Marketing 360 Proficiency Exam Study Guide
|
|
|
- Berniece Garrett
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Marketing 360 Proficiency Exam Study Guide AMA definition of Marketing - an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders. Marketing seeks to discover the needs and wants of prospective customers and to satisfy them. The key to achieving these two objectives is the idea of exchange, which is the trade of things of value between buyer and seller so that each is better off after the trade. Utility - the benefits or customer value received by users of the product. There are four kinds of utilities: form, place, time and possession. Form utility - the value to consumers that comes from the production or alteration of a good or services. Place utility - the value to consumers of having a good or service available where needed. Time utility - the value to consumers of having a good or service available when needed. Possession utility - the value to consumers of making an item easy to purchase so consumers can use it. The Evolution of the Market Orientation: Production Era - the central notion was that products would sell themselves. Sales Era - competition grew from the production era and salespeople were hired to sell products. Marketing Concept Era - the idea that an organization should strive to satisfy the needs of consumers while also trying to achieve the organization s goals. Customer Era - efforts are focused on continuously collecting information about customers needs, sharing this information across departments, and using it to create customer value. Market - people with both the desire and the ability to buy a specific product. Marketing mix - product, price, promotion, place. Also known as the Four P s. These are the controllable factors for a manager. The three basic ideas in the marketing concept are customer orientation, total company effort, and profit. Market penetration - a marketing strategy of increasing sales of present products in existing markets.
2 Market development - a marketing strategy of selling existing products to new markets. Product development - a marketing strategy of selling new products to existing markets. Diversification - a marketing strategy of developing new products and selling them in new markets. Target market - one or more specific groups of potential consumers toward which an organization directs its marketing program. Market segmentation - aggregating prospective buyers into groups or segments that have common needs and will respond similarly to a marketing action. The five major environmental factors in marketing: social, technological, economic, competitive, and regulatory. Lanham Act , provides for registration of a company s trademarks. Sherman Antitrust Act -1890, forbids contracts, combinations, or conspiracies in restraint of trade and actual monopolies or attempts to monopolize any part of trade or commerce. Robinson-Patman Act , makes it unlawful to discriminate in prices charged to difference purchasers of the same product, where the effect may substantially lessen competition or help to create a monopoly. Exclusive dealing - an arrangement a manufacturer makes with a reseller to handle only its products and not those of competitors. Requirement contracts - require a buyer to purchase all or part of its needs for a product from one seller for a period of time. Exclusive territorial distributorships - when a manufacturer grants a distributor the sole rights to sell a product in a specific geographical area. Tying arrangement - a seller requires the purchaser of one product to also buy another item in the line. Federal Trade Commission - concerned with the deceptive or misleading advertising and unfair business practices and has the power to issue cease and desist orders and order corrective advertising. Discretionary income - the money that remains after paying for taxes and necessities. Consumer Bill of Rights - the right to safety, to be informed, to choose, and to be heard. Purchase decision process: 1. problem recognition 2. information search 3. alternative evaluation
3 4. purchase decision 5. postpurchase behavior Problem recognition - perceiving a difference between a person s ideal and actual situation big enough to trigger a decision. Information search - seeking out a solution to your problem or need. It suggests criteria to use for the purchase, yields brand names that might meet the criteria, and develops consumer value perceptions. Alternative evaluation - evaluating all possible options in your consideration set (the group of brands that a consumer would consider acceptable from among all the brands in the product class of which he or she is aware) Purchase decision - must decide from whom to buy and when to buy. Postpurchase behavior (evaluation) - after buying a product, the consumer compares it with his or her expectations and is either satisfied or dissatisfied. Situational influences - have an impact on your purchase decision: the purchase task, social surroundings, physical surroundings, temporal effects, and antecedent states. Involvement - the personal, social, and economic significance of the purchase to thecustomer. Motivation - the energizing force that stimulates behavior to satisfy a need. Personality - refers to a person s consistent behaviors or responses to recurring situations. Self-concept - the way people see themselves and they way they believe others to see them. Perception - the process by which an individual selects, organizes and interprets information to create a meaningful picture of the world. Hierarchy of needs: physiological, safety, social, personal. Selective exposure - when consumers pay attention to messages that are consistent with their attitudes and beliefs and ignore messages that are inconsistent. Selective perception - a filtering of exposure, comprehension, and retention. Subliminal perception - seeing or hearing messages without being aware of them. Lifestyle - a mode of living that is identified by how people spend their time and resources, what they consider important in their environment, and what they think of themselves and the world around them.
4 Family life cycle - concept that describes the distinct phases that a family progresses through from formation to retirement, each phase bringing with it identifiable purchasing behaviors. Social class - the relatively permanent, homogeneous divisions in a society into which people sharing similar values, interests, and behavior can be grouped. Derived demand - the demand for industrial products and services is driven by, or derived from, demand for consumer products and services. Reciprocity - an industrial buying practice in which two organizations agree to purchase each other s products and services. Buying center - share common goals, risks, and knowledge important to a purchase decision. Make-buy decision - an evaluation of whether components and assemblies will be purchased from outside suppliers or built by the company itself. Value analysis - a systematic appraisal of the design, quality, and performance of a product to reduce purchasing costs. New buy - completely new purchase. Straight rebuy - routine reorder. People in the Buying Center: Users - the people in the organization who actually use the product or service, such as a secretary who will use a new word processor. Influences - affect the buying decision, usually by helping define the specifications for what is bought. Buyers - have formal authority and responsibility to select the supplier and negotiate the terms of the contract. Deciders - have the formal or informal power to select or approve the supplier that receives the contract. Gatekeepers - control the flow of information in the buying center. Tariff - a tax imposed by a government on goods entering its border. Quota - a restriction placed on the amount of a product allowed to enter or leave a country. Strategic alliances - agreements among two or more independent firms to cooperate for the purpose of achieving common goals such as a competitive advantage or customer value creation.
