Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a hydrophilic nonionic polymer
|
|
|
- Eleanore Ford
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effet of polyethylene glyol on the liquid liquid phase transition in aqueous protein solutions Onofrio Annunziata, Neer Asherie, Aleksey Lomakin, Jayanti Pande, Olutayo Ogun, and George B. Benedek* Department of Physis, Center for Materials Siene and Engineering, and Materials Proessing Center, Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology, Cambridge, MA Contributed by George B. Benedek, August 22, 2002 We have studied the effet of polyethylene glyol (PEG) on the liquid liquid phase separation (LLPS) of aqueous solutions of bovine D-rystallin ( D), a protein in the eye lens. We observe that the phase separation temperature inreases with both PEG onentration and PEG moleular weight. PEG partitioning, whih is the differene between the PEG onentration in the two oexisting phases, has been measured experimentally and observed to inrease with PEG moleular weight. The measurements of both LLPS temperature and PEG partitioning in the ternary D-PEGwater systems are used to suessfully predit the loation of the liquid liquid phase boundary of the binary D-water system. We show that our LLPS measurements an be also used to estimate the protein solubility as a funtion of the onentration of rystallizing agents. Moreover, the slope of the tie-lines and the dependene of LLPS temperature on polymer onentration provide a powerful and sensitive hek of the validity of exluded volume models. Finally, we show that the inrease of the LLPS temperature with PEG onentration is due to attrative protein protein interations. PEG ternary mixtures solubility partitioning Polyethylene glyol (PEG) is a hydrophili nonioni polymer used in many biohemial and industrial appliations. Due to its nontoxi harater, this hemial an be found in osmetis, food, and pharmaeutial produts. The mild ation of PEG on the biologial ativity of ell omponents explains the suess of this polymer in biotehnologial appliations. PEG is ommonly used for liquid liquid partitioning and preipitation of biomaromoleules (1, 2). In protein rystallography, PEG is onsidered the most suessful preipitating agent for the prodution of protein rystals, the ruial step for the determination of the moleular struture of a protein. All these appliations make PEG by far the most widely used polymer in aqueous solutions of biologial moleules (1, 3). Due to the extensive pratial use of PEG as a preipitating agent for proteins, it is of fundamental importane to understand protein protein and protein PEG interations in protein PEG water ternary systems. These interations are often desribed in terms of a depletion fore, whih arises beause the polymer is depleted in the region between adjaent proteins (4, 5). Depletion fore models have been suessful in desribing the effet of nonadsorbing polymers on olloidal suspensions (6 10). Protein PEG water solutions have been investigated by several tehniques (4, 5, 11 14). Small-angle x-ray- (4) and lightsattering (5) measurements generally onfirmed that total protein protein interations an be desribed in terms of depletion effets. The mirosopi interpretation used in the above studies is derived from olloid polymer models. To model the effet of PEG, a depletion omponent is added to the original protein protein pair interation potential. This mirosopi modeling, however, does not provide information about the atual protein PEG interations in the ternary system. Dialysis experiments, whih desribe the effet of PEG partitioning (i.e., the differene of PEG onentration) between two solutions separated by a membrane not permeable to protein moleules, give information on protein PEG interations only when protein protein interations are absent (12, 15). Studies of the solubility of protein rystals in the presene of PEG have been arried out to investigate protein protein and protein PEG interations. However, to interpret the results, assumptions about the properties of the rystal are required. Moreover, simple exluded volume models fail to desribe protein solubility as a funtion of PEG moleular weight (16). The disrepany between model and experiment beomes partiularly large for PEG of lower moleular weights (11). Furthermore, the magnitude of the protein PEG interations hanges from protein to protein in a way that does not orrelate with the simple exluded volume senario (11, 15). Liquid liquid phase separation (LLPS) an be used as a diret tool for probing both protein protein and protein PEG interations. It has been shown that the position of the liquid liquid boundaries provides insight about the nature and magnitude of the protein protein interations (17 20). The advantage of LLPS analysis with respet to measurements of protein solubility is that data interpretation requires no assumptions regarding rystal phase properties (11, 21). LLPS is important also for the analysis of nonequilibrium properties of the system. Beause the nuleation of protein rystals is enhaned in proximity of the LLPS, this phase boundary is believed to be impliated in protein rystallization kinetis (22, 23). We present an experimental investigation of the effet of low moleular weight PEG on the LLPS of aqueous solutions of bovine D-rystallin ( D). D is a member of the -rystallin family of lens proteins, whih are involved in atarat formation (24). The phase diagram of aqueous -rystallins has been well haraterized, and several members of the family, inluding D, have attrative interations leading to LLPS of the orresponding aqueous solutions (17, 20, 25, 26). D is a protein with a simple globular struture (27) and is weakly harged at the ph value ( 7) used in our measurements (28). The experiments were performed at a PEG onentration of 5% in weight, whih falls within the range of onentrations used for protein rystal growth (3). The LLPS properties of the protein PEG water ternary system are desribed by a oexistene surfae in the phase diagram. This oexistene surfae represents the LLPS temperature as a funtion of protein onentration, 1, and PEG onentration, 2. At a fixed temperature, the LLPS properties of the system are desribed by an isothermal oexistene urve, whih gives the onentrations ( 1 I, 2 I ) and ( 1 II, 2 II ) of the oexisting phases, I and II. The partitioning of the omponents in the two oexisting phases is desribed by tie-lines onneting the points ( 1 I, 2 I ) and ( 1 II, 2 II ) of the oexistene urve. The ritial point, ( 1, 2 ), is defined as the point of the oexistene urve where the ondition ( 1 I, 2 I ) ( 1 II, 2 II ) ours. The loation of this point as a funtion of the temperature is desribed by a ritial line on the oexistene surfae. Abbreviations: PEG, polyethylene glyol; LLPS, liquid liquid phase separation; D, D-rystallin. *To whom orrespondene should be addressed. [email protected]. BIOPHYSICS gi doi pnas PNAS Otober 29, 2002 vol. 99 no
