Performance comparison of phenotypic and molecular methods for detection and differentiation of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis
|
|
|
- Chester Preston
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ahmad et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:230 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Performance comparison of phenotypic and molecular methods for detection and differentiation of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis Suhail Ahmad *, Ziauddin Khan, Mohammad Asadzadeh, Ajmal Theyyathel and Rachel Chandy Abstract Background: Candida albicans is the most pathogenic Candida species but shares many phenotypic features with Candida dubliniensis and may, therefore, be misidentified in clinical microbiology laboratories. Candidemia cases due to C. dubliniensis are increasingly being reported in recent years. Accurate identification is warranted since mortality rates are highest for C. albicans infections, however, C. dubliniensis has the propensity to develop resistance against azoles more easily. We developed a duplex PCR assay for rapid detection and differentiation of C. albicans from C. dubliniensis for resource-poor settings equipped with basic PCR technology and compared its performance with three phenotypic methods. Methods: Duplex PCR was performed on 122 germ tube positive and 12 germ tube negative isolates of Candida species previously identified by assimilation profiles on Vitek 2 ID-YST system. Typical morphologic characteristics on simplified sunflower seed agar (SSA), and reaction with a commercial (Bichro-Dubli) latex agglutination test were also performed. The assay was further applied on 239 clinical yeast and yeast-like fungi and results were confirmed by DNA sequencing of internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of rdna. Results: The results of duplex PCR assay for 122 germ tube positive and 12 germ tube negative isolates of Candida species were comparable to their identification by Vitek 2 ID-YST system, colony characteristics on SSA and latex agglutination test. Application of duplex PCR also correctly identified all 148 C. albicans and 50 C. dubliniensis strains among 239 yeast-like fungi. Conclusions: The data show that both, duplex PCR and Bichro-Dubli are reliable tests for rapid (within few hours) identification of clinical yeast isolates as C. dubliniensis or C. albicans. However, duplex PCR may be applied directly on clinical yeast isolates for their identification as C. dubliniensis or C. albicans as it does not require prior testing for germ tube formation or latex Candida agglutination. Keywords: Candida albicans, Candida dubliniensis, Detection, Differentiation, Duplex PCR * Correspondence: suhail_ah@hsc.edu.kw Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, P. O. Box 24923, Safat 13110, Kuwait 2012 Ahmad et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Ahmad et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:230 Page 2 of 5 Background Candida albicans is the predominant pathogenic Candida species in susceptible human host. Infections caused by non-albicans Candida spp. have, however, also increased in recent years and may account for up to 60% of all episodes of candidemia or invasive candidiasis at some centers [1,2]. Candida dubliniensis, first described in 1995 from oral cavities of human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals [3], is increasingly being reported from patients with candidemia in recent years [1,2,4]. C. dubliniensis shares several phenotypic characteristics, such as ability to form chlamydospores on cornmeal agar and germ tubes in serum with C. albicans. Since germ tube test is routinely used for the differentiation of C. albicans from other Candida species, identification based solely on this test leads to misidentification of some C. albicans isolates in routine diagnostic laboratories [5]. Accurate identification is warranted since C. dubliniensis exhibits increased adherence to buccal epithelial cells and is more likely to develop resistance against fluconazole and other azoles [6,7]. Several phenotypic tests based on colony morphology and physiological assimilation tests have been developed to distinguish C. albicans from C. dubliniensis. Commercially available yeast identification systems (Vitek 2 ID- YST, API 20C and ID32C) based on utilization of various compounds have been used for differentiating various Candida spp., however, these methods are expensive and require at least 1 2 days to report results [8]. Formation of rough/fringed colonies by germ tube positive isolates on differential media such as Niger seed agar [9], simplified sunflower seed agar (SSA) [10], or tobacco agar [11], or inability to grow in a hypertonic Sabouraud dextrose broth containing 6.5 M NaCl [12] are often used to differentiate C. albicans from C. dubliniensis. Acommercial latex agglutination test (Bichro-Dubli Fumouze) is also available [13]. However, prior presumptive identification of C. albicans/c. dubliniensis is required before phenotypic methods could be used for their differentiation. Also, variations in growth conditions (incubation temperature, repeated subculturing and storage) may impede accurate identification of these two species by phenotypic tests. Unambiguous identification can be established only by molecular techniques and PCR-based methods are mostly employed [5]. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionizationtime of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has also been exploited recently for identification and differentiation of cultured yeast isolates including even closely related Candida spp. [14]. However, the high cost of the equipment is a major impediment for its widespread use in resource-limited settings. In this study, we have developed a novel duplex PCR assay by using primers derived from unique rdna sequences for rapid detection and differentiation of C. albicans and C. dubliniensis. The performance of duplex PCR was compared with three phenotypic methods for identification of clinical isolates as C. albicans or C. dubliniensis. Methods Reference strains and clinical isolates Candida dubliniensis (CD 36/CBS 7987/ATCC MYA- 646), C. albicans (ATCC 90028), Candida parapsilosis (ATCC 10233), Candida glabrata (ATCC 15545), Candida tropicalis (ATCC 750) and Candida krusei (CBS 6258) were used as reference Candida species. One hundred thirty-four clinical isolates representing C. dubliniensis (n = 67), C. albicans (n = 55), C. parapsilosis (n = 2), C. glabrata (n = 2), C. tropicalis (n = 2), Candida lusitaniae (n = 2), Candida krusei (n = 2) and Candida kefyr (n = 2) were tested by both phenotypic and molecular tests. All isolates of