Review Paper Praca poglądowa Pediatr Endocrino Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3:101-93
|
|
|
- Angel Thompson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Paper Praca poglądowa Pediatr Endocrino Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3: Silver-Russell Syndrome Part I: Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Background Zespół Silver-Russela cz. 1 charakterystyka kliniczna i podstawy genetyczne 1 Anna Marczak-Hałupka, 2 Maria A. Kalina, 3,4 Anna Tańska, 3 Krystyna H. Chrzanowska 1 Department of Infants and Newborn Pathology, Paediatric Centre, Sosnowiec, Poland 1 Oddział Niemowlęcy i Patologii Noworodka, Centrum Pediatrii, Sosnowiec, Polska 2 Department of Paediatrics, Paediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland 2 Katedra i Klinika Pediatrii, Endokrynologii i Diabetologii Dziecięcej, Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny, Katowice, Polska 3 Department of Medical Genetics, The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw, Poland 3 Zakład Genetyki Medycznej, Instytut Pomnik Centrum Zdrowia Dziecka, Warszawa, Polska 4 West Midlands Genetics Laboratories, Birmingham Women s Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Edgbaston, Birmingham, UK Abstract Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS) is a rare, clinically and genetically heterogeneous entity, caused by (epi)genetic alternations. It is characterized by prenatal and postnatal growth retardation, relative macrocephaly, the triangular face and body asymmetry. About 40-60% of cases are caused by hypomethylation of 11p.15.5 Imprinting Centre Region 1 (ICR1) on the paternal chromosome, and maternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 7 (UPD(7)mat) is found in 5-10% of cases. There are suggested correlations between genotype and the phenotype. Psychomotor development may be delayed, usually mildly, with school difficulties and speech delay more common in patients with UPD(7)mat. Children with 11p15 hypomethylation are shorter and lighter at birth in comparison to children with UPD(7)mat, however further deceleration tends to be more apparent in the latter group. The onset of puberty tends to occur early, with acceleration of bone age, resulting in less apparent growth spurt. Failure to thrive and feeding problems are characteristic for the infant period, and further development of a child may be conditioned by additional congenital defects. Key words: Silver-Russell syndrome, epigenetics, intrauterine growth restriction, 11p15 epimutation, UPD(7)mat, genomic imprinting Streszczenie Zespół Silvera i Russella jest rzadką jednostką, zróżnicowaną klinicznie i genetycznie, u której podłoża leżą zmiany (epi)genetyczne. Charakteryzuje się zaburzeniami wzrastania w okresie płodowym i postnatalnym, względną makrocefalią, trójkątnym kształtem twarzy i asymetrią ciała. Około 40 60% przypadków spowodowanych jest hipometalacją centrum piętnowania ICR1 w regionie 11p.15.5 chromosomu pochodzenia ojcowskiego, a u 5 10% pacjentów stwierdza się matczyną disomię chromosomu 7 (UPD(7) mat). W literaturze opisywane są korelacje fenotypowo-genotypowe. Rozwój psychomotoryczny może być opóźniony, zwykle w łagodnym stopniu, a zaburzenia mowy i trudności szkolne częściej występują w przypadku pacjentów z UPD(7)mat. Dzieci z hipometylacją 11p15 są mniejsze przy urodzeniu w porównaniu z dziećmi z UPD(7)mat, jednak postnatalne zwolnienie wzrastania jest bardziej wyrażone w grupie UPD(7)mat. Początek dojrzewania występuje stosunkowo wcześnie, z akceleracją wieku kostnego i słabiej wyrażonym skokiem pokwitaniowym. Okres niemowlęcy charakteryzuje się słabym przyrostem masy ciała i trudnościami w żywieniu, a dalszy rozwój dziecka warunkowany jest w znacznym stopniu współwystępującymi wadami wrodzonymi Słowa kluczowe: zespół Silvera i Russella, zmiany epigenetyczne, wewnątrzmaciczne opóźnienie wzrastania, epimutacja regionu 11p15, UPD(7)mat, piętnowanie rodzicielskie 102 Prof. dr hab. n. med. Krystyna H. Chrzanowska Zakład Genetyki IP CZD Al. Dzieci Polskich 20; Warszawa tel.: ; fax: k.chrzanowska@ipczd.pl Received: Accepted: Conflict of interests: none declared.
2 Silver-Russell Syndrome Part I: Clinical Characteristics and Genetic... Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3: Introduction The aim of this two-part review is presentation of Silver- Russell syndrome, an exemplary disorder of intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR). It may be connected with long-term sequelae, thus requiring multidisciplinary approach, including endocrine monitoring of the somatic development. Its clinical presentation and genetic background are provided in the first part of the review, followed by the diagnostic algorithm and management in part two. Definition Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS; Russell-Silver syndrome, RSS; Silver-Russell dwarfism; OMIM#180860) is a rare, clinically and genetically heterogeneous entity, basis of which is formed by epigenetic alternations. It is characterized by prenatal and postnatal growth retardation, relative macrocephaly, the triangular face and body asymmetry. Historical notes The first description of the syndrome was provided by Silver et al. in 1953, who presented two unrelated children with low birth weight, short stature, body hemihypertrophy and elevated urinary concentrations of gonadotropins [1]. Shortly after the first report, in 1954, Russell et al. independently presented clinical data of five unrelated patients with intrauterine hypotrophy, triangular facial gestalt, micrognathia and wide mouth with narrow lips. Besides, body asymmetry was found in two of those children [2]. Not until four decades after the first clinical descriptions, was it shown that genetic factors were involved in the pathomechanism of SRS. Identification of uniparental maternal disomy of chromosome 7 (UPD(7)mat) in a child with IUGR contributed to systematic and comparative examinations in patients with SRS and in children with IUGR [3]. It was shown that the mechanism of UPD(7)mat was responsible for about 4-10% of SRS cases [4] Further research focused on the p15 region of chromosome 11, containing genes connected with foetal growth. Interesting findings pertained to the duplication of the region p15 on the maternal chromosome 11 in a child with IUGR [4]. Duplications of the same region on the paternal chromosome were found in some cases of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, which, by contrast, is characterised by excessive growth. Subsequent findings of hypomethylation of the ICR (imprinting control region) of p15 on the maternal copy of the chromosome 11, contributed to the statement that alternations in 11p15 region should be taken into account in patients with growth disorders, even without apparent dysmorphic features [5, 6]. Epidemiology Silver-Russell syndrome is a rare entity, and its prevalence is estimated as high as / population [7]. Most cases are