Masters Thesis- Criticality Alarm System Design Guide with Accompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope Production L
|
|
|
- Alyson Bridges
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PNNL Prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contrat DE-AC05-76RL01830 Masters Thesis- Critiality Alarm System Design Guide with Aompanying Alarm System Development for the Radioisotope Prodution L BA Greenfield Deember 2009
2 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an aount of work sponsored by an ageny of the United States Government. Neither the United States Government nor any ageny thereof, nor Battelle Memorial Institute, nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the auray, ompleteness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, produt, or proess dislosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Referene herein to any speifi ommerial produt, proess, or servie by trade name, trademark, manufaturer, or otherwise does not neessarily onstitute or imply its endorsement, reommendation, or favoring by the United States Government or any ageny thereof, or Battelle Memorial Institute. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not neessarily state or reflet those of the United States Government or any ageny thereof. PACIFIC NORTHWEST NATIONAL LABORATORY operated by BATTELLE for the UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY under Contrat DE-AC05-76RL01830 Printed in the United States of Ameria Available to DOE and DOE ontrators from the Offie of Sientifi and Tehnial Information, P.O. Box 62, Oak Ridge, TN ; ph: (865) fax: (865) Available to the publi from the National Tehnial Information Servie, U.S. Department of Commere, 5285 Port Royal Rd., Springfield, VA ph: (800) fax: (703) online ordering: This doument was printed on reyled paper. (9/2003)
3
4 CRITICALITY ALARM SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDE WITH ACCOMPANYING ALARM SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT FOR THE RADIOCHEMICAL PROCESSING LABORATORY IN RICHLAND, WASHINGTON BY BRYCE GREENFIELD ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE - COMPUTER SCIENCE WHATCOM TECHNICAL COLLEGE 2004 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE - NUCLEAR ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO 2007 THESIS Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Siene Nulear Engineering The University of New Mexio Albuquerque, New Mexio Deember, 2009
5 Aknowledgements I would like to thank Dr. Robert Bush. Your tireless effort and dediation is inspiring. The ountless hours you have spent orreting my assignments and instruting me is truly appreiated. My work has been well reeived here at PNNL, and I feel that the redit is due to your patiene and ommitment to delivering a quality eduation to your students. To all of my ommittee members, I would like to extend a heartfelt thank you for all that you have done. Through both undergrad and graduate levels Dr. Gary Cooper and Dr. Taro Ueki ontributed so muh to my eduation. The rigor of your lasses may not have been entirely appreiated at the time, but is now more appreiated than you ould know. Unfortunately I had finished my oursework before Dr. Adam Heht arrived at UNM. However, from the very ineption of this thesis writing proess, he has offered his help and guidane, whih was extremely valuable. To all of those individuals at PNNL who have given me assistane over the last three years, thank you. With no exeption, every staff member that I have enountered has been more than willing to lend a hand. Andrew Prihard deserves speial mention. From the moment I arrived at the lab, he has painstakingly mentored me and taken the time to not just answer my questions, but to make me understand those answers. His never wavering patiene and endless amounts of knowledge make him the ideal mentor. And finally to my wife, Robin, words an not onvey the heartfelt appreiation and love I have for you. Without your support I would be lost. iii
6 CRITICALITY ALARM SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDE WITH ACCOMPANYING ALARM SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT FOR THE RADIOCHEMICAL PROCESSING LABORATORY IN RICHLAND, WASHINGTON BY BRYCE GREENFIELD ABSTRACT OF THESIS Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Siene Nulear Engineering The University of New Mexio Albuquerque, New Mexio Deember, 2009
7 CRITICALITY ALARM SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDE WITH ACCOMPANYING ALARM SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT FOR THE RADIOCHEMICAL PROCESSING LABORATORY IN RICHLAND, WASHINGTON by Brye Greenfield B.S., Nulear Engineering, University of New Mexio, 2007 M.S., Nulear Engineering, University of New Mexio, 2009 ABSTRACT A detailed instrutional manual was reated to guide ritiality safety engineers through the proess of designing a ritiality alarm system (CAS) for Department of Energy (DOE) hazard lass 1 and 2 failities. Regulatory and tehnial requirements were both addressed. A list of design tasks and tehnial subtasks was ompiled and analyzed to provide onise diretion for how to omplete the analysis. An example of the appliation of the design methodology, the Critiality Alarm System developed for the Radiohemial Proessing Laboratory (RPL) of Rihland, Washington is also inluded. The analysis for RPL utilized the Monte Carlo ode MCNP5 for establishing detetor overage in the faility. Based on the design methodology, signifiant improvements to the existing CAS were made that inrease the reliability, transpareny, and overage of the system. v
8 Table of Contents Aknowledgements... iii ABSTRACT... v List of Figures... vii List of Tables... viii Chapter 1 Introdution... 1 Minimum Aident of Conern... 2 Objetive... 3 Overview of Chapters... 4 Chapter 2 Literature Review... 6 Chapter 3 Design Proess Overview Design Methodology Chapter 4 Appliation of Guideline Methodology Chapter 5 Conlusion Summary Future Work Enhanements Definitions Appendix A: RPL Building Shematis with Aident and Detetor Loations Appendix B: CAS Component Desriptions Tehnial Desription of the Comparator Panel Tehnial Desription of the Radiation Detetors Appendix C: Material Definitions for Codes Appendix D: Shedule of Deliverables Appendix E: Assumptions Used in the CAS Design of RPL Modeling Assumptions Translation notes Appendix F: MCNP5 Input Deks Referenes vi
9 List of Figures Figure 1. Design proess flow sheet Figure 2. UNCSR dose redution fators for various shield thiknesses Figure 3. UNCSR sample slide rule for U(93.2)O 2 -(NO 3 ) H/X= Figure 4. Experimental setup for the NIST Sphere Benhmarks Figure rad ars for the outlying MAC s in the basement of RPL Figure rad ars for the outlying MAC s in the first floor of RPL Figure 7. RPL Basement shown with modeled aident loations and the existing detetor plaement Figure 8. RPL First floor shown with modeled aident loations and the existing detetor plaement Figure 9. RPL Seond floor layout Figure 10. Standard onrete material definition of 2.3g/ density Figure 11. Graph of the total ross-setion of 113 Cd Figure 12. Neutron energy spetrum for the spontaneous fission of 252 Cf Figure 13. Neutron energy spetrum grouped into 4eV and 20 MeV energy bins for the spontaneous fission of 252 Cf plotted on a log sale Figure 14. Existing alibration spetrum Figure 15. Average neutron energy spetrum during the Minimum Aident of Conern grouped into 4eV and 20 MeV energy bins Figure 16. Existing NCD alibration setup Figure 17. Revised NCD alibration setup with the added HDPE Figure 18. Modified alibration spetrum grouped into 4eV and 20 MeV energy bins.. 87 Figure 19. RPL Basement showing aident loations and NCD loations Figure 20. RPL First Floor showing aident loations and NCD loations Figure 21. RPL Seond Floor showing aident loations, no NCD are loated on this floor vii
10 List of Tables Table 1. Experimental normalized fission rates for 235 U and 239 Pu Table 2. MCNP5 Computational results with omparison to experimental results Table 3. Plutonium minimum aident senario data Table Cf alibration soure information Table 5. Detetor ounts for eah MAC loation in RPL Table 6. As modeled MAC loations in RPL Table 7. Corresponding Data Used in the Histograms Table 8. Comparison of deterministi transport results to standard Monte Carlo results 89 Table 9. Detetor ounts for preliminary sensitivity analysis for maximum loading within the faility viii
