Chromosomal Microarray Analysis (CMA)
|
|
|
- Maximilian Taylor
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Chromosomal Microarray Analysis (CMA) Medical Genetics Laboratories Department of Molecular and Human Genetics Baylor College of Medicine
3 Table of Contents Overview of CMA Examples of Common Findings Examples of Mosaicism Examples of Complex Abnormalities Examples of Small Copy Number Variants CMA Comprehensive-CMA plus SNPS Resolving Variants of Uncertain Significance Prenatal CMA Considerations Prenatal CMA Case Examples Types of Cancer Arrays Conclusion
4 Overview of CMA
5 Chromosomal Microarray Analysis CMA is an array-based comparative genomic hybridization methodology that allows for analysis of the chromosomes for a large number of genetic disorders. With a single test, CMA can identify the abnormalities that are detectable by both routine chromosome analysis and FISH analysis. CMA has greater sensitivity than older methods of chromosome analysis.
6 Genomic Resolution Karyotype [4-5 Mb, whole genome] FISH [40 to 250 kb per probe, single site] CMA [average resolution ~30kb, whole genome]
7 Limits of Resolution Chromosome vs. Array CGH Analysis Chromosome 1 Limits of detection for G-banded chromosome analysis is 4-5 Mb 4 Mb region of microarray data showing a 1 Mb deletion encompassing ~70 oligos
8 What is included? Whole genome copy number analysis Coverage is more dense at genomic sites associated with known genetic conditions Currently 180,000 to 400,000 probes (oligos) covering the genome (depending on version) Exon coverage of disease-associated genes (depending on version) Pericentromeric regions useful for detecting marker chromosomes Subtelomeric regions Backbone coverage (30kb resolution) Verification of results by FISH analysis and/or partial karyotype when indicated Parental studies to determine if observed copy number changes are inherited or de novo
9 CMA Process [A] Experimental Procedure [B] Laser Scanner Patient Control [D] Array Profile Hybridization of genomic DNA to the array of small DNA fragments (oligo probes) Mix [C] Actual Array Laser Scanner Duplication Deletion Shinawi, M. and Cheung, S.W. (2008) The array CGH and its clinical applications. Drug discovery today, 13,
10 1. Evolution of CMA - increasing pixels! Feb 2004 July 2005 Nov 2006 Mar 2007 Feb 2008 June 2009 VERSION V4 BAC V5 BAC V6 BAC V6 OLIGO V7 OLIGO V8 OLIGO 180K Interrogating probes 366 BACs 853 BACs 1475 BACs 44K oligos 105K oligos oligos 420 genes >1700 genes Genomic disorders >140 >140 (+61 regions *) (exons) Subtelomeric regions # of clones / subtel ~ 4 ~10 ~10 ~10 (x20) NA NA Coverage per subtel ~ 5 Mb ~ 10 Mb ~ 10 Mb ~ 10 Mb NA NA Pericentromeric regions none # clone / region ~3 ~ 3-5 ~ 3-5 ~3-5 (x20) NA NA 1 clone per 1 clone per Backbone coverage NA NA 1 band 1 band 30 kb 30 kb LCR regions Design Improvement FISH test + subtel More Disorders + subtel + pericentr More disorders BAC clones + each chr oligo band emulation More More Disorders Disorders mito + mito + exon + LCR regions coverage Detection Rate 6.50% 9.04% ~12% ~12.5% ~15.4% TBD
11 N >46,000 Evolution of CMA - increasing pixels! Whole Genome Coverage June 2009 Oct 2010 July 2011 July V8.0 OLIGO V 8.3 OLIGO V9.0 OLIGO VERSION V8 OLIGO +SNP Screen V OLIGO +SNP Screen +SNP Screen Interrogating probes 180K Oligos 400K Oligos 180K Oligos 400K Oligos 400K Oligos >1700 genes >1700 genes 1779 genes 1936 genes 4864 genes Genomic disorders Exon coverage Exon coverage Exon coverage Exon coverage Exon coverage HG18 HG18 HG19 HG19 HG19 Subtelomeric regions Pericentromeric regions Backbone coverage 30 kb 30 kb 30 kb 30 kb 30 kb LCR regions Design Improvement More Disorders More Disorders Mito Mito + exon + exon coverage coverage + 120K SNP More Disorders More Disorders More Disorders Mito Mito Mito + exon coverage + exon coverage + exon coverage + Additional 79 Additional 200 Additional 2500 genes genes +120K SNP genes +120K SNP 38 non-coding regulatory elements
12 Advantages of CMA Screens for a large number of disorders simultaneously Detects conditions that are difficult to identify clinically Atypical or mild phenotypes; e.g., VCFS/DiGeorge Conditions that lack distinctive features Detects deletions and duplications simultaneously Detects submicroscopic unbalanced chromosome rearrangements Detects mosaicism (as low as 10%) Cheung et al. (2007) Am J Med Genet A. (15): Detects interstitial subtelomeric deletions/ duplications
13 Limitations of CMA Does not detect balanced translocations, inversions, low level mosaicism, point mutations Can detect copy number variants (CNVs) of unknown clinical significance Most are easily resolved by parental studies, however, clinicians should carefully evaluate parental phenotypes and developmental histories so data can be appropriately interpreted. CNVs <500 kb containing no identified genes at time of analysis are not reported CNVs >300 kb containing genes, even if clinical significance is unknown, are reported CNVs <300 kb must contain a gene known to be associated with disease in order to be reported
14 Examples of Common Findings
15 Normal Result
16 Trisomy 21 Chromosome 21-specific plot
17 DiGeorge Syndrome / VCFS Top: Whole genome view of CMA data Bottom: Left: FISH confirmation Inset: Partial karyotype of chromosome 22 (arrow points to deleted 22) Right: Chromosome 22-specific oligo plot of CMA data.
