2014 Student Readiness Report
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Blankenship
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SmarterServices.com SMARTER
2 2 INTRODUCTION According to the 2013 Survey of Online Learning conducted by the Babson Survey Research Group over 7.1 million students were taking at least one online course during The 6.1% growth rate represents over 400,000 additional students taking at least one online course. Seventy-four percent of academic leaders rate the learning outcomes in online education as the same or superior to those in face-to-face courses. Sixty-nine percent of higher education institutions say that online learning is a critical part of their long-term strategy. In addition to the increased numbers of online courses, many institutions are now providing hybrid courses which are combinations of online and on-campus delivery systems. Even fully on-campus courses often use learning management systems and other technology to distribute content and foster collaboration and communication within the course. Self-directed and self-regulated learning models are used even in on-campus courses. Previous studies found that among academic leaders, 64 percent believe that it takes more discipline for a learner to succeed in an online course (Sloan Consortium, 2006 & 2007), therefore, placing additional responsibility on students to be self-directed learners. Many of the students taking online, hybrid or technology rich courses are adult learners who are returning to college after several years with family and/or in the work force. Other students are traditional aged college students who have studied in primary and secondary schools with little or no technology integration or distance learning experience. To what degree are these students ready to learn in a distance or technology rich environment? What types of support would be beneficial to help these students succeed at learning in a new paradigm? The literature on human performance indicates that student success is typically a function of three factors Aptitude, Attitude and Situation. Historically schools have done a great job collecting data about a student s aptitude with prior GPA and standardized test scores. Most college admission decisions are made based on aptitude. However, college students, especially adult learners, often drop out because of factors related to their situation in life and/or their attitude toward the learning experience. It is these noncognitive indicators of student performance which are measured with the SmarterMeasure Learning Readiness Indicator. A predictive metric of student performance is not complete when based on just aptitude and demographic factors. A more complete picture of a learner s propensity for success and persistence can be taken with the noncognitive variables which the assessment measures. The purpose of the is to provide summary data from thousands of students at hundreds of colleges regarding their reported levels of readiness for studying online or in a technology rich environment. This data can inform educational leaders as they design and provide instruction and support students who are studying at a distance. The information in this report is aggregate data taken from the students scores on the SmarterMeasure Learning Readiness Indicator between the dates of June 1, 2013, and May 31, Data from secondary school students and trial accounts was not included in this report.
3 3 The SmarterMeasure Learning Readiness Indicator, is a web-based assessment which measures a learner's readiness for succeeding in an online and/or technology rich learning program based on noncognitive indicators of success. SmarterMeasure indicates the degree to which an individual student possesses attributes, skills and knowledge that contribute to success in learning. All seven components of SmarterMeasure are grounded in theoretical research and practice. The purpose of the SmarterMeasure Learning Readiness Indicator is not to measure levels of academic skills. SmarterMeasure is designed to measure the levels of the non-cognitive traits, attributes and skills that learners possess that make distance learning or technology rich learning a good fit for them. The seven components of SmarterMeasure are: Individual Attributes - motivation, procrastination, willingness to ask for help, etc. Life Factors - Availability of time, support from family and employers, finances, etc. Learning styles - Based on the multiple intelligences model Technical Competency - Skills with using technology Technical Knowledge - Knowledge of technology terms On-screen Reading Rate and Recall Keyboarding Speed and Accuracy This is the sixth year that this report has been produced. In 2011 the title of the report was changed from the National Online Student Readiness Report to the Student Readiness Report to accommodate the fact that students in Canada and Puerto Rico are represented as well as students taking hybrid and/or technology rich on-campus courses. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF FINDINGS Demographic Profile: In the twelve month period represented in this report, a total of 460,406 SmarterMeasure assessments were taken or provisioned. This is a 28% decrease from 639,324 from the prior year. This is largely due to the enrollments declining at one major, for-profit institution during this time period. For the purpose of this report, data from the K-12 students as well as all data from demonstration accounts was removed. Also for the purposes of this analysis only, records of persons who completed the entire exam were included. A total of 319,952 complete records were analyzed to determine descriptive statistics. A random sample of 2% (N= 6288) complete records was selected for the comparison of means across the demographic variables to control for the effects of a large sample. Data from 367 colleges and universities was analyzed for this report. This is a 33% increase from 275 schools from the prior year s report. The SmarterMeasure Learning Readiness Indicator was developed in The chart below illustrates assessment usage by year.
4 Of the 460,406 SmarterMeasure testing instances from June 1, 2013 and May 31, 2014: 67% were female (2013 = 69%, 2012 = 70%, 2011 = 71%, 2010 = 72%, 2009 = 66%) 55% were Caucasian/White (2013 = 54%, 2012 = 59%, 2011 = 62%, 2010 = 59%, 2009 = 61%) The percentage of students who have never taken an online course is decreasing. (2014 = 51%, 2013 = 54%, 2012 = 54%, 2011 = 55%, 2010 = 60%, 2009 = 65%) This is an indicator that distance learning is becoming a more common educational delivery system. 39% were traditional aged (24 and younger) college students (2013 = 40%, 2012 = 35%, 2011 = 30%, 2010 = 28%, 2009 = 32%) 71% were students at an associate s level institution (2013 = 53%, 2012 = 52%, 2011 = 45%, 2010 = 55%, 2009 = 67%) 76% were from public institutions, and 24% were from private institutions. This figure excludes the large set of data from one major for-profit institution. 25% had social as their dominant learning style (2013 = 22%, 2012 = 22%, 2011 = 22%, 2010 = 28%, 2009 = 28%) 46% scored within the 80% to 89% range on the individual attributes scale (2013 = 47%, 2012 = 45%, 2011 = 45%, 2010 = 45%, 2009 = 42%) 26% recalled 90% or more of the reading passage (2013 = 28%, 2012 = 27%, 2011 = 27%, 2010 = 28%, 2009 = 28%)
5 5 25% demonstrated 100% accuracy on the Keyboarding skills test (2013 = 25%, 2012 = 32%, 2011 = 30%, 2010 = 29%, 2009 = 27%) and typed an average of words per minute (2012 = 27.73, 2011, 27.46, 2010 = 27.64, ) 35% exhibited between 70% - 79% of mastery of technical knowledge (2013 = 36%, 2012 = 37%, 2011 = 37%, 2010 = 33%, 2009 = 33%) 44% scored 100% on the technical competency skills tests (2013 = 47%, 2012 = 52%, 2011 = 53%, 2010 = 45%, 2009 = 58%) 43% scored 80% - 89% on the life factors section (2013 = 43%, 2012 = 43%, 2011 = 44%) Six-Year Trend Analysis This is the sixth year that the Student Readiness Report has been produced. An analysis of the frequency data over the past five years yields some interesting observations about trends in distance learning. Females continue to take more distance learning courses than males. Ethnic diversity among distance learning students is remaining relatively constant. Fewer students are experiencing distance learning for the first time. Distribution of ages of distance learning students is remaining somewhat constant. Social continues to be the dominant learning style. Individual attributes scores are remaining constant. Reading recall scores are remaining constant. Keyboarding skills are remaining constant. Technical knowledge scores are remaining constant. Technical competency scores are remaining within a constant range Female 66% 72% 71% 70% 69% 67% Caucasian/White 61% 59% 62% 59% 54% 55% New to Online Learning 65% 60% 55% 54% 54% 51% Traditional Age 32% 28% 30% 35% 40% 39% Associates Level 67% 55% 45% 52% 53% 71% Social as Dominant Learning Style 28% 28% 22% 22% 22% 25% 80% - 89% on Individual Attributes 42% 45% 45% 45% 47% 46% Recalled 90% + on Reading 28% 28% 27% 27% 28% 26% 100% Accurate on Keyboarding 27% 29% 30% 32% 25% 25% 70% to 79% on Technical Knowledge 33% 33% 37% 37% 36% 35% 100% on Technical Competency 58% 45% 53% 52% 47% 44%
6 6 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% % A matrix was developed to illustrate the trends over a six year period of demographic factors that have had statistically significant higher means. A profile of a successful distance learning student is emerging with six demographic variables having a statistically significant higher mean for six years in a row on one or more constructs measured by SmarterMeasure. Females have had the highest means for six years in Individual Attributes. Males have had the highest means for six years in Technical Knowledge. Caucasians have had the highest means for six years in Technical Knowledge. Students who have taken five or more online courses have had the highest means for six years in Individual Attributes and Technical Knowledge.