C. albicans and C. dubliniensis were positive by germ tube test. Identity of C. dubliniensis strains was also confirmed by sequencing of internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region (containing ITS-1, 5.8S rrna and ITS-2) of rdna as described previously [15]. Additionally, 239 clinical yeast isolates including C. albicans (n = 148), C. dubliniensis (n = 50), C. parapsilosis (n = 5), C. glabrata (n = 5), C. lusitaniae (n = 5), C. tropicalis (n = 5), Candida haemulonii (n = 3), Candida rugosa (n = 2), Trichosporon species (n = 4) and Cryptococcus species (n = 6) and one isolate each of C. krusei, Candida guilliermondii, C. orthopsilosis, C. metapsilosis, C. nivariensis and C. bracarensis were also tested by duplex PCR. The isolates were cultured as part of standard patient care and no individual patient approval was needed for their subsequent use. The project under which the study was performed was approved by the Ethical Committee of Faculty of Medicine, Health Sciences center, Kuwait University. Phenotypic identification and characterization Clinical isolates were speciated by carbohydrate assimilation profile using Vitek 2 ID-YST system (biomerieux, Marcy-lEtoile, France) and tested for germ tube formation in horse serum. All germ tube positive isolates were presumptively identified as C. albicans/c. dubliniensis. Germ tube positive isolates showing fringed/rough colonies on SSA [10] were identified as C. dubliniensis. Bichro- Dubli (Fumouze Diagnotics, Levallois-Perret, France) latex agglutination test for identification of C. dubliniensis strains was performed on all germ tube positive isolates according to manufacturer s recommendations. Template DNA preparation, duplex PCR assay and DNA sequencing For molecular studies, a loop full of yeast colony from Sabouraud dextrose agar plate was suspended in 1 ml of sterile water in a microcentrifuge tube containing 50 mg
3 Ahmad et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:230 Page 3 of 5 Chelex-100 (Sigma-Aldrich Co.), the contents were heated at 95 C for 20 min and then centrifuged. The supernatant was transferred to a new tube and typically 2 μl was used in PCR. Species-specific identity of C. albicans and C. dubliniensis strains was performed by duplex PCR by using primers targeting sequences in ITS-1 and ITS-2 regions of rdna. Species-specificity of primer pairs CALF (5 0 -TGGTAAGGCGGGATCG- CTT-3 0 ) + CALR (5 0 -GGTCAAAGTTTGAAGATATAC) and CDUF (5 0 -AAACTTGTCACGAGATTATTTTT) + CDUR (5 0 -AAAGTTTGAAGAATAAAATGGC-3 0 ) for C. albicans and C. dubliniensis, respectively, was indicated by BLAST searches ( BLAST/Blast.cgi?). PCR amplification was performed in a final volume of 50 μl containing 1x AmpliTaq DNA polymerase buffer I and 2 units of AmpliTaq DNA polymerase (Perkin Elmer), 10 pmol of CALF + CALR + CDUF + CDUR primers, 2 μl of template DNA and 100 μm of each dntp. Cycling conditions included an initial denaturation at 95 C for 5 min followed by 30 cycles of 95 C for 1 min, 55 C for 30 s and 72 C for 1 min and a final extension at 72 C for 10 min. PCR products (20 μl) were run on 2% (w/v) agarose gels, as described previously [16]. The species-specific identity of clinical yeast isolates was established by sequencing of ITS region of rdna. The ITS region was amplified by using panfungal primers ITS1 [17] and CTSR [18] and the amplicons were purified and sequenced as described in detail previously [15,19]. Results Duplex PCR amplification with CALF + CALR + CDUF + CDUR primers yielded an amplicon of ~100 bp and ~325 bp only with DNA from reference strains of C. albicans and C. dubliniensis, respectively, but not from other Candida species, as expected (data not shown). Of 134 clinical Candida spp. isolates, 122 were positive for germ tube formation and 12 were germ tube negative. Vitek 2 ID-YST system identified the isolates as C. dubliniensis (n = 67), C. albicans (n = 55), C. parapsilosis (n = 2), C. glabrata (n = 2), C. tropicalis (n = 2), C. lusitaniae (n = 2), C. krusei (n = 2) and C. kefyr (n = 2). Duplex PCR correctly identified all 67 C. dubliniensis and 55 C. albicans isolates (data from 11 selected isolates are shown in Figure 1) while negative results were obtained for the remaining 12 germ tube negative isolates (Table 1). Growth on SSA correctly identified 67 of 122 germ tube positive isolates as C. dubliniensis. Bichro- Dubli test was positive for 64 of 67, weakly positive for 2 of 67 and negative for 1 of 67 isolates identified as C. dubliniensis by Vitek 2 ID-YST system and ITS region sequencing. Bichro-Dubli test was negative for 55 of 122 germ tube positive isolates identified as C. albicans by Vitek 2 ID-YST system as well as 12 germ tube negative M M Figure 1 Agarose gel of duplex PCR assay from representative isolates of C. albicans (lanes 1 3, 5, 10, 11) and C. dubliniensis (lanes 4, 6 9). No amplification was obtained in control (no DNA added) tubes. The duplex PCR test was uniformly negative for other Candida species or yeast-like fungi. Lane M is 100 bp DNA ladder and the positions of migration of 100 bp, 300 bp and 600 bp fragments are marked. isolates of six other Candida species (Table 1). Thus, duplex PCR accurately identified all 55 C. albicans and 67 C. dubliniensis strains among a panel of 134 wellcharacterized Candida spp. isolates with 100% sensitivity and specificity. Direct application of duplex PCR on a panel of 239 clinical isolates of yeast-like fungi correctly identified all 148 C. albicans and 50 C. dublininsis strains. The remaining isolates representing other Candida spp. or other yeast-like fungi yielded negative results. The results were confirmed by direct DNA sequencing of ITS region of rdna. Discussion The results of duplex PCR assay described here were completely concordant with species-specific identification of C. dubliniensis and C. albicans strains by Vitek 2 ID-YST system and colony characteristics (fringed/rough colonies) on SSA. However, both, Vitek 2 ID-YST system and growth on SSA usually require hours before results are available. Furthermore, identification of C. dubliniensis strains on SSA requires prior testing for germ tube formation while Vitek 2 ID-YST system is expensive and thus, is not readily available in resourcepoor settings [10]. The requirement for minimal amount of genomic DNA for duplex PCR allows the whole procedure to be completed within 4 hours. Furthermore, since duplex PCR employs species-specific primers for both, C. albicans and C. dubliniensis, it can be directly applied on clinical isolates of yeast and yeast-like fungi. Indeed, direct application of duplex PCR on a panel of 239 clinical isolates of yeast-like fungi correctly identified all 50 C. dublininsis and 148 C. albicans strains.