18 DiGeorge Syndrome / VCFS del 22q11.2
19 Microduplication 22q11.2 Syndrome (3 Mb ) Duplication of the DiGeorge / Velocardiofacial Syndrome region on chromosome 22q11.2
20 Microduplication 22q11.2 Syndrome (3 Mb ) Chromosome 22 Partial karyotype of chromosome 22 (arrow indicates duplicated 22) FISH confirmation 3 red signals indicates duplication
21 Example of Mosaicism
22 Mosaicism Example Indication Microcephaly, congenital vertical talus arr 18q21.2q23( )x1.nuc ish 18q21.2(RP11-25O3x1)[45/200]dn Chromosomal Microarray Analysis revealed an approximately 28.2 Mb LOSS in copy number in the distal and subtelomeric regions of the long arm of chromosome 18 suggestive of mosaicism. This deletion includes the critical region of chromosome 18q deletion syndrome (OMIM ). FISH analysis and partial chromosome analysis revealed mosaicism for a deletion in the long arm of one chromosome 18 in 22% (45/200) of interphase cells examined. The remaining 78% (155/200) of cells showed a normal hybridization pattern. UPDATE: Parental FISH analysis with the above clone showed no evidence of the same LOSS in the father (KCL144199). UPDATE: Parental FISH analysis with the above clone showed no evidence of the same LOSS in the mother (KCL ). Therefore, this result most likely represents a de novo event. Genetic counseling is warranted.
23 Mosaicism (contin d) Indication Microcephaly, congenital vertical talus
24 Examples of Complex Abnormalities
25 Complex X Chromosome Abnormality
26 Complex X Chromosome Abnormality Chromosome X-specific plot
27 Complex Chromosome 1 Abnormality A Chr 1 BCM array B Nimblegen 2.1 TAR region duplication 1q41q42 microdeletion syndrome region not duplicated 3.1 Mb (dup) 1q ,378, ,471, Mb (dup) 1q42.3q43 232,592, ,988,147 C D van der Woude E 4.7 Mb (del) 1q ,060, ,804,762 F 0.3 Mb nml AKT3 not deleted G 1.8 Mb (del) del 1q43 237,337, ,105,025 RP11-279E18 D1Z1 RP11-339I11 D1Z1 RP11-478H16 RP5-1090A23 RP11-478H16 RP5-1090A23
28 Complex Chromosome 1 Abnormality A. CMA identified a complex rearrangement including two gains and two losses in chromosome 1q. B. High density array CGH using Nimblegen 2.1M array showed a 0.3 Mb single copy sequence between the distal duplication and deletion. C. Chromosome analysis showed that the gained materials (red arrow) due to the duplications were translocated into the 1q32 region. D-G. FISH analyses confirmed the deletions in 1q32.2 (D) and 1q43 (E) and the two copy number gains (F). In addition, FISH analysis on metaphase cells (G) suggested an inversion between the two regions with copy number gains and showed the duplicated segments of 1q42.12 and 1q42.3q43 were located next to each other as indicated by a white arrow. Liu et al. Cell In Press
29 Evaluation for a Marker chromosome
30 Evaluation for a Marker Chromosome Chromosome 1-specific plot marker CMA identified that the marker chromosome originated from chromosome 1.
31 Examples of Small Copy Number Variants (including exon deletions)
32 Deletion of an Exon of ERBB4 on 2q34 INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS: Chromosomal Microarray Analysis revealed a LOSS in copy number in the distal long arm of chromosome 2, spanning a minimum of Mb and a maximum of Mb. This deletion disrupts the ERBB4 (erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4) gene. A recent publication describes haploinsufficiency of ERBB4 gene in a patient with early myoclonic encephalopathy and profound psychomotor delay (Eur J Hum Genetics Mar 17(3):378-82). Clinical correlation is recommended and genetic counseling is warranted.
33 Deletion of an Exon of ERBB4 on 2q34 Whole chromosome 2
34 Deletion of Exons of EP300 on 22q13.32 Figure 3 A. Profile of the microarray analysis showing the deleted region as indicated in the red circle [the gain on Xp as shown in green dots is also present in the mother (data not shown)]; B. The deleted oligos displayed in the UCSC genome browser corresponds to the exons of the CREBBP gene. C. The MLPA profile demonstrated copy number changes in the 2 exons of the CREBBP gene (exons 27-28). D. The deletion profile is present in the child but not in the parents indicating the deletion is de novo in origin.
35 Deletion of Exons of EP300 on 22q13.32 A B C CREBBP exons deletion 27 28
36 CMA Comprehensive CMA +SNP
37 400 K CMA comprehensive showing normal CMA with a paternal UPD15 (Isodisomy) Chromosome 15 Whole genome Copy number plot Agilent-SNP In house array Agilent-SNP Genome Workbench Illumina
38 CMA Comprehensive (180K + SNP Screen) Normal CMA profile AOH observed in close relative mating (example : father and daughter mating)
39 Resolving Variants of Uncertain Significance
40 Examples of Clone Plots Current case Nonpolymorphic clone plot Current case Polymorphic clone plot Highly unusual Common variant
41 Resolving Variants of Uncertain Significance Mother Father Fetus Chr 12 CNV (paternal) Trisomy 21
42 Incidental finding [from the father while absent from the fetus] Proband Mother Father
43 Prenatal CMA Considerations
44 Why Consider Prenatal CMA? Combined incidence of known microdeletion/ duplication syndromes is at least ~1/1000 Many are not detected on standard chromosome analysis, especially in prenatal samples with lower resolution Many have moderate to severe phenotypes after birth, but no prenatal signs that would raise suspicion and trigger specific FISH testing Women of all ages are equally likely to have affected pregnancies No screening tools have been developed for microdeletion / microduplication disorders
45 Baylor Prenatal CMA Clinical Protocol Parental samples required for testing Informed consent strongly recommended Entire sample can be sent to Baylor (30+cc amniotic fluid {>16 wk gestation} or 30+ CVS) for routine cytogenetics and CMA OR direct sample may be split (15cc amniotic fluid or 15 mg dcvs) can be sent and remainder sent to another lab for routine cytogenetics. Direct CMA testing on direct CVS or direct amniotic fluid with (collected >16 weeks gestation) with culture in reserve. Maternal cell contamination studies Reporting in 7-10 days from direct sample
46 Pre-test discussion A pre-test discussion should include: How the testing works What is being tested for Possible test results Benefits of testing Limitations/risks of testing Assessment of the individual s understanding of the testing Assessment of parental clinical and developmental history
47 Possible Test Results No abnormality detected No gain or loss of chromosomal material was detected in the regions tested A gain or loss was detected that is known / expected to be benign (i.e. does not cause disease) Abnormality detected A gain or loss of chromosomal material known to result in a defined genetic condition has been detected Results of uncertain significance A gain or loss of chromosomal material not known to result in a defined genetic condition has been detected This means that a change was found, but there is little or no medical knowledge about the particular change. Whether the change may lead to medical problems and what types of problems it may cause is uncertain. In this case additional testing is performed, including analysis of DNA from the parents.
