Clinical Utility of Sonography in Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis
|
|
|
- Prosper Snow
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Article Clinical Utility of Sonography in Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis Nuran Sabir, MD, Semra Demirlenk, MD, Baki Yagci, MD, Nevzat Karabulut, MD, Sibel Cubukcu, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to investigate the efficacy of sonography in the detection of plantar fasciitis (PF) compared with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in subjects with inferior heel pain. Methods. Seventy-seven patients with unilateral (n = 9) and bilateral (n = 68) heel pain were studied. Seventy-seven age- and sex-matched asymptomatic subjects served as a control group. Magnetic resonance imaging was used to establish a diagnosis of PF with sagittal T1-weighted, T2- weighted, and short tau inversion recovery sequences. The sonographic appearances of PF were compared with MRI findings. Plantar fascia and heel pad thickness were also measured on both imaging modalities. Results. Compared with MRI, sonography showed 80% sensitivity and 88.5% specificity in assessing PF. A strong correlation was found between plantar fascia and fat pad thickness measurements done by sonography (P <.001; r = 0.854) and MRI (P <.001; r = 0.798). Compared with the asymptomatic volunteers, patients with PF had significant increases in plantar fascia and heel pad thicknesses, weight, and body mass index (P =.0001). Heel pad thickness was also significantly increased with pain duration (P =.021). Conclusions. Although MRI is the modality of choice in the morphologic assessment of different plantar fascia lesions, sonography can also serve as an effective tool and may substitute MRI in the diagnosis of PF. Key words: magnetic resonance imaging; plantar fasciitis; sonography. Abbreviations BMI, body mass index; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PF, plantar fasciitis; STIR, short tau inversion recovery; TE, echo time; TR, repetition time Received December 4, 2004, from the Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Pamukkale University, Denizli, Turkey (N.S., S.D., B.Y., N.K.); and Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Faculty of Medicine, Akdeniz University, Antalya, Turkey (S.C.). Revision requested December 16, Revised manuscript accepted for publication May 10, Address correspondence to Nuran Sabir, MD, Yenisehir, Ferah Evler Blok B, Sokak 17, 17, Denizli, Turkey. nuransabir@hotmail.com Plantar fasciitis (PF) is the most common cause of inferior heel pain, with poorly understood etiology and confusing terminology. 1 It is known to affect middle-aged women and younger, predominantly male, runners. 2 The role of radiology in the management of PF is to make an accurate diagnosis as early as possible because effective treatment of PF requires precise diagnosis and differentiation from other causes of heel pain. 3 Imaging may also be of value in the followup of these patients, particularly athletes, to time appropriate recommencement of physical activity. 4,5 Conventional radiographic studies of patients with painful heel syndrome are often unrewarding, 6 and calcaneal uptake at radionuclide scintigraphy is a frequent but nonspecific finding. 7 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has emerged as an important noninvasive diagnostic imaging technique for assessment of foot conditions, with multiplanar imaging capability and inherent superiority in contrast resolution Sonography has also proved to be an excellent imaging technique for the 2005 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24: /05/$3.50
2 Clinical Utility of Sonography in Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis assessment of tendon disorders in various parts of the body The plantar aponeurosis, similar to tendons elsewhere, is shown sonographically as a homogeneous echogenic band with internal linear interfaces on longitudinal sections. 16 Sonography has also the advantages of being noninvasive, well tolerated by patients, and inexpensive, and it provides excellent spatial resolution for superficial structures. Previous studies reported that mechanical stress and inflammation result in tendon thickening, with hypoechoic areas within the plantar fascia 17 and, occasionally, peritendon fluid collection, 18 but these studies were done in a limited number of patients. However, this study was performed in a bigger population with inferior heel pain to evaluate the effectiveness of sonography as a primary modality in diagnosing PF. To date, to our knowledge a correlation of sonographic and MRI findings of PF has not been performed. Therefore, in this prospective study, we aimed to test the utility of sonography in the evaluation of PF in patients with inferior heel pain using the MRI findings as a reference standard. Materials and Methods Subjects The study population consisted of 77 patients with heel pain and the physical characteristics of PF. Nine of the study group had unilateral heel symptoms, and 68 had bilateral heel symptoms, giving a total of 145 symptomatic heels. There were 66 women and 11 men with a mean age ± SD of 45.9 ± 11.8 years (range, years). Body weight and height of all the subjects were recorded, and, accordingly, the body mass index (BMI; weight/height 2 ) was calculated. In addition, heels of 77 asymptomatic volunteers were recruited into the study as a control group and were examined to provide