11 Chapter 1 Introdution There are a variety of hazards faing those who work with fissile material; the most severe of those hazards is a runaway hain reation known as a ritiality aident. A ritiality aident an release enormous amounts of radiation that may injure or kill those who are near it. Great are is taken to minimize the hane of a ritiality aident ourring, but the possibility annot be totally eliminated. Therefore it is this minimal possibility that must be aepted and planned for. One way to lessen the potential impat of an aident event is to install a Critiality Alarm System. The purpose of a CAS is to promptly detet a ritiality aident and immediately issue an audible evauation warning to personnel. It has been shown that rapid evauation away from ritiality aidents an onsiderably redue the dose reeived by personnel (MLaughlin et al., 2000). Getting people out quikly an derease injury and save lives. This is the motivation to design and implement detetion systems in failities where aidents ould our. Federal standards exist that establish the performane requirements of these systems and disuss their appliability. But nowhere, be it federal or private, is there a standard on how to design them. Currently, there exists no onsolidated body of work that addresses how to design a CAS. Beause these alarm systems have the potential to save lives, it is of the utmost importane that they be rigorously designed. It is the fous of this thesis to provide an instrutional guide for the design of a robust CAS that will perform its funtions with the highest reliability. 1
12 All non-reator failities that handle greater than or equal to: 700g of 235 U 500g of 233 U 450g of 239 Pu 450g of any ombination of these three isotopes are required by the Department of Energy to install and operate a ritiality alarm system (U.S. DOE, 2005). For the speifi performane and detetor overage requirements expeted of a CAS, DOE Order 420.1B defers to ANSI/ANS Critiality Alarm Systems. ANSI/ANS is the primary standard used to judge the aeptability of a CAS design. A CAS is generally omprised of 3 main omponents as desribed in Appendix B: a omparator panel, alarms, and radiation detetors. Seletion and plaement of the detetors is the most diffiult part of a CAS design. The detetors must operate with a high degree of reliability and require infrequent serviing or repair. The detetors, as well as the system in general, also need to minimize the potential for false alarms. The final and most important requirement of the detetors is that they must respond immediately to the Minimum Aident of Conern (MAC). Minimum Aident of Conern The Minimum Aident of Conern represents the smallest aident in terms of fission yield and dose rate that the Critiality Alarm System must detet. ANSI/ANS defines the MAC as one that delivers the equivalent of an absorbed dose rate in free air of 0.2 Gy/min (20 rad/min) at 2 meters from the reating material. The design 2
13 engineer must determine what likely senarios, speifi to the faility, would meet this definition. The engineer must determine the forms of the reating materials, onfiguration, onentration, and quantities involved in an aident that will reah the MAC dose rates. Establishing the appropriate MAC for the targeted faility is not trivial and requires onsiderable effort. The MAC represents the most diffiult aident senario that the CAS must detet. Therefore, the MAC is used extensively during the design phase to prove or disprove adequate detetor overage in the faility. ANSI/ANS establishes what adequate overage is by requiring that no single hannel may ause an alarm or fault. This means that at least two detetors will alarm for every MAC regardless of the aident loation. Proving the CAS meets the overage requirements of ANSI/ANS is the ultimate goal of the design engineer and is the benhmark for an effetive Critiality Alarm System. Objetive The purpose of this thesis is to provide a thorough guide to CAS design. Eah step of the design proess is disussed in detail to show why the step is needed and how to best omplete it. Estimates for the time ommitment of eah step are inluded, as well as potential pitfalls that may be enountered. A omplete CAS design for the Radioisotope Prodution Laboratory of Rihland, Washington is inluded in this thesis to provide lear illustrations of what is being explained. The inluded CAS design provides orresponding examples for eah topi disussed in the Design Proess Overview setion. 3
14 A Critiality Alarm System designed based on this methodology will meet and exeed all urrent regulatory requirements. Overview of Chapters Chapter 2 provides a synopsis of the major federal requirements and standards that apply to CAS design. Eah speifi doument is briefly summarized and disussed. After reading this hapter, the reader should have an understanding of the relevant regulations that drive the implementation and design requirements of a CAS. A general sense of how the regulations affet the system design is disussed. A more detailed analysis of the ANSI/ANS standard on Critiality Aident Alarm Systems ompletes the hapter. Chapter 3 begins by giving a oneptual overview of what goes into the design of a CAS. A design proess flow sheet is provided to illustrate how different design riteria affet the projet. Following the proess overview is the Design Methodology. An outline of tasks to be ompleted is presented as well as a tehnially-oriented subtask listing. The flow sheet and task outline form the foundation of how the remainder of the doument is organized. Chapter 4 uses a CAS developed for the Radioisotope Prodution Laboratory(RPL) in Rihland, Washington to illustrate how to apply the methodology presented in Chapter 3. The task and tehnial subtask layout desribed in the previous hapter is applied to the RPL CAS. Results are given and evaluated for the MAC, overage requirements, spetrum analysis, sensitivity analysis, and validation benhmarks. MCNP5 inputs (the faility model, validation benhmarks, spetrum 4
15 analysis, MAC, and sensitivity analysis) are provided in Appendix D for the different RPL speifi models disussed. The onlusion portion of the thesis draws all the setions together by highlighting and summarizing the major points. The improvements made to the RPL CAS are also listed with some disussion on their potential impats on the faility with respet to safety and operations. The potential for future work in this area is also evaluated. 5
16 Chapter 2 Literature Review There are a multitude of douments that regulate the design and performane of a CAS. The final ompliane memo for a CAS must not only referene the appliable regulations but inlude an atual opy of them in an appendix. This is done beause the rules hange over time. It is ruial to have a hard opy of what the rules were at the time the analysis was performed. Doing so helps avoid liability for future design onditions and performane requirement alterations as well as providing doumentation for future system analyses and upgrades. To begin evaluating the regulations the engineer needs to reognize that different faility lassifiations require different sets of regulations. The largest differene in regulations is whether or not the faility ontains a reator. The rules are signifiantly different for reator and non-reator failities. This analysis fouses on CAS systems for non-reator failities. An important note, some of the standards disussed apply to all types of failities; however it is just as ruial to justify why the standard is not appliable as it is to show why it is. Below is list of the douments that should be pulled and heked for relevane for non-reator failities. 1) DOE 420.1B Faility Safety (USDOE, 1997) 2) ANSI/ANS Nulear Critiality Safety in Operations with Fissionable Material Outside of Reators 3) ANSI/ANS Critiality Aident Alarm Systems 4) ANSI/ANS Criteria for Nulear Critiality Safety Controls in Operations with Shielding and Confinement 5) ANSI/ANS Nulear Critiality Control with Speial Atinide Elements 6) ANSI/ANS Proedures for Nulear Critiality Safety 6
17 These are the federal regulations and standards related to Nulear Critiality Safety and Critiality Aident Alarm Systems. There will also be ompany speifi proedures for how to omply with these douments. If the final ompliane report does not apply to both federal and ompany speifi proedure, it will not be aepted. The language used in the final reports will vary from ompany to ompany so the format of the report itself will not be disussed. The analysis performed for a Paifi Northwest National Laboratory faility had to omply with the following internal douments: 1) MEA001 Nulear Critiality Safety Basis Memo Evaluation, Doumentation and Approval 2) NQA1 Quality Control 3) MA250 Critiality Safety Manual 4) MA500 Nulear Material Control and Aountability Plan 5) Radiohemial Proessing Laboratory Doumented Safety Analysis 6) Radiohemial Proessing Laboratory Tehnial Safety Review 7) Critiality Safety Speifiation 1 8) Critiality Safety Speifiation 2 9) Critiality Safety Speifiation 3 Eah of the douments listed above has the possibility of impating the design, implementation, and final ompliane report. The need to thoroughly analyze eah doument for appliability and to make a detailed list of notes while doing so to keep trak of them all is vital to the suessful ompletion of the analysis. Beause the seond list of requirements is ompany speifi, they will not be disussed in detail. Most of the ompany speifi douments are ontrolled and not available for publi release. Topis that are typially universal regardless of the ompany, like quality ontrol and method 7