7 7 * 2009 * 2010 * 2011 * 2012 * 2013 * 2014 Individual Attributes Reading Recall Reading Rate Keyboarding Accuracy Keyboarding Rate Females ***** * ** * * ** * *** * * *** * Males **** * ***** * Caucasian *** ** * ***** ** * ** * * African American *** * * ** **** ** ** ** AN, AI, PI ** ** ** *** * * ** ** * * * * Latino/Hispanic * 5 Prior Courses ***** ** ** * ***** ** *** ** ** *** *** ** * * * * * * 4 Prior Courses * * * * * 3 Prior Courses * 24 and younger * * * * *** ** * ** *** * * * * * * * * * 55 and older ***** ** *** ** * 60+ Assoc. College * * * Bac. College ** * ** * *** ** Masters * * * * ** ** * ** ** * Special Focus ** * * * * ** Institution Doct. Granting * ** Private for-profit * Technical Knowledge Life Factors Academic Attributes Help Seeking Persistence **** ** Procrastination *** * Time Management *** * Locus of Control ** *
8 8 Private not-for-profit ** ** * ** * *** ** * * * * ** * Public * * ** ** * DESCRIPTION OF FINDINGS Gender: Of the students taking SmarterMeasure during the 2013/2014 academic year and of those who reported gender, 67% were female and 33% were male. Independent sample t-tests were calculated to determine if there are statistically significant differences between the means of gender and the constructs measured by SmarterMeasure. For scoring and reporting purposes each of the constructs measured by SmarterMeasure are quantified on a 0 to 100 scale. This scale is considered the composite score for that construct. Females were found to have statistically significant higher means on the construct of individual attributes, Keyboarding rate and life factors. Males were found to have statistically significant higher means on the constructs of reading rate and technical knowledge. It should be noted that for many students a high reading rate could be interpreted as a negative attribute since it may indicate that the student skimmed the passage. Ethnicity: The majority of students included in this report were Caucasian / White (55%). The second largest group was African American (24%). Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine if there are statistically significant differences between the means of the different ethnic groups and the constructs measured by SmarterMeasure. Statistically significant differences in means were reported in all constructs based on ethnicity. African- Americans reported the highest mean for Individual Attributes. Caucasian/White reported the highest mean for Reading Recall, Technical Knowledge, Technical Competency and Life Factors. Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander reported the highest mean for Keyboarding Accuracy and Rate. Number of Online Courses Taken: Institutions typically provide SmarterMeasure to students who have not yet taken an online or technology rich course. However, students who are new to one institution may have already taken an online course at another institution. This fact may impact their level of readiness to learn online. As a result, a demographic question is asked in SmarterMeasure to measure the number of online courses a student has already taken. The majority (51%) of students reported that they had never taken an online course prior to taking the SmarterMeasure assessment. The percentage of students who have never taken an online course is decreasing. (2014 = 51%, 2013 = 54%, 2012 = 54%, 2011 = 55%,
9 = 60%, 2009 = 65%) This is an indicator that distance learning is becoming a more common educational delivery system. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine the impact that a person taking prior online courses has on their readiness. The results demonstrated that experience matters with online learning. In each of the eight constructs measured, as persons took more online courses their readiness measures improved. The differences in the means were statistically significant in all of the seven scales. The greatest difference in means from students with no prior online course experience and those who had taken five or more courses continued (fourth consecutive year) to be in the area of technical knowledge. This indicates that with experience students can learn to use the technology required for online courses. Learners who had taken five or more prior online courses had statistically significant higher means for the constructs of Individual Attributes, Keyboarding Rate, Technical Knowledge, Technical Competency and Life Factors. Those who had taken two prior courses had the highest means for Keyboarding Accuracy. This paralleled the findings from the prior year. Age Range: Learners are asked to report their age range. A large percentage (39%) of students taking SmarterMeasure during Academic Year 2013/2014 were college-age students (18 24). This is parallel to 40% the prior year. This indicates that the assessment is being used in more traditional collegiate programs, not solely in online programs which historically have been populated mostly by adult learners. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine if differences exist between age ranges. Significant differences did exist in six of the eight constructs measured. Generally speaking, age does matter as demonstrated below. For constructs related to personal maturity, older students had the highest means. For constructs related to technical matters, younger students had the highest means. This was consistent with the prior five years findings. As was stated earlier in this report, a higher mean for Reading Rate is not necessarily a good measure as it likely indicates that one is not spending enough time on the reading passage. Institution Type: For analysis in this report, educational institutions using SmarterMeasure are classified by the type of institution. Available types include: (1) Doctorate-granting University, (2) Master s College or University, (3) Baccalaureate College, (4) Associates College and (5) Other/Specialized. This report excluded data from special focus institutions, corporations and K12 institutions. The majority (71%) of test takers were from Associates Colleges. Eight percent were from Master s Colleges and Universities, 4% from Doctorate-granting Universities, 6% were from Baccalaureate Colleges and 11% from Other/Specialized. Seventy-six percent of data was from public institutions and 24% from private institutions. This distribution is parallel to the prior year. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine if differences exist between students of different types of institutions. Significant differences did exist on six of the seven constructs measured. Master s Colleges and Universities had the highest means for Individual Attributes, Life Factors, Keyboarding Rate, and Technical Knowledge. Associates Colleges had the highest means for Reading
10 10 Recall and Technical Competency Comparisons were also made between for-profit and not-for-profit institutions. Statistically significant differences in means existed in seven of the eight constructs measured. Public institutions had the highest mean for Life Factors and Keyboarding Accuracy. Private not-for-profit institutions had the highest means for Individual Attributes, Reading Recall, Keyboarding Rate, Technical Knowledge, and Technical Competency. Dominant Learning Styles: Students learn using a variety of learning styles. Most persons are able to adapt their learning style to the format of the content. However, many persons do have a dominant learning style which defines their preferred method of receiving information. This analysis found that the most common dominant learning style was Social at 25%. (2013 = 22%, 2012 = 22%, 2011 = 22%, 2010 = 28%, 2009 = 28%) The least common dominant learning style was Visual (5%). The percentages of each learning style were within two percentage points of the prior year s measurement. This is an indicator of the reliability of the learning styles instrument. This finding is of interest to instructional designers who seek to construct online courses which appeal across the learning styles. Individual Attributes: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students are asked several questions which quantify their levels of individual attributes. The following individual attributes are measured: (1) help seeking, (2) time management, (3) procrastination, (4) persistence, (5) academic attributes and (6) locus of control. These six individual attributes are reported in aggregate on a scale of 0 to 100 with 100 indicating a very high level of the attributes. Forty-six percent of students scored within the 80 89% range. The distribution of Individual Attributes scores is parallel to the findings of prior years. (80 89% range %, %, 2012 = 45%, 2011 = 45%, 2010 = 45%, 2009 = 42%) Reading Rate and Recall: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students read a brief passage and then complete a quiz to measure the degree to which they can recall the information. The rationale is that much information in online courses is presented via text on-screen, and a person s ability to remember what they have read is important. This report is encouraging in that 26% of students recalled 90% or more of what they read. Twenty-four percent recalled 80% 89% of what they read. So over half of the students recalled 80% or more of what they had read. These findings replicated the findings from the prior year. The mean score was The average reading words per minute was 184 words per minute. The average words per minute for an American when reading for comprehension is 200 words per minute. Some students skim the reading passage, so reading rates in excess of 500 wpm were not factored into this average. However, one should not place too much stock in reading rate. Some students skim over the reading passage in SmarterMeasure and do not take the time to appropriately read it. As schools have conversations with students, they discuss the reality that when reading academic content, readers must not try to read too quickly.
11 11 Keyboarding Speed and Accuracy: The average Keyboarding speed was words per minute. (2013 = 26.24, 2012 = 27.73, 2011 = 27.46, 2010 = 27.64, 2009 = 28.02) This figure is the Adjusted Words per Minute and is adjusted to factor in the number of errors. However, the standard deviation of Adjusted Words per Minute was high at , so considerable variance was exhibited in Keyboarding skills among students who took SmarterMeasure during this academic year. Overall, students demonstrated a high degree of accuracy when Keyboarding. Twenty-five percent of students demonstrated 100% accuracy on the Keyboarding skills test. ( %, %, %, %) It is worthy of note that the average Keyboarding rate has been decreasing over the past six years. This may be an indication of weaker keyboarding skills. Technical Knowledge: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students are asked a series of questions which measure the degree to which they possess knowledge about technical terms and software usage. Technical Knowledge is measured on a scale of with 100 being a high degree of Technical Knowledge. Thirty-five percent of students exhibited between 70% 79% of mastery of Technical Knowledge. (2013 = 36%, 2012 = 37%, 2011 = 37%, 2010 = 33%, 2009 = 33%) The mean Technical Knowledge score was with standard deviation of Technical Competency: Students are asked to complete a series of skill tests to demonstrate their level of competency with basic technical tasks. Overall, students performed well on this element of SmarterMeasure with 44% scoring 100%. (2013 = 47%, 2012 = 54%, 2011 = 53%, 2010 = 45%, 2009 = 58%) The mean technical competency score was with a standard deviation of Life Factors: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students are asked a series of questions which measure several factors that are external to the learner. These factors include: availability of time, appropriateness of a place to study, one s reason for taking online courses, resources available to the learner and academic skills. Forty-three percent scored in the 80% - 89% range. The mean Life Factors score was with a standard deviation of BRIEF LITERATURE REVIEW ON LEARNER READINESS With the shift toward online learning, it is important to explore the adoption of online education. Previous studies found that among academic leaders, 64 percent believe that it takes more discipline for a learner to succeed in an online course (Sloan Consortium, 2006); therefore, placing additional responsibility on students to be self-directed learners. Before the start of an online program or course, it should be determined if a learner's instructional need can be resolved through a distance education approach (Willis & Lockee, 2004). Assessing the pre-requisite skills of the distance learner is critical (Hsiu-Mei & Liaw, 2004; Simonson et al., 2003). Learners need to have enough pre-requisite skills of technological
12 12 proficiency and a strong motivation to learn by technology (Hsiu-Mei & Liaw, 2004). In a study by Kuh, (2005) of twenty highly engaged institutions, one common characteristic was to know the students where they came from, their preferred learning styles, their talents, and when and where they need help (p. 301). Because of the difficulty in accommodating a group of learners with a wide range of acquired skills, requirements for pre-requisite skills should be set (Falvo & Solloway, 2004). A researched method of examining the notion of online readiness is listed using three aspects: (a) Student's preference for online form of instructional delivery as compared to traditional face to face instruction; (b) Student confidence in using electronic communication for learning and competence and confidence in the use of Internet and computer-mediated communication; and (c) Ability to engage in autonomous learning (P. J. Smith et al., 2003). Hall (2008, para 27) stated that "the primary value of the surveys may lie in raising awareness for any student considering enrolling in a distance education course." Pamela Dupin-Bryant of Utah State University - Toole conducted a study which was published in The American Journal of Distance Education titled "Pre-entry Variables Related to Retention in Online Distance Education". This study identified pre-entry variables related to course completion and noncompletion in university online distance education courses. Four hundred and sixty-four students who were enrolled in online distance education courses participated in the study. Discriminant analysis revealed six pre-entry variables were related to retention, including cumulative grade point average, class rank, number of previous courses completed online, searching the Internet training, operating systems and file management training, and Internet applications training. Results indicate prior educational experience and prior computer training may help distinguish between individuals who complete university online distance education courses and those who do not. SmarterMeasure measures all of the variables that this study indicated as indicators of success except for class rank. Literature Review Resources Dupin-Bryant, P. A. (2004). Pre-entry variables related to retention in online distance education. American Journal of Distance Education, 18(4), Falvo, D. A., & Solloway, S. (2004). Constructing community in a graduate course about teaching with technology. TechTrends: Linking Research & Practice to Improve Learning, 48(5), 56. Hsiu-Mei, H., & Liaw, S.-S. (2004). Guiding distance educators in building web-based instructions. International Journal of Instructional Media, 31(2), 125. Simonson, M., Smaldino, S., Albright, M., & Zvacek, S. (2003). Teaching and learning at a distance. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc. Willis, L. L., & Lockee, B. B. (2004). A pragmatic instructional design model for distance learning. International Journal of Instructional Media, 31(1), 9.
