CHAPTER 14 DEVELOPING AND MARKETING PRODUCTS
|
|
|
- Anne Anastasia Powers
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 14 DEVELOPING AND MARKETING PRODUCTS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the impact globalization is having on international marketing activities. 2. Describe the types of things that managers must consider when developing international product strategies. 3. Discuss the factors that influence international promotional strategies and the blending of product and promotional strategies. 4. Explain the elements that managers must take into account when designing international distribution strategies. 5. Discuss the elements that influence international pricing strategies. CHAPTER OUTLINE: Introduction Globalization and Marketing Standardization Versus Adaptation Influence of National Business Environments Developing Product Strategies Laws and Regulations Cultural Differences Brand and Product Names Selecting International Brand and Product Names National Image Counterfeit Goods and Black Markets Shortened Product Life Cycles Creating Promotional Strategies Push and Pull Strategies International Advertising Standardizing or Adapting Advertisements Case: The Elusive Euro-Consumer Blending Product and Promotional Strategies Communicating Promotional Messages Product/Communications Extension (Dual Extension)</ Product Extension/Communications Adaptation Product Adaptation/Communications Extension Product/Communications Adaptation (Dual Adaptation) Product Invention Designing Distribution Strategies Designing Distribution Channels Degree of Exposure Channel Length and Cost Influence of Product Characteristics Special Distribution Problems Lack of Market Understanding Theft and Corruption Developing Pricing Strategies Worldwide Pricing 1
2 Dual Pricing Factors That Affect Pricing Decisions Transfer Prices Arm s Length Pricing Price Controls Dumping A Final Word A comprehensive set of specially designed PowerPoint slides (designated PPT below) is available for use with Chapter 14. These slides and the lecture outline below form a completely integrated package that simplifies the teaching of this chapter s material. Lecture Outline 1. INTRODUCTION Globalization affects international business activities, industries, and products differently. Some companies market an identical product worldwide, whereas others must adjust marketing strategies across national markets. 2. GLOBALIZATION AND MARKETING Globalization is transforming the way some products are marketed internationally. Some companies implement a global strategy that uses similar promotional messages and themes to market the same product around the world. Others find that their products require physical changes to suit the tastes of consumers abroad. How do managers decide when marketing strategies need modifying? A. Standardization versus Adaptation (PPT #3) 1. U.S. researcher Theodore Levitt argued that because the world is becoming standardized and homogeneous, companies should market the same products in the same way in all countries. Technology, claimed Levitt, causes needs and preferences to converge throughout the world. 2. Companies reduce production and marketing costs by standardizing the physical features of their products and marketing strategies. 3. Other researchers say that standardization is just one strategy for going international successfully. They say standardization is not always the best strategy and advise smaller companies to adapt to local cultures while exploiting their unique images to gain local market share. 4. Influence of National Business Environments a. Consumers in different national markets want products that reflect their tastes; business environments affect consumer preferences and industrial buyers. b. Certain products do appeal to practically all cultures. c. Product standardization is more likely when nations share the same level of economic development. 3. DEVELOPING PRODUCT STRATEGIES (PPT #4-6) Factors in many international product strategy issues. 2
3 A. Laws and Regulations 1. Companies must adapt their products to satisfy laws and regulations in a target market. 2. The fact that many developing countries have fewer consumer-protection laws creates an ethical issue; lower levels of education and experience mean that consumers need protection. 3. Many governments impose fewer regulations to hold down production costs and consumer prices. B. Cultural Differences 1. Companies sometimes must adapt their products to suit local buyers preferences rooted in culture. 2. Not all companies modify products but find a different cultural need that it satisfies. C. Brand and Product Names 1. Brand name is the name of one or more items in a product line that identifies the source or character of the items. Consumers assign products a certain value based on experiences with a brand. 2. Brand names help consumers select, recommend, or reject products; they also function as legal property that owners can protect from competitors. 3. A consistent worldwide brand image is important as more consumers and businesspeople travel internationally. 4. Companies must review its brand image and update it if needed. 5. Selecting International Brand and Product Names a. Products in international markets need carefully selected names whether standardized or localized. b. Company and product names are made up of morphemes semantic elements, or language building blocks. c. Brand names seldom offend people in international markets, but product names do. D. National Image 1. Value customers obtain from a product is influenced by the image of the country in which it is designed, manufactured, or assembled. 2. Image can be positive for some products but negative for others. 3. Because it affects buyers perceptions of quality and reliability, national image is an important element of product policy. 4. National image can and does change over time. E. Counterfeit Goods and Black Markets 1. Counterfeit goods are imitation products passed off as legitimate trademarks, patents, or copyrighted works. 2. Counterfeit brand name consumer goods, such as watches, perfumes, clothing, movies, music, and computer software are sold to consumers on the black market. 3. Topping the list for counterfeits: China, India, Russia, Thailand, and Turkey. Counterfeiting is worth from $50 billion to $80 billion globally. 4. Counterfeit goods can damage buyers images of a brand when the counterfeits are of inferior quality to the original. Buyers who purchase a brand expect a level of craftsmanship and satisfaction; when the product 3
4 fails to deliver on expectations, the buyer is dissatisfied and the company s reputation is tarnished. F. Shortened Product Life Cycles 1. Companies traditionally managed to extend a product s life by introducing it into different markets consecutively; products were first in industrialized countries and later in developing markets. 2. Advances in telecommunications have alerted consumers around the world to the latest product introductions; consumers in developing and emerging markets demand the latest products. 3. Companies now undertake new product development at a rapid pace and shorten product life cycles. 4. CREATING PROMOTIONAL STRATEGIES Efforts by companies to reach distribution channels and target customers through communications such as personal selling, advertising, public relations, and direct marketing are called its promotion mix. A. Push and Pull Strategies (PPT #7-9) 1. Pull strategy: Create buyer demand that will encourage channel members to stock a company s product. Buyer demand is generated in order to pull products through distribution channels to end-users. 2. Push strategy: Pressure channel members to carry a product and promote it to final users. Manufacturers of products sold in department and grocery stores often use a push strategy. 3. The strategy to use depends on the type of distribution system, access to mass media, and the type of product. a. Distribution system. Implementing a push strategy is difficult when channel members wield a great deal of power relative to that of producers. It can be ineffective when distribution channels are lengthy: It might be easier to use a pull strategy. b. Access to mass media. Developing and emerging markets have fewer forms of mass media, making it difficult to increase consumer awareness and generate product demand. Many consumers cannot afford cable or satellite television, or glossy magazines, so advertisers use billboards and radio. c. Type of product. A pull strategy is appropriate when buyers display brand loyalty; brand-loyal buyers know what they want before they buy it. Push strategies are appropriate for inexpensive consumer goods for buyers who are not brand loyal; low brand loyalty means that a buyer purchases one of the brands carried by the retailer. B. International Advertising International advertising differs from domestic advertising. Cultural similarities mean that ads are only slightly modified in different nations. Cultural differences may mean that entirely new ads must be created. 1. Standardizing or Adapting Advertisements a. Most advertising in any one nation is produced solely for that domestic audience. Companies that advertise in multiple markets 4