4 Ahmad et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:230 Page 4 of 5 Table 1 Performance comparison of duplex PCR with Vitek 2 ID-YST system, Bichro-Dubli Fumouze latex agglutination test and colony characteristics on simplified sunflower seed agar (SSA) for identification and differentiation of C. albicans and C. dubliniensis Candida species No. of isolates No. of isolates yielding correct identification with tested Vitek 2 ID-YST SSA* Bichro-Dubli Duplex PCR C. albicans C. dubliniensis C. glabrata 2 2 Not done 0 0 C. parapsilosis 2 2 Not done 0 0 C. tropicalis 2 2 Not done 0 0 C. lusitaniae 2 2 Not done 0 0 C. krusei 2 2 Not done 0 0 C. kefyr 2 2 Not done 0 0 *Fringed/rough colonies during growth on simplified sunflower seed agar (SSA). Although several PCR-based methods using rdna as target have been described previously, they either involve two separate PCR reactions for each strain [16,20,21] or further manipulations (such as restriction digestion to generate restriction fragment length polymorphism or DNA sequencing) are needed for species-specific identification [16,22-24]. These additional steps add to the cost of the test and/or consume additional time thus delaying results. Other investigators have used PCRbased methods targeting intronic sequences for differentiation of C. albicans from C. dubliniensis [25-27]. However, these approaches may lead to misidentification of some isolates since intronic sequences may vary significantly [27]. A real-time PCR assay using melting point analysis was described recently for detection and differentiation of C. albicans and C. dubliniensis strains but involves separate reactions for each Candida spp. and expensive probe primers [28]. Although two realtime PCR assays using SYBR Green dye have also been described, these assays either require prior presumptive identification of C. albicans/c. dubliniensis strains by another (such as germ tube) test and/or two rounds of real-time PCR assays are needed [29,30]. Furthermore, the difference in T m values for C. albicans and C. dubliniensis strains in the two reports was either small (<0.5 C) or negligible which may lead to misidentification of some isolates. Performance of another rapid (Bichro-Dubli Fumouze latex agglutination) test was also compared with duplex PCR results. The 98.5% sensitivity and specificity of 100% of Bichro-Dubli test is in agreement with the reported sensitivity (97% to 100%) and specificity (100%) values suggested by the kit manufacturer. Similar values have also been reported in other studies for identification of C. dubliniensis isolates [31,32]. Although Bichro- Dubli test is also a rapid method for identification of C. dubliniensis, the test can only be applied on isolates previously identified as C. albicans/c. dubliniensis either by germ tube formation of by application of another (Bichro Latex Albicans) latex agglutination test [13,32]. This increases both, the cost and the time to report results for Bichro-Dubli test. The use of chromogenic differential media such as CHROMagar W Candida has also been implemented in many clinical microbiology laboratories for identification and differentiation of both C. albicans and C. dubliniensis, thus diminishing the need for germ tube test. However, the production of light green (for C. albicans) or dark green (for C. dubliniensis) color is inconsistent when large number of isolates are screened, thus requiring further cultivation on a bird-seed agar medium for their accurate identification [33]. Conclusions A duplex PCR assay has been developed and extensively evaluated for the detection and differentiation of clinical isolates as C. dubliniensis or C. albicans. The method may be applied directly on clinical yeast isolates for their identification as C. dubliniensis or C. albicans as it does not require prior testing for germ tube formation or other such tests and is suitable for resource-limited clinical microbiology laboratories equipped with basic PCR technology. A limitation of the study is that other Candida and yeast-like organisms will require additional testing for their species-specific identification. Abbreviations ITS: Internal transcribed spacer; SSA: Simplified sunflower seed agar; rdna: Ribosomal DNA. Competing interests The authors declare that no competing interests exist. Authors contributions SA and ZK designed the study, arranged financial support and analyzed the data. MA, AT and RC performed the experiments. All authors contributed in writing the manuscript and approved the final version.
5 Ahmad et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:230 Page 5 of 5 Acknowledgments The study was supported by KURA grant no. MI01/08. Received: 10 June 2012 Accepted: 24 September 2012 Published: 25 September 2012 References 1. Horn DL, Neofytos D, Anaissie EJ, Fishman JA, Steinbach WJ, Olyaei AJ, Marr KA, Pfaller MA, Chang CH, Webster KM: Epidemiology and outcomes of candidemia in 2019 patients: data from the prospective antifungal therapy alliance registry. Clin Infect Dis 2009, 48: Miceli MH, Díaz JA, Lee SA: Emerging opportunistic yeast infections. Lancet Infect Dis 2011, 11: Sullivan DJ, Westerneng TJ, Haynes KA, Bennett DE, Coleman DC: Candida dubliniensis sp. nov.: phenotypic and molecular characterization of a novel species associated with oral candidosis in HIV-infected individuals. Microbiology 1995, 141: Khan Z, Ahmad S, Joseph L, Chandy R: Candida dubliniensis: an appraisal of its clinical significance as a bloodstream pathogen. PLoS One 2012, 7:e Ells R, Kock JLF, Pohl CH: Candida albicans or Candida dubliniensis. Mycoses 2011, 54: Pinjon E, Moran GP, Coleman DC, Sullivan DJ: Azole susceptibility and resistance in Candida dubliniensis. Biochem Soc Trans 2003, 33: Fleischhacker M, Prasligh J, Moran G, Ruhnke M: Longitudinal genotyping of Candida dubliniensis isolates reveals strain maintenance, microevolution, and the emergence of itraconazole resistance. J Clin Microbiol 2010, 48: Pincus DH, Coleman DC, Pruitt WR, Padhye AA, Salkin IF, Geimer M, Bassel A, Sullivan DJ, Clarke M, Hearn V: Rapid identification of Candida dubliniensis with commercial yeast identification systems. J Clin Microbiol 1999, 37: Al-Mosaid A, Sullivan D, Salkin IF, Shanley D, Coleman DC: Differentiation of Candida dubliniensis from Candida albicans on staib agar and caffeic acid-ferric citrate agar. J Clin Microbiol 2001, 39: Khan ZU, Ahmad S, Mokaddas E, Chandy R: Simplified sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seed agar for differentiation of Candida dubliniensis from Candida albicans. Clin Microbiol Infect 2004, 10: Khan ZU, Ahmad S, Mokaddas E, Chandy R: Tobacco agar, a new medium for differentiating Candida dubliniensis from Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol 2004, 42: Alves SH, Milan EP, de Laet Sant Ana P, Oliveira LO, Santurio JM, Colombo AL: Hypertonic sabouraud broth as a simple and powerful test for Candida dubliniensis screening. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2002, 43: Marot-Leblond A, Beucher B, David S, Nail-Billaud S, Robert R: Development and evaluation of a rapid latex agglutination test using monoclonal antibody to identify Candida dubliniensis colonies. J Clin Microbiol 2006, 44: Dhiman N, Hall L, Wohlfiel SL, Buckwalter SP, Wengenack NL: Performance and cost analysis of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for routine identification of yeast. J Clin Microbiol 2011, 49: Al-Sweih N, Ahmad S, Khan ZU, Khan S, Chandy R: Prevalence of Candida dubliniensis among germ tube-positive Candida isolates in a maternity hospital in Kuwait. Mycoses 2005, 48: Ahmad S, Khan Z, Mokaddas E, Khan ZU: Isolation and molecular identification of Candida dubliniensis from non-human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in Kuwait. J Med Microbiol 2004, 56: White TJ, Burns TD, Lee SB, Taylor JW: Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. InPCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Edited by Innis MA, Gelfand GH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ. San Diego: Academic; 1990: Ahmad S, Khan Z, Mustafa AS, Khan ZU: Semi-nested PCR for diagnosis of candidemia: comparison with culture, antigen detection, and biochemical methods for species identification. J Clin Microbiol 2002, 40: Ahmad S, Khan ZU, Joseph L, Asadzadeh M, Theyyathel A: Genotypic heterogeneity and molecular basis of 5-flucytosine resistance among Candida dubliniensis isolates recovered from clinical specimens in Kuwait. Med Mycol 2012, 50: Lau A, Halliday C, Chen SC, Playford EG, Stanley K, Sorrell TC: Comparison of whole blood, serum and plasma for early detection of candidemia by multiplex-tandem PCR. J Clin Microbiol 2010, 48: Lung Than TL, Chong PP, Ng KP, Seow HF: Detection of 10 medically important Candida species by seminested polymerase chain reaction. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2011, 72: Williams DW, Coulter WA, Wilson MJ, Potts AJ, Lewis MA: Identification of Candida dubliniensis, based on ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. Br J Biomed Sci 2001, 58: Graf B, Trost A, Eucker J, Gobel UB, Adam T: Rapid and simple differentiation of Candida dubliniensis from Candida albicans. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2004, 48: Romeo O, Racco C, Criseo G: Amplification of the hyphal wall protein 1 gene to distinguish Candida albicans from Candida dubliniensis. J Clin Microbiol 2006, 44: Romeo O, Criseo G: First molecular method for discriminating between Candida africana, Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis by using hwp1 gene. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2008, 62: Bosco-Borgeat ME, Taverna CG, Cordoba S, Isla MG, Murisengo OA, Szusz W, Vivot W, Davel G: Prevalence of Candida dubliniensis fungemia in Argentina: identification by a novel multiplex PCR and comparison of different phenotypic methods. Mycopathologia 2011, 172: Riberio PM, Querido SM, Back-Brito GN, Mota AJ, Koga-Ito CY, Jorge AO: Research on Candida dubliniensis in a Brazilian yeast collection obtained from cardiac transplant, tuberculosis, and HIV-positive patients, and evaluation of phenotypic tests using agar screening methods. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2011, 71: Fricke S, Fricke C, Schimmelpfennig C, Oelkrug C, Schonfelder U, Blatz R, Zilch C, Faber S, Hilger N, Ruhnke M, Rodloff AC: A real-time PCR assay for the differentiation of Candida species. J Appl Microbiol 2010, 109: Somogyvari F, Doczi I, Serly J, Ahmad S, Nagy E: Rapid discrimination between Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis by using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2007, 58: Khan ZU, Mustafa AS, Alam FF: Real-time LightCycler polymerase chain reaction and melting temperature analysis for differentiation of clinically important Candida species. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2009, 42: Sahand IH, Moragues MD, Robert R, Quindos G, Ponton J: Evaluation of Bichro-Dubli Fumouze W to distinguish Candida dubliniensis from Candida albicans. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2006, 55: Chryssanthou E, Fernandez V, Petrini B: Performance of commercial latex agglutination tests for the differentiation of Candida dubliniensis and Candida albicans in routine diagnostics. APMIS 2007, 115: Pasligh J, Radecke C, Fleischhacker M, Ruhnke M: Comparison of phenotypic methods for the identification of Candida dubliniensis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2010, 43: doi: / Cite this article as: Ahmad et al.: Performance comparison of phenotypic and molecular methods for detection and differentiation of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis. BMC Infectious Diseases :230. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Protocols. Internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) region. Niklaus J. Grünwald, Frank N. Martin, and Meg M. Larsen (2013)
 Protocols Internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) region Niklaus J. Grünwald, Frank N. Martin, and Meg M. Larsen (2013) The nuclear ribosomal RNA (rrna) genes (small subunit, large subunit and 5.8S) are
Protocols Internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) region Niklaus J. Grünwald, Frank N. Martin, and Meg M. Larsen (2013) The nuclear ribosomal RNA (rrna) genes (small subunit, large subunit and 5.8S) are
Effect of Denture Wearing on Occurrence of Candida Species in the Oral Cavity
 Effect of Denture Wearing on Occurrence of Candida Species in the Oral Cavity Hiroyuki Mizugai, DDS, PhD* Emiko Isogai* Kimiharu Hirose Itsuo Chiba* *Department of Preventive Dentistry, Health Sciences
Effect of Denture Wearing on Occurrence of Candida Species in the Oral Cavity Hiroyuki Mizugai, DDS, PhD* Emiko Isogai* Kimiharu Hirose Itsuo Chiba* *Department of Preventive Dentistry, Health Sciences
The Prognostic and Diagnostic Markers of Invasive Candidiasis in Patients During Chemotherapy
 Polish Journal of Microbiology 2005, Vol. 54, No 3, 207 213 The Prognostic and Diagnostic Markers of Invasive Candidiasis in Patients During Chemotherapy AGNIESZKA MAGRYΠ1, MARIA KOZIO -MONTEWKA 1, EL
Polish Journal of Microbiology 2005, Vol. 54, No 3, 207 213 The Prognostic and Diagnostic Markers of Invasive Candidiasis in Patients During Chemotherapy AGNIESZKA MAGRYΠ1, MARIA KOZIO -MONTEWKA 1, EL
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System
 PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
Candidemia - beyond albicans and azoles: clinical and epidemiological review in a tertiary centre
 Original article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201502.03138 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Candidemia - beyond
Original article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201502.03138 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Candidemia - beyond
MIKI TAMURA, KAYO WATANABE, YUZURU MIKAMI,* KATSUKIYO YAZAWA,
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2001, p. 4309 4315 Vol. 39, No. 12 0095-1137/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4309 4315.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2001, p. 4309 4315 Vol. 39, No. 12 0095-1137/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4309 4315.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus-
 Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Evaluation of a Rapid Immunochromatographic Assay for Identification of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 4956 4960 Vol. 42, No. 11 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.4956 4960.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 4956 4960 Vol. 42, No. 11 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.4956 4960.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Surveillance cultures PRO. Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen
 Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
Kurt Espersen ICU 4131 Rigshospitalet Copenhagen Difficult to Diagnose Systemic Candidal Infection Immunsuppression in critically ill patients Frequent manifestation of fungus in ICU Fungi were isolated
Short Report: Failure of Burkholderia pseudomallei to Grow in an Automated Blood Culture System
 Accepted for Publication, Published online October 13, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018 In order to provide our readers with timely
Accepted for Publication, Published online October 13, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018 In order to provide our readers with timely
ABSTRACT. Promega Corporation, Updated September 2008. http://www.promega.com/pubhub. 1 Campbell-Staton, S.
 A Modified Wizard SV Genomic DNA Purification System Protocol to Purify Genomic DNA... A Modified Wizard SV Genomic DNA Purification System Protocol to Purify Genomic DNA from Shed Reptile Skin ABSTRACT
A Modified Wizard SV Genomic DNA Purification System Protocol to Purify Genomic DNA... A Modified Wizard SV Genomic DNA Purification System Protocol to Purify Genomic DNA from Shed Reptile Skin ABSTRACT
Intended Use: The kit is designed to detect the 5 different mutations found in Asian population using seven different primers.
 Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
Candida SPECIES DISTRIBUTION IN CLINICAL SAMPLES
 264 Candida SPECIES DISTRIBUTION IN CLINICAL SAMPLES Rui Fernandes Master Student Faculty of Health Sciences UFP Analysis Laboratory Dr. Edgar Botelho Moniz, S.A. 20504@ufp.edu.pt Ana Viegas Student Faculty
264 Candida SPECIES DISTRIBUTION IN CLINICAL SAMPLES Rui Fernandes Master Student Faculty of Health Sciences UFP Analysis Laboratory Dr. Edgar Botelho Moniz, S.A. 20504@ufp.edu.pt Ana Viegas Student Faculty
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
Identification of the VTEC serogroups mainly associated with human infections by conventional PCR amplification of O-associated genes
 Identification of the VTEC serogroups mainly associated with human infections by conventional PCR amplification of O-associated genes 1. Aim and field of application The present method concerns the identification
Identification of the VTEC serogroups mainly associated with human infections by conventional PCR amplification of O-associated genes 1. Aim and field of application The present method concerns the identification
Introduction. Materials and methods
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2014, 30: 391 INVESTIGATION OF VIRULENCE FACTORS AND DETERMINATION OF ANTIFUNGAL SUSCEPTIBILITIES OF CANDIDA STRAINS ISOLATED AT SULEYMAN DEMIREL UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL AYSE AYNALI
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2014, 30: 391 INVESTIGATION OF VIRULENCE FACTORS AND DETERMINATION OF ANTIFUNGAL SUSCEPTIBILITIES OF CANDIDA STRAINS ISOLATED AT SULEYMAN DEMIREL UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL AYSE AYNALI
Received 5 June 2009/Returned for modification 31 July 2009/Accepted 23 October 2009
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 2010, p. 154 161 Vol. 48, No. 1 0095-1137/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01096-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antifungal Susceptibility
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 2010, p. 154 161 Vol. 48, No. 1 0095-1137/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01096-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antifungal Susceptibility
Terra PCR Direct Polymerase Mix User Manual
 Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Terra PCR Direct Polymerase Mix User Manual Cat. Nos. 639269, 639270, 639271 PT5126-1 (031416) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain
Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Terra PCR Direct Polymerase Mix User Manual Cat. Nos. 639269, 639270, 639271 PT5126-1 (031416) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain
HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit
 Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 HBV Quantitative Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: HD-0002-01 For Use with LightCycler 1.0/LightCycler2.0/LightCycler480 (Roche) Real Time PCR Systems (Pls ignore
Prevalence of Oral Candida Infections in Diabetic Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No.1, March 2006 Prevalence of Oral Candida Infections in Diabetic Patients Khaled H Abu-Elteen, PhD * Mawieh A Hamad, PhD * Suleiman A. Salah, PhD ** Objective: The
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No.1, March 2006 Prevalence of Oral Candida Infections in Diabetic Patients Khaled H Abu-Elteen, PhD * Mawieh A Hamad, PhD * Suleiman A. Salah, PhD ** Objective: The
The Techniques of Molecular Biology: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting
 Revised Fall 2011 The Techniques of Molecular Biology: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting The techniques of molecular biology are used to manipulate the structure and function of molecules such as DNA and proteins
Revised Fall 2011 The Techniques of Molecular Biology: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting The techniques of molecular biology are used to manipulate the structure and function of molecules such as DNA and proteins
VLLM0421c Medical Microbiology I, practical sessions. Protocol to topic J10
 Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title:Isolation and identification of Candida species in patients with orogastric cancer: susceptibility to antifungal drugs, attributes of virulence in vitro and immune response
Author's response to reviews Title:Isolation and identification of Candida species in patients with orogastric cancer: susceptibility to antifungal drugs, attributes of virulence in vitro and immune response
The Variability in the Fungal Ribosomal DNA (ITS1, ITS2, and 5.8 S rrna Gene): Its Biological Meaning and Application in Medical Mycology
 The Variability in the Fungal Ribosomal DNA (ITS1, ITS2, and 5.8 S rrna Gene): Its Biological Meaning and Application in Medical Mycology M. Korabecna * Department of Biology, Faculty of Medicine in Pilsen,
The Variability in the Fungal Ribosomal DNA (ITS1, ITS2, and 5.8 S rrna Gene): Its Biological Meaning and Application in Medical Mycology M. Korabecna * Department of Biology, Faculty of Medicine in Pilsen,
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
NimbleGen DNA Methylation Microarrays and Services
 NimbleGen DNA Methylation Microarrays and Services Sample Preparation Instructions Outline This protocol describes the process for preparing samples for NimbleGen DNA Methylation microarrays using the
NimbleGen DNA Methylation Microarrays and Services Sample Preparation Instructions Outline This protocol describes the process for preparing samples for NimbleGen DNA Methylation microarrays using the
Table of Contents. I. Description... 2. II. Kit Components... 2. III. Storage... 2. IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3
 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR
 Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
IIID 14. Biotechnology in Fish Disease Diagnostics: Application of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 IIID 14. Biotechnology in Fish Disease Diagnostics: Application of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic organisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa,
IIID 14. Biotechnology in Fish Disease Diagnostics: Application of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic organisms such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa,
Technical Manual No. 0173 Update Date 10112010
 TissueDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0173 Update Date 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
TissueDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0173 Update Date 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
First Strand cdna Synthesis
 380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
RT-PCR: Two-Step Protocol
 RT-PCR: Two-Step Protocol We will provide both one-step and two-step protocols for RT-PCR. We recommend the twostep protocol for this class. In the one-step protocol, the components of RT and PCR are mixed
RT-PCR: Two-Step Protocol We will provide both one-step and two-step protocols for RT-PCR. We recommend the twostep protocol for this class. In the one-step protocol, the components of RT and PCR are mixed
MYCOLOGY PARASITOLOGY RHEUMATOID FACTORS VIROLOGY SAMPLE COLLECTION
 C A T A L O G U E C L I N I C A L D I A G N O S T I C S couv BACTERIOLOGYOGY MYCOLOGY PARASITOLOGY RHEUMATOID FACTORS VIROLOGY SAMPLE COLLECTION couv EXPORT DEPARTMENT Orders, technical and commercial
C A T A L O G U E C L I N I C A L D I A G N O S T I C S couv BACTERIOLOGYOGY MYCOLOGY PARASITOLOGY RHEUMATOID FACTORS VIROLOGY SAMPLE COLLECTION couv EXPORT DEPARTMENT Orders, technical and commercial
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Antifungal Therapy. Empiric Therapy, Combination Therapy, and the Question of Central Venous Catheters
 Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Antifungal Therapy Empiric Therapy, Combination Therapy, and the Question of Central Venous Catheters Douglas Fish, Pharm.D. Professor of Pharmacy, University of Colorado