13 SUMMARY DATA AND ANALYSIS Data were collected for this report from students who took the SmarterMeasure assessment from June 1, 2013, to May 31, In the twelve month period represented in this report, a total of 460,406 SmarterMeasure assessments were taken. For the purpose of this report, data from the K-12 students as well as all data from demonstration accounts was removed. A random sample of 2% (N = 6,288) complete records was selected for the comparison of means across the demographic variables. DEMOGRAPHIC FREQUENCIES Note that schools have the option of not collecting demographic data from students. So the total number of demographic records analyzed does not equal the total number of assessments taken. Gender: Of the students taking SmarterMeasure during the 2013/2014 academic year and of those who reported gender, 67% were female and 33% were male. Gender Distribution 65467, 33% Male Female , 67%
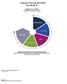
14 14 Ethnicity: The majority of students included in this report were Caucasian / White (55%). The second largest group was African American (24%). 6054, 3% 24723, 13% 43768, 24% African-American 8115, 4% 1821, 1% American Indian or Alaskan Native Asian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic , 55% Other Race Ethnicity N % African-American % American Indian or Alaskan Native % Asian or Pacific Islander % Caucasian / White % Latino / Hispanic % Other Race % It should be noted that schools do have the option to opt out of asking this question to students, and if schools do ask the ethnicity question, it is not a required question.
15 15 Number of Online Courses Taken: Institutions typically provide SmarterMeasure to students who have not yet taken an online or technology rich course. However, students who are new to one institution may have already taken an online course at another institution. This fact may impact their level of readiness to learn online. As a result, a demographic question is asked in SmarterMeasure to measure the number of online courses a student has already taken. The majority (51%) of students reported that they had never taken an online course prior to taking the SmarterMeasure assessment. The percentage of students who have never taken an online course is decreasing. (2014 = 51%, 2013 = 54%, 2012 = 54%, 2011 = 55%, 2010 = 60%, 2009 = 65%) This is an indicator that distance learning is becoming a more common educational delivery system. Number of Prior Online Courses Taken , 4% 13283, 7% 18922, 9% 31555, 16% 25773, 13% , 51%
16 16 Age Range: Learners are asked to report their age range. A large percentage (39%) of students taking SmarterMeasure during Academic Year 2013/2014 were college-age students (18 24). This is parallel to 40% the prior year. This indicates that the assessment is being used in more traditional collegiate programs, not solely in online programs which historically have been populated mostly by adult learners. Distribution of Age Ranges % % % 60+ 1% % % % % % %
17 17 Institution Type: For analysis in this report, educational institutions using SmarterMeasure are classified by the type of institution. Available types include: (1) Doctorate-granting University, (2) Master s College or University, (3) Baccalaureate College, (4) Associates College and (5) Other/Specialized. This report excluded data from special focus institutions, corporations and K12 institutions. The majority (71%) of test takers were from Associates Colleges. Eight percent were from Master s Colleges and Universities, 4% from Doctorate-granting Universities, 6% were from Baccalaureate Colleges and 11% from Other/Specialized. Seventy-six percent of data was from public institutions and 24% from private institutions. This distribution is parallel to the prior year. Distribution of Institution Type Other / Specialized 11% Master's Colleges and Universities 8% Doctorategranting Universities 4% Baccalaureate Colleges 6% Associates Colleges 71% Private forprofit 20% Private notfor-profit 4% Public 76%
18 18 SECTION FREQUENCIES Dominant Learning Styles: Students learn using a variety of learning styles. Most persons are able to adapt their learning style to the format of the content. However, many persons do have a dominant learning style which defines their preferred method of receiving information. This analysis found that the most common dominant learning style was Social at 25%. (2013 = 22%, 2012 = 22%, 2011 = 22%, 2010 = 28%, 2009 = 28%) The least common dominant learning style was Visual (5%). The percentages of each learning style were within two percentage points of the prior year s measurement. This is an indicator of the reliability of the learning styles instrument. This finding is of interest to instructional designers who seek to construct online courses which appeal across the learning styles. Distribution of Dominant Learning Styles Physical 8% Visual 5% Solitary 16% Aural 19% Logical 14% Social 25% Verbal 13% Social Verbal Logical Aural Solitary Physical Visual
19 19 Individual Attributes: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students are asked several questions which quantify their levels of individual attributes. The following individual attributes are measured: (1) help seeking, (2) time management, (3) procrastination, (4) persistence, (5) academic attributes and (6) locus of control. These six individual attributes are reported in aggregate on a scale of 0 to 100 with 100 indicating a very high level of the attributes. Forty-six percent of students scored within the 80 89% range. The distribution of Individual Attributes scores is parallel to the findings of prior years. (80 89% range %, %, 2012 = 45%, 2011 = 45%, 2010 = 45%, 2009 = 42%) Scores on the Individual Attributes Assessment
20 20 Reading Rate and Recall: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students read a brief passage and then complete a quiz to measure the degree to which they can recall the information. The rationale is that much information in online courses is presented via text on-screen, and a person s ability to remember what they have read is important. This report is encouraging in that 26% of students recalled 90% or more of what they read. Twenty-four percent recalled 80% 89% of what they read. So over half of the students recalled 80% or more of what they had read. These findings replicated the findings from the prior year. The mean score was The average reading words per minute was 184 words per minute. The average words per minute for an American when reading for comprehension is 200 words per minute. Some students skim the reading passage, so reading rates in excess of 500 wpm were not factored into this average. However, one should not place too much stock in reading rate. Some students skim over the reading passage in SmarterMeasure and do not take the time to appropriately read it. As schools have conversations with students, they discuss the reality that when reading academic content, readers must not try to read too quickly. Scores on the Reading Recall Assessment Less than 10% 10-19% 20-29% 30-39% 40-49% 50-59% 60-69% 70-79% 80-89% %
21 21 Keyboarding Speed and Accuracy: The average Keyboarding speed was words per minute. (2013 = 26.24, 2012 = 27.73, 2011 = 27.46, 2010 = 27.64, 2009 = 28.02) This figure is the Adjusted Words per Minute and is adjusted to factor in the number of errors. However, the standard deviation of Adjusted Words per Minute was high at , so considerable variance was exhibited in Keyboarding skills among students who took SmarterMeasure during this academic year. Overall, students demonstrated a high degree of accuracy when Keyboarding. Twenty-five percent of students demonstrated 100% accuracy on the Keyboarding skills test. ( %, %, %, %) It is worthy of note that the average Keyboarding rate has been decreasing over the past six years. This may be an indication of weaker keyboarding skills. Distribution of Keyboarding Speed and Accuracy 80% or less 4% 100% 25% 80% - 89% 11% 90% - 99% 60% 80% or less 80% - 89% 90% - 99% 100% Average Words Per Minute by Academic Year AY 08/09 AY 09/10 AY 10/11 AY 11/12 AY 12/13 AY 13/14
22 22 Technical Knowledge: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students are asked a series of questions which measure the degree to which they possess knowledge about technical terms and software usage. Technical Knowledge is measured on a scale of with 100 being a high degree of Technical Knowledge. Thirty-five percent of students exhibited between 70% 79% of mastery of Technical Knowledge. (2013 = 36%, 2012 = 37%, 2011 = 37%, 2010 = 33%, 2009 = 33%) The mean Technical Knowledge score was with standard deviation of Scores on Technical Knowledge Less than 10% 10-19% 20-29% 30-39% 40-49% 50-59% 60-69% 70-79% 80-89% %
23 23 Technical Competency: Students are asked to complete a series of skill tests to demonstrate their level of competency with basic technical tasks. Overall, students performed well on this element of SmarterMeasure with 44% scoring 100%. (2013 = 47%, 2012 = 54%, 2011 = 53%, 2010 = 45%, 2009 = 58%) The mean technical competency score was with a standard deviation of Scores on Technical Competency % or less 80% - 89% 90% - 99% 100%
24 24 Life Factors: On the SmarterMeasure assessment, students are asked a series of questions which measure several factors that are external to the learner. These factors include: availability of time, appropriateness of a place to study, one s reason for taking online courses, resources available to the learner and academic skills. Forty-three percent scored in the 80% - 89% range. The mean Life Factors score was with a standard deviation of Scores on Life Factors % 60-69% 70-79% 80-89% %
25 25 COMPARISON OF MEANS Because this data set is so large (N=460,406), any comparison of means such as an independent sample t-test or an ANOVA will yield a statistically significant difference due to the magnitude of the sample size. To control for this impractical significance, a random sample of 2% (N=6288) of the records which had completed the full assessment was selected for analysis in this section. Random cases were selected using the random sample tool in SPSS (Statistical Program for Social Sciences). It should be noted that when interpreting means for Reading Rate that a higher mean rate may not truly be indicative of faster readers. It could be indicative of readers who skimmed the passages instead of properly reading it. The average English-speaking adult reading speed when reading for comprehension is words per minute. Mean reading speeds in excess of that should be evaluated accordingly. To test this assumption, discriminant analysis was computed to determine if one s reading rate could be used to indicate their reading recall. Readers who likely skimmed the passaged were identified as those having reading rates of 400 wpm or higher. Using these two groups of normal and abnormally high readers, discriminant analysis was able to correctly classify their reading recall on a scale of based on their reading rate 72.9% of the time. So more than 7 out of 10 times, readers who skim the passage also attain low scores on the reading recall section of SmarterMeasure.
