients, with a documented fracture on a conventional radiograph, in particular if affected by multiple fractures of uncertain age and non-localized pain, usually undergo adjunctive imaging in the form of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and bone scan imaging. Bone scintigraphy cannot aid in differentiating acute from chronic fractures, since the bone scan may show elevated tracer uptake for as long as 12 months after the fracture (8-11). Instead, increased tracer uptake at the level of a vertebral compression fracture is highly predictive of a positive clinical response after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty (8). A literature review revealed the lack of studies dedicated to pre-operative evaluation of VCFs. This is the first investigation to compare the role of scintigraphy and MRI in the evaluation of patients treated with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Our main aim was to delineate the utility and the importance of the two diagnostic imaging techniques in the pre-procedural assessment of differently aged vertebral fractures in order to clarify and standardize the international guidelines in pre-operative patient evaluation and management X/2005 $
2 Materials and Methods From January 2002 to July 2003, 30 patients (F=17, M=13; ages ranged from 50 to 91 years, mean age 70) with vertebral collapses were treated. Respectively, 24 (F=16, M=8) had fractures due to osteoporosis and 6 (F=1, M=5) due to primary and metastatic osteolytic neoplasms (4 myelomas and 2 metastasis). Twenty-three patients underwent a single level treatment (8 Dorsal: D7 number of patients 3, D8 n=1, D10 n=1, D12 n=3; 15 Lumbar: L1 n=4, L2 n=3, L3 n=3, L4 n=3, L5 n=2), while 7 were treated at multiple levels (9 Dorsal: D7 n=2, D9 n=1, D10 n=1, D11 n=2, D12 n=3; 8 Lumbar: L1 n=2, L2 n=2, L3 n=2, L4 n=1, L5 n=1) for 40 levels in total (Table I). MRI of the spine is the most useful test for defining the cause of spinal pain, evidencing epidural or neural foraminal disease and cord compression caused by tumor extension or bone fragment retropulsion, determining fracture age, ruling out a malignant tumor and selecting the appropriate treatment. MRI (Philips, Gyroscan Intera Master, 1.5 Tesla, Holland) was executed in T1 (TR 450 msec - TE 13 msec - NSA 4 - FOV Matrix 256), T2 (TR 2952 msec - TE 120 msec - NSA 6 - FOV Matrix 512) and STIR T2 (TR 1650 msec - TE 22 msec - NSA 3 - FOV Matrix 304) sequences to show altered signal intensity. Two experienced radiologists independently evaluated the images obtained by MRI, both being unaware of each others findings. Bone scintigraphy was performed 3 hours post-intravenous administration of ~ 740 MBq of Tc 99 m-methylene diphosphonate (Tc 99m-MDP) using a large field-of-view dual head single photon emission computed tomography system fitted with low-energy high resolution collimators (Millennium VG from General Electric, Milwaukee, USA). Whole-body acquisition was done using the continuous method in a 256 x 1024 matrix. For spinal lesions, planar static images of the areas of interest were then acquired in a 256 x 256 matrix for 5 minutes per view. Two experienced nuclear medicine physicians independently evaluated the scan findings. Results In this study, 40 painful vertebral levels were treated; in 16, the pre-procedural assessement was more accurate through evaluation with MRI STIR-sequences, 10 with bone scan scintigraphy, while in the remaining 14 the contribution of both these techniques was equivalent (Table II). Ten patients underwent a kyphoplasty procedure (F=5, M=5), whereas another 20 were treated utilizing vertebroplasty (F=12, M=8). The procedures were successfully performed on our group of patients, whose vertebral body resistance was considerably increased and improvement was swift and persistent in reducing all symptoms (12-17), decreasing from an average of 7.8 points of VAS to 2.2 (VAS of Huskisson = Visual analog scale, pain score with points assigned subjectively from patient pre- and post-procedure in a range between 0 absence of grief and 10 maximum pain) (Table III). Moreover, in those patients treated with kyphoplasty, normal vertebral body morphology was restored with a clinical and radiological reduction of the kyphosis and with Table I. Description of the 30 patients enrolled in the study. Patient Treatment Gender Age Treated Related levels pathology 1 Kyphoplasty m 19/08/33 L1 osteoporosis 2 Kyphoplasty m 19/02/55 D7 osteoporosis 3 Kyphoplasty f 05/09/26 L4 osteoporosis 4 Kyphoplasty f 18/07/30 D7 osteoporosis 5 Kyphoplasty f 06/04/31 D12 osteoporosis 6 Kyphoplasty f 17/10/40 L3 osteoporosis 7 Kyphoplasty f 28/02/28 L2, L4 osteoporosis 8 Kyphoplasty m 08/08/33 L2 osteoporosis 9 Kyphoplasty m 19/01/42 L2 osteoporosis 10 Kyphoplasty m 28/11/44 L4 myeloma 11 Vertebroplasty f 30/05/25 L5/D7 osteoporosis 12 Vertebroplasty f 08/07/44 L1 osteoporosis 13 Vertebroplasty m 16/07/34 D11, myeloma L1/D7 14 Vertebroplasty f 28/09/17 L5 osteoporosis 15 Vertebroplasty f 01/11/45 D7 osteoporosis 16 Vertebroplasty f 28/01/37 D12 osteoporosis 17 Vertebroplasty f 25/12/23 D11, osteoporosis D12 18 Vertebroplasty f 20/05/50 L1 osteoporosis 19 Vertebroplasty m 14/01/34 D9, D10/ myeloma D12, L3 20 Vertebroplasty f 24/07/21 L4 metastasis 21 Vertebroplasty m 12/01/21 L1 osteoporosis 22 Vertebroplasty f 02/04/31 L3 osteoporosis 23 Vertebroplasty m 22/09/39 L2 myeloma 24 Vertebroplasty m 16/03/33 D8 metastasis 25 Vertebroplasty f 08/08/33 L3 osteoporosis 26 Vertebroplasty f 07/02/43 D12, L1 osteoporosis 27 Vertebroplasty m 08/12/13 D10 osteoporosis 28 Vertebroplasty m 19/01/42 L5 osteoporosis 29 Vertebroplasty m 26/09/55 L2, L3 osteoporosis 30 Vertebroplasty f 31/10/20 D12 osteoporosis a positive effect on the lumbar compensatory hyperlordosis (18-23). No conditions were found where there were extravasations of PMMA in the epidural or foraminal sites with marrow or radicular compression. Discussion This retrospective study, conducted at our institution, yielded 33 percutaneous treatment sessions that were performed after obtaining, in the same day, MRI and bone scan imaging for painful, osteoporotic and neoplastic compression fractures in 30 patients. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty proved to be effective treatments to induce a reduction in or relief from spinal pain in patients and a reinforcement of the vertebral body (24-27). The patient selection for interventional radiology procedures is often complicated by the presence of multiple fractures or 1056