2 Materials and Methods Bovine D, whih has a moleular mass of 20,700 g mol, was isolated from 1- to 6-week-old alf lenses, obtained by overnight express from Anteh (Tyler, TX). Pure D was isolated and purified from these lenses by standard proedures desribed elsewhere (25, 29). The purity of the native sample was at least 95%, based on both ion-exhange and size-exlusion HPLC. The purified D was dialyzed exhaustively into sodium phosphate buffer (0.1 M, ph 7.1) that ontained sodium azide (0.02%). PEG with moleular masses ranging from 200 to 3,350 g mol (PEG200 PEG3350) and tetraethylene glyol (TEG, moleular mass g mol) were purhased from Sigma Aldrih and used without further purifiation. Sample moleular mass and polydispersity were analyzed by eletrospray ionization mass spetrometry at the Biopolymers Laboratory at the Center for Caner Researh at the Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology. Estimates of the average moleular mass were in agreement with the nominal values provided by the ompany. All polymers had a narrow moleular mass distribution with a polydispersity of about Protein PEG aqueous solutions were prepared as follows. Solutions ontaining dilute D in phosphate buffer were onentrated by ultrafiltration. When the desired protein onentration was reahed, a known weight of PEG was added to the protein solution. The onentration of D in the samples was determined by UV absorption at 280 nm, using the extintion oeffiient value of 2.11 mg 1 ml m 1 (26). The onentration of PEG in the samples was alulated by using the mass of PEG and the total volume of the solution. The volumetri ontribution of eah omponent is obtained by multiplying the mass of the omponent by the orresponding speifi volume, i.e., 0.71 ml g for D (30), 0.84 ml g for PEG (15) and ml g for the buffer. The LLPS temperature for a given protein PEG aqueous solution was determined by gradually lowering the temperature of the sample until louding was observed. The loud point was determined by the examination of the transmitted intensity temperature profile as previously desribed by Liu et al. (31). The oexisting phases were obtained by quenhing the sample at fixed temperature beneath the oexistene surfae. If after about 24 hours the two oexisting phases had not separated by gravity, entrifugation was used for the separation. The protein onentration in eah phase was determined by UV absorption. To determine the PEG onentration in eah of the oexisting phases, an aliquot of known weight was taken from eah phase, and the PEG was separated from the protein by ultrafiltration (Amion Miroon YM-10). The protein-free solution was weighed and the orresponding onentration of PEG determined by using a standardized refrative index detetor (Perkin Elmer LC-30 RI). The onentration of PEG in eah aliquot was then alulated from its measured value in the protein-free solution. To ensure that possible differenes in phosphate onentration in the two phases did not affet the results, the refrative index measurements were performed after isorati elution of the protein-free solution on a size-exlusion HPLC olumn, by using sodium phosphate buffer (0.1 M, ph 7.1) with a flow rate of 1 ml min. An Ohpak SB HQ olumn (size 8mm 300 ml) from Phenomenex was used for the PEG200 and PEG400 solutions. For PEG1000, the Superdex 75 HR olumn (size mm) from Amersham Pharmaia Bioteh was preferred for its higher resolution. The proedure was verified with protein PEG aqueous solutions of known omposition. In all ases, the measured protein and PEG onentrations in the two oexisting phases were onsistent with the protein and PEG onentrations in the original homogeneous samples. Fig. 1. LLPS temperature at onstant PEG onentration of 50 mg ml for the D-PEG-water ternary system. The average moleular masses are: 200 g mol ( ), 400 g mol (F), 1,000 g mol (}), 1,450 g mol (Œ), and 3,350 g mol ( ). The solid urves are guides for the eye. The values for the D-tetraethylene glyol-water ternary system are represented by open squares ( ). We draw the oexistene urve for the D-water binary system (dashed urve). The vertial bars ( ) loate the ritial point. Results We desribe the omposition of the D-PEG-water systems by the protein (omponent 1) onentration 1 and the PEG (omponent 2) onentration inside the protein-free volume, 2s. If is the protein speifi volume and 1 is the protein volume fration, then 2s is equal to 2 (1 ). The hoie of 2s instead of 2 to present our results is justified by the following argument. We onsider as a referene system one in whih the partiles of omponent 2 have a negligible size and do not introdue speifi hemial interations in the system. In this referene ase, the different values of 2 between the two oexisting phases are entirely determined by the exlusion of omponent 2 from the volume oupied by omponent 1. Here, the ondition of hemial equilibrium is expressed by the relation: 2s II 2s. Thus, in our systems, any observed differene in I 2s between two oexisting phases is related to the finite size and speifi hemial properties of the PEG moleules. In Fig. 1, we present our measurements of the LLPS temperature, T ph, for D-PEG-water ternary solutions at onstant PEG onentration of 2s 50 mg ml and with several polymer average moleular masses: 200 g mol (filled squares), 400 g mol (irles), 1,000 g mol (diamonds), 1,450 g mol (upright triangles), and 3,350 g mol (inverted triangles). We also report measurements of temperature of phase separation for the D gi doi pnas Annunziata et al.