48 Benefits of CMA testing CMA testing may discover an abnormality that may not have been detected by routine chromosome testing. The information gained from CMA testing may be important for making decisions about the pregnancy or for making medical decisions about the baby s care after delivery.
49 Limitations of CMA testing Detection rates It is possible that the baby could have one of the medical conditions included in the CMA test, but the CMA test was unable to detect the condition. For some conditions included in the CMA test, 99% of cases can be detected. For others, the detection rate may be lower because they can have multiple underlying causes. Findings of uncertain significance It is possible that the test will detect an abnormality for which there is very little medical information available to predict the type of problems that may develop in the baby. Expectant parents may be left with ambiguity and this may increase their anxiety about the pregnancy Need for further testing and impact on family members As with any genetic test, results may indicate a need for further testing and may also impact other family members.
50 Assessment of Patient Understanding Patients should understand that: CMA DOES NOT test for ALL genetic conditions Detection rates are not 100% Even if the results are normal, the baby could still have a birth defect(s) or mental retardation from causes not detected by the CMA testing
51 Prenatal CMA Case Examples
52 Case 1 CVS (13 weeks) Indication: AMA, Abnormal ultrasound (nuchal thickening) and Normal chromosome analysis referred to us for CMA 8.7 Mb loss in 4q21.23q22.1 Copy number loss of this region is associated with CNS overgrowth, facial anomalies, hypotonia and developmental delay [PMID ]
53 Case 1 CVS (13 weeks) Confirmation of the deletion by FISH. In retrospect, perhaps karyotype shows deletion. Deleted chromosome Deleted chromosome
54 Case 2 Indication: AMA, parental concern Duplication detected at 17p11.2 involving RAI1. Duplication of RAI1 has been associated with Potocki-Lupski syndrome. FISH using the probe FLI in green used in the clinical laboratory confirmed an additional copy of RAI1. The control probe PMP22 in red shows the expected 2 signals.
55 Case 3: Origin of Marker Chromosome Indication: Karyotype analysis performed at another laboratory showed a supernumerary small marker chromosome in 5 of 18 cells (28%). FISH studies with probes specific for chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 18, 21, 22, X and Y were unable to identify the origin of the marker. CMA detected a 10 Mb (maximum 19 Mb) gain in copy number on the short arm of chromosome 20. Metaphase FISH analysis confirmed that the marker chromosome was an isochromosome 20p resulting in tetrasomy for 20p, and was observed in 20% (4/20) of the cells examined.
56 Case 3: Origin of Marker Chromosome Mar 20 20
57 Types of Cancer arrays HEME-ONC Array(44K) 180K CGH/SNP Cancer Array (CCMC Design) BCM 400K CGH/SNP Cancer Array
58 Utility of Heme-Onc CMA First cancer gene targeted oligonucleotide microarray for genome profiling of hematological malignancies at a high resolution. Heme-Onc CMA is for: Acute leukemias CLL Multiple myeloma Lymphomas Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) Higher sensitivity for detection of abnormalities in CLL than the current FISH panel
59 Heme-Onc Array Design Guideline Even Distribution Target Genes Implicated in Cancer V X X Targeted Regions: Selected Genes (494) Regions Implicated in Leukemia Excluding Regions: Repetitive Elements Low Copy Repeats Assembly Gaps Copy Number Polymorphism (TCAG V1+UCSC)
60 Heme-Onc Array Design Example Gene 10X Backbone Regions X
61 Resolution of the Heme-Onc Array 494 genes 1 OLIGO per 7.5 kb Backbone region 1 OLIGO per 78 kb
62 Case 1: Indication CLL 1. The initial chromosome study showed an abnormal clone with deleted chromosome 11q and deleted chromosome 13q in 10% of the cells examined. 46,XY,del(11)(q13q23),del(13)(q14q22)[3]/46,XY[27] 2. These findings were consistent with the CMA results (blue circles) 3. FISH confirmation showed that the deletions are present in >40% of cells. 4. CMA also detected additional findings as indicated in the pink box.
63 Case 1: Indication CLL 2p16 gain 42% deleted by FISH 45% deleted by FISH
64 Case 2: Indication CLL 1. Initial FISH results using CLL FISH panel nuc ish(p53x1)[27/500] 5% nuc ish(d13s319x0)[113/500] 27% nuc ish(cep12x3)[119/500] 27% 2. These findings were consistent with the CMA results (blue circles) 3. CMA also detected additional findings as indicated in the pink boxes
65 Case 2: Indication CLL dup15q dup 11q del 9p
66 Case 3: Indication MDS 1. Initial chromosome analysis detected two abnormal clones 47,XX,inv(3)(q21q26),+mar[11]/46,idem,-7[9] 2. CMA detected a loss of chromosome 7 (red circle) except for the pericentromeric region (blue arrow). 3. Subsequent FISH analysis using a centromere probe for chromosome 7 confirmed the marker chromosome is derived from chromosome CMA is able to detect gain or loss of genomic material but not balanced rearrangements such as the inverted chromosome 3 present in this case.