5 Back translation - a translated word or phrase is retranslated into the original language by a different interpreter to catch errors. Exporting - producing goods in one country and selling them in another country. Licensing - a company offers the right to a trademark, patent, trade secret, or similarly valued items of intellectual property in return for a royalty or a fee. Joint venture - when a foreign company and a local firm invest together to create a local business. Direct investment - a domestic firm actually investing in and owning a foreign subsidiary or division. This is the highest level of commitment a company can make when entering a global market. Dumping - when a firm sells a product in a foreign country below its domestic price or below its actual cost. Global approach - an international marketing strategy that assumes that the way a product is used and the needs it satisfies are universal. Marketing research - the process of defining a marketing problem and opportunity, systematically collecting and analyzing information, and recommending actions. Constraints - the restrictions placed on potential solutions to a problem. Sampling - selecting representative elements from a population. Target market targeting - aggregating prospective buyers into groups that have common needs and will respond similarly to a marketing action. Product positioning - refers to the place an offering occupies in consumers minds on important attributes relative to competitive products. Product repositioning - changing the place an offering occupies in a consumer s mind relative to competitive products. Perceptual map - a means of displaying or graphing in two dimensions the location of products or brands in the minds of consumers to enable a manager to see how consumers perceive competing products or brands relative to its own and then take marketing actions. The 80/20 Rule - Eighty percent of a firm s sales are obtained from twenty percent of its customers. Relationship marketing - an organizations effort to develop a long-term, cost-effective link with individual customers for mutual benefit. Direct forecast - involves estimating the value to be forecast without any intervening steps.
6 Lost-horse forecast - involves making a forecast using the last known value and modifying it according to positive or negative factors expected in the near future. Survey of buyers intentions forecast - involves asking prospective customers if they are likely to buy the product during some future time period. Salesforce survey forecast - involves asking the firm s salespeople to estimate sales during a coming period. Company sales potential - the expected level of sales that business firm can reasonably achieve, given a particular level and type of marketing effort and a particular set of environmental conditions. Secondary data - facts and figures that have already been recorded before the project at hand. Can be broken into internal secondary data(exist inside the business) and external secondary data(published data from outside of the organization). Primary data - facts and figures that are newly collected for the project. Panel - sample of consumers or stores from which researchers take a series of measurements. Experiment - involves obtaining data by manipulating factors under tightly controlled conditions to test cause and effect. Observational data - facts and figures obtained by watching, either mechanically or in person, how people actually behave. Line - a group of closely related product items that are considered to be a until because of marketing, technical, or end-use considerations. Convenience good - items that the consumer purchases frequently, conveniently, and with minimum shopping effort. Shopping goods - items for which a consumer compares several alternatives on criteria, such as price, quality, or style. Specialty goods - items that a consumer makes a special effort to search out and buy. Unsought goods - items that a consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not initially want. Buyer s Product Adoption Process: Adoption, Trial, Interest, Evaluation Supplies - similar to consumer convenience goods and consist of products such as stationary, paper clips, and brooms. Industrial services - intangible activities to assist the industrial buyer. Accessory equipment - includes tools and office equipment and is usually purchased in small-order sizes by buyers.
7 Continuous innovation - no new behaviors must be learned Dynamically continuous innovation - only minor changes in behavior are required for use. Discontinuous innovation - involves making the consumer learn entirely new consumption patterns in order to use the product. Market testing - the stage of the new product process that involves exposing actual products to prospective consumers under realistic purchase conditions to see if they will buy. Product life cycle - describes the stages a new product goes through in the marketplace: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Introduction stage - occurs when a product is first introduced to its intended target market. Growth stage - characterized by rapid increases in sales. This is the stage in which competitors appear. Maturity stage - characterized by a slowing of total industry sales or product class revenue. Marginal competitors begin to leave the market. Decline stage - when sales and profits begin to drop. Deletion - dropping the product from the company s product line. Harvesting - when a company retains the product but reduces marketing costs. Line extensions - the practice of using current brand name to enter a new market segment in its product class. Subbranding - combines a corporate or family brand with a new brand. Brand extension - the practice of using a current brand name to enter a completely different product class. Private branding - manufactures products but sells them under the brand name of a wholesaler or retailer. Family branding - when a company uses one name for all its products in a product class, when the company s trade name is used. Brand name - any word, device, or combination of these used to distinguish a seller s goods or services. Trade name - a commercial, legal name under which a company does business. Trademark - identifies that a firm has legally registered it s brand name or trade name so the firm has its exclusive use, thereby preventing others from using it.
8 Commercialization - the stage of the new-product process that involves positioning and launching a new product in full-scale production and sales. Mixed branding - where a firm markets products under its own name and that of a reseller because the segment attracted to the reseller is different from its own market. Penetration pricing - setting a low initial price on a new product to appeal immediately to the mass market. Skimming pricing - setting the highest initial price that customers really desiring the product are willing to pay. Odd-even pricing - setting prices a few dollars or cents under an even number. Individual branding - a manufacturer s branding strategy in which a distinct name is given to each of its products. Loss-leader pricing - using this method of pricing, many retailers deliberately sell below their normal prices to attract and induce additional store traffic. Bundle pricing - the marketing of two or more products in a single package price. Yield management pricing - the charging of different prices to maximize revenue for a set amount of capacity at any given time. Price lining pricing - a line of products at a number of different specific pricing points. Prestige pricing - involves setting a high price so that quality or status conscious consumers will be attracted to the product and buy it. Standard markup pricing - adding a fixed percentage to cost of all items in a specific product class. Elastic demand - exists when a 1 percent decrease in price produces more than a 1 percent increase in quantity demand, thereby actually increasing sales revenue. Inelastic demand - exists when a 1 percent decrease in price produces less than a 1 percent increase in quantity demand, thereby actually decreasing sales revenue. Marginal cost - the change in total cost that results from producing and marketing one additional unit of a product. Administering prices - when firms consciously set their own prices. Marketing channel - consists of individuals and firms involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by consumers or industrial users. Direct channel - a producer and ultimate consumers deal directly with each other. Indirect channel - intermediaries are inserted between the producer and consumers and perform numerous channel functions.