5 must determine the aspects of the advertising campaign that can be standardized and those that cannot. b. To pursue a global marketing strategy, a company tries to get the most for its advertising expenditure. An increasingly popular method is marketing over the World Wide Web. Companies that use direct marketing (such as telemarketing or leaflets through the mail) have had mixed results with Web ads. c. Companies reach a global audience by sponsoring global sporting events, such as the Olympics, World Cup Soccer, and Formula One automobile racing. 2. Case: The Elusive Euro-Consumer a. The integration of EU nations causes marketers to think they can standardize advertising to appeal to the Euro-consumer. But the Euro-consumer remains a rare, almost mythical, creature who eludes the world s best advertisers. b. Well-known international advertising agencies have tried a pan- European advertising approach only to fail due to national differences; Europe s many languages create translation issues for marketers. c. Successful pan-european ads contain visuals, few words, and a focus on the product. C. Blending Product and Promotional Policies (PPT #10-15) When companies extend marketing to international markets, they develop communication strategies that blend product and promotional policies. A company s communication strategy for a market considers the nature of the product and the promotion mix. There are five product/promotional methods. 1. Communicating Promotional Messages a. Marketing communication is the process of sending promotional messages about products to target markets. b. Marketing internationally often means translating promotional messages from one language to another. Marketers must also be knowledgeable of cultural nuances that affect how buyers interpret a promotional message. c. Laws that govern promotion in another country can force changes in marketing communication. d. Marketing communication is typically considered a circular process (Figure 14.1): i. The company with an idea to communicate is the source. ii. The idea is encoded (translated into images, words, and symbols) into a promotional message. iii. The promotional message is sent to the audience (potential buyers) through various media radio, television, newspapers, magazines, billboards, and direct mailings. The audience receives the message, decodes the message, and interprets its meaning. iv. Information in the form of feedback (purchase or nonpurchase) flows to the source of the message. v. The decoding process can be disrupted by the presence of noise anything that disrupts the audience s ability to receive and interpret the promotional message. Language 5
6 barriers between the company and potential buyers create noise if a company s promotional message is incorrectly translated into the local language. 2. Product/Communications Extension (Dual Extension) a. Extends the same home-market product and marketing promotion into target markets. Under certain conditions, it can be the simplest and most profitable strategy. b. May grow more popular as the information age ties the world together. Best suited for companies that use a global strategy; upscale personal items with global brand names. c. Useful to companies who are low-cost leaders in their industries; one product and one promotional message keep costs down. 3. Product Extension, Communications Adaptation a. Extends the same product into new target markets, but alters its promotion. Communications require adaptation because the product satisfies a different need, serves a different function, or appeals to a different type of buyer. b. Contains costs because the product does not undergo any alterations; developing new promotional campaigns is expensive. c. Low economic development can demand that communications be adapted to local conditions. In developing countries, television and radio coverage are limited and the Web is years behind; marketers use door-to-door personal selling and regional product shows or fairs. 4. Product Adaptation, Communications Extension a. Requires a company to adapt its product to the international market yet retain the original marketing communication. b. Company may adapt its product for reasons such as legal requirements in the local market. Governments can require certain local materials, labor, or other resources in local production process; if the same materials are not available locally, the product may be modified. c. Can be costly, especially if the company invests in production facilities to remain close to changing buyer preferences. A firm can implement this strategy successfully if it sells a differentiated product and charges a higher price to offset production costs. 5. Product/Communications Adaptation (Dual Adaptation) a. Adapts both the product and its marketing communication to suit the target market. The product itself is adapted to match the needs or preferences of local buyers. The promotional message is adapted to explain how the product meets those needs and preferences. b. High cost means few companies employ this strategy; it can be implemented successfully if a large and profitable market segment exists. 6. Product Invention a. Requires that an entirely new product be developed for the target market. Product invention is necessary when many differences exist between the domestic and target markets. 6
7 b. One reason for invention is that local buyers cannot afford a product because of low purchasing power. c. Product inventions can arise due to lack of infrastructure. 5. DESIGNING DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS (PPT #16) Planning, implementing, and controlling the physical flow of a product from its point of origin to its point of consumption is called distribution. The physical path that a product follows on its way to customers is called a distribution channel. Companies along this channel that work together in delivering products to customers are called channel members or intermediaries. Manufacturers of goods are not the only producers who need distribution channels; service providers such as consulting companies, health-care organizations, and news services need distribution. Companies develop their international distribution strategies based on two related decisions: (1) how to get the goods into a country and (2) how to distribute goods within a country. A. Designing Distribution Channels (PPT #17) When managers establish distribution policies, they consider the market exposure needed and the cost of distribution. 1. Degree of Exposure a. Exclusive channel: Manufacturer grants the right to sell its product to one or a limited number of resellers. Gives control over sales to channel members such as wholesalers and retailers; this helps constrain distributors from selling competing brands. b. An exclusive channel creates a barrier that makes it difficult or impossible for outsiders to penetrate the channel. c. Intensive channel: Producer grants the right to sell its product to many resellers. Provides convenience because of the many outlets through which a product is sold. It does not create strong barriers to channel entry, nor provide control over reseller decisions such as what competing brands to sell. d. Obstacle for small companies that choose intensive channels is gaining shelf space. This is exacerbated by the increasing global trend toward retailers developing their own private label brands brands created by retailers themselves. 2. Channel Length and Cost a. Channel length refers to the number of intermediaries between the producer and the buyer. b. Zero-level channel (called direct marketing): producers sell directly to final buyers. c. One-level channel: One intermediary between producer and buyer. Two intermediaries make up a two level channel, etc. d. The more intermediaries, the more costly it becomes because each one adds a fee for services. B. Influence of Product Characteristics (PPT #18) 1. Value density: Value of a product relative to its weight and volume; an important variable in formulating distribution policies. 7