18 validation, will be disussed to illustrate how related to these topis tasks an be onduted. Throughout the range of ANSI/ANS douments, the same definitions are used for the terms shall, should, and may. These terms are defined throughout the standards as follows: The word "shall'' is used to denote a requirement, the word "should to denote a reommendation, and the word "may" to denote permission, neither a requirement nor a reommendation. To onform with this standard, all operations shall be performed in aordane with its requirements but not neessarily with its reommendations (ANSI/ANS 8.3, 1997). To avoid misinterpreting what has been said, it is important to keep in mind how these words are defined when reading the standards. To establish faility and program safety requirements for the DOE, a good starting point for all of these regulations and standards is the Department of Energy Order 420.1B Faility Safety. This doument is the fundamental regulatory driver for a CAS in a federal faility. DOE 420.1B then breaks down what is required from a CAS, but it generally does not list the requirements. What Order 420.1B does is referene the douments that speifially list the tehnial requirements, whih are typially ANSI/ANS standards. Order 420.1B is strutured this way, no doubt, beause the ANSI/ANS standards are periodially reanalyzed and updated. There are some key setions of Order 420.1B that must be read and understood: Nulear Safety 4.3 Nulear Critiality Safety Speifi Requirements 8
19 It should be notied that Order 420.1B augments many setions of the different ANSI/ANS standards. Why it is important to note these modifiations is disussed further in Design Proess Overview Task II. There is a setion in Order e part 4 that addresses what is known as quasistati ritiality aidents. Quasistati aidents are tremendously hallenging to detet and are not addressed within this Thesis. Order 420.1B then direts the user to ANSI/ANS , whih is the overarhing ritiality safety standard. All other ritiality related standards address implementing the general philosophy ontained in ANSI/ANS ) ANSI/ANS Nulear Critiality Safety in Operations with Fissionable Material Outside Reators: Sope This standard is appliable to operations with fissionable materials outside nulear reators, exept for the assembly of these materials under ontrolled onditions, suh as in ritial experiments. Generalized basi riteria are presented and limits are speified for some single fissionable units of simple shape ontaining U-233, U-235, or Pu- 239, but not for multiunit arrays. Requirements are stated for establishing the validity and areas of appliability of any alulational method used in assessing nulear ritiality safety. This standard does not inlude the details of administrative ontrols, the design of proesses or equipment, the desription of instrumentation for proess ontrol, nor detailed riteria to be met in transporting fissionable materials. This standard lays out the general methodology and tehniques for how work with fissionable materials should be arried out. It thoroughly disusses what an aeptable analysis would be for meeting safety requirements, and then it disusses what must happen if this analysis is based on omputer simulations. This standard also disusses how omputer systems must be validated using established experimental benhmarks to ensure that the ode is performing as laimed. 9
20 2) ANSI/ANS Critiality Aident Alarm System Sope This standard is appliable to all operations involving fissionable materials in whih inadvertent ritiality an our and ause personnel to reeive unaeptable exposure to radiation. This standard is not appliable to detetion of ritiality events where no exessive exposure to personnel is redible, nor to nulear reators or ritial experiments. This standard does not inlude details of administrative ations or of emergeny response ations that our after alarm ativation. This standard ontains a range of vital information. There is so muh useful material in this standard that to disuss it all would be to almost reprodue it in its entirety. The most important parts with regard to design impat are the desription of the overage requirement, false alarm tolerane, detetor failure, and the minimum aident of onern. Eah of these parameters should be understood beause eah an impat the physial layout of the system. A brief disussion on the interplay among these parameters is useful to illustrate how one an affet another, and to show how important this standard is to CAS design. The overage requirement is the number of detetors that must alarm for the MAC. To meet the overage requirement, the engineer would like the threshold (trip) setting for the detetors to be as low as possible, but if set too low, then there is a greater risk of false alarms. If the CAS is designed to meet only the minimum detetor overage requirement, then a fault at any one node takes the entire system out of ompliane, thereby stopping work in the faility. However, the more detetors required for the system, then the greater the ost of installation and operation beomes. The most important piee of information this standard supplies is the general definition of the MAC. The minimum aident of onern an be thought of oneptually as the worst ase senario for what a ritiality safety engineer must design for. ANSI/ANS
21 defines the minimum aident of onern as the smallest event in terms of yield and dose that a ritiality alarm system must detet. It then goes on to define the MAC even further as to deliver the equivalent of an absorbed dose rate in free air of 0.2 Gy/min (20 rad/min) at 2 meters from the reating material. For the system to be aepted in a DOE faility, CAS must be able to detet the MAC. The purpose of the MAC definition is to give a lear lower limit of what must be deteted, while still giving the ritiality engineer some freedom with how to design the system. The standard does this by listing a minimum dose rate and by not listing how this dose rate is deteted. From a pratial sense not defining what the dose results from, neutrons, gammas, et., lets the engineer deide what partiles the system should detet. Having some freedom here allows the alarm system to be tailored to the individual faility. 3) ANSI/ANS Criteria for Critiality Safety Controls in Operations with Shielding and Confinement: Sope This standard is appliable to operations outside of nulear reators with U-235 U-233, Pu-239, and other fissile and fissionable materials in whih shielding and onfinement are provided for protetion of personnel and the publi, exept the assembly of these materials under ontrolled onditions, suh as in ritial experiments. Criteria are provided that may be used for ritiality ontrol under these onditions. The standard does not inlude the details of administrative proedures for ontrol (whih are onsidered to be management prerogatives) nor details regarding the design of proesses and equipment or desriptions of instrumentation for proess ontrol. This standard outlines a possible exeption to requiring a CAS in a faility that is over the mass limit utoff but has large amounts of shielding. This obviously warrants some attention beause nothing makes projet managers angrier than spending thousands 11
22 of dollars on ompletely unneessary work. Without going into great detail, the standard s basis for omission of a CAS deals with suffiient shielding requirements, remote operation, and personnel restritions. 4) ANSI/ANS Administrative Praties for Nulear Critiality Safety: Sope This standard provides riteria for the administration of a nulear ritiality safety program for outside-of-reator operations in whih there exists a potential for nulear ritiality aidents. Responsibilities of management, supervision, and the nulear ritiality safety staff are addressed. Objetives and harateristis of operating and emergeny proedures are inluded. This addresses the administration of a ritiality safety program. Like the other standards mentioned in this setion, it referenes many of the other ritiality foused ANSI/ANS standards inluding ANSI/ANS Critiality Aident Alarm Systems. This standard is more foused on how programs are implemented and doumented. Beause the CAS design will have to be administered adherent to this standard, it should be reviewed during the CAS design proess. 5) ANSI/ANS Neutron and Gamma-ray Fluene-to-Dose Fators: Sope This standard presents data reommended for omputing the biologially relevant dosimetri quantity in neutron and gamma-ray radiation fields. Speifially, this standard is intended to for use by shield designers to alulate effetive dose equivalent per unit fluene for neutron energies from 1eV to 14 MeV and for gamma-ray energies from 0.01 to 12 MeV. Establishing maximum permissible exposure limits is outside the sope of this standard. This is used onvert gamma-ray fluene to dose in free air. The previous analysis of the RPL used this standard in onjuntion with the MAC to find the smallest, and therefore most limiting, neutron fluene resultant from a ritiality aident. It should be 12