3 Table 1. The values of the parameters haraterizing the ternary oexistene surfaes 2s,mg ml T,K ( T ph 1 ) 2s, 10 3 Kmg 1 ml ( 2s 1 ) Tph 2s 10 3 mg 1 ml, ( T ph 2s ) 1, K 1 mg 1 ml T 0,K PEG PEG PEG tetraethylene glyol-water at the same value of 2s (open squares). TEG essentially has the same moleular weight as PEG200, but, in ontrast to PEG, is monodisperse. We see from the figure that the two sets of measurements, for TEG and for PEG200, overlap within the experimental error and onlude that the effets due to polydispersity are small. In Fig. 1, we also show the oexistene urve for the binary aqueous protein system (dashed urve) (29). The phase boundaries of the ternary systems are loated at higher T ph than that of the binary system, and the differene inreases with PEG moleular weight. The ritial points, shown by vertial bars in Fig. 1, were identified by the examination of the transmitted intensity temperature profile as previously desribed by Liu et al. (31). In all ases, the value of protein ritial onentration (about 290 mg ml) is not affeted by PEG within the experimental error. On the other hand, the slope of T ph at the ritial point, ( T ph 1 ) 2s, is positive and inreases with the PEG moleular weight, in ontrast with the zero slope required for the protein water binary system. In Table 1, we report the values of the PEG onentration, 2s, the ritial temperature, T, and the slope ( T ph 1 ) 2s. In Fig. 2, we present our experimental data (filled irles) of the oexisting values ( I 1, I 2s ) and ( II 1, II 2s ) for the D-PEG-water solutions having PEG average moleular weight: 200 g mol (279.2 K, ase A), 400 g mol (281.7 K, ase B), and 1000 g mol (290.3 K, ase C). The pairs of points representing the oexisting phases are onneted by straight lines (tie-lines). The dashed urves are eye guides representing the oexisting urves. In all three ases, the oexisting phases were obtained by quenhing samples with the same initial protein onentration of 300 mg ml but with different initial PEG onentrations. The temperatures for the measurements of the oexistene urves were hosen so that they lie above the ritial temperature of the protein water binary system but below the ritial temperature of the orresponding ternary system in Fig. 1. Beause the protein ritial onentration, 1, is equal to the average onentration ( I 1 II 1 ) 2 in the limit of I 1 II 1 0, we determine 1 by plotting ( I 1 II 1 ) 2 as a funtion of I 1 II 1. The resulting values of the ritial onentrations (vertial bars in Fig. 2) are, within the experimental error, the same as the value reported for the binary protein water system. An interesting feature of the phase diagram is that the differene of PEG onentration between the two oexisting phases inreases as the PEG moleular weight inreases. To desribe the effet of PEG moleular weight on PEG partitioning, we onsider the normalized slope of the tie-lines at the ritial point: ( 2s 1 ) Tph 2s. This I quantity an be obtained by plotting the inremental ratio (ln 2s ln II 2s ) ( I 1 II 1 ) as a funtion of I 1 II 1 and onsidering the limit of I 1 II 1 0. In Table 1, we an see that ( 2s 1 ) Tph 2s inreases with the PEG moleular weight. The protein volume fration in the protein-rih phase is omparable to the protein volume fration in the rystal, whih is ( mg ml) (27, 32). The nonnegligible values of PEG onentration of the protein-rih phases reported for the D-PEG1000-water system suggest that the rystal phase ould aommodate polymer oils with moleular weight equal to or lower than 1,000 g mol. The behavior of the oexistene surfae is desribed by the three slopes ( 2s 1 ) Tph, ( T ph 2s ) 1, and ( T ph 1 ) 2s, whih are related to eah other by the mathematial relationship: T ph 1 2s T ph 2s 1 2s 1 T ph. [1] It is important to observe that Eq. 1 is true only for ternary systems. Due to the presene of the two buffer salts (dibasi and Fig. 2. Coexisting surfaes at onstant temperature for the D-PEG-water ternary system with PEG average moleular mass: 200 g mol (279.2 K, ase A), 400 g mol (281.7 K, ase B), and 1,000 g mol (290.3 K, ase C). The pairs of points representing the oexisting phases (F) are onneted by the tie-lines (solid lines). The dashed urves are guides for the eye, and the vertial bars ( ) loate the ritial point. BIOPHYSICS Annunziata et al. PNAS Otober 29, 2002 vol. 99 no
4 monobasi sodium phosphate), our protein aqueous solutions ontain more than three omponents. We know that salt partitioning is unimportant if PEG is not in the solution, beause the protein-buffer system is well desribed as a binary system [for example, the ritial point is at the maximum of the LLPS urve (26)]. Therefore, in the protein PEG buffer system, it is only beause of the presene of PEG that salt partitioning may our. We will show that Eq. 1 suessfully desribes our experimental results, whih suggests that salt partitioning is insignifiant insofar as the validity of Eq. 1 is onerned. We apply Eq. 1 on the ritial line of the oexistene surfaes. Beause the ritial temperature, T, of the D PEG water systems (with 2s 50 mg ml) is higher than the ritial temperature, T 0, of the D-water system (Fig. 1), the quantity ( T ph 2s ) 1 is positive. At the ritial point, the slope ( 2s 1 ) Tph of the oexistene surfae is negative beause it oinides with the slope of the tie-lines (Fig. 2). Eq. 1 shows that the slope ( T ph 1 ) 2s is positive, as found experimentally (Fig. 1 and Table 1). The slope ( T ph 2s ) 1 an be alulated, by using Eq. 1, from the values of 2s,( T ph 1 ) 2s, and ( 2s 1 ) Tph 2s reported in Table 1. We have assumed that the quantity, ( 2s 1 ) Tph 2s, whih is obtained from our measurements of oexistene urves, is not a funtion of the temperature and PEG onentration