3 Masala et al: MRI and Bone Scan Imaging in Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty Table II. Different accuracy in pre-procedural evaluation of vertebral body fractures with MRI and bone scan scintigraphy, also evaluating the underling pathology. Role of Scintigraphy = MRI -Stir 14 levels Role of Scintigraphy < MRI -Stir 16 levels Role of Scintigraphy > MRI -Stir 10 levels Osteoporosis > Scintigraphy 6 > MRI-STIR 11 Scintigraphy = MRI 12 Myeloma > Scintigraphy 2 > MRI-STIR 5 Scintigraphy = MRI 2 Metastasis > Scintigraphy 2 > MRI-STIR 0 Scintigraphy = MRI 0 Total of Patients = 30 Total of Levels = 40 non-localized pain. MRI and bone scan imaging performed in the same day are quite useful in triaging patients before performing percutaneous therapy. In MRI the signal intensity of a benign compression fracture varies according to the age of the fracture. Acute osteoporotic fractures (<2 months old) characteristically show a focal band-like area of low signal intensity adjacent to the fractured endplate on T1WI. On T2WI, a collapsed vertebra is essentially isointense with adjacent non-collapsed vertebrae. On post-contrast mediumenhanced T1WI images, there is partial or complete equalization of the signal intensity of the collapsed vertebra with that of the adjacent non-collapsed vertebrae (termed "return to normal signal intensity"). Particularly the sequences with suppression of fat are of valid assistance in the determination of the age of the fracture; showing the presence of intraspongious edema testifies for a recent fracture and is predictive of a favorable response to an interventional procedure over the spine (28, 29). On spinecho T1-weighted images (T1WI), a malignant compression fracture shows complete replacement of normal bone marrow with diffuse low signal intensity in the whole of the vertebral body. On spin-echo T2-weighted images (T2WI), normal to high signal intensity is seen in the collapsed vertebra; the distribution of signal intensity can either be homogeneous or heterogeneous. Abnormal enhancement is seen in the vertebrae on post-contrast medium-enhanced images, particularly those obtained after fat suppression. The enhancement effect is mostly marked and inhomogeneous with diffuse or patchy distribution. Rarely, incomplete bone Table III. Visual analog scale, pain score with points assigned subjectively from patient pre- and post-procedure in a range between 0 absence of grief and 10 maximum pain. Patient VAS PRE VAS POST marrow replacement (round or irregular foci of low signal intensity on T1WI) with some residual normal bone marrow signal is seen in the vertebral body. The morphological features that are considered to be suggestive of malignant compression fractures include a convex bulge involving the whole of the posterior cortex of the vertebral body, involvement of the pedicles and the presence of an epidural and/or paraspinal soft tissue mass. The size of the low signal intensity areas seen on T1WI in acute compression fractures remains unchanged (or even increased) in the initial 2-4 months and then gradually reverts to normal. Chronic benign osteoporotic fractures usually show normal signal intensity of the vertebral body on both T1WI and T2WI. In particular, the suppression fat sequence is of valid assistance in the determination of the age of the fracture; showing the presence of intraspongious edema, testifies for a recent fracture and is predictive of a favorable response to interventional procedure over the spine (28, 29). Diffusion-weighted MRI is a recent tool that may help to distinguish metastatic from osteoporotic vertebral compression 1057
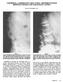
4 a b Figure 1 a,b. Patient, 78 years old, female, vertebral compression fracture of L4 due to osteoporosis; pain onset with minor trauma 2 months before treatment. a) Pre-treatment sagittal MRI (T2-weighted TSE with fat suppression sequence) shows increased signal intensity in the whole vertebra revealing the presence of intraspongious edema. b) Increased tracer uptake at the level of a VCF, revealed by bone scan imaging, is highly predictive of positive clinical response to percutaneous treatment. fractures (30, 31). Malignant compression fractures demonstrate hypointense or isointense signals compared to adjacent vertebrae on diffusion-weighted MR sequences. However, in some patients, imaging findings remain equivocal. In cases in which the etiology of a compression fracture is in question, a biopsy can easily be performed coaxially through the needle, before injection of the cement. Bone scan imaging with Tc 99m-MDP evaluates qualitatively the activity of osteoblastic cells through uptake of the tracer within the vertebral body. Bone scans provide useful information about bone turnover and, thereby, identify any vertebral fracture that has an ongoing healing process. Bone scans are sensitive for the detection of fractures, but they have low specificity for the diagnosis of underlying disease. An additional limitation of bone scanning is that increased bone turnover can be detected as long as 1 year following a vertebral fracture, not permitting the differentiation of acute from chronic fractures. This limits the ability of a bone scan to demonstrate the acuity of an osteoporotic vertebral fracture, and it is not helpful for determining the source of the pain. Distinguishing among vertebral fractures, neoplasms and infections is difficult on a bone scan, unless multiple metastatic lesions are clearly identified. Bone scanning plays a role in identifying osteoporotic fractures in patients who have negative findings on plain radiographs and in identifying additional fractures at other levels. Increased tracer uptake at the level of a VCF, revealed by bone scan imaging, is highly predictive of positive clinical response to percutaneous treatment. In multiple myeloma bone scintigraphy may demonstrate increased uptake, but may be normal or equivocal (32). MRI imaging offers the advantage over bone scan imaging of accurately assessing vertebral levels involved by fractures and the presence and degree of bony retropulsion. Conversely, bone scan imaging is superior to MRI in showing the whole skeletal system and providing a functional assessment of bone turnover, which is increased in healing fractures. 1058
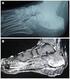