23 noted at the time of this analysis, ANSI/ANS ould not be used beause the standards status had been hanged from Ative to Histori. The status was hanged to Histori beause the standard was not reevaluated within the 10 year time frame designated by ANSI/ANS. The ritiality safety engineer should be autious about using it until the status is updated. Based on the faility desription, the judgment an be made as to whih ANSI/ANS standards are appliable. As stated previously, it is important to make lear arguments why or why not eah standard is speifially appliable to the design. These arguments will be inluded in the final report and heked over by quality ontrol engineers. Of all the ANSI/ANS standards, the most appliable is obviously Critiality Aident Alarm Systems. This doument will likely guide the majority of the tehnial design and warrant a good deal of attention. 13
24 Chapter 3 Design Proess Overview Below is a brief overview of what goes into a omplete CAS design. Eah of the following steps is disussed in greater detail in the Methodology setion. Throughout the design phase, frequent reviews of ompleted work and of the progress being made are advisable. In suh a long proess there are innumerable hanes for mistakes to be made. If mistakes are made early on and go unnotied, they an render the finished produt useless. It is strongly reommended to have senior ritiality safety engineers or other peers periodially review ompleted work. To provide an itemized summary of what lays ahead, the rather sprawling job of CAS design has been ondensed into seven major tasks, whih are: I. Beome familiar with the faility where the CAS will be installed; II. Obtain, read, and summarize all of the pertinent standards and guidelines; then ompare ompany speifi requirements to others, so that the most likely senarios for the Minimum Aident of Conern an be found; III. Outline a shedule of deliverables; IV. Evaluate and hoose a omputer simulation pakage to perform the analysis based on validation benhmarks that learly demonstrate the ode hosen will perform as expeted; V. Design and model the ritiality alarm system for the faility; VI. Show the alibration method follows simple and onise methodology for setting the minimum detetor trip points; and VII. Assemble the final report; 14
25 The tasks are roughly in hronologial order. Lengthy projets suh as this, more often than not, require tasks to be juggled simultaneously or to be moved around to meet deadlines. This projet will likely be no different. The list above was onstruted to help the novie engineer move from the beginning of the projet to the end with organization and traeability. 15
26 Design Methodology This setion fouses on how to arry out the design of the CAS. Eah task from the outline listed at the beginning of this Chapter is thoroughly desribed. The approah to eah task, as well as any orresponding potential issues, is examined. Task VI ontains the majority of the tehnial design, and it inludes a numbered list of speifi tehnial subtasks. This numbered list is then revisited in the Appliation of Design Methodology Chapter where the same numbering is applied to the RPL Critiality Alarm System analysis. I. Beome familiar with the faility where the CAS will be installed Initial Phase Begin by onduting walk downs of the targeted faility. Take general notes of the layout and the onstrution materials of the building. If a urrent CAS exists, make thorough notes about it; pay espeially lose attention to the detetors and their urrent loations. New CAS system installation and validation is very expensive so there is strong motivation to utilize existing omponents. While in the faility, talk to people to get a sense of what day-to-day operations are like. The engineer needs to develop a sense for what typially ours in the faility beause it will help avoid inorret assumptions during the modeling phase. Some questions to ask personnel are: How often are renovations performed? What fissile material movements our? Where are operations with fissile material onduted? 16
27 Do people and/or laboratories move around? Are there any neutronially signifiant materials present? II. Obtain, read, and summarize all of the pertinent standards and guidelines; then ompare ompany speifi requirements to others, so that the most likely senarios for the Minimum Aident of Conern an be found; After the walk downs are ompleted, the engineer should have a better understanding of the operations and environment that the CAS design must aommodate. Using this knowledge, pull all of the referenes listed in the literature review setion. Do not worry initially about whether or not they are speifially appliable. Spend the time to read them. Most are not terribly long. Pay lose attention to the sope of eah doument. Obtain hard opies of all the referenes beause they are often required in the final CAS design report. Make a summary of eah doument inluding: Sope/appliability speify any diret requirements for the faility. Tehnial limits. Repeat this proess for the ompany speifi regulations. Depending on the size of the ompany, it may or may not have a doument lerk or department. If so, these personnel an be tasked to find and assemble all the appliable douments. Also, some ompanies maintain libraries that will have most if not all of the douments required. For example, the Hanford Tehnial Library at PNNL employs fulltime librarians that an be tasked with loating projet speifi doumentation. 17
28 After all of the standards and guidelines have been assembled and summarized, it is time to selet the most limiting aident senarios to be modeled. It was found that inserting the summarized lists into a spreadsheet was very useful. The determination of whih requirements represent the most limiting aident senario is not always lear. For example, one standard may define a dose rate where another may define fluene. Unless the differene in magnitude for eah situation is onsiderable, it an be diffiult to disern what the most limiting parameter is. Therefore, it is reommended to perform some quik alulations to verify any onjeture. One an aurate assessment of the most likely minimum aident senarios has been made, the assessment must be heked by experiened ritiality safety engineers. PNNL requires that the limiting design onditions be peer reviewed, and there is a very expliit list of who an review what types of work. If for some reason, quality assurane is not required at this level, the engineer should seek it out independently. To reiterate, these limiting ases drive the analysis, so if they are inomplete, the design an be inomplete. An example of a final limiting ase assessment is shown in Design Methodology Minimum Aident of Conern subtask. III. Outline a shedule of deliverables The management responsible for the projet may provide a time frame or they may ask the engineer for an assessment of the expeted duration of the projet. It is generally benefiial for all those involved to have the person(s) with the most appliable experiene onstrut the time line. It is muh more diffiult to make an aurate judgment of how long a task will take if the individual has never performed it before. 18
29 The shedule is also highly dependent on the size of the faility that the CAS is being designed for. The length of time to omplete the design phase seems to roughly sale with faility size. There are several fators that drive this relationship. The larger the faility is, the longer it will take to model. The larger the model, the longer it will take to QA. The number of potential aident loations inreases with building size, whih adds to both the omputational time and the analysis phase. For referene, the RPL building desription is given in Chapter 4 as well as shematis for eah floor in Appendix A. It took approximately four months to perform the analysis and write the final report. The time it will take to draft the report depends on ompany requirements and individual writing speed. The final Basis Memo for PNNL was written, reviewed, and re-written in about 80 hours. More on the report is disussed later in this setion. There are a few key fators that an redue the CAS design time. Most time saving fators are human-based. For example omputer ode writing skills, general ritiality safety knowledge, and regulatory knowledge an all aid the design engineer in ompleting tasks more quikly. For all the duration times listed from this point on, it is assumed that the user has the skills of an average entry-level engineer. IV. Evaluate and hoose a omputer simulation pakage to perform the analysis based on validation benhmarks that learly demonstrate the ode hosen will perform as expeted ANSI/ANS requires that any ode used for ritiality analysis be validated prior to its use. This part of the proess is really several tasks ombined: hoosing a ode, evaluating the odes usability, and validating the odes auray relative to the speifi situation being modeled. The goal in this step is to hoose a omputer simulation 19