67 Case 3: Origin of the marker chromosome inv(3) marker Chr mar derived from chr
68 Case 4: Indication MDS Right Panel: Initial chromosome analysis detected an abnormal clone: 46,XY,-7,+mar[11]/46,XY[10] Bottom Panel: CMA detected a gain of chromosome 3q and a loss and gain of chromosome 7q. chr 3 nl 7 marker
69 Case 4: CMA Results continued Chr 3 Chr 3 Chr 7 Marker chromosome is an isoderivative 7 ider(7)(q22)t(3;7)(q25.3;q22)
70 Case 5: Indication-CLL- Homozygous loss on 13q14 A. CMA detected a LOSS of copy number (deletion) on chromosome 13. B. The chromosome 13-specific plot shows the coverage and the boundaries of the deleted segment. C. The size of the deleted segment and genes involved. D. The size of the segment within the deletion showing a homozygous LOSS and the genes involved.
71 Case 5: Indication-CLL- Homozygous loss on 13q14 A. B. C. Copy number LOSS on chromosome 13 D. Homozygous loss
72 Case 5: Indication-CLL- Homozygous loss on 13q14 Confirmation FISH analysis using the CLL FISH panel from Vysis E. E. 63% (313/500) cells had one signal for D13S319 (red) probe. F. F. 27% (146/500) cells had no signals (homozygous loss) for D13S319 probe localized to chromosome 13q14 consistent with the results from array CGH. 13q14 Red Signal 13q34 Aqua Signal 12cen Green Signal
73 180K CGH/SNP Cancer Array (CCMC Design)
74 180K CGH/SNP Cancer Array (CCMC Design) 44K 60K 105K 180K MLL DDX6 CBL2 Backbone Backbone 512 cancer genes or cancer-related genes Average of 2 probes per exon. Average resolutions <10 Kb (large exons) to <10 Kb (cancer genomic regions) in targeted regions. ~30 Kb in backbone regions.
75 Myelodysplastic Syndrome (180K CGH/SNP Array) 4 copies 3 copies 1 copy 0 copy BBBB ABBB AAAB AAAA Myelodysplastic Syndrome Partial Chromosome 6p Amplification to 4 copies SNP data show 0, 1, 3, 4 copies
76 Unbalanced Balance Translocation Acute Myeloid Leukemia (180K CGH Array, CCMC Design) Red: D7S486 Green: D7Z1 3p Mb 3q Mb 3q Kb 12p Mb 57 Mb 36 Mb Red arrow: deletions; green arrow: duplication
77 BCM 400K CGH/SNP Cancer Array
78 BCM 400K CGH/SNP Cancer Array 400K MLL DDX6 Backbone Backbone 2,300 cancer genes or cancer-related genes 235 cancer associated-mirnas Average of 6 probes per exon. Average resolutions <1 Kb (large exons) to <10 Kb (cancer genomic regions) in targeted regions. ~12 Kb in backbone regions.
79 Myelodysplastic Syndrome (BCM 400K CGH/SNP Array) 3 copies Copy Gain LOH Triplication of one allele 1 copy Copy Loss LOH Homozygous deletion 3 copies Copy Gain LOH Triplication of one allele SNP CGH
80 Conclusion CMA is a powerful molecular cytogenetic tool for detecting genomic imbalances both in constitutional as well as in cancer diagnostics CMA is a high resolution technology capable of detecting chromosomal DNA copy number changes throughout the genome Baylor designed CMA detects chromosomal abnormalities that would go undetected by older techniques such as karyotype or non-exon focused arrays
81
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH)
 Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) rarechromo.org Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) Chromosomes Chromosomes are structures that contain the genetic information (DNA) that tells the body
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) rarechromo.org Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) Chromosomes Chromosomes are structures that contain the genetic information (DNA) that tells the body
The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 9. The following chapter is called "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)". The author is Dr. Maria Lalioti. Slide 2 The learning objectives of this chapter are: To learn the
REI Pearls: Pitfalls of Genetic Testing in Miscarriage
 The Skinny: Genetic testing of miscarriage tissue is controversial and some people question if testing is helpful or not. This summary will: 1) outline the arguments for and against genetic testing; 2)
The Skinny: Genetic testing of miscarriage tissue is controversial and some people question if testing is helpful or not. This summary will: 1) outline the arguments for and against genetic testing; 2)
Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing Number 12.04.116
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing Number 12.04.116
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities
 Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
Basic Human Genetics: Reproductive Health and Chromosome Abnormalities Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and
Information leaflet. Centrum voor Medische Genetica. Version 1/20150504 Design by Ben Caljon, UZ Brussel. Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel
 Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Wissenschaftliche Highlights der GSF 2007
 H Forschungszentrum für Umwelt und Gesundheit GmbH in der Helmholtzgemeinschaft Wissenschaftlich-Technische Abteilung Wissenschaftliche Highlights der GSF 2007 Abfrage Oktober 2007 Institut / Selbst. Abteilung
H Forschungszentrum für Umwelt und Gesundheit GmbH in der Helmholtzgemeinschaft Wissenschaftlich-Technische Abteilung Wissenschaftliche Highlights der GSF 2007 Abfrage Oktober 2007 Institut / Selbst. Abteilung
BlueFuse Multi Analysis Software for Molecular Cytogenetics
 BlueFuse Multi Analysis Software for Molecular Cytogenetics A powerful software package designed to detect and display areas of potential chromosomal abnormality within the genome. Highlights Seamless
BlueFuse Multi Analysis Software for Molecular Cytogenetics A powerful software package designed to detect and display areas of potential chromosomal abnormality within the genome. Highlights Seamless
Each person normally has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all. We inherit one chromosome per pair from our mother and one from our father.
 AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
AP Psychology 2.2 Behavioral Genetics Article Chromosomal Abnormalities About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal abnormality (1, 2). These are caused by errors in the number or structure of chromosomes.