sporadic, with equal gender distribution. Until now there have been several hundred cases described in the literature, comprising all racial groups. The number of reports is still increasing, mainly due to multicentre investigations, focusing on genetic factors confirming clinical diagnosis of SRS. Clinical description Prenatal and postnatal growth retardation along with craniofacial dysmorphy and body asymmetry are the major features constituting the clinical presentation of SRS. It should be emphasized that the phenotype, which is described below, changes with age, particularly on the face and the characteristic features are maintained until the age of 3 years [8-10]. The shape Table I. Craniofacial features of children with SRS Tabela I. Cechy twarzoczaszki u dzieci z SRS Part of the head Forehead Fontanels and sutures Eyes Ears Nose Chin Mouth Oral cavity and teeth Characteristic high, frontal bossing wide, late closure wide palpebral fissures, dense eyelashes, bluish sclera occipital rotation prominent nasal bridge, round tip micrognathia wide, downturned corners, narrow lips high palate, narrow dental arches with crowding of teeth, abnormal size and shape of teeth, premolar hypodontia 103
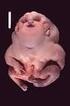
3 Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3: Marczak-Hałupka A., Kalina M.A., Tańska A., Chrzanowska K.H. of the face tends to get rounder in females and the jaw enlarges in males [8]. Thus photographs from the early childhood may be helpful in diagnosing the syndrome in older children. Besides, long follow-up of children with SRS proved the need of interdisciplinary care due to health problems appearing in different periods of life, related to various systems and organs. The head The face has a characteristic appearance [8,11 13] [table 1]. It is generally small, with triangular shape, hypoplasia of the mid-part, and variable asymmetry in a proportion of children are observed [fig. 1A, 1B]. Head circumference is within the centile norm for the age and gender, most often below the population mean. However it exceeds the number of standard deviations (SD) for the length or height of the body. Along with the characteristic shape of the skull, it results in the relative macrocephaly [8,11,14,15]. Growth and body proportions Most children with SRS are full term babies, however their auxologic parameters at birth, apart from the head circumference, are significantly smaller in relation to the healthy population, and also as compared to other children born small for gestational age (SGA) without SRS [8-10, 15, ]. According to data provided by Binder et al., mean standard deviation score (SDS) for the mass and length at birth is -3 SDS [16]. Essential information about further course of spontaneous growth was provided by Wollmann et al. [11] Observation comprising over 380 patients with clinical diagnosis of SRS showed increasing height deficit during the first 3 years of life. Then, between 4 and 10 years of age, height velocity was stable, parallel to the 3 rd centile, with the mean height SD equal to -4.3 SDS. Mean final height was cm ± 7.8 cm for men and ± 9.0 cm for women. Weight changes are parallel to height. Failure to thrive is often a striking feature in infancy, requiring feeding aids. Children with SRS present poorly developed subcutaneous tissue and usually are underweight, with body mass index (BMI) rarely exceeding 25 th centile in adolescence [9]. It should be emphasized that mean values of weight and height deficits, as well as growth dynamics may differ depending on the epi(genotype). It is observed that SRS children with 11p15 hypomethylation are shorter and lighter at birth in comparison to children with UPD(7)mat. However height deficit is sustained at the same level in the first group, whereas deceleration is observed more often in children with UPD(7)mat. Initial length deficit in the latter group is not as significant as in children with 11p15 hypomethylation. Thus, in the UPD(7)mat group relative macrocephaly at birth may not be as apparent [15]. Fig. 1. The head of a 3-month old infant with Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS) caused by 11p15.5 hypomethylation; en face (1A) and the profile (2B) Ryc. 1. Głowa 3 miesięcznego niemowlęcia z zespołem Silver-Russella spowodowana hypometylacją 11p15,5 1a twarz 2 profil 104
4 Silver-Russell Syndrome Part I: Clinical Characteristics and Genetic... Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3: Body proportions are also disturbed by asymmetry of the trunk, head and limbs, observed in about one third of patients with SRS. It is related more often to the 11p15 hypomethylation, possibly resulting from the mosaicism of the hypomethylation level in different tissues [8, 10, 17, 18]. Asymmetry can be apparent not only as differences of the length, but also of the circumference of extremities. The difference of the limbs length may reach 2.5 cm, causing significant scoliosis later in life, increasing body disproportions [8]. Puberty Data on sexual development in SRS children are based on general trend of puberty in SGA children. Pubic hair appear earlier (pubarche praecox), and other pubertal signs, including menarche, may also occur relatively early but not necessarily precociously, progressing quickly [16,19]. However there are also case reports of delayed puberty, primary amenorrhea and congenital defects of the genitourinary system [17] [table 2]. In children with SRS, bone age is delayed in the first years of life and then it advances parallel to growth [11]. Generally, in children with SGA, including SRS, acceleration of the bone age and height velocity takes place in earlier stages of sexual development, resulting in shorter period of puberty and less apparent growth spurt [11,19]. It is also suggested that occurrence of visceral adiposity with insulin resistance already in the childhood, may influence the onset of puberty in SGA children [19]. Table II. Congenital defects and clinical features in patients with SRS Tabela II. Wady wrodzone i objawy klinicznie zespołu Silver-Russela Systemic involvement [reference] Skeletal [8, 12, 16] Gastrointestinal [9, 10 22] Genitourinary [8, 10, 16] Cardiovascular [10, 23] Ophthalmological [24] Dental [13, 11] Other [8-10] Clinical features Limb asymmetry Scoliosis Lumbar hypolordosis Hip dysplasia 5 th finger clinodactyly 2/3 toe syndactyly Brachydactyly Camptodactyly Arthrogryposis Failure to thrive, poor sucking, food aversion in infancy Gastro-oesphageal reflux Esophagitis Renal anomalies Defects of the posterior urethral valve Hypospadias Cryptorchidism, Anorchia, Inguinal hernia Absent/hypoplastic vagina, Hypoplastic/bicornuate uterus Congenital heart defects ASD, VSD, PDA Total anomalous pulmonary venous return, Triatriatum sinistrum Refractive errors Visual acuity disturbances Strabismus Small optic discs Increased tortuosity of retinal vessels Strabismus Malocclusion Crowded teeth Hypodontia Hypoglycemia Excessive sweating Café-au-lait patches Delayed closure of fontanels Otitis media Metabolic syndrome 105