within our experimental domain. The alulated values of ( T ph 2s ) 1, reported in Table 1, are onsistent with the experimentally observed dependene of the ritial temperature as a funtion of PEG moleular weight (Fig. 1). Indeed, we an quantitatively ompare the experimental hange of ritial temperature between the ternary and the binary systems, shown in Fig. 1 for eah PEG moleular weight, with the hange predited from the alulated values of ( T ph 2s ) 1. Speifially, we may estimate the ritial temperature, T 0, of the D-water system from the expression: T 0 T ( T ph 2s ) 1 2s. Thereby, we obtain the alulated values of T 0, whih are reported in last olumn of Table 1. These are in aeptable agreement with the experimental value of K (29). Hene, using only the information obtained from the properties of the ternary oexistene surfaes, we are able to estimate reliably the loation of the binary liquid liquid phase boundary. This information an be most valuable when LLPS of protein water systems is not experimentally observable beause it is inaessible due to either the freezing of the system or the denaturation of the protein at high temperature, whih is important for proteins with lower onsolute ritial points (33). Disussion Our previous analysis shows that the behavior of the oexistene surfaes at the ritial point an be desribed by two distint features: the slope of the tie-lines and the dependene of LLPS temperature on PEG onentration. To analyze the physial fators that determine these two features of the oexistene surfaes, we introdue the free energy of the system. We define the quantity F, representing the differene, at onstant volume, V, and temperature, T, between the Helmholtz free energy of the virtually inompressible protein PEG water system and the pure water system. The hanges of F due to the replaement (at onstant volume) of 1 water moles by 1 mole of protein and 2 water moles by 1 mole of PEG are respetively desribed by the differenes of hemial potentials, 1 protein 1 water and 2 PEG 2 water. A ternary inompressible system may be equivalently treated as a binary ompressible system where 1 and 2 are the hemial potentials of the two effetive omponents (17). The quantities 1 and 2 will be indiated as the protein and PEG effetive hemial potentials. It is onvenient to introdue the redued free energy fˆ (F F 0 ) RTV, where F 0 is the standard free energy, and R is the ideal gas onstant. If the onentration of PEG, 2, is relatively small, the redued free energy is, to first-order approximation with respet to 2, given by the following equation: fˆ 1, 2, T fˆ 1,0,T 2 ln 2 e 2 1, T. [2] In Eq. 2, fˆ( 1,0,T) is the redued free energy of the binary protein water system, whereas 2 ln( 2 e) and 2 ( 1, T) are the ontributions to the redued free energy assoiated with the replaement of water moleules by PEG moleules at onstant V and T. The ontribution of PEG to the ideal mixing entropy of the system is represented by the term 2 ln( 2 e), whereas the quantity 2 ( 1, T) is the first term in a series expansion desribing the hange of the redued free energy over and above the ideal mixing entropy. This approximation is aeptable beause our experimental PEG onentrations are generally well below the threshold for polymer polymer interpenetration, i.e., we are in the dilute regime (5). If we differentiate Eq. 2 with respet to the onentrations, 1 and 2, at onstant V and T, we obtain the following expressions for the redued effetive hemial potentials: ˆ 1 1, 2, T ˆ 1 1, T 2 1 T, ˆ 2 1, 2, T ln 2 1, T, [3a] [3b] where ˆ i ( i i 0 ) RT (with i 1, 2), i 0 (T) ( F 0 i ) T,V V, and the quantity ˆ 1 ( 1, T) ˆ 1( 1,0,T) is the protein effetive hemial potential orresponding to the protein water binary system. The two rossderivatives of the hemial potentials, ( ˆ 1 2 ) 1,T and ( ˆ 2 1 ) 2,T, are both equal to ( 1 ) T. This quantity haraterizes the protein PEG interations. Eq. 3a and 3b fully haraterize all the experimental observable features of the oexistene surfaes. Speifially, they enable us to analyze the quantities ( 2 1 ) ˆ 2,T (i.e., the slope of the tie-lines) and ( T ph 2 ) 1. The Slope of the Tie-Lines. If we differentiate Eq. 3a with respet to 2 at onstant 1 and T, and Eq. 3b with respet to 1 at onstant ˆ2 and T, we obtain: ˆ 1 2 1,T 1 1 T 2 2. [4] 1 ˆ 2,T Experimentally, the quantity ( 2 1 ) ˆ an be found from the limiting value of the slope of the tie-lines 2,T at the ritial point. If we apply Eq. 4 to our experimental tie-line, we observe that ( ˆ 1 2 ) 1,T ( 1 ) T is positive and inreases with the PEG moleular weight. The slope of the tie-lines an be used to predit the effet of PEG on protein solubility. If protein rystals (solid phase) are in thermodynami equilibrium with the liquid phase, ˆ1 must be equal to its value in the solid phase, ˆ1S. For relatively low protein onentrations, ˆ 1 ( 1, T) ln 1. Thus, using the equality of hemial potentials and Eq. 3a, we find: ln 1 ˆ 1S ( 1 ) T 2 (11). This relationship gives the protein solubility, 1, as a funtion of PEG onentration, 2. The dependene of ˆ1S on 1 and 2 is expeted to be very weak. Thus the frational derease of protein solubility with PEG onentration is fully determined by the value of ( 1 ) T, whih is proportional to the slope of the tie-line (see Eq. 4). Therefore the magnitude of ( 2 1 ) ˆ 2,T 2 haraterizes the effetiveness of a protein preipitating agent suh as PEG. The Exluded Volume Model of Protein PEG Interations. We now analyze the experimental oexisting values ( I, 2 I ) and ( II, 2 II ) to gain insight about the physial fators that determine the quantity and its dependene on 1. We apply a simple exluded volume model that diretly relates PEG partitioning to the gi doi pnas Annunziata et al.