Agilent CytoGenomics Software A Complete Solution for Cytogenetic Research Data Analysis
 Agilent CytoGenomics Software A Complete Solution for Cytogenetic Research Data Analysis Technical Overview Streamlines the cytogenetic research workflow for finding CNCs, LOH, and UPD Enables manual sample
Agilent CytoGenomics Software A Complete Solution for Cytogenetic Research Data Analysis Technical Overview Streamlines the cytogenetic research workflow for finding CNCs, LOH, and UPD Enables manual sample
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing?
 Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia
 Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia XIII Corso di Formazione Malformazioni Congenite dalla Diagnosi Prenatale alla Terapia Postnatale unipv.eu Carrara, 24 ottobre 2014 Legend:Bluebars
Roberto Ciccone, Orsetta Zuffardi Università di Pavia XIII Corso di Formazione Malformazioni Congenite dalla Diagnosi Prenatale alla Terapia Postnatale unipv.eu Carrara, 24 ottobre 2014 Legend:Bluebars
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome.
 Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Chromosomes, Karyotyping, and Abnormalities (Learning Objectives) Learn the components and parts of a metaphase chromosome. Define the terms karyotype, autosomal and sex chromosomes. Explain how many of
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) Factsheet
 Introduction NIPT, which analyzes cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood, is a new option in the prenatal screening and testing paradigm for trisomy 21 and a few other fetal chromosomal aneuploidies.
Introduction NIPT, which analyzes cell-free fetal DNA circulating in maternal blood, is a new option in the prenatal screening and testing paradigm for trisomy 21 and a few other fetal chromosomal aneuploidies.
General Guidelines and Quality Assurance for Cytogenetics
 General Guidelines and Quality Assurance for Cytogenetics A common European framework for quality assessment for constitutional, acquired and molecular cytogenetic investigations. E.C.A. Permanent Working
General Guidelines and Quality Assurance for Cytogenetics A common European framework for quality assessment for constitutional, acquired and molecular cytogenetic investigations. E.C.A. Permanent Working
Array Comparative Genomic Hybridisation (CGH)
 Array Comparative Genomic Hybridisation (CGH) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is array CGH? Array CGH is a new test that is now offered to all patients referred with learning disability
Array Comparative Genomic Hybridisation (CGH) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is array CGH? Array CGH is a new test that is now offered to all patients referred with learning disability
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
*Please consult the online schedule for this course for the definitive date and time for this lecture.
 CHROMOSOMES AND DISEASE Date: September 29, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am- 8:50 am * Room: G-202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Jim Evans 4200A Biomolecular Building jpevans@med.unc.edu Office Hours: by appointment
CHROMOSOMES AND DISEASE Date: September 29, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am- 8:50 am * Room: G-202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Jim Evans 4200A Biomolecular Building jpevans@med.unc.edu Office Hours: by appointment
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives
 What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
What Is Genetic Counseling? Helping individuals and families understand how genetics affects their health and lives What does the career involve? Explore family histories to identify risks Reducing risks
RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI
 RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS -RM Clinically recognized consecutive or non consecutive pregnancy losses before
RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS DR.RAJALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN SPECIALIST GYNECOLOGIST ZULEKHA HOSPITAL DUBAI RECURRENT PREGNANCY LOSS -RM Clinically recognized consecutive or non consecutive pregnancy losses before
Cancer. 9p21.3 deletion. t(12;21) t(15;17)
 CANCER FISH PROBES INDIVIDUAL AND PANEL S Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) ALL FISH Panel (includes all probes below) 8010 LSI MYB/CEP6 LSI p16 (CDKN2A) LSI BCR/ABL with ASS LSI ETV6 (TEL)/AML1 (RUNX1)
CANCER FISH PROBES INDIVIDUAL AND PANEL S Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) ALL FISH Panel (includes all probes below) 8010 LSI MYB/CEP6 LSI p16 (CDKN2A) LSI BCR/ABL with ASS LSI ETV6 (TEL)/AML1 (RUNX1)
Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis
 Microarray Data Analysis Workshop MedVetNet Workshop, DTU 2008 Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis Carsten Friis ( with several slides from
Microarray Data Analysis Workshop MedVetNet Workshop, DTU 2008 Comparative genomic hybridization Because arrays are more than just a tool for expression analysis Carsten Friis ( with several slides from
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE
 AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
VALIDATED MOLECULAR SOLUTIONS FOR CYTOGENETICISTS. PRODUCTS AND METHODOLOGIES Not for distribution in the USA
 PRODUCTS AND METHODOLOGIES Not for distribution in the USA VALIDATED SOLUTIONS FOR MOLECULAR CYTOGENETICISTS 2 A GLOBAL LEADER IN HUMAN AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH PerkinElmer is a global scientific leader
PRODUCTS AND METHODOLOGIES Not for distribution in the USA VALIDATED SOLUTIONS FOR MOLECULAR CYTOGENETICISTS 2 A GLOBAL LEADER IN HUMAN AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH PerkinElmer is a global scientific leader
March 19, 2014. Dear Dr. Duvall, Dr. Hambrick, and Ms. Smith,
 Dr. Daniel Duvall, Medical Officer Center for Medicare, Hospital and Ambulatory Policy Group Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, Maryland 21244 Dr. Edith Hambrick,
Dr. Daniel Duvall, Medical Officer Center for Medicare, Hospital and Ambulatory Policy Group Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, Maryland 21244 Dr. Edith Hambrick,
The genetic screening of preimplantation embryos by comparative genomic hybridisation
 Vol. 11, Suppl. 3 51 The genetic screening of preimplantation embryos by comparative genomic hybridisation Maria V Traversa 1, James Marshall, Steven McArthur, Don Leigh Genea, Sydney, Australia Received:
Vol. 11, Suppl. 3 51 The genetic screening of preimplantation embryos by comparative genomic hybridisation Maria V Traversa 1, James Marshall, Steven McArthur, Don Leigh Genea, Sydney, Australia Received:
Chromosomal Abnormalities
 Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Special Report: acgh for the Genetic Evaluation of Patients with Developmental Delay/ Mental Retardation or Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Technology Evaluation Center Special Report: acgh for the Genetic Evaluation of Patients with Developmental Delay/ Mental Retardation or Autism Spectrum Disorder Assessment Program Volume 23, No. 10 April
Technology Evaluation Center Special Report: acgh for the Genetic Evaluation of Patients with Developmental Delay/ Mental Retardation or Autism Spectrum Disorder Assessment Program Volume 23, No. 10 April
The Human Genome Project
 The Human Genome Project Brief History of the Human Genome Project Physical Chromosome Maps Genetic (or Linkage) Maps DNA Markers Sequencing and Annotating Genomic DNA What Have We learned from the HGP?