26 26 Gender: Independent sample t-tests were calculated to determine if there are statistically significant differences between the means of gender and the constructs measured by SmarterMeasure. For scoring and reporting purposes each of the constructs measured by SmarterMeasure are quantified on a 0 to 100 scale. This scale is considered the composite score for that construct. Females were found to have statistically significant higher means on the construct of individual attributes, Keyboarding rate and life factors. Males were found to have statistically significant higher means on the constructs of reading rate and technical knowledge. It should be noted that for many students a high reading rate could be interpreted as a negative attribute since it may indicate that the student skimmed the passage. Note: In the following tables the highest mean is underlined for ease of interpretation. Statistically significant differences in means are indicated in a bold, red font. Group Statistics Gender N Mean Std. Deviation Significance Individual Attributes Male Female Reading Recall Male Female Reading Rate Male Female Keyboarding Accuracy Male Female Keyboarding Rate Male Female Technical Knowledge Male Female Technical Competency Male Female Life Factors Male Female
27 27 Ethnicity: Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine if there are statistically significant differences between the means of the different ethnic groups and the constructs measured by SmarterMeasure. Statistically significant differences in means were reported in all constructs based on ethnicity. African-Americans reported the highest mean for Individual Attributes. Caucasian/White reported the highest mean for Reading Recall, Technical Knowledge, Technical Competency and Life Factors. Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander reported the highest mean for Keyboarding Accuracy and Rate. Std. N Mean Deviation Significance Individual Attributes African American Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total Life Factors African American Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total Reading Recall African American Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total Reading Rate African American Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander
28 28 Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total Keyboarding African American Accuracy Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total Keyboarding Rate African American Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total Technical Knowledge African American Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total Technical African American Competency Alaskan Native, American Indian or Pacific Islander Caucasian / White Latino / Hispanic Other Race Total
29 29 Number of Online Courses Taken: Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine the impact that a person taking prior online courses has on their readiness. The results demonstrated that experience matters with online learning. In each of the eight constructs measured, as persons took more online courses their readiness measures improved. The differences in the means were statistically significant in all of the seven scales. The greatest difference in means from students with no prior online course experience and those who had taken five or more courses continued (fourth consecutive year) to be in the area of technical knowledge. This indicates that with experience students can learn to use the technology required for online courses. Learners who had taken five or more prior online courses had statistically significant higher means for the constructs of Individual Attributes, Keyboarding Rate, Technical Knowledge, Technical Competency and Life Factors. Those who had taken two prior courses had the highest means for Keyboarding Accuracy. This paralleled the findings from the prior year. N Mean Std. Deviation Significance Individual Attributes Total Life Factors Total Reading Recall
30 Total Keyboarding Accuracy Total Keyboarding Rate Total Technical Knowledge Total Technical Competency Total
31 31 Age Range: Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine if differences exist between age ranges. Significant differences did exist in six of the eight constructs measured. Generally speaking, age does matter as demonstrated below. For constructs related to personal maturity, older students had the highest means. For constructs related to technical matters, younger students had the highest means. This was consistent with the prior five years findings. As was stated earlier in this report, a higher mean for Reading Rate is not necessarily a good measure as it likely indicates that one is not spending enough time on the reading passage. Age Range 2014 Highest Mean 2013 Highest Mean 2012 Highest Mean 2011 Highest Mean 2010 Highest Mean 2009 Highest Mean 24 and younger Reading Rate Keyboarding Rate Keyboarding Accuracy Technical Competency Reading Recall Technical Knowledge Reading Rate Keyboarding Accuracy Reading Recall Keyboarding Rate Technical Knowledge Technical Competency Life Factors Keyboarding Rate Reading Rate Technical Knowledge Reading Recall Technical Competency Keyboarding Rate Learning Styles Reading Rate Technical Knowledge Keyboarding Rate Reading Rate Keyboarding Accuracy Technical Knowledge Individual Attributes 55 and Individual older Attributes Individual Attributes Life Factors Individual Attributes Life Factors Keyboarding Accuracy Individual Attributes Reading Recall Keyboarding Accuracy Life Factors Reading Recall Life Factors Keyboarding Rate Keyboarding Accuracy Technical Knowledge Individual Attributes Reading Recall
32 32 N Mean Std. Deviation Significance Individual Attributes 24 and younger and older Total Life Factors 24 and younger and older Total Reading Recall 24 and younger and older Total Keyboarding Accuracy 24 and younger and older Total Keyboarding Rate 24 and younger and older Total
33 33 Technical Knowledge 24 and younger and older Total Technical Competency 24 and younger and older Total
34 34 Institution Type: Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was calculated to determine if differences exist between students of different types of institutions. Significant differences did exist on six of the seven constructs measured. Master s Colleges and Universities had the highest means for Individual Attributes, Life Factors, Keyboarding Rate, and Technical Knowledge. Associates Colleges had the highest means for Reading Recall and Technical Competency Comparisons were also made between for-profit and not-for-profit institutions. Statistically significant differences in means existed in seven of the eight constructs measured. Public institutions had the highest mean for Life Factors and Keyboarding Accuracy. Private not-for-profit institutions had the highest means for Individual Attributes, Reading Recall, Keyboarding Rate, Technical Knowledge, and Technical Competency. For the purpose of this analysis data from corporations, special focus institutions and K12 institutions was excluded. N Mean Std. Deviation Significance Individual Attributes Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University Doctorate-Granting University Total Life Factors Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University Doctorate-Granting University Total Reading Recall Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University Doctorate-Granting University Total Keyboarding Accuracy Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University
35 35 Doctorate-Granting University Total Keyboarding Rate Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University Doctorate-Granting University Total Technical Knowledge Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University Doctorate-Granting University Total Technical Competency Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University Doctorate-Granting University Total Reading Rate Associates College Baccalaureate College Master's Colleges and University Doctorate-Granting University Total N Mean Std. Deviation Significance Individual Attributes Private for-profit Private not-for-profit Public Total Life Factors Private for-profit
36 36 Private not-for-profit Public Total Reading Recall Private for-profit Private not-for-profit Public Total Keyboarding Accuracy Private for-profit Private not-for-profit Public Total Keyboarding Rate Private for-profit Private not-for-profit Public Total Technical Knowledge Private for-profit Private not-for-profit Public Total Technical Competency Private for-profit Private not-for-profit Public Total Reading Rate Private for-profit Private not-for-profit Public Total
37 37 ADDITIONAL ANALYSIS OF INDIVIDUAL ATTRIBUTES The construct of individual attributes measured by the SmarterMeasure Learning Readiness Indicator contains the following factors: (1) help seeking, (2) time management, (3) procrastination, (4) persistence, (5) academic attributes and (6) locus of control. These factors are attributes of a person which can impact the degree to which they are comfortable and confident taking an online course. Help Seeking is the degree to which a person is willing to ask for help when needed. Time Management is the degree to which a person can plan for the appropriate use of their time. Procrastination is the degree to which a person completes tasks in a timely manner. Persistence is the degree to which a person maintains activity with a task until completion. Academic Attributes are indicative of a person s prior academic success. Locus of Control is the degree to which a person feels that they are in control of their outcomes. Each of these factors was measured on a composite score ranging from 1 16 with 16 being a high degree of the attributes. The bar charts below present a frequency report of the scores for each factor on the scale of 1 16 with 16 being a high degree of the desired measure of the attribute. These charts represent the frequencies of the random sample of 2% of the total data set. Help Seeking Time Management
38 38 Procrastination Persistence Academic Attributes Locus of Control Additional analysis was conducted to determine if significant differences existed between the demographic groups and these individual attributes factors.
Online Student Readiness as a Predictor of Online Student Satisfaction
 2011 White Paper Online Student Readiness as a Predictor of Online Student By Dr. Mac Adkins, SmarterServices; and Julie Bryant, Noel-Levitz. Online education continues to be a rapidly expanding trend
2011 White Paper Online Student Readiness as a Predictor of Online Student By Dr. Mac Adkins, SmarterServices; and Julie Bryant, Noel-Levitz. Online education continues to be a rapidly expanding trend
South Dakota DOE 2013-2014 Report Card
 School Classification: Focus Title I Designation: Schoolwide Performance Indicators * No bar will display at the school or district level if the subgroup does not meet minimum size for reporting purposes.
School Classification: Focus Title I Designation: Schoolwide Performance Indicators * No bar will display at the school or district level if the subgroup does not meet minimum size for reporting purposes.
College Enrollment, Persistence, and Graduation: Statewide Results
 College Enrollment, Persistence, and Graduation: Statewide Results 72 Percent of Public High School Graduates Enroll in College 46 Percent Graduate in Six Years Summary Among students in the public high
College Enrollment, Persistence, and Graduation: Statewide Results 72 Percent of Public High School Graduates Enroll in College 46 Percent Graduate in Six Years Summary Among students in the public high
South Dakota DOE 2014-2015 Report Card
 Performance Indicators School Performance Index District Classification: - Exemplary Schools 1 / 24 Schools 4.17% Status Schools 1 / 24 Schools 4.17% Progressing Schools 19 / 24 Schools * No bar will display
Performance Indicators School Performance Index District Classification: - Exemplary Schools 1 / 24 Schools 4.17% Status Schools 1 / 24 Schools 4.17% Progressing Schools 19 / 24 Schools * No bar will display
