Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain
|
|
|
- Caren Carr
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, Human Kinetics, Inc. CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effect of Foot Orthoses as Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain Jordan Anderson and Justin Stanek Clinical Scenario: Plantar fasciitis is a debilitating and painful problem present in the general population. It most often presents with moderate to severe pain in the proximal inferior heel region and is most commonly associated with repeated trauma to the plantar fascia. Plantar fasciitis, itself, is an injury at the site of attachment at the medial tubercle of the calcaneus, often due to excessive and repetitive traction. Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain and is estimated to affect 2 million people in the United States alone. Focused Clinical Question: For adults suffering from plantar fasciitis, are foot orthoses a viable treatment option to reduce pain? Keywords: orthotics, temporary custom foot orthotic, conservative therapy, prefabricated orthotic Clinical Scenario Plantar fasciitis is a debilitating and painful problem present in the general population. It most often presents with moderate to severe pain in the proximal inferior heel region and is most commonly associated with repeated trauma to the plantar fascia. Plantar fasciitis, itself, is an injury at the site of attachment at the medial tubercle of the calcaneus, often due to excessive and repetitive traction. Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain and is estimated to affect 2 million people in the United States alone. Focused Clinical Question For adults suffering from plantar fasciitis, are foot orthoses a viable treatment option to reduce pain? Summary of Search, Best Evidence Appraised, and Key Findings The literature search yielded 4 total studies meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria: 1 randomly controlled trial, 1 retrospective cohort study, 1 prospective repeated-measures study, and 1 prospective cohort study. One randomly controlled trial found a 95% improvement in symptoms with a silicone insert 8 weeks posttreatment. 2 The authors are with the Dept of Kinesiology and Recreation, Illinois State University, Normal, IL. The same randomly controlled trial showed that a prefabricated insert was better for reducing symptoms of plantar fasciitis than a custom-made orthotic insert (P =.0074). 2 A retrospective cohort study found a significant (P.0001) decrease in symptoms after 5 weeks of using a prefabricated heel pad along with a custom-made orthotic device. 3 One prospective repeated-measures study demonstrated a 75% reduction in disability ratings after 12 to 17 days use of a custom semirigid orthotic. 4 A prospective cohort study found that the use of temporary custom foot orthotics followed by a stretching protocol significantly (P.001) increased foot and ankle function in the short term and up to 12 weeks. 5 Clinical Bottom Line Custom orthoses are a clinically effective tool to decrease the pain associated with plantar fasciitis. Evidence has shown that this benefit can last up to 12 weeks. More research must be conducted to determine the effect of long-term use of custom orthotics on pain measures. The athletic population also needs more research investigating the effectiveness of custom orthoses. Search Strategy Terms Used to Guide Search Strategy Patient/Client Group: plantar fasciitis or heel pain Intervention/Assessment: Orthoses or inserts or prefabricated inserts or custom orthotics 130
2 Foot Orthoses to Treat Plantar Fasciitis 131 Comparison: none Outcome: pain and/or functional ability Sources of Evidence Searched PubMed CINAHL SPORTDiscus The Cochrane Library MEDLINE PEDro Database Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Inclusion Criteria Subjects diagnosed with plantar fasciitis Symptoms duration of at least 6 months Use of some form of custom orthoses or prefabricated inserts Use of some pain scale (verbal or Likert) as outcome measures At least 2 weeks of intervention treatment Exclusion Criteria Use of other therapeutic modality such as ultrasound, electroshock, etc Undiagnosed plantar fasciitis No pain scale (verbal or Likert), questionnaire only Acute heel pain (symptoms 6 mo) Case-study, case-control, expert opinion, or caseseries designs Results of Search A total of 4 relevant studies were located and categorized as shown in Table 1 (based on Levels of Evidence, Centre for Evidence Based Medicine, 2011). Best Evidence The studies identified in Table 2 were classified as having the best evidence. They were selected based on their high level of evidence and because of their relevance to the clinical question. The specific clinical application of orthotics was also the main intervention of all the included studies. Implications for Practice, Education, and Future Research The studies included in this critically appraised topic all addressed the use of orthotics to treat plantar fasciitis. The main outcome measure examined was pain. All 4 critically appraised articles demonstrated that orthotics were a viable treatment option for plantar fasciitis, and all reduced pain significantly. In the controlled study, patients who used a prefabricated insert had a significant reduction in pain compared with a stretching-only group. 2 Concurrently, a separate study found that the use of orthoses followed by a stretching protocol reduced all subjects pain at junctures of measurement (2, 4, 6, 8 wk). The 2 cohort studies also showed a significant reduction in pain when using custom orthotics. 3,4 One cohort study specifically looked at pain while walking, a common chief complaint with plantar fasciitis. 