The Human Genome Project Brief History of the Human Genome Project Physical Chromosome Maps Genetic (or Linkage) Maps DNA Markers Sequencing and Annotating Genomic DNA What Have We learned from the HGP?
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number
 Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number A WHITE PAPER FROM BIODISCOVERY, INC. Rapid technological advancements, such as high-density acgh and SNP arrays as well as next-generation sequencing
Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number A WHITE PAPER FROM BIODISCOVERY, INC. Rapid technological advancements, such as high-density acgh and SNP arrays as well as next-generation sequencing
your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing.
 your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing. Accurate answers about your baby s health simply, safely, sooner. What is the verifi Prenatal
your questions answered the reassurance of knowing A guide for parents-to-be on noninvasive prenatal testing. Accurate answers about your baby s health simply, safely, sooner. What is the verifi Prenatal
Fact Sheet 14 EPIGENETICS
 This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
This fact sheet describes epigenetics which refers to factors that can influence the way our genes are expressed in the cells of our body. In summary Epigenetics is a phenomenon that affects the way cells
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING
 REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
REQUEST FOR IMAGe SYNDROME TESTING Please provide the following information. We cannot perform your test without ALL of this information. PLEASE PRINT ALL ANSWERS PATIENT INFORMATION* FIRST NAME MI LAST
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making. Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina
 Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Genetic Counseling: A Profession in the Making Jessica Hooks, MS Genetic Counselor University of South Carolina Definition the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological
Supporting Information
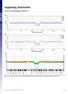 Supporting Information Yin et al. 10.1073/pnas.1518151112 Fig. S1. Characteristic Z scores of a section of DNA encompassing a deletion in sample 14,945 at (A) varying concentrations of abnormal DNA at
Supporting Information Yin et al. 10.1073/pnas.1518151112 Fig. S1. Characteristic Z scores of a section of DNA encompassing a deletion in sample 14,945 at (A) varying concentrations of abnormal DNA at
Clinical Policy Title: Array comparative genomic hybridization testing
 Clinical Policy Title: Array comparative genomic hybridization testing Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.03 Effective Date: Sept 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: May 13, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: August 19,
Clinical Policy Title: Array comparative genomic hybridization testing Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.03 Effective Date: Sept 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: May 13, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: August 19,
Noninvasive Prenatal Screening for Fetal Aneuploidies and Microdeletions Using Cell-Free Fetal DNA
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Noninvasive Prenatal Screening for Fetal Aneuploidies and Microdeletions
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Noninvasive Prenatal Screening for Fetal Aneuploidies and Microdeletions
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis
 Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
Number 12.04.59 Effective Date August 1, 2016 Revision Date(s) 07/12/16; 10/13/15; 12/08/14; 12/09/13; 02/14/12 Replaces 2.04.59
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES CODING DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES APPENDIX HISTORY Genetic Testing, Including Chromosomal Microarray (CMA) Analysis
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES CODING DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES APPENDIX HISTORY Genetic Testing, Including Chromosomal Microarray (CMA) Analysis
Robertsonian Translocations
 Robertsonian Translocations rarechromo.org Robertsonian translocations A Robertsonian translocation is an unusual type of chromosome rearrangement caused by two particular chromosomes joining together.
Robertsonian Translocations rarechromo.org Robertsonian translocations A Robertsonian translocation is an unusual type of chromosome rearrangement caused by two particular chromosomes joining together.
National Medical Policy
 National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Chromosomal Microarray Analysis for Prenatal Testing and Intellectual Disability, Developmental Delay, and Multiple
National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Chromosomal Microarray Analysis for Prenatal Testing and Intellectual Disability, Developmental Delay, and Multiple
Consent to Perform Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) using. Comparative Genomic Hybridization (acgh) or Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
 Consent to Perform Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) using Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (acgh ) or Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Purpose The purpose of Preimplantation Genetic Screening
Consent to Perform Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) using Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (acgh ) or Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Purpose The purpose of Preimplantation Genetic Screening
4.2 Meiosis. Meiosis is a reduction division. Assessment statements. The process of meiosis
 4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
4.2 Meiosis Assessment statements State that meiosis is a reduction division of a diploid nucleus to form haploid nuclei. Define homologous chromosomes. Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing
National Down Syndrome Society
 National Down Syndrome Society The national advocate for the value, acceptance and inclusion of people with Down syndrome What is Down Syndrome? Down syndrome is the most commonly occurring chromosomal
National Down Syndrome Society The national advocate for the value, acceptance and inclusion of people with Down syndrome What is Down Syndrome? Down syndrome is the most commonly occurring chromosomal
Executive summary. Current prenatal screening
 Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
Executive summary Health Council of the Netherlands. NIPT: dynamics and ethics of prenatal screening. The Hague: Health Council of the Netherlands, 2013; publication no. 2013/34. In recent years, new tests
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES. Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD
 LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome
 First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
First Trimester Screening for Down Syndrome What is first trimester risk assessment for Down syndrome? First trimester screening for Down syndrome, also known as nuchal translucency screening, is a test
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) for Fanconi Anemia and HLA matching
 Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) for Fanconi Anemia and HLA matching Andria G. Besser, BEd, MS, CGC Licensed Genetic Counselor Reproductive Genetics Institute Chicago, IL Outline PGD overview In
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) for Fanconi Anemia and HLA matching Andria G. Besser, BEd, MS, CGC Licensed Genetic Counselor Reproductive Genetics Institute Chicago, IL Outline PGD overview In
A test your patients can trust.
