Previously Published Works UC Berkeley
|
|
|
- Jonas Oliver
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Previously Published Works UC Berkeley A University of California author or department has made this artile openly available. Thanks to the Aademi Senate s Open Aess Poliy, a great many UC-authored sholarly publiations will now be freely available on this site. Let us know how this aess is important for you. We want to hear your story! Peer Reviewed Title: Miropower generation using ombustion: Issues and approahes Journal Issue: PROCEEDINGS OF THE COMBUSTION INSTITUTE, 29 Author: Fernandez-Pello, Carlos, University of California, Berkeley Publiation Date: Series: UC Berkeley Previously Published Works Permalink: Additional Info: The published version of this artile is available at: journaldesription.ws_home/703522/desription Original Citation: A.C. Fernandez-Pello AC, Miropower generation using ombustion: Issues and approahes, PROCEEDINGS OF THE COMBUSTION INSTITUTE 29: Part 1, Published Web Loation: Keywords: miniaturization, miro eletro mehanial devies, MEMS, miroombustion, speifi energy, turbines, engines, rokets, FABRICATION Abstrat: The push toward the miniaturization of eletro-mehanial devies and the resulting need for miro-power generation (milli-watts to watts) with low-weight, long-life devies has led to the reent esholarship provides open aess, sholarly publishing servies to the University of California and delivers a dynami researh platform to sholars worldwide.
2 development of the field of miro-sale ombustion. The onept behind this new field is that sine batteries have low speifi energy, and liquid hydroarbon fuels have a very high speifi energy, a miniaturized power generating devie, even with a relatively ineffiient onversion of hydroarbon fuels to power would result in inreased lifetime and/or redued weight of an eletroni or mehanial system that urrently requires batteries for power. In addition to the interest in miniaturization, the field is also driven by the potential fabriation of the devies using Miro Eletro Mehanial Systems (MEMS) or rapid prototyping tehniques, with their favorable harateristis for mass prodution and low ost. The miro-power generation field is very young, and still is in most ases in the feasibility stage. However, onsidering that it is a new frontier of tehnologial development, and that only a few projets have been funded, it an be said that signifiant progress has been made to date. Currently there is onsensus, at least among those working in the field, that ombustion in the miro-sale is possible with proper thermal and hemial management. Several meso-sale and miro-sale ombustors have been developed that appear to operate with good ombustion effiieny. Some of these ombustors have been applied to energize thermoeletri systems to produe eletrial power, although with low overall effiieny. Several turbines/engines have also been, or are being, developed, some of them urrently produing positive power, also with low effiieny to date. Miro-rokets using solid or liquid fuels have been built and shown to produe thrust. Hydrogen-based miro size fuel ells have been suessfully developed, and there is a need to develop reliable reformers (or diret-onversion fuel ells) for liquid hydroarbons so that the fuel ells beome ompetitive with batteries. In this work, some of the tehnologial issues related to meso and miro-sale ombustion and the operation of thermohemial devies for power generation will be disussed. Some of the systems urrently being developed will be presented and desribed. Copyright Information: All rights reserved unless otherwise indiated. Contat the author or original publisher for any neessary permissions. esholarship is not the opyright owner for deposited works. Learn more at esholarship provides open aess, sholarly publishing servies to the University of California and delivers a dynami researh platform to sholars worldwide.
3 Miro-Power Generation Using Combustion: Issues and Approahes A. Carlos Fernandez-Pello Department of Mehanial Engineering, University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA , USA FAX: (510) Colloquium: 14. New Conepts in Combustion Tehnology. Miro-ombustors Prepared for presentation as a Topial Review at the Twenty-Ninth International Symposium on Combustion, July 21-26, 2002, Sapporo, Japan
4 ABSTRACT The push toward the miniaturization of eletro-mehanial devies and the resulting need for miro-power generation (milli-watts to watts) with low-weight, long-life devies has led to the reent development of the field of miro-sale ombustion. The onept behind this new field is that sine batteries have low speifi energy, and liquid hydroarbon fuels have a very high speifi energy, a miniaturized power generating devie, even with a relatively ineffiient onversion of hydroarbon fuels to power would result in inreased lifetime and/or redued weight of an eletroni or mehanial system that urrently requires batteries for power. In addition to the interest in miniaturization, the field is also driven by the potential fabriation of the devies using Miro Eletro Mehanial Systems (MEMS) or rapid prototyping tehniques, with their favorable harateristis for mass prodution and low ost. The miro-power generation field is very young, and still is in most ases in the feasibility stage. However, onsidering that it is a new frontier of tehnologial development, and that only a few projets have been funded, it an be said that signifiant progress has been made to date. Currently there is onsensus, at least among those working in the field, that ombustion in the miro-sale is possible with proper thermal and hemial management. Several meso-sale and miro-sale ombustors have been developed that appear to operate with good ombustion effiieny. Some of these ombustors have been applied to energize thermoeletri systems to produe eletrial power, although with low overall effiieny. Several turbines/engines have also been, or are being, developed, some of them urrently produing positive power, also with low effiieny to date. Miro-rokets using solid or liquid fuels have been built and shown to produe thrust. Hydrogen-based miro size fuel ells have been suessfully developed, and there is a need to develop reliable reformers (or diret-onversion fuel ells) for liquid hydroarbons so that the fuel ells beome ompetitive with batteries. In this work, some of the tehnologial issues related to meso and miro-sale ombustion and the operation of thermohemial devies for power generation will be disussed. Some of the systems urrently being developed will be presented and desribed. 1
5 INTRODUCTION The last few years have experiened a growing trend in the miniaturization of mehanial and eletro-mehanial engineering devies, whih follows that initiated by the areas of miroeletronis, biomehanis, and moleular biology, and that is in large part the result of the progress made in miro-fabriation tehniques. High preision fabriation of devies in the entimeter sale range are being made using miro-fabriation tehniques suh as eletrodisharge mahining (EDM), laser beam mahining (LBM) or foused ion beam mahining (FIBM) [1,2]. Devies in the millimeter sale range are being fabriated using Miro-Eletro- Mehanial Systems (MEMS), rapid prototyping and bath-manufaturing tehniques [3,4], and materials that are similar to those used in the integrated iruit /mirohip industry. Although initially the miro-devies produed using EDM, LBM or FIBM were primarily related to biomediine, and those fabriated using MEMS were sensors and atuators, reently other more omplex mehanial devies suh as pumps, motors, miro-rovers, and miro-airplanes are being developed. The interest in produing miniaturized mehanial devies opens exiting new opportunities for ombustion, espeially in the field of miro-power generation, beause of the need for power supply devies with high speifi energy (small-size, low weight, long duration). Typial portable onsumer eletronis suffer from short operation yles between harges or replaement, and their overall weight onsists largely of battery weight. Similarly, other more advaned MEMS based devies depend on battery systems that oupy signifiant frations of both mass and volume of the entire devie. A typial example of this problem is depited in Fig. 1 that shows a MEMS sensing /ommuniation network devie of a few mm 3 volume powered by one of the smallest batteries urrently available [5]. Miniature mehanial devies suh as miro-rovers, miro-robots, and miro-airplanes are also limited by the weight of the available 2
6 power systems. The need to redue system weight, inrease operational lifetimes, and redue unit ost has engendered the field of miro-power generation [6-9], high-speifi-energy miroeletro-mehanial power systems. The onept behind this new field is to utilize the high speifi energy of liquid hydroarbon fuels in ombustion driven miro-devies to generate power. The potential advantage of using liquid hydroarbon ombustion to produe power is shown graphially in Fig. 2. Liquid hydroarbons have an extremely high speifi energy, (typially 45 MJ/kg), are easily transportable and are quite safe [10]. Top batteries urrently available (Lithium) have an energy density of 1.2 MJ/kg (0.6 MJ/kg for an Alkaline battery). Thus, a miniature ombustion devie with a mere 3% system effiieny would ompete with top batteries simply from the fat that the fuel is easily replaeable. Although higher effiienies are needed for ombustion systems to displae batteries, the high effiienies obtained in large-sale power systems enourage the development of miniaturized power generation devies using ombustion, with the expetation that devies with ompetitive effiienies an be developed. Furthermore, there are speifi appliations were mehanial power, or simply heat, is desired (rovers, airplanes, Stirling engine, et) and were a ombustion based devie will have the added advantage of providing this power diretly. In addition to the interest in miniaturization, the field is also driven by the potential fabriation of the devies using MEMS or rapid prototyping tehniques, with their mass prodution and low ost harateristis. There is of ourse the added issue of environmental onsiderations related to the use of ombustion. Given the small size of the devies being onsidered, however, their CO 2 and H 2 O emissions and heat release would be omparable to that of the human being for the meso-sale size, and signifiant less for the miro-sale ones [11]. Sine it is likely that the miro-devies will have ombustion effiienies smaller than those of 3