4 With pain being the most debilitating symptom of plantar fasciitis, these studies all show a clinical application for using orthotics to treat pain in patients with plantar fasciitis. It is worth noting that some, not all, of the literature reviewed also included quality-of-life questionnaires such as the Functional Foot Index scale. These scales use a series of questions to determine things other than pain, such as disability or function levels. Most of these studies also saw an improvement in these questionnaires. However, since different questionnaires are often used, we chose not to include these results, as they cannot be generalized across articles, unlike a simple visual analogue scale or Likert scale. Orthotics can be relatively inexpensive compared with many modalities commonly used to treat plantar fasciitis. Orthotics reduce symptoms, theoretically, by reducing and absorbing shock that is normally absorbed by the already taxed plantar fascia. Another theory behind some orthotic devices is to attempt to correct postural deviations or muscle deficiencies that may predispose one to get plantar fasciitis. A reduction in pain can also help ward off extremely costly surgical treatments. In all the studies, the orthotics were made in house and were often made after attending a class or workshop to teach Table 1 Summary of Study Designs of Articles Retrieved Level of evidence Study design Number located Reference 2 Randomized controlled trial 1 Pfeffer et al 2 3 Cohort study 2 Seligman et al 3 3 Nonrandomized controlled cohort study or follow-up study Gross et al 4 1 Drake et al 5
3 Table 2 Characteristics of Included Studies Pfeffer et al 2 Seligman et al 3 Gross et al 4 Drake et al 5 Study design Randomly controlled trial Retrospective cohort study Cohort study Prospective cohort study Subjects 236 total patients (160 women, 76 men). Fifteen centers for orthopedic foot and ankle treatment centers participated. Subjects were 16 y or older. Most patients reported pain of 6 mo or less. Those with any systemic, significant musculoskeletal complaints, sciatica, or local nerve entrapment were excluded. No subjects had had previous treatment of the injury. 10 total subjects from a hand and foot orthotic clinic in Ontario, Canada. Data from these subjects were included in the analysis if they had a diagnosis of unilateral or bilateral heel pain associated with plantar fasciitis and if before and after orthotic-use data were available on the parameter of interest. Subjects were excluded if they were nonambulatory, noncommunicative, or unable to complete the interviewer-administered questionnaire and/or had spasticity due to a neurologic disorder. Five of the 10 subjects had also tried other treatment options without relief. 15 total subjects (8 men and 7 women). Subjects were 18 y or older and reported having medial-arch or heel pain for a period of at least 1 mo before participation in the study. An additional inclusion criterion was tenderness to palpation along the posteromedial aspect of the longitudinal arch or over the medial calcaneal tubercle. Subjects were excluded if they reported any other lower extremity injury during the previous 6 mo; receiving a plantar steroid injection within the previous 3 mo; use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications within the previous 1 wk; use of custom foot orthotics previously; any other painful foot condition such as bunion, corn, or ingrown toe nail; or any other lower extremity neuromuscular condition that affected activities of daily living. 15 subjects. Subjects reported heel pain and first-step pain in the morning for at least 12 wk. Inclusion criteria included being 18 y older, symptom duration of longer than 4 wk. Subjects also had to have 2 out of the following 3 symptoms: symptom reproduction with palpation of the proximal plantar fascia insertion or midsubstance of the plantar fascia, positive Windlass test, or first-step pain after period of inactivity. Participants were excluded if they had symptoms consistent with lumbar radiculitis, radiculopathy, or myelopathy; a history of foot or ankle fracture, with or without the presence of hardware from an openreduction internal fixation; known or suspected pregnancy; systemic rheumatic disease; or were undergoing litigation for any medical condition or had a positive sign or symptom for tarsal tunnel syndrome. 132
4 Intervention investigated Outcome measures Control groups for this study were those assigned to the Achilles and plantar-fascia stretching-only group. Subjects were told to do the stretching approximately 10 min twice a day. The experimental groups were assigned to 1 of 4 orthotic devices including a silicone heel pad, a felt insert, a rubber heel cup, and a custom-made polypropylene neutral orthosis. The participants wore the devices for activities of daily living at home and were instructed not to drastically alter the time they wore their shoes from a normal day. Primary measure: Foot Function Index Secondary measure: Foot Function Index pain subset questions Subject data were collected retrospectively from a clinic. Each subject wore both heel pads and customfit orthotics for 5 and a half weeks. All patients then reported their pain verbally or with a Likert-type scale. Pain was ranked from 1 to 10. These scores were then compared with the scores given on the subjects/ first visit to the clinic. Primary measure: pain at time of initial visit vs pain after 5 wk of heel-pad and orthotic use Subjects were asked to complete the Foot Function Index questionnaire followed by walking 100 m at a self-selected speed. Their times were recorded and subjects then completed a visual analogue scale (for pain). Bilateral custom semirigid foot orthotics were made for each subject. Subjects