5 Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3: Marczak-Hałupka A., Kalina M.A., Tańska A., Chrzanowska K.H. Psychomotor development Psychomotor delay, observed even in half of the SRS patients, is usually mild [8, 10, 14]. It has been reported that in UPD(7)mat group, school difficulties and speech problems occur more often [17]. Lai et al. assessed full scale IQ, using Wechsler test, in 25 children with clinical diagnosis of SRS at the mean age of 8.8 years. Impairment of cognitive abilities was found in approximately half of the subjects, with the reading rate age 2 years behind the chronological age [14]. Similar investigations were also conducted in Poland, finding normal IQ in nearly 40% of cases, whereas in about 20% of subjects the value of full scale IQ was lower than 69, indicating intellectual disability in some children with SRS [20]. Noekler and Wollmann carried out comparative analysis of cognitive abilities In children with SRS and their health siblings, showing higher IQ scores by 8 points in the control group. Intellectual development was not influenced by additional parameters like birth weight and length, intensity of phenotypic features or growth hormone therapy [21]. Delay of the motor development is connected probably with decreased muscular tone and relative macrocephaly in the neonatal period, and the mean age of walking is 20 months according to Wakeling et al [10]. About 38 64% of SRS patients display hypomethylation at the imprinting center region 1 (ICR1) on 11p15.5.This epigenetic defect leads to the downregulation of paternally expressed IGF2 which encodes major foetal growth factor and the biallelic expression of H19 [25, 26] [fig. 2B]. Most of the SRS patients with imprinting aberrations show mosaic distribution of the epimutation what makes the molecular diagnosis challenging. Uneven distribution of epimutation in different tissues can result in false-negatives when almost normal methylation level is presented in lymphocytes [27]. About 7 10% of patients with SRS phenotype carry maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 7 (UPD(7)mat). Interestingly, maternal UPD of chromosome 11 (UPD(11)mat) have been reported only once [6, 28]. Chromosomal duplications of 7p11.2-p13 and deletion of the paternal allele 7q32 region have also been confirmed in patients with Silver-Russell syndrome features [29, 30].Furthermore, chromosomal imbalances i.e., duplications of maternal 11p15.5 region [Fig. 2C], structural aberrations of chromosome 7, rearrangements of other chromosomes and point mutations are associated with an increased recurrence risk and the need of identifying carriers in the family [28]. Congenital defects It is suggested that congenital abnormalities are more common in patients with ICR1 hypomethylation. Diversity as well intensity of defects depend on the degree of ICR methylation in different tissues [10, 17] [table 2]. Aetiopathogenesis Silver-Russell syndrome is an imprinting disorder caused by the epigenetic abnormalities at chromosome 11p15.5. Imprinted genes, expression of which is determined by their parental origin, are involved in various aspects of human growth. They tend to cluster, thus the imprinting control is not usually limited to a single gene at an imprinted locus. Chromosome 11p15.5 contains a cluster of imprinted genes that play a vital role in the control of foetal growth. The cluster consists of two neighbouring imprinted domains, the IGF2/H19 domain in the telomeric region and the KCNQ1OT1/CDKN1C domain in the centromeric region, each under control of its own imprinting centre, ICR1 and ICR2, respectively. ICR1 is methylated on the paternal allele and that methylation protects from binding CTCF protein which allows the enhancer downstream of H19 gene access to the IGF2 promoter. On the maternal allele the ICR1 is unmethylated and CTCF binds to it. CTCF acts as an insulator and prevents the activation of IGF2 promoter by enhancer, at the same time it induces activation of the H19 promoter (encoding a noncoding RNA). Methylated on the maternal allele ICR2 allows expression of CDKN1C and KCNQ1 genes. On the unmethylated paternal allele expression of KCNQ1OT1 (long noncoding RNA) regulates the imprinting of the domain [25][fig. 2A]. Fig. 2. Scheme of epigenetic regulation of 11p15.5 region (2A) and possible (epi)mutations detectable in SRS. Hypomethylation of the 11p15.5 region (2B) which leads to the downregulation of paternally expressed IGF2 gene. Imbalance of IGF2 expression is also caused by maternal duplication of that region (2C). 106
6 Silver-Russell Syndrome Part I: Clinical Characteristics and Genetic... Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3: Recently Brioude et al. reported one family with maternally transmitted dominant CDKN1C mutation. The author has proved that gain-of-function mutations in CDKN1C can lead to severe prenatal and postnatal growth retardation [31]. Also overexpression of the CDKN1C gene due to maternal duplication of the ICR2 domain is causally associated with SRS and it has been described in a three generation family associated with SRS [32]. The aetiology of almost half of SRS cases is so far unknown. Numerous (sub)-microscopic chromosome imbalances with SRS phenotype have been published recently. In 1-2% of SRS cases maternal duplications of the whole 11p15 chromosomal region have been reported. It has been shown that up to 19% of patients with short stature and features reminiscent to SRS carry relevant pathogenic chromosome aberrations, among which the most common were deletions in 1q21, 12q14 15q26, 17p13, and 22q11 [6, 26] In the last few years a notable number of SRS patients have been reported with aberrant methylation at disease specific 11p15.5 locus as well as with methylation abnormalities at other chromosomal sites. In the group of patient with ICR1 hypomethylation about 7.1% of them had affected other loci. This observation defined new subgroup of patients known to be predisposed to multilocus methylation defects (MLMDs). In order to specify the frequency and distribution of molecular changes, in patients clinically diagnosed as SRS, the molecular test should combine assays with broad range of detection of mutations, epimutations, translocations and multilocus methylation defects [28]. Key points Clinical presentation The clinical hallmark of SRS is prenatal and postnatal growth retardation Characteristic phenotype includes triangular face with relative macrocephaly, body asymmetry, 5 th finger clinodactyly; the spectrum of congenital defects may be wide Feeding problems in infancy result in failure to thrive Children with 11p15 hypomethylation are shorter and lighter at birth in comparison to children with UPD(7)mat, however further deceleration tends to be more apparent in the latter group. Puberty may occur early, with acceleration of