30 pakage that an show detetor overage and to perform suffiient analysis of the ode pakage hosen, to prove that it does operate as assumed. Meeting this goal is the fous of this setion, and it is highly reommended that this goal be met before the design phase is undertaken. There are some ommon sense reasons for performing the tasks mentioned above, but there is also a regulation that learly invokes the need to do them as well. DOE Order 420 mandates that all failities ategorized hazard level 1 or 2 must implement a quality assurane program to oversee and ensure the legitimay of the work being performed. So throughout the design proess all of the work performed, must be heked in aordane with the faility speifi QA program. At PNNL, as it should be elsewhere, the ode pakage used to perform ANY analysis most ertainly falls into QA spae. A brief word of aution, ANY ode used to perform analysis on the system that will be inluded in any way in the final report must be validated and put through QA. Hopefully it is obvious then that it would be wise for the engineer to pik as few odes as possible to simplify this requirement. It should also be noted that many ompanies maintain a list of approved ode pakages that are speifi down to the version and release dates. If the ode the engineer would like to use is not on this list, it an not be used. One the ode has been seleted, if not already familiar with it, spend a few days learning the basis. It is important to do this beause the validation phase is somewhat time onsuming and requires a working knowledge of the ode to omplete. Naturally, it is a good use of time to ensure that the work an be ompleted in a timely manner with the seleted ode pakage. It is just ommon sense to not waste time validating software 20
31 that will never be used. After getting aquainted with how the ode works, it is time to proeed with the validation phase. Note, that validation is required for every projet, and must be inluded in the final report regardless of whether similar work has been previously performed. Computer ode validation is aomplished by modeling known, well doumented, and very similar real world experiments. Then the results of the simulation are ompared to atual real world experiment data. The ode is deemed aeptable when it is shown to model similar situations with a prerequisite auray. The auray varies from ompany to ompany. The most important part of the validation proess is the seletion of relevant benhmarks. The term, relevant benhmark is used in referene to established experiments that are well doumented and reviewed and that learly demonstrate the phenomena being investigated. To put it simply, if modeling fission in 235 U, then find a 235 U benhmark to ompare it to. But this is indeed too simple an explanation. Depending on the situation it is also usually important to math the energy spetrum, hemial state of the material, geometry, and in some ases the magnitude of the fluene. The loser the benhmark physially resembles the system being investigated, the easier it will be to argue that the results obtained from the model are indeed aeptable. Lukily there exists a olletion of benhmarks that fulfill these requirements. In the last 50 years there has been a wide variety of ritiality experiments onduted all over the world. These experiments were used to gain an understanding of a range of phenomena. Sine these experiments were onduted, an organization has been formed to find and assemble them into a readily aessible database. Currently that 21
32 organization is the Nulear Energy Ageny (NEA) and their database is known as The International Handbook of Evaluated Critiality Safety Benhmark Experiments (IHECSBE) (NEA, 2008). The NEA has foused on ompiling and heking the validity of the experiments and then issuing very high quality detailed reports about there findings. Many evaluated experiments also inlude omputer input and output files for the experiment. The IHECSBE database is a widely aeptable soure for validation benhmarks and offers a large variety of experiments. V. Design and model the ritiality alarm system for the faility; As a ertain professor of mine always used to say, Here lies the meat and potatoes of your work. Contained in this setion are guidelines on how to omplete the more tehnial aspets of this projet. Below is an outline of the design phase of the projet. Eah number represents a subtask of the design proess. 1) Find the MAC inluding fluene and spetrum 2) Identify potential loations for detetor plaement 3) Model the faility a. Assumptions/omissions/simplifiations b. Dimensions. Materials Used in Computational Models d. Detetors e. Soure f. Tallies g. Aident Loations 4) Find ount rates of the ritiality detetors for known onditions 5) Model the Calibration/Counting Setup to find the Detetor Cell Tally Effiienies 6) Adjust the value for the detetor minimum trip setting 7) Verify that adequate overage has been obtained at the new minimum trip setting 8) Modify the Calibration Proedure 22
33 9) Apply Variane Redution as needed 10) Perform sensitivity analysis on the final CAS design Eah numbered item is disussed in greater detail below. Chapter 4 desribes these steps when applied to the design of the RPL ritiality alarm system. Figure 1, a design proess flow sheet, is inluded to illustrate how eah piee of Task 5 is used to establish detetor overage. Eah box olored in grey represents the output of the different subtasks. 23
34 1) MAC 2) Detetor Plaement Validation w/ Benhmarks 3) Faility Model Tallies of the Fluene Striking the Radiation Detetors with Energy Distribution 5) Detetor Calibration Model 4) Experimentally Determined Detetor Count Rate Ratio of Partiles striking the Tally Surfae Resulting in a Count Detetor Count Rate for the MAC 6) Minimum Detetor Trip Setting 9) Variane Redution 8) New Calibration Proedure 7) Required Detetor Coverage 10) Sensitivity Analysis Final Report Figure 1. Design proess flow sheet 24
35 Subtask 1 - Find the MAC Fluene and spetrum What the engineer seeks here is the determination of whih aident is the most diffiult aident to detet. The justifiation for the need to do this was disussed previously in Design Methodology Task II. How to atually make the determination is the fous of this setion. To find the MAC, start with the definition listed in ANSI/ANS Then pik the most probable physial senarios that are most likely to reah the ANSI/ANS dose limit with the smallest number of detetable partiles. So if the system employs gamma detetors, then look for the aident ondition that maximizes the number of neutrons that ontribute to the absorbed dose rate and vie a versa for a neutron detetion system. Of ourse, it is not reasonable to model every oneivable aident senario to be able to say with absolute ertainty what the right answer is. What is reasonable is to pik a handful of the most likely andidates and model those. To make a guess of what the likely aident senarios are, it is very useful to remember the shielding properties of both gamma rays and neutrons. Low Z materials shield neutrons the best: inreasing density, high Z materials shield gamma rays the best. It is lear that maximizing this disrepany will likely generate the most limiting aident ondition for the respetive partiles. If both Uranium and Plutonium are present in the faility, then fission from eah isotope should be looked at to determine whih is more diffiult to detet. Several aident onditions were analyzed for both Plutonium and Uranium inluding bare metal spheres, metal shielded ask type senarios, and water refleted soures. Eventually it 25