8 2. As a rule, the lower a product s value density the more localized the distribution system. Commodities have low value-density ratios value is low relative to their cost of shipping. 3. Products with high value-density ratios include emeralds, semiconductors, and premium perfumes. Because the cost of transporting these products is small relative to their values, they can be processed or manufactured and then shipped. C. Special Distribution Problems (PPT #19) A country s distribution system develops over time and reflects its unique cultural, political, legal, and economic traditions. The distribution system of each nation has its own unique pros and cons. 1. Lack of Marketing Understanding Can create frustration and financial loss. 2. Theft and Corruption Presents obstacles to distribution. 6. DEVELOPING PRICING STRATEGIES (PPT #20) The pricing policy must match a company s overall international strategy. A. Worldwide Pricing (PPT #21) 1. Establishes one selling price for all international markets. 2. Difficult to achieve for four reasons: a. Production costs differ from one nation to another. b. Producing in just one location cannot guarantee the same selling price in international markets because of the different cost of reaching different markets. c. Purchasing power of local buyers must be considered. d. Fluctuating currency values can raise or lower a product s price abroad. B. Dual Pricing (PPT #22) 1. Product has a different selling price (typically higher) in export markets than it has in the home market. 2. When a product has a higher selling price in the target market than it does in the home market, it is called price escalation, which results from exporting costs and currency fluctuations. 3. Product s export price may be lower than the price in the home market. 4. Some companies decide that domestic sales are to cover expenses for R&D, administration, and overhead; exports cover only additional costs associated with exporting and selling in a target market (e.g., tariffs). 5. To apply dual pricing in international marketing, a company must keep domestic and international buyers separate. If a company cannot keep its buyers separate, they could undermine the policy through arbitrage buying products at lower prices and reselling them at higher prices. C. Issues That Affect Pricing Decisions (PPT #23) Several key factors affect pricing decisions. 1. Transfer Prices a. Price charged for products transferred between a company and a subsidiary. 8
9 b. Companies enjoyed freedom in setting transfer prices; subsidiaries in countries with high tax rates reduced their taxes by charging a low price for output to subsidiaries. The subsidiary lowered the parent company s taxes by reducing profits in the high-tax country. c. Large firms used transfer pricing to manage their global taxes and become more price-competitive. 2. Arm s-length Pricing a. Free-market price that unrelated parties charge one another. b. Although companies had great latitude in assigning transfer prices, many governments are assigning them arm s-length prices to clamp down on tax evasion. There is also pressure on companies to be good corporate citizens in target markets. c. Developing and emerging markets are hurt by lost revenue when international companies manipulate prices to reduce tariffs and corporate taxes. Need revenue for schools, hospitals, and infrastructure. These in turn benefit companies by improving the productivity and efficiency of the local business environment. 3. Price Controls a. Upper or lower limits placed on the prices within a country. b. Upper-limit price controls provide price stability in an inflationary economy (when prices are rising). Companies that want to raise prices must apply to government authorities. c. Lower-limit price controls prohibit the lowering of prices below a certain level. d. Governments impose lower-limit prices to help local companies compete against the less expensive imports of international companies or to ward off price wars. 4. Dumping a. Price of a good is lower in export markets than in the domestic market. b. Accusations of dumping are often made against foreign competitors when inexpensive imports flood a domestic market. c. Although charges of dumping normally result from deliberate efforts to undercut the prices of competitors in the domestic market, changes in exchange rates can cause unintentional dumping. d. Antidumping tariffs punish producers in the offending nation by increasing the price of their products. 7. A FINAL WORD Despite the academic debate over globalization and the extent to which companies should standardize their international marketing activities, many companies continue to adapt to local conditions. Sometimes this takes the form of only slightly modifying promotional campaigns and at other times it can require the creation of an entirely new product. The causes of alterations in promotional aspects of marketing strategy can be cultural, such as language differences. They can also be legal such as requirements to produce locally so as to help ease local unemployment or to spur local industry around the production facility. Other companies are able to reap the rewards of standardization and centralized production that can result from the ability to sell one product worldwide. 9
Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies. Section 17.1 Promotion and Promotional Mix Section 17.2 Types of Promotion
 Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
Unit 6 Promotion Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies Chapter 18 Visual Merchandising and Display Chapter 19 Advertising Chapter 20 Print Advertisements Chapter 17 Promotional Concepts and Strategies
CHAPTER 11 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY AND ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 11 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY AND ORGANIZATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the stages of identification and analysis that precede strategy selection. 2. Identify the two international strategies
CHAPTER 11 INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY AND ORGANIZATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the stages of identification and analysis that precede strategy selection. 2. Identify the two international strategies
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: Promotional Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Promotion. The Traditional Communication Model. Noise.
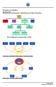 Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Principles of Marketing Lecture 13a: al Mix Decisions: Advertising and Sales Target Market Product Place Price Personal Selling Mass Selling Sales Advertising Publicity The Traditional Communication Model
Estimating Market Potential. Estimating Market Potential. Elastic and Inelastic Demand Curves Determinants of Demand Elasticity. Estimation by analogy
 Estimating Market Potential Estimation by analogy comparing data from similar countries problems: geography, culture, tradition and historical reasons Income elasticity of demand market s level of development
Estimating Market Potential Estimation by analogy comparing data from similar countries problems: geography, culture, tradition and historical reasons Income elasticity of demand market s level of development
Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage. PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz
 Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Industry group of firms that produce
Strategic Elements of Competitive Advantage PPT 6 (First ppt slides after the mid-term) Assist. Prof. Dr. Ayşen Akyüz Industry Analysis: Forces Influencing Competition Industry group of firms that produce
Non-personal communication
 Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
Week 8: Promotions Integrated Marketing Communications: advertising, Sales Promotion, Public Relations, and Direct Marketing Strategic Goals Of Marketing Communication Create awareness Build positive images
CHAPTER 15 PROMOTION STRATEGIES: ADVERTISING. a) China b) Russia c) India d) all of them permit advertising (X)
 CHAPTER 15 PROMOTION STRATEGIES: ADVERTISING MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. This country does not allow advertising. a) China b) Russia c) India d) all of them permit advertising (X) 2. The relationship between advertising
CHAPTER 15 PROMOTION STRATEGIES: ADVERTISING MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. This country does not allow advertising. a) China b) Russia c) India d) all of them permit advertising (X) 2. The relationship between advertising
Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs
 PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
PURDUE EXTENSION EC-730 Marketing s Four P s: First Steps for New Entrepreneurs Cole Ehmke, Joan Fulton, and Jayson Lusk Department of Agricultural Economics Marketing your business is about how you position
Descriptions of the Three Markets in The New Shoe Simulation Ted Mitchell The Home Market
 Descriptions of the Three Markets in The New Shoe Simulation Ted Mitchell In marketing management, a market is a group of final customers who respond in a homogeneous way to a marketing mix. If two customers
Descriptions of the Three Markets in The New Shoe Simulation Ted Mitchell In marketing management, a market is a group of final customers who respond in a homogeneous way to a marketing mix. If two customers
Seminar. The Organization of International Business Chapter 15. 11 Kasım 14 Salı 15-
 Seminar The Organization of International Business Chapter 15 Learning Objectives p Profile the evolving process of organizing a company for international business p Describe the features of classical
Seminar The Organization of International Business Chapter 15 Learning Objectives p Profile the evolving process of organizing a company for international business p Describe the features of classical
Determining Your Advertising Objectives
 Determining Your Advertising Objectives by BNET Editorial Tags: marketing, advertising, sales Clear objectives for an advertising campaign are essential. Do you want to generate leads or encourage brand
Determining Your Advertising Objectives by BNET Editorial Tags: marketing, advertising, sales Clear objectives for an advertising campaign are essential. Do you want to generate leads or encourage brand
Slide 1. Welcome to Chapter 11. This chapter is called Marketing. The author is Vicente Lluch.