7 the larger devies, it is expeted that the frational prodution of unburned hydroarbons and CO, will be omparatively larger. On the other hand, batteries have their own environmental issues, and their prodution and disposal present an environmental hazard. The power-generation devies addressed in the present review are those that aim to generate power in the range of a few watts to milliwatts. This is in ontrast with the so-alled miroturbines, whih generate power of the order of kilowatts and are not miro in the present sense but rather in the sense of being smaller than their larger ounterparts. Power generation in the watts range has multiple appliations, suh as eletroni devies (laptops, phones, et), and miniaturized mehanial systems (small robots, rovers, airplanes, et.). The orresponding ombustion devies are of the order of one entimeter in size (meso-sale), and their mirofabriation tehniques are relatively onventional (EDM), in some ases with some MEMS omponents. Power generation in the milliwatt range (miro-sale) has its appliation primarily in miro-eletroni omponents (sensors, transmitters, et), with the ultimate goal of inorporating the power-generation devie into the miro-eletroni omponent. These power generation devies are onstruted using primarily MEMS. The ultimate goal is to have power generation in a hip. The system would then inorporate in the same unit the power devie, the miroproessor to ontrol the overall system, and some sort of sensor/emitter or atuator. The miro-power generation field is young (4 to 6 years) beause its interest has resulted from the reent development of fabriation tehniques to miniaturize mehanial devies, and still is in most ases in the feasibility stage. However, onsidering that it is a new frontier of tehnologial development, and that only a few projets have been funded to date (primarily by government agenies that fund advaned oneptual projets, suh as DARPA [8,9]), it an be said that signifiant and enouraging progress has been made. Several miro-ombustors have 4
8 been fabriated that appear to operate with good ombustion effiieny [12-14]. Some of these ombustors have been applied to energize thermoeletri systems to produe power. The system effiieny is urrently too low, but the limitation appears to be in the thermoeletri omponent and not in the ombustion proess itself. Several turbines/engines have also been or are being developed, some of them urrently produing positive power, although again with low effiieny [6,15,16]. Here the problem appears to be in fabriation and thermal management that either limit the toleranes in moving parts (leakage, low ompression ratio), or ause redued effiieny of individual omponents (ompressor, ombustion hamber). Fuel ells are also being developed [17], and although not a ombustion devie, they have issues that are of interest to the ombustion ommunity. Although hydrogen-based miro-fuel ells have been suessfully developed [17], there is a need to produe reliable reformers (or diret onversion fuel ells) so that they an be used with liquid hydroarbons, and an beome ompetitive with the batteries. Still not looked at is the potential omplementarity of the different systems (ogeneration), suh as using the exhaust heat from engines to run thermoeletri generators, fuel ell reformers, or Stirling engines. The ombined systems ould result in improved overall onversion effiienies. Also worth mentioning is that small-sale ombustion has other useful appliations than power generation and heat prodution for use in power yles. Positioning of loalized heat is an example of its potential appliations. Another interesting example is the use of arrays of mesosale burners to produe distributed ombustion in large sale gas turbine ombustors, whih has the potential for inter-turbine reheat, and for premix or highly vitiated ombustion, to redue NOx [18]. 5
9 Some of the tehnologial issues related to miro-sale ombustion and thermo-hemial devies for power generation are disussed below. Many of the systems urrently being developed are also presented and briefly disussed. THERMOPHYSICAL ISSUES The harateristi length of the miro-ombustors being developed to date, even in MEMS size systems, is suffiiently larger than the moleular mean-free path of the air and other gases flowing through the systems that the physial-hemial behavior of the fluids is fundamentally the same as their maro-sale ounterparts. For example, the Knudsen number for air flowing through a 0.1 mm wide hannel is of the order of 10-3, whih is muh smaller than that for freemoleule flow (Kn >1). Consequently, the standard hypotheses of thermo-fluid suh as the noslip ondition and the ontinuum medium will still apply. However, the small size of the mirodevies or their omponents auses partiular harateristis of the fluid mehanis, heat transfer and ombustion involved in the devie operation. Some of the saling issues involved in miro-ombustors an be understood by normalizing the onservation equations of momentum, energy, and speies in terms of the harateristi length and parameters of the devie, and analyzing their terms as the length sale is redued. The normalized 1-D form of the governing equations for the gas and solid phase and their relevant boundary onditions an be written as (symbols are defined in the nomenlature) t l u u t u + u x = ρ p 2 u 2 1 p 1 u + ν 2 ρ x Re x + gl u 2 (1) t l u 2 T T 1 T Q + u = α + Da 2 t x Pe x C T p w& (2) 6
10 t l u y t y i + u x 2 1 yi = D 2 LePe x 1 + Da y i i w& (3) T s t = Foα s T 2 s 2 x (4) The relevant normalized boundary onditions for these equations are: µ u u u = 0 τ = µ τ l y T = T w s T s x T = λ x T s λ = Bi( T 1) x s y i y i = 0 = ( LePe) y i x The harateristi length of the omponents of large power systems is large and generally the Reynolds and Pelet numbers are also large. Thus the fluid flows are mostly turbulent, and as seen from Eqs. (1) (3) the visous and diffusive effets are small ompared to the onvetive effets. It is also dedued that the harateristi time in these onvetive dominated flows is t = l u, whih is normally referred to as residene time. The boundary onditions provide information about wall effets that usually have a small influene on the overall system. As the size of the devies is redued, the harater of the governing equations and the importane of the different terms in the equations hange. As the harateristi length of the devie is redued, the Reynolds and Pelet numbers derease and fluid flow tends to be less turbulent, so the visous effets and the diffusive transport of mass and heat beome inreasingly important. From the point of view of ombustion, an important issue is the magnitude of the residene time, beause it dereases as the length of the ombustor dereases, and it has to be larger than the hemial time, t & " = ρ w, for omplete ombustion to our. 7
11 For miro-devies (MEMS sale) with very small harateristi lengths and onsequently small Reynolds and Pelet numbers, the flow is primarily laminar. Also as an be seen from Eqs. (1)-(3), the visous and diffusive terms an beome dominant, and the onvetive and buoyant effets beome negligible. In this ase the harateristi time beomes t = l u Pe = l 2 α (for unity Prandtl and Lewis numbers), normally referred to as the diffusion time. Sine turbulent mixing is small, speies mixing will be primarily by diffusion. In this regard the diffusion time is important sine it has to be smaller than the residene time for omplete mixing to our. Conerning ombustion, the soure term of Eq. (2) beomes fatored by Pe, whih gives rise to a Damkohler number based on a diffusion time, i.e., Da 2 = l w& ρα. The value of the Damkohler number (ether based on residene or diffusion time) is important to determine whether ombustion will be ompleted in the ombustion hamber of the miro-devie sine it is neessary that the hemial time be smaller than the physial time. Turning to the solid phase, the Fourier number inreases as the length sale is dereased, whih results in a quasi-steady behavior of the solid temperature. The harateristi time of heat ondution through the solid is t 2 s = l α s. Sine the thermal diffusivity of the miro-devies materials (Si, SiC) is of the same order of magnitude as that of air, the gas and solid diffusion times will be similar, whih has impliations in the heat transfer harateristis from the gas to, or from, the solid, partiularly if there are periodi heat fluxes at their boundary with harateristi times muh different than the diffusion time. From the relevant boundary onditions of the gas phase onservation equations, it is dedued that as the length sale is redued while keeping the wall and flow variables fixed, the veloity gradients and wall fritional effets inrease, as do the gas temperature and speies gradients at the wall. Beause of the high gradients, however, it will be diffiult to keep the differene 8