5 Masala et al: MRI and Bone Scan Imaging in Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty a b Figure 2 a,b. Patient, 75 years old, male, vertebral compression fracture of D7 and D11 due to secondary osteoporosis based on high corticosteroid doses; pain onset with minor trauma 7 months before treatment. a) Pre-treatment sagittal MRI (T2-weighted TSE with fat suppression sequence) shows normal signal intensity in the collapsed vertebrae. b) Bone scan imaging, tracer uptake at the level of a VCF still remain increased after several months from vertebral fractures (left rib uptake was due to a recent trauma). MRI is extremely useful in the evaluation of VCFs, especially when fractures of different ages are present, because it demonstrates characteristic changes in the marrow signal that vary with the age of the fracture. Acute and subacute fractures, less than 90 days old, are hypointense in signal on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2- weighted and short T1 inversion recovery (STIR) sequences. To our knowledge, there have been no previous studies comparing the use of adjunctive imaging strategies, beyond plain film imaging to properly select patients who will experience pain relief with vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. This chart review was performed to analyze and characterize the role of MRI and bone scan imaging as part of the preprocedural work up in those patients candidated to undergo spinal interventional procedures. In our experience, supported by the results of this study, we consider it fundamental that the patient undergo a pre-operative MRI- STIR and scintigraphic evaluation in the presence of a vertebral fracture dated less than 3/4 months (Figure 1 a,b). Contrary to this, because the signal intensity areas seen on MRI-STIR in acute and subacute compression fractures change after 2-4 months and gradually revert to normal, the gold standard in the evaluation of old fractures (>3/4 months) becomes bone scan scintigraphy (Figure 2 a,b). The absent or equivocal tracer uptake in multiple myeloma bone scintigraphy make it necessary to perform an MRI evaluation in order to analyze and characterize these vertebral collapses. However, in order to confirm these results and to clarify and standardize international guidelines in pre-operative 1059
6 patient evaluation and management, a larger series of patients comparatively evaluated with this two techniques is necessary. References 1 Stallmeyer MJ, Zoarski GH and Obuchowski AM: Optimizing patient selection in percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14: , McKiernan F, Jensen R and Faciszewski T: The dynamic mobility of vertebral compression fractures. J Bone Miner Res 18: 24-29, Wu SS, Lachmann E and Nagler W: Current medical, rehabilitation, and surgical management of vertebral compression fractures. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 12: 17-26, Papaioannou A, Watts NB, Kendler DL, Yuen CK, Adachi JD and Ferko N: Diagnosis and management of vertebral fractures in elderly adults. Am J Med 113: , Ahrar K, Schomer DF and Wallace MJ: Kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Semin Intervent Radiol 19: , Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P and Le Gars D: Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie 33: , Wong W, Reiley MA and Garfin S: Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty. JWI 2: , Maynard AS, Jensen ME, Schweickert PA, Marx WF, Short JG and Kallmes DF: Value of bone scan imaging in predicting pain relief from percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21: , Cook GJ, Hannaford E, See M, Clarke SE and Fogelman I: The value of bone scintigraphy in the evaluation of osteoporotic patients with back pain. Scand J Rheumatol 31: , Kucukalic-Selimovic E and Begic A: Value of bone scintigraphy for detection and ageing of vertebral fractures in patients with severe osteoporosis and correlation between bone scintigraphy and mineral bone density. Med Arh 58: , Stabler A, Krimmel K, Seiderer M, Gartner C, Fritsch S and Raum W: The nuclear magnetic resonance tomographic differentiation of osteoporotic and tumor-related vertebral fractures. The value of subtractive TR gradient-echo sequences, STIR sequences and Gd- DTPA. Rofo 157: , 1992 (German). 12 Gangi A, Wong LLS, Guth S and Dietemann JL: Percutaneous vertebroplasty: indications, technique, and results. Semin Intervent Radiol 19: , Garfin SR, Yuan HA and Reiley MA: New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 26: , Linville DA II: Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. South Med 95: , Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME and Deramond H: Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22: , Peters KR, Guiot BH, Martin PA and Fessler RG: Vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: current practice and evolving techniques. Neurosurgery 51: , Masala S, Fiori R, Massari F and Simonetti G: Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: new equipment for vertebral fractures treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 22: 75-79, Coumans JV, Reinhardt MK and Lieberman IH: Kyphoplasty for vertebral compression fractures: 1-year clinical outcomes from a prospective study. J Neurosurg 99: 44-50, Dudeney S, Lieberman IH, Reinhardt MK and Hussein M: Kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteolytic vertebral compression fractures as a result of multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 20: , Hardouin P, Fayada P, Leclet H and Chopin D: Kyphoplasty. Joint Bone Spine 69: , Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK and Bell G: Initial outcome and efficacy of "kyphoplasty" in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 26: , Ledlie JT and Renfro M: Balloon kyphoplasty: one-year outcomes in vertebral body height restoration, chronic pain, and activity levels. J Neurosurg 98: 36-42, Masala S, Cesaroni A, Sergiacomi G, Fiori R, Massari F, Manenti G, Nard PVI and Simonetti G: Percutaneous kyphoplasty: new treatment for painful vertebral body fractures. In Vivo 18: , Zoarski GH, Snow P, Olan WJ, Stallmeyer MJ, Dick BW, Hebel JR and De Deyne M: Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: quantitative prospective evaluation of long-term outcomes. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13: , Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Duncan TD, Garfin SR and Wong WH: Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures. Clin Imag 26: 1-5, Fourney DR, Schomer DF, Nader R, Chlan-Fourney J, Suki D, Ahrar K, Rhines LD and Gokaslan ZL: Percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for painful vertebral body fractures in cancer patients. J Neurosurg 98: 21-30, Amar AP, Larsen DW, Esnaashari N, Albuquerque FC, Lavine SD and Teitelbaum GP: Percutaneous transpedicular polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty for the treatment of spinal compression fractures. Neurosurgery 49: , Baker LL, Goodman SB, Perkash I, Lane B and Enzmann DR: Benign versus pathologic compression fractures of vertebral bodies: assessment with conventional spin-echo, chemical-shift, and STIR MR imaging. Radiology 174: , Gaitanis IN, Hadjipavlou AG, Katonis PG, Tzermiadianos MN, Pasku DS and Patwardhan AG: Balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of pathological vertebral compressive fractures. Eur Spine J [Epub ahead of print]. 30 Maeda M, Sakuma H, Maier SE and Takeda K: Quantitative assessment of diffusion abnormalities in benign and malignant vertebral compression fractures by line scan diffusion-weighted imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181: , Chan JH, Peh WC, Tsui EY, Chau LF, Cheung KK, Chan KB, Yuen MK, Wong ET and Wong KP: Acute vertebral body compression fractures: discrimination between benign and malignant causes using apparent diffusion coefficients. Br J Radiol 75: , Bataille R, Chevalier J, Rossi M and Sany J: Bone scintigraphy in plasma-cell myeloma. A prospective study of 70 patients. Radiology 145: , Received June 9, 2005 Accepted September 1,