the bone age and height velocity in earlier stages of sexual development, resulting in less apparent growth spurt Psychomotor development may be delayed, including speech delay, depending on the genotype and severity of the phenotype Genetic defects 40-60% of SRS cases are caused by hypomethylation at the ICR1 in 11p15 (loss of paternal methylation) which occur in mosaic state in the affected tissues of the body Maternal UPD7 has been implicated in 5%-10% of SRS. Up to 19% of SRS-like patients carry structural chromosomal aberrations. Some patients with ICR1 hypomethylation also display multilocus methylation defects (MLMDs). In patients with family history of SRS-like phenotypes CDKN1C point mutation or microduplication of the ICR2 domain should be taken into account. References 1. Silver HK, Kiyasu W, George J, Deamer WC. Syndrome of congenital hemihypertrophy, shortness of stature, and elevated urinary gonadotropins. Pediatrics.1953; 12: Russell A. A syndrome of intra-uterine-dwarfism recognizable at birth with cranio-facial dysostosis, disproportionate short arms, and other anomalies (5 examples). Proc Soc Med. 1954; 47: Kotzot D, Schmitt S, Bernasconi et al. Uniparental disomy 7 in Silver-Russell syndrome and primordial growth retardation. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4: Fisher AM, Thomas NS, Cockwell A et al. Duplications of chromosome 11p15 of maternal origin result in a phenotype that includes growth retardation. Hum Genet. 2002;111: Gicquel C, Rossignol S, Cabrol S et al. Epimutation of the telomeric imprinting center region on chromosome 11p15 in Silver-Russell syndrome. Nature Genet 2005; 37: Eggermann T, Spengler S, Gogiel M et al. Epigenetic and genetic diagnosis of Silver-Russell syndrome. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2012;12: Abu-Amero S, Monk D, Frost J et al.. The genetic aetiology of Silver- -Russell syndrome. J Med Genet. 2008;45: Price SM, Stanhope R, Garrett C et al. The spectrum of Silver-Russell syndrome: a clinical and molecular genetic study and new diagnostic criteria.j Med Genet. 1999;36(11): Netchine I, Rossignol S, Dufourg MN et al. 11p15 imprinting center region 1 loss of methylation is a common and specific cause 107
7 Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 2014;21,3: Marczak-Hałupka A., Kalina M.A., Tańska A., Chrzanowska K.H. of typical Russell-Silver syndrome: clinical scoring system and epigenetic-phenotypic correlations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92: Wakeling EL, Amero SA, Alders M et al. Epigenotype-phenotype correlations in Silver-Russell syndrome. J Med Genet. 2010;47: Wollmann HA, Kirchner T, Enders H, et al. Growth and symptoms in Silver-Russell syndrome: review on the basis of 386 patients. Eur J Pediatr. 1995;154: Abraham E, Altiok H, Lubicky JP. Musculoskeletal manifestations of Russell-Silver syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(5): Kozarzewska M, Matosek A, Olczak-Kowalczyk D i wsp. Objawy kliniczne w jamie ustnej w zespole Silvera i Russella. Opis przypadku. Nowa Stomatologia 2009; 1-2; Lai KY, Skuse D, Stanhope R, Hindmarsh P. Cognitive abilities associated with the Silver-Russell syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1994;71: Binder G, Seidel AK, Martin DD, Schweizer R et al. The endocrine phenotype in silver-russell syndrome is defined by the underlying epigenetic alteration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93: Binder G, Liebl M, Woelfle J, et al. Adult height and epigenotype in children with Silver-Russell syndrome treated with GH. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013;80: Bruce S, Hannula-Jouppi K, Peltonen J et al. Clinically distinct epigenetic subgroups in Silver-Russell syndrome: the degree of H19 hypomethylation associates with phenotype severity and genital and skeletal anomalies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94: Bartholdi D, Krajewska-Walasek M, Ounap K et al. Epigenetic mutations of the imprinted IGF2-H19 domain in Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS): results from a large cohort of patients with SRS and SRS- -like phenotypes. J Med Genet. 2009;46: Verkauskiene R, Petraitiene I, Albertsson Wikland K. Puberty in children born small for gestational age. Horm Res Paediatr. 2013;80: Sieńko M, Petriczko E, Biczysko-Mokosa A i wsp. Ocena zdolności intelektualnych u dzieci z zespołem Silver-Russell. Pediatr Endocrinol 2010; 2: Noeker M, Wollmann HA. Cognitive development in Silver-Russell syndrome: a sibling-controlled study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2004;46: Anderson J, Viskochil D, O Gorman M, Gonzales C. Gastrointestinal complications of Russell-Silver syndrome: a pilot study. Am J Med Genet ;113: Ghanim M, Rossignol S, Delobel B et al. Possible association between complex congenital heart defects and 11p15 hypomethylation in three patients with severe Silver-Russell syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2013;161A: Gronlund MA, Dahlgren J, Aring E et al. Ophthalmological findings in children and adolescents with Silver-Russell syndrome. Brit J Ophthal 2011; 95: Azzi S, Abi Habib W, Netchine I. Beckwith-Wiedemann and Russell- -Silver Syndromes: from new molecular insights to the comprehension of imprinting regulation. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2014; 21: Fokstuen S, Kotzot D. Chromosomal rearrangements in patients with clinical features of Silver-Russell syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2014; 164A: Zeschnigk M, Albrecht B, Buiting K et al. IGF2/H19 hypomethylation in Silver-Russell syndrome and isolated hemihypoplasia. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008;16: Eggermann T, Heilsberg AK, Bens S et al. Additional molecular findings in 11p15-associated imprinting disorders: an urgent need for multi-locus testing. J Mol Med 2014; 92: Monk D, Wakeling EL, Proud V et al. Duplication of 7p11.2-p13, including GRB10, in Silver-Russell syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2000; 66: Eggermann T, Spengler S, Begemann M et al. Deletion of the paternal allele of the imprinted MEST/PEG1 region in a patient with Silver-Russell syndrome features. Clin Genet 2012; 81: Brioude F, Oliver-Petit I, Blaise A et al. CDKN1C mutation affecting the PCNA-binding domain as a cause of familial Russell Silver syndrome. J Med Genet 2013; 50: Bonaldi A, Mazzeu JF, Costa SS, Honjo RS, Bertola DR, Albano LM, Furquim IM, Kim CA, Vianna-Morgante AM. Microduplication of the ICR2 domain at chromosome 11p15 and familial Silver-Russell syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A(10):
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Chromosomal Abnormalities
 Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease
 The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
Each person normally has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all. We inherit one chromosome per pair from our mother and one from our father.
 AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
Fact Sheet 14 EPIGENETICS
 This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
a guide to understanding moebius syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association
 a guide to understanding moebius syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding moebius syndrome this parent s guide to Moebius syndrome is designed to answer questions
a guide to understanding moebius syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding moebius syndrome this parent s guide to Moebius syndrome is designed to answer questions
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 24; 23-11-2011
 SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME030-C1 BWS/RSS Lot C1-0711. As compared to version B2 (lots B2-0309, B2-1109 & B2-1110), three probes for H19 and two for KCNQ1 have been replaced. One H19 has been removed and
SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME030-C1 BWS/RSS Lot C1-0711. As compared to version B2 (lots B2-0309, B2-1109 & B2-1110), three probes for H19 and two for KCNQ1 have been replaced. One H19 has been removed and
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities
 Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder. Chapter 14. Copyright 2008 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
The Newborn With a Congenital Disorder Chapter 14 Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Prior Authorization Form
 Prior Authorization Form Growth Hormone This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date. Fax signed forms to CVS/Caremark at
Prior Authorization Form Growth Hormone This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date. Fax signed forms to CVS/Caremark at
Cerebral palsy, neonatal death and stillbirth rates Victoria, 1973-1999
 Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1)
 Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1) What is RSMD1? The congenital muscular dystrophies are a group of conditions which share early presentation
Rigid spine syndrome (RSS) (Congenital muscular dystrophy with rigidity of the spine, including RSMD1) What is RSMD1? The congenital muscular dystrophies are a group of conditions which share early presentation
Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
 Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP Kozmac@georgetown.edu cck2@gunet.georgetown.edu Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP Kozmac@georgetown.edu cck2@gunet.georgetown.edu Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics Michigan Birth Defects Registry
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics Michigan Birth Defects Registry BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April 30, 2014
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics Michigan Birth Defects Registry BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April 30, 2014
FDA Approved Indications
 Preferred Agents: Humatrope (somatropin) Nutropin (somatropin) Medication Nutropin AQ (somatropin) Nutropin AQ NuSpin (somatropin) Non-Preferred Agents: Genotropin (somatropin) Omnitrope (somatropin) Norditropin
Preferred Agents: Humatrope (somatropin) Nutropin (somatropin) Medication Nutropin AQ (somatropin) Nutropin AQ NuSpin (somatropin) Non-Preferred Agents: Genotropin (somatropin) Omnitrope (somatropin) Norditropin
Obtaining insurance coverage for human growth hormone treatment for Idiopathic Short Stature In 2003, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved
 Obtaining insurance coverage for human growth hormone treatment for Idiopathic Short Stature In 2003, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of growth hormone (GH) for the long-term treatment
Obtaining insurance coverage for human growth hormone treatment for Idiopathic Short Stature In 2003, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of growth hormone (GH) for the long-term treatment
The Genetics of Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS)
 The Genetics of Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) Introduction Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is an overgrowth disorder caused by changes in the activity of growth promoting and growth suppressing genes.
The Genetics of Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) Introduction Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is an overgrowth disorder caused by changes in the activity of growth promoting and growth suppressing genes.
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy. Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay.
 Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Developmental Disorders
 Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
 Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta? 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: bonelink@oif.org The Osteogenesis
Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta? 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: bonelink@oif.org The Osteogenesis
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics
 G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS
 DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
Chapter 7 COGNITION PRACTICE 240-end Intelligence/heredity/creativity Name Period Date
 Chapter 7 COGNITION PRACTICE 240-end Intelligence/heredity/creativity Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Creativity
Chapter 7 COGNITION PRACTICE 240-end Intelligence/heredity/creativity Name Period Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Creativity
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April 15, 2008
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by April
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
The etiology of orthodontic problems Fifth session
 بنام خداوند جان و خرد The etiology of orthodontic problems Fifth session دکتر مھتاب نوری دانشيار گروه ارتدنسی Course Outline( 5 sessions) Specific causes of malocclusion Genetic Influences Environmental
بنام خداوند جان و خرد The etiology of orthodontic problems Fifth session دکتر مھتاب نوری دانشيار گروه ارتدنسی Course Outline( 5 sessions) Specific causes of malocclusion Genetic Influences Environmental
USEFULNESS OF BONE AGE IN PAEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY. Rina Balducci Center of Pediatric Endocrinology, Department of Public Health and Cell Biology
 USEFULNESS OF BONE AGE IN PAEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY Gian Luigi Spadoni and Stefano Cianfarani Rina Balducci Center of Pediatric Endocrinology, Department of Public Health and Cell Biology Tor Vergata University,
USEFULNESS OF BONE AGE IN PAEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY Gian Luigi Spadoni and Stefano Cianfarani Rina Balducci Center of Pediatric Endocrinology, Department of Public Health and Cell Biology Tor Vergata University,
Prader-Willi Syndrome
 U.S.A. Prader-Willi Syndrome MEDICAL ALERT: A Diagnosis and Reference Guide for Physicians and Other Health Professionals Prader-Willi Syndrome Basic Facts 1. PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME (PWS) is an uncommon
U.S.A. Prader-Willi Syndrome MEDICAL ALERT: A Diagnosis and Reference Guide for Physicians and Other Health Professionals Prader-Willi Syndrome Basic Facts 1. PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME (PWS) is an uncommon
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING
 REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS
 AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS JAGWINDER SANDHU, MD CHILD, ADOLESCENT AND ADULT PSYCHIATRIST 194 N HARRISON STREET PRINCETON, NJ 08540 PH: 609 751 6607 Staff Psychiatrist Carrier clinic Belle Mead NJ What is
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS JAGWINDER SANDHU, MD CHILD, ADOLESCENT AND ADULT PSYCHIATRIST 194 N HARRISON STREET PRINCETON, NJ 08540 PH: 609 751 6607 Staff Psychiatrist Carrier clinic Belle Mead NJ What is
Fact sheet: UK 2-18 years Growth Chart
 Fact sheet: UK 2-18 years Growth Chart This chart will most commonly be used for the assessment of individual children, rather than for population growth monitoring purposes and includes a number of new
Fact sheet: UK 2-18 years Growth Chart This chart will most commonly be used for the assessment of individual children, rather than for population growth monitoring purposes and includes a number of new
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA)
 Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence
 a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence this parent s guide to Pierre Robin Sequence is designed
a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence this parent s guide to Pierre Robin Sequence is designed
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb.