9 Industrial distributor - performs a variety of marketing channel functions, including selling, stocking, and delivering a full product assortment and financing. Direct marking channels - allow customers to buy products by interacting with various advertising media without a face-to-face meeting with a salesperson. Dual distribution - an arrangement whereby a firm reaches different buyers by employing two or more different types of channels for the same basic product. Strategic channel alliances - whereby one firm s marketing channel is used to sell another firm s products. Rack jobber - furnish the racks or shelves that display merchandise in retail stores, perform all channel functions, and sell on consignment to retailers. Cash and carry wholesalers - take title to merchandise but sell only to buyers who call on them, pay cash for merchandise, and furnish their own transportation for merchandise. Drop shippers/desk jobbers - wholesalers that own the merchandise they sell but do not physically handle, stock, or deliver it. Merchant wholesaler - independently owned firms that take title to the merchandise they handle. The three basic functions performed by intermediaries are transactional functions, logistical functions, and facilitating functions. Contractual management system - professionally managed and centrally coordinated marketing channels designed to achieve channel economies and maximum marketing impact. Wheel of retailing - describes how new forms of retail outlets enter the market. Logistics - involves those activities that focus on getting the right amount of the right products to the right places at the right time at the lowest possible cost. Logistics management - the practice of organizing the cost-effective flow of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods, and related information from point of origin to point of consumption to satisfy customer requirements. Just-in-time concept - an inventory supply system that operates with very low inventories and requires fast, on-time delivery. Supply chain - a sequence of firms that perform activities required to create and deliver a good or service to consumers or industrial users. Supply chain management - the integration and organization of information and logistics activities across firms in a supply chain for the purpose of creating and delivering goods and services that provide value to consumers.
10 Cross-docking - a practice that involves uploading products from suppliers, sorting products for individual stores, and quickly reloading products on trucks, which will deliver the products to specific stores. Extranet - an internet/web-based network that permits secure business to business communication between a manufacturer and its suppliers, distributors, and sometimes other partners. Total logistics cost - includes expenses associated with transportation, materials handling and warehousing, inventory, stockouts, order processing, and return goods handling. Depth of product line - means that the store carries a large assortment of each item. Breadth of product line - refers to the variety of different items a store carries. Limited-line stores - stores that carry a considerable assortment of a related line items. Single-line stores - stores that carry tremendous depth in one primary line of merchandise. Both limited-line and single-line stores are often referred to as specialty outlets. Scrambled merchandising - offering several unrelated product lines in a single store. Promotional Mix - advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations, and direct marketing. Advertising - any paid form of nonpersonal communication about an organization, good, service, or idea by an identified sponsor. Personal selling - the two-way flow of communication between a buyer and seller, designed to influence a person s or group s purchase decision. Public relations - a form of communication management that seeks to influence the feelings, opinions, or beliefs held by customers, prospective customers, stockholders, suppliers, employees, and other publics about a company and its products or services. Sales promotion - a short-term inducement of value offered to arouse interest in buying a good or service. Direct marketing - uses direct communication with consumers to generate a response in the form of an order, a request for further information, or a visit to a retail outlet. Noise - extraneous factors that can work against effective communication by distorting a message or the feedback received. Encoding - the process of having the sender transform an idea into a set of symbols. Decoding - the reverse, or the process of having the receiver take a set of symbols, the message, and transform them back to an idea.
11 Response - the impact the message had on the receiver s knowledge, attitudes, or behaviors. Feedback - the sender s interpretation of the response and indicates whether the message was decoded and understood as intended. Push strategy - directing the promotional mix to channel members to gain their cooperation in ordering and stocking the product. Pull strategy - directing promotional mix at ultimate consumers to encourage them to ask the retailer for a product. Premiums - consists of merchandise offered free or at a significant savings over its retail price. Deals - short term price reductions. Contests - consumers apply their skill or analytical or creative thinking to try to win a prize. Continuity program - a sales promotion tool used to encourage and reward repeat purchases by acknowledging each purchase made by a consumer and offering a premium as purchases accumulate. Product advertisements: --Pioneering advertisements - tell people what a product is, what it can do, and where it can be found. --Competitive - advertising that promotes a specific brand s features. --Reminder - used to reinforce previous knowledge of a product Institutional advertisements - to build goodwill or an image for an organization rather than promote a specific good or service. Forms of media: Television, Radio, Magazines(most detailed), Newspapers, Yellow Pages, Internet, Billboards Hierarchy of effects - Awareness, Interest, Evaluation, Trial, Adoption. Awareness - the consumer s ability to recognize and remember the product or brand name. Interest - an increase in the consumer s desire to learn about some of the features of the product or brand. Evaluation - The consumer s appraisal of the product or brand on important attributes. Trial - The consumer s actual first purchase and use of the product or brand.
12 Adoption - through a favorable experience on the first trial, the consumer s repeated purchase and use the product or brand. Integrated marketing communications - the concept of designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities to provide a consistent message across all audiences. Rating - the percentage of households in a market that are tuned in to a particular television show or radio station. Personal selling process - Prospecting, preapproach, approach, presentation, close, follow-up. Order taker - processes routine orders and reorders for products that were already sold by the company. The primary responsibility of order takers is to preserve an ongoing relationship with existing customers and maintain sales. Order getter - sells in a conventional sense and identifies prospective customers, provides customers with information, persuades customers to buy, closes sales, and follows up on customers use of product or service. Sales engineer - salesperson who specializes in identifying, analyzing, and solving customer problems and brings know-how and technical expertise to the selling situation but often does no actually sell products and services. Missionary salespeople - do not directly solicit orders but rather concentrate on performing promotional activities and introducing new products. Developing an advertising program: 1. Identify the target audience 2. Specifying advertising objectives 3. Setting the advertising budget 4. Designing the advertisement 5. Creating the actually message. 6. Selecting the right media. Reach - the number of different people or households exposed to an advertisement. Frequency - the average number of times a person in the target audience is exposed to a message or advertisement. For a message to be communicated effectively, the sender and receiver must have a mutually shared field of experience. Publicity tools - methods of obtaining nonpersonal presentation of an organization, good, or service without a direct cost. Objective and task budgeting most closely relates to the marketing concept.
13 A common practice in evaluating a salesperson is for sales management to compare the salesperson s performance with the performance of other salespersons operating under similar selling conditions, or to compare selling expenses with sales by various member of the sales force. The need-satisfaction presentation is a selling format that emphasizes probing and listening by salespeople to identify what prospective buyers are interested in, want, and need. Stimulus-response presentation - assumes that given the appropriate stimulus by a salesperson, the prospect will buy. Formula selling presentation - based on the view that a presentation consists of information that must be provided in an accurate, thorough, and step by step manner.