 Slide 1 Welcome to Chapter 11 This chapter is called Marketing. The author is Vicente Lluch. Slide 2 In this chapter we will address the learning objectives by answering the following questions: What is
Slide 1 Welcome to Chapter 11 This chapter is called Marketing. The author is Vicente Lluch. Slide 2 In this chapter we will address the learning objectives by answering the following questions: What is
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLANNING CHECKLIST. For Development of Overall International Business Plan
 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLANNING CHECKLIST For Development of Overall International Business Plan Thomas B. McVey 1 Introduction: The following Checklist is designed to be used by a Company s senior management
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLANNING CHECKLIST For Development of Overall International Business Plan Thomas B. McVey 1 Introduction: The following Checklist is designed to be used by a Company s senior management
Marketing: Promotion Basics
 Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: 39 Marketing: Promotion Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher Write a short, accurate definition for each of the following
Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: 39 Marketing: Promotion Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher Write a short, accurate definition for each of the following
GLOBAL MARKETING MIX
 GLOBAL MARKETING MIX http://www.tutorialspoint.com/international_business_management/global_marketing_mix.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Global Marketing combines the promotion and selling of goods and
GLOBAL MARKETING MIX http://www.tutorialspoint.com/international_business_management/global_marketing_mix.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Global Marketing combines the promotion and selling of goods and
REVIEW ONE. Name: Class: Date: Matching
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A REVIEW ONE Matching Complete the following using these terms. a. outsourcing b. diversity c. entrepreneur d. competitive differentiation e. strategic alliance f. capital g. vision
Name: Class: Date: ID: A REVIEW ONE Matching Complete the following using these terms. a. outsourcing b. diversity c. entrepreneur d. competitive differentiation e. strategic alliance f. capital g. vision
RED BANK REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL CURRICULUM MAP Course Title: Hospitality & Entertainment Marketing Grade Levels: 11, 12
 What is Hospitality Marketing Marketing Basics Hotel Marketing: A competitive Industry The Importance of Hospitality Marketing Types of Hospitality Markets Key Players in Hospitality Operations Selling
What is Hospitality Marketing Marketing Basics Hotel Marketing: A competitive Industry The Importance of Hospitality Marketing Types of Hospitality Markets Key Players in Hospitality Operations Selling
Advertising media - A
 Advertising media - A There is a large variety of media available to advertisers, and therefore advertisers must choose the medium/media which best deliver their message to potential customers in the most
Advertising media - A There is a large variety of media available to advertisers, and therefore advertisers must choose the medium/media which best deliver their message to potential customers in the most
Global Marketing. Fourth Edition. Kate Gillespie and. H. David Hennessey. 13 Routledge % Taylor & Francis Croup NEW YORK AND LONDON
 Global Marketing Fourth Edition Kate Gillespie and H. David Hennessey 13 Routledge % Taylor & Francis Croup NEW YORK AND LONDON Detailed Contents Preface Acknowledgments xix xxv 1 Introduction to Global
Global Marketing Fourth Edition Kate Gillespie and H. David Hennessey 13 Routledge % Taylor & Francis Croup NEW YORK AND LONDON Detailed Contents Preface Acknowledgments xix xxv 1 Introduction to Global
The Transformational Toy Manufacturing Industry
 The Transformational Toy Manufacturing Industry The Toy Manufacturing Industry The U.S. toy manufacturing industry is a highly concentrated industry including approximately 700 companies that generate
The Transformational Toy Manufacturing Industry The Toy Manufacturing Industry The U.S. toy manufacturing industry is a highly concentrated industry including approximately 700 companies that generate
What this topic is about. The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing
 Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Effective Marketing What this topic is about The purpose of marketing Different approaches to marketing Segmentation Niche &mass markets B2C & B2B marketing What is Marketing? The process of identifying,
Bingo glossary marketing mix
 Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Bingo glossary marketing mix The management process which identifies customer wants, anticipates their future wants and then goes about satisfying them profitably. Where the market has been divided up
Chapter One Integrated Marketing Communications
 1 Chapter One Integrated Marketing Communications 1-1 1 Virgin Atlantic Still Red Hot 25 th Anniversary campaign Bold, distinctive imagery Global campaign Integrated across many platforms and channels
1 Chapter One Integrated Marketing Communications 1-1 1 Virgin Atlantic Still Red Hot 25 th Anniversary campaign Bold, distinctive imagery Global campaign Integrated across many platforms and channels
Push & Pull Marketing
 Push & Pull Marketing As we face the new year, foremost in the minds of business owners are how they will increase revenues in the current economic environment. This paper discusses two specific types
Push & Pull Marketing As we face the new year, foremost in the minds of business owners are how they will increase revenues in the current economic environment. This paper discusses two specific types
Understanding the Flow of Counterfeit and Gray Market Goods though the U.S. Automotive and Commercial Vehicle Parts Marketplace
 Understanding the Flow of Counterfeit and Gray Market Goods though the U.S. Automotive and Commercial Vehicle Parts Marketplace MEMA Brand Protection Council January 20091 Understanding the Flow of Counterfeit
Understanding the Flow of Counterfeit and Gray Market Goods though the U.S. Automotive and Commercial Vehicle Parts Marketplace MEMA Brand Protection Council January 20091 Understanding the Flow of Counterfeit
Lancôme. Jill Rose Lauren Ruegemer
 Lancôme Jill Rose Lauren Ruegemer Solution We suggest: Lancôme follow a differentiated market coverage strategy by introducing Lancôme Hyp. Lancôme change consumers perceptions and preferences for higher
Lancôme Jill Rose Lauren Ruegemer Solution We suggest: Lancôme follow a differentiated market coverage strategy by introducing Lancôme Hyp. Lancôme change consumers perceptions and preferences for higher
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18
 MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
MKTG301: PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING DEFINITIONS: CHAPTER 18 Communication (1) The process of conveying a message to others, which requires six elements: a source, a message, a channel of communication, a
ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX
 ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX 1. A company's total marketing communications mix consists of a special blend of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct-marketing tools
ADVERTISING IN PROMOTIONAL MIX 1. A company's total marketing communications mix consists of a special blend of advertising, sales promotion, public relations, personal selling, and direct-marketing tools
ICC POLICY STATEMENT ON FREEDOM OF COMMERCIAL COMMUNICATION POLICY STATEMENT
 ICC POLICY STATEMENT ON FREEDOM OF COMMERCIAL COMMUNICATION POLICY STATEMENT Prepared by the ICC Commission on Marketing and Advertising 240/474 rev November 2015 Freedom of commercial communication Prepared
ICC POLICY STATEMENT ON FREEDOM OF COMMERCIAL COMMUNICATION POLICY STATEMENT Prepared by the ICC Commission on Marketing and Advertising 240/474 rev November 2015 Freedom of commercial communication Prepared
A primer in Entrepreneurship