were told to wear the orthotics as much as possible for the next d during waking hours. Each subject kept a daily log of wear time. Subjects then returned d later to complete the pain and disability section of the Foot Function Index. Participants then completed the timed 100-m walk again followed by another visual analogue pain scale. They were then contacted 2 6 mo later to assess whether or not they still used their orthotics. Primary measure: 10-cm visual analogue scale Secondary measure: Foot Function Index questionnaire (pain and disability subsections) Tertiary measure: 100-m-walk times Bilateral custom semirigid foot orthotics were made for each subject. Subjects were told to wear the orthotics as much as possible for the next d during waking hours. Primary measures: First-step heel pain via numeric pain-rating scale and Foot and Ankle Ability Measure activities of daily living subscale. Secondary measures: Foot and Ankle Ability Measure sports subscale and the global rating of change score. (continued) 133
5 Table 2 (continued) Pfeffer et al 2 Seligman et al 3 Gross et al 4 Drake et al 5 Main findings Analysis of pain scores revealed improvements in all groups that are demonstrated by a negative mean change score during the follow-up questionnaire. Patients with higher overall pain in the initial questionnaire improved more (P =.0001). Those with longer duration of pain improved the least (P =.010). Controlling for these factors caused the difference between groups to parallel the findings with the response rates more closely, this being that the prefabricated inserts showed more improvement than custom orthoses. None of the treatment groups produced a statistically significant difference in pretreatment and posttreatment pain scores; however, all groups did lower their mean pain scores in the posttreatment questionnaire. Preorthotic scores were recorded at the initial visit, and postorthotic scores were recorded at the followup visit. Higher scores indicated worse pain. At the initial visit, the mean score was 5.70 ± 1.95 of 10 (range ). Scores recorded an average of 5 wk after using the customized orthotic were 1.85 ± 1.13 (range ). The mean difference in scores over the 5-wk period was 4.17 ± 1.92 (range ). All subjects ranked their pain as being less after using the orthotic, and t-test analysis indicated a highly significant difference in pre post scores (t 6.22; 95% CI, ; P.0001). Preorthotic 100-m-walk times (mean = 81.2 ± 15.3 s) were not significantly different (t = 0.39, P =.70) from postorthotic walk times (mean = 80.6 ± 13.8 s). Preorthotic pain ratings for the 100-m walk (mean = 3.0 ± 1.7) were significantly greater (t = 1, P.005) than postorthotic pain ratings (mean = 0.7 ± 0.7). In addition, only 1 subject (6%) had a postorthotic 100-m-walk pain rating that was greater than the preorthotic value (a 2-mm difference). The percentage reduction in pain subsection scores after the intervention was 66%, and the percentage reduction in disability-subsection scores was 75%. Wilcoxon matchedpairs signed-ranks test results indicated that postorthotic values were significantly less (t = 0, P.005) than preorthotic values for both subsections of the Foot Function Index. All subjects had postorthotic Foot Function Index scores that were less than preorthotic values for both subsections of this instrument. Repeated-measures ANOVAs revealed statistically significant changes at all 3 follow-up times compared with baseline for all 3 primary outcomes (NPRS, P <.001; FAAM-A, P =.001; FAAM-S, P <.001). The mean GRC scores at 2, 4, and 12 wk were 4.4, 4.5, and 4.2, respectively. No participants reported adverse effects from wearing the total-contact foot orthotics, and all participants completed the study at 12 wk. Level of evidence Validity score 5/10 in the PEDro database N/A N/A N/A 134
6 Conclusions This article shows that Achilles and plantar-fascia stretching are effective for reducing mean pain scores in patients with proximal heel pain/ plantar fasciitis. The addition of an orthotic device may also decrease these scores even more. Prefabricated devices were shown to be more effective than custom devices but not to a statistically significant level. This was attributed by the author as potentially being an effect of the type of material used in the orthotics (more cushioning material vs less). The study also showed that subjects with a longer reported duration of symptoms had less of a decrease in pain scores than those with short duration of symptoms (P =.010). It was also found that those with a higher initial pain score on the questionnaire had the largest decrease in pain scores at the 8-wk follow-up (P =.0001). Overall, this article suggests that the use of a prefabricated orthotic along with Achilles and plantar-fascia stretching may decrease overall pain in an 8-wk period. This study, though of poor design, showed strong significance (P.0001) in decreasing pain scores with the use of a custom heel-pad and orthotics in elderly patients after a 5-wk time period. Although the study was done in older patients, the strong significance could translate to a normal population. Another study investigating this is warranted, along with a better study design. This article suggests that using the custom heel-pad and orthotic devices is a useful intervention for the treatment of heel pain associated with plantar fasciitis. This study, though of poor design, showed statistical significance between preintervention and postintervention scores of the Functional Foot Index questionnaire and its subsections. The postintervention measurements were significantly lower (P =.005) than the preintervention scores. This study could advocate for the use of custom orthotics to treat symptoms