 The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
The Patterns and Public Health Impact of Heart Defects in Texas Pediatric Cardiac Care Conference VI Dell Children s Medical Center, Feb. 7-8, 2013 Mark Canfield, Ph.D. Manager, Birth Defects Epidemiology
New Estimates of the Economic Benefits of Newborn Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism in the US
 The findings and conclusions in this presentation have not been formally disseminated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and should not be construed to represent any agency determination
The findings and conclusions in this presentation have not been formally disseminated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and should not be construed to represent any agency determination
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS
 TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
The sensitive marker for glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Estimation of GFR from Serum Cystatin C:
 The sensitive marker for glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Estimation of GFR from Serum Cystatin C: The good correlation allows close estimation of GFR Cystatin C GFR GFR in serum estimated* measured* n
The sensitive marker for glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Estimation of GFR from Serum Cystatin C: The good correlation allows close estimation of GFR Cystatin C GFR GFR in serum estimated* measured* n
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Central core disease
 Central core disease Central core disease falls under the umbrella of congenital myopathies which are characterised by muscle weakness and wasting. It is a rare condition, and symptoms are usually present
Central core disease Central core disease falls under the umbrella of congenital myopathies which are characterised by muscle weakness and wasting. It is a rare condition, and symptoms are usually present
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
APPENDIX 5 MBCHB CURRENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Appendix 5 166
 APPENDIX 5 MBCHB CURRENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Appendix 5 166 CORE CURRICULUM IN CHILD HEALTH This document is a guide for undergraduates, and summarises the key knowledge, skills and attitudes that it is
APPENDIX 5 MBCHB CURRENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Appendix 5 166 CORE CURRICULUM IN CHILD HEALTH This document is a guide for undergraduates, and summarises the key knowledge, skills and attitudes that it is
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
Management and Treatment Guidelines for Cornelia de Lange Syndrome
 Management and Treatment Guidelines for Cornelia de Lange Syndrome These cards highlight routine care for people with CdLS needed by specific age groups, including infancy, early and late childhood, adolescence
Management and Treatment Guidelines for Cornelia de Lange Syndrome These cards highlight routine care for people with CdLS needed by specific age groups, including infancy, early and late childhood, adolescence
Growth Hormone Therapy
 Growth Hormone Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.011 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 10/28/2011 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s) of Service:
Growth Hormone Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.011 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 10/28/2011 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s) of Service:
Non-covered ICD-10-CM Codes for All Lab NCDs
 Non-covered ICD-10-CM s for All Lab NCDs This section lists codes that are never covered by Medicare for a diagnostic lab testing service. If a code from this section is given as the reason for the test,
Non-covered ICD-10-CM s for All Lab NCDs This section lists codes that are never covered by Medicare for a diagnostic lab testing service. If a code from this section is given as the reason for the test,
Medicaid Disability Manual
 Part B The following sections apply to individuals under age 18. If the criteria in Part B do not apply, Part A criteria may be used when those criteria give appropriate consideration to the effects of
Part B The following sections apply to individuals under age 18. If the criteria in Part B do not apply, Part A criteria may be used when those criteria give appropriate consideration to the effects of
Health Reform Minnesota. Health Care Home Care Coordination Tiering-Billing Workshop October 1, 2014
 Health Reform Minnesota Health Care Home Care Coordination Tiering-Billing Workshop October 1, 2014 Objectives Gain a better understanding of how to use the HCH Care Coordination Tier Assignment tool for
Health Reform Minnesota Health Care Home Care Coordination Tiering-Billing Workshop October 1, 2014 Objectives Gain a better understanding of how to use the HCH Care Coordination Tier Assignment tool for
How To Test For Medical Genetics
 Realizacja specjalizacji w zakresie genetycznej diagnostyki laboratoryjnej. Warszawa 22 czerwca 2010. Ministerstwo Zdrowia. Current status of counselling and medical diagnostics in the public health service
Realizacja specjalizacji w zakresie genetycznej diagnostyki laboratoryjnej. Warszawa 22 czerwca 2010. Ministerstwo Zdrowia. Current status of counselling and medical diagnostics in the public health service
Prehistoric skulls have minimal malocclusions. Why do contemporary industrialized societies have such a high incidence of malocclusion?