a baseline as to the normal appearance of the plantar fascia. The control subjects were age and sex matched to the symptomatic patients and included 63 women and 14 men with a mean age of 42 ± 7.5 years (range, years). The local Institutional Review Board approved the study, and informed consent was obtained from each subject imaged under the research protocol. Radiologic evaluation of the changes in the heels of the study and control groups was fulfilled prospectively from April 2003 to March Radiologic Examinations Sonograms and MR images were evaluated independently by 2 different radiologists in a blinded fashion. Magnetic resonance images were interpreted by an experienced musculoskeletal radiologist (N.S.), and sonography was performed by a 4-year radiology resident (S.D.) who had completed a 1-year sonography rotation including 3 months of training in musculoskeletal sonography. Furthermore, before the study, the radiologist was taught how to approach the sonographic examination of the plantar fascia. Both heels were imaged in all patients irrespective of the laterality of the symptoms. There was a maximum of 3 days duration between sonographic and MRI examinations. Sonographic examinations were performed with a commercially available scanner (LOGIQ 500 PRO; GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI) and a 6.0- to 9.0-MHz linear transducer. The subjects lay prone with their feet hanging free over the end of the examination couch and their ankles dorsiflexed to 90. Care to keep the beam perpendicular to the plantar fascia was taken at all times to avoid anisotropy. Sagittal imaging of the plantar fascia was performed, and its thickness was measured at a standard reference point where the plantar fascia crosses the anterior aspect of the inferior border of the calcaneus (Figure 1). Plantar fascia thickness greater than 4 mm was considered abnormal. 13,19 Heel fat pad thickness was also measured at the same region between the skin fat pad interface and the fat pad calcaneal bone interface. Three measurements of the plantar fascia and heel fat pad were taken to avoid error due to transducer obliquity, and the average of the 3 was recorded. Uniform hyperechogenicity of the plantar fascia was considered a normal finding. The changes in the echogenicity of the symptomatic fascia were evaluated as a hypoechoic fascia that stood in contrast to the adjacent hyperechoic fat of the heel pad. Sonographic findings of PF were assessed as thickening of the plantar fascia, reduced echogenicity of the plantar fascia (Figure 2), and loss of the fascia edge sharpness (Figures 3 and 4). Because solitary or combinations of findings could be seen in the same patient, patients were analyzed according to the number of the displayed sonographic findings. According to the localization of the sonographic findings within the plantar fascia and the subclassification that was used in MRI, 20 PF was subclassified into 1042 J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24:
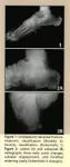
3 Sabir et al A B Figure 1. A, Longitudinal sonogram from a 41-year-old woman, inferior calcaneal region, plantar aspect of the foot, showing the normal internal longitudinal fibrillar pattern within the plantar fascia (arrows). B, Diagram showing the location and the obtained measurements both for the plantar fascia (PF) and the heel fat pad (FP). C indicates calcaneus; and P, probe. enthesopathy, musculoaponeurositis, and rupture. Enthesopathy was diagnosed when the above-mentioned sonographic findings were seen at the site of insertion of the plantar fascia. However, musculoaponeurositis was considered when the sonographic findings were seen over many centimeters extending through the central part/body of the plantar fascia. Rupture was identified when there was loss of an internal longitudinal fibrillar pattern with thickening, blurring of the edges, and an anechoic area in the plantar fascia. 14,17 Magnetic resonance imaging was performed with a 1.5-T unit (Gyroscan Intera-Power; Philips Medical Systems, Eindhoven, the Netherlands) with a superconductive system using an extremity coil. Sagittal T1-weighted (repetition time [TR], 500 milliseconds; echo time [TE], 18 milliseconds) spin echo, T2-weighted (TR, 3881 milliseconds; TE, 120 milliseconds) gradient echo, and short tau inversion recovery (STIR; TR, 2414 milliseconds; TE, 60 milliseconds; inversion time, 160 milliseconds) sequences were taken. T1-weighted sagittal sections after intravenous administration of gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Magnevist; Schering AG, Berlin, Germany) were also obtained. The plantar fascia is normally of homogeneous low signal intensity with either uniform or minimal tapering along its course. The thickness of the plantar fascia was measured at a point just anterior to the calcaneal insertion. Heel pad thickness was also taken by measuring the thickness of the subcutaneous tissue at a point between the calcaneal insertion of the plantar fascia and the skin (Figure 1). Care was taken to do all the measurements at the same location on MRI as taken on sonography. The pathologic appearance of the plantar fascia was evaluated according to the morphologic findings, namely, enthesopathy, musculoaponeurositis, and rupture. 20 Enthesopathy was diagnosed when there was a thickened plantar fascia at its origin on T1-weighted images (Figure 5A) and abnormal high intersubstance signal intensity on T2-weighted and STIR images (Figure 5C). Contrast enhancement of the thickened plantar fascia on the T1-weighted sequence was regarded as reflecting an active inflammatory process (Figure 5B). Musculoaponeurositis was diagnosed when there was a thickened fascia over several centimeters in the central part of the plantar fascia, usually irregular but continuous. It generated a low-intensity signal on T1- and T2- weighted images (Figure 6) because of minimal Figure 2. Sagittal sonogram of the inferior calcaneal region from a 43-year-old woman showing prominent thickening, measuring 7.3 mm (arrows), and hypoechogenic changes in the plantar fascia. J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24:
4 Clinical Utility of Sonography in Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis plantar fascia thickness with fat pad thickness measured by both sonography and MRI. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of sonographic findings were assessed. The significance of differences between the control group and patients with PF was determined by an independent samples t test. A linear regression test was computed between plantar fascia and heel fat pad thicknesses, weight, height, and BMI. Results Figure 3. Sagittal heel sonogram from a 39-year-old man showing enthesopathic changes as a grossly thickened hypoechoic plantar fascia measuring 8.1 mm with loss of edge sharpness. inflammatory reactions; no contrast enhancement was seen on postcontrast T1-weighted images. Rupture of the plantar fascia was another morphologic entity that was displayed as a disruption of plantar fascia continuity with abnormal loss of its low signal intensity on T1-weighted MR images at the site of the rupture and a considerable amount of enhancement. Statistical Analysis Findings related to PF from both imaging modalities were compared. Mean values, SDs, and ranges of age, weight, height, BMI, and sonographic and MRI measurements of plantar fascia and heel fat pad thicknesses were calculated. The Pearson correlation test was used to correlate Figure 4. Sagittal heel sonogram from a 45-year-old woman showing thickening, reduced echogenicity, and fluid collection in the paratenon (arrow). Table 1 shows the significant increase in plantar fascia thickness, heel fat pad thickness, weight, and BMI in patients with PF in relation to the control group (P =.0001). In 77 patients with pain, a total of 145 heels were assessed by both sonography and MRI. Evidence of PF was observed in 66 (45.5%) of 145 (60 bilateral and 6 unilateral) heels by sonography and 68 (46.9%) of 145 heels (62 bilateral and 6 unilateral) by MRI. Plantar fasciitis was subclassified, and we found that 42 (28.9%) of 145 heels had enthesopathy by sonography, compared with 46 (31.7%) of 145 by MRI. Musculoaponeurositis was diagnosed in 11 (7.5%) of 145 by sonography and in 20 (13.8%) of 145 by MRI. Only 2 (1.3%) of 145 had rupture shown on both sonography and MRI. Seventy-nine (54.4%) and 77 (53.1%) of 145 symptomatic heels showed no evidence of PF findings on sonography and MRI, respectively (Table 2). Sonographic findings of PF were seen particularly in cases of enthesopathy, in which the mean thickness of the plantar fascia was 4.9 ± 0.9 mm. Sonographic findings of PF were identified mainly as thickening of the plantar fascia in 62 (42.7%) of 145 heels, reduced echogenicity of the plantar fascia in 56 (38.6%) of 145 heels, and loss of the fascia edge sharpness in 42 (28.9%) of 145 heels (Figures 2 and 3A). All the sonographic findings were seen in 41 of 145 heels, whereas at least 2 sonographic findings were seen in 12 of 145 heels, and only 1 finding was seen in 13 of 145 heels. The other additional findings were perifascial fluid, seen in 5 (3.4%) of 145 heels (Figure 4), and intratendinous calcification, seen in 2 (1.3%) of 145. Correlating with MRI findings as a reference standard in this study, sonography showed 80.9% sensitivity (55 of 68) and 85.7% specificity (66 of 77) in assessing PF J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24:
5 Sabir et al Figure 5. Enthesopathy of the plantar fascia. A and B, T1- weighted precontrast (A) and postcontrast (B) sagittal MR images showing a thickened plantar fascia at its calcaneal origin and signal intensity changes reflecting edema in perifascial soft tissues. Contrast enhancement of the plantar fascia and perifascial soft tissue is shown in B (arrow). C, Sagittal STIR image showing reveals the increased intrasubstance signal intensity of the thickened plantar fascia with surrounding hyperintense perifascial soft tissue edema. The abnormal high marrow signal intensity at the calcaneal insertion is also shown. Achilles tendinitis is also shown, suggesting a common stress mechanism. A However, sonography revealed higher sensitivity in diagnosing PF in patients with enthesopathy than in those with musculoaponeurosis (91.3% versus 55%). In the symptomatic heels, sonographic findings showed an 83.3% positive predictive value and an 83.5% negative predictive value. There was a strong correlation between plantar fascia thickness and fat pad thickness measured both by sonography (P =.0001; r = 0.854) and MRI (P =.0001; r = 0.798). The linear regression test also revealed that fat pad thickness inversely affected plantar fascia thickness (t = 2.755; P =.007). Discussion B The results of this study show that sonography can be used to diagnose PF confidently in most cases. In our study, PF was considered present when the plantar fascia thickness was