36 was determined for the neutron detetion system in RPL that optimally moderated Plutonium and water solutions yielded the fewest neutrons for the required dose rate. Of ourse Plutonium and water mixtures are not very physially meaningful for hemial reasons, but that is not as important as establishing an absolute lowest bounding aident ondition. Computer models should be made for the most likely aident senarios: one omplete set using 235 U soures, and one omplete set using 239 Pu soures. For the aident senarios, the dose rate in free air from neutrons and photons must be found. Finding this dose rate per neutron and per photon is neessary to determine the orresponding minimum fluene for the aident. The smallest fluene found then identifies the most diffiult aident to detet for the ANSI/ANS MAC definition. An advantage of using MCNP5 is absorbed dose an be tallied diretly by using the F6 Tally, whih is disussed further in the 2) f. Tallies subtask. MCNP5 makes a trak length estimate in a designated ell for the absorbed dose there. The dose onversion equation listed as a footnote an be used to onvert the result of a standard F6 tally to a final neutron fission soure term. 1 KENO an not diretly tally absorbed dose at a loation. To find dose with KENO, the fluene must first be found with the ode and then onverted to dose by using published fluene to dose fators. One suh standard is ANSI/ANS Neutron and Gamma-ray Fluene to Dose Fators. Be aware that urrently the status of this standard has been hanged to Historial, beause it has not been reevaluated in the mandatory ten year review period. 1 F6 Result (MeV/g)*1.00e6 (ev/mev)* e-12 (erg/ev)*0.01 (g-rad/erg)*ν(neutrons/fission) 26
37 The result of the most limiting fluene found from the MAC absorbed dose analysis will be used as the soure weighting fator in the faility model. This weighting fator will therefore sale the results of the simulations to the orret MAC. Subtask 2 - Identify potential loations for detetor plaement Before the faility an be modeled in subtask 3, a preliminary number and loation of the ritiality detetors must be found. As stated in ANSI/ANS , there must be at least two detetors that will alarm for every MAC. It is up to the user if a greater degree of overage is desired. This initial detetor plaement should be viewed as a starting point, and not as the omplete effort for detetor plaement. It should be noted that for the projet, eah detetor represents a signifiant installation and maintenane ost. From a fisal standpoint then, the engineer should optimize the design to use the fewest number of detetors to meet the overage needs. To simply install dozens of detetors throughout the faility would be very expensive. Also, every detetor must be periodially realibrated and servied, whih adds ost over the lifetime of the system. It was found that the fastest and simplest method for determining detetor plaement was to use the Updated Nulear Critiality Slide Rule (UNCSR) (Hopper & Broadhead, 1998). The UNCSR an be used to estimate dose resultant from a user speified fission yield. This referene allows the user to selet the fission yield and then see the orresponding dose from neutrons, gamma rays, and the total at a distane. The UNCSR also provides dose redution fators as a funtion of shielding thikness. This allows the yield to be adjusted for different thiknesses of intereding materials. 27
38 Preliminary plaement of the detetors needed in the faility an be made by inserting the yield from the MAC into the UNCSR. Then using engineering judgment, suffiient aident loations should be hosen for a good estimate of the overage. For eah aident loation hosen, the UNCSR an be used to find the absorbed dose in rads, at a distane. It is reommended that floor by floor drawings of the faility are obtained and the appropriate saling fators established. To begin plaing the detetors, the user must pik a threshold value of dose that represents a detetable fluene for the system. There are a number of ways to reah an estimation of the detetion threshold. For both neutron and gamma ray-based systems, the average energy from fission an be used to alulate fluene as a funtion of absorbed dose in free air. Equation 1 shows the relationship between absorbed dose and fluene. Dose in Air = Φ*E avg /ρ air (1) In Equation 1, Φ is the fluene in # of partiles per MAC, E avg is the average partile energy from fission, and ρ air is the density of air. Equation 1 does not ontain time values or rates beause the dose is assumed to be entirely from prompt fission. The values found with Equation 1 have to be orreted for the amount of intervening shielding. The UNCSR provides tables that make it easy to approximate the redution aused by shielding. Figure 2 shows a table of dose redution fators for prompt fission, whih is inluded in the UNCSR. 28
39 Figure 2. UNCSR dose redution fators for various shield thiknesses One the dose threshold value is found and orreted for shielding, the orresponding distane for the MAC an be established with the slide rule. Figure 3 is an example of a slide rule provided in the UNCSR. 29
40 Figure 3. UNCSR sample slide rule for U(93.2)O 2 -(NO 3 ) H/X=500 30
41 Using faility drawings, plot an ar of that distane value on the drawing(s) for eah aident loation. Areas with the most overlapping ars will logially see the greatest number of aidents and are therefore the optimal loations to plae detetors. If the faility has multiple stories, then the proess is repeated for eah floor. One a detetor layout is found for eah floor, then the faility as whole an be examined. Keep in mind that partiles will travel through floors and eilings. The UNCSR an be used to find the neutron fluene redution rates through the floors and eilings for the MAC. Do not spend an extensive amount of time trying to get a perfet detetor arrangement here beause the omputer simulations will provide more aurate guidane. Examples of how the ars an be drawn are inluded in the orresponding subtask in Chapter 4. Subtask 3 - Modeling the faility a. Assumptions/omissions/simplifiations Assumptions, if any, must be learly doumented beause they will need to be inluded as an appendix to the final report. The QA engineer will hek the validity of the laims made to ensure that they all result in inreased model onservatism. The guiding priniple for making assumptions is that they are allowable so long as they inrease the amount of onservatism, not derease it. An example assumption ould be to not model the dirt surrounding the building to save omputational time. This is an example of an aeptable assumption beause it only results in dereasing the number of partiles that ould be refleted bak into the faility from the MAC. Therefore the same guiding priniple still holds of being able to detet the worst ase possible. An 31
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 07/14 * Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online
Table of Contents. Appendix II Application Checklist. Export Finance Program Working Capital Financing...7
 Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS
 Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Virginia Department of Taxation INCOME TAX WITHHOLDING GUIDE FOR EMPLOYERS www.tax.virginia.gov 2614086 Rev. 01/16 Table of Contents Introdution... 1 Important... 1 Where to Get Assistane... 1 Online File
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Pre-Experience Postgraduate Programmes Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
 Form 5500 Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Servie Department of Labor Employee Benefits Seurity Administration Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
Form 5500 Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Servie Department of Labor Employee Benefits Seurity Administration Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING I
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING I CS 10 Catalog Desription PREREQUISITE: CS 21. Introdution to the systems development life yle, software development models, analysis and design tehniques and tools, and validation
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING I CS 10 Catalog Desription PREREQUISITE: CS 21. Introdution to the systems development life yle, software development models, analysis and design tehniques and tools, and validation
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurance Plan Exclusively for NBAC members Issued by The Prudential Insurance Company of America (Prudential)
 Plan Basis The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane Plan Exlusively for NBAC members Issued by The Prudential Insurane Company of Ameria (Prudential) What does it over? The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane
Plan Basis The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane Plan Exlusively for NBAC members Issued by The Prudential Insurane Company of Ameria (Prudential) What does it over? The D.C. Long Term Disability Insurane
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE
 UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
BENEFICIARY CHANGE REQUEST
 Poliy/Certifiate Number(s) BENEFICIARY CHANGE REQUEST *L2402* *L2402* Setion 1: Insured First Name Middle Name Last Name Permanent Address: City, State, Zip Code Please hek if you would like the address