of plantar fasciitis in patients. One strength of the study is the duration of symptoms that most subjects had entering the study (at least 1 mo); this shows that the orthotics could be responsible for the reduction of symptoms and disability from a longstanding occurrence. Future research must include stronger study designs in a prospective fashion. In addition, the long-term effects of these custom orthotics need to be investigated. This study is of relatively poor design and did not control well for confounding variables. The study was of prospective design and otherwise had good methodology. Because of the nonrandomized nature of the study and the lack of a control group, the authors are unable to state that the decrease in symptoms is due solely to the total-contact foot orthotic or the stretching. However, based on the significant results (P.001) it can be determined that the orthotics and stretching program more than likely assisted with the decrease in symptoms. Subjects were also verbally instructed to try not to alter their current weight-bearing activity habits. All subjects showed decreases in the outcome measurements and reported no adverse effects of the total-contact foot orthotics. This puts this intervention in a relatively low risk category as far as negative outcomes are concerned. Abbreviations: NPRS indicates numeric pain-rating scale; FAAM-A, Foot and Ankle Ability Measure; FAAM-S, Foot and Ankle Ability Measure Sports Subscale; GRC, Global Rating of Change Score. 135
7 136 Anderson and Stanek clinicians how to make the orthotic devices. This makes orthotics time efficient and easy to distribute. There are a variety of orthosis types available in a variety of price ranges, as well. However, there are a few limitations of this treatment. For one, pain was reduced in all patients but was not completely resolved. Disability and functional questionnaires did show improvement along with the diminished pain but did not reflect complete resolution of symptoms. As inexpensive as orthotics can be, they may still be out of the financial range of some patients or clinics. Future research needs to be conducted looking at the use of orthotics during athletic activity. The included studies did not specify the types of activities performed while the subjects were wearing the orthotics. Although theoretically the effects of the orthotics should not change with different activities, it cannot be stated for certain that athletes would receive the same benefits as nonathletes. Research also needs to be done on the long-term effects of wearing the orthotics on pain associated with plantar fasciitis. Future research should also examine the treatment techniques employed to achieve a complete resolution of symptoms. References 1. Stuber K, Kristmanson K. Conservative therapy for plantar fasciitis: a narrative review of randomized controlled trials. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2006;50(2): Pfeffer G, Bacchetti P, Deland J, et al. Comparison of custom and prefabricated orthoses in the initial treatment of proximal plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 1999;20(4): Seligman D, Dawson D. Customized heel pads and soft orthotics to treat heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003;84(10): Gross M, Byers J, Krafft J, Lackey E, Melton K. The impact of custom semirigid foot orthotics on pain and disability for individuals with plantar fasciitis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2002;32(4): Drake M, Bittenbender C, Boyles R. The short-term effects of treating plantar fasciitis with a temporary custom foot orthosis and stretching. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41(4):
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
How To Treat Heel Pain
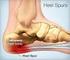 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study
 Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation
 RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
RX: Custom Thermoplastic AFO Compliance Documentation Doctor Name: Phone: Patient Name: HICN: DOB: Indicate Quality ARIZONA THERMOPLASTIC ARTICULATED AFO, DORSI-ASSIST CROW L4631 A bivalved custom molded
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis
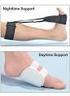 Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Adult Advisor: Plantar Fasciitis Page 1 of 3 Plantar Fasciitis What is plantar fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the bottom of the foot between the ball of the foot and the heel.
Heel Steroid Injection
 Heel Steroid Injection Evidence of effectiveness 2 systematic reviews (2 included) ~/ ~ 2 experimental studies (2 included) ~/ -/~ 1 observational (1 included) 2.5/3 Evidence of safety and harm Generic
Heel Steroid Injection Evidence of effectiveness 2 systematic reviews (2 included) ~/ ~ 2 experimental studies (2 included) ~/ -/~ 1 observational (1 included) 2.5/3 Evidence of safety and harm Generic
Clinical Scenario. Focused Clinical Question. Summary of Search, Best Evidence Appraised, and Key Findings
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 72-78 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effectiveness of Low-Level Laser Therapy Combined With an Exercise Program to Reduce
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2013, 22, 72-78 2013 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.jsr-journal.com CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Effectiveness of Low-Level Laser Therapy Combined With an Exercise Program to Reduce
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Plantar Fascitis
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 2 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Assessment... 3 7.2 Treatment...