Increase in Vertebral Body Height after Vertebroplasty
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:185 189, February 2003 Increase in Vertebral Body Height after Vertebroplasty Akio Hiwatashi, Toshio Moritani, Yuji Numaguchi, and Per-Lennart Westesson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:185 189, February 2003 Increase in Vertebral Body Height after Vertebroplasty Akio Hiwatashi, Toshio Moritani, Yuji Numaguchi, and Per-Lennart Westesson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine
 Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty
 Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 10/26/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.007 01/11/2005 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 10/26/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s) of Service:
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging
 Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases
 September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
September 2002 Radiologic Diagnosis of Spinal Metastases Natalie J. M. Dailey, Harvard Medical Student Year III Our Patient s Presenting Story 70 year old male Presents to the hospital for laparascopic
Bone Disease in Myeloma
 Bone Disease in Myeloma Washington, DC August 8, 2009 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma Vascular Cytokines
Bone Disease in Myeloma Washington, DC August 8, 2009 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma Vascular Cytokines
Acute Osteoporotic and Neoplastic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Fluid Sign at MR Imaging 1
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Andrea Baur, MD Axel Stäbler, MD Susanne Arbogast, MD Hans Roland Duerr, MD Reiner Bartl, MD Maximilian Reiser, MD Index terms: Osteoporosis, 30.56 Spine, fractures, 30.411
Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Andrea Baur, MD Axel Stäbler, MD Susanne Arbogast, MD Hans Roland Duerr, MD Reiner Bartl, MD Maximilian Reiser, MD Index terms: Osteoporosis, 30.56 Spine, fractures, 30.411
OVCF of the thoracic and lumbar spine can be a source of
 Published August 26, 2010 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2223 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND
Published August 26, 2010 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2223 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.O. Ortiz R. Bordia Injury to the Vertebral Endplate-Disk Complex Associated with Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures BACKGROUND
Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures
 Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures Kook Jin Chung Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University Korea 2 1. Introduction As the number
Osteoporotic Verterbal Compression Fractures Kook Jin Chung Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University Korea 2 1. Introduction As the number
Uniextrapedicular Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Thoracic Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
 Uniextrapedicular Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Thoracic Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Zhaohui Ge, MD; Rong Ma, MD; Zhen Chen, MD; Huiyong Zhang, MD; Huiqiang Ding, MD; Siming Liang, MD; Zhigang
Uniextrapedicular Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Thoracic Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Zhaohui Ge, MD; Rong Ma, MD; Zhen Chen, MD; Huiyong Zhang, MD; Huiqiang Ding, MD; Siming Liang, MD; Zhigang
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Compression Fractures
 September 2006 Compression Fractures Eleanor Adams Harvard Medical School Year IV Overview Spine Anatomy Thoracolumbar Fractures Cases Compression Fractures, Ddx Radiologic Tests of Choice Treatment Options
September 2006 Compression Fractures Eleanor Adams Harvard Medical School Year IV Overview Spine Anatomy Thoracolumbar Fractures Cases Compression Fractures, Ddx Radiologic Tests of Choice Treatment Options
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Sohag Faculty of Medicine, Sohag University, Sohag, Egypt
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(2):145-50 Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating vertebral compression caused by malignancy, osteoporosis, and infections
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(2):145-50 Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating vertebral compression caused by malignancy, osteoporosis, and infections
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary
 X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
Percutaneous vertebroplasty, initially conceived and developed
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. McDonald A.T. Trout L.A. Gray A. Dispenzieri K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty in Multiple Myeloma: Outcomes in a Large Patient Series BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Despite the
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. McDonald A.T. Trout L.A. Gray A. Dispenzieri K.R. Thielen D.F. Kallmes Vertebroplasty in Multiple Myeloma: Outcomes in a Large Patient Series BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Despite the
Osteoporosis and Vertebral Compression (Spinal) Fractures Fact Sheet
 Osteoporosis and Vertebral Compression (Spinal) Fractures Fact Sheet About Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is estimated to affect 200 million women worldwide. 1 Worldwide, osteoporosis causes more than nine
Osteoporosis and Vertebral Compression (Spinal) Fractures Fact Sheet About Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is estimated to affect 200 million women worldwide. 1 Worldwide, osteoporosis causes more than nine
New Technologies in Spine
 New Technologies in Spine Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Compression Fractures Steven R. Garfin, MD,* Hansen A. Yuan, MD, and Mark A. Reiley, MD SPINE Volume 26,
New Technologies in Spine Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Compression Fractures Steven R. Garfin, MD,* Hansen A. Yuan, MD, and Mark A. Reiley, MD SPINE Volume 26,
Despite recent advances in medical
 RADIOLOGIC DECISION-MAKING Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: New Treatment for Vertebral Compression Fractures THOMAS A. PREDEY, M.D., LUKE E. SEWALL, M.D., and STEVEN J. SMITH, M.D. La Grange Memorial Hospital,
RADIOLOGIC DECISION-MAKING Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: New Treatment for Vertebral Compression Fractures THOMAS A. PREDEY, M.D., LUKE E. SEWALL, M.D., and STEVEN J. SMITH, M.D. La Grange Memorial Hospital,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE. CP57 Version: V3
 GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