 Prof. Dr. Institute for Strategy and Business Economics Spring semester2008 Chapter 5: Industry and Competitor Analysis Table of Contents I. Industry Analysis II. IV. The Importance of Industry Versus
Prof. Dr. Institute for Strategy and Business Economics Spring semester2008 Chapter 5: Industry and Competitor Analysis Table of Contents I. Industry Analysis II. IV. The Importance of Industry Versus
Chapter 6. Transfer Pricing Methods. 6.1. Introduction to Transfer Pricing Methods
 Chapter 6 Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1. Introduction to Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1.1. This part of the Chapter describes several transfer pricing methods that can be used to determine an arm s length
Chapter 6 Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1. Introduction to Transfer Pricing Methods 6.1.1. This part of the Chapter describes several transfer pricing methods that can be used to determine an arm s length
Achieving Competitive Advantage with Information Systems
 Chapter 3 Achieving Competitive Advantage with Information Systems 3.1 Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES How does Porter s competitive forces model help companies develop
Chapter 3 Achieving Competitive Advantage with Information Systems 3.1 Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES How does Porter s competitive forces model help companies develop
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
 Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
Integrated Marketing Strategy Dr. Richard Sjolander 2003 The Purpose of Integrated Marketing s is to Communicate with a Target Audience Promotion: or Applied marketing communication Attempts to: Inform
European Payment Card Systems for the 21 st Century. A paper from MasterCard Europe
 U European Payment Card Systems for the 21 st Century A paper from MasterCard Europe For four decades, MasterCard Europe 1 has been working successfully with European banks to deliver secure, efficient
U European Payment Card Systems for the 21 st Century A paper from MasterCard Europe For four decades, MasterCard Europe 1 has been working successfully with European banks to deliver secure, efficient
Chapter 2: Analyzing a Dealership s Financial Statements & Operations
 Chapter 2: Analyzing a Dealership s Financial Statements & Operations To analyze a dealership s operations, a close look must be taken at the day to day operations as well as examining the dealership s
Chapter 2: Analyzing a Dealership s Financial Statements & Operations To analyze a dealership s operations, a close look must be taken at the day to day operations as well as examining the dealership s
CHAPTER 11 PRODUCT STRATEGIES: BRANDING AND PACKAGING DECISIONS
 CHAPTER 11 PRODUCT STRATEGIES: BRANDING AND PACKAGING DECISIONS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following cannot be used as a trademark? a) a word b) a name c) a symbol d) a device e) all of them can be
CHAPTER 11 PRODUCT STRATEGIES: BRANDING AND PACKAGING DECISIONS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following cannot be used as a trademark? a) a word b) a name c) a symbol d) a device e) all of them can be
The Marketing Plan. The business must make decisions on how to apply its resources to the target market(s).
 The Marketing Plan The most important part of a business plan is the Marketing Plan. To keep one s business on course this plan must be geared toward the business s mission its product and service lines,
The Marketing Plan The most important part of a business plan is the Marketing Plan. To keep one s business on course this plan must be geared toward the business s mission its product and service lines,
Marketing Planning How to Identify a Target Market and Prepare a Customer Profile
 Marketing Planning How to Identify a Target Market and Prepare a Customer Profile 1. What You Should Know Before Getting Started In order to market your product or service, it is imperative that you tailor
Marketing Planning How to Identify a Target Market and Prepare a Customer Profile 1. What You Should Know Before Getting Started In order to market your product or service, it is imperative that you tailor
An Introduction to Integrated Marketing Communications
 An Introduction to Integrated Marketing Communications Using IMC To Market Las Vegas 1 Creating a Unique Brand Identity for Las Vegas *Click outside of the video screen to advance to the next slide Taking
An Introduction to Integrated Marketing Communications Using IMC To Market Las Vegas 1 Creating a Unique Brand Identity for Las Vegas *Click outside of the video screen to advance to the next slide Taking
Economic Systems. 1. MARKET ECONOMY in comparison to 2. PLANNED ECONOMY
 Economic Systems The way a country s resources are owned and the way that country takes decisions as to what to produce, how much to produce and how to distribute what has been produced determine the type
Economic Systems The way a country s resources are owned and the way that country takes decisions as to what to produce, how much to produce and how to distribute what has been produced determine the type
Creating value through the marketing mix An Aldi case study
 Creating value through the marketing mix An Aldi case study Introduction In increasingly competitive markets, consumers have a greater choice over where they buy their goods and services. For an organization
Creating value through the marketing mix An Aldi case study Introduction In increasingly competitive markets, consumers have a greater choice over where they buy their goods and services. For an organization
Highlight. 21 October 2015. OTT Services A Digital Turning Point of the TV Industry
 OTT Services A Digital Turning Point of the TV Industry Highlight 21 October 2015 The widespread availability of high-speed internet in developed countries like the US, the UK, and Korea has given rise
OTT Services A Digital Turning Point of the TV Industry Highlight 21 October 2015 The widespread availability of high-speed internet in developed countries like the US, the UK, and Korea has given rise
Chapter 5 Supply-Side Channel Analysis: Channel Structure and Membership Issues,
 Marketing Channels Making a decision on the channel structure is writing out a description of the channel member s types within the channel, the number or intensity of the type members which are within
Marketing Channels Making a decision on the channel structure is writing out a description of the channel member s types within the channel, the number or intensity of the type members which are within
Successful Sales and Marketing Strategies
 Successful Sales and Marketing Strategies Tim Hoerr Dennis Beard Don Elmore Mac MacGregor 1 Agenda Introduction: Dennis Beard Sales & marketing from a business development perspective: Tim Hoerr Marketing:
Successful Sales and Marketing Strategies Tim Hoerr Dennis Beard Don Elmore Mac MacGregor 1 Agenda Introduction: Dennis Beard Sales & marketing from a business development perspective: Tim Hoerr Marketing:
Marketing at McDonald s
 at McDonald s Careers McDonald s is one of the best known brands worldwide. This case study shows how McDonald s aims to continually build its brand by listening to its customers. It also identifies the
at McDonald s Careers McDonald s is one of the best known brands worldwide. This case study shows how McDonald s aims to continually build its brand by listening to its customers. It also identifies the
Chapter 19 Advertising. Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates
 Chapter 19 Advertising Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates Advertising Media Key Terms promotional advertising institutional advertising media print media transit advertising
Chapter 19 Advertising Section 19.1 Advertising Media Section 19.2 Media Measurement and Rates Advertising Media Key Terms promotional advertising institutional advertising media print media transit advertising
Written by: Richard P. Biggs, CEO Atlantric LLC Portland, OR, USA 1 678 231 9195 ~ www.atlantric.com
 10 Reasons to go International The international marketplace offers a world of business opportunities for American companies seeking to sell or source products worldwide. Not only can you tap into a world