12 between the wall and the bulk flow variables fixed sine the resulting inrease in head loss and heat and mass transfer will tend to redue it. This implies that in miro-devies it will be diffiult to keep flow veloities, and temperature and mass onentration differenes, of the same magnitude as in their large ounterparts. In the solid, on other hand, sine the Biot number will tend to derease (fatored by the orresponding inrease in the heat transfer oeffiient), the solid temperature gradient will also tend to derease as indiated by the wall boundary ondition. It is expeted therefore that miro-devies will have nearly uniform solid phase temperatures, unless the boundary heat transfer oeffiient is large enough for Bi>0.1, whih is unlikely. Thus, the wall effets will be very important from the point of view of ombustion in miroombustors. The tendeny will be for the presene of small Damkohler numbers (weak ombustion) due to heat losses through the ombustor walls that redue the reation rate and onsequently inrease the hemial time, while the small dimensions redue the physial time. The impliations of these trends on the operation of small-sale ombustion devies are disussed with some detail below. Fluids The small diameter of the hannels for the reatant intake, the produt exhaust, and the atual ombustion hamber onstrain the flows in miro-devies to relatively small Reynolds number. For example, for a 100 W meso-sale devie using a stoihiometri mixture of otane/air and with a system effiieny of 10%, the volumetri flow rate of gaseous mixture will be approximately 0.4 l/s. Assuming a 5 mm diameter intake tube, the Reynolds number will be of the order of 5000 or below, depending on the gas temperature. Similarly, for a 100 mw mirosale devie with a 0.5 mm diameter intake, the Reynolds number will be around 50. Thus, the flow will be primarily laminar for the small devies and onsequently mixing of different speies 9
13 will be primarily by diffusion. Also as stated above, visous effets will be important, whih together with the large aspet ratios in the miro-hannels, implies that fritional losses will be high and that inreased pumping will be required. On the other hand, visous fores help in some of the problems harateristi of these devies, suh as leakage of gases through joints or through moving surfaes. This ould be important in IC, engines sine their effiieny is strongly dependent on the ompression ratio, whih will be affeted by the leakage at the piston (rotor)/housing surfaes. Unexpeted behavior may result in those ases with extremely small length sales (~µm), suh as in some MEMS devies or their omponents. The most obvious effet is that the flow in these ases operates in the near-stokesian regime where the Reynolds number is often less than one. Small hanges in temperature, for example, an signifiantly hange the volumetri flow rate as an fluid-wall interations that are normally ignored in marosopi flows. Also the small length sales of the hannels result in high veloity gradients in the fluid. As seen from the aforementioned boundary onditions, this results in high wall fritional losses, and high onvetive heat transfer oeffiients. These in turn an result in large pressure losses, high heat transfer to or from the fluid to the wall, and enhaned diffusive mixing. As in their large-sale ounterparts, the miro-ombustors must use the ambient air as the soure of oxygen to both redue volume and to maintain their performane edge in energy density. This implies that the liquid hydroarbon must be evaporated and mixed with the air prior to entering the ombustion hamber in premixed systems, or injeted diretly in the ombustion hamber in non-premixed systems. The small length sales have a large impat on the dynamis and energy requirements assoiated with phase hange and two-phase flows. It has been observed, for example, that the phase hange from liquid to vapor in MEMS size hannels ours 10
14 abruptly and in an unstable fashion [19], quite differently from the transition observed in large tubes [20]. This is partially due to the large surfae area to volume ratio in miro-hannels that enhanes the nuleation and wetting effets at the wall, and to the behavior of bubbles that is strongly affeted by the small length sales and signifiantly differs from marosopi behavior. To inrease fuel evaporation or to injet the fuel into the ombustion hamber, it may be onvenient to atomize the liquid. As the devies beome smaller, the atomization devie and the droplets must also be redued in size. Sine the surfae energy of a droplet is inversely proportional to the radius of urvature, a derease in the system s dimensions will inrease the pressure and energy requirements for atomization. Although some MEMS-based simple atomizers (plain orifie type) have been developed [21], it appears that more elaborate devies or tehniques to produe miron size droplets that will evaporate and mix with the air in the available miro-sale residene time will be needed. MEMS-based miro-eletrospray atomizers [22,23] appear to be good potential andidates for miro-ombustors [24,25]. The low Reynolds number oupled with the planar nature of MEMS devies makes mixing of the reatants a potential problem in miro-systems. Although the small diameter of the hannels helps their diffusive mixing, the residene time of the fluids in the hannels is also small, and may be insuffiient to ensure omplete mixing. For example, for a gaseous fuel/air mixture flowing through a 0.5 mm hannel, the diffusion time will be of the order of 0.02 se, and if flow veloity is of the order of 1 m/s, the hannel length would have to be 25 mm to ensure diffusive mixing. This hannel length may be too long for the devie, or result in signifiant pressure losses. Thus, in some ases where mixing of speies may need to be enhaned, different dynami mixing approahes (flow instabilities, ultrasound, et) may have to be implemented, even though they will introdue fabriation omplexities and will onsume 11
15 valuable energy. To date, several approahes have been used to inrease mixing rates, primarily of liquids [26-28]. The main problems with these approahes are fabriation omplexity, system size, and inreased pressure drops. Although these works are geared to mix liquids, similar onepts ould be applied to mixing gases. Thermal At the length sales of miro-ombustion devies, heat transfer by natural onvetion beomes small beause the indued buoyant flow is small (Eq. (1)). However, heat transfer by ondution through the gas to the surrounding surfaes and by fored onvetion in the intake and exhaust hannels and in the ombustion hamber is signifiant beause of the temperature gradients are higher as the harateristi length is dereased. Heat transfer by radiation also inreases as the harateristi length dereases beause of the large view fator. In addition, as the sale of the devie is redued, the surfae-to-volume ratio inreases, whih ombined with the enhaned heat flux, results in heat transfer effets beoming very important at the surfae or boundary of the devie. This has advantages in omponents that use heat transfer in their operation, suh as evaporators or heat exhangers, sine it enhanes their heat exhanging harateristis. It may beome problemati however in devies where surfae heat losses may deter their performane as may our with ombustion hambers due to wall quenhing. It should be noted that the small buoyany and the low thermal ondutivity of air (λ a ~ 0.03 W/mK) render the heat losses from a ombustor relatively small when ompared to its total heat generation. The order of magnitude of the heat losses from a ombustor to the surrounding air an be obtained with a simple 1-D, steady state alulation. The heat flux from a flowing hot gas in the ombustion hamber, through the ombustor housing, to the still ambient air surrounding the ombustor an be approximately alulated by 12
16 q A Tg Ta = (5) 1 l h g λ λ s a + h ra l Where the subsript g represents the hot gases in the ombustion hamber and the subsript a represents the air surrounding the ombustor. Considering, for example, a meso-size ombustor with a harateristi length of l =20 mm apable of providing around 50W power [15], a ombustion gas and ambient air temperatures of T g =1,000 C and T a =20 C respetively, a heat transfer oeffiient of the gases flowing through the ombustion hamber of h g =100 W/m 2 K, (onvetion and radiation), a SiC ombustor housing (λ s = 500 W/mK), and a linearized radiative heat transfer oeffiient from the housing to the ambient air h ra =130 W/m 2 K, Eq.(5) gives for the heat flux 0.05 W/mm 2. Assuming that the ombustor s ombustion hamber has a 25 mm 2 area, the heat loss from the ombustion gases would be around 1.3 W, i.e., ~3% of the ombustor output. Several observations an also be dedued from Eq. (5). One is that beause of the large thermal ondutivity of the housing (SiC, steel, et), the solid ondution term is negligible at these small sales, and that heat ondution through air is also small ompared with radiation. Thus in order to redue the heat losses from the ombustion hamber it is important to redue radiative heat loss from the ombustor housing to the ambient air. For this purpose a material like silia aero-gel would be good to insulate the ombustor sine it has exellent insulating properties both for ondution and radiation. If instead of still air, there is a fored flow as in an intake manifold or in a gas turbine ompressor, the heat transfer from the ombustion hamber to the inoming air would be 13
17 onsiderably larger than the one alulated above ( λ a l in Eq. (5) would be replaed by a heat transfer oeffiient, h a >100 W/m 2 K) The enhaned heat transfer to the inoming gas in the intake manifold of the ombustor is of partiular onern in devies using premixed reatants for ombustion. While pre-heating the reatants will aid in sustaining ombustion to sales smaller than the quenhing distane, it may result in the auto-ignition of the mixture in the inlet port. Thus, insulating measures must be taken to ontrol the amount of heat that will be transferred to the inoming fuel/air mixture. Furthermore, heating of the reatants in the intake manifold will result in a smaller mass harge in the ombustion hamber due to the redued density, thus reduing the potential net power output of the devie. The lower density will also result in higher ompression work per unit mass, and onsequently lower overall system effiienies. This is partiularly ritial in gas turbines sine the power requirements of the ompressor determine their overall effiieny. In these ases thermal management beomes essential in order to redue heat losses and inrease the performane of the devies. As noted earlier, most miro-devies tend to operate at a relatively uniform temperature beause of their small size. For example, the Biot number for a steel or a silion devie with a length sale of 10 mm, and subjeted to moderate onvetion and radiation (ombined onvetion and radiation heat transfer oeffiient of 100 W/m 2 K), will be of the order of 0.002, whih is onsiderably smaller than that normally onsidered suffiient for a lumped heat transfer analysis (Bi<0.1). Thus a uniform temperature ould approximately desribe the devie s internal temperature (boundary ondition for Eq. (2)). Redued thermal gradients will redue thermal expansion stresses and subsequent misalignments in moving parts. However, it introdues potential problems whenever large thermal gradients are needed for high performane of the devie suh as in thermoeletri generators. This is also a problem for gas-yle type 14