 A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
A test your patients can trust. A simple, safe, and accurate non-invasive prenatal test for early risk assessment of Down syndrome and other conditions. informaseq Prenatal Test Simple, safe, and accurate
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Patient Information. Ordering Physician Information. Indication for Testing (REQUIRED)
 EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
Microarray Technology
 Microarrays And Functional Genomics CPSC265 Matt Hudson Microarray Technology Relatively young technology Usually used like a Northern blot can determine the amount of mrna for a particular gene Except
Microarrays And Functional Genomics CPSC265 Matt Hudson Microarray Technology Relatively young technology Usually used like a Northern blot can determine the amount of mrna for a particular gene Except
Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13)
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 117 Information sheet to help
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Trisomy 13 (also called Patau s syndrome or T13) Information for parents Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 117 Information sheet to help
Genetics and Pregnancy Loss
 Genetics and Pregnancy Loss Dorothy Warburton Genetics and Development (in Pediatrics) Columbia University, New York Estimates of Pregnancy Loss from Conception 1000 fertilized eggs (27% are lost) 728
Genetics and Pregnancy Loss Dorothy Warburton Genetics and Development (in Pediatrics) Columbia University, New York Estimates of Pregnancy Loss from Conception 1000 fertilized eggs (27% are lost) 728
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests
 Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Prenatal screening and diagnostic tests Contents Introduction 3 First trimester routine tests in the mother 3 Testing for health conditions in the baby 4 Why would you have a prenatal test? 6 What are
Balanced. translocations. rarechromo.org. Support and Information
 Support and Information Rare Chromosome Disorder Support Group, G1, The Stables, Station Rd West, Oxted, Surrey. RH8 9EE Tel: +44(0)1883 723356 info@rarechromo.org I www.rarechromo.org Balanced Unique
Support and Information Rare Chromosome Disorder Support Group, G1, The Stables, Station Rd West, Oxted, Surrey. RH8 9EE Tel: +44(0)1883 723356 info@rarechromo.org I www.rarechromo.org Balanced Unique
Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA
 Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
Page 1 of 5 Biology Behind the Crime Scene Week 4: Lab #4 Genetics Exercise (Meiosis) and RFLP Analysis of DNA Genetics Exercise: Understanding how meiosis affects genetic inheritance and DNA patterns
CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS
 CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS The purpose of the logbook is to show that the applicant has been significantly involved in the evaluation and counselling of patients seeking
CAGC Certification Logbook of Clinical Experience INSTRUCTIONS The purpose of the logbook is to show that the applicant has been significantly involved in the evaluation and counselling of patients seeking
MEDICAL GENETICS GENERAL OBJECTIVE SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 SUBJECT MEDICAL GENETICS CREDITS Total: 4.5 Theory 2.5 Practical 2 GENERAL OBJECTIVE To provide students with terminology and knowledge from the field of human genetics that will enable them to understand
SUBJECT MEDICAL GENETICS CREDITS Total: 4.5 Theory 2.5 Practical 2 GENERAL OBJECTIVE To provide students with terminology and knowledge from the field of human genetics that will enable them to understand
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES
 PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES BRCA GENETIC TESTING The purpose of this document is to provide guidance to providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance Program (CMAP) on the requirements for
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES BRCA GENETIC TESTING The purpose of this document is to provide guidance to providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance Program (CMAP) on the requirements for
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number
 Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Chapter 8: Variation in Chromosome Structure and Number Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Know the principles and terminology associated with variations
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) and Childhood Diagnostic Evaluation
 IG O Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) and Childhood Diagnostic Evaluation KD Carsten Bergmann carsten.bergmann@bioscientia.de carsten.bergmann@uniklinik-freiburg.de Controversies Conference on ADPKD
IG O Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) and Childhood Diagnostic Evaluation KD Carsten Bergmann carsten.bergmann@bioscientia.de carsten.bergmann@uniklinik-freiburg.de Controversies Conference on ADPKD
Interpret software. User guide. version 11
 Interpret software User guide version 11 This protocol booklet and its contents are Oxford Gene Technology (Operations) Limited 2008. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or any substantial part of
Interpret software User guide version 11 This protocol booklet and its contents are Oxford Gene Technology (Operations) Limited 2008. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or any substantial part of
Test Information Sheet
 Test Information Sheet GeneDx 207 Perry Parkway Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Phone: 888-729-1206 Fax: 301-710-6594 E-mail: wecare@genedx.com www.genedx.com/oncology OncoGene Dx: High/Moderate Risk Panel Sequence
Test Information Sheet GeneDx 207 Perry Parkway Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Phone: 888-729-1206 Fax: 301-710-6594 E-mail: wecare@genedx.com www.genedx.com/oncology OncoGene Dx: High/Moderate Risk Panel Sequence
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Human Genome and Human Genome Project. Louxin Zhang
 Human Genome and Human Genome Project Louxin Zhang A Primer to Genomics Cells are the fundamental working units of every living systems. DNA is made of 4 nucleotide bases. The DNA sequence is the particular
Human Genome and Human Genome Project Louxin Zhang A Primer to Genomics Cells are the fundamental working units of every living systems. DNA is made of 4 nucleotide bases. The DNA sequence is the particular
Human Chromosomes lab 5
 Human Chromosomes lab 5 Objectives Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to: describe the structure of human chromosomes with reference to size, centromere position, and presence or absence
Human Chromosomes lab 5 Objectives Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to: describe the structure of human chromosomes with reference to size, centromere position, and presence or absence
Test Information Sheet
 Test Information Sheet GeneDx 207 Perry Parkway Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Phone: 888-729-1206 Fax: 301-710-6594 E-mail: wecare@genedx.com www.genedx.com/oncology OncoGene Dx: Breast/Ovarian Cancer Panel Sequence
Test Information Sheet GeneDx 207 Perry Parkway Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Phone: 888-729-1206 Fax: 301-710-6594 E-mail: wecare@genedx.com www.genedx.com/oncology OncoGene Dx: Breast/Ovarian Cancer Panel Sequence