Robert G. Crosby III, Dirk Davis, Riste Simnjanovski. California Baptist University, Riverside, USA. Introduction
 US-China Education Review A, September 2015, Vol. 5, No. 9, 602-609 doi:10.17265/2161-623x/2015.09.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Evidence-Based Online Course Development Practices Using Three Years of Incoming
US-China Education Review A, September 2015, Vol. 5, No. 9, 602-609 doi:10.17265/2161-623x/2015.09.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Evidence-Based Online Course Development Practices Using Three Years of Incoming
Annual Report of Life Insurance Examinations Calendar Year 2010
 Annual Report of Life Insurance Examinations Calendar Year 2010 OVERVIEW This report was prepared according to the provisions of section 626.2415, Florida Statutes, and is published annually using data
Annual Report of Life Insurance Examinations Calendar Year 2010 OVERVIEW This report was prepared according to the provisions of section 626.2415, Florida Statutes, and is published annually using data
Student Profile -Statistics on enrollment at University of Florida
 Page 26 AGENDA ITEM: XI Florida Polytechnic University Board of Trustees December 2, 2015 Subject: 2015 Student, Faculty and Staff Profile Proposed Board Action No Action Required- Information Only Background
Page 26 AGENDA ITEM: XI Florida Polytechnic University Board of Trustees December 2, 2015 Subject: 2015 Student, Faculty and Staff Profile Proposed Board Action No Action Required- Information Only Background
May 2006. Minnesota Undergraduate Demographics: Characteristics of Post- Secondary Students
 May 2006 Minnesota Undergraduate Demographics: Characteristics of Post- Secondary Students Authors Tricia Grimes Policy Analyst Tel: 651-642-0589 Tricia.Grimes@state.mn.us Shefali V. Mehta Graduate Intern
May 2006 Minnesota Undergraduate Demographics: Characteristics of Post- Secondary Students Authors Tricia Grimes Policy Analyst Tel: 651-642-0589 Tricia.Grimes@state.mn.us Shefali V. Mehta Graduate Intern
Michigan Department of Community Health
 Michigan Department of Community Health January 2007 INTRODUCTION The Michigan Department of Community Health (MDCH) asked Public Sector Consultants Inc. (PSC) to conduct a survey of licensed dental hygienists
Michigan Department of Community Health January 2007 INTRODUCTION The Michigan Department of Community Health (MDCH) asked Public Sector Consultants Inc. (PSC) to conduct a survey of licensed dental hygienists
WEB TABLES. Characteristics of Associate s Degree Attainers and Time to Associate s Degree U.S. DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION MARCH 2012 NCES 2012-271
 WEB TABLES U.S. DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION MARCH 2012 NCES 2012-271 Characteristics of Associate s Degree Attainers and Time to Associate s Degree The number of associate s degrees conferred by U.S. postsecondary
WEB TABLES U.S. DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION MARCH 2012 NCES 2012-271 Characteristics of Associate s Degree Attainers and Time to Associate s Degree The number of associate s degrees conferred by U.S. postsecondary
School of Nursing 2014-2015 Fact Book IV
 School of Nursing 2014-2015 Fact Book IV Professor Lisa O Steen COEHP Assessment Council COEHP Assessment Scheme for Continuous Improvement Purposeful Assessment, Data Collection, Analysis, Plans for Improvement,
School of Nursing 2014-2015 Fact Book IV Professor Lisa O Steen COEHP Assessment Council COEHP Assessment Scheme for Continuous Improvement Purposeful Assessment, Data Collection, Analysis, Plans for Improvement,
401(k) PARTICIPANTS AWARENESS AND UNDERSTANDING OF FEES
 401(k) PARTICIPANTS AWARENESS AND UNDERSTANDING OF FEES February 2011 401(k) PARTICIPANTS AWARENESS AND UNDERSTANDING OF FEES February 2011 Copyright 2011 AARP Research & Strategic Analysis 601 E Street,
401(k) PARTICIPANTS AWARENESS AND UNDERSTANDING OF FEES February 2011 401(k) PARTICIPANTS AWARENESS AND UNDERSTANDING OF FEES February 2011 Copyright 2011 AARP Research & Strategic Analysis 601 E Street,
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) 2015 Alumni Survey Results
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) 2015 Alumni Survey Results This report summarizes the results of CTL s 2015 Teacher Endorsement Alumni Survey. CTL conducted this survey to determine the
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) 2015 Alumni Survey Results This report summarizes the results of CTL s 2015 Teacher Endorsement Alumni Survey. CTL conducted this survey to determine the
Opening Slide. Michael Treviño. Director of Undergraduate Admissions University of California System June 2016
 Opening Slide Michael Treviño Director of Undergraduate Admissions University of California System June 2016 UC s Commitment to Diversity Mindful of its mission as a public institution, the University
Opening Slide Michael Treviño Director of Undergraduate Admissions University of California System June 2016 UC s Commitment to Diversity Mindful of its mission as a public institution, the University
Barriers to Enrollment: High School Students Perceptions of What it Will Take to Go to College
 Barriers to Enrollment: School Students Perceptions of What it Will Take to Go to College MiraCosta College Spring 2008 Prepared by: School Relations and Diversity Outreach Office & Institutional Research
Barriers to Enrollment: School Students Perceptions of What it Will Take to Go to College MiraCosta College Spring 2008 Prepared by: School Relations and Diversity Outreach Office & Institutional Research
OPERATING STANDARDS FOR IDENTIFYING AND SERVING GIFTED STUDENTS
 OPERATING STANDARDS FOR IDENTIFYING AND SERVING GIFTED STUDENTS Ohio Administrative Code 3301-51-15 March 2008 3301-51-15 Operating standards for identifying and serving gifted students. (A) Definitions
OPERATING STANDARDS FOR IDENTIFYING AND SERVING GIFTED STUDENTS Ohio Administrative Code 3301-51-15 March 2008 3301-51-15 Operating standards for identifying and serving gifted students. (A) Definitions
Comparison of Research Designs Template
 Comparison of Comparison of The following seven tables provide an annotated template to guide you through the comparison of research designs assignment in this course. These tables help you organize your
Comparison of Comparison of The following seven tables provide an annotated template to guide you through the comparison of research designs assignment in this course. These tables help you organize your
Pearson Student Mobile Device Survey 2015
 Pearson Student Mobile Device Survey 2015 National Report: College Students Report date: Revised June, 2015 Conducted by Harris Poll This report contains public findings Table of Contents Background &
Pearson Student Mobile Device Survey 2015 National Report: College Students Report date: Revised June, 2015 Conducted by Harris Poll This report contains public findings Table of Contents Background &
A Comparison of Training & Scoring in Distributed & Regional Contexts Writing
 A Comparison of Training & Scoring in Distributed & Regional Contexts Writing Edward W. Wolfe Staci Matthews Daisy Vickers Pearson July 2009 Abstract This study examined the influence of rater training
A Comparison of Training & Scoring in Distributed & Regional Contexts Writing Edward W. Wolfe Staci Matthews Daisy Vickers Pearson July 2009 Abstract This study examined the influence of rater training
Allen Elementary School
 Allen Elementary School April 4, 216 Dear Parents and Community Members: We are pleased to present you with the (AER), which provides key information on the 214-15 educational progress for the. The AER
Allen Elementary School April 4, 216 Dear Parents and Community Members: We are pleased to present you with the (AER), which provides key information on the 214-15 educational progress for the. The AER
Living in the Red Hawks Community
 http://www.collegeportraits.org/nj/msu 1 of 1 7/23/2014 9:58 AM Founded in 1908, is New Jersey s second largest university. It offers all the advantages of a large university a comprehensive undergraduate
http://www.collegeportraits.org/nj/msu 1 of 1 7/23/2014 9:58 AM Founded in 1908, is New Jersey s second largest university. It offers all the advantages of a large university a comprehensive undergraduate
bachelor s degree-granting institutions were located.
 WEB Profile of 2007 08 2007-08 First-Time Bachelor s TABLES Degree Recipients U.S. DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION in 2009 OCTOBER 2012 NCES 2013-150 These Web Tables provide wideranging information on the demographic
WEB Profile of 2007 08 2007-08 First-Time Bachelor s TABLES Degree Recipients U.S. DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION in 2009 OCTOBER 2012 NCES 2013-150 These Web Tables provide wideranging information on the demographic
Certified Peer Counselor Training Application
 Certified Peer Counselor Training Application Instructions Please type or print clearly. All sections of the form must be completed for the application to be accepted. These instructions explain how to
Certified Peer Counselor Training Application Instructions Please type or print clearly. All sections of the form must be completed for the application to be accepted. These instructions explain how to
Thank you for your interest in applying to the Exploring College Program! This packet contains all the necessary forms for application.
 APPLICATION INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for your interest in applying to the Program! This packet contains all the necessary forms for application. Program Information is a four-year enrichment program, generously
APPLICATION INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for your interest in applying to the Program! This packet contains all the necessary forms for application. Program Information is a four-year enrichment program, generously
The Math TLC Master s in Mathematics for Secondary Teachers Program
 Math TLC Master s Application Form Page 1 The Math TLC Master s in Mathematics for Secondary Teachers Program Electronic Application Form Instructions Save your completed application a filename of the
Math TLC Master s Application Form Page 1 The Math TLC Master s in Mathematics for Secondary Teachers Program Electronic Application Form Instructions Save your completed application a filename of the
Mind Maps: Useful Schematic Tool for Organizing and Integrating Concepts of Complex Patient Care in the Clinic and Classroom
 Mind Maps: Useful Schematic Tool for Organizing and Integrating Concepts of Complex Patient Care in the Clinic and Classroom But But what are student perceptions? Dr. Genevieve Pinto Zipp Dr. Catherine
Mind Maps: Useful Schematic Tool for Organizing and Integrating Concepts of Complex Patient Care in the Clinic and Classroom But But what are student perceptions? Dr. Genevieve Pinto Zipp Dr. Catherine
The Benefits of Community Service Employment (PY2006)
 The Benefits of Community Service Employment (PY2006) Prepared for Senior Service America, Inc. By The Charter Oak Group, LLC April 2008 The Benefits of Community Service The customer satisfaction data
The Benefits of Community Service Employment (PY2006) Prepared for Senior Service America, Inc. By The Charter Oak Group, LLC April 2008 The Benefits of Community Service The customer satisfaction data
STUDENTS PERCEPTIONS OF ONLINE LEARNING AND INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS: A QUALITATIVE STUDY OF UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS USE OF ONLINE TOOLS
 STUDENTS PERCEPTIONS OF ONLINE LEARNING AND INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS: A QUALITATIVE STUDY OF UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS USE OF ONLINE TOOLS Dr. David A. Armstrong Ed. D. D Armstrong@scu.edu ABSTRACT The purpose
STUDENTS PERCEPTIONS OF ONLINE LEARNING AND INSTRUCTIONAL TOOLS: A QUALITATIVE STUDY OF UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS USE OF ONLINE TOOLS Dr. David A. Armstrong Ed. D. D Armstrong@scu.edu ABSTRACT The purpose