5 Fig. 3. Dependene of the size ratio, q, as a funtion of the square root of the PEG average moleular weight, M n. The filled irles (F) are the value obtained by fitting the experimental oexisting ompositions with Eq. 2; the open irles (E) are the values alulated from the polymer gyration radii and the protein moleular volume. The dashed lines are guides for the eye. differene in free volume frations between the two oexisting phases. If we assume that PEG moleules an be desribed as ideal polymer oils and that protein moleules have a spherial shape, then due to steri hindrane, eah protein will be surrounded by an adjaent region where the enters of mass of the oils are exluded, and the width,, of the resulting depletion layer will be proportional to the gyration radius, R g, of the polymer oil (4 14). If is the volume fration available to the enters of mass of the oils, the ondition of hemial equilibrium ˆ 2( 1 I, 2 I, T) ˆ 2( 1 II, 2 II, T) beomes 2 I I 2 II II, where 2 is the polymer onentration in the free volume (9, 34) and the free volume fration,, is equal to exp( ) (see Eq. 3b). It has been theoretially shown that, in the ase of ideal polymer oils and relatively large hard spheres, 1.1R g (35). An approximate expression for the free volume fration,, asa funtion of the hard sphere volume fration,, is given by the well established saled partile theory (34, 36, 37): 1 exp A B 2 C 3, [5] where (1 ), A 3q 3q 2 q 3, B 9q 2 2 3q 3, C 3q 3, and q R is the depletion layer thikness normalized with respet to the hard sphere radius, R. The prefator, 1, ineq.5, is the volume fration not oupied by the spheres, whereas the exponential fator desribes the effet of the depletion layers. When is small, 1 (1 q) 3 and 4 (1 q) 3 R 3 3 is the exluded volume onneted with eah sphere. As inreases, the average distane between adjaent spheres dereases, and beomes larger than 1 (1 q) 3 beause the depletion layers overlap. Beause II I 2 2 (q, II ) (q, I ), we substitute the expression for provided by Eq. 5 into the ratio of the free volume frations, and thereby we an determine an apparent q value for eah experimental tie-line. We find that, within the experimental error, this quantity does not depend on the tie-line position in the oexistene urve. We present the average value of the apparent q as a funtion of the square root of PEG moleular weight as the filled irles in Fig. 3. We note that the q values alulated by using 1 (1 q) 3 are only 10% smaller than the values alulated by using the omplete expression for and so onlude that the overlapping of depletion layers ontributes only marginally to the apparent q values reported in Fig. 3. We have also onsidered the effet of the PEG moleular weight polydispersity. Beause the polydispersity of PEG is given by a narrow Poisson distribution funtion to be applied to PEG (38, 39), it an be shown that the polymer distribution in eah of the two oexisting phases is essentially the same as in the original homogeneous system, and hene polydispersity does not signifiantly modify the slope of the tie-lines. In Fig. 3, we also present the theoretial q values (open irles), alulated by using q 1.1R g R. R g for PEG is taken from ref. 15, whereas R is estimated from the moleular weight and speifi volume of D. As seen in Fig. 3, both theoretial q and the apparent q vary as the square root of the PEG moleular weight as expeted for a Gaussian oil (40). However, the apparent values of q are numerially 50% smaller than the orresponding theoretial values. This signifiant disrepany represents the deviation of the atual D-PEG interations relative to the sphere-ideal oil ase. It has been found that q R g R in the ase of bovine serum albumin, hymotrypsinogen, and RNase, whereas q 0.5R g R in the ase of -latoglobulin and lysozyme (12, 15). The differene between the values obtained for the various proteins suggests that the departure from the exluded volume model is related to diret interations of PEG with protein surfae residues (15). Our results learly suggest the presene of suh speifi interations in the D-PEG-water systems. It appears that weak attrative interations between PEG and D indue a flattening of the polymer oils near the protein surfae and a orresponding redution of the depletion layer thikness. The Spinodal Boundaries and the Dependene of the LLPS Temperature on PEG Conentration. The spinodal surfae (40), whih desribes the spinodal temperature, T sp, as a funtion of protein and PEG onentrations, defines the boundary between the stable domain (( ˆ 1 1 ) ˆ 0) and the unstable domain 2,T (( ˆ 1 1 ) ˆ 0) of a homogeneous protein PEG water system. The spinodal 2,T ondition, ( ˆ 1 1 ) ˆ 0, an be used to determine the spinodal temperature, T 2,Tsp sp, as a funtion of 1 and 2. Indeed, on differentiating Eq. 3a with respet to 1 at onstant ˆ2 and T, we obtain: ˆ ˆ 2,T ˆ 1 1 T 1 T T 2. [6] In the ase of hard sphere-ideal polymer oil exluded volume interations, exp( ), and the differene ( 1 ) 2 T ( ) T beomes equal to the quantity, ( ) T. Ifwe use Eq. 5, we find that, when both and q are small, ( 2 2 ) T is approximately equal to 12q 3. Although Eq. 5 is inaurate insofar as high-order derivatives suh as ( 2 2 ) T are onerned, it usefully desribes the general features of the exluded volume model. Indeed, due to the overlapping of adjaent depletion layers, ( 2 2 ) T must be positive and must inrease as the depletion layer thikness inreases. These general features of the exluded volume model an be used to understand the effet of PEG on initially stable 2 protein aqueous solutions. In fat, beause ( 1 ) T ( ) T is positive, Eq. 6 predits that as the polymer onentration inreases, ( ˆ 1 1 ) ˆ dereases and an be made to reah zero, i.e., a spinodal boundary. 2,T Thus, suffiient PEG an in priniple indue phase separation at any given temperature. This is true even if the protein protein interations are repulsive. We now use the spinodal ondition to analyze the dependene of the LLPS temperature on PEG onentration. We hoose the spinodal ondition beause the spinodal surfae is tangent to the oexistene surfae on the ritial line, and beause it is math- BIOPHYSICS Annunziata et al. PNAS Otober 29, 2002 vol. 99 no