18 devies (heat engines) beause their effiieny depends on the ratio of the high and low temperature reservoirs, and it may be diffiult to attain or maintain a large temperature ratio. The solution of these problems again requires omplex thermal management. Regarding thermal management, omplex strutures with highly insulating materials, vauum gaps and/or omplex thermal oatings may be needed to insulate and redue heat transfer from high to low temperature regions. However, thermal management is not only restrited to spatial temperature gradients, but also to transient heat transport. Very different harateristi time in the gas or the solid, or in the periodi heat input from intermittent ombustion may result in quasi-insulating onditions at the boundary. For example, if the ombustion time in a ompression ignition engine is muh shorter than heat transfer time through the engine housing, heat losses from the ombustion reation to the wall ould be negligible beause the lak of time to transfer the heat. Combustion Combustion in miro-sale systems presents problems related to the time available for the ombustion reation to our, and to the possible quenhing of the ombustion reation by the wall. Near-wall hemial kinetis, i.e. potential low wall temperature and radial depletion haraterize the ombustion reation. One again, the basi requirement for miro-ombustion to our is that the physial time available for ombustion (residene time) must be larger than the time required for the hemial reation to our (ombustion time). For gas-phase ombustion in flow systems suh as in a gas turbine ombustor, the residene time is determined by the size of the ombustion hamber and the flow rate of the reatant stream through the hamber. For losed systems suh as in internal ombustion engines, in addition to the size of the hamber, the rpm of the engine also determines the residene time. For atalyti ombustion the diffusion of speies 15
19 to the wall and speies absorption/desorption at the wall also determine the residene time. Sine in general the residene time will be small in miro-ombustors, it is important to have small hemial times to ensure ompletion of the ombustion proess within the ombustor. In general, small hemial times are obtained by ensuring high ombustion temperatures, whih in turn an be ahieved by reduing the heat losses in the ombustion hamber, preventing radial depletion at the wall, inreasing the reatants temperature, using stoihiometri mixtures, and using highly energeti fuels. As engine size or ombustion volume dereases, the surfae-to-volume ratio inreases, resulting in inreased ombustor surfae heat losses and inreased potential destrution of radial speies at the wall. These mehanisms will inrease the hemial time and possibly prevent the onset of the gas-phase ombustion reation, or lead to quenhing of an ongoing reation. Thermo-hemial management tehniques that an be used to overome quenhing are, among others, the use of exess enthalpy ombustors, generating adiabati walls by staking planar devies in a symmetrial fashion (insulated temperature boundary ondition), establishing high temperature erami walls, and using surfae oatings. The earliest work on exess enthalpy, reirulating, burners, was onduted by Weinberg and o-workers [10, 29, 30]. In these works, the ombustion reation was optimized by using the enthalpy of the produts to preheat the fuel air mixtures, in what is known as Swiss roll ombustor shown in Fig. 3. As a result of the enthalpy exhange obtained by reirulating the exhaust, steady ombustion has been obtained with mixtures well below the normal flammability limits. Stable ombustion, (desribed as flameless by the authors of Ref. [31]) has also been observed at temperatures below the expeted homogeneous ombustion temperatures of the fuels tested but above their normal atalyti temperatures [31]. The onept of reirulating the exhaust to redue the heat losses 16
20 from the ombustion region and to pre-heat the inoming reatants has been further implemented to attain ombustion in thin tubes [32, 33] with diameters smaller than the quenhing distanes that are reported in the literature. It has also been used to develop miro-ombustors suh as that shown in Fig. 4 [33]. Conerning the quenhing distane, it is worth mentioning that the magnitude reported in the literature is onsidered often as the limiting sale for miro-sale ombustion. This is a oneptual error, beause the quenhing distane depends on the reation rate, and thus on the temperature, speies and radial onentration (it is related to heat and radials losses to the wall). The problem of wall quenhing an be redued or prevented by inreasing the wall temperature (the quenhing distane is approximately inversely proportional to the square root of the temperature), or equivalently preventing the heat losses to the wall (adiabati wall). Elevated operating temperatures of the ombustor walls not only help preventing quenhing, but also by reduing the hemial time also help ounter the adverse effet of the small physial time inherent in miro-ombustors. The physial time of the ombustor will be given by the above indiated residene time, diffusion time, or the rpm if an engine. An order of magnitude of this time is from 1 to 10 ms (a 10 mm gas turbine ombustor with 1 to 10 m/s flow veloity, or a rotary IC engine at 4,000 to 40,000 rpm). Thus hemial times of 1 ms or less are neessary for the operation of the ombustors, whih requires elevated, but not too high, temperatures. Cerami materials, suh as SiO 2, SiC, and Si 3 N 4, an withstand temperatures of around 1700K, whih are high enough to ensure short hemial times, and thus are good andidates for miroombustors. The small sale of the devies and their uniform temperature operation redue the problems of frature inherent in the use of erami materials in large-sale ombustors. Coating 17
21 the ombustor walls with inert materials an also redue radial reombination and hemial quenhing at relatively low temperatures [34]. If the reatants are not pre-mixed and the fuel is liquid, additional time and volume will be required for fuel evaporation and mixing. The time an be signifiant when ompared to the gaseous premixed residene time, beause the liquid evaporation, and the mixing at the low Reynolds numbers expeted in these systems, are generally slow. As suh, alternatives to spray ombustion in liquid-fueled miro-ombustors are urrently being explored. Partiularly interesting is the onept of burning the liquid fuel while forming a liquid film along the wall of the ombustion hamber [35]. The advantage of this approah is that the wall film redues heat losses from the ombustor sine it keeps the ombustor walls ooled (at the liquid boiling point). It also inhibits wall quenhing beause the gas phase ombustion ours away from the wall, while maintaining suffiiently large vaporization rates beause of the large surfae to volume ratio of the miro-ombustors. The researhers have proven the onept in a miniaturized ylindrial ontinuous ombustor that indues a swirling air flow that keeps the film of liquid fuel on the wall. The devie is projeted to deliver power levels varying from 10 watts to kilowatts [35]. One important aspet of miro-sale ombustion that should be kept in mind is that although the inrease of the surfae-to-volume ratio of the ombustor presents a problem for gas-phase ombustion, it favors atalyti ombustion. Although the atalyti reation is generally slower than the gas-phase reation, and surfae heat loss is a problem that also affets the atalyti reation, the relative inrease of surfae area and the lower temperatures of the atalyti reation suggest that miro-sale ombustors using atalyti reation may be easier to implement than those using gas-phase reations. For example, it was noted in the above referred Swiss roll 18
22 ombustor that hydrogen-air mixtures ould be ignited at room temperature and other fuels (butane and propane) at less than 200 C if a atalyst were deposited on the surfaes of the ombustion volume [31]. The role of atalytially ative surfaes within miro-hannels is under investigation to stabilize the flame struture, determine extintion limits, optimize ombustion effiienies and redue emissions [14,31,36-38]. The devie being developed in [37] is a single pass ounterflow heat exhanger that is designed with an inorporated atalyti surfae. The small sale greatly enhanes both thermal and mass transfer, whih an result in volumetri heat generation rates of up to 10 W/mm 3, and therefore onfirms the potential of miro-tehnologybased energy onversion and hemial systems. Although the potential solutions to the low temperatures and short residene times seemingly inherent in miro-sale ombustors ould result in ompetitive operating devies, further understanding of low temperature hemial kinetis (homogeneous and atalyti), and the development of highly reative energeti fuels is likely to be neessary to ahieve this goal. Also needed are aurate theoretial models of the physio-hemial proess involved in the ombustion hamber. APPROACHES TO MICRO-POWER GENERATION USING COMBUSTION Although the field of miro-sale power generation using ombustion is very new, there are urrently several ongoing projets to develop miro-sale ombustors and power generators that are relatively well advaned. The ultimate objetive of most of these projets is to develop a portable, autonomous power generation system using ombustion with improvement in energy density over batteries. A brief desription of some of these projets is presented here. There are a few other projets that have been reently initiated but that have not been referened here for lak of suffiient information about them. The projets have been grouped into three ategories: 19