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18
 MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
over-the-counter selling personal selling field selling network marketing telemarketing outbound telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling
 personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
personal selling over-the-counter selling field selling network marketing outbound telemarketing telemarketing inbound telemarketing inside selling relationship selling consultative selling cross-selling
Non-personal communication
 Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
2 Most producers use to bring their products to market. A detailers B intermediaries C expediters D agents
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1.Caterpillar (famous for earth moving equipment) has a powerful partnership with its dealers. Which of the following is one of the basic principles upon which this successful
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1.Caterpillar (famous for earth moving equipment) has a powerful partnership with its dealers. Which of the following is one of the basic principles upon which this successful
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing
 Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
Preliminary Certificate in Marketing April 5 th, 2015 Examination PCM I 2015 85 th Intake, 25 th Year Candidate s Registration Number (As per in the examination admission form / Student ID) 0 0 0 0 0 For
Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies. Section 17.1 Promotion and Promotional Mix Section 17.2 Types of Promotion
 Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion
 Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
Marketing: Advertising and Sales Promotion Food Communication II Section G Communication Mix Strategies All of the information has been adapted from: Kotler P. Armstrong, G., 2004. Principles of Marketing.
RENAISSANCE COLLEGE OF COMMERCE & MANAGEMENT, INDORE Subject- Management of The Sales Force
 Objectives Type Questions 1 Personal selling involves the two-way flow of communication between a buyer and seller, often in a faceto-face encounter, designed to influence a person's or a group's: A) self-esteem.
Objectives Type Questions 1 Personal selling involves the two-way flow of communication between a buyer and seller, often in a faceto-face encounter, designed to influence a person's or a group's: A) self-esteem.
Skills Knowledge Energy Time People and decide how to use themto accomplish your objectives.
 Chapter 8 Selling With a Strategy Strategy Defined A strategy is a to assemble your resources Skills Knowledge Energy Time People and decide how to use themto accomplish your objectives. In selling, an
Chapter 8 Selling With a Strategy Strategy Defined A strategy is a to assemble your resources Skills Knowledge Energy Time People and decide how to use themto accomplish your objectives. In selling, an
Why do firms create new products?
 Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
Why do firms create new products? 1. Changing Customer Needs: When they add products, services, and processes to their offerings, firms can create and deliver value more effectively by satisfying the changing
Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling
 Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Understand the purpose
Chapter 14: Retailing, Direct Marketing, and Wholesaling Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Understand the purpose
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
 Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: Promotional Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Promotion. The Traditional Communication Model. Noise.
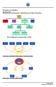 Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs
 PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
ADVERTISING AND SALES PROMOTION
 C.B.C.S.S. B.Com Programme Semester V Complementary Course- 1 ADVERTISING AND SALES PROMOTION 1. Promotion mix includes Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Advertising and a) Marketing b) Sales c) Publicity
C.B.C.S.S. B.Com Programme Semester V Complementary Course- 1 ADVERTISING AND SALES PROMOTION 1. Promotion mix includes Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Advertising and a) Marketing b) Sales c) Publicity
PROMOTION TRHOUGH THE MARKETING CHANNEL
 Chapter 12 PROMOTION TRHOUGH THE MARKETING CHANNEL Chapter Objectives One of the major tools the manufacturer uses for implementing an integrated promotional program is selling support by channel members.
Chapter 12 PROMOTION TRHOUGH THE MARKETING CHANNEL Chapter Objectives One of the major tools the manufacturer uses for implementing an integrated promotional program is selling support by channel members.
C) Provide year-end bonuses to reward the sales force personnel who perform the best.
 Exam 3-1 1. White Chemical Company is examining its selling strategy and one of the issues it believes needs attention is the role its sales staff has in undertaking sales support (non-selling) activities;
Exam 3-1 1. White Chemical Company is examining its selling strategy and one of the issues it believes needs attention is the role its sales staff has in undertaking sales support (non-selling) activities;
Chapter 8 Product Concepts
 Marketing Management Chapter 8 Product Concepts Product-Introduction The customer never buys a product buy only a bundle of satisfaction Product represents anticipated and even unanticipated solutions
Marketing Management Chapter 8 Product Concepts Product-Introduction The customer never buys a product buy only a bundle of satisfaction Product represents anticipated and even unanticipated solutions
MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING
 C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING 16-1 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries
C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING 16-1 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries
WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY
 WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY THE FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS OF THE DEFINITION OF A CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY Corporate Strategy Mission of the firm Strategic thrusts and
WORKSHOP #4 CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY THE FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS OF THE DEFINITION OF A CUSTOMER TARGETING (MARKETING) STRATEGY Corporate Strategy Mission of the firm Strategic thrusts and
UNDERSTANDING PRICING
 UNDERSTANDING PRICING Price is not just a number on a tag or an item. A) Throughout most of history prices were set by negotiation between buyers and sellers. B) Setting one price for all buyers is a relatively
UNDERSTANDING PRICING Price is not just a number on a tag or an item. A) Throughout most of history prices were set by negotiation between buyers and sellers. B) Setting one price for all buyers is a relatively
Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan
 Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan Question No: ( Marks: 3 ) How public relations are helpful in creating goodwill for organizations? ANSWER Corporations use marketing public relations
Mkt501 final term subjective Solve Questions By Adnan Awan Question No: ( Marks: 3 ) How public relations are helpful in creating goodwill for organizations? ANSWER Corporations use marketing public relations
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies. Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process
 Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Chapter 26 Pricing Strategies Section 26.1 Basic Pricing Policies Section 26.2 Strategies in the Pricing Process Basic Pricing Policies Key Terms markup pricing cost-plus pricing one-price policy flexible-price
Marketing your business
 Marketing your business Business COACH series For the size of your business How to get started A step-by-step guide Business Coach series Marketing for enhanced profits Simply stated, marketing encompasses
Marketing your business Business COACH series For the size of your business How to get started A step-by-step guide Business Coach series Marketing for enhanced profits Simply stated, marketing encompasses
ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX
 ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX 1. A company's total marketing communications mix consists of a special blend of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct-marketing tools
ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX 1. A company's total marketing communications mix consists of a special blend of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct-marketing tools
Guide to Market Research and Analysis
 The Orangeville & Area Small Business Enterprise Centre (SBEC) 87 Broadway, Orangeville ON L9W 1K1 519-941-0440 Ext. 2286 or 2291 [email protected] www.orangevillebusiness.ca Supported by its Partners:
The Orangeville & Area Small Business Enterprise Centre (SBEC) 87 Broadway, Orangeville ON L9W 1K1 519-941-0440 Ext. 2286 or 2291 [email protected] www.orangevillebusiness.ca Supported by its Partners:
Marketing Management. 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term.
 Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
Marketing Management 1 Many people are surprised when they realize how may different ideas and activities are included in the term. 1. Marketing 2. Manufacturing 3. Labeling 2 One of the most important
Basic Marketing Principles. Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi
 Basic Marketing Principles Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi Learning Objectives Define marketing in official and real
Basic Marketing Principles Author: Mickey Smith, RPh, PhD Director, Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management University of Mississippi Learning Objectives Define marketing in official and real
Principles of Marketing. by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond
 Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh.
 A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh. *Farooq Hossan *Issa Ahammad Abstract In Bangladesh extensive road network has been made in the rural areas as part of the infrastructural
A review of Marketing strategy of motorcycle products in Bangladesh. *Farooq Hossan *Issa Ahammad Abstract In Bangladesh extensive road network has been made in the rural areas as part of the infrastructural
Week 9 Personal Selling, Relationship Building, and Sales Management
 Week 9 Personal Selling, Relationship Building, and Sales Management Personal Selling - Definition Use of personal selling depends partially on the nature of product Use personal selling when products
Week 9 Personal Selling, Relationship Building, and Sales Management Personal Selling - Definition Use of personal selling depends partially on the nature of product Use personal selling when products
Marketing. Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Carl McDaniel. South-Western College Publishing Thomson Learning,.
 Marketing SECOND EDITION C J Charles W. Lamb, Jr. MJ. Neeley Professor of Marketing MJ. Neeley School of Business Texas Christian University Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Alvin C. Copeland Endowed Chair of Franchising
Marketing SECOND EDITION C J Charles W. Lamb, Jr. MJ. Neeley Professor of Marketing MJ. Neeley School of Business Texas Christian University Joseph F. Hair, Jr. Alvin C. Copeland Endowed Chair of Franchising
INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS
 INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS What is IMC & why IMC? IMC is the concept and practice of designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities Ad, PS, SP, PR, publicity,
INTEGRATED MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS What is IMC & why IMC? IMC is the concept and practice of designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities Ad, PS, SP, PR, publicity,
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENT IN MARKETING: TRENDS AND CHALLENGES
 EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENT IN MARKETING: TRENDS AND CHALLENGES Georgine Fogel, Salem International University INTRODUCTION Measurement, evaluation, and effectiveness have become increasingly important
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENT IN MARKETING: TRENDS AND CHALLENGES Georgine Fogel, Salem International University INTRODUCTION Measurement, evaluation, and effectiveness have become increasingly important
Contents. Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing. Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22. Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38
 Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Getting and Finding Purchasing, Managers, Buyers, and Purchasing Agents Jobs. The Ultimate Guide for Job Seekers and Recruiters
 Getting and Finding Purchasing, Managers, Buyers, and Purchasing Agents Jobs The Ultimate Guide for Job Seekers and Recruiters Copyright Notice of Rights All rights reserved. No part of this book may be
Getting and Finding Purchasing, Managers, Buyers, and Purchasing Agents Jobs The Ultimate Guide for Job Seekers and Recruiters Copyright Notice of Rights All rights reserved. No part of this book may be
Executive Cover Memo. The Allround brand is in a favorable position, but the cold medicine is also becoming a
 Executive Cover Memo The Allround brand is in a favorable position, but the cold medicine is also becoming a cash cow. I believe that Allround needs to increase its unit sales with both grocery stores
Executive Cover Memo The Allround brand is in a favorable position, but the cold medicine is also becoming a cash cow. I believe that Allround needs to increase its unit sales with both grocery stores
Contents. Chapter 1 Introduction to Sales Management 3-16. Chapter 2 The Sales Organization 17-40. Chapter 3 Sales Functions and Policies 41-54
 Contents Part- I: The Sales Perspective Chapter 1 Introduction to Sales Management 3-16 Chapter 2 The Sales Organization 17-40 Chapter 3 Sales Functions and Policies 41-54 Chapter 4 Personal Selling 55-80
Contents Part- I: The Sales Perspective Chapter 1 Introduction to Sales Management 3-16 Chapter 2 The Sales Organization 17-40 Chapter 3 Sales Functions and Policies 41-54 Chapter 4 Personal Selling 55-80
Estimating Market Potential. Estimating Market Potential. Elastic and Inelastic Demand Curves Determinants of Demand Elasticity. Estimation by analogy
 Estimating Market Potential Estimation by analogy comparing data from similar countries problems: geography, culture, tradition and historical reasons Income elasticity of demand market s level of development
Estimating Market Potential Estimation by analogy comparing data from similar countries problems: geography, culture, tradition and historical reasons Income elasticity of demand market s level of development
1. Planning - Establishing organizational goals and deciding how to accomplish them
 1 : Understanding the Management Process Basic Management Functions 1. Planning - Establishing organizational goals and deciding how to accomplish them SWOT analysis - The identification and evaluation
1 : Understanding the Management Process Basic Management Functions 1. Planning - Establishing organizational goals and deciding how to accomplish them SWOT analysis - The identification and evaluation
Marketing (Marketing Principles)
 Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
Marketing (Marketing Principles) Main Aim(s) of the Unit: To provide students with a foundation for the analysis of marketing within organizations including decision making processes, segmentation, the
COURSE SYLLABUS Southeast Missouri State University
 COURSE SYLLABUS Southeast Missouri State University Department of Management and Marketing Course No: MK342 Title of Course: Professional Selling Revision: Spring 2012 I. Catalog Description and Credit
COURSE SYLLABUS Southeast Missouri State University Department of Management and Marketing Course No: MK342 Title of Course: Professional Selling Revision: Spring 2012 I. Catalog Description and Credit
Business Concept Assessment
 Business Concept Assessment Frank Moyes and Stephen Lawrence Deming Center for Entrepreneurship Leeds School of Business University of Colorado Boulder 1 Business Concept Assessment Opportunity/Need 1.