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People
 The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fasciitis. Heel Pain - common causes. Plantar Fasciitis 1/16/2012. Robert A Erdin III, MD
 PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
PLANTAR FASCIITIS Robert A Erdin III, MD Special thanks to the AOFAS and David Richardson MD for slide reproductions Most common symptom related to the foot leading a patient to seek professional care
Prepared by:jane Healey (Email: janie_healey@yahoo.com) 4 th year undergraduate occupational therapy student, University of Western Sydney
 1 There is fair (2b) level evidence that living skills training is effective at improving independence in food preparation, money management, personal possessions, and efficacy, in adults with persistent
1 There is fair (2b) level evidence that living skills training is effective at improving independence in food preparation, money management, personal possessions, and efficacy, in adults with persistent
FEET and PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS. Louise Skipp Podiatrist, Sirona Care and Health, Bath
 FEET and PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Louise Skipp Podiatrist, Sirona Care and Health, Bath What would you like to know? Common problems Practical tips What you can do to help yourself When to seek help and from
FEET and PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Louise Skipp Podiatrist, Sirona Care and Health, Bath What would you like to know? Common problems Practical tips What you can do to help yourself When to seek help and from
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN
 PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
Critical Review: Sarah Rentz M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
 Critical Review: In children with cerebral palsy and a diagnosis of dysarthria, what is the effectiveness of speech interventions on improving speech intelligibility? Sarah Rentz M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate
Critical Review: In children with cerebral palsy and a diagnosis of dysarthria, what is the effectiveness of speech interventions on improving speech intelligibility? Sarah Rentz M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 6, 395 401, 2002 The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain Hakan ÖZDEMI%R,* Aysun ÖZDEMI%R,** Yetkin SOYUNCU* and Mustafa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Effect of the silicone heel pad on plantar fasciitis
 29th Pak Orthocon 2015 S-123 Effect of the silicone heel pad on plantar fasciitis Noman Shakeel Niazi, 1 Suhail Niaz Khan Niazi, 2 Khalid Niazi Khan Niazi, 3 Madiha Iqbal 4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Objectives:
29th Pak Orthocon 2015 S-123 Effect of the silicone heel pad on plantar fasciitis Noman Shakeel Niazi, 1 Suhail Niaz Khan Niazi, 2 Khalid Niazi Khan Niazi, 3 Madiha Iqbal 4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Objectives:
Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010
 Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
Brief report Hart Walker Reviewer Adrian Purins AHTA Edited by P Larking ACC Date report completed 18 January 2010 1. Background Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that arise from brain damage
CUSTOM ORTHOTICS/SHOES FAQ AND GLOSSARY
 CUSTOM ORTHOTICS/SHOES FAQ AND GLOSSARY What is GSC s new orthotics and orthopedic shoe policy? Only certain health professionals can prescribe and provide you with custom orthotics, orthopedic shoes,
CUSTOM ORTHOTICS/SHOES FAQ AND GLOSSARY What is GSC s new orthotics and orthopedic shoe policy? Only certain health professionals can prescribe and provide you with custom orthotics, orthopedic shoes,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Chiropractic adjustments and orthotics reduced symptoms for standing workers
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Chiropractic adjustments and orthotics reduced symptoms for standing workers John Zhang, PhD, MD a WINTER 2005 Number 4 Volume 4 a Logan College of Chiropractic, Chesterfield, MO. Submit
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Chiropractic adjustments and orthotics reduced symptoms for standing workers John Zhang, PhD, MD a WINTER 2005 Number 4 Volume 4 a Logan College of Chiropractic, Chesterfield, MO. Submit
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy. Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883
 Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Physician Labeling. ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.)
 Physician Labeling ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.) CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Physician Labeling ( Clinical Application of the Duolith SD1 will be added to Operating Manuals upon PMA Approval.) CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Preventing Potential Claims of Negligence What Would You Do Settle or Go to Trial?
 Preventing Potential Claims of Negligence What Would You Do Settle or Go to Trial? Ross E. Taubman, DPM PICA President and Chief Medical Officer 2013 APMA YOUNG PHYSICIANS INSTITUTE April 12 14 PICA Headquarters
Preventing Potential Claims of Negligence What Would You Do Settle or Go to Trial? Ross E. Taubman, DPM PICA President and Chief Medical Officer 2013 APMA YOUNG PHYSICIANS INSTITUTE April 12 14 PICA Headquarters
Is manual physical therapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults post whiplash injury?