Attempts to differentiate benign and malignant. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Fractures
 Original Article 808 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Fractures Tsai-Sheng Fu, MD; Li-Hui Chen, MD; Jen-Chung Liao, MD;Po-Liang Lai, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Wen-Jer
Original Article 808 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Fractures Tsai-Sheng Fu, MD; Li-Hui Chen, MD; Jen-Chung Liao, MD;Po-Liang Lai, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Wen-Jer
Percutaneous Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Percutaneous Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures A Meta-analysis of Complications Michael J. Lee, MD, Mark Dumonski, MD, Patrick Cahill, MD, Tom Stanley, MD, Daniel Park, MD, and Kern Singh, MD
Percutaneous Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures A Meta-analysis of Complications Michael J. Lee, MD, Mark Dumonski, MD, Patrick Cahill, MD, Tom Stanley, MD, Daniel Park, MD, and Kern Singh, MD
The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize
 SPRING 2013 Robot-Guided Spine Surgery Christopher R. Good, M.D., F.A.C.S. and Blair K. Snyder, P.A.-C. The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize patient function and accelerate a return to a
SPRING 2013 Robot-Guided Spine Surgery Christopher R. Good, M.D., F.A.C.S. and Blair K. Snyder, P.A.-C. The goals of modern spinal surgery are to maximize patient function and accelerate a return to a
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
were assessed using a subset of patients who had responded to the Brief Pain Inventory and the Edmonton Symptom Assessment Scale.
 Pain Medicine 2011; *: ** ** Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Vertebral Compression Fracture Treatment with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Experience in 407 Patients with 1,156 Fractures in a Tertiary Cancer Centerpme_1278
Pain Medicine 2011; *: ** ** Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Vertebral Compression Fracture Treatment with Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Experience in 407 Patients with 1,156 Fractures in a Tertiary Cancer Centerpme_1278
Use of FDG-PET in differentiating benign from malignant compression fractures
 Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:405 413 DOI 10.1007/s00256-008-0452-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Use of FDG-PET in differentiating benign from malignant compression fractures Miriam A. Bredella & Brendan Essary & Martin
Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:405 413 DOI 10.1007/s00256-008-0452-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Use of FDG-PET in differentiating benign from malignant compression fractures Miriam A. Bredella & Brendan Essary & Martin
Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures
 Journal of Clinical Imaging 26 (2002) 1 5 Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures Daphne J. Theodorou a, Stavroula J. Theodorou
Journal of Clinical Imaging 26 (2002) 1 5 Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures Daphne J. Theodorou a, Stavroula J. Theodorou
Vesselplasty: A New Technical Approach to Treat Symptomatic Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Flors et al. Vesselplasty to Treat Symptomatic VCFs Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Vesselplasty: A New Technical Approach
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Flors et al. Vesselplasty to Treat Symptomatic VCFs Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Vesselplasty: A New Technical Approach
A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma
 Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP October 2013 A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP Our Learning Agenda Introduction of our patient His imaging data and findings
Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP October 2013 A Diagnostic Chest XRay: Multiple Myeloma Daniela Marinho Tridente, VI FCMSCSP Our Learning Agenda Introduction of our patient His imaging data and findings
62 M.J.B. Stallmeyer and G.H. Zoarski
 5 Patient Evaluation and Selection M.J.B. Stallmeyer and Gregg H. Zoarski Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) can occur as a result of osteoporosis, malignant primary bone tumors, osteolytic metastases,
5 Patient Evaluation and Selection M.J.B. Stallmeyer and Gregg H. Zoarski Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) can occur as a result of osteoporosis, malignant primary bone tumors, osteolytic metastases,
VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES: DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES
 VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES: DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES Kevin D. Harrington, M.D. Figure 1 Lateral radiograph of a sixty-six year old woman with known breast cancer and scintigraphically
VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES: DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES Kevin D. Harrington, M.D. Figure 1 Lateral radiograph of a sixty-six year old woman with known breast cancer and scintigraphically
Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures
 Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Arcata Chiropractic Office Larry J. Kleefeld D.C. Spinal Compression Fractures A Patient's Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures Introduction Compression fractures are the most common type of fracture
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Comparing Pain Reduction Following Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:583-590 ISSN 1533-3159 Meta-analysis Comparing Pain Reduction Following Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures J. Brian Gill, MD, Mark Kuper,
Pain Physician 2007; 10:583-590 ISSN 1533-3159 Meta-analysis Comparing Pain Reduction Following Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures J. Brian Gill, MD, Mark Kuper,
Metastatic Bone Disease and Multiple Myeloma 16000122-01
 Metastatic Bone Disease and Multiple Myeloma 16000122-01 1 Southwest Spine Institute Douglas S. Won, MD Spine Surgery Specialist Director of Southwest Spine Institute Clinical Asst. Professor, UT Southwestern
Metastatic Bone Disease and Multiple Myeloma 16000122-01 1 Southwest Spine Institute Douglas S. Won, MD Spine Surgery Specialist Director of Southwest Spine Institute Clinical Asst. Professor, UT Southwestern
Bone Disease in Myeloma. St. Petersburg, Russia September 16, 2009
 Bone Disease in Myeloma St. Petersburg, Russia September 16, 2009 Bi Brian G.M. GMDurie, M.D. MD Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
Bone Disease in Myeloma St. Petersburg, Russia September 16, 2009 Bi Brian G.M. GMDurie, M.D. MD Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty J. Kevin McGraw, MD, John Cardella, MD, John Dean Barr, MD, John M. Mathis, MD, Orestes Sanchez, MD, Marc