Business Concept Assessment Frank Moyes and Stephen Lawrence Deming Center for Entrepreneurship Leeds School of Business University of Colorado Boulder 1 Business Concept Assessment Opportunity/Need 1.
Marketing Management SUMMARY. Chapter 14 One to One: Trade Communication, Direct Marketing & Personal Selling
 Marketing Management SUMMARY Chapter 14 One to One: Trade Communication, Direct Marketing & Personal Selling Chapter 14 Trade Sales Promotion: Targeting The B2B Customer Trade Promotions - Focus on members
Marketing Management SUMMARY Chapter 14 One to One: Trade Communication, Direct Marketing & Personal Selling Chapter 14 Trade Sales Promotion: Targeting The B2B Customer Trade Promotions - Focus on members
Bingo glossary marketing mix
 Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
MARK 3323 - IMC Dr. Freling EXAM II REVIEW
 MARK 3323 - IMC Dr. Freling EXAM II REVIEW Chapter 5 Advertising, Integrated Brand Promotion, & Consumer Behavior Chapter 6 Market Segmentation, Positioning, and the Value Proposition Chapter 7 Advertising
MARK 3323 - IMC Dr. Freling EXAM II REVIEW Chapter 5 Advertising, Integrated Brand Promotion, & Consumer Behavior Chapter 6 Market Segmentation, Positioning, and the Value Proposition Chapter 7 Advertising
Mass selling, sales promotion
 Lecture 26: Personal Selling and Sales Force Management Target Market Product Place Promotion Price Personal Selling Advertising Sales Promotion Number and kind of salespersons needed Selection and training
Lecture 26: Personal Selling and Sales Force Management Target Market Product Place Promotion Price Personal Selling Advertising Sales Promotion Number and kind of salespersons needed Selection and training
Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan
 Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan EBP Business Plan Designer Written by Matthew Parfitt EBP International Sales Executive The Essential
Essential Guide for Business Plan Creation Basic 12 step guide for executing a successful Business Plan EBP Business Plan Designer Written by Matthew Parfitt EBP International Sales Executive The Essential
II B.COM [ECOMMERCE] [2014-2017] Semester IV Core: Online Marketing - 404B Multiple Choice Questions.
![II B.COM [ECOMMERCE] [2014-2017] Semester IV Core: Online Marketing - 404B Multiple Choice Questions. II B.COM [ECOMMERCE] [2014-2017] Semester IV Core: Online Marketing - 404B Multiple Choice Questions.](/thumbs/39/19184462.jpg) 1 of 22 1/30/2016 12:05 PM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
1 of 22 1/30/2016 12:05 PM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
Buying a Franchise. www.vetbizresourcecenter.org Copyright 2009 Virginia SBDC Network All rights reserved
 Buying a Franchise An important step in the small business startup process is deciding whether or not to go into business at all. Each year, thousands of potential entrepreneurs are faced with this difficult
Buying a Franchise An important step in the small business startup process is deciding whether or not to go into business at all. Each year, thousands of potential entrepreneurs are faced with this difficult
Managing Mass Communication: Advertising, Sales Promotion, Events and Experiences, and Public Relations
 The best advertising is done by satisfied customers. Managing Mass Communication: Advertising, Sales Promotion, Events and Experiences, and Public Relations www.aenike.ub.ac.id Developing and Managing
The best advertising is done by satisfied customers. Managing Mass Communication: Advertising, Sales Promotion, Events and Experiences, and Public Relations www.aenike.ub.ac.id Developing and Managing
Pricing and Credit Decisions
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Dynamic Network Services (http://www.dyn.com) 1 Setting a Price Discuss the role of cost and demand factors in setting a price. Cost Determination for Pricing Total cost includes
CHAPTER OUTLINE Spotlight: Dynamic Network Services (http://www.dyn.com) 1 Setting a Price Discuss the role of cost and demand factors in setting a price. Cost Determination for Pricing Total cost includes
LCCI International Qualifications. Level 3 Certificate in Selling and Sales Management. Extended Syllabus. Effective from 2007
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Selling and Sales Management Extended Syllabus Effective from 2007 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. [email protected]
LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Selling and Sales Management Extended Syllabus Effective from 2007 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. [email protected]
Chapter 10 Sample Questions on Advertising, PR and Promotion
 Chapter 10 Sample Questions on Advertising, PR and Promotion 1. One issue facing advertisers is that consumers screen out messages that are not relevant to them. 2. Glenn is using a push strategy to promote
Chapter 10 Sample Questions on Advertising, PR and Promotion 1. One issue facing advertisers is that consumers screen out messages that are not relevant to them. 2. Glenn is using a push strategy to promote
Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 41 Value of Information In this lecture, we look at the Value
Operations and Supply Chain Management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 41 Value of Information In this lecture, we look at the Value
MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING
 C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries are needed.
C H A P T E R S I XT E E N MARKETING CHANNELS AND WHOLESALING AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Explain what is meant by a marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries are needed.