 Is manual physical therapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults post whiplash injury? Clinical Bottom Line Manual therapy may have a role in the
Is manual physical therapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults post whiplash injury? Clinical Bottom Line Manual therapy may have a role in the
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Using Might Splints in the Treatment
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 287-297 @ 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Using Might Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis in the Athlete David J. Pezzullo Plantar fasciitis is
Taking Care of Flat Feet in Children
 1 Contact: Customer Service Foot Levelers, Inc. P.O. Box 12611 Roanoke, VA 24027-2611 (800) 553-4860 Ext. 3189 service@footlevelers.com Taking Care of Flat Feet in Children by Mark N. Charrette, DC Flatfoot
1 Contact: Customer Service Foot Levelers, Inc. P.O. Box 12611 Roanoke, VA 24027-2611 (800) 553-4860 Ext. 3189 service@footlevelers.com Taking Care of Flat Feet in Children by Mark N. Charrette, DC Flatfoot
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
33 % of whiplash patients develop. headaches originating from the upper. cervical spine
 33 % of whiplash patients develop headaches originating from the upper cervical spine - Dr Nikolai Bogduk Spine, 1995 1 Physical Treatments for Headache: A Structured Review Headache: The Journal of Head
33 % of whiplash patients develop headaches originating from the upper cervical spine - Dr Nikolai Bogduk Spine, 1995 1 Physical Treatments for Headache: A Structured Review Headache: The Journal of Head
Clinical bottom line. For more detailed evidence on the effectiveness of injections for tennis elbow, please see the CAT on:
 Short Question: Specific Question: In patients presenting with acute or chronic tendinopathies, what is the incidence of harm for those receiving steroid injections compared to those receiving usual care?
Short Question: Specific Question: In patients presenting with acute or chronic tendinopathies, what is the incidence of harm for those receiving steroid injections compared to those receiving usual care?
Clinical Reasoning The patient presents with no red flags and no indications of maladaptive behaviour in regard to fear avoidance.
 The McKenzie Institute International 2014 Vol. 3, No. 3 CASE REVIEW: A CLINICIAN S PERSPECTIVE Case Review: 35-Year-Old Male with History of Low Back Pain Brian Østergaard Sørensen, PT, Dip.MDT Introduction
The McKenzie Institute International 2014 Vol. 3, No. 3 CASE REVIEW: A CLINICIAN S PERSPECTIVE Case Review: 35-Year-Old Male with History of Low Back Pain Brian Østergaard Sørensen, PT, Dip.MDT Introduction
Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 483-488 ORIGINAL STUDY Clinical outcome of surgical intervention for recalcitrant infero-medial heel pain Friedl SINNAEVE, Geoffroy VANDEPUTTE From the Heilig Hartziekenhuis
Plantar fasciitis: p. 1/6. E.M.S. Electro Medical Systems S.A. Ch. de la Vuarpillière 31 CH-1260 Nyon Switzerland
 Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
By: Jerry Ryan, M.D., University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, Wisconsin
 UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
UAmerican Family PhysicianU September 1995 Use of Posterior Night Splints in the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a frequent cause of heel pain in athletes, as well as in persons who
Plantar fasciitis - suspected
 Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Proximal plantar fasciitis suspected Clinical presentation History Examination Consider alternative causes of plantar heel pain Heel pad pain Neurologic plantar heel pain Arthritic plantar heel pain Traumatic
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments of Rheumatoid Foot and Ankle
 Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting about two to three million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is a symmetric disease, meaning that it will usually involve
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller John.Miller@unh.edu Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT:
 UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
UTILIZING STRAPPING AND TAPING CODES FOR HEALTH CARE REIMBURSEMENT: A GUIDE TO BILLING FOR SPIDERTECH PRE-CUT APPLICATIONS AND TAPE Billing and coding taping and strapping services can be a complex issue.
Joshua A. Cleland, PT, DPT, PhD, OCS, FAAOMPT
 Joshua A. Cleland, PT, DPT, PhD, OCS, FAAOMPT Franklin Pierce University Presentations at Scientific Meetings: Changes in Pain and Cervical Range of Motion after Cervical or Thoracic Thrust Manuscript
Joshua A. Cleland, PT, DPT, PhD, OCS, FAAOMPT Franklin Pierce University Presentations at Scientific Meetings: Changes in Pain and Cervical Range of Motion after Cervical or Thoracic Thrust Manuscript
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
How You Can Do Research in Your Practice: Case Studies
 How You Can Do Research in Your Practice: Case Studies SCCA Convention 2014 Luke Henry, D.C. 1 Introduction Why you should be interested in research Enhance chiropractic education Increases recognition
How You Can Do Research in Your Practice: Case Studies SCCA Convention 2014 Luke Henry, D.C. 1 Introduction Why you should be interested in research Enhance chiropractic education Increases recognition
ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY
 C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
C H A P T E R 3 3 ADVANCEMENTS IN PLANTAR FASCIA SURGERY James L. Bouchard, DPM Andrea Cass, DPM INTRODUCTION It has been estimated that 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome get
Is electrotherapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults with supraspinatus tendonitis?