Society of Interventional Radiology Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty J. Kevin McGraw, MD, John Cardella, MD, John Dean Barr, MD, John M. Mathis, MD, Orestes Sanchez, MD, Marc
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging
 Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
.org. Metastatic Bone Disease. Description
 Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Metastatic Bone Disease Page ( 1 ) Cancer that begins in an organ, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and then spreads to bone is called metastatic bone disease (MBD). More than 1.2 million new cancer
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013
 Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Case Report. Central Neurocytoma. Fotis Souslian, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota
 1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
Spinal Compression Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Spinal Compression Fractures 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
CHARACTERSTIC RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
 OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures
 Yu et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures Chia-Wei Yu, Ming-Kai Hsieh, Lih-Huei Chen *, Chi-Chien
Yu et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures Chia-Wei Yu, Ming-Kai Hsieh, Lih-Huei Chen *, Chi-Chien
National Medical Policy
 National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Kyphoplasty NMP62 Effective Date*: October 2003 Updated: August 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT NOTICE at the
National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Kyphoplasty NMP62 Effective Date*: October 2003 Updated: August 2015 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT NOTICE at the
The Lewin Group undertook the following steps to identify the guidelines relevant to the 11 targeted procedures:
 Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
RESEARCH STUDY KCMJ 2014; 10(1): 11-17
 RESEARCH STUDY KCMJ 4; 0(): -7 Nadia Hassan Ali ALSalihi (FICMS) ( diag. rad) Discrimination of Malignant from Acute Benign Compression Spinal Fractures with Magnetic Resonance imaging ARTICLE INFORMATION
RESEARCH STUDY KCMJ 4; 0(): -7 Nadia Hassan Ali ALSalihi (FICMS) ( diag. rad) Discrimination of Malignant from Acute Benign Compression Spinal Fractures with Magnetic Resonance imaging ARTICLE INFORMATION
Spinal Surgery Functional Status and Quality of Life Outcome Specifications 2015 (01/01/2013 to 12/31/2013 Dates of Procedure) September 2014
 Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Understanding. Balloon Kyphoplasty and Myeloma-Induced Vertebral Compression Fractures
 Understanding Balloon Kyphoplasty and Myeloma-Induced Vertebral Compression Fractures International Myeloma Foundation 12650 Riverside Drive, Suite 206 North Hollywood, CA 91607 USA Telephone: 800-452-CURE
Understanding Balloon Kyphoplasty and Myeloma-Induced Vertebral Compression Fractures International Myeloma Foundation 12650 Riverside Drive, Suite 206 North Hollywood, CA 91607 USA Telephone: 800-452-CURE
KYPHON. Reimbursement Guide. Physician Reimbursement. Balloon Kyphoplasty Procedure. ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes. CPT Codes and Payment
 KYPHON Balloon Kyphoplasty Procedure Reimbursement Guide ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes Providers should report the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code that most accurately describes the patient s condition. Please refer
KYPHON Balloon Kyphoplasty Procedure Reimbursement Guide ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes Providers should report the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code that most accurately describes the patient s condition. Please refer
Diagnosis of Recurrent Prostate Tumor at Multiparametric Prostate MRI: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Diagnosis of Recurrent Prostate Tumor at Multiparametric Prostate MRI: Pearls and Pitfalls Mark Notley, MD; Jinxing Yu, MD; Ann S. Fulcher, MD; Mary A. Turner, MD; Don Nguyen, MD Virginia Commonwealth
Diagnosis of Recurrent Prostate Tumor at Multiparametric Prostate MRI: Pearls and Pitfalls Mark Notley, MD; Jinxing Yu, MD; Ann S. Fulcher, MD; Mary A. Turner, MD; Don Nguyen, MD Virginia Commonwealth
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
UMHS-PUHSC JOINT INSTITUTE
 Imaging Biomarkers for Staging and Assessing Response to Therapy in Multiple Myeloma Qian Dong, MD. Radiology University of Michigan Wei Guo, MD. Orthopedic Oncology Peking University Second Hospital Team
Imaging Biomarkers for Staging and Assessing Response to Therapy in Multiple Myeloma Qian Dong, MD. Radiology University of Michigan Wei Guo, MD. Orthopedic Oncology Peking University Second Hospital Team
POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY
 POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY Postoperative spine imaging, either by surgery or by mini-invasive procedures, is a complex tool and depends
POST-OPERATIVE SPINE IMAGING M.Muto Chief Neuroradiology Dept Cardarelli Hospital Naples ITALY Postoperative spine imaging, either by surgery or by mini-invasive procedures, is a complex tool and depends
Contents. Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1. 2. Spinal Imaging 7. 3. Spinal Biomechanics 23. 4. History and Physical Examination of the Spine 33
 Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Objectives. Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment. Level of Fracture. Neuro exam Muscle Grading
 Objectives Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment Johannes Bernbeck,, MD Review and apply the understanding of incidence and etiology of VCF. Examine conservative and operative management
Objectives Spinal Fractures: Classification Diagnosis and Treatment Johannes Bernbeck,, MD Review and apply the understanding of incidence and etiology of VCF. Examine conservative and operative management
Department of Orthopedics, Wuhu No. 2 People s Hospital, Wannan Medical College, Anhui, China
 Treatment of vertebral body compression fractures using percutaneous kyphoplasty guided by a combination of computed tomography and C-arm fluoroscopy with finger-touch guidance to determine the needle
Treatment of vertebral body compression fractures using percutaneous kyphoplasty guided by a combination of computed tomography and C-arm fluoroscopy with finger-touch guidance to determine the needle
biij Diffusion weighted MR imaging in acute vertebral compression fractures: differentiation between malignant and benign causes
 Available online at http://www.biij.org/2006/2/e12 doi: 10.2349/biij.2.2.e12 biij Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion weighted MR imaging in acute vertebral compression
Available online at http://www.biij.org/2006/2/e12 doi: 10.2349/biij.2.2.e12 biij Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion weighted MR imaging in acute vertebral compression