Are you planning to apply for a counselor-approved fee waiver? Yes No Are you applying for financial aid? Yes No
 universal college application Transfer Admissions Application This form is developed for, and is to be used by, the members of the Universal College Application. All members evaluate this form equally
universal college application Transfer Admissions Application This form is developed for, and is to be used by, the members of the Universal College Application. All members evaluate this form equally
RESEARCH APPRENTICESHIP PROGRAM FOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS (RAP)
 RESEARCH APPRENTICESHIP PROGRAM FOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS (RAP) Please key or type all answers. Hand written applications will not be accepted. Once your part of the application is complete, print form,
RESEARCH APPRENTICESHIP PROGRAM FOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS (RAP) Please key or type all answers. Hand written applications will not be accepted. Once your part of the application is complete, print form,
Survey of Clinical Trial Awareness and Attitudes
 Survey of Clinical Trial Awareness and Attitudes Purpose of the Study Over $2 billion per year is spent on recruiting patients for clinical trials, yet slow patient enrollment is the primary cause of delay
Survey of Clinical Trial Awareness and Attitudes Purpose of the Study Over $2 billion per year is spent on recruiting patients for clinical trials, yet slow patient enrollment is the primary cause of delay
Journal of College Teaching & Learning July 2008 Volume 5, Number 7
 Prerequisite Coursework As A Predictor Of Performance In A Graduate Management Course Amy McMillan-Capehart, East Carolina University Tope Adeyemi-Bello, East Carolina University ABSTRACT There have been
Prerequisite Coursework As A Predictor Of Performance In A Graduate Management Course Amy McMillan-Capehart, East Carolina University Tope Adeyemi-Bello, East Carolina University ABSTRACT There have been
Understanding Your Test Record and Profile Chart for the PSB-Nursing School Aptitude Examination (RN)
 Understanding Your Test Record and Profile Chart for the PSB-Nursing School Aptitude Examination (RN) This data sheet has been prepared to help you understand the meaning of the scores you earned on the
Understanding Your Test Record and Profile Chart for the PSB-Nursing School Aptitude Examination (RN) This data sheet has been prepared to help you understand the meaning of the scores you earned on the
Education. Date of discharge (if applicable) [Required] Total number of service years. [Required] Total years and months active duty
![Education. Date of discharge (if applicable) [Required] Total number of service years. [Required] Total years and months active duty Education. Date of discharge (if applicable) [Required] Total number of service years. [Required] Total years and months active duty](/thumbs/25/5778623.jpg) Veteran Scholarships Application Basic Information [Required] Contact Information - must be 10-15 digits long and may include only numbers, hyphens, and spaces. - name@myschool.edu First name: Middle initial:
Veteran Scholarships Application Basic Information [Required] Contact Information - must be 10-15 digits long and may include only numbers, hyphens, and spaces. - name@myschool.edu First name: Middle initial:
WHITTIER COLLEGE. Application for Admission Teacher Credential Program. Department of Education & Child Development
 WHITTIER COLLEGE Department of Education & Child Development Application for Admission Teacher Credential Program 13406 E. Philadelphia Street P.O. Box 634 Whittier, CA 90608 562-907- 4248 Fax: 562-464-
WHITTIER COLLEGE Department of Education & Child Development Application for Admission Teacher Credential Program 13406 E. Philadelphia Street P.O. Box 634 Whittier, CA 90608 562-907- 4248 Fax: 562-464-
Michigan Technological University College Portrait. The Huskies Community. Carnegie Classification of Institutional Characteristics
 Page 1 of 11 College Portrait Michigan Tech was founded in 1885 and today is a leading public research university developing new technologies and preparing students to create the future for a prosperous
Page 1 of 11 College Portrait Michigan Tech was founded in 1885 and today is a leading public research university developing new technologies and preparing students to create the future for a prosperous
Demographic Analysis of the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community Using 2010 Census and 2010 American Community Survey Estimates
 Demographic Analysis of the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community Using 2010 Census and 2010 American Community Survey Estimates Completed for: Grants & Contract Office The Salt River Pima-Maricopa
Demographic Analysis of the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community Using 2010 Census and 2010 American Community Survey Estimates Completed for: Grants & Contract Office The Salt River Pima-Maricopa
Teaching college microeconomics: Online vs. traditional classroom instruction
 Teaching college microeconomics: Online vs. traditional classroom instruction ABSTRACT Cynthia McCarty Jacksonville State University Doris Bennett Jacksonville State University Shawn Carter Jacksonville
Teaching college microeconomics: Online vs. traditional classroom instruction ABSTRACT Cynthia McCarty Jacksonville State University Doris Bennett Jacksonville State University Shawn Carter Jacksonville
COLLEGE PREPARATION QUESTIONNAIRE
 COLLEGE PREPARATION QUESTIONNAIRE A. High School Attended: B. Month and year graduated from high school: C. I was enrolled in college track classes during high school (select one): Yes: No: D. Gender:
COLLEGE PREPARATION QUESTIONNAIRE A. High School Attended: B. Month and year graduated from high school: C. I was enrolled in college track classes during high school (select one): Yes: No: D. Gender:
Executive Summary. Metro Nashville Virtual School
 Metropolitan Nashville-Davidson City Public Schools Dr. James V Witty, Principal 4805 Park Ave Nashville, TN 37209-3436 Document Generated On September 26, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Description
Metropolitan Nashville-Davidson City Public Schools Dr. James V Witty, Principal 4805 Park Ave Nashville, TN 37209-3436 Document Generated On September 26, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Description
Teaching Hybrid Principles Of Finance To Undergraduate Business Students Can It Work? Denise Letterman, Robert Morris University
 Teaching Hybrid Principles Of Finance To Undergraduate Business Students Can It Work? Denise Letterman, Robert Morris University ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between
Teaching Hybrid Principles Of Finance To Undergraduate Business Students Can It Work? Denise Letterman, Robert Morris University ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between
Bryan Middle School. Bryan Middle School. Not Actual School Data. 100 Central Dr Anywhere, DE 19900 (555) 555-5555. Administration.
 O Hare School District Emma Haviland 100 Central Dr Anywhere, DE 19900 (555) 555-5555 Administration Principal Assistant Principal Assistant Principal Emma Haviland Stan Westfield Barbara Powell Accountability
O Hare School District Emma Haviland 100 Central Dr Anywhere, DE 19900 (555) 555-5555 Administration Principal Assistant Principal Assistant Principal Emma Haviland Stan Westfield Barbara Powell Accountability
INSTITUTIONAL REPORT FOR CONTINUING ACCREDITATION: CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT PATHWAY. Name of Institution Dates/Year of the Onsite Visit
 INSTITUTIONAL REPORT FOR CONTINUING ACCREDITATION: CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT PATHWAY Name of Institution Dates/Year of the Onsite Visit Insert Name(s) of Unit Head/Author(s) NCATE IR Template for Continuing
INSTITUTIONAL REPORT FOR CONTINUING ACCREDITATION: CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT PATHWAY Name of Institution Dates/Year of the Onsite Visit Insert Name(s) of Unit Head/Author(s) NCATE IR Template for Continuing
TEXAS ENGINEERING FOUNDATION 2015-2016 Scholarship Application for Graduating Texas High School Seniors
 TEXAS ENGINEERING FOUNDATION 2015-2016 Scholarship Application for Graduating Texas High School Seniors Application deadline is January 8, 2016 The chapters of the Texas Society of Professional Engineers
TEXAS ENGINEERING FOUNDATION 2015-2016 Scholarship Application for Graduating Texas High School Seniors Application deadline is January 8, 2016 The chapters of the Texas Society of Professional Engineers
MT. SAN JACINTO COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN NURSING LVN-RN APPLICATION www.msjc.edu/alliedhealth
 www.msjc.edu/alliedhealth Filing Period: September 1 st September 15 th It is the student s responsibility to request and ensure that all documents are in the Nursing & Allied Health Office by the application
www.msjc.edu/alliedhealth Filing Period: September 1 st September 15 th It is the student s responsibility to request and ensure that all documents are in the Nursing & Allied Health Office by the application
Nursing Scholarship Program High School Seniors & College Nursing Program Applicants
 ALSO AVAILABLE ONLINE HTTP://WWW.HNEF.ORG Nursing Scholarship Program High School Seniors & College Nursing Program Applicants Thank you for your interest in the Healthcare and Nursing Nursing Scholarship
ALSO AVAILABLE ONLINE HTTP://WWW.HNEF.ORG Nursing Scholarship Program High School Seniors & College Nursing Program Applicants Thank you for your interest in the Healthcare and Nursing Nursing Scholarship
College Name Regular Decision Early Decision Restrictive Early Action Early Action I am applying for the term beginning
 universal college application First-Year Admissions Application This form is developed for, and is to be used by, the members of the Universal College Application. All members evaluate this form equally
universal college application First-Year Admissions Application This form is developed for, and is to be used by, the members of the Universal College Application. All members evaluate this form equally
IMPACT OF LEARNING COMMUNITIES IN DEVELOPMENTAL ENGLISH ON COMMUNITY COLLEGE STUDENT RETENTION AND PERSISTENCE
 J. COLLEGE STUDENT RETENTION, Vol. 12(1) 7-24, 2010-2011 IMPACT OF LEARNING COMMUNITIES IN DEVELOPMENTAL ENGLISH ON COMMUNITY COLLEGE STUDENT RETENTION AND PERSISTENCE RANDALL A. BARNES San Diego City
J. COLLEGE STUDENT RETENTION, Vol. 12(1) 7-24, 2010-2011 IMPACT OF LEARNING COMMUNITIES IN DEVELOPMENTAL ENGLISH ON COMMUNITY COLLEGE STUDENT RETENTION AND PERSISTENCE RANDALL A. BARNES San Diego City
NEVADA STATE COLLEGE SCHOOL OF EDUCATION SPEECH PATHOLOGY PROGRAM
 NEVADA STATE COLLEGE SPEECH PATHOLOGY PROGRAM Application Procedure/Time Line: Applications for admission to the Speech Pathology Program are accepted twice each year. All application materials must be
NEVADA STATE COLLEGE SPEECH PATHOLOGY PROGRAM Application Procedure/Time Line: Applications for admission to the Speech Pathology Program are accepted twice each year. All application materials must be
Wesleyan Pre-College Access Program
 Wesleyan Pre-College Access Program What is the Pre-College Access Program? Wesleyan University s Pre-College Access Program is a comprehensive program developed to enhance the academic skills and preparation
Wesleyan Pre-College Access Program What is the Pre-College Access Program? Wesleyan University s Pre-College Access Program is a comprehensive program developed to enhance the academic skills and preparation
Nursing Scholarship Program High School Seniors & College Nursing Program Applicants
 ALSO AVAILABLE ONLINE www.hnef.org Nursing Scholarship Program High School Seniors & College Nursing Program Applicants Thank you for your interest in the Healthcare and Nursing Nursing Scholarship Program.
ALSO AVAILABLE ONLINE www.hnef.org Nursing Scholarship Program High School Seniors & College Nursing Program Applicants Thank you for your interest in the Healthcare and Nursing Nursing Scholarship Program.