 Is electrotherapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults with supraspinatus tendonitis? Is one modality of electrotherapy more effective than another?
Is electrotherapy more effective than other physical therapy approaches in reducing pain and disability in adults with supraspinatus tendonitis? Is one modality of electrotherapy more effective than another?
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis with Stenosis Successfully Treated with Cox Distraction Manipulation
 Cox Technic Case Report #92 (sent February 2011 2/8/11 ) 1 Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis with Stenosis Successfully Treated with Cox Distraction Manipulation Presented By Robert E. Patterson Jr., D.C.
Cox Technic Case Report #92 (sent February 2011 2/8/11 ) 1 Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis with Stenosis Successfully Treated with Cox Distraction Manipulation Presented By Robert E. Patterson Jr., D.C.
Runner's Injury Prevention
 JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
JEN DAVIS DPT Runner's Injury Prevention Jen Davis DPT Orthopedic Physical Therapy Foot Traffic 7718 SE 13th Ave Portland, OR 97202 (503) 482-7232 Jen@runfastpt.com www.runfastpt.com!1 THE AMAZING RUNNER
Claims Administrator guideline: Decision based on MTUS Chronic Pain Treatment Guidelines Physical Medicine.
 Case Number: CM14-0149119 Date Assigned: 09/30/2014 Date of Injury: 03/01/2007 Decision Date: 01/28/2015 UR Denial Date: 08/21/2014 Priority: Standard Application Received: 09/15/2014 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Case Number: CM14-0149119 Date Assigned: 09/30/2014 Date of Injury: 03/01/2007 Decision Date: 01/28/2015 UR Denial Date: 08/21/2014 Priority: Standard Application Received: 09/15/2014 HOW THE IMR FINAL
Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy
 Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
Pain Physician 2007; 10:313-318 ISSN 1533-3159 Case Series Case Series on Chronic Whiplash Related Neck Pain Treated with Intraarticular Zygapophysial Joint Regeneration Injection Therapy R. Allen Hooper
OUTPATIENT PHYSICAL AND OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY PROTOCOL GUIDELINES
 OUTPATIENT PHYSICAL AND OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY PROTOCOL GUIDELINES General Therapy Guidelines 1. Therapy evaluations must be provided by licensed physical and/or occupational therapists. Therapy evaluations
OUTPATIENT PHYSICAL AND OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY PROTOCOL GUIDELINES General Therapy Guidelines 1. Therapy evaluations must be provided by licensed physical and/or occupational therapists. Therapy evaluations
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
In preschool children with flat feet what are the indications of non-surgical treatment? An evidence based case report.
 In preschool children with flat feet what are the indications of non-surgical treatment? An evidence based case report. Introduction. The paediatric flat foot is a controversial topic. And although flat
In preschool children with flat feet what are the indications of non-surgical treatment? An evidence based case report. Introduction. The paediatric flat foot is a controversial topic. And although flat
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Physical Therapy Perspective on Ataxia. Roger Fong, MPT University of Chicago Medical Center March, 2010
 Physical Therapy Perspective on Ataxia Roger Fong, MPT University of Chicago Medical Center March, 2010 Definition: Physical Therapist Physical therapy dynamic profession with an established theoretical
Physical Therapy Perspective on Ataxia Roger Fong, MPT University of Chicago Medical Center March, 2010 Definition: Physical Therapist Physical therapy dynamic profession with an established theoretical
Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises
 Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises - 12 Week Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Solution - 1 3 Month Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Program Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Structure
Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises Effective Plantar Fasciitis Exercises - 12 Week Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Solution - 1 3 Month Plantar Fasciitis Exercise Program Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Structure
Issued and entered this _6th_ day of October 2010 by Ken Ross Commissioner ORDER I PROCEDURAL BACKGROUND
 STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY, LABOR & ECONOMIC GROWTH OFFICE OF FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE REGULATION Before the Commissioner of Financial and Insurance Regulation In the matter of XXXXX Petitioner
STATE OF MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY, LABOR & ECONOMIC GROWTH OFFICE OF FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE REGULATION Before the Commissioner of Financial and Insurance Regulation In the matter of XXXXX Petitioner
Most Common Running Injuries
 Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Most Common Running Injuries 1. Achilles Tendonitis 2. Chrondomalacia Runner s Knee 3. Iliotibial Band (ITB) syndrome 4. Plantar Fasciitis 5. Shin Splints Achilles Tendonitis inflammation of the Achilles