6 ematially more onvenient than the oexistene ondition. If we apply the spinodal ondition to Eq. 6 and differentiate the seond member with respet to both 2 and T sp at onstant 1, we obtain in the limit of 2 approahing zero: T sp Tsp 2. [7] ˆ 1 1 T sp 2 1 Tsp The quantity ( 2 ˆ 1 1 T sp ) is equal to ( 2 e 2 1 ) Tsp RT 2 sp, where e is the internal energy per unit volume of the protein water binary system. On addition of another protein moleule to the system, the mean distane between the proteins must derease, promoting more protein protein interations. From this seond-order effet, it follows that the quantity ( 2 e 2 1 ) Tsp is negative for attrative protein protein interations, zero for hard-ore interations (i.e., hard spheres), and positive for repulsive interations. Eq. 7 orretly desribes the sign of the dependene of the LLPS temperature as a funtion of PEG onentration for the D-PEG-water systems. The LLPS temperature inreases as the PEG onentration inreases beause of the attrative nature of the protein protein interations [( 2 ˆ 1 1 T sp ) 0]. Also, ( T sp 2 ) 1 inreases with PEG moleular weight beause ( 1 ) T 2 ( ) T inreases as the depletion layer thikness inreases. Conlusion Our experimental findings and theoretial analysis demonstrate that liquid liquid phase transition in ternary protein PEG water systems is a powerful tool for understanding the effet of PEG as a preipitating agent. We have shown that suh studies an be used to loate the phase boundary for binary protein water systems, whih is very useful if this phase separation is hidden. We an also predit the hange of protein solubility as a funtion of the onentration of rystallizing agents. Moreover, the slope of the tie-lines and the dependene of LLPS temperature on polymer onentration provide a sensitive hek of the validity of exluded volume models for protein polymer interations. The inrease of the LLPS temperature with PEG onentration is due to attrative protein protein interations. We aknowledge Ajay Pande, Alexander Chernov, Annette Tardieu, Peter Vekilov, and Seth Fraden for useful ritial omments. This work was supported by National Aeronautis and Spae Administration Grant NAG (to G.B.B.) and National Institutes of Health Grants EY05217 (to G.B.B.) and EY10535 (to J.P.). 1. Albertsson, P. A. (1986) Partition of Cell Partiles and Maromoleules (Wiley, New York). 2. Abbott, N. L., Blankshtein, D. & Hatton, T. A. (1991) Maromoleules 24, MPherson, A. (1999) Crystallization of Biologial Maromoleules (Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press, Plainview, NY). 4. Finet, S. & Tardieu, A. (2001) J. Cryst. Growth 232, Kulkarni, A. M., Chatterjee, A. P., Shweizer, K. S. & Zukoski, C. F. (2000) J. Chem. Phys. 113, Asakura, S. & Oosawa, F. (1954) J. Chem. Phys. 22, Vrij, A. (1976) Pure Appl. Chem. 48, Gast, A. P., Hall, C. K. & Russell, W. B. (1983) J. Colloid Interfae Si. 96, Lekkerkerker, H. N. W., Poon, W. C. K., Pusey, P. N., Stroobants, A. & Warren, P. B. (1992) Europhys. Lett. 20, Ilett, S. M., Orrok, A., Poon, W. C. K. & Pusey, P. N. (1995) Phys. Rev. E 51, Atha, D. H. & Ingham, K. C. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, Arakawa, T. & Timasheff, S. N. (1985) Biohemistry 24, Abbott, N. L., Blankshtein, D. & Hatton, T. A. (1992) Maromoleules 25, Vergara, A., Paduano, L. & Sartorio, R. (2002) Maromoleules 35, Bhat, R. & Timasheff, S. N. (1992) Protein Si. 1, Edmond, E. & Ogston, A. G. (1968) Biohem. J. 109, Lomakin, A., Asherie, N. & Benedek, G. B. (1996) J. Chem. Phys. 104, Malfois, M., Bonneté, F., Belloni, L. & Tardieu, A. (1996) J. Chem. Phys. 105, Lomakin, A., Asherie, N. & Benedek, G. B. (1998) Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, Asherie, N., Lomakin, A. & Benedek, G. B. (1999) Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA 96, Yu, M., Arons, J. S. & Smit, J. A. M. (1994) J. Chem. Tehnol. Biotehnol. 60, ten Wolde, P. R. & Frenkel, D. (1997) Siene 277, Galkin, O. & Vekilov, P. G. (2000) Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA 97, Benedek, G. B. (1997) Invest. Ophthalmolo. & Visual Si. 38, Thomson, J. A., Shurtenberger, P., Thurston, G. M., Thomson, J. A. & Benedek, G. B. (1987) Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA 84, Broide, M. L., Berland, C. R., Pande, J., Ogun, O. & Benedek, G. B. (1991) Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA 88, Chirgadze, Yu. N., Driessen, H. P. C., Wright, G., Slingsby, C., Hay, R. E. & Lindley, P. F. (1996) Ata Crystallogr. D 52, MDermott, M. J., Gawinowiz-Kolks, M. A., Chiesa, R. & Spetor, A. (1988) Arh. Biohem. Biophys. 262, Asherie, N., Pande, J., Lomakin, A., Ogun, O., Hanson, S. R. A., Smith, J. B. & Benedek, G. B. (1998) Biophys. Chem. 75, Shurtenberger, P., Chamberlin, R. A., Thurston, G. M., Thomson, J. A. & Benedek, G. B. (1989) Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, Liu, C., Asherie, N., Lomakin, A., Pande, J., Ogun, O. & Benedek, G. B. (1996) Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA 93, Matthews, B. W. (1968) J. Mol. Biol. 33, Galkin, O., Chen, K., Nagel, R. L., Hirsh, R. E. & Vekilov, P. G. (2002) Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA 99, Lekkerkerker, H. N. W. (1990) Colloid Surf. 51, Tuinier, R., Vliegenthart, G. A. & Lekkerkerker, H. N. W. (2000) J. Chem. Phys. 105, Widom, B. (1963) J. Chem. Phys. 39, Lebowitz, J. L., Helfand, E. & Praestgaard, E. (1965) J. Chem. Phys. 43, Flory, P. J. (1940) J. Am. Chem. So. 62, Vergara, A., Paduano, L., Sartorio, R. & Vitagliano, V. (1999) J. Phys. Chem. B 103, Tanford, C. (1961) Physial Chemistry of Maromoleules (Wiley, New York) gi doi pnas Annunziata et al.