23 miro-ombustors, heat engines, and rokets. Although ombustors and rokets are not power generators by themselves, they an be used in onjuntion with other devies (thermoeletri, piezoeletri, inert fluid yles, et) to produe eletrial power, and are therefore inluded here beause of their ombustion omponent. Furthermore, diret mehanial power generation is also of interest, and as mentioned above it is another of the assets of using ombustion for power prodution. Miro-ombustors/reators. Several miro-ombustors and hemial reators are urrently being developed, either to use in onjuntion with piezoeletri and thermoeletri materials to produe power, or to use as fuel reformers in fuel ells. The obvious advantage of these devies is that they don t have moving parts, but the problem generally lies in the low effiieny of the omplete system. Although there are some thermoeletri materials that have attrative effiienies, they suffer from the diffiulty of maintaining a large temperature drop aross the thermoeletri material, beause of the small sale of the devies, and beause good thermal onduting materials generally are also good eletrial ondutors. Thus good thermal management, or the possibility of deoupling the thermal and the eletrial ondutivities, is key for the suess of these devies. The Swiss roll approah has been used to develop thermoeletri power generation devies using miro-sale ombustion [12,14]. The referened researhers have demonstrated that their devie an produe power, although to date with low effiieny. New designs of this type of power generation devies have been reently proposed based on thermodynami analysis that promise to provide better effiienies [39]. The speifi proposed design onsists of a setion where heat is transferred to the inoming reatants followed by another setion that disards unonverted heat to the old surroundings. 20
24 The goal of the University of Southern California projet [12, 31] is to develop a highly miniaturized, integrated, monolithially and bath-fabriated power generator with no moving parts, apable of powering devies down to MEMS sales. With its 3-D Swiss roll harateristis, the reator shown in Fig. 5 appears to be well suited for MEMS size devies beause the heat losses are greatly redued. Compliation presently appears in the implementation of the thermoletri unit. To date maro-sale and meso-sale ombustors have been fabriated and tested. Low temperature, self-sustained ombustion has been demonstrated in these larger reators [31, 36]. The hemial energy onversion and power generation devie at the MEMS sale developed at Prineton University [14] onsists of a reirulating atalyti, 12.5mmx12.5 mmx5.0mm miro-reator (2-D Swiss roll) made of alumina erami and platinum as atalyst and a thermopile unit, as shown in Fig. 6. A prototype devie has been operated with hydrogen and with butane. Continuous operation with hydrogen has been demonstrated over a wide range of fuel-air mixtures and hemial energy inputs from 2 to 12 watts, at an operation temperature of 300 C. The devie generated eletrial power suffiient to power a 100 mw light bulb. Plans to inrease the effiieny of the eletrial generator by staking several devies to redue heat losses are urrently underway. These researhers expet that staking two dimensional ombustors may be as effiient a method to redue heat losses as a three-dimensional onfiguration A thermoeletri power generator based on atalyti ombustion in a miro-mahined ombustion hamber has been developed at the University of Mihigan [40] (Fig. 7). The ombustion hamber is 2mmx8mmx0.5mm and is overed by a dieletri diaphragm that integrates polysilion-pt thermopiles. Using hydrogen/air mixtures the devie has produed 21
25 power levels of the order of 1µW/thermoouple. The researhers expet to be able to reah power levels of 10 µw/thermoouple with geometrial modifiations that will inrease the temperature gradients on the diaphragm. A miro-sale power devie that inludes a ombustion-driven fuel reformer and fuel ell has been developed at Paifi Northwest National Labs [41]. The miro-sale fuel reformer strips hydrogen from a hydroarbon fuel (suh as methanol) and the hydrogen-rih stream is then fed to a fuel ell to generate eletrial power. To date a 10 to 500 mw steam reformer system has been assembled and fabriated with a reator volume of around 0.5 mm 3. In preliminary testing, the fuel reformer, utilizing methanol or butane, was able to provide up to 100 mw of hydrogen at an effiieny of up to 4.8%. The devie was able to operate independent of any additional external heating, even during start-up. At Yale University a meso-sale (~16x10 3 mm 3 ) atalyti ombustor operating with a liquid fuel eletrosprayed into the ombustor hamber has been developed [24]. The ombustor is to be oupled with diret energy onversion modules for power generation. Tests have been onduted with n-dodeane and JP8 jet fuel at rates of 10 g/hr and equivalene ratios varying from 0.35 to 0.7. Temperatures in the atalyti surfae are reported to be in the range of ºC, depending on the equivalene ratio. Combustion effiienies of the order of 97% have been reported with n-dodeane. The appliation of eletrospraying for liquid fuel ombustion in smallsale ombustors is an important ontribution of this work, sine it appears that the tehnique is potentially appliable in MEMS sale devies. A hemial fuel proessing miro-system for power generation in MEMS appliations is being developed at MIT [42, 43]. The miro-system will onsist of integrated miro-fabriated atalyti reators, flow sensors, heaters, miro-valves, miro-pumps and ontrollers. Several 22
26 alternative tehnologies for miro fuel proessing are being evaluated, inluding hydrogen generation for fuel ells, and thermoeletri and thermovoltai power generation. Gas Turbines/IC Engines The MIT Gas Turbine Laboratory is developing a MEMS-based gas turbine power generator with a total volume of approximately 300 mm 3, designed to produe W [6,7]. This projet an be viewed as the pioneering researh in MEMS-based miro-sale power generation, and is for most purposes the most advaned. A shemati of the miro-gas-turbine is shown in Fig. 8, it inludes a radial ompressor/turbine unit, a ombustion hamber and an eletrial generator inorporated in the ompressor. The ompressor and the turbine, 12 mm in diameter and 3 mm thik, are made of traditional CMOS materials, and designed to rotate at more than 1million rpm. Although the gas turbine has not produed positive power yet, the development of the different omponents is well advaned, with the turbine, ompressor and ombustor operating independently. Heat transfer from the ombustion hamber to the ompressor/intake air, together with the diffiulty in ahieving good fabriation toleranes, appear to be dominant problems keeping the effiieny of the turbine low. Some major aomplishments inlude the ahievement of rotation of the turbine at 1.3 million rpm by using air bearings, and the ontinuous operation of a silion based ombustor using H 2 /air mixtures [44]. More reently a atalyti silion miroombustor has been developed and operated with hydroarbon mixtures [45]. At the UC Berkeley Combustion Laboratories, a researh projet is urrently underway to develop a liquid hydroarbon fueled internal ombustion rotary (Wankel-type) engine with sizes that are well below those ommerially available [15,46-48]. Two engines are urrently being developed, a meso-sale mini-rotary-engine designed to deliver power on the order 30 W, and a miro-sale miro-rotary-engine designed to produe power in the mw range. The mini- 23
27 rotary engine is EDM-fabriated from steel, with an epitrohoidal-shaped housing and a rotor approximately 10 mm in size. The simplest version of one of these mini-engines is shown in Fig. 9. A test benh for the mini-rotary engine has been developed and tests have been onduted with different mini-rotary engine designs to examine the effets of sealing, ignition, design, and thermal management on effiieny. Testing has been performed using hydrogen-air mixtures to failitate ignition, and a range of spark and atalyti glow plug designs as the ignition soure. Net power output of up to 3.7 watts at 9000 rpm have been obtained, although with low effiieny (~0.2%). A major reason for the low effiieny of the engine is its low ompression ratio, due to leakage between the rotor apex tip seals and the housing and over the rotor faes. The size of the engine is at the lower sale limit of EDM fabriation, and it is diffiult to attain the required toleranes for good sealing, even using apex seals. Work is urrently underway to improve sealing and ompression ratios by implementing different rotor apex tip and rotor fae seal designs [15,46]. As per the miro-rotary-engine, the projet aims at developing an engine with a rotor in the mm range size, using MEMS tehniques. The rotary engine is well suited for the MEMS fabriation tehniques beause of its planar onstrution, redued number of parts, and selfvalving operation. The fabriation of two MEMS based miro-engines, one made of SiC with a 2.3 mm rotor (Fig. 9) and another of Si with a 1 mm rotor is well advaned (Fig. 10) [47,48]. Initial measurement of the fabriated engine piees indiates that the fabriation proess has produed viable engine parts for an initial investigation into sealing and material harateristis. The housing spur gear and rotor through-holes have been fabriated using a self-masking method to produe strutures 150 µm in diameter and µm in height. Issues still remain with the fabriation proess. Signifiant lateral ething of the spur gear profile and non-uniform eth rates 24