10 Reasons to go International The international marketplace offers a world of business opportunities for American companies seeking to sell or source products worldwide. Not only can you tap into a world
Once a company determines it has exportable products, it must still consider other factors, such as the following:
 EXPORT STRATEGY ASSESSING A PRODUCT'S EXPORT POTENTIAL There are several ways to gauge the overseas market potential of products and services. (For ease of reading, products are mentioned more than services
EXPORT STRATEGY ASSESSING A PRODUCT'S EXPORT POTENTIAL There are several ways to gauge the overseas market potential of products and services. (For ease of reading, products are mentioned more than services
Chapter 11: Campaign Management
 Chapter 11: Campaign Management Overview Topics discussed: Campaign Management Process Campaign Planning and Development Campaign Execution Analysis & Control Campaign Feedback 2 Campaign A series of interconnected
Chapter 11: Campaign Management Overview Topics discussed: Campaign Management Process Campaign Planning and Development Campaign Execution Analysis & Control Campaign Feedback 2 Campaign A series of interconnected
Germany. Type: Large Market; Large Share. Original Equipment Rank. Aftermarket Rank
 Germany Type: Large Market; Large Share Germany ranks number 4 on ITA s list of top U.S. auto parts export markets. After several years of declining auto sales, Western Europe has slowly begun to show
Germany Type: Large Market; Large Share Germany ranks number 4 on ITA s list of top U.S. auto parts export markets. After several years of declining auto sales, Western Europe has slowly begun to show
CONTENTS WHAT IS ONLINE MARKETING? WHY IT'S IMPORTANT HOW TO GET STARTED // TRADITIONAL MARKETING // TYPES OF ONLINE MARKETING
 CONTENTS WHAT IS ONLINE MARKETING? // TRADITIONAL MARKETING // TYPES OF ONLINE MARKETING // MARKETING TYPE PROS AND CONS WHY IT'S IMPORTANT // NEW BUSINESS GENERATION // CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP DEVELOPMENT
CONTENTS WHAT IS ONLINE MARKETING? // TRADITIONAL MARKETING // TYPES OF ONLINE MARKETING // MARKETING TYPE PROS AND CONS WHY IT'S IMPORTANT // NEW BUSINESS GENERATION // CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP DEVELOPMENT
SECTION A Consists of a separate multiple choice paper. Each question is worth one mark. Attempt all 25 questions.
 Foundations of Marketing: B1072: 2012/13 Exam Paper This examination is in TWO sections. SECTION A Consists of a separate multiple choice paper. Each question is worth one mark. Attempt all 25 questions.
Foundations of Marketing: B1072: 2012/13 Exam Paper This examination is in TWO sections. SECTION A Consists of a separate multiple choice paper. Each question is worth one mark. Attempt all 25 questions.
DEVELOPING AND UTILIZING ELECTRONIC MEDIA
 1 CHAPTER 7-2/E DEVELOPING AND UTILIZING ELECTRONIC MEDIA Summary In summary, the term electronic media encompasses television, radio and telephone. Television and radio are commonly referred to as broadcast
1 CHAPTER 7-2/E DEVELOPING AND UTILIZING ELECTRONIC MEDIA Summary In summary, the term electronic media encompasses television, radio and telephone. Television and radio are commonly referred to as broadcast
Accenture 2013 Global Consumer Pulse Survey. Global & U.S. Key Findings
 Accenture Global Consumer Pulse Survey Global & U.S. Key Findings Contents Executive Summary Overview of the Switching Economy Key Findings Methodology and Survey Sample Copyright Accenture All rights
Accenture Global Consumer Pulse Survey Global & U.S. Key Findings Contents Executive Summary Overview of the Switching Economy Key Findings Methodology and Survey Sample Copyright Accenture All rights
Rexjournal ISSN 2321-1067 Renewable Research Journal
 Digital Marketing: Opportunities and Threats Rima Dinesh Puri Abstract Internet has become part of our daily lives. It plays role in various fields, may be to make friend or let friendship last, watching
Digital Marketing: Opportunities and Threats Rima Dinesh Puri Abstract Internet has become part of our daily lives. It plays role in various fields, may be to make friend or let friendship last, watching
Telecommunications, Media, and Technology. Leveraging big data to optimize digital marketing
 Telecommunications, Media, and Technology Leveraging big data to optimize digital marketing Leveraging big data to optimize digital marketing 3 Leveraging big data to optimize digital marketing Given
Telecommunications, Media, and Technology Leveraging big data to optimize digital marketing Leveraging big data to optimize digital marketing 3 Leveraging big data to optimize digital marketing Given
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications
 Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
Chapter 15: Integrated Marketing Communications Pride/Ferrell Foundations of Marketing Fourth Edition Prepared by Milton Pressley University of New Orleans Objectives 1. Discuss the nature of integrated
Monopolistic Competition
 Monopolistic Chapter 17 Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to: Permissions Department, Harcourt College
Monopolistic Chapter 17 Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to: Permissions Department, Harcourt College
A primer in Entrepreneurship
 Prof. Dr. Institutefor Strategy and Business Economics Where we are: Step 1 Step 2 Developing Successful Business Ideas 2008 Prentice Hall Chapter 5: Industry and Competitor Analysis Table of Contents
Prof. Dr. Institutefor Strategy and Business Economics Where we are: Step 1 Step 2 Developing Successful Business Ideas 2008 Prentice Hall Chapter 5: Industry and Competitor Analysis Table of Contents
OUTLINE FOR AN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLAN
 OUTLINE FOR AN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLAN Please type your plan single-spaced. The first stage in developing an international business plan is to undertake a preliminary country analysis. Presented below
OUTLINE FOR AN INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS PLAN Please type your plan single-spaced. The first stage in developing an international business plan is to undertake a preliminary country analysis. Presented below
Marketing Research Core Body Knowledge (MRCBOK ) Learning Objectives
 Fulfilling the core market research educational needs of individuals and companies worldwide Presented through a unique partnership between How to Contact Us: Phone: +1-706-542-3537 or 1-800-811-6640 (USA
Fulfilling the core market research educational needs of individuals and companies worldwide Presented through a unique partnership between How to Contact Us: Phone: +1-706-542-3537 or 1-800-811-6640 (USA
Principles of Marketing. by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond
 Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
Principles of Marketing by Jeff Tanner and Mary Anne Raymond Chapter 8 Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers 2010 Flat World Knowledge, Inc. Marketing Channels and Channel Partners Learning
MKTG 680. Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion. Standardization vs.
 MKTG 680 Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion Global Marketing Communications The primary purpose of marketing communications is to tell
MKTG 680 Chapter 13-14 Global Marketing Communications Decisions: Advertising, Public Relations, Sales Promotion Global Marketing Communications The primary purpose of marketing communications is to tell
Mobile Marketing Trends and small businesses
 Mobile Marketing Trends and small businesses LEGAL NOTICE The Publisher has strived to be as accurate and complete as possible in the creation of this report, notwithstanding the fact that he does not
Mobile Marketing Trends and small businesses LEGAL NOTICE The Publisher has strived to be as accurate and complete as possible in the creation of this report, notwithstanding the fact that he does not
Chapter 2 Market Structure, Types and Segmentation
 Market Structure There are a variety of differing market structures which are separated by the levels of competition that exist within each market and the market conditions in which the businesses operate.