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I
 DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Chapter 1: Introduction
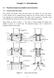 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
1 CHAPTER 6 PROPERTIES OF GASES
 CHAPTER 6 PROPERTIES OF GASES 6. The Ideal Gas Equation In 660, the Honorable Robert Boyle, Father of Chemistry and seventh son of the Earl of Cork, and one of the founders of the Royal Soiety of London,
CHAPTER 6 PROPERTIES OF GASES 6. The Ideal Gas Equation In 660, the Honorable Robert Boyle, Father of Chemistry and seventh son of the Earl of Cork, and one of the founders of the Royal Soiety of London,
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Lecture 24: Spinodal Decomposition: Part 3: kinetics of the
 Leture 4: Spinodal Deoposition: Part 3: kinetis of the oposition flutuation Today s topis Diffusion kinetis of spinodal deoposition in ters of the onentration (oposition) flutuation as a funtion of tie:
Leture 4: Spinodal Deoposition: Part 3: kinetis of the oposition flutuation Today s topis Diffusion kinetis of spinodal deoposition in ters of the onentration (oposition) flutuation as a funtion of tie:
HEAT EXCHANGERS-2. Associate Professor. IIT Delhi E-mail: [email protected]. P.Talukdar/ Mech-IITD
 HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: [email protected] Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: [email protected] Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
4.15 USING METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION HIGH RESOLUTION VISIBLE DATA FOR THE IMPOVEMENT OF THE RAPID DEVELOPPING THUNDERSTORM PRODUCT
 4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
Conversion of short optical pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
purpose of this paper to show that "retention coefficients" can
 Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 77, No. 3, pp. 1632-1636, Marh 1980 Medial Sienes Predition of peptide retention times in high-pressure liquid hromatography on the basis of amino aid omposition (lipophiliity/separation
Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 77, No. 3, pp. 1632-1636, Marh 1980 Medial Sienes Predition of peptide retention times in high-pressure liquid hromatography on the basis of amino aid omposition (lipophiliity/separation
4. FLUID SATURATION AND CAPILLARY PRESSURE 4.1 Fluid Saturations
 4. FLUID SATURATION AND CAILLARY RESSURE 4.1 Fluid Saturations We have seen that the viability of a reservoir depends upon three ritial parameters. The first two of these are the porosity of the reservoir
4. FLUID SATURATION AND CAILLARY RESSURE 4.1 Fluid Saturations We have seen that the viability of a reservoir depends upon three ritial parameters. The first two of these are the porosity of the reservoir
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
A Comparison of Default and Reduced Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T
 9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynamic Cycles of Reciprocating and Rotary Engines - R.S.
 THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
The Reduced van der Waals Equation of State
 The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers
 Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
Earthquake Loss for Reinforced Concrete Building Structures Before and After Fire damage
 Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units
 Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units or, Why CGS Units Make You Cool Prashanth S. Venkataram February 24, 202 Abstrat In this paper, I ompare the merits of Gaussian CGS and SI units in a variety of different
Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units or, Why CGS Units Make You Cool Prashanth S. Venkataram February 24, 202 Abstrat In this paper, I ompare the merits of Gaussian CGS and SI units in a variety of different
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
3 Game Theory: Basic Concepts
 3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
3 Game Theory: Basi Conepts Eah disipline of the soial sienes rules omfortably ithin its on hosen domain: : : so long as it stays largely oblivious of the others. Edard O. Wilson (1998):191 3.1 and and
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Masters Thesis- Criticality Alarm System Design Guide with Accompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope Production L
 PNNL-18348 Prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contrat DE-AC05-76RL01830 Masters Thesis- Critiality Alarm System Design Guide with Aompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope
PNNL-18348 Prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contrat DE-AC05-76RL01830 Masters Thesis- Critiality Alarm System Design Guide with Aompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope
Pattern Recognition Techniques in Microarray Data Analysis
 Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
In many services, the quality or value provided by the service increases with the time the service provider
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 57, No. 1, January 2011, pp. 40 56 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 11 5701 0040 informs doi 10.1287/mns.1100.1250 2011 INFORMS Quality Speed Conundrum: Trade-offs in Customer-Intensive
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 57, No. 1, January 2011, pp. 40 56 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 11 5701 0040 informs doi 10.1287/mns.1100.1250 2011 INFORMS Quality Speed Conundrum: Trade-offs in Customer-Intensive
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
Comay s Paradox: Do Magnetic Charges Conserve Energy?