 Prehistoric skulls have minimal malocclusions. Why do contemporary industrialized societies have such a high incidence of malocclusion? C1 This historic skull has good facial form, beautiful dental occlusion
Prehistoric skulls have minimal malocclusions. Why do contemporary industrialized societies have such a high incidence of malocclusion? C1 This historic skull has good facial form, beautiful dental occlusion
Causes of Birth Defects
 Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Trasposable elements: P elements
 Trasposable elements: P elements In 1938 Marcus Rhodes provided the first genetic description of an unstable mutation, an allele of a gene required for the production of pigment in maize. This instability
Trasposable elements: P elements In 1938 Marcus Rhodes provided the first genetic description of an unstable mutation, an allele of a gene required for the production of pigment in maize. This instability
ICD-9-CM/ICD-10-CM Codes for MNT
 / Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
/ Codes for MNT ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes are used by physicians and medical coders to assign medical diagnoses to individual patients. It is not within the scope of practice
Population prevalence rates of birth defects: a data management and epidemiological perspective
 Population prevalence rates of birth defects: a data management and epidemiological perspective Merilyn Riley Abstract The Victorian Birth Defects Register (VBDR) is a population-based surveillance system
Population prevalence rates of birth defects: a data management and epidemiological perspective Merilyn Riley Abstract The Victorian Birth Defects Register (VBDR) is a population-based surveillance system
2016 CODING FOR FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS
 2016 CODING FOR FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Listed below are the most commonly used codes applicable to FASD patient care. Code Description ICD-10-CM Primary Diagnosis P04.3 Newborn (suspected to
2016 CODING FOR FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Listed below are the most commonly used codes applicable to FASD patient care. Code Description ICD-10-CM Primary Diagnosis P04.3 Newborn (suspected to
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics. January 2006
 Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics January 2006 1. BACKGROUND ICSI has been shown to be effective for male factor infertility and it also
Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics January 2006 1. BACKGROUND ICSI has been shown to be effective for male factor infertility and it also
OVERALL PERFORMANCE. Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment
 OVERALL PERFORMANCE Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment Name: University: This resident completed the standardized assessment of history -taking, physical examination
OVERALL PERFORMANCE Pediatrics In-Training History and Physical Examination (HPE) Assessment Name: University: This resident completed the standardized assessment of history -taking, physical examination
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
 GROWTH IN CHARGE: FOR THE PHYSICIAN Kim Blake, M.D. IWK Grace Health Centre, 5850 University Ave., Halifax, Nova Scotia B3J 3G9, Canada kblake@is.dal.ca (902)420-6499 Growth in children with CHARGE has
GROWTH IN CHARGE: FOR THE PHYSICIAN Kim Blake, M.D. IWK Grace Health Centre, 5850 University Ave., Halifax, Nova Scotia B3J 3G9, Canada kblake@is.dal.ca (902)420-6499 Growth in children with CHARGE has
Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease
 Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder affecting about one out of every 350 African Americans. Most children
Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Educator s Guide to Sickle Cell Disease Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder affecting about one out of every 350 African Americans. Most children
Role of Body Weight Reduction in Obesity-Associated Co-Morbidities
 Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME
 GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME Genetic testing for mutations in fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and other genes has become an important and reliable option to aid in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome and related
GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME Genetic testing for mutations in fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and other genes has become an important and reliable option to aid in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome and related
Growth Hormone Deficiency
 Growth Hormone Deficiency What is growth hormone deficiency? 1,2 Growth hormone deficiency is when your body doesn t make enough growth hormone. Growth hormone is one of many hormones made by the pituitary
Growth Hormone Deficiency What is growth hormone deficiency? 1,2 Growth hormone deficiency is when your body doesn t make enough growth hormone. Growth hormone is one of many hormones made by the pituitary
Muscular Dystrophy. By. Tina Strauss
 Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
Validation and Replication
 Validation and Replication Overview Definitions of validation and replication Difficulties and limitations Working examples from our group and others Why? False positive results still occur. even after
Validation and Replication Overview Definitions of validation and replication Difficulties and limitations Working examples from our group and others Why? False positive results still occur. even after
Early Signs of Puberty in Very Young Children with Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Early Signs of Puberty in Very Young Children with Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Occasionally I see a parent on a message board asking about early signs of
www.complexchild.com Early Signs of Puberty in Very Young Children with Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Occasionally I see a parent on a message board asking about early signs of
What women can do to optimise their health during pregnancy and that of their baby Claire Roberts
 Periconception Planning to Protect Pregnancy and Infant Health 2015 What women can do to optimise their health during pregnancy and that of their baby Claire Roberts Pregnancy Complications Preterm Birth
Periconception Planning to Protect Pregnancy and Infant Health 2015 What women can do to optimise their health during pregnancy and that of their baby Claire Roberts Pregnancy Complications Preterm Birth
Information leaflet. Centrum voor Medische Genetica. Version 1/20150504 Design by Ben Caljon, UZ Brussel. Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel
 Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Autism and Intellectual Disabilities
 Autism and Intellectual Disabilities (DSM IV & V) Accessibility Politecnico di Milano Autism (I) A total of six (or more) items from (A), (B), and (C), with at least two from (A), and one each from (B)
Autism and Intellectual Disabilities (DSM IV & V) Accessibility Politecnico di Milano Autism (I) A total of six (or more) items from (A), (B), and (C), with at least two from (A), and one each from (B)
Family History and Diabetes. Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional
 Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13)
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 117 Information sheet to help
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 117 Information sheet to help
Heritability: Twin Studies. Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait
 TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
CSP. Genetic testing in children with developmental delay. Common Sense Pathology. CONTENTS Who/when to test What tests to order Case studies
 CSP Common Sense Pathology FEBRUARY 2011 A REGULAR CASE-BASED SERIES ON PRACTICAL PATHOLOGY FOR GPs CONTENTS Who/when to test What tests to order Case studies Genetic testing in children with developmental
CSP Common Sense Pathology FEBRUARY 2011 A REGULAR CASE-BASED SERIES ON PRACTICAL PATHOLOGY FOR GPs CONTENTS Who/when to test What tests to order Case studies Genetic testing in children with developmental
Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations Disclaimer Coding Information References Policy History