MKT 3525 SALES MANAGEMENT FINAL
 MKT 3525 SALES MANAGEMENT FINAL Chapter 3: Territory Management Sales opportunity management - Generating new accounts - Managing existing accounts - Sales versus profits - Personal time management A process
MKT 3525 SALES MANAGEMENT FINAL Chapter 3: Territory Management Sales opportunity management - Generating new accounts - Managing existing accounts - Sales versus profits - Personal time management A process
FDU-Vancouver Bachelor of Science in Business Administration International Business Concentration Course Descriptions
 FDU-Vancouver Bachelor of Science in Business Administration International Business Concentration Course Descriptions Business Foundational Courses General Education DSCI 1234 Mathematics for Business
FDU-Vancouver Bachelor of Science in Business Administration International Business Concentration Course Descriptions Business Foundational Courses General Education DSCI 1234 Mathematics for Business
Unit 4: Marketing Principles
 Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Unit 4: Marketing Principles Unit code: F/601/0556 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 credits Aim This unit aims to provide learners with understanding and skills relating to the fundamental concepts and principles
Chapter 6. Transfer Pricing Methods. 6.1. Introduction to Transfer Pricing Methods
 Chapter 6 Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1. Introduction to Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1.1. This part of the Chapter describes several transfer pricing methods that can be used to determine an arm s length
Chapter 6 Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1. Introduction to Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1.1. This part of the Chapter describes several transfer pricing methods that can be used to determine an arm s length
Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma
 Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma 2006 Frank Lynn & Associates, Inc. All Rights Reserved 0 Distributor/Reseller Marketing Over the last 50 years, changes in
Distributor/Reseller Marketing A Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma 2006 Frank Lynn & Associates, Inc. All Rights Reserved 0 Distributor/Reseller Marketing Over the last 50 years, changes in
Getting the Intelligence to Build Demand-Driven Supply Networks
 Getting the Intelligence to Build Demand-Driven Supply Networks Introduction Building an effective Demand-Driven Supply Network (DDSN) presents an ongoing challenge. Most companies remain in the early
Getting the Intelligence to Build Demand-Driven Supply Networks Introduction Building an effective Demand-Driven Supply Network (DDSN) presents an ongoing challenge. Most companies remain in the early
Promotions: Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
 1 Marketing Communication Mix or Promotion Mix Promotions: Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy Design Stores that Sell the Product Price Package 2 The Changing Communications Environment The Need
1 Marketing Communication Mix or Promotion Mix Promotions: Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy Design Stores that Sell the Product Price Package 2 The Changing Communications Environment The Need
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications
 Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
Assessment Vocabulary Strategies. Advertiser. Describe three types of positions typically found in an advertising agency.
 What is Advertising (1-2 days) (1) The student knows business concepts and explains how business satisfies economic needs. The student is expected to: (A) Categorize business activities as production,
What is Advertising (1-2 days) (1) The student knows business concepts and explains how business satisfies economic needs. The student is expected to: (A) Categorize business activities as production,
Marketing channels exist to create utility for. Customers
 Channel Objectives Global Marketing Channels and Physical Distribution Global Marketing Chapter 12 1 Marketing channels exist to create utility for customers Place utility availability of a product or
Channel Objectives Global Marketing Channels and Physical Distribution Global Marketing Chapter 12 1 Marketing channels exist to create utility for customers Place utility availability of a product or
Uses and Limitations of Ratio Analysis
 Uses and Limitations of Ratio Analysis Balkrishna Parab ACS, AICWA [email protected] F inancial statement analysis involves comparing the firm s performance with that of other firms in the same
Uses and Limitations of Ratio Analysis Balkrishna Parab ACS, AICWA [email protected] F inancial statement analysis involves comparing the firm s performance with that of other firms in the same
Market Analysis, Segmentation & Consumer Buying Behavior
 Market Analysis, Segmentation & Consumer Buying Behavior Market Analysis If you are preparing a marketing plan, where s the best place to look for information about macro trends? Marketing Jeopardy Michael
Market Analysis, Segmentation & Consumer Buying Behavior Market Analysis If you are preparing a marketing plan, where s the best place to look for information about macro trends? Marketing Jeopardy Michael
MKTG 680. Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion. Standardization vs.
 MKTG 680 Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion Global Marketing Communications The primary purpose of marketing communications is to tell
MKTG 680 Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion Global Marketing Communications The primary purpose of marketing communications is to tell
Measuring and Evaluating Results
 Introduction Measuring and evaluating results will provide you and your associates with the vital information you need for making key strategic and tactical decisions prior to, at and after the trade shows,
Introduction Measuring and evaluating results will provide you and your associates with the vital information you need for making key strategic and tactical decisions prior to, at and after the trade shows,
Fundamentals of Marketing Management
 Fundamentals of Management Dr. P.V. (Sundar) Managing World-Class Organizations What is? Process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products
Fundamentals of Management Dr. P.V. (Sundar) Managing World-Class Organizations What is? Process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions
 Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
Management and Marketing Course Descriptions Management Course Descriptions HRM 301 Human Resources Management (3-0-3) Covers all activities and processes of the human resources function that include recruitment,
17. A divisional sales manager is ranked higher than a regional sales manager in the upward sequence of job movements during a sales career.
 1 Student: 1. Selling is a separate discipline rather than a component of marketing. 2. For the last two decades, Gallup has found that used car salespeople were rated higher on perceived honesty and ethical
1 Student: 1. Selling is a separate discipline rather than a component of marketing. 2. For the last two decades, Gallup has found that used car salespeople were rated higher on perceived honesty and ethical
Sample of Best Practices
 Sample of Best Practices For a Copy of the Complete Set Call Katral Consulting Group 954-349-1281 Section 1 Planning & Forecasting Retail Best Practice Katral Consulting Group 1 of 7 Last printed 2005-06-10
Sample of Best Practices For a Copy of the Complete Set Call Katral Consulting Group 954-349-1281 Section 1 Planning & Forecasting Retail Best Practice Katral Consulting Group 1 of 7 Last printed 2005-06-10
Position Descriptions include the current benchmark job description used by participants to facilitate job matching.