Poliy/Certifiate Number(s) BENEFICIARY CHANGE REQUEST *L2402* *L2402* Setion 1: Insured First Name Middle Name Last Name Permanent Address: City, State, Zip Code Please hek if you would like the address
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OpenScape 4000 CSTA V7 Connectivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1. Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76D1
 OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON COLLEGE OF NURSING. NURS 6390-004 Introduction to Genetics and Genomics SYLLABUS
 THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON COLLEGE OF NURSING NURS 6390-004 Introdution to Genetis and Genomis SYLLABUS Summer Interession 2011 Classroom #: TBA and 119 (lab) The University of Texas at Arlington
THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON COLLEGE OF NURSING NURS 6390-004 Introdution to Genetis and Genomis SYLLABUS Summer Interession 2011 Classroom #: TBA and 119 (lab) The University of Texas at Arlington
BUILDING CODE SUMMARY GENERAL NOTES DESIGN BUILD ELECTRICAL DESIGN BUILD MECHANICAL & PLUMBING GENERAL NOTES GENERAL NOTES G101
 D D BUILDING CODE SUMMARY GENERAL NOTES PROJECT DESCRIPTION: THIS PROJECT IS THE MINOR RENOVATION OF AN EXISTING OUTPATIENT CLINIC. SCOPE CONSISTS OF PAINT, CARPET, TILE, AND UPGRADE TO DIGITAL X-RAY BUILDING
D D BUILDING CODE SUMMARY GENERAL NOTES PROJECT DESCRIPTION: THIS PROJECT IS THE MINOR RENOVATION OF AN EXISTING OUTPATIENT CLINIC. SCOPE CONSISTS OF PAINT, CARPET, TILE, AND UPGRADE TO DIGITAL X-RAY BUILDING
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
i e AT 21 of 2006 EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006
 i e AT 21 of 2006 EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Employment At 2006 Index i e EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Index Setion Page PART I DISCRIMINATION AT RECRUITMENT ON TRADE UNION GROUNDS 9 1 Refusal of employment on grounds
i e AT 21 of 2006 EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Employment At 2006 Index i e EMPLOYMENT ACT 2006 Index Setion Page PART I DISCRIMINATION AT RECRUITMENT ON TRADE UNION GROUNDS 9 1 Refusal of employment on grounds
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Practices
 Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
F220 Series. Installation Instructions. Photoelectric Smoke/Heat Detectors
 F0 Series EN Installation Instrutions Photoeletri Smoke/Heat Detetors F0 Series Installation Instrutions.0 General Information EN.0 General Information. F0-B6 Series Bases Use with the F0 Series Heat and
F0 Series EN Installation Instrutions Photoeletri Smoke/Heat Detetors F0 Series Installation Instrutions.0 General Information EN.0 General Information. F0-B6 Series Bases Use with the F0 Series Heat and
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Account Contract for Card Acceptance
 Aount Contrat for Card Aeptane This is an Aount Contrat for the aeptane of debit ards and redit ards via payment terminals, on the website and/or by telephone, mail or fax. You enter into this ontrat with
Aount Contrat for Card Aeptane This is an Aount Contrat for the aeptane of debit ards and redit ards via payment terminals, on the website and/or by telephone, mail or fax. You enter into this ontrat with
SCHEME FOR FINANCING SCHOOLS
 SCHEME FOR FINANCING SCHOOLS UNDER SECTION 48 OF THE SCHOOL STANDARDS AND FRAMEWORK ACT 1998 DfE Approved - Marh 1999 With amendments Marh 2001, Marh 2002, April 2003, July 2004, Marh 2005, February 2007,
SCHEME FOR FINANCING SCHOOLS UNDER SECTION 48 OF THE SCHOOL STANDARDS AND FRAMEWORK ACT 1998 DfE Approved - Marh 1999 With amendments Marh 2001, Marh 2002, April 2003, July 2004, Marh 2005, February 2007,
Entrepreneur s Guide. Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015. newpa.com
 Entrepreneur s Guide Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015 newpa.om The Entrepreneur s Guide: Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania was prepared by the Pennsylvania Department
Entrepreneur s Guide Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015 newpa.om The Entrepreneur s Guide: Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania was prepared by the Pennsylvania Department
TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING
 INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre
 Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Board Building Recruiting and Developing Effective Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations
 Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit
Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit Organizations Board Development Board Building Reruiting and Developing Effetive Board Members for Not-for-Profit
Unit 12: Installing, Configuring and Administering Microsoft Server
 Unit 12: Installing, Configuring and Administering Mirosoft Server Learning Outomes A andidate following a programme of learning leading to this unit will be able to: Selet a suitable NOS to install for
Unit 12: Installing, Configuring and Administering Mirosoft Server Learning Outomes A andidate following a programme of learning leading to this unit will be able to: Selet a suitable NOS to install for
Information Security 201
 FAS Information Seurity 201 Desktop Referene Guide Introdution Harvard University is ommitted to proteting information resoures that are ritial to its aademi and researh mission. Harvard is equally ommitted
FAS Information Seurity 201 Desktop Referene Guide Introdution Harvard University is ommitted to proteting information resoures that are ritial to its aademi and researh mission. Harvard is equally ommitted
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System
 DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
Retirement Option Election Form with Partial Lump Sum Payment
 Offie of the New York State Comptroller New York State and Loal Retirement System Employees Retirement System Polie and Fire Retirement System 110 State Street, Albany, New York 12244-0001 Retirement Option
Offie of the New York State Comptroller New York State and Loal Retirement System Employees Retirement System Polie and Fire Retirement System 110 State Street, Albany, New York 12244-0001 Retirement Option
protection p1ann1ng report
 ( f1re protetion p1ann1ng report I BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES NO. 15 OF A SERIES A Comparison of Insurane and Constrution Costs for Low-Rise Multifamily
( f1re protetion p1ann1ng report I BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES NO. 15 OF A SERIES A Comparison of Insurane and Constrution Costs for Low-Rise Multifamily
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman bowman@vt.edu Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
ru ILllYC UT 3 IMC IrrCRCIYLL3 AND SIMLARITIES BETWEEN CALIFORNIA AND h.tlnols
 ru ILllYC UT 3 IMC IrrCRCIYLL3 AND SIMLARITIES BETWEEN CALIFORNIA AND h.tlnols Foreward This paper outlines some of the signifiant differenes and similarities between the eletri power environments whih
ru ILllYC UT 3 IMC IrrCRCIYLL3 AND SIMLARITIES BETWEEN CALIFORNIA AND h.tlnols Foreward This paper outlines some of the signifiant differenes and similarities between the eletri power environments whih
Customer Reporting for SaaS Applications. Domain Basics. Managing my Domain
 Produtivity Marketpla e Software as a Servie Invoiing Ordering Domains Customer Reporting for SaaS Appliations Domain Basis Managing my Domain Managing Domains Helpful Resoures Managing my Domain If you
Produtivity Marketpla e Software as a Servie Invoiing Ordering Domains Customer Reporting for SaaS Appliations Domain Basis Managing my Domain Managing Domains Helpful Resoures Managing my Domain If you
NASDAQ Commodity Index Methodology
 NASDAQ Commodity Index Methodology January 2016 1 P a g e 1. Introdution... 5 1.1 Index Types... 5 1.2 Index History... 5 1.3 Index Curreny... 5 1.4 Index Family... 6 1.5 NQCI Index Setors... 6 2. Definitions...
NASDAQ Commodity Index Methodology January 2016 1 P a g e 1. Introdution... 5 1.1 Index Types... 5 1.2 Index History... 5 1.3 Index Curreny... 5 1.4 Index Family... 6 1.5 NQCI Index Setors... 6 2. Definitions...
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability
 Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Transfer of Functions (Isle of Man Financial Services Authority) TRANSFER OF FUNCTIONS (ISLE OF MAN FINANCIAL SERVICES AUTHORITY) ORDER 2015
 Transfer of Funtions (Isle of Man Finanial Servies Authority) Order 2015 Index TRANSFER OF FUNCTIONS (ISLE OF MAN FINANCIAL SERVICES AUTHORITY) ORDER 2015 Index Artile Page 1 Title... 3 2 Commenement...
Transfer of Funtions (Isle of Man Finanial Servies Authority) Order 2015 Index TRANSFER OF FUNCTIONS (ISLE OF MAN FINANCIAL SERVICES AUTHORITY) ORDER 2015 Index Artile Page 1 Title... 3 2 Commenement...