28 aross the wafer redues the number of useable parts fabriated during the manufaturing proess. Modifiations to the fabriation proess and STS eth reipe are being implemented to redue the Si eth unertainties. A method for obtaining real-time DRIE-eth depths using a Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spetrometer is urrently being investigated and installed. The urrent fabriation proess an produe aeptable engine parts, but at the expense of low yield. After fabriation of miro-rotary engine housings and rotors with a 100:1 sidewall straightness, the rotor and housing will be manually assembled. This first generation mirorotary engine will be tested by ompressed air to determine engine leakage and wear harateristis. The Si engine will be tested first, followed by SiC oated Si piees and then Silion Nitride (Si 3 N 4 ) oated parts. The objetive of these tests is to investigate the long-term wear, lubriity, and toughness of the materials. Initial studies of miro-fluidis, heat transfer and ombustion are underway or will soon follow. Thermal management approahes applied, or being onsidered for appliation, for these miniaturized rotary engines inlude: reirulating the exhaust around the ombustion setion of the housing and pakaging the engine in an aerogel/vauum ontainer to redue heat losses, using atalyti surfaes to sustain ombustion at low temperatures, and using the exhaust heat to evaporate the liquid fuel. A free-piston "knok" miro-engine based on homogeneous harge ompression ignition (HCCI) of hydroarbon fuels is being developed at Honeywell [49], with a goal of generating ~10 W of eletrial power in a 10 3 mm 3 pakage volume. In order to ahieve reliable autoignition of the fuel and to develop these power densities, the engine must operate at kilohertz frequenies, plaing requirements about the allowable ignition delay times. These operating frequenies generate nearly adiabati ompression and expansion sine the timesale of the ompression and expansion events are muh less than the harateristi thermal diffusion time, 25
29 leading to a higher overall thermal effiieny. To date, ompression ignition has been ahieved in a piston/ylinder unit 3 mm in diameter operating for several yles. Sealing problems in the piston/ylinder appear to have limited the effiieny of the engine, and material resistane has limited its life. Attempts to resolve the sealing problem by using a liquid piston are being pursued. A free piston/ylinder eletrial power generator based on a ferromagneti piston osillating in a magneti field is under development at Georgia Teh [16]. The piston is propelled by the alternated ombustion of a hydroarbon fuel/air mixture at eah end of the ylinder (Fig. 10). The magneti field is produed by permanent magneti MEMS arrays that surround the ylinder assembly. The system also inorporates MEMS igniters. A power generator with a 4.3 m stroke and 13.4 m 3 displaement has been developed, and 12 W of eletrial power has been extrated to date, although with poor effiieny due in part to sealing problems in the piston ylinder unit. A rotationally osillating free-piston engine that forms four distint ombustion hambers from a single base struture (housing) and a swing arm is under development at University of Mihigan [50]. The devie operates on a four-stroke Otto yle. The swing arm (piston) is osillatory, making mehanial torque ineffiient but relatively simple for diret eletrial power generation. The design goals of this meso-sale devie are the prodution of 20W using a liquid hydroarbon with a projeted system mass of 54 g and a volume of 17x10 3 mm 3. Miro-Rokets Several miro-roket projets are urrently underway, most of them MEMS-fabriated, and designed for spae appliations suh as miro-satellite positioning [51,52]. A solid fueled mirorokets fabriated at TRW is shown in Fig. 11 [53]. It is designed for orbit and station keeping of pio-satellites or miro-spaeraft. It onsists of a three-layer sandwih ontaining the thrust 26
30 hambers where a lead styphnate propellant is housed, Si 3 N 4 burst diaphragms, and miroresistors that are used as igniters. When the resistor is energized, the propellant ignites, raising the pressure in the hamber and rupturing the diaphragm. Initial testing has produed 10-4 Newton-seond of impulse and 100 W of power. A HTPB and Ammonium Perhlorate fueled silion sounding miro-roket with a mass of 1 gram has been fabriated at UC Berkeley (Fig. 12) to propel sensors to test the atmosphere [54]. The miro-roket generated thrust (peak, 4 mn) for an 8 seond burn. At MIT, a high pressure, bipropellant miro-roket engine has been manufatured and tested. The roket weights 1.2 g and with a hamber pressure of 12 atm has generated 1 N thrust and delivered 750 W of thrust [55]. A liquid propellant miro-thruster for small spaeraft appliations is being developed at The Pennsylvania State University [56]. A prototype mirothruster has been suessfully tested with gaseous reatants. Propellants being explored inlude environmental friendly energeti oxidizers, with alohol as fuel and water as the liquid arrier CONCLUDING REMARKS The field of miro-power generation, both eletrial and mehanial, is basially in a feasibility stage, and although signifiant progress has been made in the last few years, there are still a number of tehnologial problems that must be resolved before the field establishes itself. The approah followed to date has been that of miniaturizing urrently used large sale devies, whih introdues many problems related to fluid flow in miro-hannels, heat and mass transport in the miro sale, ombustion in small volumes, design, fabriation and diagnostis. The solution of these problems requires a variety of fundamental and applied researh and manufaturing development that preedes the development of the miro devies themselves. 27
31 The researh needs unique to the development of ombustion systems at the small sale inlude: mixing and pumping in low Reynolds number flows, simulation of distributed reations, low temperature hemial kineti modeling, investigative diagnostis, materials seletion, fabriation of high aspet ratio strutures and omplex geometries, assembly, testing and haraterization. Materials must be able to sustain the high temperature, harsh hemial environment, stress, and wear due to ombustion events. Emissions and noise must be redued to aeptable levels. High preision, high aspet ratio strutures are neessary to provide adequate sealing for high ompression ratios. A repeatable and simple assembly tehnique must be developed in order to mass produe these devies and lastly, the devies need to be tested and haraterized to optimize their performane. One an speulate that some of these problems ould be avoided if the approah to develop miro-power devies would be based on enlarging small (bio-related) systems rather than miniaturizing large ones. However, it is likely that this approah will also have its own problems. In any ase, it is important to keep in mind that, beause the speifi energy of liquid hydroarbon fuels is around 100 times larger than that of seondary batteries, there is a lot of room for development of miro devies that use ombustion to produe power. Furthermore, given the urrent need for power (eletrial and mehanial) in the small sale the potential payoff is very large. NOMENCLATURE A surfae area = l h + h λ, Bi Biot number, Bi ( o r ) s D Diffusion oeffiient Da Damkohler number, Da = w& l ρu Fo g Fourier number, Fo = α gravity s t l 2 28
32 h ombined onvetive and linearized radiation heat transfer oeffiient h= h o + h r h o onvetive heat transfer oeffiient h r linearized radiation heat transfer oeffiient h r = εσf 12 (T s +T a )(T s 2 +T a 2 ) Kn Knudsen number, Kn = λ f /l Le Lewis number Le = α D l harateristi length of the devie Pe Pelet number, Pe = lu α p pressure p normalized pressure p = p p p q harateristi pressure heat rate Re Reynolds number, Re = u l υ t time t normalized time t = t t t T harateristi time temperature T normalized temperature T = T T T u harateristi temperature veloity u normalized veloity u = u u u w& " harateristi veloity reation rate & = " " " " w& normalized reation rate w w w " w& harateristi reation rate x spatial oordinate x normalized spatial oordinate x = x x x y i harateristi spatial oordinate mass fration of speie i y i normalized mass fration of speie i y i = yi yi y i harateristi mass fration of speie i & & Greek 29
33 α λ λ f thermal diffusivity thermal ondutivity mean free path µ dynami visosity ν kinemati visosity Subsript a air harateristi value g gas i speie i r radiation s solid (devie housing) Supersript - normalized variable or property with its harateristi value ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The author would like to aknowledge the help and ontribution of Dr. David Walther to the preparation of this manusript, his ontribution was essential to the ompletion of the work. He would also like to thank Profs. Forman Williams, Frederik Dryer, Paul Ronney and Derek Dunn-Runking and Dr. Howard Ross for their omments and suggestions to improve the manusript. Thanks are due to the diretors and researhers of the Berkeley Sensors and Atuators Center (BSAC), partiularly Professors Al Pisano and Dorian Liepmann and the U.C. Berkeley Combustion Proesses Laboratory (CPL) researhers and visitors, partiularly Professors Kenji Miyasaka and Kaoru Maruta, Dr. Kelvin Fu and Mr. Aaron Knobloh and Fabian Martinez. This work was partially supported by DARPA under ontrat # DABT