Controversies in Hospital Medicine: Antifungal Therapy Empiric Therapy, Combination Therapy, and the Question of Central Venous Catheters Douglas Fish, Pharm.D. Professor of Pharmacy, University of Colorado
19th Swiss TB Symposium Münchenwiler, 25.03.2010
 19 th SWISS TUBERCULOSIS SYMPOSIUM Update on culture and identification Münchenwiler, 25.03.2010 Dr. Thomas Bodmer, M.D. Institute for Infectious Diseases Culture of mycobacteria Cultivation of MTB in
19 th SWISS TUBERCULOSIS SYMPOSIUM Update on culture and identification Münchenwiler, 25.03.2010 Dr. Thomas Bodmer, M.D. Institute for Infectious Diseases Culture of mycobacteria Cultivation of MTB in
Cloning Blunt-End Pfu DNA Polymerase- Generated PCR Fragments into pgem -T Vector Systems
 Promega Notes Number 71, 1999, p. 10 Blunt-End Pfu DNA Polymerase- Generated PCR Fragments into pgem -T Vector Systems By Kimberly Knoche, Ph.D., and Dan Kephart, Ph.D. Promega Corporation Corresponding
Promega Notes Number 71, 1999, p. 10 Blunt-End Pfu DNA Polymerase- Generated PCR Fragments into pgem -T Vector Systems By Kimberly Knoche, Ph.D., and Dan Kephart, Ph.D. Promega Corporation Corresponding
Rapid Acquisition of Unknown DNA Sequence Adjacent to a Known Segment by Multiplex Restriction Site PCR
 Rapid Acquisition of Unknown DNA Sequence Adjacent to a Known Segment by Multiplex Restriction Site PCR BioTechniques 25:415-419 (September 1998) ABSTRACT The determination of unknown DNA sequences around
Rapid Acquisition of Unknown DNA Sequence Adjacent to a Known Segment by Multiplex Restriction Site PCR BioTechniques 25:415-419 (September 1998) ABSTRACT The determination of unknown DNA sequences around
BuccalAmp DNA Extraction Kit QuickExtract DNA Extraction Solution 1.0
 QuickExtract DNA Extraction Solution 1.0 Cat. Nos. BQ0901S (CR, SC, RB, BS), BQ0908S (CR, SC, RB, BS), BQ0916S (CR, SC, RB, BS), QE09050, QEC091H, QEC89100, MB100BR, and MB100SP Please store the QuickExtract
QuickExtract DNA Extraction Solution 1.0 Cat. Nos. BQ0901S (CR, SC, RB, BS), BQ0908S (CR, SC, RB, BS), BQ0916S (CR, SC, RB, BS), QE09050, QEC091H, QEC89100, MB100BR, and MB100SP Please store the QuickExtract
Gene Expression Assays
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
Highly specific and sensitive quantitation
 PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
MagExtractor -Genome-
 Instruction manual MagExtractor-Genome-0810 F0981K MagExtractor -Genome- NPK-101 100 preparations Store at 4 C Contents [1] Introduction [2] Components [3] Materials required [4] Protocol 1. Purification
Instruction manual MagExtractor-Genome-0810 F0981K MagExtractor -Genome- NPK-101 100 preparations Store at 4 C Contents [1] Introduction [2] Components [3] Materials required [4] Protocol 1. Purification
DNA Integrity Number (DIN) For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments
 DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
TransformAid Bacterial Transformation Kit
 Home Contacts Order Catalog Support Search Alphabetical Index Numerical Index Restriction Endonucleases Modifying Enzymes PCR Kits Markers Nucleic Acids Nucleotides & Oligonucleotides Media Transfection
Home Contacts Order Catalog Support Search Alphabetical Index Numerical Index Restriction Endonucleases Modifying Enzymes PCR Kits Markers Nucleic Acids Nucleotides & Oligonucleotides Media Transfection
Troubleshooting the Single-step PCR Site-directed Mutagenesis Procedure Intended to Create a Non-functional rop Gene in the pbr322 Plasmid
 Troubleshooting the Single-step PCR Site-directed Mutagenesis Procedure Intended to Create a Non-functional rop Gene in the pbr322 Plasmid Lina Jew Department of Microbiology & Immunology, University of
Troubleshooting the Single-step PCR Site-directed Mutagenesis Procedure Intended to Create a Non-functional rop Gene in the pbr322 Plasmid Lina Jew Department of Microbiology & Immunology, University of
CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Mycoplasma Testing Products & Services. M-175 CELLshipper Mycoplasma Detection Kit (In-house sample preparation and slide fixation)
 Cell Culture Testing M-1500 Real-Time PCR with Broth Enrichment A specific and sensitive method for the detection of mycoplasma using Real-Time PCR coupled with a pre-enrichment procedure to enhance method
Cell Culture Testing M-1500 Real-Time PCR with Broth Enrichment A specific and sensitive method for the detection of mycoplasma using Real-Time PCR coupled with a pre-enrichment procedure to enhance method
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Introduction. Introduction. Why do we need microbiological diagnostics of udder infections? Microbiological diagnostics How is it done?
 Introduction Microbiological diagnostics of udder infections Karin Persson Waller National Veterinary Institute (SVA) Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala, Sweden Mastitis = in most cases
Introduction Microbiological diagnostics of udder infections Karin Persson Waller National Veterinary Institute (SVA) Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala, Sweden Mastitis = in most cases
Research priorities in medical mycology
 Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
360 Master Mix. , and a supplementary 360 GC Enhancer.
 Product Bulletin AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix and 360 DNA Polymerase AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix AmpliTaq Gold 360 DNA Polymerase 360 Coverage for a Full Range of Targets AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix
Product Bulletin AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix and 360 DNA Polymerase AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix AmpliTaq Gold 360 DNA Polymerase 360 Coverage for a Full Range of Targets AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix
EU Reference Laboratory for E. coli Department of Veterinary Public Health and Food Safety Unit of Foodborne Zoonoses Istituto Superiore di Sanità
 Identification and characterization of Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC) by Real Time PCR amplification of the main virulence genes and the genes associated with the serogroups mainly associated
Identification and characterization of Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC) by Real Time PCR amplification of the main virulence genes and the genes associated with the serogroups mainly associated
Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005
 Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle GmbH German Accreditation Body Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Period of validity: 26.03.2012 to 25.03.2017
Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle GmbH German Accreditation Body Annex to the Accreditation Certificate D-PL-13372-01-00 according to DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Period of validity: 26.03.2012 to 25.03.2017
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR. A = B (1+e) n. A=amplified products, B=input templates, n=cycle number, and e=amplification efficiency.
 QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR Application: Quantitative RT-PCR is used to quantify mrna in both relative and absolute terms. It can be applied for the quantification of mrna expressed from endogenous genes, and
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR Application: Quantitative RT-PCR is used to quantify mrna in both relative and absolute terms. It can be applied for the quantification of mrna expressed from endogenous genes, and
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit
 ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D4010 & D4011
 Page 0 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. D4010 & D4011 Highlights Quick (5 minute) spin column recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC), viral, phage, (wga)dna, etc.)
Page 0 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. D4010 & D4011 Highlights Quick (5 minute) spin column recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC), viral, phage, (wga)dna, etc.)