 Level Guides, Position Descriptions Introduction This section includes the following: Level Guides set forth the criteria (i.e., the experience, education, skills, duties/tasks, and supervision given/received)
Level Guides, Position Descriptions Introduction This section includes the following: Level Guides set forth the criteria (i.e., the experience, education, skills, duties/tasks, and supervision given/received)
http://wps.pearsoned.co.uk/ema_uk_he_harker_mktgintro_1/127/32609/8347930.cw/content/index.h tml
 Basics of Logistics Management http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0073529931/student_view0/chapter16/multiple_choice_quiz.html http://wps.pearsoned.co.uk/ema_uk_he_harker_mktgintro_1/127/32609/8347930.cw/content/index.h
Basics of Logistics Management http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0073529931/student_view0/chapter16/multiple_choice_quiz.html http://wps.pearsoned.co.uk/ema_uk_he_harker_mktgintro_1/127/32609/8347930.cw/content/index.h
Guide to Effective Retail Merchandise Management A Step by Step Guide to Merchandising in a Retail Store
 Guide to Effective Retail Merchandise Management A Step by Step Guide to Merchandising in a Retail Store By BizMove Management Training Institute Other free books by BizMove that may interest you: Free
Guide to Effective Retail Merchandise Management A Step by Step Guide to Merchandising in a Retail Store By BizMove Management Training Institute Other free books by BizMove that may interest you: Free
Key Terms. DECA Ryerson 2015-16 Case Guides Business to Business Marketing
 Key Terms Acquisition Costs: The incremental costs involved in obtaining a new customer. Agent: A business entity that negotiates, purchases, and/or sells, but does not take title to the goods. Benchmark:
Key Terms Acquisition Costs: The incremental costs involved in obtaining a new customer. Agent: A business entity that negotiates, purchases, and/or sells, but does not take title to the goods. Benchmark:
K-12 Entrepreneurship Standards
 competitiveness. The focus will be on business innovation, change and issues related to the United States, which has achieved its highest economic performance during the last 10 years by fostering and
competitiveness. The focus will be on business innovation, change and issues related to the United States, which has achieved its highest economic performance during the last 10 years by fostering and
Marketing: Mastering the Process
 Marketing: Mastering the Process Course Description This course teaches you key components of marketing strategy and tactics including: identification, analysis and selection of target markets; development
Marketing: Mastering the Process Course Description This course teaches you key components of marketing strategy and tactics including: identification, analysis and selection of target markets; development
Strategic Brand Management Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity
 Strategic Brand Management Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity Part 1 Opening Perspectives 开 放 视 觉 Chapter 1 Brands and Brand Management ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Strategic Brand Management Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity Part 1 Opening Perspectives 开 放 视 觉 Chapter 1 Brands and Brand Management ------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTER 14 DEVELOPING AND MARKETING PRODUCTS
 CHAPTER 14 DEVELOPING AND MARKETING PRODUCTS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the impact globalization is having on international marketing activities. 2. Describe the types of things that managers must
CHAPTER 14 DEVELOPING AND MARKETING PRODUCTS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the impact globalization is having on international marketing activities. 2. Describe the types of things that managers must
MARKETING 26 THE ROAD TO THE CONSUMER
 26 THE ROAD TO THE CONSUMER Insurance. In setting up any kind of business you will need to consider several types of insurance coverage, including 8 : General business liability, including product liability
26 THE ROAD TO THE CONSUMER Insurance. In setting up any kind of business you will need to consider several types of insurance coverage, including 8 : General business liability, including product liability
EXAMINING DIRECT & INTERACTIVE MARKETING APPLICATIONS IN A VARIETY OF SECTORS
 1 CHAPTER 14-2E EXAMINING DIRECT & INTERACTIVE MARKETING APPLICATIONS IN A VARIETY OF SECTORS Summary The applications of direct and interactive marketing are almost endless. This chapter has explored
1 CHAPTER 14-2E EXAMINING DIRECT & INTERACTIVE MARKETING APPLICATIONS IN A VARIETY OF SECTORS Summary The applications of direct and interactive marketing are almost endless. This chapter has explored
Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy
 Chapter Thirteen Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. CRICKET LEE Fitlogic Developed a system of clothes sizing called
Chapter Thirteen Marketing: Helping Buyers Buy McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. CRICKET LEE Fitlogic Developed a system of clothes sizing called
Technical Sales Training for the Laboratory Professional
 Technical Sales Training for the Laboratory Professional 10 CEU Credit Hours Produced by: ARUP Business Affiliations & The Institute for Learning Salt Lake City, Utah Training Outline The Profession of
Technical Sales Training for the Laboratory Professional 10 CEU Credit Hours Produced by: ARUP Business Affiliations & The Institute for Learning Salt Lake City, Utah Training Outline The Profession of
Blackblot PMTK Marketing Review. <Comment: Replace the Blackblot logo with your company logo.>
 Company Name: Product Name: Date: Contact: Department: Location: Email: Telephone: Blackblot PMTK Marketing Review Document Revision History:
Company Name: Product Name: Date: Contact: Department: Location: Email: Telephone: Blackblot PMTK Marketing Review Document Revision History:
advertise to announce that a product is for sale or that a service is offered in order to encourage people to buy it or to use it
 Aa Acquisition process by which a company buys another company advertise to announce that a product is for sale or that a service is offered in order to encourage people to buy it or to use it advertiser
Aa Acquisition process by which a company buys another company advertise to announce that a product is for sale or that a service is offered in order to encourage people to buy it or to use it advertiser
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT BLOCK TRADE REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT BLOCK TRADE REPORTING REQUIREMENTS Block Trades and Distributions What is a block trade? Many people use the term block trade colloquially. Technically, a block trade is
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT BLOCK TRADE REPORTING REQUIREMENTS Block Trades and Distributions What is a block trade? Many people use the term block trade colloquially. Technically, a block trade is
The Research of Vancl Network Marketing
 The Research of Vancl Network Marketing WU Zhonghua School of Business Administration, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, China, 330013 [email protected] Abstract: In recent years, the garment
The Research of Vancl Network Marketing WU Zhonghua School of Business Administration, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, China, 330013 [email protected] Abstract: In recent years, the garment
SPORT MARKETING MIX STRATEGIES
 Alexandru Lucian MIHAI Faculty: Marketing, Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania SPORT MARKETING MIX STRATEGIES Keywords Sport marketing Marketing mix Market position JEL Classification M31 Abstract
Alexandru Lucian MIHAI Faculty: Marketing, Academy of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania SPORT MARKETING MIX STRATEGIES Keywords Sport marketing Marketing mix Market position JEL Classification M31 Abstract
Descriptions of the Three Markets in The New Shoe Simulation Ted Mitchell The Home Market
 Descriptions of the Three Markets in The New Shoe Simulation Ted Mitchell In marketing management, a market is a group of final customers who respond in a homogeneous way to a marketing mix. If two customers
Descriptions of the Three Markets in The New Shoe Simulation Ted Mitchell In marketing management, a market is a group of final customers who respond in a homogeneous way to a marketing mix. If two customers