Market Structure There are a variety of differing market structures which are separated by the levels of competition that exist within each market and the market conditions in which the businesses operate.
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e
 Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part II: Strategic Actions: Strategy Formulation Chapter 8: International Strategy 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or
Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases 9e Part II: Strategic Actions: Strategy Formulation Chapter 8: International Strategy 2011 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or
Agricultural Marketing. Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities. Commodity or Niche? MARKETS DEFINED
 Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities Mykel Taylor Assistant Professor Dept. of Agricultural Economics NCKS Commercial Enterprises Conference February 25, 2012 Agricultural Marketing Commodity
Direct Marketing Strategies and Opportunities Mykel Taylor Assistant Professor Dept. of Agricultural Economics NCKS Commercial Enterprises Conference February 25, 2012 Agricultural Marketing Commodity
Analyzing International Opportunities 12
 12: Analyzing International Opportunities 1 C H A P T E R T W E L V E Analyzing International Opportunities 12 Learning Objectives Explain each of the four steps in the market- and site-screening process.
12: Analyzing International Opportunities 1 C H A P T E R T W E L V E Analyzing International Opportunities 12 Learning Objectives Explain each of the four steps in the market- and site-screening process.
Contents. Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing. Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22. Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38
 Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Contents Part- I: Introduction to Services Marketing Chapter 1 Understanding Services 3-22 Chapter 2 The Nature of Services Marketing 23-38 Part- II: The Customer Experience Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior
Guide to Market Research and Analysis
 The Orangeville & Area Small Business Enterprise Centre (SBEC) 87 Broadway, Orangeville ON L9W 1K1 519-941-0440 Ext. 2286 or 2291 [email protected] www.orangevillebusiness.ca Supported by its Partners:
The Orangeville & Area Small Business Enterprise Centre (SBEC) 87 Broadway, Orangeville ON L9W 1K1 519-941-0440 Ext. 2286 or 2291 [email protected] www.orangevillebusiness.ca Supported by its Partners:
ADVERTISING Curriculum Content Frameworks
 ADVERTISING Curriculum Content Frameworks Prepared by Jackie Phillips, El Dorado High School Facilitated by Karen Chisholm, Program Manager Office of Assessment and Curriculum Arkansas Department of Workforce
ADVERTISING Curriculum Content Frameworks Prepared by Jackie Phillips, El Dorado High School Facilitated by Karen Chisholm, Program Manager Office of Assessment and Curriculum Arkansas Department of Workforce
Netflix Strategic Analysis
 XMBA 2013 Netflix Strategic Analysis Global Strategic Thinking Joey M. Reed, XMBA 2013 4/17/2013 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In 1999, Reed Hastings launched an online movie rental service called, Netflix. The company
XMBA 2013 Netflix Strategic Analysis Global Strategic Thinking Joey M. Reed, XMBA 2013 4/17/2013 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In 1999, Reed Hastings launched an online movie rental service called, Netflix. The company
Coca-Cola Case Analyses. <Student Name> <Name and Section # of course> <Instructor Name> <Date>
 Running Head: COCA-COLA CASE Coca-Cola Case Analyses Coca-Cola Case 2 Coca-Cola Case Analyses This paper is about the company Coca-Cola
Running Head: COCA-COLA CASE Coca-Cola Case Analyses Coca-Cola Case 2 Coca-Cola Case Analyses This paper is about the company Coca-Cola
Chapter 13 International Trade: Does it Jeopardize American Jobs
 Chapter 13 International Trade: Does it Jeopardize American Jobs Multiple Choice Questions 1. In 2006, trade made up percent of the U.S. economy. a. 1.3 b. 5.0 C. 11.5 d. 22.7 2. In 2005, the U.S. experienced
Chapter 13 International Trade: Does it Jeopardize American Jobs Multiple Choice Questions 1. In 2006, trade made up percent of the U.S. economy. a. 1.3 b. 5.0 C. 11.5 d. 22.7 2. In 2005, the U.S. experienced
ACPSA Issue Brief #4: Arts and Cultural Contributions to the Creative Economy
 Office of Research & Analysis National Endowment for the Arts January 2015 ACPSA Issue Brief #4: Arts and Cultural Contributions to the Creative Economy The United States currently lacks an official definition
Office of Research & Analysis National Endowment for the Arts January 2015 ACPSA Issue Brief #4: Arts and Cultural Contributions to the Creative Economy The United States currently lacks an official definition
MTV vs. Cartoon Network in the United States and Brazil
 MTV vs. Cartoon Network in the United States and Brazil Jan Young MBA 04 2004 by The Trustees of Columbia University in the City of New York. All rights reserved. CHAZEN WEB JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS
MTV vs. Cartoon Network in the United States and Brazil Jan Young MBA 04 2004 by The Trustees of Columbia University in the City of New York. All rights reserved. CHAZEN WEB JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS
Entertainment Marketing
 September Sports & Entertainment Marketing 1 Marketing Concepts Explain basic marketing What is marketing? concepts.. What are the activities Define marketing mix. involved? Define 7 key marketing flier
September Sports & Entertainment Marketing 1 Marketing Concepts Explain basic marketing What is marketing? concepts.. What are the activities Define marketing mix. involved? Define 7 key marketing flier
A Service of SRI World Group, Inc. 74 Cotton Mill Hill A-255 Brattleboro, VT 05301 (802) 251-0110
 A Service of SRI World Group, Inc. 74 Cotton Mill Hill A-255 Brattleboro, VT 05301 (802) 251-0110 www.csrwire.com Printed on recycled paper Introduction Today, forward-thinking companies understand that
A Service of SRI World Group, Inc. 74 Cotton Mill Hill A-255 Brattleboro, VT 05301 (802) 251-0110 www.csrwire.com Printed on recycled paper Introduction Today, forward-thinking companies understand that
LECTURE 1 Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications. Marketing satisfying needs and wants through the exchange process.
 LECTURE 1 Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications Marketing satisfying needs and wants through the exchange process. The Marketing Management Process 1. Situation analysis (PESTL). 2. Objectives.
LECTURE 1 Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications Marketing satisfying needs and wants through the exchange process. The Marketing Management Process 1. Situation analysis (PESTL). 2. Objectives.