greater than 4 mm with reduced echogenicity, loss of definition of the borders of the fascia distal to the anteroinferior border of the calcaneus, or both. 13,20 Many previous studies also used these criteria as diagnostic parameters in PF. 15,17,18,21 However, most of the studies were performed in a smaller study population, and, to our knowledge, no study subclassified PF with sonography or correlated sonographic findings with MRI. We also analyzed the presence of different sonographic findings of PF, namely, a thickened fascia, reduced echogenicity, and loss of definition in the fibrillar echo texture, in the same patient. The thickening and hypoechoic changes of the fascia were frequent findings in our study. These findings were in accordance with those of C Figure 6. Musculoaponeurositis. T1-weighted sagittal MR image of the plantar fascia shows thickening and irregularity of the body of the plantar fascia (arrow). J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24:
6 Clinical Utility of Sonography in Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis Table 1. Independent Samples t Test Showing the Difference Between the Patients With PF and the Control Group Plantar Fascia Heel Pad Thickness, mm Thickness, mm Subjects Weight, kg Height, cm BMI, kg/m 2 MRI Sonography MRI Sonography PF (n = 68) 86.5 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 2.1 Control (n = 154) 72.1 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 1.6 Values are mean ± SD. All variables were significant (P =.0001). Cardinal et al 17 and Akfirat et al. 13 However, the hypoechoic changes were not constant features in a report by Gibbon and Long. 18 Among the other sonographic features of fasciitis shown in our study were perifascial edema, seen as loss of edge sharpness in 42 (29.9%) of 145 heels, and perifascial fluid, seen in 5 (3.4%) of 145. Perifascial edema and collection of fluid were reported by Gibbon and Long 18 (5%) and by Akfirat et al 13 as 10%. This finding is not in accordance with our result because we considered edema a different finding from fluid collection; however, both are part of fascial and perifascial inflammation resulting from repetitive microtears attributed to mechanical stress on the plantar fascia. 11,21 The plantar fascia is similar to the Achilles and patellar tendons in having a paratenon rather than a tendon sheath. 18 Fluid distension of the paratenon is usually associated with perifascial edema, which clearly explains the change in echogenicity and loss of the edge sharpness of the plantar fascia. Sonography showed all 3 findings in 41 of 145 heels, whereas at least 2 sonographic findings were seen in 12 of 145 heels, and only 1 finding was seen in 13 of 145 heels. Therefore, we think that sonography can be helpful in making the diagnosis of PF with even 1 available sonographic finding; however, the combination of findings will give more confidence to the diagnosis and reflect symptom severity. Sonography showed findings of PF in 55 of 68 heels diagnosed as PF by MRI, giving sensitivity of 80.9%; conversely, sonographic findings were negative in 66 of 77 heels normally having a positive MRI diagnosis, giving specificity of 85.7%. The morphologic changes in the plantar fascia were determined by both imaging modalities at the calcaneal insertion and in the central component of the fascia, and, accordingly, PF was subclassified into enthesopathy, musculoaponeurositis, and rupture of the plantar fascia (Table 2). The results of subclassification in both modalities were correlated. The subclassification of PF can be important for enabling a sufficiently fine analysis to describe the lesion precisely as well as to clearly differentiate the chronic and diffuse forms of the condition as musculoaponeurositis from the acute forms of enthesopathy and rupture, for which surgery may be indicated to alleviate a major functional loss. In correlating sonographic and MRI findings of PF, sonographic findings were positive in 11 symptomatic heels, whereas MRI gave negative results. This may be due to inaccurate positioning of the patient s foot inside the extremity coil, which sometimes even needed to be supported by foam pads, or it might be due to improper image plane positioning. However, sonography was shown to be easier in manipulating and examining the patient. Acutely, the pain and tenderness of PF are localized deep in the heel pad along the insertion of the plantar aponeurosis at the medial calcaneal tuberosity. For this, localized tenderness without swelling can also be present over the anteromedial portion of the plantar surface of the calcaneus during examination with the ultrasound probe, which can help in directly correlating sonographic findings with patient symptoms. Conversely, MRI findings were positive in Table 2. Sonographic and MRI Positive and Negative Findings of PF and Its Subtypes in 145 Symptomatic Heels MRI Findings Sonographic Enthesopathy Musculoaponeurositis Rupture Overall Findings Total Total J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24:
7 Sabir et al 13 symptomatic heels, whereas sonography revealed negative findings. This might be due to the somewhat low sensitivity of sonography in diagnosing musculoaponeurotic types of PF that affect mostly the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, whereas the proximal part of the plantar fascia and, especially, the site of the calcaneal attachment are more clearly displayed. Magnetic resonance imaging can be accepted as a standard for an imaging technique that is sufficiently sensitive to identify the disease process and the morphologic changes affecting the plantar fascia Care must be taken in the diagnosis of PF to rule out other similar clinical findings such as subcalcaneal bursitis, calcaneal stress fracture, tarsal tunnel syndrome, and calcaneal osteomyelitis. 25 Moreover the perifascial soft tissue edema and enhancement of the inflamed plantar fascia were explained as a reflection of an active inflammatory phase secondary to degeneration or tearing of the fascia. Limited bone marrow edema in the subperiosteal part of the medial calcaneal tuberosity may also be observed. Conversely, the prominent thickening of the plantar fascia and mild thickening of the adjacent heel fat pad, measured both by MRI and sonography, reflects the soft tissue involvement secondary to stress due to repetitive trauma from excessive job-related standing and walking, changes in footwear, athletic activities, and obesity. In these conditions, microtears occur, mainly in the origin of the plantar fascia, and draw out a local inflammatory reaction. The heel fat pad cushions heel strikes and allows the skin to resist forces during different physical activities. The thickness of this adipose tissue decreases after the age of 40 years, with loss of shock absorbency. 26,27 The mild thickening of the heel fat pad, measured both by MRI and sonography, in the symptomatic group of this study might also be due to the local inflammatory process affecting the area. The significant correlation of BMI with the thickness of the plantar fascia and heel fat pad was explained as a result of a stress mechanism due to the increase in vertical forces, which may lead to increased plantar pressure and gradual collapse of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. 28 We agree that aging and being overweight, in addition to chronic overuse situations, result in a weakening of the ligamentous support and increase the stress on the plantar fascia, which is the most important structure for dynamic arch support. Conversely, the inverse effect of heel fat pad thickness on plantar fascia thickness could be interpreted by the fact that aging and being overweight decrease the heel fat pad shock absorbance function, which in turn increases the stress factor over the plantar fascia. Our study confirmed that sonography is as promising a tool as MRI in diagnosing PF. The greater spatial resolution of sonography for superficial structures, ease of patient manipulation, and real-time capability to correlate findings directly to patient symptoms provide advantages over MRI in the assessment of patients with PF. In subclassifying PF, sonography was more sensitive (91.3%) in diagnosing enthesopathy than musculoaponeurositic changes of the plantar fascia, for which the sensitivity fell to 55%. This can be accepted as a limitation of this study, which could be overcome in the future by use of a higher-frequency probe. Also, this study included only 2 cases of rupture of the PF, which were shown on both sonography and MRI; more rupture cases should be evaluated to improve the specificity of sonography in this entity. Nevertheless, sonography is noninvasive, less expensive, readily available, easier, and faster than other imaging modalities in the diagnosis of PF and can also be performed at the bedside. These all suggest that sonography is capable of confirming or excluding PF and can be as valuable as MRI in treating patients with heel pain. References 1. DeMaio M, Paine R, Mangine RE, Drez D Jr. Plantar fasciitis. Orthopedics 1993; 16: Tanz SS. Heel pain. Clin Orthop 1963; 28: Barret SL, O Malley R. Plantar fascitis and other causes of heel pain. Am Fam Physician 1999; 59: Morrison WB. Magnetic resonance imaging of sports injuries of the ankle. Top Magn Reson Imaging 2003;14: Kier R. Magnetic resonance imaging of plantar fasciitis and other causes of heel pain. Magn Reson Imaging Clin North Am 1994; 2: Hill JJ Jr, Cutting PJ. Heel pain and body weight. Foot Ankle 1989; 9: J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24:
8 Clinical Utility of Sonography in Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis 7. William PL. The painful heel. Br J Hosp Med 1987; 38: Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Farooki S, Kakitsubata Y, Resnick D. Disorders of the plantar aponeurosis: a spectrum of MR imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001; 176: Hajek PC, Baker LL, Bjorkengren A, Sartoris DJ, Neumann CH, Resnick D. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle: normal anatomy. Skeletal Radiol 1986; 15: Zhu F, Johnson JE, Hirose CB, Bae KT. Chronic plantar fasciitis: acute changes in the heel after extracorporeal high-energy shock wave therapy observations at MR imaging. Radiology 2005; 234: Berkowitz JF, Kier R, Rudicel S. Plantar fasciitis: MR imaging. Radiology 1991; 179: Fornage BD. The hypoechoic normal tendon: a pitfall. J Ultrasound Med 1987; 6: Akfirat M, Sen C, Gunes T. Ultrasonographic appearance of the plantar fasciitis. Clin Imaging 2003; 27: Falsetti P, Frediani B, Acciai C, et al. Ultrasonographic study of Achilles tendon and plantar fascia in chondrocalcinosis. J Rheumatol 2004; 31: Erdem CZ, Sarikaya S, Erdem LO, Ozdolap S, Gundogdu S. MR imaging features of foot involvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Radiol 2005; 53: Yu JS. Pathologic and post-operative conditions of the plantar fascia: review of MR imaging appearance. Skeletal Radiol 2000; 29: Narvaez JA, Narvaez J, Ortega R, Aguilera C, Sanchez A, Andia E. Painful heel: MR imaging findings. Radiographics 2000; 20: Recht MP, Donley BG. Magnetic resonance imaging of the foot and ankle. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2001; 9: Weber JM, Vidt LG, Gehl RS, Montgomery T. Calcaneal stress fractures. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 2005; 22: Singh D, Angel J, Bently G, Trevino SG. Fortnightly review: plantar fasciitis. BMJ 1997; 315: Parichasuk S. The heel-pad in plantar heel pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1994; 76: D Ambrogi E, Giurato L, D Agostino MA, et al. Contribution of plantar fascia to the increased forefoot pressures in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: Kane D, Greaney T, Shanahen M, et al. The role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis and management of idiopathic plantar fasciitis. Rheumatology 2001; 40: Wall JR, Harkness MA, Crawford A. Ultrasound diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle 1993; 14: Cardinal E, Chhem RK, Beauregard CG, Aubin B, Pelletier M. Plantar fasciitis: sonographic evaluation. Radiology 1996; 201: Gibbon WW, Long G. Ultrasound of the plantar aponeurosis (fascia). Skeletal Radiol 1999; 28: Tsai WC, Chiu MF, Wang CL, Tang FT, Wong MK. Ultrasound evaluation of plantar fasciitis. Scand J Rheumatol 2000; 29: Roger B, Grenier PH. MRI of plantar fasciitis. Eur Radiol 1997; 7: J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24:
The Correlation Between Plantar Fascia Thickness and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES The Correlation Between Plantar Fascia Thickness and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis Sarah Mahowald, DPM* Bradford S. Legge, DPM John F. Grady, DPM* Background: The purpose of this study
ORIGINAL ARTICLES The Correlation Between Plantar Fascia Thickness and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis Sarah Mahowald, DPM* Bradford S. Legge, DPM John F. Grady, DPM* Background: The purpose of this study
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Wearing high heels and plantar fasciitis; MRI evaluation
 Wearing high heels and plantar fasciitis; MRI evaluation Poster No.: C-0809 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. A. Z. Khodair, R. L. Younes; Qwuesna/EG Extremities, Musculoskeletal
Wearing high heels and plantar fasciitis; MRI evaluation Poster No.: C-0809 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. A. Z. Khodair, R. L. Younes; Qwuesna/EG Extremities, Musculoskeletal
The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation
 Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Article Sonography of Partial-Thickness Quadriceps Tendon Tears With Surgical Correlation Samuel La, MD, David P. Fessell, MD, John E. Femino, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David Jamadar, MB, BS, Curtis Hayes,
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk Pictorial review Abstract
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES. Anthony Hewitt
 DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
DIAGNOSING SCAPHOID FRACTURES Anthony Hewitt Introduction Anatomy of the scaphoid Resembles a deformed peanut Articular cartilage covers 80% of the surface It rests in a plane 45 degrees to the longitudinal
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
How To Treat Heel Pain
 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain
 Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Ulnar sided Wrist Pain 1 Susan Cross, 1 Anshul Rastogi, 2 Brian Cohen, 1 Rosy Jalan 1 Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK 2 London Orthopaedic Centre Contact: susan.cross@bartshealth.nhs.uk
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem
 Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Sports Radiology : Making a diagnosis or solving a problem Professor Dr John George University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre University of Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract: Aim:
Plantar fasciitis - suspected
 Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department
 Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Commonly Missed Fractures in the Emergency Department Taylor Sittler MS IV - UMASS Images courtesy of Jim Wu, MD, Sanjay Shetty, MD and Mary Hochman, MD Diagnostic Errors in the ED Taylor Sittler, MS IV
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
The Plantar Soft Tissues. Sabrina Covert February 28, 2008
 The Plantar Soft Tissues Sabrina Covert February 28, 2008 Objectives 1) Review normal plantar anatomy of the foot 2) Describe optimal technique for MR Imaging of the foot 3) Review the most common abnormalities
The Plantar Soft Tissues Sabrina Covert February 28, 2008 Objectives 1) Review normal plantar anatomy of the foot 2) Describe optimal technique for MR Imaging of the foot 3) Review the most common abnormalities
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF THE PLANTAR PLATE FOR IDENTIFICATION OF PLANTAR PLATE TEARS Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica Knight, DPM Weil
1991 :super specialties perceptions
 Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Ved Chaturvedi, MD, DM Research & Referral Hospital New Delhi President Indian Rheumatology Association MSK Ultrasound..A decade experience of bedside MSK US by a clinician. Was it worth it.? 1991 :super
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Platelet-Rich Plasma Rehabilitation Guidelines
 UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Platelet-Rich Plasma Rehabilitation Guidelines What is Tendinopathy? Tendons are strong bands of connective tissue comprised primarily of a substance called collagen. Mechanically,
UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Platelet-Rich Plasma Rehabilitation Guidelines What is Tendinopathy? Tendons are strong bands of connective tissue comprised primarily of a substance called collagen. Mechanically,
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy
 Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Ultrasound Tissue Characterization an innovative method to visualize and monitor Patellar Tendinopathy Hans T.M. van Schie DVM, PhD UTC Imaging, Netherlands Scoring with Patellar Tendinopathy? no one size
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN
 PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Ankle Sports injuries. Ben Yates
 Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Ankle Sports injuries Ben Yates Common Extra-articular Conditions Lateral collateral ligament sprains (grades 1,2,3) Functional instability Mechanical instability Achilles tendonopathy (Achillodynia) superficial
Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts
 CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
CME Article Sonography of Wrist Ganglion Cysts Variable and Noncystic Appearances George Wang, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Felix Y. Feng, MD, Gandikota Girish, MBBS, FRCS, FRCR, Elaine M. Caoili, MD, Catherine
Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain)
 Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal March 2003 Prepared by: Timothy Daniels, MD, FRCSC Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Michael s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Dermatomyositis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 10/11/2015 History Child with several month history of weakness, arthralgias and palpable abnormalities at the knee Diagnosis Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Drilling
 Technical dvance Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Drilling Juan D. erná-serna, MD, Francisco Martinez, MD, Manuel Reus, MD, Juan D. erná-mestre, MD Objective. The
Technical dvance Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Drilling Juan D. erná-serna, MD, Francisco Martinez, MD, Manuel Reus, MD, Juan D. erná-mestre, MD Objective. The
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
and/or diseases of the foot and ankle. Advances in technology have allowed
 Continuing CLINICAL PODIATRY Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Heel Pain Via Ultrasound- Guided Injection This modality is both precise and cost-effective. Objectives After reading this continuing
Continuing CLINICAL PODIATRY Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Heel Pain Via Ultrasound- Guided Injection This modality is both precise and cost-effective. Objectives After reading this continuing
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Diagnostic accuracy of shoulder ultrasound performed by a single operator
 Radiology Australasian Radiology (2007) 51, 226 229 Diagnostic accuracy of shoulder ultrasound performed by a single operator DM Cullen, WH Breidahl and GC Janes Perth Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Centre,
Radiology Australasian Radiology (2007) 51, 226 229 Diagnostic accuracy of shoulder ultrasound performed by a single operator DM Cullen, WH Breidahl and GC Janes Perth Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Centre,
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People
 The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging
 Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar
 EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Subcutaneous desmoid tumors: characteristic "sun-burst" appearance on MRI and ultrasound
 Subcutaneous desmoid tumors: characteristic "sun-burst" appearance on MRI and ultrasound Poster No.: C-2241 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Milos, T. Moritz, M. Bernathova,
Subcutaneous desmoid tumors: characteristic "sun-burst" appearance on MRI and ultrasound Poster No.: C-2241 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Milos, T. Moritz, M. Bernathova,
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body. It attaches the calf muscles (soleus and gastrocnemius)
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body. It attaches the calf muscles (soleus and gastrocnemius)
Rotator cuff tears Acute or chronic? Mary Obele ANZSOM September 2012 Acknowledgement: ACC
 Rotator cuff tears Acute or chronic? Mary Obele ANZSOM September 2012 Acknowledgement: ACC Anatomy Epidemiology Asymptomatic rotator cuff tears: prevalence is 35% (5) 15% full thickness and 20% partial
Rotator cuff tears Acute or chronic? Mary Obele ANZSOM September 2012 Acknowledgement: ACC Anatomy Epidemiology Asymptomatic rotator cuff tears: prevalence is 35% (5) 15% full thickness and 20% partial
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains
 Article Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains Yannick Guillodo, MD, Patrick Riban, MD, Xavier Guennoc, MD, Frédéric Dubrana, MD, PhD, Alain Saraux, MD, PhD Objective.
Article Usefulness of Ultrasonographic Detection of Talocrural Effusion in Ankle Sprains Yannick Guillodo, MD, Patrick Riban, MD, Xavier Guennoc, MD, Frédéric Dubrana, MD, PhD, Alain Saraux, MD, PhD Objective.