А А А дламая АмАяАяАсАяАя АК А АВдлАмАК АКАВАК
 Аядл АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК 2 АяАяА АВА АсдлАя А А А длая АяАяАсАяАя АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК Ас. apple apple АУ fi applefi АвАвАУ- fi applefi - АУapple applefi apple fi fi fi applefi-. (. 2-184, 2-185) АУ apple
Аядл АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК 2 АяАяА АВА АсдлАя А А А длая АяАяАсАяАя АК А АВдлАК АКАВАК Ас. apple apple АУ fi applefi АвАвАУ- fi applefi - АУapple applefi apple fi fi fi applefi-. (. 2-184, 2-185) АУ apple
Benign Versus Malignant Compression Fracture: A Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Benign Versus Malignant Compression Fracture: A Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sopa Pongpornsup MD*, Phromphiang Wajanawichakorn MD*, Nasuda Danchaivijitr MD* * Department of Radiology,
Benign Versus Malignant Compression Fracture: A Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sopa Pongpornsup MD*, Phromphiang Wajanawichakorn MD*, Nasuda Danchaivijitr MD* * Department of Radiology,
VERTEBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURE AND KIENBOCK S DISEASE TREATMENTS
 TREATMENTS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be
TREATMENTS Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Medical Coverage Guideline must be
Cement augmentation for vertebral fractures in patients with multiple myeloma
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 551-557 ORIGINAL STUDY Cement augmentation for vertebral fractures in patients with multiple myeloma Haroon Majeed, Rajendranath Bommireddy, Zdenek Klezl From Royal Derby
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 551-557 ORIGINAL STUDY Cement augmentation for vertebral fractures in patients with multiple myeloma Haroon Majeed, Rajendranath Bommireddy, Zdenek Klezl From Royal Derby
Extraspinal Malignancies Found Incidentally on Lumbar Spine MRI: Prevalence and Etiologies
 J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 85-91 Extraspinal Malignancies Found Incidentally on Lumbar Spine MRI: Prevalence and Etiologies Chen-Ju Fu 1 Huan-Wu Chen 1,2 Chen-Te Wu 1 Lih-Huei Chen 3 Yon-Cheong Wong 1,2 Li-Jen
J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 85-91 Extraspinal Malignancies Found Incidentally on Lumbar Spine MRI: Prevalence and Etiologies Chen-Ju Fu 1 Huan-Wu Chen 1,2 Chen-Te Wu 1 Lih-Huei Chen 3 Yon-Cheong Wong 1,2 Li-Jen
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
Spine Clinic Neurospine Specialists, Orthopaedics and Neurosurgery
 Spine Clinic Neurospine Specialists, Orthopaedics and Neurosurgery REVISION SPINE SURGERY Revision surgery is a very complex field which requires experience, training and evaluation in a very individual
Spine Clinic Neurospine Specialists, Orthopaedics and Neurosurgery REVISION SPINE SURGERY Revision surgery is a very complex field which requires experience, training and evaluation in a very individual
Cervical Spine Imaging
 March 20, 2006 Cervical Spine Imaging Johannes Kratz, Harvard Medical School Year IV 1 Overview Background Clinical Cases Diagnostic Tests and a Decision-Tree Algorithm Examples of Cervical Spine Evaluations
March 20, 2006 Cervical Spine Imaging Johannes Kratz, Harvard Medical School Year IV 1 Overview Background Clinical Cases Diagnostic Tests and a Decision-Tree Algorithm Examples of Cervical Spine Evaluations
Long-Term Benefits of Percutaneous Anatomical Restoration of Vertebral Compression Fractures Linked to Malignancy
 DOI: DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.12294-14.1 Received: 16.11.2014 / Accepted: 17.2.2015 Published Online: 24.02.2016 Original Investigation Long-Term Benefits of Percutaneous Anatomical Restoration of Vertebral
DOI: DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.12294-14.1 Received: 16.11.2014 / Accepted: 17.2.2015 Published Online: 24.02.2016 Original Investigation Long-Term Benefits of Percutaneous Anatomical Restoration of Vertebral
Health Quality Ontario The provincial advisor on the quality of health care in Ontario
 Health Quality Ontario The provincial advisor on the quality of health care in Ontario ONTARIO HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT SERIES Vertebral Augmentation Involving Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty for Cancer-Related
Health Quality Ontario The provincial advisor on the quality of health care in Ontario ONTARIO HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT SERIES Vertebral Augmentation Involving Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty for Cancer-Related
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
ARTICLES. Prevalence of Herniated Intervertebral Discs of the Cervical Spine in Asymptomatic Subjects Using MRI Scans: A Qualitative Systematic Review
 Please note that this electronic prepublication galley may contain typographical errors and may be missing artwork, such as charts, photographs, etc. Pagination in this version will differ from the published
Please note that this electronic prepublication galley may contain typographical errors and may be missing artwork, such as charts, photographs, etc. Pagination in this version will differ from the published
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery
 Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
Complications in Adult Deformity Surgery Proximal Junctional Kyphosis: Thoracolumbar and Cervicothoracic Sigurd Berven, MD Professor in Residence UC San Francisco Disclosures Research/Institutional Support:
The Risk of New Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in the Year after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 The Risk of New Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in the Year after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Maurits H.J. Voormolen, MD, Paul N.M. Lohle, MD, PhD, Job R. Juttmann, MD, PhD, Yolanda van der
The Risk of New Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in the Year after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Maurits H.J. Voormolen, MD, Paul N.M. Lohle, MD, PhD, Job R. Juttmann, MD, PhD, Yolanda van der
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI. Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007
 Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Imaging of Hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis with CR, US and MRI Azar Bahrami, PGY4 Radiology Rounds Jan, 31, 2007 Introduction RA most common type of inflammatory Arthritis with prevalence of 1% Accurate and
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease)
 Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Spine University s Guide to Vertebral Osteonecrosis (Kummel's Disease) 2 Introduction Kummel's disease is a collapse of the vertebrae (the bones that make up the spine). It is also called vertebral osteonecrosis.