A National Call to Action: School Counselors Ensuring College and Career Readiness. College Board National Office for School Counselor Advocacy
 A National Call to Action: School Counselors Ensuring College and Career Readiness College Board National Office for School Counselor Advocacy Presented By: Jennifer A. Reed, Director of Counselor Advocacy
A National Call to Action: School Counselors Ensuring College and Career Readiness College Board National Office for School Counselor Advocacy Presented By: Jennifer A. Reed, Director of Counselor Advocacy
Changes in the Demographic Characteristics of Texas High School Graduates. Key Findings
 Changes in the Demographic Characteristics of Texas High School Graduates 2003 2009 Key Findings The number of Texas high school graduates increased by 26,166 students, an 11 percent increase from 2003
Changes in the Demographic Characteristics of Texas High School Graduates 2003 2009 Key Findings The number of Texas high school graduates increased by 26,166 students, an 11 percent increase from 2003
College Board Announces Scores for New SAT with Writing Section
 Contact: Caren Scoropanos, Chiara Coletti 212 713-8052 cscoropanos@collegeboard.org ccoletti@collegeboard.org Embargoed until 10:30 a.m. (Eastern Time) Tuesday, August 29, 2006 Immediately after the embargo,
Contact: Caren Scoropanos, Chiara Coletti 212 713-8052 cscoropanos@collegeboard.org ccoletti@collegeboard.org Embargoed until 10:30 a.m. (Eastern Time) Tuesday, August 29, 2006 Immediately after the embargo,
Testing Services. Association. Dental Report 3 Admission 2011 Testing Program. User s Manual 2009
 American Dental Association Department of Testing Services Dental Report 3 Admission 2011 Testing Program User s Manual 2009 DENTAL ADMISSION TESTING PROGRAM USER'S MANUAL 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page History
American Dental Association Department of Testing Services Dental Report 3 Admission 2011 Testing Program User s Manual 2009 DENTAL ADMISSION TESTING PROGRAM USER'S MANUAL 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page History
Evaluation of Online Courses Fall 2000 to Fall 2001
 Evaluation of Online Courses Fall 2000 to Fall 2001 Institutional Assessment, Research and Planning May 2002 Dr. Andreea M. Serban, Director Steven Fleming, Analyst Office Web Site http://www.sbcc.net/rt/ir/institutionalresearch.htm
Evaluation of Online Courses Fall 2000 to Fall 2001 Institutional Assessment, Research and Planning May 2002 Dr. Andreea M. Serban, Director Steven Fleming, Analyst Office Web Site http://www.sbcc.net/rt/ir/institutionalresearch.htm
Progress Report Phase I Study of North Carolina Evidence-based Transition to Practice Initiative Project Foundation for Nursing Excellence
 Progress Report Phase I Study of North Carolina Evidence-based Transition to Practice Initiative Project Foundation for Nursing Excellence Prepared by the NCSBN Research Department INTRODUCTION In 2006,
Progress Report Phase I Study of North Carolina Evidence-based Transition to Practice Initiative Project Foundation for Nursing Excellence Prepared by the NCSBN Research Department INTRODUCTION In 2006,
were weighted to correct for variance in the likelihood of selection for a given case and to balance the sample to
 The following data come from two surveys. The first dataset comes from a representative survey of 656 human resources professionals (employers) from the Philadelphia, Los Angeles, Detroit and El Paso-Las
The following data come from two surveys. The first dataset comes from a representative survey of 656 human resources professionals (employers) from the Philadelphia, Los Angeles, Detroit and El Paso-Las
February 2003 Report No. 03-17
 February 2003 Report No. 03-17 Bright Futures Contributes to Improved College Preparation, Affordability, and Enrollment at a glance Since the Bright Futures program was created in 1997, Florida s high
February 2003 Report No. 03-17 Bright Futures Contributes to Improved College Preparation, Affordability, and Enrollment at a glance Since the Bright Futures program was created in 1997, Florida s high
Participation in Postsecondary Remedial Education
 1 Participation in Postsecondary Remedial Education Summary Participation in postsecondary remedial education in the first year of college is a key measure demonstrating students readiness to do college-level
1 Participation in Postsecondary Remedial Education Summary Participation in postsecondary remedial education in the first year of college is a key measure demonstrating students readiness to do college-level
Alabama A&M University Student Academic Program Assessment Mechanical Engineering
 I. Alabama A&M University Degree program type: 1 Undergraduate 14 100% 2 Graduate 0 0% Mean 1.00 Gender: 1 Male 9 64% 2 Female 5 36% Mean 1.36 Age group: 1 18-20 0 0% 2 21-23 10 71% 3 24-25 3 21% 4 26-30
I. Alabama A&M University Degree program type: 1 Undergraduate 14 100% 2 Graduate 0 0% Mean 1.00 Gender: 1 Male 9 64% 2 Female 5 36% Mean 1.36 Age group: 1 18-20 0 0% 2 21-23 10 71% 3 24-25 3 21% 4 26-30
1. My placement in calculus was determined by (Mark all that apply): 2. Did you take the SAT exam? 3. My SAT scores were: Page 1
 You have been selected to be part of a national survey of calculus instruction in colleges and universities across the United States. This research project is conducted by the Mathematical Association
You have been selected to be part of a national survey of calculus instruction in colleges and universities across the United States. This research project is conducted by the Mathematical Association
The Millennial Small Business Owner: 2011
 2015 U.S. Bank Small Annual The Millennial Small Owner September 15, 2015 This information is not intended to be a forecast of future events or guarantee of future results. It is not intended to serve
2015 U.S. Bank Small Annual The Millennial Small Owner September 15, 2015 This information is not intended to be a forecast of future events or guarantee of future results. It is not intended to serve
Dual Enrollment Program. Rhona Free
 Dual Enrollment Program Eastern Connecticut State University Quinebaug Valley Community College Rhona Free Eastern Connecticut State University Dual Enrollment Program Eastern Connecticut State University/Quinebaug
Dual Enrollment Program Eastern Connecticut State University Quinebaug Valley Community College Rhona Free Eastern Connecticut State University Dual Enrollment Program Eastern Connecticut State University/Quinebaug
From Higher Education to Work in West Virginia, 2012
 From Higher Education to Work in West Virginia, 2012 Eric Bowen, Research Associate John Deskins, PhD, Director January 2014 Copyright 2014 WVU Research Corporation Funding for this research was provided
From Higher Education to Work in West Virginia, 2012 Eric Bowen, Research Associate John Deskins, PhD, Director January 2014 Copyright 2014 WVU Research Corporation Funding for this research was provided
Total Males Females 34.4 36.7 (0.4) 12.7 17.5 (1.6) Didn't believe entitled or eligible 13.0 (0.3) Did not know how to apply for benefits 3.4 (0.
 2001 National Survey of Veterans (NSV) - March, 2003 - Page 413 Table 7-10. Percent Distribution of Veterans by Reasons Veterans Don't Have VA Life Insurance and Gender Males Females Not Applicable 3,400,423
2001 National Survey of Veterans (NSV) - March, 2003 - Page 413 Table 7-10. Percent Distribution of Veterans by Reasons Veterans Don't Have VA Life Insurance and Gender Males Females Not Applicable 3,400,423
DATA COACHING WORKSHOP DAY 1 PRESENTED BY SARITA SIQUEIROS THORNBURG, JILL PATNODE & KRISSY SOLTMAN
 DATA COACHING WORKSHOP DAY 1 PRESENTED BY SARITA SIQUEIROS THORNBURG, JILL PATNODE & KRISSY SOLTMAN January 28, 2014 Success for Each Child and Eliminate the Opportunity Gap Welcome and Introductions Overview
DATA COACHING WORKSHOP DAY 1 PRESENTED BY SARITA SIQUEIROS THORNBURG, JILL PATNODE & KRISSY SOLTMAN January 28, 2014 Success for Each Child and Eliminate the Opportunity Gap Welcome and Introductions Overview
students to complete their degree online. During the preliminary stage of included Art, Business, Computer Science, English, Government, History, and
 Texas Woman s University College of Arts and Sciences Bachelor of General Studies Program Undergraduate Program Review May 2012 I. PROGRAM REVIEW AND MISSION A. History Texas Woman s University has a proud
Texas Woman s University College of Arts and Sciences Bachelor of General Studies Program Undergraduate Program Review May 2012 I. PROGRAM REVIEW AND MISSION A. History Texas Woman s University has a proud
Emergency Room Services Satisfaction Survey
 Emergency Room Services Satisfaction Survey Date: «NameF» «NameL» «AddressLine1» «AddressLine2» «City», «StateCode» «Zip» Dear Member: TML MultiState Intergovernmental Employee Benefits Pool (IEBP) appreciates
Emergency Room Services Satisfaction Survey Date: «NameF» «NameL» «AddressLine1» «AddressLine2» «City», «StateCode» «Zip» Dear Member: TML MultiState Intergovernmental Employee Benefits Pool (IEBP) appreciates
Using Predictive Analytics to Understand Student Loan Defaults
 Using Predictive Analytics to Understand Student Loan Defaults RP Group Conference April 8, 2016 Tina Merlino, Research Analyst Lindsay Brown, Research Analyst Tina Lent, Director of Financial Aid, Scholarships
Using Predictive Analytics to Understand Student Loan Defaults RP Group Conference April 8, 2016 Tina Merlino, Research Analyst Lindsay Brown, Research Analyst Tina Lent, Director of Financial Aid, Scholarships
Comparing Blogs, Wikis, and Discussion Boards. as Collaborative Learning Tools
 Collaborative Learning Tools 1 Running head: Collaborative Learning Tools Comparing Blogs, Wikis, and Discussion Boards as Collaborative Learning Tools Susan L Connell San Diego State University Collaborative
Collaborative Learning Tools 1 Running head: Collaborative Learning Tools Comparing Blogs, Wikis, and Discussion Boards as Collaborative Learning Tools Susan L Connell San Diego State University Collaborative
forum Forecasting Enrollment to Achieve Institutional Goals by Janet Ward Campus Viewpoint
 forum Campus Viewpoint Forecasting Enrollment to Achieve Institutional Goals by Janet Ward As strategic and budget planning commences at community colleges, baccalaureate institutions, and comprehensive
forum Campus Viewpoint Forecasting Enrollment to Achieve Institutional Goals by Janet Ward As strategic and budget planning commences at community colleges, baccalaureate institutions, and comprehensive
Persistence and Attainment of 2003 04 Beginning Postsecondary Students: After 6 Years
 Persistence and Attainment of 2003 04 Beginning Postsecondary Students: After 6 Years First Look DECEMBER 2010 Alexandria Walton Radford Lutz Berkner MPR Associates, Inc. Sara C. Wheeless Bryan Shepherd
Persistence and Attainment of 2003 04 Beginning Postsecondary Students: After 6 Years First Look DECEMBER 2010 Alexandria Walton Radford Lutz Berkner MPR Associates, Inc. Sara C. Wheeless Bryan Shepherd
Policy Number: 2-121 Policy Name: Undergraduate Admission (formerly 2-102) A. Requirements for assured admission for residents of Arizona.