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes
 Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute June 14, 2014 Disclosures I have
Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute June 14, 2014 Disclosures I have
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis. A radiologic tour of a patient encounter
 Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Approach to Lower Extremity Osteomyelitis A radiologic tour of a patient encounter David Guo,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC, October 2009 Our learning goals Review lower extremity anatomy Discuss
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
Shoulder Pain and Weakness
 Shoulder Pain and Weakness John D. Kelly IV, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 11 - NOVEMBER 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions and learning objectives, click here. A
Shoulder Pain and Weakness John D. Kelly IV, MD THE PHYSICIAN AND SPORTSMEDICINE - VOL 32 - NO. 11 - NOVEMBER 2004 For CME accreditation information, instructions and learning objectives, click here. A
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain
 A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
www.noc.nhs.uk Achilles Tendinopathy: Advice and Management Delivering Excellence oxsport@noc Department of Sport and Exercise Medicine
 www.noc.nhs.uk Achilles Tendinopathy: Advice and Management Delivering Excellence oxsport@noc Department of Sport and Exercise Medicine Are we speaking your language? If you would like information in another
www.noc.nhs.uk Achilles Tendinopathy: Advice and Management Delivering Excellence oxsport@noc Department of Sport and Exercise Medicine Are we speaking your language? If you would like information in another
Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 130-136 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan
Runner's Injury Prevention
 JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
Practical Aspects of Ultrasonography Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Dr. Andrew K. Brown Senior Lecturer & Consultant Rheumatologist Content Practical RA Assessment Advantages of ultrasonography Potential
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Integra. Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
Integra Subtalar MBA and bioblock Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Introduction Description... 2 Indications... 2 Contraindications... 2 Surgical Technique Step 1: Incision and Dissection...3
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Ulcers. Laurie Duckett D.O. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Ulcers Laurie Duckett D.O. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences Lecture Objectives Identify risk factors Initiate appropriate
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Ulcers Laurie Duckett D.O. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences Lecture Objectives Identify risk factors Initiate appropriate
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults
 Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults AUTHOR TRACY ALDRIDGE, NAME, Location M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, Illinois Heel pain is a common condition in adults that may
Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults AUTHOR TRACY ALDRIDGE, NAME, Location M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, Illinois Heel pain is a common condition in adults that may
Dr Dan Gill Department of Radiology Windsor Regional Hospital Oxford Medical Imaging Erie St Clair Radiology
 Dr Dan Gill Department of Radiology Windsor Regional Hospital Oxford Medical Imaging Erie St Clair Radiology -5000 Olympic athletes and team officials -1350 Paralympic athletes and team officials -82
Dr Dan Gill Department of Radiology Windsor Regional Hospital Oxford Medical Imaging Erie St Clair Radiology -5000 Olympic athletes and team officials -1350 Paralympic athletes and team officials -82
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME. Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4.
 OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association
 Taking Care of Your KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association Taking Care of Your Knees When the mother of the hero Achilles dipped him in the river Styx, she held
Taking Care of Your KNEES A Physical Therapist s Perspective American Physical Therapy Association Taking Care of Your Knees When the mother of the hero Achilles dipped him in the river Styx, she held
The medial plica of the knee continues to be the subject of. Magnetic Resonance Characteristics of Medial Plica of the Knee
 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING Magnetic Resonance Characteristics of Medial Plica of the Knee Correlation With Arthroscopic Resection Carol A. Boles, MD,* Jerome Butler,* Jonathon A. Lee, MD,* Myles L. Reedy,
MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING Magnetic Resonance Characteristics of Medial Plica of the Knee Correlation With Arthroscopic Resection Carol A. Boles, MD,* Jerome Butler,* Jonathon A. Lee, MD,* Myles L. Reedy,
Most Common Running Injuries
 Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Case Report Calcaneal Insufficiency Fracture Secondary to Celiac Disease Induced Osteomalacia A Rare Cause of Heel Pain
 583310FASXXX10.1177/1938640015583310Foot & Ankle SpecialistFoot & Ankle Specialist research-articlexxxx vol. XX / no. X Foot & Ankle Specialist 1 Case Report Calcaneal Insufficiency Fracture Secondary
583310FASXXX10.1177/1938640015583310Foot & Ankle SpecialistFoot & Ankle Specialist research-articlexxxx vol. XX / no. X Foot & Ankle Specialist 1 Case Report Calcaneal Insufficiency Fracture Secondary
Internal Impingement in the Overhead Athlete: A Correlation of Findings on MRI and Arthroscopic Evaluation
 Internal Impingement in the Overhead Athlete: A Correlation of Findings on MRI and Arthroscopic Evaluation Lee D Kaplan, MD J Towers, MD PJ McMahon, MD CH Harner,, MD RW Rodosky,, MD Thrower s shoulder
Internal Impingement in the Overhead Athlete: A Correlation of Findings on MRI and Arthroscopic Evaluation Lee D Kaplan, MD J Towers, MD PJ McMahon, MD CH Harner,, MD RW Rodosky,, MD Thrower s shoulder
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair
 UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair There are two types of cartilage in the knee, articular cartilage and cartilage. Articular cartilage is made up of collagen,
UW Health Sports Rehabilitation Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair There are two types of cartilage in the knee, articular cartilage and cartilage. Articular cartilage is made up of collagen,
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital
 By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
By Agnes Tan (PT) I-Sports Rehab Centre Island Hospital Physiotherapy Provides aids to people Deals with abrasion and dysfunction (muscles, joints, bones) To control and repair maximum movement potentials