Targeted. sequencing solutions. Accurate, scalable, fast TARGETED
 Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation
 PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Recommendations for the use of chromosome microarray in pregnancy. June 2015
 Recommendations for the use of chromosome microarray in pregnancy June 2015 Unique document number Document name Version number 1 Produced by G144 Date active June 2015 Date for review June 2018 Comments
Recommendations for the use of chromosome microarray in pregnancy June 2015 Unique document number Document name Version number 1 Produced by G144 Date active June 2015 Date for review June 2018 Comments
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics
 G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
Core Facility Genomics
 Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Launching a Cancer Genetic Laboratory to Enhance Diagnosis and Treatment
 Launching a Cancer Genetic Laboratory to Enhance Diagnosis and Treatment Arthur L. Beaudet, M.D. Department of Molecular and Human Genetics Baylor College of Medicine ORIGIN AND PRECEDENT Decades of experience
Launching a Cancer Genetic Laboratory to Enhance Diagnosis and Treatment Arthur L. Beaudet, M.D. Department of Molecular and Human Genetics Baylor College of Medicine ORIGIN AND PRECEDENT Decades of experience
Cytogenetic and Molecular Diagnosis in Gestational Disorders
 Cytogenetic and Molecular Diagnosis in Gestational Disorders Katherine Geiersbach, M.D. Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, Cytogenetics
Cytogenetic and Molecular Diagnosis in Gestational Disorders Katherine Geiersbach, M.D. Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, Cytogenetics
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
Worksheet - COMPARATIVE MAPPING 1
 Worksheet - COMPARATIVE MAPPING 1 The arrangement of genes and other DNA markers is compared between species in Comparative genome mapping. As early as 1915, the geneticist J.B.S Haldane reported that
Worksheet - COMPARATIVE MAPPING 1 The arrangement of genes and other DNA markers is compared between species in Comparative genome mapping. As early as 1915, the geneticist J.B.S Haldane reported that
Design of conditional gene targeting vectors - a recombineering approach
 Recombineering protocol #4 Design of conditional gene targeting vectors - a recombineering approach Søren Warming, Ph.D. The purpose of this protocol is to help you in the gene targeting vector design
Recombineering protocol #4 Design of conditional gene targeting vectors - a recombineering approach Søren Warming, Ph.D. The purpose of this protocol is to help you in the gene targeting vector design
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics. January 2006
 Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics January 2006 1. BACKGROUND ICSI has been shown to be effective for male factor infertility and it also
Minimum standards for ICSI use, screening, patient information and follow-up in WA fertility clinics January 2006 1. BACKGROUND ICSI has been shown to be effective for male factor infertility and it also
Laboratory Testing for Her2 Status in Breast Cancer
 Laboratory Testing for Her2 Status in Breast Cancer Katherine Geiersbach, M.D. Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology May 28, 2015 Overview Clinical relevance of Her2 status for treatment of breast
Laboratory Testing for Her2 Status in Breast Cancer Katherine Geiersbach, M.D. Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology May 28, 2015 Overview Clinical relevance of Her2 status for treatment of breast
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 12; 02-12-2012
 SALSA MLPA probemix P083-C1 CDH1 Lot C1-0211. As compared to previous B1 version, new in version C1: two CDH1 probes and several reference probes have been replaced/added. In addition, the 88 and 96nt
SALSA MLPA probemix P083-C1 CDH1 Lot C1-0211. As compared to previous B1 version, new in version C1: two CDH1 probes and several reference probes have been replaced/added. In addition, the 88 and 96nt
Prenatal Testing Special tests for your baby during pregnancy
 English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
English April 2006 [OTH-7750] There are a number of different prenatal (before birth) tests to check the development of your baby. Each test has advantages and disadvantages. This information is for people
Patient information on soft markers
 Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
Patient information on soft markers Before you read this section remember the following important points. The vast majority of babies with soft markers are normal. Soft markers are frequently seen in healthy
Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2)
 Single Gene Disorders Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2) Some Definitions Alleles variants of a given DNA sequence at a particular location (locus) in the genome. Often used more narrowly to describe alternative
Single Gene Disorders Genetics Review for USMLE (Part 2) Some Definitions Alleles variants of a given DNA sequence at a particular location (locus) in the genome. Often used more narrowly to describe alternative
Rapid Aneuploidy and CNV Detection in Single Cells using the MiSeq System
 i Technical Note: Reproductive Health Rapid Aneuploidy and CNV Detection in Single Cells using the MiSeq System Comparison between data generated from single cells using 24sure array-based screening and
i Technical Note: Reproductive Health Rapid Aneuploidy and CNV Detection in Single Cells using the MiSeq System Comparison between data generated from single cells using 24sure array-based screening and
The Genetics of Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS)
 The Genetics of Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) Introduction Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is an overgrowth disorder caused by changes in the activity of growth promoting and growth suppressing genes.
The Genetics of Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) Introduction Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is an overgrowth disorder caused by changes in the activity of growth promoting and growth suppressing genes.
Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice. Supplementary Guidelines
 Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice Next-generation Sequencing: Standardization of Clinical Testing (Nex-StoCT) Workgroup Principles and Guidelines Supplementary
Assuring the Quality of Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Laboratory Practice Next-generation Sequencing: Standardization of Clinical Testing (Nex-StoCT) Workgroup Principles and Guidelines Supplementary
Biological Sciences Initiative. Human Genome
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Targeted Variant Test Requisition Form (3/4/2015)
 Targeted Variant Test Requisition Form (3/4/2015) Instructions: Please provide clinical features of family members. All testing must be ordered by a qualified healthcare provider. See Test Selection Box
Targeted Variant Test Requisition Form (3/4/2015) Instructions: Please provide clinical features of family members. All testing must be ordered by a qualified healthcare provider. See Test Selection Box