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings
 Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Cervical Spine: Postmortem Assessment of Accident Injuries Comparison of Radiographic, MR Imaging, Anatomic, and Pathologic Findings 1 Radiology, November, 2001;221:340-346. Axel Stäbler, MD, Jurik Eck,
Bone Disease in Myeloma
 Bone Disease in Myeloma Boston, Massachusetts Saturday, July 26, 2008 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
Bone Disease in Myeloma Boston, Massachusetts Saturday, July 26, 2008 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs
 Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Quantitative Comparison of Conventional and Oblique MRI for Detection of Herniated Spinal Discs Doug Dean ENGN 2500: Medical Image Analysis Final Project Outline Introduction to the problem Based on paper:
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Vertebral Fragility Fracture
 CLINICAL PATHWAY Musculoskeletal Health Vertebral Fragility Fracture Vertebral Fragility Fracture Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Key Points of the Vertebral Fragility Fracture Pathway
CLINICAL PATHWAY Musculoskeletal Health Vertebral Fragility Fracture Vertebral Fragility Fracture Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Key Points of the Vertebral Fragility Fracture Pathway
bmr@ku.edu Category scientific abstract Relevant author disclosures - none
 SP IMPLICATIONS OF VERTEBRAL ENDPLATE DEFECTS AND OSSIFICATION PHENOMENA Rothschild Bruce, Jonhan Ho, Youssef Masharawi Northeast Ohio Medical University, Rootstown, OH, 7 USA Department of Dermatopathology,
SP IMPLICATIONS OF VERTEBRAL ENDPLATE DEFECTS AND OSSIFICATION PHENOMENA Rothschild Bruce, Jonhan Ho, Youssef Masharawi Northeast Ohio Medical University, Rootstown, OH, 7 USA Department of Dermatopathology,
Insufficiency fracture of the tibial plateau : An often missed diagnosis
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 587-591 ORIGINAL STUDY Insufficiency of the tibial plateau : An often missed diagnosis Narayana PRASAD, Judy M. MURRAY, Deepak KUMAR, Stephen G. DAVIES From the Royal Glamorgan
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 587-591 ORIGINAL STUDY Insufficiency of the tibial plateau : An often missed diagnosis Narayana PRASAD, Judy M. MURRAY, Deepak KUMAR, Stephen G. DAVIES From the Royal Glamorgan
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Multiple Myeloma. Abstract. Introduction
 Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
Multiple Myeloma Abstract Multiple Myeloma is a plasma cell cancer that causes an overproduction of plasma cells. Multiple Myeloma is a difficult disease to diagnosis because symptoms might not be present
Management of Painful Vertebral Hemangiomas with Kyphoplasty: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review
 Pain Physician 2009; 12:E297-E303 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Reports Management of Painful Vertebral Hemangiomas with Kyphoplasty: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review Jonathan O. Jones, MD 1, Brian
Pain Physician 2009; 12:E297-E303 ISSN 2150-1149 Case Reports Management of Painful Vertebral Hemangiomas with Kyphoplasty: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review Jonathan O. Jones, MD 1, Brian
Balloon Kyphoplasty. Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures.
 Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
Balloon Kyphoplasty Overview Balloon Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to treat vertebral body compression fractures. The technique is designed to: Reduce and stabilise the fracture in a controlled
ICD 10 CM IMPLEMENTATION DATE OCT 1, 2015
 Presented by: Teri Romano, RN, MBA, CPC, CMDP ICD 10 CM IMPLEMENTATION DATE OCT 1, 2015 Source: http://journal.ahima.org/2015/02/04/us house committee to hold hearing on icd 10 implementation/ 2 2015 Web_Non
Presented by: Teri Romano, RN, MBA, CPC, CMDP ICD 10 CM IMPLEMENTATION DATE OCT 1, 2015 Source: http://journal.ahima.org/2015/02/04/us house committee to hold hearing on icd 10 implementation/ 2 2015 Web_Non
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
 Original Article 261 Minimally Invasive Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Shang-Won Yu, MD; Tsai-Sheng Fu, MD; Po-Liang Lai, MD; Wen-Jer Chen,
Original Article 261 Minimally Invasive Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture Lih-Huei Chen, MD; Chi-Chien Niu, MD; Shang-Won Yu, MD; Tsai-Sheng Fu, MD; Po-Liang Lai, MD; Wen-Jer Chen,
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression
 Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression 1 Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine November 2009, Volume 11, pp.
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Associated with Kyphosis or Sagittal Sigmoid Alignment: Outcome after Anterior or Posterior Decompression 1 Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine November 2009, Volume 11, pp.
SPINAL FRACTURES OUR TREATMENT GUIDE
 SPINAL FRACTURES OUR TREATMENT GUIDE 7 Cervical Spinal fractures are common around the world and can have a major impact on your quality of life. If not treated soon enough, they can even make carrying
SPINAL FRACTURES OUR TREATMENT GUIDE 7 Cervical Spinal fractures are common around the world and can have a major impact on your quality of life. If not treated soon enough, they can even make carrying
Nonsurgical treatment of an upper thoracic spinal subdural hemorrhage
 (2001) 39, 657 ± 661 ã 2001 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Nonsurgical treatment of an upper thoracic spinal subdural
(2001) 39, 657 ± 661 ã 2001 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Nonsurgical treatment of an upper thoracic spinal subdural