Applying Customer Analytics to Promotion Decisions WHITE PAPER
 Applying Customer Analytics to Promotion Decisions WHITE PAPER SAS White Paper Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 1 MEASURING EFFECTIVENESS OF MASS PROMOTIONS.... 1 ASKING THE RIGHT QUESTIONS.... 2 GETTING
Applying Customer Analytics to Promotion Decisions WHITE PAPER SAS White Paper Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 1 MEASURING EFFECTIVENESS OF MASS PROMOTIONS.... 1 ASKING THE RIGHT QUESTIONS.... 2 GETTING
The Implications of Marketing Trends
 The Implications of Marketing Trends Advertising in Canada plays a significant role in the Canadian economy with expenditures expecting to grow to more than $23.3 billion by 211. Advertising Expenditures
The Implications of Marketing Trends Advertising in Canada plays a significant role in the Canadian economy with expenditures expecting to grow to more than $23.3 billion by 211. Advertising Expenditures
Power Struggles and Sales Promotion
 Chapter 18 Sales Promotion Power Struggles and Sales Promotion Sales promotion plays a key strategic role in the channel of distribution Big name brands need to supported with sales promotion and POP in
Chapter 18 Sales Promotion Power Struggles and Sales Promotion Sales promotion plays a key strategic role in the channel of distribution Big name brands need to supported with sales promotion and POP in
Views on media channels marketers and consumers views on effectiveness
 Views on media channels marketers and consumers views on effectiveness Executive Summary How do Australian consumers want to hear from brands and how well do marketers know their audience? Two surveys
Views on media channels marketers and consumers views on effectiveness Executive Summary How do Australian consumers want to hear from brands and how well do marketers know their audience? Two surveys
PROJECT PROPOSAL: PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS AND FIGHT AGAINST COUNTERFEITING IN THE T/C SECTOR
 PROJECT PROPOSAL: PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS AND FIGHT AGAINST COUNTERFEITING IN THE T/C SECTOR Protecting intellectual property and dealing with counterfeiting are vital to the textiles
PROJECT PROPOSAL: PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS AND FIGHT AGAINST COUNTERFEITING IN THE T/C SECTOR Protecting intellectual property and dealing with counterfeiting are vital to the textiles
THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE THEORY AS A GROWTH STRATEGY
 THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE THEORY AS A GROWTH STRATEGY Management Marketing - Tourism Ec. Ecaterina Nicoleta Ciurez Ph.D University of Craiova, Faculty of Economics and Business Administration, Craiova,
THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE THEORY AS A GROWTH STRATEGY Management Marketing - Tourism Ec. Ecaterina Nicoleta Ciurez Ph.D University of Craiova, Faculty of Economics and Business Administration, Craiova,
MKTG 680. Chapter 8 Exporting, Importing, and Sourcing. Introduction. Introduction. Export Selling vs. Export Marketing
 MKTG 680 Chapter 8 Exporting, Importing, and Sourcing Introduction Export Selling vs. Export Marketing Export selling involves selling the same product, at the same price, with the same promotional tools
MKTG 680 Chapter 8 Exporting, Importing, and Sourcing Introduction Export Selling vs. Export Marketing Export selling involves selling the same product, at the same price, with the same promotional tools
BRAND REPUTATION AND COSTUMER TRUST
 BRAND REPUTATION AND COSTUMER TRUST Reza Mohammad Alizadeh Movafegh 1, Hamid Fotoohi 2 1 M.A. Student of Business Management, Islamic Azad University, Rasht Branch, Rasht, Iran 2 Department of Agricultural
BRAND REPUTATION AND COSTUMER TRUST Reza Mohammad Alizadeh Movafegh 1, Hamid Fotoohi 2 1 M.A. Student of Business Management, Islamic Azad University, Rasht Branch, Rasht, Iran 2 Department of Agricultural
BEER INSTITUTE ADVERTISING AND MARKETING CODE. Introduction
 BEER INSTITUTE ADVERTISING AND MARKETING CODE Introduction Beer is a legal beverage meant to be consumed responsibly. Its origins are ancient, and it has held a respected position in nearly every culture
BEER INSTITUTE ADVERTISING AND MARKETING CODE Introduction Beer is a legal beverage meant to be consumed responsibly. Its origins are ancient, and it has held a respected position in nearly every culture
1. MEDIA OVERVIEW 1 WEEK DEDICATED COURSE
 Module 1: 1. MEDIA OVERVIEW 1 WEEK DEDICATED COURSE 2. MARKETING MANAGEMENT a. Consumer behavior b. Management skills c. Market Research d. The Brand -product & corporate branding e. Public Relations f.
Module 1: 1. MEDIA OVERVIEW 1 WEEK DEDICATED COURSE 2. MARKETING MANAGEMENT a. Consumer behavior b. Management skills c. Market Research d. The Brand -product & corporate branding e. Public Relations f.
ECOMMERCE FOR BRANDS FOUR WAYS FOR BRANDS TO SELL MORE WITH THEIR WEBSITE
 ECOMMERCE FOR BRANDS FOUR WAYS FOR BRANDS TO SELL MORE WITH THEIR WEBSITE INTRODUCTION ecommerce is expected to become a $188 billion dollar industry in 2011. While setting up and managing an ecommerce
ECOMMERCE FOR BRANDS FOUR WAYS FOR BRANDS TO SELL MORE WITH THEIR WEBSITE INTRODUCTION ecommerce is expected to become a $188 billion dollar industry in 2011. While setting up and managing an ecommerce
Advertising Research
 Advertising Research By Jerry W. Thomas A growing share of consumergoods media spending is shifting away from traditional advertising media (television, radio, print, and outdoor). The proliferation of
Advertising Research By Jerry W. Thomas A growing share of consumergoods media spending is shifting away from traditional advertising media (television, radio, print, and outdoor). The proliferation of
South Plainfield Public Schools Sports & Entertainment Marketing Scope and Sequence of Curriculum Grades 10-12 Date August 2011
 Unit (Domain): Part I: What is Sports and Entertainment Marketing? Essential Question(s): What seven key functions is the basis of all marketing activities? What is sports marketing? What is entertainment
Unit (Domain): Part I: What is Sports and Entertainment Marketing? Essential Question(s): What seven key functions is the basis of all marketing activities? What is sports marketing? What is entertainment
CHAPTER 6 BUSINESS-GOVERNMENT TRADE RELATIONS
 CHAPTER 6 BUSINESS-GOVERNMENT TRADE RELATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the political, economic, and cultural motives behind governmental intervention in trade. 2. List and explain the methods governments
CHAPTER 6 BUSINESS-GOVERNMENT TRADE RELATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the political, economic, and cultural motives behind governmental intervention in trade. 2. List and explain the methods governments
Using Choice-Based Market Segmentation to Improve Your Marketing Strategy
 Using Choice-Based Market Segmentation to Improve Your Marketing Strategy Dr. Bruce Isaacson, President of MMR Strategy Group Dominique Romanowski, Vice President of MMR Strategy Group 16501 Ventura Boulevard,
Using Choice-Based Market Segmentation to Improve Your Marketing Strategy Dr. Bruce Isaacson, President of MMR Strategy Group Dominique Romanowski, Vice President of MMR Strategy Group 16501 Ventura Boulevard,