 Policy Revision Dates: 6/15, 2/13 Page 1 2-121 Undergraduate Admission A. Requirements for assured admission for residents of Arizona. 1. Each university will admit all undergraduate applicants who are
Policy Revision Dates: 6/15, 2/13 Page 1 2-121 Undergraduate Admission A. Requirements for assured admission for residents of Arizona. 1. Each university will admit all undergraduate applicants who are
Chapter 5: Analysis of The National Education Longitudinal Study (NELS:88)
 Chapter 5: Analysis of The National Education Longitudinal Study (NELS:88) Introduction The National Educational Longitudinal Survey (NELS:88) followed students from 8 th grade in 1988 to 10 th grade in
Chapter 5: Analysis of The National Education Longitudinal Study (NELS:88) Introduction The National Educational Longitudinal Survey (NELS:88) followed students from 8 th grade in 1988 to 10 th grade in
The Non-English Speaking Population in Hawaii
 Data Report 2011 The Non-English Speaking Population in Hawaii Introduction The report examines social, economic and demographic characteristics of people in Hawaii who speak language other than English
Data Report 2011 The Non-English Speaking Population in Hawaii Introduction The report examines social, economic and demographic characteristics of people in Hawaii who speak language other than English
Descriptive Statistics
 Descriptive Statistics Primer Descriptive statistics Central tendency Variation Relative position Relationships Calculating descriptive statistics Descriptive Statistics Purpose to describe or summarize
Descriptive Statistics Primer Descriptive statistics Central tendency Variation Relative position Relationships Calculating descriptive statistics Descriptive Statistics Purpose to describe or summarize
Changes in Self-Employment: 2010 to 2011
 Changes in Self-Employment: 2010 to 2011 American Community Survey Briefs By China Layne Issued January 2013 ACSBR/11-21 INTRODUCTION From December 2007 to June 2009, the United States experienced an economic
Changes in Self-Employment: 2010 to 2011 American Community Survey Briefs By China Layne Issued January 2013 ACSBR/11-21 INTRODUCTION From December 2007 to June 2009, the United States experienced an economic
CeO CENTER FOR EDUCATIONAL OPPORTUNITY University of Wisconsin Madison
 CeO CENTER FOR EDUCATIONAL OPPORTUNITY University of Wisconsin Madison FOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS ONLY We are pleased that you have expressed an interest in the University of Wisconsin-Madison and CeO. Please
CeO CENTER FOR EDUCATIONAL OPPORTUNITY University of Wisconsin Madison FOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS ONLY We are pleased that you have expressed an interest in the University of Wisconsin-Madison and CeO. Please
THE CHALLENGES OF BUSINESS OWNERSHIP: A COMPARISON OF MINORITY AND NON-MINORITY WOMEN BUSINESS OWNERS
 THE CHALLENGES OF BUSINESS OWNERSHIP: A COMPARISON OF MINORITY AND NON-MINORITY WOMEN BUSINESS OWNERS Cheryl L. Adkins, adkinscl@longwood.edu, Longwood University, Farmville, VA 23909 Sally W. Gilfillan,
THE CHALLENGES OF BUSINESS OWNERSHIP: A COMPARISON OF MINORITY AND NON-MINORITY WOMEN BUSINESS OWNERS Cheryl L. Adkins, adkinscl@longwood.edu, Longwood University, Farmville, VA 23909 Sally W. Gilfillan,
Survey of Nurses 2012
 Survey of Nurses 2012 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In 2012, the Michigan Center for Nursing conducted the ninth annual survey of nurses licensed in Michigan. The samples for this survey and previous surveys were
Survey of Nurses 2012 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In 2012, the Michigan Center for Nursing conducted the ninth annual survey of nurses licensed in Michigan. The samples for this survey and previous surveys were
ILLINOIS DISTRICT REPORT CARD
 -63-56-6- McHenry CHSD 56 McHenry CHSD 56 McHenry, ILLINOIS 2 ILLINOIS DISTRICT REPORT CARD and federal laws require public school districts to release report cards to the public each year. Starting in
-63-56-6- McHenry CHSD 56 McHenry CHSD 56 McHenry, ILLINOIS 2 ILLINOIS DISTRICT REPORT CARD and federal laws require public school districts to release report cards to the public each year. Starting in
Florida. Who attends Florida's public schools? Total 2010-11 Public Elementary and Secondary Enrollment: 2,643,347
 Florida Who attends Florida's public schools? Total 2010-11 Public Elementary and Secondary Enrollment: 2,643,347 Student Enrollment by Race/Ethnicity Student Enrollment by Income, Disability, and English
Florida Who attends Florida's public schools? Total 2010-11 Public Elementary and Secondary Enrollment: 2,643,347 Student Enrollment by Race/Ethnicity Student Enrollment by Income, Disability, and English
Western Illinois University School of Nursing
 Western Illinois University School of Nursing APPLICATION FOR ADMISSION Baccalaureate of Science in Nursing RETURN THIS FORM TO: Western Illinois University School of Nursing Waggoner Hall 339 1 University
Western Illinois University School of Nursing APPLICATION FOR ADMISSION Baccalaureate of Science in Nursing RETURN THIS FORM TO: Western Illinois University School of Nursing Waggoner Hall 339 1 University
For Immediate Release: Thursday, July 19, 2012 Contact: Jim Polites 860.713.6525
 For Immediate Release: Thursday, July 19, 2012 Contact: Jim Polites 860.713.6525 2012 CMT, CAPT RESULTS SHOW SOME INCREASES, WHILE GAPS IN ACHIEVEMENT PERSIST The Connecticut State Department of Education
For Immediate Release: Thursday, July 19, 2012 Contact: Jim Polites 860.713.6525 2012 CMT, CAPT RESULTS SHOW SOME INCREASES, WHILE GAPS IN ACHIEVEMENT PERSIST The Connecticut State Department of Education
Using hemispheric preference as a predictor of success in a limited-residency information systems doctoral program
 Using hemispheric preference as a predictor of success in a limited-residency information systems doctoral program Steven R. Terrell, Nova Southeastern University, terrell@nova.edu Abstract Due to the
Using hemispheric preference as a predictor of success in a limited-residency information systems doctoral program Steven R. Terrell, Nova Southeastern University, terrell@nova.edu Abstract Due to the
Alumni Perceptions of AACSB Accreditation to the Undergraduate Program
 Alumni Perceptions of AACSB Accreditation to the Undergraduate Program Juan M. Dempere, Metropolitan State College of Denver Ramon Griffin, Metropolitan State College of Denver Paul Camp, Metropolitan
Alumni Perceptions of AACSB Accreditation to the Undergraduate Program Juan M. Dempere, Metropolitan State College of Denver Ramon Griffin, Metropolitan State College of Denver Paul Camp, Metropolitan
2008-09 Annual Report. M i c h i g a n T e c h. create the. future. change the. world
 2008-09 Annual Report M i c h i g a n T e c h Graduate School create the future change the world Message From the Dean I am extremely pleased to present this edition of Michigan Tech s Graduate School
2008-09 Annual Report M i c h i g a n T e c h Graduate School create the future change the world Message From the Dean I am extremely pleased to present this edition of Michigan Tech s Graduate School
Lewis University Cohort Program
 An agency of the Regional Offices of Education for Will & Grundy-Kendall Counties 2705 McDonough Street Joliet, IL 60436 (815) 744-8334 Fax (815) 744-8396 Lewis University Cohort Program Middle School
An agency of the Regional Offices of Education for Will & Grundy-Kendall Counties 2705 McDonough Street Joliet, IL 60436 (815) 744-8334 Fax (815) 744-8396 Lewis University Cohort Program Middle School
Pearson Student Mobile Device Survey 2014
 Pearson Student Mobile Device Survey 2014 National Report: College Students Conducted by Harris Poll Field dates: February 13 March 12, 2014 Report date: May 16, 2014 Table of Contents Background & Objectives
Pearson Student Mobile Device Survey 2014 National Report: College Students Conducted by Harris Poll Field dates: February 13 March 12, 2014 Report date: May 16, 2014 Table of Contents Background & Objectives
Transitioning English Language Learners in Massachusetts: An Exploratory Data Review. March 2012
 Transitioning English Language Learners in Massachusetts: An Exploratory Data Review March 2012 i This document was prepared by the Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Mitchell
Transitioning English Language Learners in Massachusetts: An Exploratory Data Review March 2012 i This document was prepared by the Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education Mitchell
Interpreting and Using SAT Scores
 Interpreting and Using SAT Scores Evaluating Student Performance Use the tables in this section to compare a student s performance on SAT Program tests with the performance of groups of students. These
Interpreting and Using SAT Scores Evaluating Student Performance Use the tables in this section to compare a student s performance on SAT Program tests with the performance of groups of students. These
The Development and Validation of a Survey Instrument for the Evaluation of Instructional Aids
 The Development and Validation of a Survey Instrument for the Evaluation of Instructional Aids Elaine Strachota Steven W. Schmidt Simone C. O. Conceição Abstract The processes associated with survey development
The Development and Validation of a Survey Instrument for the Evaluation of Instructional Aids Elaine Strachota Steven W. Schmidt Simone C. O. Conceição Abstract The processes associated with survey development
COLLIN COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT NURSING PROGRAM NURSING EDUCATION PERFORMANCE INITIATIVE RECOGNIZED BEST PRACTICE DISSEMINATION PLAN
 COLLIN COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT NURSING PROGRAM NURSING EDUCATION PERFORMANCE INITIATIVE RECOGNIZED BEST PRACTICE DISSEMINATION PLAN SEPTEMBER 2009 Education Performance Initiative Page 2 Education
COLLIN COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT NURSING PROGRAM NURSING EDUCATION PERFORMANCE INITIATIVE RECOGNIZED BEST PRACTICE DISSEMINATION PLAN SEPTEMBER 2009 Education Performance Initiative Page 2 Education
Iowa School District Profiles. Central City
 Iowa School District Profiles Overview This profile describes enrollment trends, student performance, income levels, population, and other characteristics of the Central City public school district. The
Iowa School District Profiles Overview This profile describes enrollment trends, student performance, income levels, population, and other characteristics of the Central City public school district. The
Drexel University College of Medicine
 Drexel University College of Medicine In the Tradition of Woman s Medical College of Pennsylvania and Hahnemann Medical College College of Medicine Transfer Application I am applying for the Second Year
Drexel University College of Medicine In the Tradition of Woman s Medical College of Pennsylvania and Hahnemann Medical College College of Medicine Transfer Application I am applying for the Second Year
The University of Southern Mississippi College Portrait The University of Southern Mississippi Hattiesburg, MS 601.266.1000 http://www.usm.
 Page 1 of 10 World-class academics with a personal touch a unique combination you won t find anywhere else! You can choose from over 90 different academic programs with opportunities for both undergraduate
Page 1 of 10 World-class academics with a personal touch a unique combination you won t find anywhere else! You can choose from over 90 different academic programs with opportunities for both undergraduate
Cardiff Elementary School School Accountability Report Card Reported Using Data from the 2010 11 School Year
 Cardiff Elementary School School Accountability Report Card Reported Using Data from the 2010 11 School Year Published During 2011 12 Every school in California is required by state law to publish a School
Cardiff Elementary School School Accountability Report Card Reported Using Data from the 2010 11 School Year Published During 2011 12 Every school in California is required by state law to publish a School
MBA for Professionals
 MBA for Professionals Program The admissions committee is pleased to accept your application for admission to the Willamette University MBA for Professionals program. Admission to this program is selective,
MBA for Professionals Program The admissions committee is pleased to accept your application for admission to the Willamette University MBA for Professionals program. Admission to this program is selective,
Towards the design of a decentralized support system for online learners (Proposal Feedback ID 493)
 Towards the design of a decentralized support system for online learners (Proposal Feedback ID 493) Olabisi Kuboni University of the West Indies, Trinidad and Tobago olabisi.kuboni@dec.uwi.edu INTRODUCTION
Towards the design of a decentralized support system for online learners (Proposal Feedback ID 493) Olabisi Kuboni University of the West Indies, Trinidad and Tobago olabisi.kuboni@dec.uwi.edu INTRODUCTION