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Guide to Claims against General Practitioners (GPs)
 Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
Patients often build up a relationship of trust with their GP over a number of years. It can be devastating when a GP fails in his or her duty to a patient. Our medical negligence solicitors understand
Treatment of Young Athletes with Spine Injuries
 Treatment of Young Athletes with Spine Injuries North American Spine Society Public Education Series Treatment of the Young Athlete Although not common, low back injuries can occur in young athletes who
Treatment of Young Athletes with Spine Injuries North American Spine Society Public Education Series Treatment of the Young Athlete Although not common, low back injuries can occur in young athletes who
Platform Presentations
 Combined Clinical Sections Guidelines Meeting Thomas G. McPoil, PT, PhD RobRoy L. Martin, PT, PhD Mark W. Cornwall, PT, PhD Orthopaedic Section Abstracts: Dane K. Wukich, MD James J. Irrgang PT, PhD Joseph
Combined Clinical Sections Guidelines Meeting Thomas G. McPoil, PT, PhD RobRoy L. Martin, PT, PhD Mark W. Cornwall, PT, PhD Orthopaedic Section Abstracts: Dane K. Wukich, MD James J. Irrgang PT, PhD Joseph
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Oncology Nursing Society received $12,473 in formula funds for
Oncology Nursing Society Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Oncology Nursing Society received $12,473 in formula funds for
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 413/98. Fasciitis (plantar); Cashier.
 SUMMARY DECISION NO. 413/98 Fasciitis (plantar); Cashier. A supermarket cashier appealed a decision of the Appeals Officer denying entitlement for plantar fasciitis. The causes of plantar fasciitis are
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 413/98 Fasciitis (plantar); Cashier. A supermarket cashier appealed a decision of the Appeals Officer denying entitlement for plantar fasciitis. The causes of plantar fasciitis are
The Physiotherapy Pilot. 1.1 Purpose of the pilot
 The Physiotherapy Pilot 1.1 Purpose of the pilot The purpose of the physiotherapy pilot was to see if there were business benefits of fast tracking Network Rail employees who sustained injuries whilst
The Physiotherapy Pilot 1.1 Purpose of the pilot The purpose of the physiotherapy pilot was to see if there were business benefits of fast tracking Network Rail employees who sustained injuries whilst
1st Edition 2015. Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash. associated disorders
 1 1st Edition 2015 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders 2 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders, 2015. This quick reference
1 1st Edition 2015 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders 2 Quick reference guide for the management of acute whiplash associated disorders, 2015. This quick reference
Flat foot and lower back pain
 Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
Flat foot and lower back pain Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, NASM Corrective Exercise Specialist with special interest in postural dysfunction & lower back problems, Level
John E. O Toole, Marjorie C. Wang, and Michael G. Kaiser
 Hypothermia and Human Spinal Cord Injury: Updated Position Statement and Evidence Based Recommendations from the AANS/CNS Joint Sections on Disorders of the Spine & Peripheral Nerves and Neurotrauma &
Hypothermia and Human Spinal Cord Injury: Updated Position Statement and Evidence Based Recommendations from the AANS/CNS Joint Sections on Disorders of the Spine & Peripheral Nerves and Neurotrauma &
Case Studies Updated 10.24.11
 S O L U T I O N S Case Studies Updated 10.24.11 Hill DT Solutions Cervical Decompression Case Study An 18-year-old male involved in a motor vehicle accident in which his SUV was totaled suffering from
S O L U T I O N S Case Studies Updated 10.24.11 Hill DT Solutions Cervical Decompression Case Study An 18-year-old male involved in a motor vehicle accident in which his SUV was totaled suffering from
Does training in workplace adjustment and posture prevent occupational overuse syndrome in workplace based computer users?
 Does training in workplace adjustment and posture prevent occupational overuse syndrome in workplace based computer users? Prepared by: Meryl Lovarini Research Project Manager and occupational therapist,
Does training in workplace adjustment and posture prevent occupational overuse syndrome in workplace based computer users? Prepared by: Meryl Lovarini Research Project Manager and occupational therapist,
Clinician Portal: Enabling a Continuity of Concussion Care
 Clinician Portal: Enabling a Continuity of Concussion Care www.concussionvitalsigns.com Clinician Portal: Enabling a Continuity of Concussion CARE The Clinician Portal advances sports concussion care by
Clinician Portal: Enabling a Continuity of Concussion Care www.concussionvitalsigns.com Clinician Portal: Enabling a Continuity of Concussion CARE The Clinician Portal advances sports concussion care by