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Mix
 Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Mix Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Specific DNA Fragment Includes Internal Negative Control Primers and Template Catalog No.: 60-2007-12 Store at 20 o C For
Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Mix Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Specific DNA Fragment Includes Internal Negative Control Primers and Template Catalog No.: 60-2007-12 Store at 20 o C For
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green)
 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase
 Cat. # R010A For Research Use PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 Features...3 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction
Cat. # R010A For Research Use PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 Features...3 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction
ID kit. imegen Anchovies II. and E. japonicus) DNA detection by. User manual. Anchovies species (E. encrasicolus. sequencing.
 User manual imegen Anchovies II ID kit Anchovies species (E. encrasicolus and E. japonicus) DNA detection by sequencing Reference: Made in Spain The information in this guide is subject to change without
User manual imegen Anchovies II ID kit Anchovies species (E. encrasicolus and E. japonicus) DNA detection by sequencing Reference: Made in Spain The information in this guide is subject to change without
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman)
 Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
CANDIDA INFECTIONS - TREATMENT GUIDELINES IN ADULT
 Page 1 of 6 TITLE: PATIENTS CANDIDA INFECTIONS - TREATMENT GUIDELINES IN ADULT GUIDELINES: These are the 2011 Guidelines for the Treatment of Candida species infections in adult patients. These recommendations
Page 1 of 6 TITLE: PATIENTS CANDIDA INFECTIONS - TREATMENT GUIDELINES IN ADULT GUIDELINES: These are the 2011 Guidelines for the Treatment of Candida species infections in adult patients. These recommendations
HCS604.03 Exercise 1 Dr. Jones Spring 2005. Recombinant DNA (Molecular Cloning) exercise:
 HCS604.03 Exercise 1 Dr. Jones Spring 2005 Recombinant DNA (Molecular Cloning) exercise: The purpose of this exercise is to learn techniques used to create recombinant DNA or clone genes. You will clone
HCS604.03 Exercise 1 Dr. Jones Spring 2005 Recombinant DNA (Molecular Cloning) exercise: The purpose of this exercise is to learn techniques used to create recombinant DNA or clone genes. You will clone
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Prospective Study of Candida Species in Patients at a Comprehensive Cancer Center
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, July 2001, p. 2129 2133 Vol. 45, No. 7 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.7.2129 2133.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, July 2001, p. 2129 2133 Vol. 45, No. 7 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.7.2129 2133.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
IMBB 2013. Genomic DNA purifica8on
 IMBB 2013 Genomic DNA purifica8on Why purify DNA? The purpose of DNA purifica8on from the cell/8ssue is to ensure it performs well in subsequent downstream applica8ons, e.g. Polymerase Chain Reac8on (PCR),
IMBB 2013 Genomic DNA purifica8on Why purify DNA? The purpose of DNA purifica8on from the cell/8ssue is to ensure it performs well in subsequent downstream applica8ons, e.g. Polymerase Chain Reac8on (PCR),
Genolution Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Life Science and Molecular Diagnostic Products
 Genolution Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Revolution through genes, And Solution through genes. Life Science and Molecular Diagnostic Products www.genolution1.com TEL; 02-3010-8670, 8672 Geno-Serum Hepatitis B
Genolution Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Revolution through genes, And Solution through genes. Life Science and Molecular Diagnostic Products www.genolution1.com TEL; 02-3010-8670, 8672 Geno-Serum Hepatitis B
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Source for figures and content: Eastern Campus Tortora, G.J. Microbiology
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Source for figures and content: Eastern Campus Tortora, G.J. Microbiology
Oropharyngeal candidiasis and resistance to antifungal drugs in patients receiving radiation for head and neck cancer
 Received: 21 Nov. 2011 Accepted: 17 May. 2012 Original Article Oropharyngeal candidiasis and resistance to antifungal drugs in patients receiving radiation for head and neck cancer Maryam Rad DMD, MSc
Received: 21 Nov. 2011 Accepted: 17 May. 2012 Original Article Oropharyngeal candidiasis and resistance to antifungal drugs in patients receiving radiation for head and neck cancer Maryam Rad DMD, MSc
United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Marketing Service, Science & Technology Microbiological Data Program
 SOP No.: MDP-QA-03 Page 1 of 6 1. Purpose To provide minimum requirements and standard procedures for quality assurance (QA) controls used in the USDA/AMS (MDP). 2. Scope This standard operating procedure
SOP No.: MDP-QA-03 Page 1 of 6 1. Purpose To provide minimum requirements and standard procedures for quality assurance (QA) controls used in the USDA/AMS (MDP). 2. Scope This standard operating procedure
FastLine cell cdna Kit
 1. FastLine cell cdna Kit For high-speed preparation of first-strand cdna directly from cultured cells without RNA purification www.tiangen.com RT100701 FastLine cell cdna Kit Cat. no. KR105 Kit Contents
1. FastLine cell cdna Kit For high-speed preparation of first-strand cdna directly from cultured cells without RNA purification www.tiangen.com RT100701 FastLine cell cdna Kit Cat. no. KR105 Kit Contents
FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE
 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
DNA Isolation Kit for Cells and Tissues
 DNA Isolation Kit for Cells and Tissues for 10 isolations of 00 mg each for tissue or 5 x 10 7 cultured cells Cat. No. 11 81 770 001 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Benefits
DNA Isolation Kit for Cells and Tissues for 10 isolations of 00 mg each for tissue or 5 x 10 7 cultured cells Cat. No. 11 81 770 001 Principle Starting material Application Time required Results Benefits
Background Information
 Background Information r One About NAT Testing NAT testing has been widely embraced by laboratories throughout the world as a means to identify CT cases because of its high degree of accuracy and reliability
Background Information r One About NAT Testing NAT testing has been widely embraced by laboratories throughout the world as a means to identify CT cases because of its high degree of accuracy and reliability
ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS
 ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract ChIP dissects the spatial and temporal dynamics of the interactions between chromatin and its associated factors CD Creative Diagnostics info@creative-
ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract ChIP dissects the spatial and temporal dynamics of the interactions between chromatin and its associated factors CD Creative Diagnostics info@creative-
All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit For reliable first-strand cdna synthesis from all RNA sources Cat. No. AORT-0020 (20 synthesis reactions) Cat. No. AORT-0050 (50 synthesis reactions) User Manual
All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit For reliable first-strand cdna synthesis from all RNA sources Cat. No. AORT-0020 (20 synthesis reactions) Cat. No. AORT-0050 (50 synthesis reactions) User Manual
Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and Power SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit
 USER GUIDE Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and Power SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4368577, 4367659, 4367660, 4368706, 4368702, 4368708 (Master Mix) and 4368711 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication
USER GUIDE Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and Power SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4368577, 4367659, 4367660, 4368706, 4368702, 4368708 (Master Mix) and 4368711 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication
STA DARD OPERATI G PROCEDURE FOR THE DETECTIO OF AFRICA SWI E FEVER VIRUS (ASFV) BY CO VE TIO AL POLYMERASE CHAI REACTIO (PCR)
 STA DARD OPERATI G PROCEDURE FOR THE DETECTIO OF AFRICA SWI E FEVER VIRUS (ASFV) BY CO VE TIO AL POLYMERASE CHAI REACTIO (PCR) jmvizcaino@vet.ucm.es Av/ Puerta de Hierro s/n. 28040 Madrid. Tel: (34) 913944082
STA DARD OPERATI G PROCEDURE FOR THE DETECTIO OF AFRICA SWI E FEVER VIRUS (ASFV) BY CO VE TIO AL POLYMERASE CHAI REACTIO (PCR) jmvizcaino@vet.ucm.es Av/ Puerta de Hierro s/n. 28040 Madrid. Tel: (34) 913944082
Fungal DNA sequencing from laser capture microdissection samples
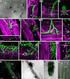 APPLICATION NOTE Laser capture microdissection and Sanger sequencing Fungal DNA sequencing from laser capture microdissection samples Introduction The direct identification of human fungal pathogens by
APPLICATION NOTE Laser capture microdissection and Sanger sequencing Fungal DNA sequencing from laser capture microdissection samples Introduction The direct identification of human fungal pathogens by
Reverse Transcription System
 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Reverse Transcription System Instruc ons for use of Product A3500 Revised 1/14 TB099 Reverse Transcription System All technical literature is available on the Internet at: www.promega.com/protocols/
TECHNICAL BULLETIN Reverse Transcription System Instruc ons for use of Product A3500 Revised 1/14 TB099 Reverse Transcription System All technical literature is available on the Internet at: www.promega.com/protocols/
Introduction. Preparation of Template DNA
 Procedures and Recommendations for DNA Sequencing at the Plant-Microbe Genomics Facility Ohio State University Biological Sciences Building Room 420, 484 W. 12th Ave., Columbus OH 43210 Telephone: 614/247-6204;
Procedures and Recommendations for DNA Sequencing at the Plant-Microbe Genomics Facility Ohio State University Biological Sciences Building Room 420, 484 W. 12th Ave., Columbus OH 43210 Telephone: 614/247-6204;
Nordic External Quality Assessment Program In Medical Mycology (NEQAMM) NEQAMM 2009
 NRMM The Nordic Reference group on Methods in medical Mycology Nordic External Quality Assessment Program In Medical Mycology (NEQAMM) NEQAMM 2009 Results and Comments Erja Chryssanthou, Victor Fernandez,
NRMM The Nordic Reference group on Methods in medical Mycology Nordic External Quality Assessment Program In Medical Mycology (NEQAMM) NEQAMM 2009 Results and Comments Erja Chryssanthou, Victor Fernandez,
SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit
 USER GUIDE SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4309155 (Master Mix) and 4306736 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication Part Number 4310251 Rev. G Revision Date September
USER GUIDE SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4309155 (Master Mix) and 4306736 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication Part Number 4310251 Rev. G Revision Date September
Introduction. Materials and Methods. imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/
 imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Molecular Identification and Antifungal Susceptibility of Candida parapsilosis sensu stricto, Candida orthopsilosis, and Candida metapsilosis in Sousse Region,
imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Molecular Identification and Antifungal Susceptibility of Candida parapsilosis sensu stricto, Candida orthopsilosis, and Candida metapsilosis in Sousse Region,
Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR
 APPLICATION NOTE Multiplex Real-Time PCR Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR Introduction Multiplex PCR is the simultaneous amplification of more than one target sequence in a single reaction [1].
APPLICATION NOTE Multiplex Real-Time PCR Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR Introduction Multiplex PCR is the simultaneous amplification of more than one target sequence in a single reaction [1].
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
DNA: A Person s Ultimate Fingerprint
 A partnership between the UAB Center for Community Outreach Development and McWane Center DNA: A Person s Ultimate Fingerprint This project is supported by a Science Education Partnership Award (SEPA)
A partnership between the UAB Center for Community Outreach Development and McWane Center DNA: A Person s Ultimate Fingerprint This project is supported by a Science Education Partnership Award (SEPA)
TEST METHOD VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION
 1 TEST METHOD VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION SWACM 2014 MICHAEL LOEFFELHOLZ, PH.D., ABMM DEPT. PATHOLOGY UNIV TEXAS MEDICAL BRANCH GALVESTON, TX 2 OBJECTIVES Define validation and verification Describe components
1 TEST METHOD VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION SWACM 2014 MICHAEL LOEFFELHOLZ, PH.D., ABMM DEPT. PATHOLOGY UNIV TEXAS MEDICAL BRANCH GALVESTON, TX 2 OBJECTIVES Define validation and verification Describe components
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna
 All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit
 - PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit Catalog Number KA2102 50 tests/kit Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Introduction and Background Intended use The PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit
- PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit Catalog Number KA2102 50 tests/kit Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Introduction and Background Intended use The PNA BRAF Mutation Detection Kit
SOP Title: Multiplex-PCR check of genomic DNA isolated from FFPE tissue for its usability in array CGH analysis
 SOP Title: Multiplex-PCR check of genomic DNA isolated from FFPE tissue for its usability in array CGH analysis The STORE processing methods were shown to be fit-for purpose for DNA, RNA and protein extraction
SOP Title: Multiplex-PCR check of genomic DNA isolated from FFPE tissue for its usability in array CGH analysis The STORE processing methods were shown to be fit-for purpose for DNA, RNA and protein extraction
Incidence and Speciation of Candida Species among Non-gravid young Females in Ilorin, North Central, Nigeria
 Full-text Available Online at J OURNAL OF A PPLIED S CIENCE AND E NVIRONMENTAL M ANAGEMENT. JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved www.ajol.info www.bioline.org.br/ja and J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manage.
Full-text Available Online at J OURNAL OF A PPLIED S CIENCE AND E NVIRONMENTAL M ANAGEMENT. JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved www.ajol.info www.bioline.org.br/ja and J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manage.
Victims Compensation Claim Status of All Pending Claims and Claims Decided Within the Last Three Years
 Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
About Our Products. Blood Products. Purified Infectious/Inactivated Agents. Native & Recombinant Viral Proteins. DNA Controls and Primers for PCR
 About Our Products Purified Infectious/Inactivated Agents ABI produces a variety of specialized reagents, allowing researchers to choose the best preparations for their studies. Available reagents include
About Our Products Purified Infectious/Inactivated Agents ABI produces a variety of specialized reagents, allowing researchers to choose the best preparations for their studies. Available reagents include
Isolation and Characterization of Candida Spp. in Jordanian Cancer Patients: Prevalence, Pathogenic Determinants, and Antifungal Sensitivity
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 57, 279-284, 2004 Epidemiological Report Isolation and Characterization of Candida Spp. in Jordanian Cancer Patients: Prevalence, Pathogenic Determinants, and Antifungal Sensitivity
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 57, 279-284, 2004 Epidemiological Report Isolation and Characterization of Candida Spp. in Jordanian Cancer Patients: Prevalence, Pathogenic Determinants, and Antifungal Sensitivity