 Comay s Paradox: Do Magneti Charges Conserve Energy? 1 Problem Kirk T. MDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Prineton University, Prineton, NJ 08544 (June 1, 2015; updated July 16, 2015) The interation energy
Comay s Paradox: Do Magneti Charges Conserve Energy? 1 Problem Kirk T. MDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Prineton University, Prineton, NJ 08544 (June 1, 2015; updated July 16, 2015) The interation energy
HOW TO CALCULATE PRESSURE ANYWHERE IN A PUMP SYSTEM? Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com April 2003
 HOW TO CALCULATE PRESSURE ANYWHERE IN A PUMP SYSTEM? Jaques Chaurette p. en. www.lihtmypump.om April 003 Synopsis Calulatin the total head of the pump is not the only task of the pump system desiner. Often
HOW TO CALCULATE PRESSURE ANYWHERE IN A PUMP SYSTEM? Jaques Chaurette p. en. www.lihtmypump.om April 003 Synopsis Calulatin the total head of the pump is not the only task of the pump system desiner. Often
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsica, vol. 21, no. 4, Dezembro, 1999 469. Surface Charges and Electric Field in a Two-Wire
 Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
On the Characteristics of Spectrum-Agile Communication Networks
 1 On the Charateristis of Spetrum-Agile Communiation Networks Xin Liu Wei Wang Department of Computer Siene University of California, Davis, CA 95616 Email:{liu,wangw}@s.udavis.edu Abstrat Preliminary
1 On the Charateristis of Spetrum-Agile Communiation Networks Xin Liu Wei Wang Department of Computer Siene University of California, Davis, CA 95616 Email:{liu,wangw}@s.udavis.edu Abstrat Preliminary
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability
 Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Physical and mathematical postulates behind relativity
 Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = mc 2, from the Classical Force Laws
 Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria [email protected],
Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria [email protected],
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
OpenScape 4000 CSTA V7 Connectivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1. Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76D1
 OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
Previously Published Works UC Berkeley
 Previously Published Works UC Berkeley A University of California author or department has made this artile openly available. Thanks to the Aademi Senate s Open Aess Poliy, a great many UC-authored sholarly
Previously Published Works UC Berkeley A University of California author or department has made this artile openly available. Thanks to the Aademi Senate s Open Aess Poliy, a great many UC-authored sholarly
Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismic Code IS 1893 (Part I)
 Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Fig. 1.1 Rectangular foundation plan.
 Footings Example 1 Design of a square spread footing of a seven-story uilding Design and detail a typial square spread footing of a six ay y five ay seven-story uilding, founded on stiff soil, supporting
Footings Example 1 Design of a square spread footing of a seven-story uilding Design and detail a typial square spread footing of a six ay y five ay seven-story uilding, founded on stiff soil, supporting
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
A Static Friction Model for Elastic-Plastic Contacting Rough Surfaces
 Lior Kogut 1 Mem. ASME e-mail: [email protected] Izhak Etsion Fellow ASME e-mail: [email protected] Dept. of Mehanial Engineering, Tehnion, Haifa 32000, Israel A Stati Frition Model for Elasti-Plasti
Lior Kogut 1 Mem. ASME e-mail: [email protected] Izhak Etsion Fellow ASME e-mail: [email protected] Dept. of Mehanial Engineering, Tehnion, Haifa 32000, Israel A Stati Frition Model for Elasti-Plasti
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
SLA-based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments
 2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS
 university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS. Discussion Paper No. 475. The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism
 RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Shool of Publi Poliy The University of Mihigan Ann Arbor, Mihigan 48109-1220 Disussion Paper No. 475 The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement
RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Shool of Publi Poliy The University of Mihigan Ann Arbor, Mihigan 48109-1220 Disussion Paper No. 475 The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 6 (5) (2013) 143-148. Research Article
 Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING
 PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING Unit Operations and Unit Proesses Dr Jasmina Khanam Reader of Pharmaeutial Engineering Division Department of Pharmaeutial Tehnology Jadavpur University Kolkatta-70003 (06--007)
PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING Unit Operations and Unit Proesses Dr Jasmina Khanam Reader of Pharmaeutial Engineering Division Department of Pharmaeutial Tehnology Jadavpur University Kolkatta-70003 (06--007)
Cement and Concrete Research
 Cement and Conrete Researh 39 (2009) 255 265 Contents lists available at SieneDiret Cement and Conrete Researh journal homepage: http://ees.elsevier.om/cemcon/default.asp Hydration kinetis modeling of
Cement and Conrete Researh 39 (2009) 255 265 Contents lists available at SieneDiret Cement and Conrete Researh journal homepage: http://ees.elsevier.om/cemcon/default.asp Hydration kinetis modeling of
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com. ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109
 Available online at www.sienediret.om SieneDiret Energy Proedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109 SHC 2013, International Conferene on Solar Heating and Cooling for Buildings and Industry September 23-25, 2013, Freiburg,
Available online at www.sienediret.om SieneDiret Energy Proedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109 SHC 2013, International Conferene on Solar Heating and Cooling for Buildings and Industry September 23-25, 2013, Freiburg,
Dynamic and Competitive Effects of Direct Mailings
 Dynami and Competitive Effets of Diret Mailings Merel van Diepen, Bas Donkers and Philip Hans Franses ERIM REPORT SERIES RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT ERIM Report Series referene number ERS-2006-050-MKT Publiation
Dynami and Competitive Effets of Diret Mailings Merel van Diepen, Bas Donkers and Philip Hans Franses ERIM REPORT SERIES RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT ERIM Report Series referene number ERS-2006-050-MKT Publiation