A Comparison of Default and Reduced Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T
 9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
i e AT 8 of 1938 THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939
 i e AT 8 of 1938 THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 The Personal Injuries (Emergeny Provisions) At 1939 Index i e THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 Index Setion
i e AT 8 of 1938 THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 The Personal Injuries (Emergeny Provisions) At 1939 Index i e THE PERSONAL INJURIES (EMERGENCY PROVISIONS) ACT 1939 Index Setion
Improved Vehicle Classification in Long Traffic Video by Cooperating Tracker and Classifier Modules
 Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Economics
 Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System NUR 204 ROLE TRANSITION FOR THE REGISTERED NURSE. Plan Of Instruction
 Alabama Department of Postseonary Euation Representing Alabama s Publi Two-Year ollege System NUR 204 ROLE TRANSITION FOR THE REGISTERED NURSE Plan Of Instrution Effetive Date: 2006 Version Number: 2006-1
Alabama Department of Postseonary Euation Representing Alabama s Publi Two-Year ollege System NUR 204 ROLE TRANSITION FOR THE REGISTERED NURSE Plan Of Instrution Effetive Date: 2006 Version Number: 2006-1
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
Software Ecosystems: From Software Product Management to Software Platform Management
 Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
AT 6 OF 2012 GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012
 i e AT 6 OF 2012 GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Gambling Duty At 2012 Index i e GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Index Setion Page PART 1 INTRODUCTORY 5 1 Short title... 5 2 Commenement... 5 3 General interpretation...
i e AT 6 OF 2012 GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Gambling Duty At 2012 Index i e GAMBLING DUTY ACT 2012 Index Setion Page PART 1 INTRODUCTORY 5 1 Short title... 5 2 Commenement... 5 3 General interpretation...
Fixed-income Securities Lecture 2: Basic Terminology and Concepts. Present value (fixed interest rate) Present value (fixed interest rate): the arb
 Fixed-inome Seurities Leture 2: Basi Terminology and Conepts Philip H. Dybvig Washington University in Saint Louis Various interest rates Present value (PV) and arbitrage Forward and spot interest rates
Fixed-inome Seurities Leture 2: Basi Terminology and Conepts Philip H. Dybvig Washington University in Saint Louis Various interest rates Present value (PV) and arbitrage Forward and spot interest rates
Procurement auctions are sometimes plagued with a chosen supplier s failing to accomplish a project successfully.
 Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Health Savings Account Application
 Health Savings Aount Appliation FOR BANK USE ONLY: ACCOUNT # CUSTOMER # Health Savings Aount (HSA) Appliation ALL FIELDS MUST BE COMPLETED. Missing fields may delay the aount opening proess and possibly
Health Savings Aount Appliation FOR BANK USE ONLY: ACCOUNT # CUSTOMER # Health Savings Aount (HSA) Appliation ALL FIELDS MUST BE COMPLETED. Missing fields may delay the aount opening proess and possibly
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
MEDICATION MANAGEMENT ASSESSMENT
 MEDICATION MANAGEMENT ASSESSMENT The Mediation Management Assessment provides evidene-based reommendations/standards for Minnesota hospitals in the development of a omprehensive mediation safety program.
MEDICATION MANAGEMENT ASSESSMENT The Mediation Management Assessment provides evidene-based reommendations/standards for Minnesota hospitals in the development of a omprehensive mediation safety program.
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
PROCEEDS OF CRIME (BUSINESS IN THE REGULATED SECTOR) ORDER 2015
 Proeeds of Crime (Business in the Regulated Setor) Order 2015 Artile 1 Statutory Doument No. 2015/0073 Proeeds of Crime At 2008 PROCEEDS OF CRIME (BUSINESS IN THE REGULATED SECTOR) ORDER 2015 Approved
Proeeds of Crime (Business in the Regulated Setor) Order 2015 Artile 1 Statutory Doument No. 2015/0073 Proeeds of Crime At 2008 PROCEEDS OF CRIME (BUSINESS IN THE REGULATED SECTOR) ORDER 2015 Approved
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Wireless Transmission Systems. Instructor
 Teleommuniation Engineering Tehnology, Texas A&M University Wireless Transmission Systems Leture Notes - Copyright Jeff M. MDougall 2 Wireless Transmission Systems Teleommuniation Engineering Tehnology,
Teleommuniation Engineering Tehnology, Texas A&M University Wireless Transmission Systems Leture Notes - Copyright Jeff M. MDougall 2 Wireless Transmission Systems Teleommuniation Engineering Tehnology,
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Application for Emergency/Minor Home Repair Program City of Coeur d'alene, CDBG Entitlement Program
 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY Date Reeived Appliation omplete By Appliation for Emergeny/Minor Home Repair Program Panhandle Area Counil The City of Coeur d'alene Emergeny/Minor Repair Program is designed to assist
FOR OFFICE USE ONLY Date Reeived Appliation omplete By Appliation for Emergeny/Minor Home Repair Program Panhandle Area Counil The City of Coeur d'alene Emergeny/Minor Repair Program is designed to assist
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
The following excerpt are pages from the North American Product Technical Guide, Volume 2: Anchor Fastening, Edition 16.
 The following exerpt are pages from the North Amerian Produt Tehnial Guide, Volume 2: Anhor Fastening, Edition 16. Please refer to the publiation in its entirety for omplete details on this produt inluding
The following exerpt are pages from the North Amerian Produt Tehnial Guide, Volume 2: Anhor Fastening, Edition 16. Please refer to the publiation in its entirety for omplete details on this produt inluding
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
' R ATIONAL. :::~i:. :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliance with the way you work PRODUCT BRIEF
 ' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Medical Assistant-Registered Application Packet
 Medial Assistant-Registered Appliation Paket Contents: 1. 651-001...Contents List/SSN Information/Mailing Information...1 page 2. 651-002...Appliation Instrutions Cheklist...2 pages 3. 651-003...Credentialing
Medial Assistant-Registered Appliation Paket Contents: 1. 651-001...Contents List/SSN Information/Mailing Information...1 page 2. 651-002...Appliation Instrutions Cheklist...2 pages 3. 651-003...Credentialing
i_~f e 1 then e 2 else e 3
 A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Robust Classification and Tracking of Vehicles in Traffic Video Streams
 Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
Proeedings of the IEEE ITSC 2006 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conferene Toronto, Canada, September 17-20, 2006 TC1.4 Robust Classifiation and Traking of Vehiles in Traffi Video Streams
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
BUSINESS PRACTICE BULLETIN The School Board of Broward County, Florida
 PAGE: 1 OF 16 (ECE) GUIDELINES FOR INFANT, TODDLER AND PRE-K PROGRAMS TOPICS IN BULLETIN: I. GENERAL INFORMATION II. CRITERIA FOR OPENING PROGRAM III. ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT IV. OPERATIONAL
PAGE: 1 OF 16 (ECE) GUIDELINES FOR INFANT, TODDLER AND PRE-K PROGRAMS TOPICS IN BULLETIN: I. GENERAL INFORMATION II. CRITERIA FOR OPENING PROGRAM III. ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT IV. OPERATIONAL
Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Research Center. Abstract
 Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Chapter 1: Introduction
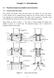 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Electronic signatures in German, French and Polish law perspective
 Artile Eletroni signatures in German, Frenh and Polish law perspetive DR CHRISTIANE BIEREKOVEN, PHILIP BAZIN AND TOMASZ KOZLOWSKI This artile presents some signifiant issues on the reognition of eletroni
Artile Eletroni signatures in German, Frenh and Polish law perspetive DR CHRISTIANE BIEREKOVEN, PHILIP BAZIN AND TOMASZ KOZLOWSKI This artile presents some signifiant issues on the reognition of eletroni