 Original Issue Date (Created): 4/1/2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 11/24/2015 Effective Date: 2/1/2016 Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations
Original Issue Date (Created): 4/1/2014 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 11/24/2015 Effective Date: 2/1/2016 Policy Product Variations Description/Background Rationale Definitions Benefit Variations
Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010
 Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS
 CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS The purpose of the logbook is to show that the applicant has been significantly involved in the evaluation and counselling of patients seeking
CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS The purpose of the logbook is to show that the applicant has been significantly involved in the evaluation and counselling of patients seeking
THE BEATIFUL FACE. Beauty. Esthetics. Beauty ESTHETICS LOCAL FASHIONS. Notion of beauty. Looking good. Orthodontics 2005
 THE BEATIFUL FACE Orthodontics 2005 Malcolm E. Meistrell,, Jr., D.D.S. Clinical Professor of Dentistry Division of Orthodontics School of Dental and Oral Surgery Columbia University Beauty Beauty Esthetics
THE BEATIFUL FACE Orthodontics 2005 Malcolm E. Meistrell,, Jr., D.D.S. Clinical Professor of Dentistry Division of Orthodontics School of Dental and Oral Surgery Columbia University Beauty Beauty Esthetics
Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy
 Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Trisomies 13 and 18. -Maternal age. (Patau and Edward s syndrome)
 Trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edward s syndrome) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is the commonest chromosomal disorder at birth, and has been considered in detail in previous annual reports 23. Other relatively
Trisomies 13 and 18 (Patau and Edward s syndrome) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) is the commonest chromosomal disorder at birth, and has been considered in detail in previous annual reports 23. Other relatively
Fact Sheet 10 DSM-5 and Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Fact Sheet 10 DSM-5 and Autism Spectrum Disorder A diagnosis of autism is made on the basis of observed behaviour. There are no blood tests, no single defining symptom and no physical characteristics that
Fact Sheet 10 DSM-5 and Autism Spectrum Disorder A diagnosis of autism is made on the basis of observed behaviour. There are no blood tests, no single defining symptom and no physical characteristics that
3/31/2015. Objectives. Alcohol. Long term effects. Substance abuse increases the risk of: Substance Abuse in Pregnancy
 Objectives Substance Abuse in Pregnancy Basics of screening and counseling Minako Watabe, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology Ventura County Medical Center 1) Discuss the risks of alcohol, tobacco, and drug use
Objectives Substance Abuse in Pregnancy Basics of screening and counseling Minako Watabe, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology Ventura County Medical Center 1) Discuss the risks of alcohol, tobacco, and drug use
Orthopaedic Issues in Adults with CP: If I Knew Then, What I Know Now
 Orthopaedic Issues in Adults with CP: If I Knew Then, What I Know Now Laura L. Tosi, MD Director, Bone Health Program Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC Epidemiology 87-93% of children born
Orthopaedic Issues in Adults with CP: If I Knew Then, What I Know Now Laura L. Tosi, MD Director, Bone Health Program Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC Epidemiology 87-93% of children born
SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY INTRODUCTION:
 SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations
SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations
A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing
 Patient Education Page 29 A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing This section describes prenatal tests that give information about your baby s health. It is your choice whether or not to have these tests
Patient Education Page 29 A Guide to Prenatal Genetic Testing This section describes prenatal tests that give information about your baby s health. It is your choice whether or not to have these tests
Child Abuse and Neglect AAP Policy Recommendations
 Child Abuse and Neglect AAP Policy Recommendations When Inflicted Skin Injuries Constitute Child Abuse Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect PEDIATRICS Vol. 110 No. 3 September 2002, pp. 644-645 Recommendations
Child Abuse and Neglect AAP Policy Recommendations When Inflicted Skin Injuries Constitute Child Abuse Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect PEDIATRICS Vol. 110 No. 3 September 2002, pp. 644-645 Recommendations
C CS. California Children Services Alameda County
 C CS California Children Services Alameda County The California Children Services (CCS) Program strives to assure access to medical services essential to the health and well-being of children with catastrophic
C CS California Children Services Alameda County The California Children Services (CCS) Program strives to assure access to medical services essential to the health and well-being of children with catastrophic
Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR) including Russell Silver Syndrome A Guide for Parents and Patients
 Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR) including Russell Silver Syndrome A Guide for Parents and Patients SERIES 1 SERIES 2 SERIES 3 SERIES 4 SERIES 5 SERIES 6 SERIES 7 SERIES 8 SERIES 9 SERIES 10 SERIES
Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR) including Russell Silver Syndrome A Guide for Parents and Patients SERIES 1 SERIES 2 SERIES 3 SERIES 4 SERIES 5 SERIES 6 SERIES 7 SERIES 8 SERIES 9 SERIES 10 SERIES
National Academy of Sciences Committee on Educational Interventions for Children with Autism
 National Academy of Sciences Committee on Educational Interventions for Children with Autism Conclusion and (The following is an adapted excerpt from Chapter 16, and, ( pp. 211-229), National Research
National Academy of Sciences Committee on Educational Interventions for Children with Autism Conclusion and (The following is an adapted excerpt from Chapter 16, and, ( pp. 211-229), National Research
Embryology. From Conception through Birth. From Conception through Death
 Embryology From Conception through Birth From Conception through Death - Immune system 18 months after birth - Lungs 3-8 years after birth - Nervous 12 years after birth - Reproductive Puberty - Skeletal
Embryology From Conception through Birth From Conception through Death - Immune system 18 months after birth - Lungs 3-8 years after birth - Nervous 12 years after birth - Reproductive Puberty - Skeletal
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Birth defects. Report by the Secretariat
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB126/10 126th Session 3 December 2009 Provisional agenda item 4.7 Birth defects Report by the Secretariat 1. In May 2009 the Executive Board at its 125th session considered an agenda item
UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities
 Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia
 Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia XIII Corso di Formazione Malformazioni Congenite dalla Diagnosi Prenatale alla Terapia Postnatale unipv.eu Carrara, 24 ottobre 2014 Legend:Bluebars
Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia XIII Corso di Formazione Malformazioni Congenite dalla Diagnosi Prenatale alla Terapia Postnatale unipv.eu Carrara, 24 ottobre 2014 Legend:Bluebars
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS
 23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: wkc15@columbia.edu SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: wkc15@columbia.edu SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
Charts of fetal size: limb bones
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology August 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 919 929 Charts of fetal size: limb bones Lyn S. Chitty a, *, Douglas G. Altman b Objective To construct new size
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology August 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 919 929 Charts of fetal size: limb bones Lyn S. Chitty a, *, Douglas G. Altman b Objective To construct new size