34 REFERENCES 1. Allen, D., Almond, H. and Logan. P. Tehnial Comparison of Miro-eletrodisharge Mahining, and Copper Vapor Laser Mahining for the Fabriation of Ink Jet Nozzles Proeedings of the SPIE, 4019, 531 (2000) Reyntjens, S. and Puers, R. J. Mihromeh. Miroeng. 11, (2001) Madou, M., Fundamentals of Mirofabriation, CRC Press, Boa Raton. (1997) Kovas, G.T.A. Miromahined Transduer Sourebook, MGraw-Hill, NY (1998) Warneke, B. et al. Computer Magazine, IEEE, Jan.2001, Epstein, A.H. et al. Miro-Heat Engines, Gas Turbines and Roket Engines The MIT Miroengine Projet, 28 th AIAA Fluid Dynamis Conferene, , (1997) 7. Epstein, A.H. et al. "Power MEMS and Miroengines." Pro. of the IEEE Transduers '97 Conferene, Chiago, IL, June Pisano, A., Miroeletromehanial Systems (MEMS) Program, DARPA/ ETO, BAA 97-43, (1997) 9. Tang, W., DARPA MTO Program, BAA Miro Power Generation (MPG), (2001) 10. Weinberg, F. Fifteenth Symposium (International) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 1 (1975) 11. Introdution to the Human Body 2nd Edition, Tortora, Gerard J., Harper Collins Publishers, 1991, New York 12. Maruta, K., Takeda, K., Sitzki, L., Borer, K., Ronney, P. D., Wussow, S., Deutshmann, O., "Catalyti Combustion in Mirohannel for MEMS Power Generation, " Third Asia- Paifi Conferene on Combustion, Seoul, Korea, June 24-27,
35 13. Jones, E. Mirosale Combustor/Evaporator Development DARPA/MEMS Projet Summaries, August 2001, pp. 16 (2001) 14. Vian, J. Gajdezko, B.F., Dryer, F.L., Milius, D.L., Aksay, I.A. and Yetter, R.A. Development of a Miroreator as a Thermal Soure for MEMS Power Generation Proeedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Symposium on Combustion, July 21-26, 2002, Sapporo, Japan (aepted) 15. Fu, K., Knobloh, A., Martinez, F., Walther, D., Fernandez-Pello, A.C., Pisano, A., Liepmann, D., Miyaska K.,and Maruta, K. Design and Experimental Results of Small- Sale Rotary Engines Pro International Mehanial Engineering Congress and Exposition (IMECE), New York, November 11-16, Allen, M.G. "Cerami Miromahining Tehnology," DARPA Workshop on Combustion-based MEMS Power Generation on the Mirosale, for the Mirosale, Washington, DC, Savinell, R. A Miro Hydrogen-Air Fuel Cell DARPA/MEMS Projet Summaries, August 2001, pp. 16 (2001) 18. Lee, S., Nelson, D., Svrek, M., Edwards, C.F. and Bowman, C.T. Mesosale Burner Arrays for Gas Turbine Reheat Appliations 2002 Spring Meeting, WSS/CI, San Diego, CA Marh 25,26 (2002) 19. Hetsroni, G., Mosyak, A. and Segal, Z. Two Phase Flow in Mirohannels Proedings of the 2001 ASME IMECE, Nov. 11, 2001, New York, NY (2001) 20. Collier, J.C. Convetive Boiling and Condensation, MGraw-Hill, (1972) 32
36 21. Rajan, N., Mehregany, M., Zorman, C.A., Stefanesu, S., Kiher, T.P. Fabriation and testing of miromahined silion arbide and nikel fuel atomizers for gas turbine engines J. Miroeletromehanial Systems, 8, IEEE, Sept. 1999, (1999) 22. Chen, G and Gomez, A., Combust. Si and Teh. 115:177 (1996) 23. Ganan-Calvo, A. M. J. Fluid Meh. 335, (1997). 24. Kyritsis, D.C., Guerrero-Arias, I., Royhoudhury, S. and Gomez, A. Mesosale Power Generation by a Catalyti Combustor using Eletrosprayed Liquid Hydroarbons Proeedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Symposium on Combustion, July 21-26, 2002, Sapporo, Japan (aepted) 25. Chigier, N. et al. Atomization and Vaporization of Liquid Fuels for Miro-Combustors to be submitted to the 2003 AIAA Aero-Si. Conferene, Reno, NV, 26. Lowe, H. et al. Miromixing Tehnology IMRET 4: 4 th Int. Conf. On Miroreation Tehnology, AIChE Meeting, Atlanta, GA, 31, (2000) 27. Liu, R.H., Stremler, M.A., Sharp, K.V., Olsen, M.G. Santiago, J.G., Adrian, R.J., and Beebe, D.J., J. Miroeletromehanial Systems, 9, 2, , (2000) 28. Zahn, J.D., Deshmukh, A.A., Papavasiliou, A. P., Pisano, A.P.,and Liepmann, D. An Integrated Mirofluidi Devie for the Continuous Sampling and Analysis of Biologial Fluids Proeedings of the 2001 ASME - IMECE, Nov.11-16, 2001, New York, N.Y. 29. Jones, A.R., Lloyd, S.A., and Weinberg, F.J., Pro. Roy. So. (London) A, 360, , (1978). 30. Lloyd, S.A., and Weinberg, F.J., Nature, 251, 47-49, (1974)S 33
37 31. Sitzki, L., Borer, K., Wussow, S. Shuster, E., Maruta, K., Ronney, P. and Cohen, A., Combustion in Mirosale Heat-Reirulating Burners, AIAA , 38 th AIAA Spae Sienes & Exhibit, Reno, NV. (2001.) 32. Cooley, B, Walther, D. and Fernandez-Pello, A.C. Exploring the Limits of Mirosale Combustion'' 1999 Fall Tehnial Meeting, Western States Setion/Combustion Institute, Irvine, CA, Otober 25, 26, (1999). 33. Peterson R.B. and Hatfield, J.M. A Catalytially Sustained Miroombustor Burning Propane, Pro International Mehanial Engineering Congress and Exposition (IMECE), New York, November 11-16, Masel R. and Shannon, M. Patent # US (2001) 35. Sirignano, W.A., Pham, T.K. and Dunn-Rankin Miniature Sale Liquid Fuel Film Combustor Proeedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Symposium on Combustion, July 21-26, 2002, Sapporo, Japan (aepted) 36. Sitzki, L, Borer, K., Shuster, E., Ronney, P. D., Wussow, S., "Combustion in Mirosale Heat-Reirulating Burners," Pro. 3 rd Asia-Paifi Conf. on Combustion, Seoul, Korea, Peterson, R.B., Small Pakages, Mehanial Engineering, p , June Maruta, K., Takeda, K. Ahn, J., Borer, K., Sitzki, L. Ronney, P. D. and Deutshmann, O. Extintion Limits of Catalyti Combustion in Miro-hannels Proeedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Symposium on Combustion, July 21-26, 2002, Sapporo, Japan (aepted) 39. Weinberg, F.J., Rowe, D.M., Min, G. and Ronney, P. On Thermoeletri Power Generation from Heat Re-irulating Combustion Systems Proeedings of the Twenty- 34
38 Ninth International Symposium on Combustion, July 21-26, 2002, Sapporo, Japan (aepted) 40. Zhang, C. Najafi, K., Bernal, L.P., Washabaugh, P.D. An Integrated Combustor- Thermoeletri Miro Power Generator 11 th Int. Conferene on Solid State Sensors & Atuators, Munih, Germany, June 10-14, Holladay, J.D., Jones, E.O., Phelps, M., and Hu, J. High-effiieny mirosale power using a fuel proessor and fuel ell, SPIE Miromahining & Mirofabriation. Paper , San Franiso, Otober, R. Srinivasan, I.-M. Hsing, P.E. Berger, K.F. Jensen, S.L. Firebaugh, M.A. Shmidt, M.P. Harold, J.J. Lerou and J.F. Ryley,, AIChE J., 43, , (1997) 43. Arana, L.R., S.B. Shaevitz, A.J. Franz, K.F. Jensen and M.A. Shmidt, A Mirofabriated Suspended-Tube Chemial Reator for Fuel Proessing, MEMS 2001, Jan 20-25, 2002, Las Vegas NV 44. Mehra, A., and I.A. Waitz, Development of a hydrogen ombustor for a mirofabriated gas turbine engine, Solid State Sensor and Atuator Workshop, Hilton Head, GA, (1998). 45. Spadaini, C.M., Zhang, X., Cadou, C. P., Miki, N., and Waitz, I. A. "Development of a Catalyti Silion Miro-Combustor for Hydroarbon-Fueled Power MEMS, MEMS 2001, Jan 20-25, 2002, Las Vegas NV, (2002) 46. Fu, K., Walther, D., Fernandez-Pello, A. C., Liepmann D. and Miyasaka, K. Preliminary Investigation of a Small-sale Rotary Internal Combustion Engine 1999 Fall Tehnial Meeting, Western States Setion/Combustion Institute, Irvine, CA, Otober 25, 26,
39 47. Fu, K., Knobloh, A., Cooley, B, Walther, D., Liepmann, D., Fernandez-Pello, A.C.and Miyasaka, K." Miro-sale Combustion Researh for Appliations to MEMS Rotary IC Engines", NHTC , Pro. 35 th ASME 2001 National Heat Transfer Conf., Anaheim, CA, (2001). 48. Fu, K., Knobloh, A., Martinez, F., Walther, D., Fernandez-Pello, A.C. Pisano, A., and Liepmann D. Design and Fabriation of a Silion-Based MEMS Rotary Engine Pro. 2001ASME International Mehanial Engineering Congress and Exposition (IMECE), New York, November 11-16, (2001) 49. Yang, W. MEMS Free Piston Knok Engine, Poster Presentation, 28 th International Symposium on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, Edinburgh, UK, July 30-August 4, Also DARPA MEMS PI Meeting Poster, Broomfield, CO, August 29, Dahm, W.A., J. Ni, K. Mijit, R. Mayor, G. Qiao, A. Benjamin, Y. Gu, Y. Lei and M. Papke, Miro Internal Combustion Swing Engine (MICSE) for Portable Power Generation Systems, AIAA Paper , 40th Aerospae Sienes Meeting, January 14-17, 2002 Reno, NV. 51. Rossi, C. et al. A New Generation of MEMS Based Mirothrusters for Mirospaeraft Appliations» Pro. MiroNanotehnology for Spae Appliations, V.1, April Mii, M.M., and Ketsdever, A.D. eds., Progress in Astronautis and Aeronautis, V. 187, AIAA, Reston, VA, Lewis, Jr., D.H. Janson, S.W., Cohen, R.B. and Antonsson, E.K., Sensors and Atuators : Physial, 80(2), (2000). 36
40 54. Lindsay, W. Teasdale, D. Milanovi, V., Pister K.and Fernandez-Pello, A.C. Thrust and Eletrial Power from Solid Propellant Mirorokets, IEEE 14th Int. Conf. on MiroEletroMehanial Systems, Interlaken, Switzerland, p , Jan London, A.P., Ayon, A.A., Epstein, A.H., Spearing, S.M., Harrison, T., Peles, Y. and Kerrebrok, J.L. Sensors and Atuators A 92, (2001) 56. Yetter, R.A., Yang, V., Milius, D.L., Aksay, I.A. and Dryer, F.L. Development of a Liquid Propellant Mirothruster for Small Spaeraft, Pro. Eastern States Setion, The Combustion Institute, Hilton Head Is., S.C., De. 2-5,
41 List of Figures 1. MEMS sensor/ommuniation devie and a hearing aid battery for power [5]. 2. Speifi energy for iso-otane and several primary and seondary battery tehnolgies. 3. Swiss-roll type, exess enthalpy ombustor and reirulation ombustor [10,29,30] 4. Single pass ounterflow, atalytially stabilized, heat exhanger/miro-ombustor [33] 5. 3-D Monolithially fabriated Swiss-roll type ombustor-thermoeletri generator [12,31] 6. 2-D Stereolithography fabriated Swiss-roll type atalyti miro-ombustor-thermoeletri generator [14] 7. Integrated atalyti ombustor-thermoeletri miro power generator [40] 8. Shemati of a silion fabriated radial inflow gas turbine, and photograph of radial ompressor [6]. A MEMS atalyti silion miro-ombustor for hydroarbon-fueled that ould be integrated with the turbine [45]. 9. EDM steel fabriated mini-rotary engine with a 10mm rotor [15] and MEMS SiC fabriated miro-rotary engine with a 3 mm rotor [47]. 10. MEMS silion fabriated miro-rotary engine with a 1 mm rotor [48]. 11. Free piston power generator using permanent magnets and integrated windings [16] 12. MEMS fabriated array of Digital-Propulsion miro-thrusters [53] 13. MEMS silion fabriated solid fuel miro-roket, and roket in operation [54] 38
42 MEMS sensor Battery Figure 1 Figure 2 39
43 Figure 3 Figure 4 40
44 Figure 5 Figure 6 41
45 TE Generator T Sensor Sensor Connetion Holes Poly-Si Heater Gas Inlet Pt Catalyst Layer Combustion Chamber Exhaust Si Inlet Tunnel T Sensor Glass Figure 7 Figure 8. 42
46 10 mm 12.5 mm µ-rotor Figure 9 Figure 10 43
47 Figure 11 Figure 12 44
48 Figure 13 45
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynamic Cycles of Reciprocating and Rotary Engines - R.S.
 THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers
 Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
' R ATIONAL. :::~i:. :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliance with the way you work PRODUCT BRIEF
 ' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING
 INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
Picture This: Molecular Maya Puts Life in Life Science Animations
 Piture This: Moleular Maya Puts Life in Life Siene Animations [ Data Visualization ] Based on the Autodesk platform, Digizyme plug-in proves aestheti and eduational effetiveness. BY KEVIN DAVIES In 2010,
Piture This: Moleular Maya Puts Life in Life Siene Animations [ Data Visualization ] Based on the Autodesk platform, Digizyme plug-in proves aestheti and eduational effetiveness. BY KEVIN DAVIES In 2010,
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
Chapter 1: Introduction
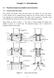 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
Sensor and actuator considerations for precision, small machines: a review
 UCRL-JRNL-11318 Sensor and atuator onsiderations for preision, small mahines: a review S. T. Smith, R. M. Seugling April 1, 005 Preision Engineering Dislaimer This doument was prepared as an aount of work
UCRL-JRNL-11318 Sensor and atuator onsiderations for preision, small mahines: a review S. T. Smith, R. M. Seugling April 1, 005 Preision Engineering Dislaimer This doument was prepared as an aount of work
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Pre-Experience Postgraduate Programmes Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
PISTONLESS DUAL CHAMBER ROCKET FUEL PUMP
 39 th AIAA/ASE/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conferene and Exhibit AIAA 2003-4479 20-23 July 2003, Huntsville Alabama PISTONLESS DUAL CHABER ROCKET FUEL PUP Steve Harrington, Ph.D. Flometris, In. Solana Beah,
39 th AIAA/ASE/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conferene and Exhibit AIAA 2003-4479 20-23 July 2003, Huntsville Alabama PISTONLESS DUAL CHABER ROCKET FUEL PUP Steve Harrington, Ph.D. Flometris, In. Solana Beah,
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
From a strategic view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise
 Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System
 DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
DOE/EIA-0618(98) Distribution Category UC-950 Deliverability on the Interstate Natural Gas Pipeline System May 1998 This report was prepared by the, the independent statistial and analytial ageny within
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Experimental Results of a Solar Cooker with Heat Storage
 Experimental Results of a Solar Cooker with Heat Storage Maria Eugênia Vieira da Silva, Klemens Shwarzer*, and Marelo Riardo Queiroz Medeiros. Universidade Federal do Ceara, Laboratório de Energia Solar
Experimental Results of a Solar Cooker with Heat Storage Maria Eugênia Vieira da Silva, Klemens Shwarzer*, and Marelo Riardo Queiroz Medeiros. Universidade Federal do Ceara, Laboratório de Energia Solar
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Michal Barzuza*
 Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Deduplication with Block-Level Content-Aware Chunking for Solid State Drives (SSDs)
 23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
HEAT EXCHANGERS-2. Associate Professor. IIT Delhi E-mail: [email protected]. P.Talukdar/ Mech-IITD
 HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: [email protected] Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: [email protected] Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
HOW TO CALCULATE PRESSURE ANYWHERE IN A PUMP SYSTEM? Jacques Chaurette p. eng. www.lightmypump.com April 2003
 HOW TO CALCULATE PRESSURE ANYWHERE IN A PUMP SYSTEM? Jaques Chaurette p. en. www.lihtmypump.om April 003 Synopsis Calulatin the total head of the pump is not the only task of the pump system desiner. Often
HOW TO CALCULATE PRESSURE ANYWHERE IN A PUMP SYSTEM? Jaques Chaurette p. en. www.lihtmypump.om April 003 Synopsis Calulatin the total head of the pump is not the only task of the pump system desiner. Often
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Performance Rating of Unitary Air-Conditioning & Air-Source Heat Pump Equipment
 ANSI/AHRI Standard 210/240 with Addenda 1 and 2 (formerly ARI Standard 210/240) 2008 Standard for Performane Rating of Unitary Air-Conditioning & Air-Soure Heat Pump Equipment Approved by ANSI in Deember
ANSI/AHRI Standard 210/240 with Addenda 1 and 2 (formerly ARI Standard 210/240) 2008 Standard for Performane Rating of Unitary Air-Conditioning & Air-Soure Heat Pump Equipment Approved by ANSI in Deember
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
Table of Contents. Appendix II Application Checklist. Export Finance Program Working Capital Financing...7
 Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
Export Finane Program Guidelines Table of Contents Setion I General...........................................................1 A. Introdution............................................................1
Green Cloud Computing
 International Journal of Information and Computation Tehnology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 431-436 International Researh Publiations House http://www. irphouse.om /ijit.htm Green Cloud
International Journal of Information and Computation Tehnology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 431-436 International Researh Publiations House http://www. irphouse.om /ijit.htm Green Cloud
4.15 USING METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION HIGH RESOLUTION VISIBLE DATA FOR THE IMPOVEMENT OF THE RAPID DEVELOPPING THUNDERSTORM PRODUCT
 4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre
 Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Active Load Balancing in a Three-Phase Network by Reactive Power Compensation
 Ative Load Balaning in a hree-phase Network by eative Power Compensation Adrian Pană Politehnia University of imisoara omania. ntrodution. Brief overview of the auses, effets and methods to redue voltage
Ative Load Balaning in a hree-phase Network by eative Power Compensation Adrian Pană Politehnia University of imisoara omania. ntrodution. Brief overview of the auses, effets and methods to redue voltage
Entrepreneur s Guide. Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015. newpa.com
 Entrepreneur s Guide Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015 newpa.om The Entrepreneur s Guide: Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania was prepared by the Pennsylvania Department
Entrepreneur s Guide Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania FEBRUARY 2015 newpa.om The Entrepreneur s Guide: Starting and Growing a Business in Pennsylvania was prepared by the Pennsylvania Department
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Practices
 Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability
 Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Optimal Sales Force Compensation
 Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
On the Characteristics of Spectrum-Agile Communication Networks
 1 On the Charateristis of Spetrum-Agile Communiation Networks Xin Liu Wei Wang Department of Computer Siene University of California, Davis, CA 95616 Email:{liu,wangw}@s.udavis.edu Abstrat Preliminary
1 On the Charateristis of Spetrum-Agile Communiation Networks Xin Liu Wei Wang Department of Computer Siene University of California, Davis, CA 95616 Email:{liu,wangw}@s.udavis.edu Abstrat Preliminary
A Promising Energy Source for Portable MEMS Devices
 A Promising Energy Source for Portable MEMS Devices S.K. Chou *, Yang Wenming, Li Zhiwang and Li Jun Department of Mechanical Engineering, National University of Singapore, 9 Engineering Drive, Singapore
A Promising Energy Source for Portable MEMS Devices S.K. Chou *, Yang Wenming, Li Zhiwang and Li Jun Department of Mechanical Engineering, National University of Singapore, 9 Engineering Drive, Singapore
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING I
 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING I CS 10 Catalog Desription PREREQUISITE: CS 21. Introdution to the systems development life yle, software development models, analysis and design tehniques and tools, and validation
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING I CS 10 Catalog Desription PREREQUISITE: CS 21. Introdution to the systems development life yle, software development models, analysis and design tehniques and tools, and validation
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL
 BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS
 university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com. ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109
 Available online at www.sienediret.om SieneDiret Energy Proedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109 SHC 2013, International Conferene on Solar Heating and Cooling for Buildings and Industry September 23-25, 2013, Freiburg,
Available online at www.sienediret.om SieneDiret Energy Proedia 48 (2014 ) 1096 1109 SHC 2013, International Conferene on Solar Heating and Cooling for Buildings and Industry September 23-25, 2013, Freiburg,
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Recent Progress in Brillouin Scattering Based Fiber Sensors
 Sensors 011, 11, 415-4187; doi:10.3390/s11040415 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.om/journal/sensors Review Reent Progress in rillouin Sattering ased Fiber Sensors Xiaoyi ao * and Liang Chen Physis
Sensors 011, 11, 415-4187; doi:10.3390/s11040415 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.om/journal/sensors Review Reent Progress in rillouin Sattering ased Fiber Sensors Xiaoyi ao * and Liang Chen Physis
Economic and Antitrust Barriers to Entry
 Eonomi and Antitrust Barriers to Entry R. Preston MAfee, Hugo M. Mialon, and Mihael A. Williams 1 Deember 1, 2003 Abstrat We review the extensive literature on barriers to entry in law and eonomis; we
Eonomi and Antitrust Barriers to Entry R. Preston MAfee, Hugo M. Mialon, and Mihael A. Williams 1 Deember 1, 2003 Abstrat We review the extensive literature on barriers to entry in law and eonomis; we
Modelling and Simulation of Closed Loop Controlled Buck Converter Fed Pmbldc Drive System
 Researh Journal of Applied Sienes, Engineering and Tehnology 3(4): 284-289, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Sientifi Organization, 2011 Reeived: Feruary 14, 2011 Aepted: Marh 15, 2011 Pulished: April 20,
Researh Journal of Applied Sienes, Engineering and Tehnology 3(4): 284-289, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Sientifi Organization, 2011 Reeived: Feruary 14, 2011 Aepted: Marh 15, 2011 Pulished: April 20,
